ANLPT: Self-Adaptive and Non-Local Patch-Tensor Model for Infrared Small Target Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
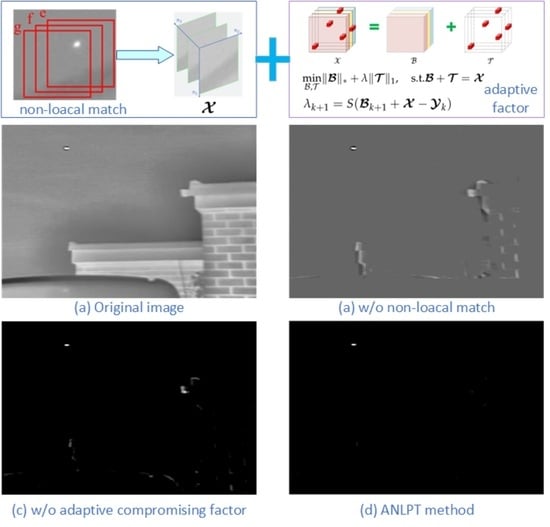
- An adaptive non-local patch-tensor model for infrared small target detection is proposed. By combining the background consistency and local similarity, the image local entropy was used to construct a non-local block tensor with good low-rank sparse characteristics for image blocks. Then, the proposed adaptive compromising factor and TRPCA were used to achieve the effective separation of background and small target;
- The mapping relationship between image local entropy and compromising factor was explored, and a dynamic and adaptive compromising factor is proposed for an effectively low-rank and sparse decomposition strategy. Our approach has a better performance when the background is not globally consistent;
- Experiments on various data sets with different characteristics show that the proposed method is more competitive than the state-of-the-art methods.
2. Notations and Fundamentals
2.1. Tensor Singular Value Decomposition(t-SVD)
| Algorithm 1: t-SVD. |
| Input: |
| foreach tube in do |
| ; |
| fordo |
| ; |
| fordo |
| ; |
| /*conj is conjugate-even vector [40]*/ |
| ; |
| ; |
| foreach tube in , and do |
| ; |
| ; |
| ; |
| Output: , , |
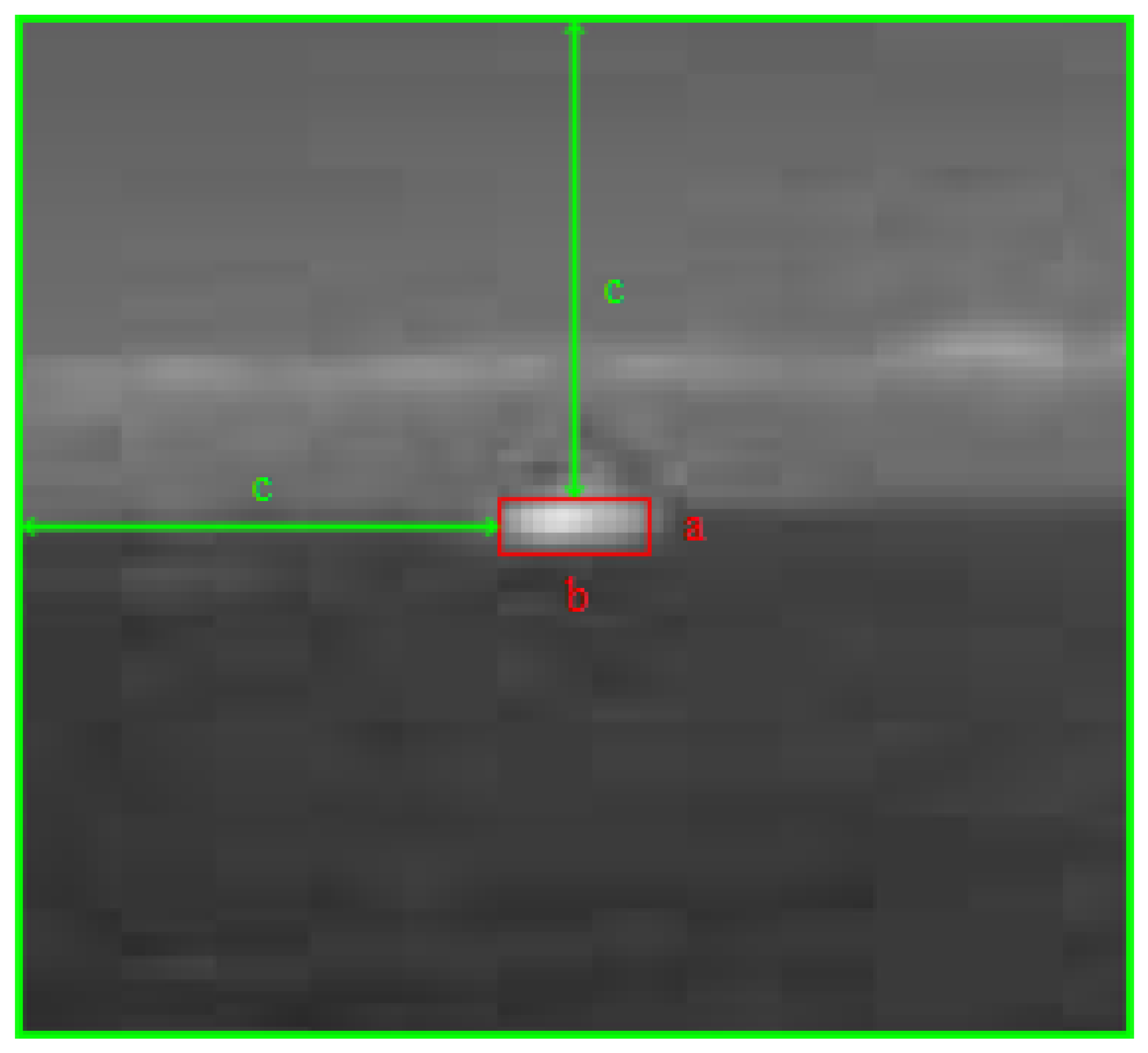
2.2. The Local Information Entropy of the Image
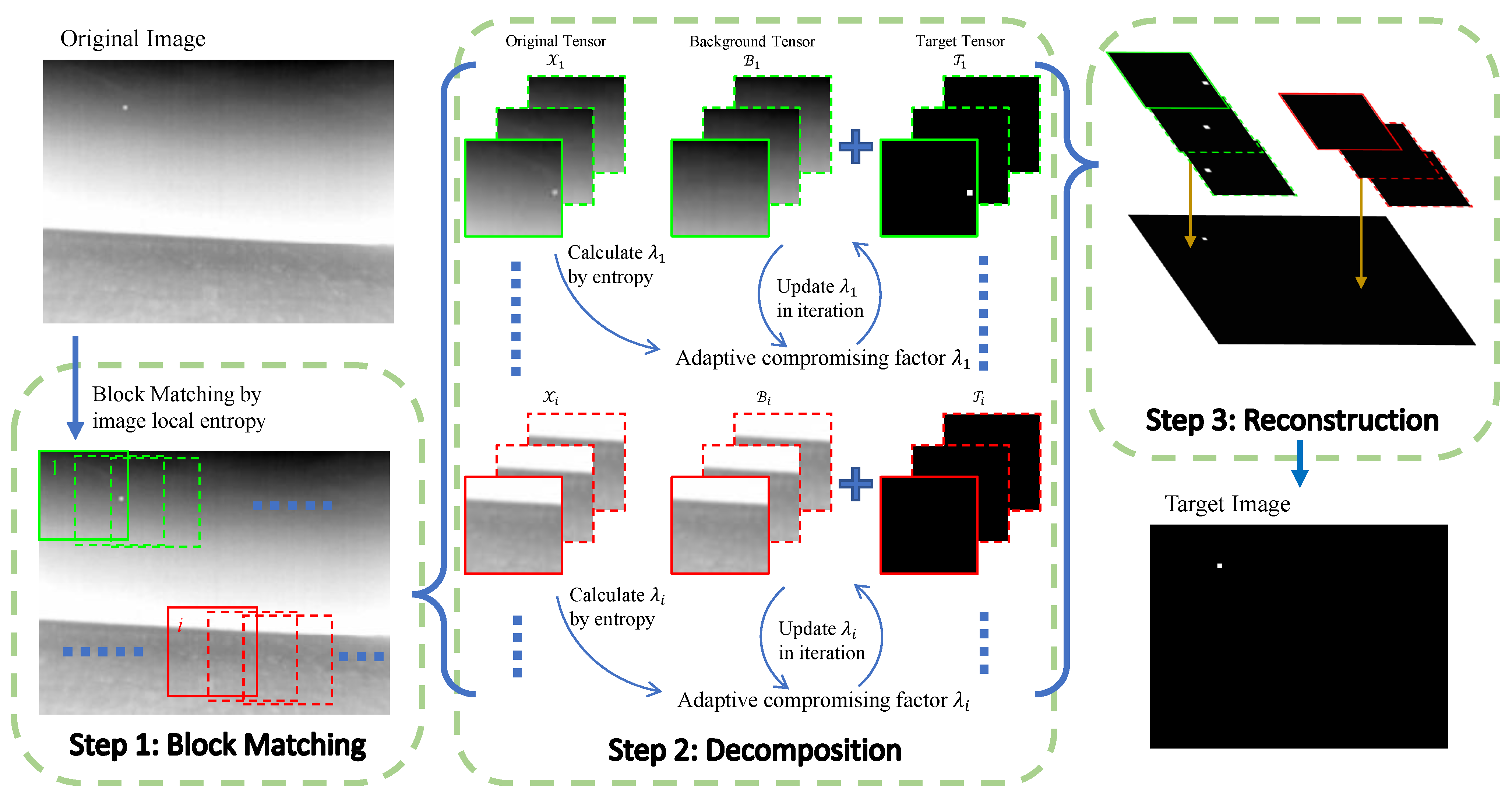
3. The Proposed Algorithm
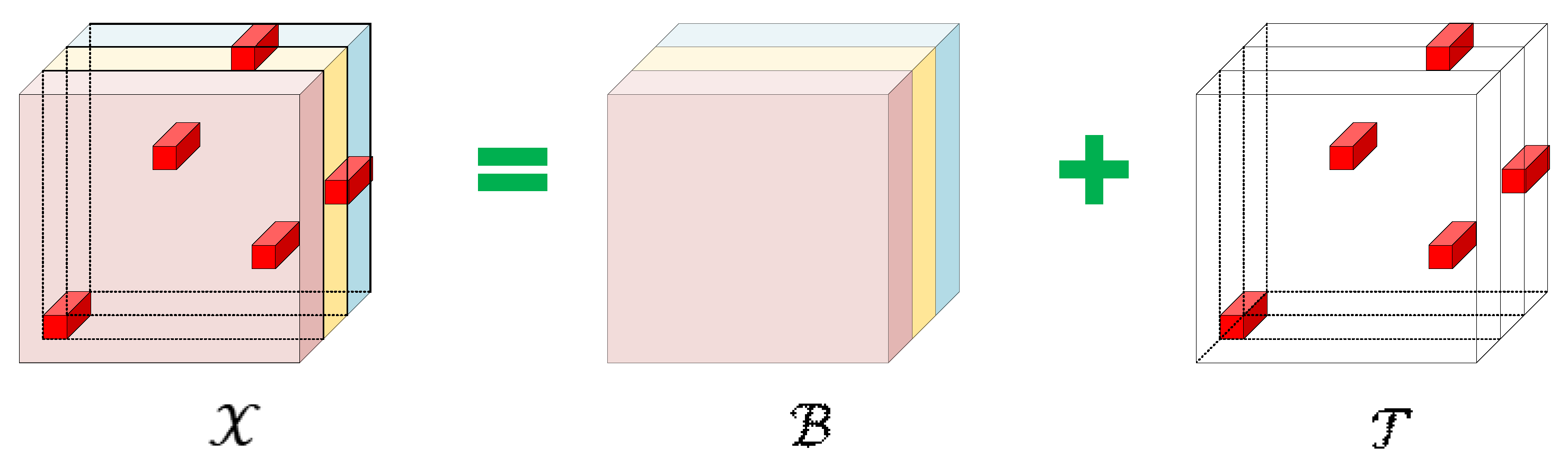
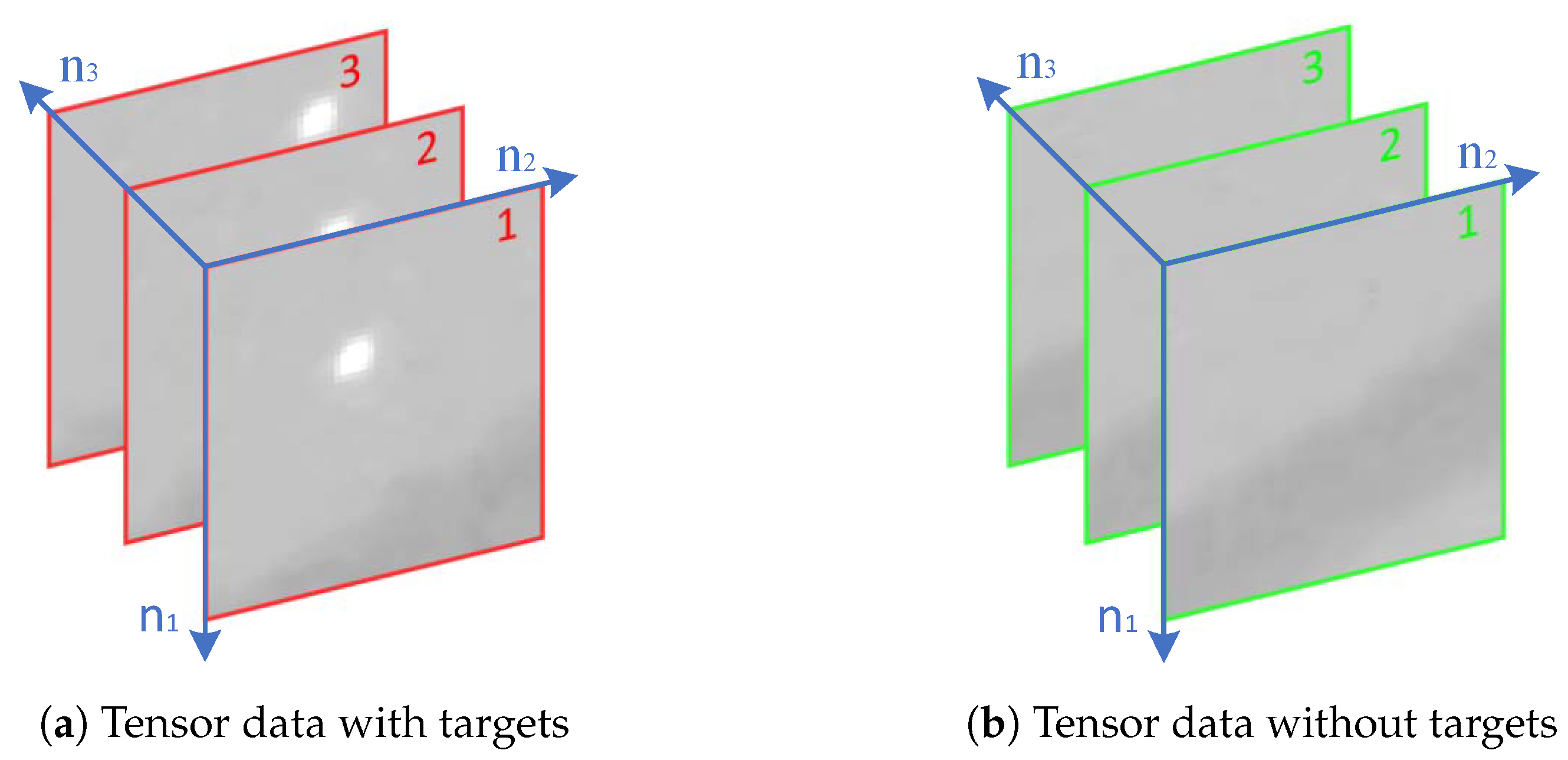
3.1. The Model Used for Low-Rank Sparse Decomposition of Tensors
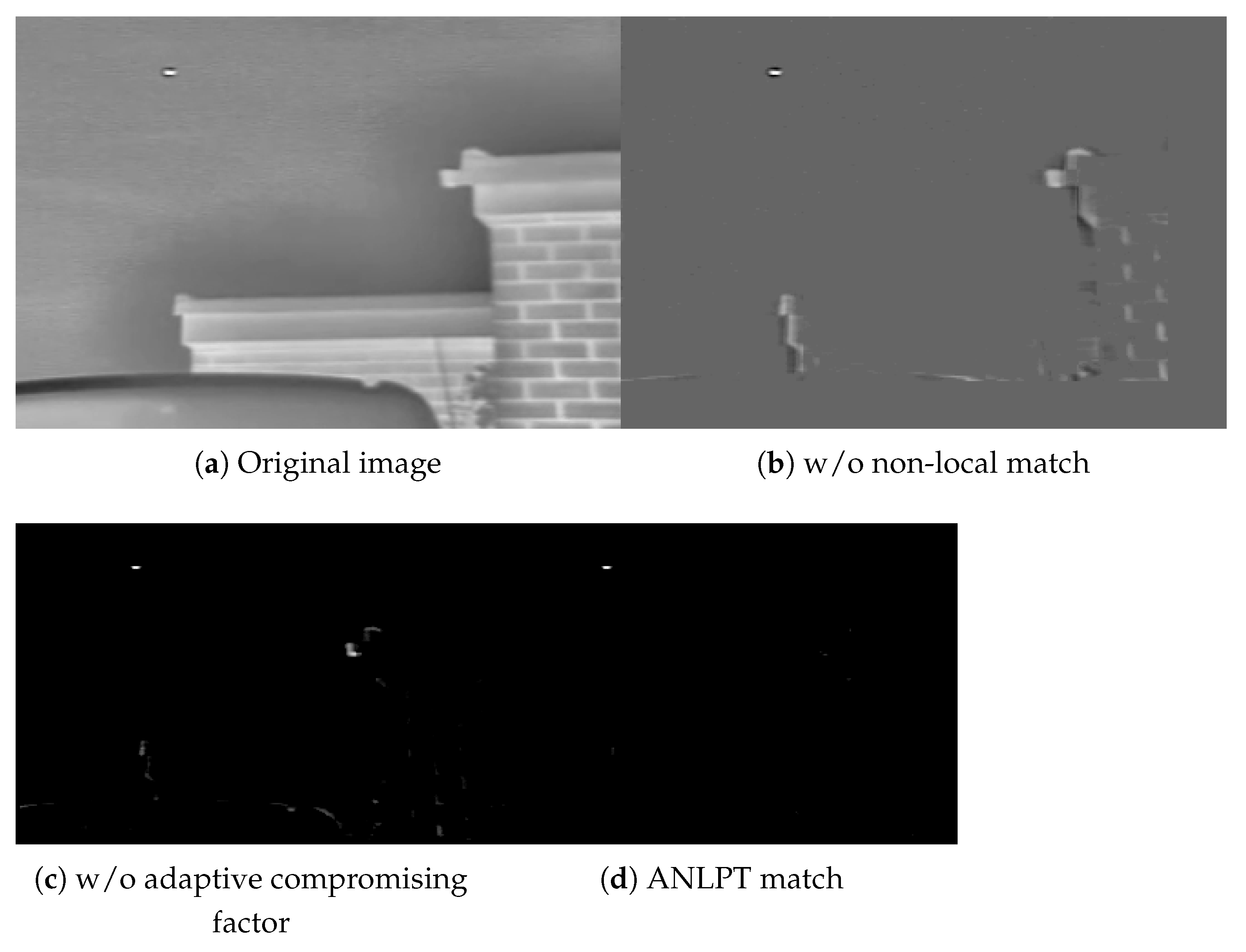
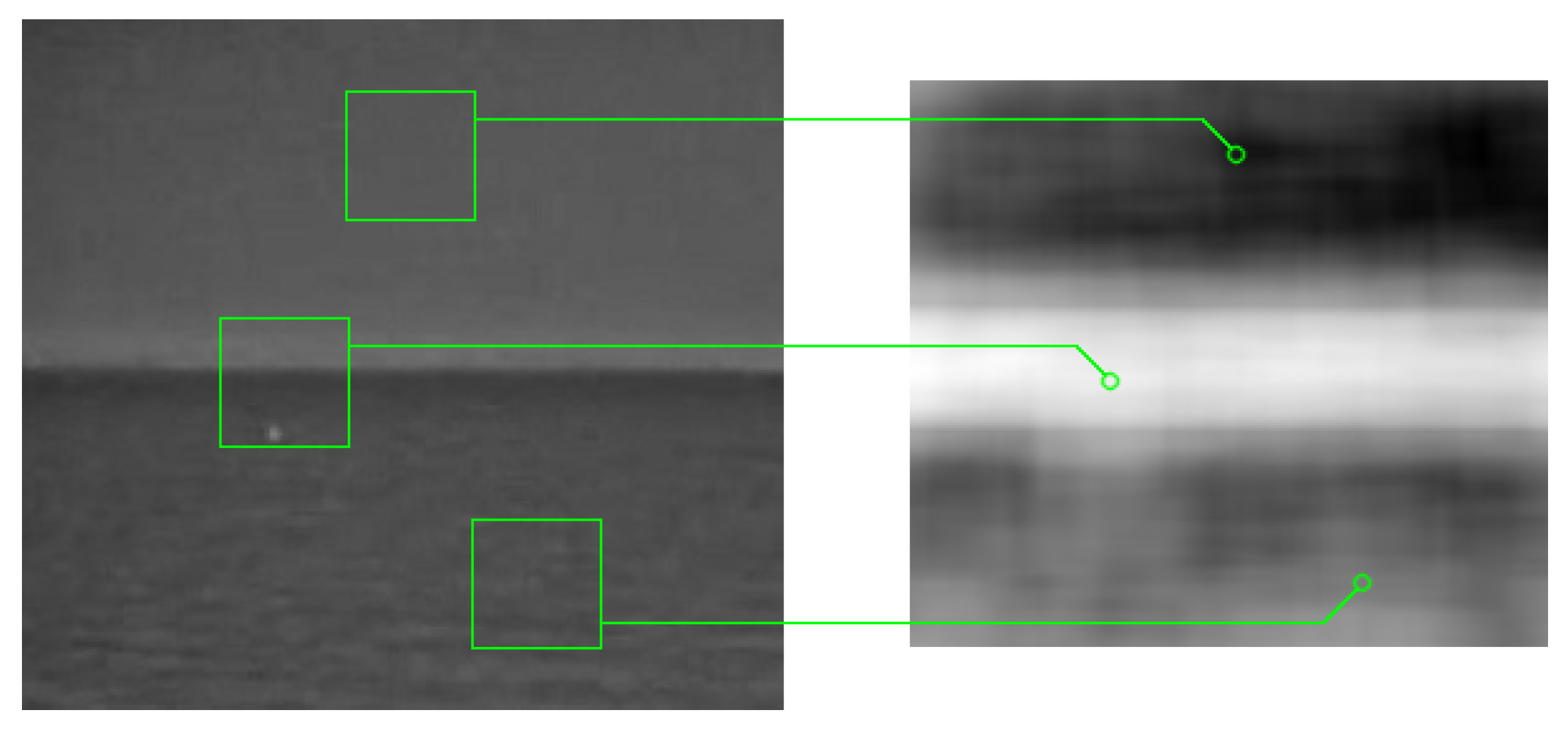
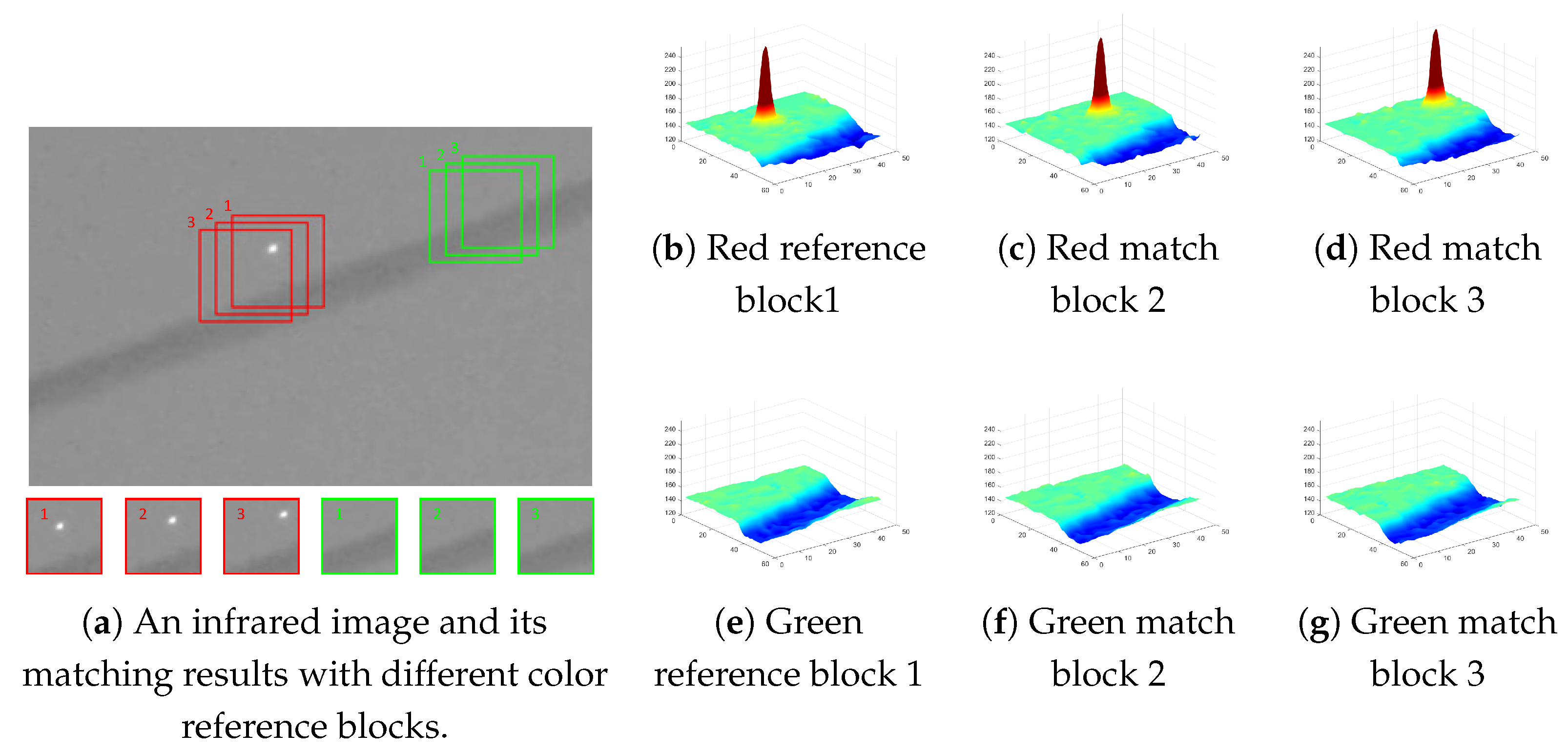
3.2. Image Block Matching Based on Local Entropy
3.3. Adaptive Dynamic Compromising Factor
3.4. Adaptive Low-Rank and Sparse Tensor Decomposition Model
3.4.1. Sparse Approximated Represented of Target by -Norm
3.4.2. Low-Rank Background Represented by Tensor Nuclear Norm
3.5. Alternating Direction Method of Multiplier (ADMM)
| Algorithm 2: t-SVT. |
| Input: |
| foreach tube in do |
| ; |
| fordo |
| ; |
| ; |
| fordo |
| ; |
| foreach tube in do |
| ; |
| Output: |
| Algorithm 3: ADMM for solving (17). |
| Input: Patch-tensor |
| Init: |
| whiledo |
| 1. Update |
| 2. Update |
| 3. Update |
| 4. Update |
| 5. Update |
| Output: Background-tensor , Target-tensor |
4. Experiments
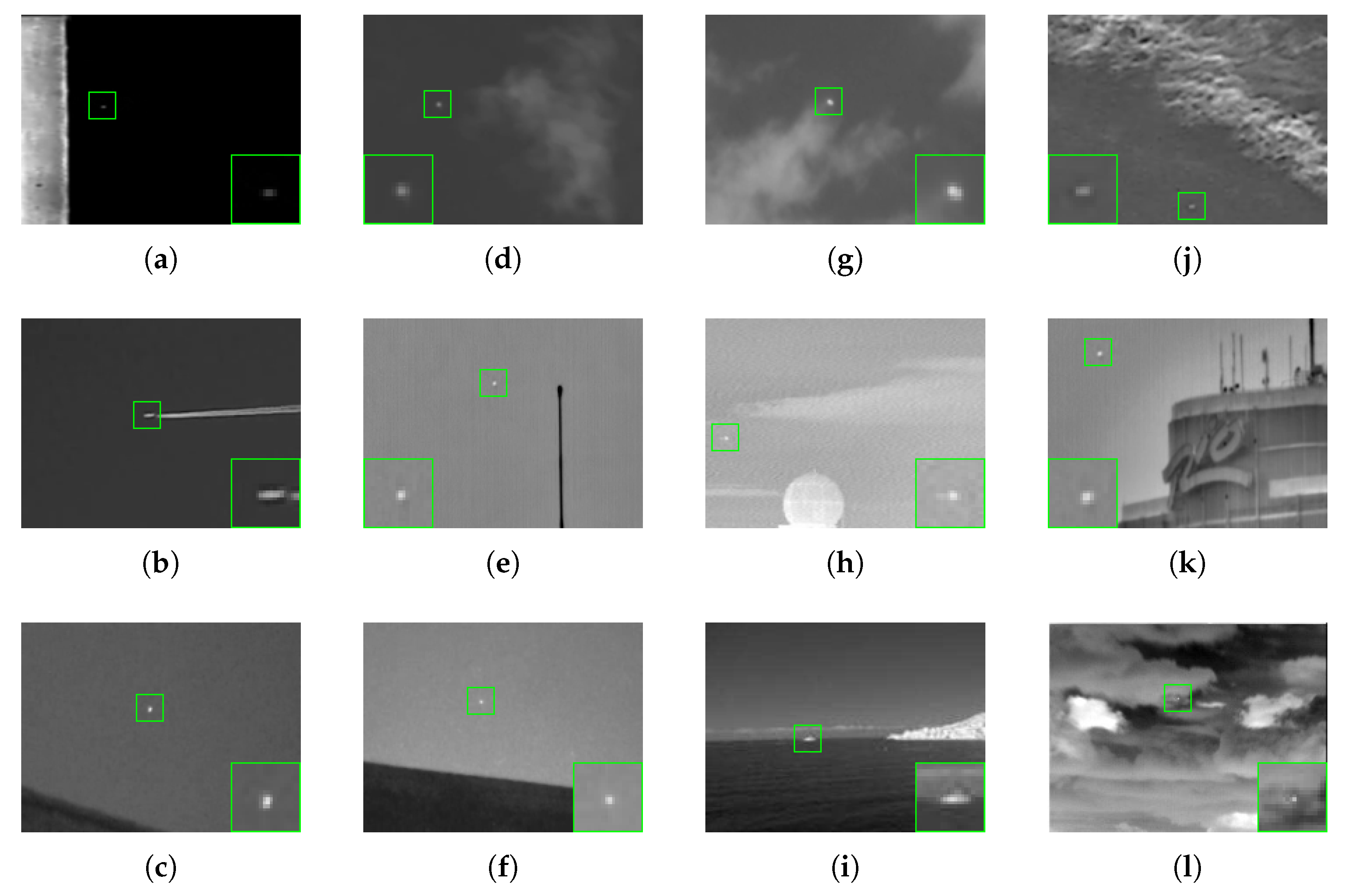
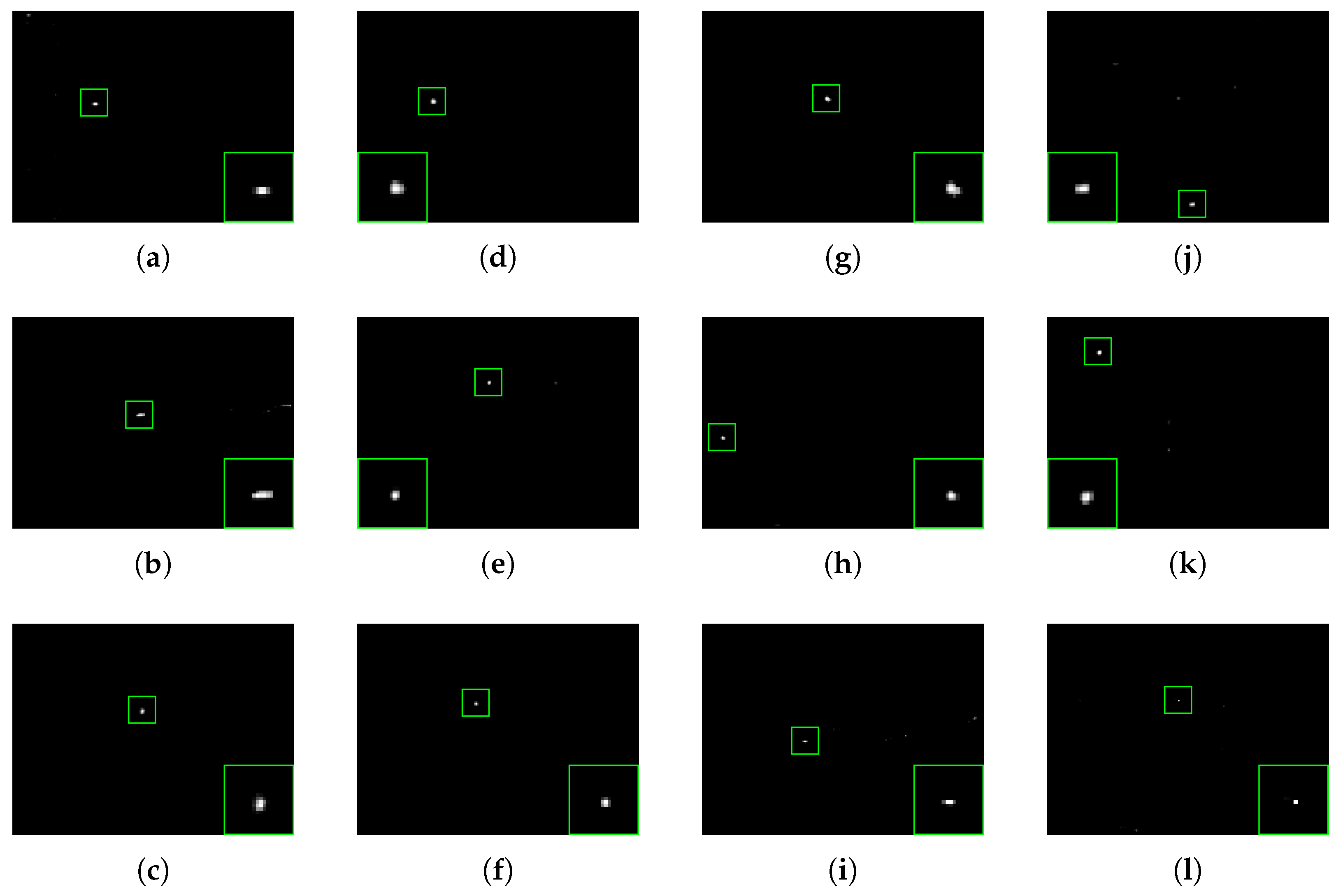
4.1. Experimental Data
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
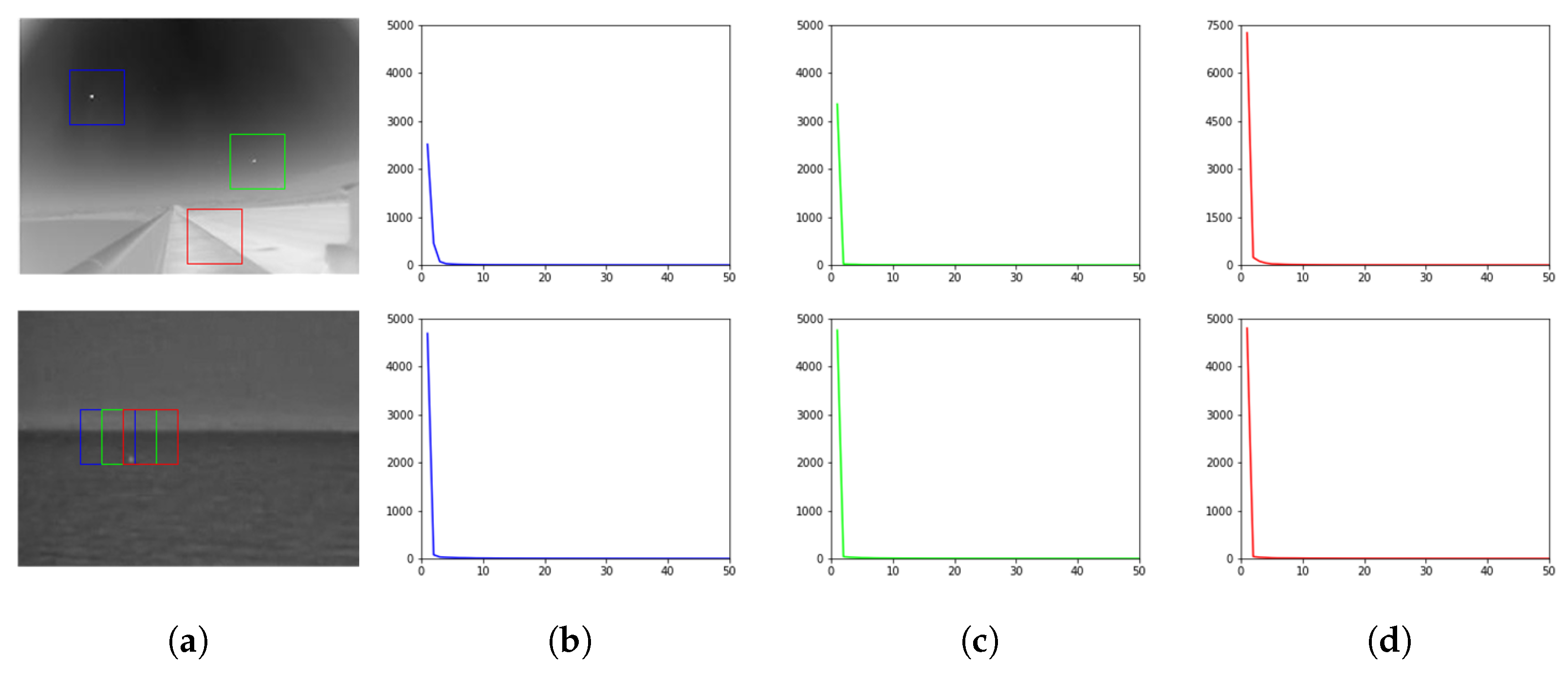
4.2.1. Signal-to-Clutter Ratio Gain (SCRG)
4.2.2. Background Suppression Factor (BSF)
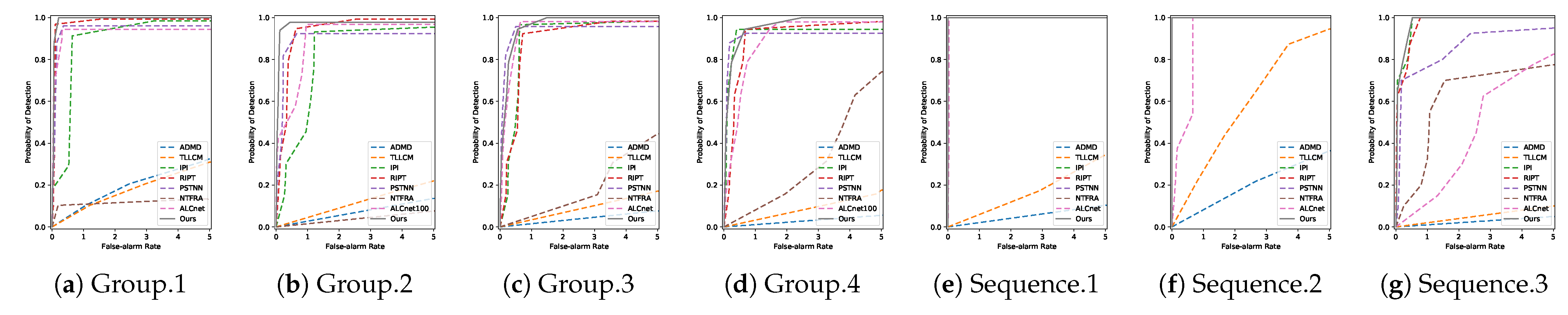
4.2.3. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC)
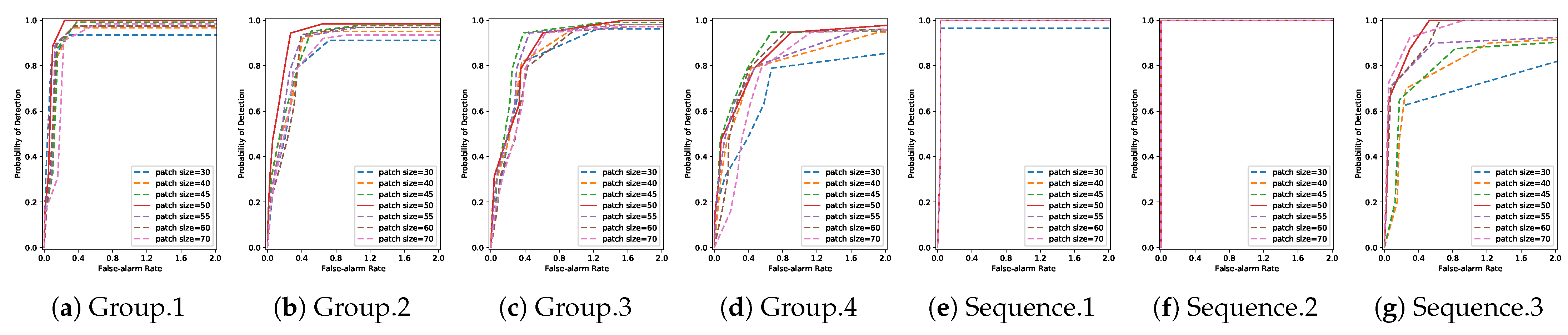
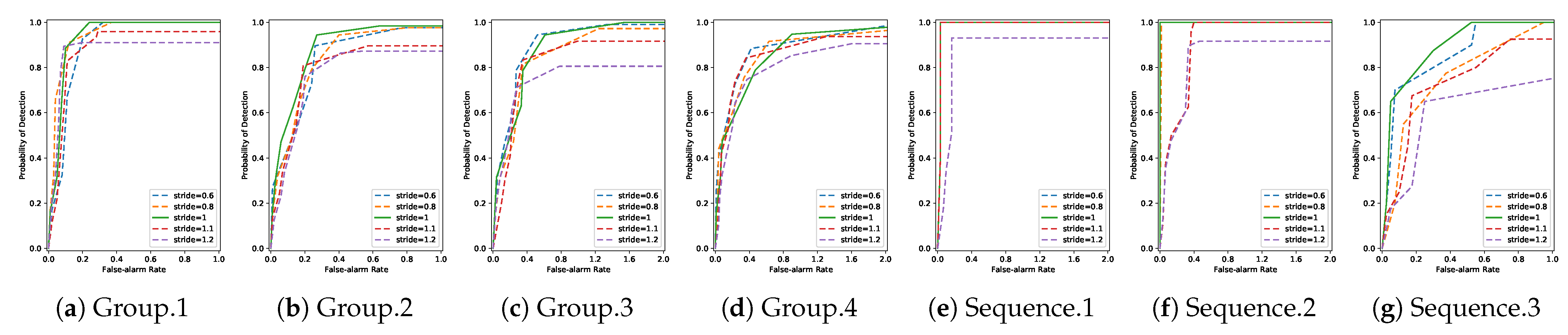
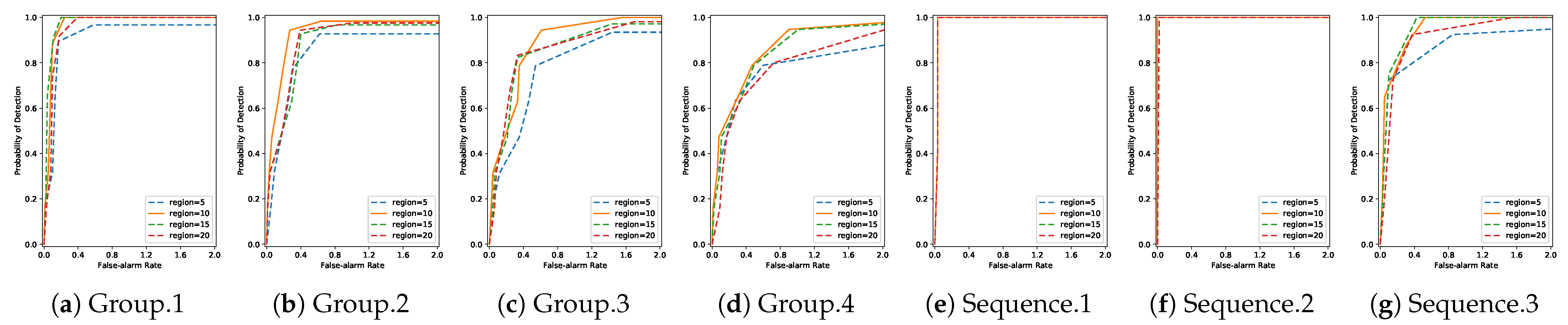
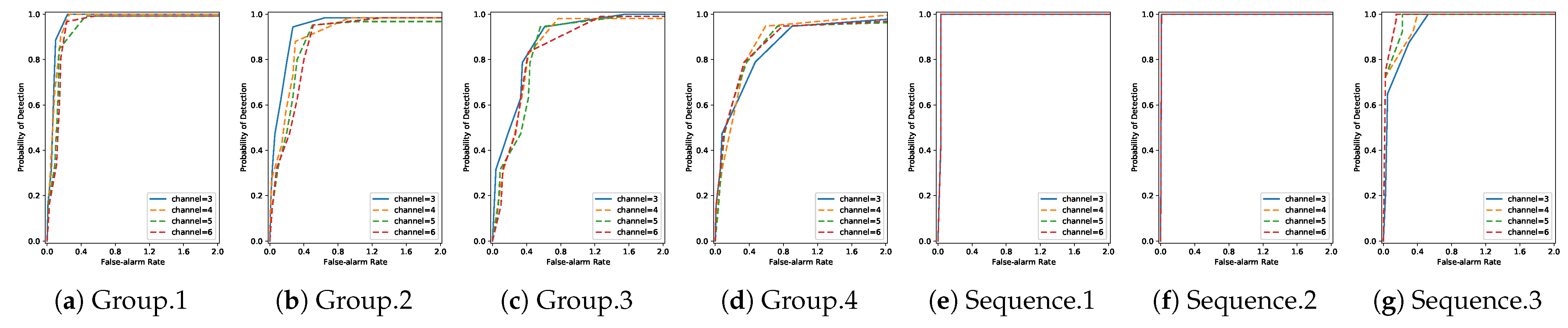
4.3. Analysis of Parameters
4.3.1. Patch Size
4.3.2. The Stride between Reference Blocks
4.3.3. Matching Region
4.3.4. The Number of Channels in the Model
4.4. Experiments and Analysis
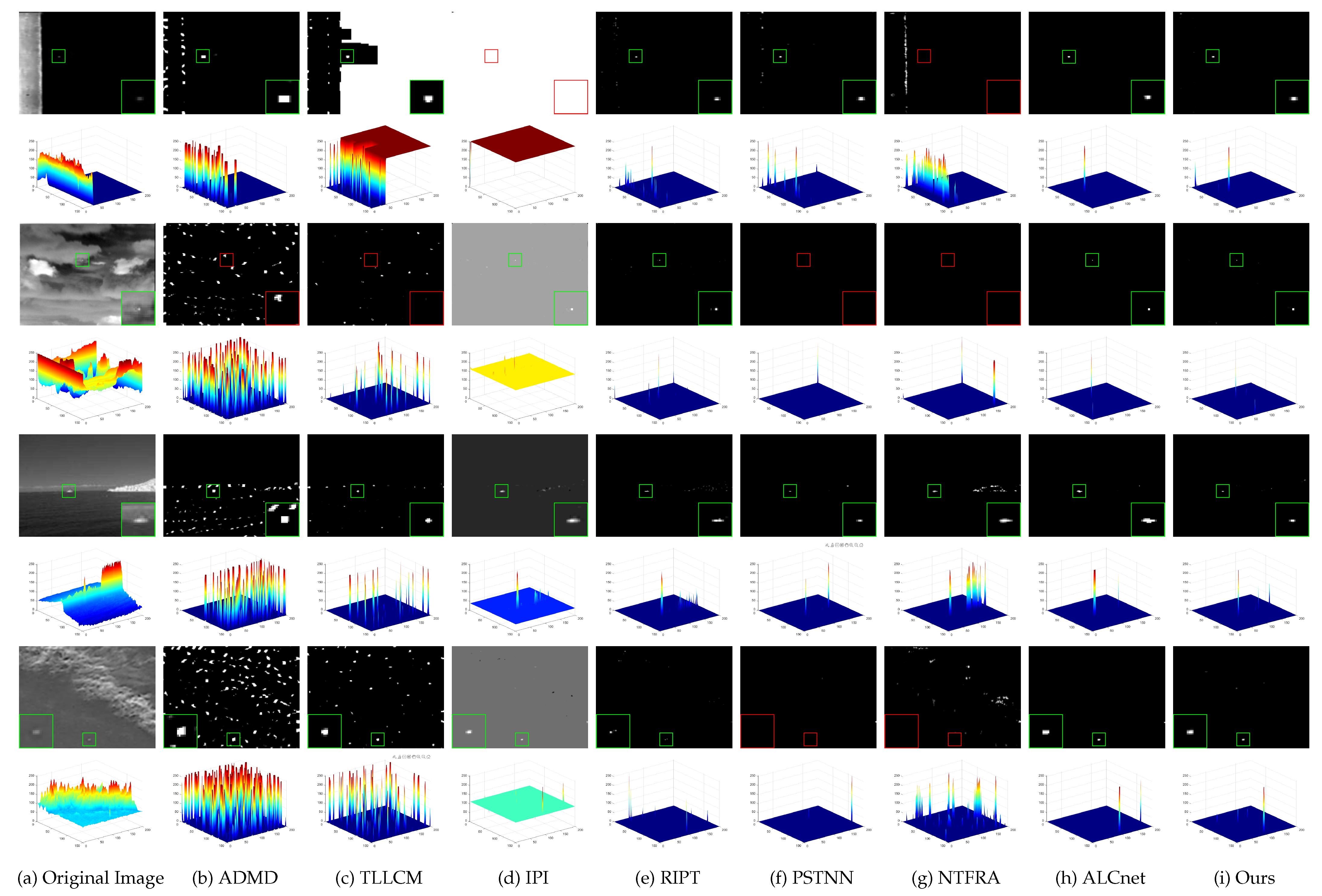
4.4.1. Experimental Results
4.4.2. Comparative Experiments and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.; Lee, J. Scale invariant small target detection by optimizing signal-to-clutter ratio in heterogeneous background for infrared search and track. Pattern Recognit. 2012, 45, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Meng, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hauptmann, A.G. Infrared Patch-Image Model for Small Target Detection in a Single Image. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 4996–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y. Spatial information based FCM for infrared ship target segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, (ICIP) 2014, Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 5127–5131. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.L.P.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xia, T.; Tang, Y.Y. A Local Contrast Method for Small Infrared Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, I.; Gagliardi, R.; Stotts, L. Optical moving target detection with 3D matched filtering. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1988, 24, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, Y.Y. Infrared moving target detection and tracking based on tensor locality preserving projection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2010, 53, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber-Shalem, R.; Hadar, O.; Rotman, S.R.; Huber-Lerner, M.; Evstigneev, S. Improving variance estimation ratio score calculation for slow moving point targets detection in infrared imagery sequences. In Proceedings of the Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 2013, San Diego, CA, USA, 28–29 August 2013; Volume 8857, p. 885707. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, S.; Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Xiao, F. Infrared Small Target Detection via Low-Rank Tensor Completion With Top-Hat Regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Shao, S.; Zhang, E.; Lin, G. Infrared Moving Small-Target Detection via Spatiotemporal Consistency of Trajectory Points. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.D.; Er, M.H.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Chan, P. Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small targets. In Proceedings of the Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 1999, Denver, CO, USA, 19–23 July 1999; Volume 3809, pp. 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.; Li, J.; Peng, Z. The design of Top-Hat morphological filter and application to infrared target detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2006, 48, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, F. Analysis of new top-hat transformation and the application for infrared dim small target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadhoud, M.; Thomas, D. The two-dimensional adaptive LMS (TDLMS) algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1988, 35, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.W.; Kim, Y.C.; Ahn, S.H.; Sohng, K.I. A novel Two-Dimensional LMS (TDLMS) using sub-sampling mask and step-size index for small target detection. IEICE Electron. Expr. 2010, 7, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.W.; Zhang, F.; Kweon, I.S. Edge directional 2D LMS filter for infrared small target detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2012, 55, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J. Detection and tracking of low-observable targets through dynamic programming. In Proceedings of the Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 1990, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–18 April 1990; Volume 1305, p. 207. [Google Scholar]
- Farajzadeh, M.; Mahmoodi, A.; Arvan, M.R. Detection of small target based on morphological filters. In Proceedings of the 20th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE2012), Tehran, Iran, 15–17 May 2012; pp. 1097–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Zhu, H.; Wei, Y.; Lu, G.; Wei, Y. Small target detection using quantum genetic morphological filter. In Proceedings of the MIPPR 2015: Automatic Target Recognition and Navigation, Enshi, China, 31 October–1 November 2015; Volume 9812, p. 98120A. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, P.; He, Y. Infrared Small Target Detection via Nonnegativity-Constrained Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1700–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y. Adaptive top-hat filter based on quantum genetic algorithm for infrared small target detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 10539–10551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Huang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, L.; Bai, S. Infrared dim and small target detecting and tracking method inspired by Human Visual System. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2014, 62, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, B. Effective Infrared Small Target Detection Utilizing a Novel Local Contrast Method. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1890–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liang, K.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L. Infrared Small Target Detection Utilizing the Multiscale Relative Local Contrast Measure. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, Z.; Chen, Z.; Shao, L. Tiny and Dim Infrared Target Detection Based on Weighted Local Contrast. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Moradi, S.; Faramarzi, I.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q. A Local Contrast Method for Infrared Small-Target Detection Utilizing a Tri-Layer Window. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Kim, S. AVILNet: A New Pliable Network with a Novel Metric for Small-Object Segmentation and Detection in Infrared Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Dai, J.; Xie, C. Dim and small target detection based on feature mapping neural networks. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 62, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L. Miss Detection vs. False Alarm: Adversarial Learning for Small Object Segmentation in Infrared Images. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8508–8517. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, C.; Fu, Q.; Han, Z. A Novel Pattern for Infrared Small Target Detection With Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 4481–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Wang, Z.; Tan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, W. RISTDnet: Robust Infrared Small Target Detection Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Lehman, J.; Molino, P.; Petroski Such, F.; Frank, E.; Sergeev, A.; Yosinski, J. An intriguing failing of convolutional neural networks and the CoordConv solution. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; pp. 9605–9616. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Gao, Z.; Xie, C. Dim and small target detection based on their living environment. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 120, 103271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y. Infrared small target and background separation via column-wise weighted robust principal component analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 77, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Ren, M. Infrared small target detection based on patch image model with local and global analysis. Int. J. Image Graph. 2018, 18, 1850002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Ni, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, G.; Deng, L. TNLRS: Target-Aware Non-Local Low-Rank Modeling With Saliency Filtering Regularization for Infrared Small Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 9546–9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, Y. Reweighted Infrared Patch-Tensor Model With Both Nonlocal and Local Priors for Single-Frame Small Target Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3752–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm. Remote Sensing. 2019, 4, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Yang, C.; Cao, S.; Li, C.; Peng, Z. Infrared Small Target Detection via Nonconvex Tensor Fibered Rank Approximation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmer, M.E.; Martin, C.D. Factorization strategies for third-order tensors. Linear Algebra Appl. 2011, 435, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, O.; Rojo, H. Some results on symmetric circulant matrices and on symmetric centrosymmetric matrices. Linear Algebra Appl. 2004, 392, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image Denoising by Sparse 3D Transform-Domain Collaborative Filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image restoration by sparse 3D transform-domain collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the Image Processing: Algorithms and Systems VI, Burlingame, CA, USA, 4–6 February 2013; Volume 6812, p. 681207. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallaro, A.; Steiger, O.; Ebrahimi, T. Tracking video objects in cluttered background. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2005, 15, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Feng, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Lin, Z.; Yan, S. Tensor Robust Principal Component Analysis with a New Tensor Nuclear Norm. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilmer, M.E.; Braman, K.; Hao, N.; Hoover, R.C. Third-Order Tensors as Operators on Matrices: A Theoretical and Computational Framework with Applications in Imaging. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 2013, 34, 148–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Moallem, P.; Sabahi, M.F. Fast and robust small infrared target detection using absolute directional mean difference algorithm. Signal Process. 2020, 177, 107727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Barnard, K. Attentional Local Contrast Networks for Infrared Small Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 9813–9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Methods | Group.1 | Group.2 | Group.3 | Group.4 | Sequence.1 | Sequence.2 | Sequence.3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | AUC | AUC | AUC | AUC | AUC | AUC | ||||||||
| ADMD | 4.3% | 0.186 | 2.2% | 0.068 | 1.7% | 0.038 | 1.8% | 0.028 | 3.0% | 0.050 | 13.6% | 0.194 | 1.0% | 0.025 |
| TLLCM | 4.8% | 0.166 | 1.4% | 0.107 | 0.8% | 0.085 | 0.7% | 0.088 | 1.0% | 0.151 | 4.1% | 0.576 | 0.5% | 0.050 |
| IPI | 28.7% | 0.886 | 34.6% | 0.767 | 51.0% | 0.830 | 80.4% | 0.861 | 100.0% | 1.000 | 100.0% | 1.000 | 96.3% | 0.973 |
| RIPT | 97.5% | 0.975 | 86.5% | 0.903 | 43.9% | 0.859 | 63.2% | 0.844 | 100.0% | 1.000 | 100.0% | 1.000 | 89.4% | 0.967 |
| PSTNN | 96.0% | 0.943 | 88.5% | 0.893 | 95.7% | 0.937 | 80.9% | 0.910 | 100.0% | 1.000 | 100.0% | 1.000 | 72.5% | 0.851 |
| NTFRA | 10.5% | 0.067 | 0.8% | 0.038 | 2.5% | 0.187 | 4.2% | 0.308 | 100.0% | 1.000 | 100.0% | 1.000 | 14.5% | 0.604 |
| ALCnet | 94.3% | 0.928 | 54.5% | 0.892 | 86.7% | 0.938 | 58.9% | 0.884 | 100.0% | 0.995 | 48.6% | 0.918 | 5.8% | 0.437 |
| Ours | 100.0% | 0.991 | 97.7% | 0.963 | 87.8% | 0.954 | 88.4% | 0.938 | 100.0% | 1.000 | 100.0% | 1.000 | 98.3% | 0.977 |
| Methods | Group.1 | Group.2 | Group.3 | Group.4 | Sequence.1 | Sequence.2 | Sequence.3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCRG | BSF | SCRG | BSF | SCRG | BSF | SCRG | BSF | SCRG | BSF | SCRG | BSF | SCRG | BSF | |
| ADMD | 1.091 | 0.168 | 1.071 | 0.237 | 1.106 | 0.331 | 1.337 | 0.624 | 2.759 | 0.742 | 2.926 | 0.298 | 1.626 | 0.510 |
| TLLCM | 1.218 | 0.270 | 1.586 | 0.429 | 1.755 | 0.707 | 1.949 | 1.460 | 2.252 | 2.426 | 3.697 | 0.643 | 4.676 | 1.992 |
| IPI | 2.474 | 0.850 | 3.476 | 1.824 | 5.522 | 3.635 | 9.670 | 8.249 | 21.387 | 10.821 | 2.950 | 1.358 | 16.142 | 19.218 |
| RIPT | 1.798 | 1.176 | 2.692 | 2.246 | 4.902 | 4.776 | 7.878 | 11.037 | 24.278 | 17.132 | 2.373 | 1.483 | 8.221 | 10.005 |
| PSTNN | 2.921 | 1.434 | 4.519 | 2.558 | 6.737 | 4.008 | 9.081 | 12.075 | 40.654 | 17.616 | 2.677 | 1.300 | 27.740 | 23.690 |
| NTFRA | 0.802 | 0.285 | 1.836 | 0.828 | 3.309 | 1.722 | 6.838 | 6.682 | 35.569 | 17.174 | 2.969 | 1.345 | 17.952 | 9.070 |
| ALCnet | 2.206 | 0.423 | 6.180 | 1.258 | 8.240 | 2.268 | 12.046 | 4.988 | 40.658 | 17.616 | 2.633 | 0.805 | 37.810 | 21.176 |
| Ours | 3.125 | 1.117 | 4.911 | 2.710 | 5.666 | 4.985 | 8.792 | 9.735 | 41.323 | 17.616 | 2.580 | 1.275 | 14.612 | 12.745 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Ding, C.; Gao, Z.; Xie, C. ANLPT: Self-Adaptive and Non-Local Patch-Tensor Model for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041021
Zhang Z, Ding C, Gao Z, Xie C. ANLPT: Self-Adaptive and Non-Local Patch-Tensor Model for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(4):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041021
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhao, Cheng Ding, Zhisheng Gao, and Chunzhi Xie. 2023. "ANLPT: Self-Adaptive and Non-Local Patch-Tensor Model for Infrared Small Target Detection" Remote Sensing 15, no. 4: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041021
APA StyleZhang, Z., Ding, C., Gao, Z., & Xie, C. (2023). ANLPT: Self-Adaptive and Non-Local Patch-Tensor Model for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sensing, 15(4), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041021