Abstract
High-resolution soil moisture (SM) information is essential for regional to global hydrological and agricultural applications. The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) offers daily global composites of SM at coarse-resolution 9 and 36 km, with data gaps limiting its local application to depict SM distribution in detail. To overcome the aforementioned problem, a downscaling and gap-filling novel approach was adopted, using random forest (RF) and artificial neural network (ANN) algorithms to downscale SMAP SM data, using land-surface variables from moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) onboard Aqua and Terra satellites from the years 2018 to 2019. Firstly, four combinations (RF+Aqua, RF+Terra, ANN+Aqua, and ANN+Terra) were developed. Each combination downscaled SMAP SM at a high resolution (1 km). These combinations were evaluated by using error matrices and in situ SM at different scales in the ShanDian River (SDR) Basin. The combination RF+Terra showed a better performance, with a low averaged unbiased root mean square error (ubRMSE) of 0.034 / and high averaged correlation (R) of 0.54 against the small-, medium-, and large-scale in situ SM. Secondly, the impact of various land covers was examined by using downscaled SMAP and in situ SM. Vegetation attenuation makes woodland more error-prone and less correlated than grassland and farmland. Finally, the RF+Terra and ANN+Terra combinations were selected for their higher accuracy in gap filling of downscaled SMAP SM. The gap-filled downscaled SMAP SM results were compared spatially with China Land Data Assimilation System (CLDAS) SM and in situ SM. The RF+Terra combination outcomes were more humid than ANN+Terra combination results in the SDR basin. Overall, the RF+Terra combination gap-filled data showed high R (0.40) and less ubRMSE (0.064 /) against in situ SM, which was close to CLDAS SM. This study showed that the proposed RF- and ANN-based downscaling methods have a potential to improve the spatial resolution and gap-filling of SMAP SM at a high resolution (1 km).
1. Introduction
Soil moisture (SM) plays a significant role in global water and energy balance [,], and it influences hydrological and atmospheric cycles [,], irrigation management, drought conditions [], and many other processes. SM can be attained from ground-truth observation (in situ) [], land surface models (LSM) possibly using data assimilation [], and remotely sensed datasets [,,]. On a regional scale, in situ SM measurements cannot reflect the exact SM distribution []. In areas where stations are sparsely distributed, data-assimilation products based on these measurements are unable to provide a complete picture of the spatial and temporal variability of surface soil moisture (SSM) [,]. Recently, remotely sensed SM products have been the only practical alternative for gaining access to a vast amount of SM data on both spatial and temporal dimensions, something that is almost impossible to achieve with in situ SM monitoring networks [,,]. Due to the large dielectric difference between dry soil and liquid water, microwave remote sensing is one of the remote-sensing technologies that can penetrate the soil surface and directly measure the SSM content. Although enormous efforts have been made in the past several decades to retrieve SM via microwave remote-sensing satellites (active and passive), these methods are not without their drawbacks. Datasets from active sensors such as the European Remote Sensing (ERS) satellite are significantly impacted by scattering caused by surface roughness and vegetation structure [,]. Passive microwaves’ products can provide more accurate SSM observations, unlike active sensors, because they are less impacted by topography, vegetation coverage, soil water content, and soil surface roughness [,], but their products contain coarse spatial resolution, and their sensing depth is also limited [].
Recent studies revealed that a combination of active and passive sensors is necessary to acquire reliable satellite-based SM data [,]. The SMAP satellite, launched by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA, Washington, DC, USA) in 2015, provided high-resolution SM on a global scale by fusing high-resolution L-band (active) radar backscatter data with L-band (passive) brightness temperature (TB) [,]. The SMAP satellite offers SM on a 36 km grid cell during both the ascending and descending passes (6:00 a.m. and 6:00 p.m., respectively). In July of 2015, the SMAP radar instrument stopped functioning, leaving the radiometer instrument as the sole functional component of the SMAP satellite and the only source of the level 2 SM data (L2SMP) [].
For investigations at the global and continental scales, the spatial resolution of the SMAP SM observation is adequate; however, it is not appropriate for applications in regional or local studies, such as agricultural and drought monitoring, without a product with a better resolution [,,,,]. Higher-resolution SM is still needed for several uses involving land surfaces, such as water resource management, agriculture, and crop production. Because of variations in climate and land-surface attributes across various locations, remote-sensing products tend to have site-specific performances that cannot be extrapolated elsewhere. Because optical/thermal infra-red (TIR) datasets often have high spatial resolutions, downscaling algorithms that utilize these datasets produce downscaled products with a similar fine resolution [,,,,,,]. Some downscaling techniques are already proposed on the bases of fine-resolution optical/TIR observations, such as vegetation indices (VIs) and land-surface temperature (LST); triangular/trapezoidal feature space [,,,]; University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) method []; Peng’s approaches (based on the vegetation temperature condition index (VTCI)) [,]; Disaggregation based on Physical And Theoretical scale Change (DisPATCh) based on some soil evaporative processes (actual evaporative fraction (EF); and soil evaporative efficiency (SEE)) [,,]. In downscaling, methods such as Peng’s, UCLA’s, EF, SEE, and DisPATCh employ an SM proxy variable to construct the interaction framework with SM. Merlin et al. [] applied actual evaporative fraction (EF) and SM indices. Using the North American Land Data Assimilation System (NLDAS) model, Fang et al. [] and Fang and Lakshmi. [] examined and compared several techniques for determining the SEE and used them to downscale AMSR-E SM over the Little Washita Watershed, Oklahoma, United States. Using this approach, the root mean square error (RMSE) of the downscaled SM ranged from 0.02 to /. However, Peng et al. [] and Malbéteau et al. [] demonstrated that simple SM proxy variables could not robustly depict the spatial and temporal variability in SM.
In recent years, various developments have been achieved in the construction of downscaling models, using ML algorithms with different data sources. It is possible to extract intricate and highly nonlinear relationships between input variables (predictors) and output variables (targets) by using ML algorithms from large datasets [,,,]. In recent times, several machine-learning methods, including RF, ANN, General Regression Neural Network (GRNN), and Support Vector Machine (SVM), have been introduced for downscaling of remotely sensed SM [,,,,,]. Intricate relationships between AMSR-E SM data and other MODIS surface-factor products were investigated in a downscaling research study by Im et al. [], using RF. The outcome shows that the RF technique can characterize the connection between AMSR-E and MODIS products with acceptable accuracy (RMSE = 0.051 /). Combining MODIS surface temperature with SM collected by SMOS, Srivastava et al. [] employed ANN, SVM, relevance vector machines, and generalized linear models and concluded that the ANN model produced superior results to other approaches. An ANN was utilized by Alemohammad et al. [] to establish a connection between low-resolution SM datasets and the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) estimates; then high-resolution NDVI data were used to generate high-spatial-resolution SM outputs. The SMAP passive SM products were downscaled by Abbaszadeh et al. [], using the RF model based on the parameters of the top 5 cm of soil in the CONUS region between April and December 2015. In the Little Washita watershed and the Walnut Gulch Experimental Watershed, the ubRMSE values for 2015 ranged from 0.02 to 0.06 / and from 0.02 to 0.07 /, respectively. They also showed that the downscaled SM products could be more accurate when other factors, such as soil texture and topography, are considered. According to the aforementioned studies, ML has the adaptability and competence to handle large amounts of remote-sensing data and nonlinear difficulties in SM downscaling. The ML techniques may be used to illustrate the nonlinear connections between SM and surface variables. As a result of their excellent generalization capacity and resilience, RF and ANN have been frequently employed in prior research [,,,].
Compared to other inland areas, the availability of SMAP SM in the SMN-SDR Basin is much lower. For instance, the SMAP SM data were unavailable for most of the SMN-SDR Basin throughout the first half of 2018 due to clouds and frozen state events. The need for gap-filling techniques to generate temporally and spatially comprehensive SMAP SM data is essential due to the importance of the SMN-SDR Basin to the global environment. Several gap-filling approaches were proposed to reconstruct the SM data to overcome the problem of missing pixels. For instance, Liu et al. [] used original SMAP SM data with maximum available pixels to improve the spatial coverage of Essential Climatic Variable (ECV) SM pixels in Europe by estimating their arithmetic means. Unfortunately, this gap-filling method is very dependent on the availability of the SMAP pixels and is thus useless when no SMAP data are available. Zhang et al. [] suggested an ANN method for reconstructing the ESA CCI missing data for China between 1982 and 2015, with several environmental parameters serving as training data. Tong et al. [] proposed RF and geostatistical methodologies to fill the SM gaps in the SMAP products as a solution to the problem of missing data in the SMAP 36 km SM Level 3 (L3) product across the Tibetan Plateau. They verified the findings and concluded that the ML approach and the geostatistical methodology can release retrievals from the limits of traditional radiative transfer models and enhance the coverage in time and space for SMAP SM products.
In light of the above insights, we built RF and ANN models by using topographic data and optical/TIR data for downscaling coarse-resolution (36 km) SMAP passive microwave SM (SPL3SMP, Version 4) data. In this study, SM was the output variable, whereas optical/TIR data and topographical data were the input factors. This study focused on achieving the following purposes: (1) to downscale coarse resolution (36 km) SMAP SM at fine resolution (1 km), using RF and ANN models; (2) to evaluate downscaled SM quality of these ML techniques, comparing with ground truth SM observations at different scales over the SMN-SDR Basin; (3) to analyze the influence of various land-cover types, primarily forests, on the downscaled SM across the study region; (4) to fill missing gaps in the SMAP SM, using ML techniques, and validate them with CLDAS data at spatial–temporal scales.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
In the northern part of China, the ShanDian River Basin (Figure 1), which includes a wireless Soil Moisture Network referred to as SMN-SDR, was the primary focus of the research. The network’s total coverage area is 10,000 . The ShanDian River Basin is situated between 115.5°E and 116.5°E and between 41.5°N and 42.5°N in latitude and longitude, respectively. This region is big enough to accommodate sufficient SMAP SSM pixels with coarse resolution. The SMN-SDR is characterized by relatively flat topography and a landscape composed mostly of farmland, grassland, and scattered woodlands and wetlands. The yearly average precipitation in most regions ranges from 300 to 500 mm [].
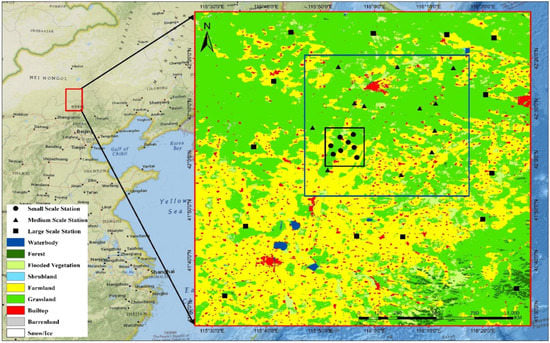
Figure 1.
The ShanDian River Basin and the network within the ShanDian River Basin (SMN-SDR), provide in situ SM measurements at an S-scale (within the black rectangle), medium scale (within the blue rectangle), and large scale (within the red rectangle).
2.2. Data
2.2.1. SMAP Data
SMAP’s global TB data are used to generate SM products with spatial resolutions of 36 km [], 9 km active–passive [], and 3 km (radar), with a temporal resolution of 1 to 3 days. Using active L-band radar and passive L-band radiometer, the SMAP satellite precisely monitors Earth’s surface at approximately 6:00 a.m. (descending) and approximately 6:00 p.m. (ascending) every day, in synchronization with the sun []. On 31 March and 13 April 2015, the radar and radiometer, respectively, began to provide SMAP imagery. Although the high spatial resolution of radars (about 1–3 km) is not comparable to the radiometer’s moderate resolution, radiometer (passive) devices are less sensitive to vegetation density and roughness of the ground than radar (active) sensors (around 40 km). The accuracy and spatial resolution of SM measurements are improved by SMAP’s integration of radar and radiometer sensors []. However, owing to a technical issue, the radar ceased supplying SMAP active microwave datasets on 7 July 2015. The near-SSM (0–5 cm) is determined by using radiometric-based methods with a volumetric accuracy of 0.04 / []. As a result, SMAP’s passive SM product is crucial for examining and analyzing in SM conditions throughout the world, and recent validation experiments have shown that it has a strong potential to accurately capture SSM dynamics [,,].
For this study, we used SMAP Level 3 passive radiometric SM product (SPL3SMP, Version 4) from 2018 and 2019, which has 36 km spatial resolution on the Equal-Area Scalable Earth (EASE) Grid. This product provides daily composites of SSM generated by daily Level 2 half-orbit granules. The NASA’s National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center (NSIDC) website (https://www.nsidc.org/data/smap/smap-data.html, last accessed on 10 April 2022) offers this dataset at no cost.
2.2.2. Land-Surface Model Data
We utilized the CLDAS soil volumetric water-content-analysis tool from the China Meteorological Data Service Centre. The CLDAS data have a spatial resolution of 0.0625° and have a temporal resolution of 1 h, covering the Asian region (0–65°N, 60–160°E). The CLDAS soil volumetric water content product has a correlation coefficient of 0.89, a root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.02 /, and a variance of 0.01 / when compared to the real ground observation data throughout all regions at a national scale []. This is shown by comparing soil volumetric water content measurements from CLDAS-V2.0 with SM observation measurements from China’s network of automated monitoring stations, all of which have undergone stringent quality controls. The CLDAS has higher spatial and temporal resolutions than either GLDAS or NLDAS SM. There are a total of four SM layers in the product, but just the topmost layer (0–10 cm) was the primary focus of this study. Hourly volumetric SM measurements were downloaded from the top layer, and then daily averages were computed.
2.2.3. MODIS Data
The quantity and quality of the datasets significantly impact the accuracy of ML approaches and the choice of algorithms [,]. For regression models, it is crucial to choose feature variables properly. The relationship between SSM and surface variables is the major step in establishing any downscaling process. In many previous studies, different important land-surface variables, such as LST, NDVI, enhanced vegetation index (EVI), surface albedo (ALBEDO), and normalized difference water index (NDWI), were used to establish a relationship with SSM. These land-surface variables mainly consist of vegetation indices, water indices, and surface reflectance, which directly influence SSM. In this study, we used some new indices related to soil wetness, such as the land-surface water index (LSWI) [] and normalized shortwave-infrared difference bare SM index (NSDSI) []. MODIS onboard the Aqua and Terra satellites are the best sources for any region to obtain all of these continuous time-series predictors. The MODIS products MYD11A1 and MOD11A1 were used to obtain daily Aqua and Terra LST at 1 km spatial resolution, respectively; MYD13A2 and MOD13A2 for 1 km resolution 16-days Aqua and Terra vegetation indices (NDVI and EVI), respectively; and 1 km resolution daily Aqua and Terra surface ALBEDO obtained from MYDTBGA and MODTBGA products, respectively. The soil wetness indices (NDWI, LSWI, and NSDSI) were calculated by processing different bands obtained from MODIS (Aqua and Terra) surface reflectance products (MYD09GA and MODO9GA), respectively. The following equations represent the soil wetness indices:
where , , and are the 2nd, 4th, 6th, and 7th surface reflectance bands, respectively, of the Aqua and Terra MYD09GA and MODO9GA products. These MODIS products are accessible via the NASA Earthdata website (https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov, last accessed on 14 April 2022), and all of the data were collected for the years 2018 and 2019.
2.2.4. Topographic Data
SM is strongly associated with elevation, slope, and aspect [,]. As a source of elevation data, we used the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) digital elevation model (DEM). Based on the DEM, the slope and aspect can be calculated. Th slope and aspect were assessed by using QGIS, and these data were received directly from the land processes distributed active archive center website (https://lpdaac.usgs.gov, last accessed on 27 April 2022).
2.2.5. In Situ SM Data
This study collected ground-based SM data from the SMN-SDR, a wireless network that measures soil moisture in the SMN-SDR Basin of North China. From 18 July 2018 to 28 September 2018, the SMN-SDR was operational during the SM experiment in the Luan River []. The SMN-SDR network’s in situ SM data was made publicly accessible via the International Soil Moisture Network (ISMN) []. The network, which consisted of 34 stations in total, was constructed using three different sample scales: large scale (100 km), medium scale (50 km), and small scale (10 km). As can be seen in Figure 1, 14 large-scale (L) stations (out of total 34 stations), 12 medium-scale (M) stations, and 8 small-scale (S) stations fit precisely inside the SMAP 9 km grid. Estimates of SM were made at five different depths (3, 5, 10, 20, and 50 cm) across all stations using Decagon EM50, USA (5TM probes) sensors. The data were recorded during 10-min (before June 2019) and 15-min (beginning June 2019) intervals. The SMN-SDR SM data at 5 cm depths (from 25 July 2018 through 31 December 2019) were utilized to check the accuracy of SMAP L3 SM in this study.
2.2.6. Precipitation Data
The SMN-SDR includes additional meteorological data, such as precipitation, in addition to multilayer soil temperature (at the same depths as the SMs). In total, 20 of the 34 stations use HOBO rain gauges (made by Austria), measuring up to 160 inches of rain at rates as high as 12.7 cm (5 inches) per hour in the SMN-SDR []. The majority of these stations are situated on small and medium scales. The HOBO rain gauge is described in further detail at (https://www.onsetcomp.com/products/data-loggers/rg3, last accessed on 18 April 2022). Each of these stations has time-series hourly data of soil temperature, precipitation, and SM. The climate in the experimental area is moderate continental, with annual precipitation averaging between 300 and 500 mm, with 70% of falling between July and September [].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The downscaled SMAP SM was qualitatively evaluated with the SMN-SDR network at two spatial scales: core validation sites (CVSs), which provide all of the S-scale (S) and a sparse network of M-scale (M) and L-scale (L) stations. In this study, these networks were utilized to compare the SMAP SM downscaled by RF and ANN at 1 km spatial resolution with in situ SM, using a series of statistical metrics, including the ubRMSE [,], correlation coefficient (R), and mean Bias []. The validating metrics are defined as follows:
where E[.] is the expectation value operator; and represent SMAP and in-situ SM values, respectively; is the standard deviation of ; and is the standard deviation of .
3. Soil Moisture Downscaling Framework
The spatial and temporal heterogeneities of the SM were employed in conjunction with high-resolution datasets to downscale the SM from the SMAP radiometer. All of the abovementioned variables, such as VIs, WIs, LST, slope, elevation, and aspect, are readily accessible at acceptable resolutions and are considered to have good explanatory power on the SM profile at various scales []. Precipitation, a covariate of the atmosphere, is used to sustain the downscaled SM’s temporal evolution. Aspect, slope, and elevation are geophysical factors that represent the variation and spatial distribution patterns of downscaled SM. To consider the impact of different kinds of vegetation on the downscaled SM spatial and temporal distribution patterns, further variables are used, such as VIs (as a measure of greenness). Low-quality pixels that might have been impacted by clouds or aerosols were omitted from the analysis by performing a thorough quality-control check and by reprojecting all the data to the same coordinate reference system (i.e., WGS 84). Furthermore, nearest-neighbor interpolation and simple arithmetic mean approaches were utilized to compensate for the differences in spatial resolution between the predictors and the response variables. Coarse-resolution predictors were resampled to a high-resolution by using nearest-neighbor interpolation, whereas high-resolution predictors (e.g., LST, Vis, and WIs) were resampled to a coarse resolution, using the simple arithmetic mean.
This research created the downscaling framework by using RF and ANN ML techniques. In the following sections, the fundamentals of these strategies and how they work are thoroughly covered. The primary contribution of this study is the development of a novel method for including the aforementioned atmospheric and geophysical variables in the RF and ANN models, which will enhance estimations of SM at finer resolutions.
3.1. Random Forest (RF)
The RF method is an ensemble learning technique that combines the outputs of many different decision trees to improve prediction accuracy []. Its advantage lies in the rapidity with which it can be trained and the precision with which the RF model can be optimized for performance []. RF relies heavily on bootstrap aggregation (bagging), a statistical technique used to produce many subgroups by repeatedly sampling the training dataset with a replacement (i.e., bootstrap samples). In this study, approximately two-thirds of each random subset (e.g., in-bag, IB) was used to train the decision trees that comprise the ensemble, while the remaining one-third (e.g., out-of-bag, OOB) was used for model verification. The final anticipated value is an average of the predictions made by the various regressors. RF may be tuned to improve its prediction ability by using a few user-defined parameters. The maximum number of parameters that may be selected at each decision tree split, the maximum depth of the decision tree, and the total number of decision trees to be developed are all interconnected. Furthermore, an appealing aspect of RF is its capacity to highlight the perceived importance of predictors by making use of OOB data. Because of its adaptability, randomization, and decorrelation, RF may be used to describe extremely nonlinear and complicated relationships. RF is easy to work with and adaptable, and it is less sensitive to changes in hyperparameters than other models. It has been shown in previous studies that the RF model is capable of representing a workable SM downscaling model, and it has also been proved to be successful in complicated nonlinear fitting [,,,,,].
3.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
The artificial neural network (ANN) is a technique of ML that originated and developed from the idea of replicating the human brain. ANNs are also known as convolutional neural networks. The pyramid of artificial intelligence (AI) depicts the progression from machine learning to ANN and further to deep learning (DL). The ANN is presently one of the most prominent ML techniques and is employed in numerous applications, including the remote sensing of SM inversion [,,,,]. ANNs have the capability of learning complicated functional forms in an adaptive manner and of capturing extremely nonlinear correlations between the inputs (predictors) and the targets (responses) []. Three essential elements are present in any neural network: the node character, the network architecture, and the learning rules. The node’s character, which includes its number of inputs and outputs, the weights assigned to each input and output, and the activation function, defines how signals are processed by the node. An activation function, which is a mathematical function, uses ANN processing to transform the result of the summing function into the node’s final output. The organization and connectivity of nodes are determined by network topology. Establishing the network’s topology requires counting the number of nodes in each layer, determining the total number of layers, and tracing the paths of the connections between the nodes. The initialization and adjustment of the weights are controlled by learning rules. The ANN trains the network via a learning process. To produce the intended output, the ANN is trained to detect patterns in the provided input datasets during the training phase. After the network has been trained, the next step is testing, where the pattern identified during training is used to create the corresponding output depending on the inputs [,,].
The training process for complicated ANNs may provide the false impression of high accuracy owing to the overfitting of the data. To prevent overfitting during iterative training, ANNs often use the regularization technique of early stopping []. In this research, a particular kind of ANN known as a multilayer perceptron (MLP) was used. It is made up of little units called perceptrons. MLP is a model built by hierarchically stacking perceptrons, layer by layer. In a particular layer, the perceptrons are independent of one another, yet each is linked to the remainder of the perceptrons in the next layer. Each layer is made up of a group of neurons that are trained by using a backpropagation technique. It is one of the most widely used methods for supervised multilayered neural network training [,,]. By altering the weight values internally, it approximates the nonlinear relationship between the input and the response. Then it is considered that the weights with the lowest error functions are the key to solving the learning problems. An ANN algorithm was implemented by using the neuralnet and h2o R-language packages, both of which have a number of pre-existing functions. One input layer, two hidden layers, and one output layer were used to make up ANN models with 200 hidden neurons in this research work. The quantity of epochs indicates how often the weights are updated by using the whole set of training data. In other words, it measures how many times the backpropagation algorithm runs across the complete training dataset. The research made use of 100 epochs. The “RectifierWithDropout” was used as the activation function. Assessment metrics between actual and anticipated values for dataset were used to complete the final model evaluation.
3.3. Downscaling Process
This study employed RF and ANN ML techniques to downscale SPL3SMP (36 km) SM to 1 km. Recently, they have become more widely used in remote sensing to address classification and regression issues, especially RF []. Both of the proposed downscaling methods are based on the same principle: establishing a statistical connection between SMAP SM and geospatial variables (elevation, slope, and aspect), and land-surface variables (NDVI, EVI, NDWI, LSWI, NSDSI, and LST) at a coarse resolution (36 km) that link input variables’ output covariates by using the following equations:
where SM is the downscaled SM data (response); is the regression function of ML techniques (RF and ANN); , , … represent the input covariates (i.e., NDVI, EVI, NDWI, LSWI, NSDSI, LST, elevation, slope, and aspect); and n is the total number of predictors. The layout of the aforementioned SM downscaling technique is briefly summarized in the following steps.
Step 1: The DEM and high-resolution MODIS surface variables (1 km) were resampled to the same coarse resolution (36 km) of the SMAP SM product. Then the regression interaction between surface parameters and SM datasets was established by using the RF and ANN models at a coarse resolution. During the regression, MODIS/Aqua and MODIS/Terra land-surface variables were used to develop four different combinations with SMAP SM, applying RF and ANN algorithms. These combinations (RF+Aqua, ANN+Aqua, RF+Terra, and ANN+Terra) elaborated the ability of these downscaling techniques and the impact of different MODIS data. These combinations were developed when both MODIS and SMAP SM datasets were available for the whole study. Due to clouds and frozen events in the study area, only those days were selected when 90% of pixels had effective values during the time period from 2018 to 2019. The qualified number of days for all the combinations against multi-scale in situ SM and different land covers for study duration is listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Number of days with available datasets for all combinations at different scales in situ SM sites and vegetation.
Step 2: A calibration of the residual error between the prediction results of the RF and ANN downscaling models and the original data is required. Residuals at coarse resolution were computed by using original SM, and estimated results were resampled bilinearly at a coarse resolution. Then the coarse-resolution (36 km) residuals were interpolated to 1 km fine resolution, using the simple kriging interpolation technique.
Step 3: The trained RF and ANN models (established in first step) were applied for 1 km surface variables to obtain 1 km downscaled SMAP SM.
Step 4: After applying a residual correction, the final downscaled results were obtained by adding the estimated SM data at 1 km to the residual at 1 km. A random selection of 70%, 15%, and 15% of the data was used as the training set, verification set, and testing set, respectively, in the development of the RF and ANN downscaling models. After establishing the best possible model by using the lowest RMSE as a benchmark, the testing set was used to assess the model’s accuracy.
4. Results
4.1. Models Evaluation
Figure 2 shows the performances of downscaling models RF and ANN with different MODIS land-surface variables for training datasets. The scatter plot for each combination was developed to compare the predicted SMAP SM at a coarse resolution (36 km) with the original coarse-resolution SMAP SM. It can be observed that there is good agreement between predicted SMAP SM and original SMAP SM for all the combinations except ANN+Aqua. Comparing RF+Aqua and ANN+Aqua combinations, the correlation value for RF+Aqua is R = 0.96, which is much higher than that of ANN+Aqua, at about R = 0.63. Comparing the RMSE for the abovementioned combinations, we can see that the RF+Aqua showed a better performance, with lower error values of RMSE and an MAE of about 0.01 /, as compared to ANN+Aqua errors RMSE and MAE values of 0.03 / and 0.02 /, respectively. Similarly, comparing RF+Terra and ANN+Terra combinations, we can see that the correlation value for RF+Terra (R = 0.97) is higher than the ANN+Terra (R = 0.88). The mean RMSE value for RF+Terra is 0.01 /, and for ANN+Terra, it is 0.03 /; meanwhile, the MAE value for both combinations is 0.01 /. In general, the comparison between different algorithms and MODIS data-based models indicated the strength of RF-based regression models over ANN-based models. Overall, the RF+Terra combination results showed better correlation and fewer errors than the other combination. The differences in the performance of these combinations can be elaborated by accounting the influence of the MODIS Aqua and Terra datasets on the downscaling algorithms (especially ANN). As we know, the MODIS Terra orbits around the earth from north to south over the equator in the morning, whereas the MODIS Aqua passes from south to north across the equator in the afternoon. Therefore, during daytime, the solar radiation induced the variations in the Aqua LST that also affects the vegetation cover and water bodies that are directly linked with VIs and WIs, respectively. It can be observed that the RF-based models are independent of the Aqua or Terra satellites’ data, while this heavily affects ANN-based models. This might be because of the randomization and robustness of the RF algorithm that help the model avoid overfitting when even thousands of variables are given simultaneously. Moreover, the spatial aggregation of high-resolution predictors, such as VIs, WIs, Albedo, and LST, had a smoothing impact on the extreme values, resulting in the training of RF and ANN models with minimal extremes, as previously indicated by Wakigari et al. []. However, this was not special to our work since existing downscaling approaches depend on calibration at a coarse spatial resolution as the initial step, making the aggregation of high spatial-resolution predictors inevitable. Despite the fact that the ANN was proven to be an effective tool for dealing with the high-dimensional datasets employed in this work, it tended to overestimate lower SM values and underestimate higher SM values.
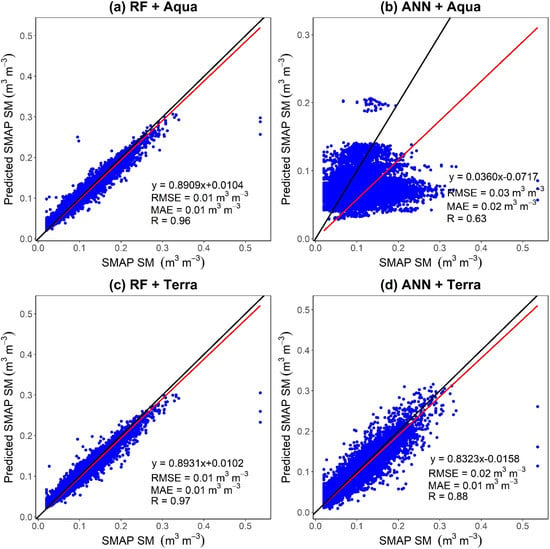
Figure 2.
Accuracy assessment of machine-learning models: (a) RF+Aqua, (b) ANN+Aqua, (c) RF+Terra, and (d) ANN+Terra against original SMAP SM.
Testing RF and ANN models using various ancillary datasets often shows that they can accurately predict SM at a coarse resolution; thus, these models were developed and implemented for predicting SM at a 1 km spatial resolution, assuming that the RF and ANN models constructed at coarse spatial resolution would also be viable for predicting SM at high geographical resolution utilizing high-spatial-resolution predictors. Since it was assumed that the RF and ANN models created at a coarse spatial resolution were equally viable for SM prediction at a high spatial resolution employing high-spatial-resolution predictors, these models were successfully applied for SM prediction at a spatial resolution of 1 km.
4.2. Comparison of Downscaled SM with In Situ Observations
Considering the better performance of RF and ANN models that present statistically and quantitatively strong relationships between land-surface variables and SSM, these models were then applied to fine-resolution variables to obtain high-resolution SM from SMAP. The validation of downscaled SM was statistically conducted with multi-scale (S-scale, M-scale, and L-scale) in situ SM observations over the SMN-SDR Basin from 2018 to 2019.
The scatter plots of the original SMAP SM and downscaled SM against the S-scale in situ SM observations are shown in Figure 3a–d, and the corresponding performance metrics are shown in Figure 4a–c. In comparison to in situ measurements, the RF+Terra-based downscaled SM showed a strong correlation (R = 0.52) and lower ubRMSE value of 0.037 /, as well as RMSE and Bias values of 0.084 / and −0.079 /, respectively. The ANN+Aqua model showed the worst performance among all the models, with less correlation (R = 0.51) and high errors (ubRMSE = 0.051 /). The ubRMSE, Bias, and R values for RF+Aqua are 0.039 /, −0.079 /, and 0.50, respectively, whereas the ANN+Terra showed slightly better performance with values of 0.048 /, −0.065 /, and 0.44, respectively. Figure 3e–h presents scatter plots of all the four model combinations’ results of downscaled SM and original SMAP SM against M-scale in situ measurements. As compared to the original SMAP SM, it can be observed that the downscaled SM provided excellent correlation with the in situ SM. The error metrics for four models are presented for M-scale in Figure 4d–f. The same as for the S-scale results, the RF+Terra model showed a high correlation (R = 0.58), less error (ubRMSE = 0.034 /), and negative biasness (Bias = −0.084) for M-scale. The RF+Aqua and ANN+Terra models showed the ubRMSE values of 0.035 / and 0.044 / and R values of 0.57 and 0.45, respectively. Similarly, the ANN+Aqua model performance was worst in terms of ubRMSE value of 0.045 / and a very high Bias value of 0.085 / but a slightly better correlation of 0.52 compared to the ANN+Terra model’s correlation value. For the L-scale, again the RF+Terra model outperformed with a high R value of 0.53 and lower ubRMSE value of 0.033 / as compared to the other models (as shown in Figure 4g–i). The lowest correlation value (R = 0.45) and highest error value (ubRMSE = 0.040 /) resulted from the ANN+Terra model. The scatter plots of downscaled SM and original SMAP SM against the L-scale in situ SM are presented in Figure 3i–l. We compared the downscaled SM from all the combination against different scales in situ SM categorized as core validation sites (S-scale) and sparse validation sites (M-scale and L-scale). The abovementioned results show that all the RF and ANN models’ outcomes presented better performance for the sparse validation site compared to core validation sites in term of higher correlation and lower error.
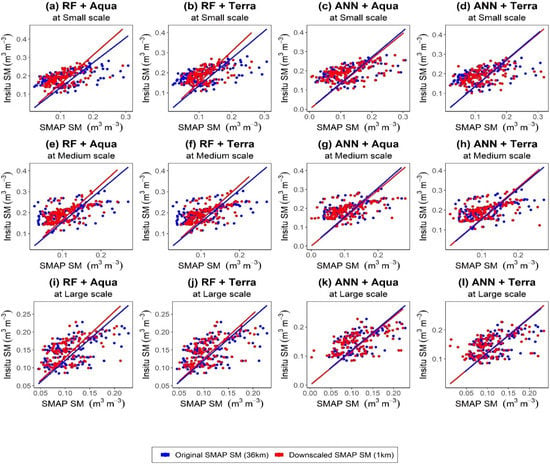
Figure 3.
Scatter plots between downscaled SM from all the models (RF+Aqua, RF+Terra, ANN+Aqua, and ANN+Terra) at (a–d) S-scale, (e–h) M-scale, and (i–l) L-scale in situ SM observations.
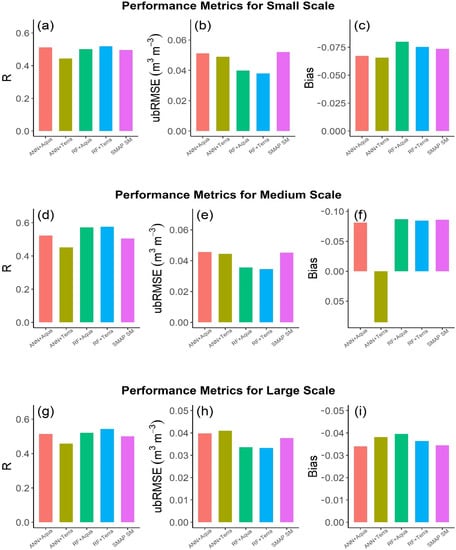
Figure 4.
Performance metrics (R, ubRMSE, and Bias) for all the models (RF+Aqua, RF+Terra, ANN+Aqua, and ANN+Terra) at (a–c) S-scale, (d–f) M-scale, and (g–i) L-scale in situ SM stations.
Overall, the performance of RF+Terra model was better than the other models at all scales (S-scale, M-scale, and L-scale) over the SMN-SDR Basin. Additionally, the ANN models (ANN+Aqua and ANN+Terra) downscaled SMs are closer to original SMAP SM than RF models, but the RF models’ results showed very good agreement with in situ SM, as shown in Figure 3. The better performance of the RF+Terra model can be due to two reasons: the first is the MODIS Terra data utilization to train the model, which is produced in the morning that is not much effected by physical surface temperature as compared to the MODIS Aqua data that obtained at afternoon; and the second reason can be the RF robustness and its suitability for complex and nonlinear relationship methodology due to its adaptive, decorrelated, and randomized features as compared to ANN models.
Figure 5 displays time series-comparisons of the original SMAP SM, in situ SM, and downscaled SM from all models (RF+Aqua, ANN+Aqua, RF+Terra, and ANN+Terra), as well as precipitation, collected data from multi-scale (S-scale, M-scale, and L-scale) stations between 2018 and 2019. The downscaled SM from all the four models agreed well with the time-series variations of the in situ SM at all the multi-scale stations. Changes in the in situ SM observations were also effectively observed by the original SMAP SM. The precipitation data were available for S-scale and M-scale in situ sites, and the downscaled SM and original SMAP SM showed good correspondence with rainfall events during the study period. However, ground observations at different footprints demonstrate significant changes, while original SMAP SM and downscaled SM records suggest only slight variations. Figure 5 shows that the original and downscaled SMAP SM are slightly more underestimated for S-scale sites compared to the M-scale and L-scale sites. The reason is the higher biasness for the core validation sites (S-scale) as compared to the sparse validation sites (M-scale and L-scale), as shown in Figure 4. It can be observed that the in situ SM data have almost constant values from the period of November 2018 to March 2019. At the same time, the original SMAP SM has no data; therefore, the downscaled SM also cannot be obtained. The reason is that the SMAP brightness temperature (TB) estimates were not available in the winter season due to frozen states. The SMAP calculates the SSM based on TB estimates directly linked with the dielectric constant. The variation in the dielectric constant is due to the soil emissivity and reflectivity, which can be increased or decreased depending on the SM quantity []. However, the frozen soil holds a very low dielectric constant, the same as the dry soil dielectric constant irrespective of the moisture content.
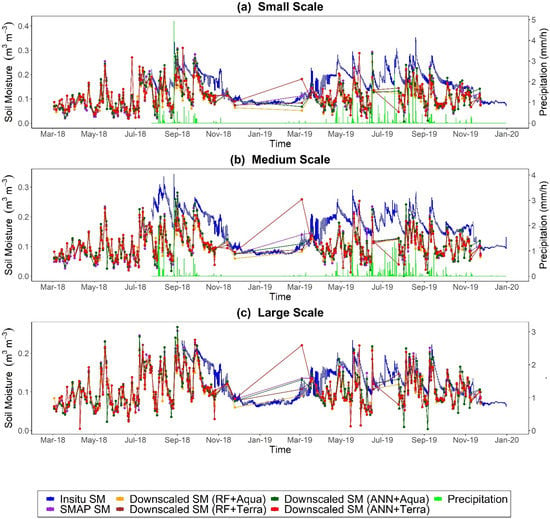
Figure 5.
Time series of downscaled SM from all the models (RF+Aqua, RF+Terra, ANN+Aqua, and ANN+Terra), original SMAP SM, precipitation, and in situ SM at (a) S-scale, (b) M-scale, and (c) L-scale stations.
4.3. Vegetation-Cover Impact on SMAP SM Downscaling Algorithms
In this part, we compare the error metrics from four developed downscaling models across the different in situ SM sites with various vegetation-type covers. The land of the SMN-SDR Basin was categorized into three types according to vegetation cover: grassland, farmland, and woodland. Grass was the major vegetation over many in situ stations, including the S-scale, M-scale, and L-scale sites, whereas the agricultural crops and forest area cover less area to contain these in situ sites. Out of total 34 in situ sites, 2 stations are located in the area covered by agricultural crops, 2 sites in the forestland, and rest of the 30 sites are covered by grass.
Figure 6 presents the scatter plots of downscaled SM and in situ SM for all the models at different vegetation-covered in situ SM stations. For grassland, to make scatter plots for the RF and ANN models, the sample datasets of downscaled SM and in situ SM were of 151 available days during the study period. The RF+Terra-based downscaled SM showed better correlation with in situ SM compared to the original SMAP SM (as shown in Figure 6a–d). The RF+Aqua and ANN+Terra models also presented better performance for grassland, but the ANN+Aqua-based downscaled SM showed the worst relation with in situ SM even when compared to the original SMAP SM. The performance metrics (R, ubRMSE, Bias) for grassland are presented in Figure 7a–c for all the models. The R values for RF+Aqua, RF+Terra, ANN+Aqua, and ANN+Terra models were 0.57, 0.59, 0.56, and 0.51; ubRMSE values were 0.034 /, 0.033 /, 0.043 /, and 0.041 /; and bias values were −0.072/, −0.069 /, −0.064 /, and −0.068 /, respectively. Through these evaluation metrics, it was concluded that the RF+Terra model outperformed the other models, followed by the RF+Aqua model and then the ANN+Terra model, and the worst performance was from the ANN+Aqua model containing high ubRMSE.
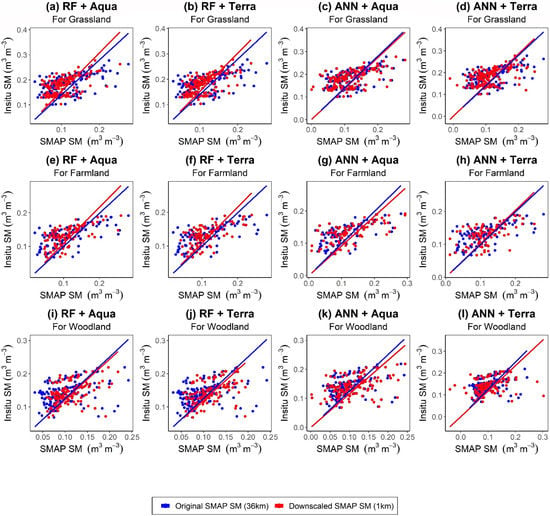
Figure 6.
Scatter plots between downscaled SM from all the models (RF+Aqua, RF+Terra, ANN+Aqua, and ANN+Terra) for (a–d) grassland, (e–h) farmland, and (i–l) woodland in situ SM observations.
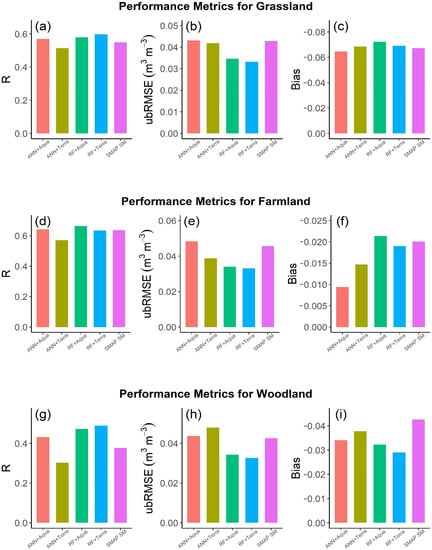
Figure 7.
Performance metrics (R, ubRMSE, and Bias) for all the models (RF+Aqua, RF+Terra, ANN+Aqua, and ANN+Terra) for (a–c) grassland, (d–f) farmland, and (g–i) woodland in situ SM stations.
Similarly, the RF+Terra models showed the best performance for farmland and woodland, with high correlation (R) values of 0.66 and 0.48, and lower error (ubRMSE) values of 0.033 / and 0.032 /, respectively. The ubRMSE values for farmland ranged from 0.033 / to 0.048 / for the RF+Aqua and ANN models. The R and bias values ranged from 0.57 to 0.65 and from −0.014 / to −0.021 /, respectively. All the RF and ANN models for the woodland showed a poor performance in terms of correlation (R) values, which ranged from 0.30 to 0.47. However, in terms of ubRMSE values, the RF+Terra and RF+Aqua models have error values less than 0.034 /. On the other hand, the ANN models have slightly high error values, about 0.047 /. Analyzing the scatter plots and errror metrics, it was observed that the models (RF+Terra and ANN+Terra) built using MODIS Terra datasets showed a better performance in terms of high correlation and fewer error values as compared to the models (RF+Aqua and ANN+Aqua) built by using MODIS Aqua datasets. The difference in the performances of the models may be due to the difference in the timing of the capturing of datasets by Aqua and Terra satellites (as discussed above).
Figure 8 shows the time-series comparison of averaged downscaled SM obtained from RF and ANN models with in situ SM and original SMAP SM, along with precipitation data. There were no precipitation data for woodland due to the absence of rain gauges in this area. The RF+Aqua- and RF+Terra-based downscaled SM showed good agreement with the in situ SM at all types of vegetation covers. The ANN+Aqua model also showed good temporal consistency for grassland and farmland, but it behaved inconsistently for some days for the woodland, as shown in Figure 8c. The original SMAP SM also showed good relevance with in situ SM, even with downscaled SM of RF and ANN models for all the vegetation types. Overall, the original SMAP SM and downscaled SM from all the models mostly restrained underestimation according to the grassland and farmland in situ SM, whereas for some days, they showed an overestimation for the woodland in situ SM. Moreover, the temporal variations of both the downscaled SM and original SMAP SM captured a good response with the rainfall events for grassland and farmland (except woodland). This shows the ability of ML techniques to enhance the spatial resolution of remotely sensed SM at different vegetation-covered regions for wet and dry periods.
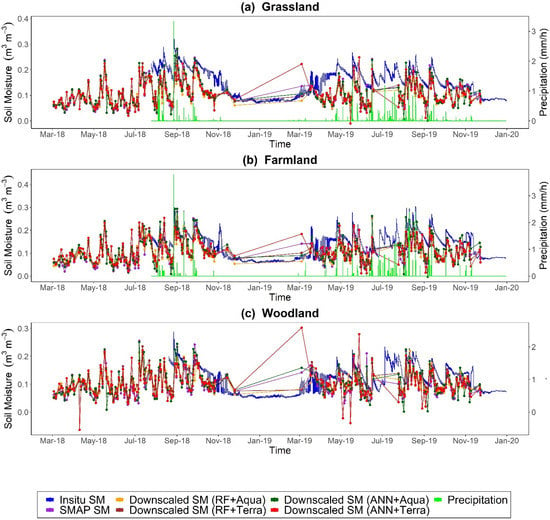
Figure 8.
Time series of averaged downscaled SM from all the models (RF+Aqua, RF+Terra, ANN+Aqua, and ANN+Terra), original SMAP SM, precipitation, and in situ SM for (a) grassland, (b) farmland, and (c) woodland stations.
4.4. Visual Assessments of the Spatial Distribution of Downscaled SM
After statistical and temporal comparison of downscaled SM, the spatial analysis was conducted to check the quality of downscaling approaches. The downscaled SM from RF and ANN-based models was visually compared with coarse resolution original SMAP SM.
Figure 9 shows the spatial distribution of coarse resolution (36 km) SMAP SM with high-resolution (1 km) downscaled SM obtained from RF+Terra and ANN+Terra models based on MODIS Terra auxiliary data. Three available consecutive overpasses (1 July 2018, 4 July 2018, and 6 July 2018) were selected for the spatial distribution of original SMAP SM and downscaled SM. The visual comparison between the high- and low-resolution SM spatial information revealed consistent spatial distribution patterns throughout the research region. In addition, the high-resolution downscaled SM pixels exist within coarse-resolution original SMAP SM pixels and agree well for each pixel.
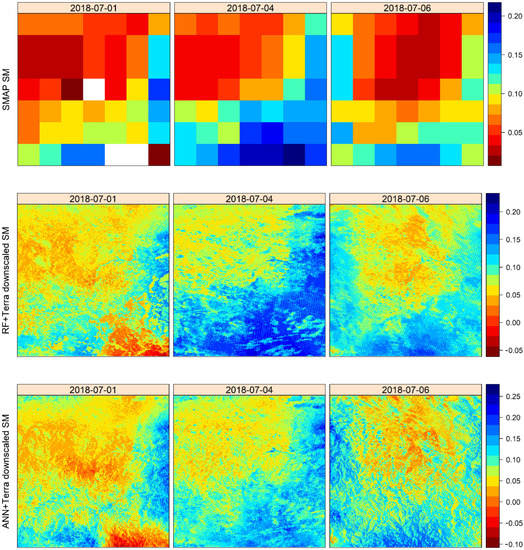
Figure 9.
Spatial patterns of 36 km SMAP SM (first row), 1 km downscaled SM from RF+Terra model (second row), and ANN+Terra model (third row) for three consecutive available days, namely 1 July 2018(first column), 4 July 2018 (second column), and 6 July 2018 (third column).
The spatial patterns based on RF+Terra model were smoother and more consistent with original SMAP SM data than the ANN+Terra model spatial patterns. Although the ANN+Terra model captured the dry pattern very well for these selective days, the RF+Terra model showed excellent results for dry-to-wet transition over the study region (shown in Figure 9). The spatial comparison proved the successful application of downscaling algorithms. For the date 1 July 2018, it can be found that the spatial distribution of SMAP SM cannot fully cover the study region, and this can be due to the cloud cover and scanning gap in case of SMAP SM observation. The gap-filling approach was applied to overcome this problem, which is explained in the next section.
The spatial-analysis results from the Aqua-based models (RF+Aqua and ANN+Aqua) for the same days as for Aqua-based models with downscaled SM and original SMAP SM are shown in Figure 10. It was observed that the RF+Aqua model captured the wet pattern very well, whereas the ANN+Aqua models captured the dry pattern efficiently. Using MODIS Aqua data, the ANN+Aqua model consistently followed the spatial pattern of coarse resolution SMAP SM. On the other hand, the RF+Aqua spatial distribution at fine resolution reasonably matched with the coarse-resolution SMAP SM pattern even with quantitative values, as presented in Figure 10.
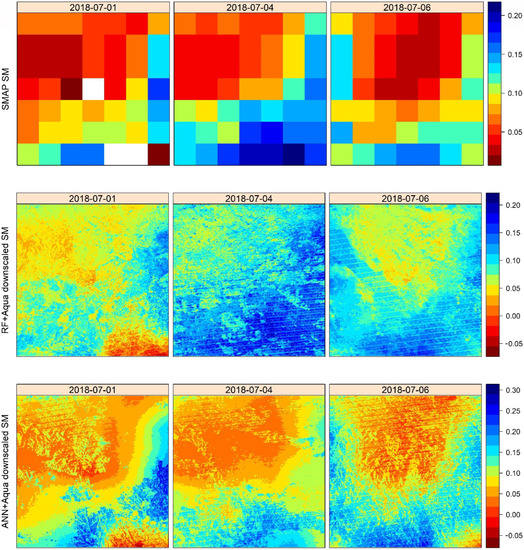
Figure 10.
Spatial patterns of 36 km SMAP SM (first row), 1 km downscaled SM from RF+Aqua model (second row), and ANN+Aqua model (third row) for three consecutive available days, namely 1 July 2018 (first column), 4 July 2018 (second column), and 6 July 2018 (third column).
Overall, the performance of all the downscaling models is acceptable, and they captured all the spatial distribution patterns over the Basin. Due to increased spatial resolution, the downscaled SM (1 km) presented more spatial details than the coarse-resolution (36 km) SMAP SM.
5. Discussion
5.1. Variable Importance of the Downscaling Models
The role of predictors on the performance of downscaling models mainly depends on the selection of input variables that strongly relate to SMAP SM []. In this research work, MODIS Aqua and Terra satellites’ datasets of land-surface variables were used as the inputs for the models. The importance of these variables for different RF and ANN models was analyzed based on the available different auxiliary datasets (MODIS Aqua/Terra). The variable importance of the model is calculated by estimating the percentage increase of mean square errors (MSE) when one variable is randomly perturbed and the others are unaltered. Usually, the categorization of predictors is based on the MSE value, and if it is close to zero, it indicates that the variable has less impact or no existence for prediction [,].
We selected the RF+Terra and ANN+Terra models’ important variables to present due to their better performances. Figure 11a shows that the LST presents higher scores than other surface variables for RF+Terra prediction, and this is due to the controlling effect of SSM on surface energy partition and exchange, which is similar to Im et al.’s [] findings. NDVI, NSDSI, and WIs (LSWI and NDWI) are also very crucial variables for RF+Terra prediction, whereas the ALBEDO has less values near zero, indicating that it does not influence the model prediction. Figure 11b shows that the NDVI and LST are more impactful than the other predictors and aspect has least importance for the prediction of ANN +Terra model. Here, one thing can be observed that EVI is the most important variable in the ANN model, whereas it has less influence on the RF model prediction; this may be due to the different method of parameter selection for models’ training and predictions. More importantly, the time-series evaluation of the RF and ANN models’ results showed the capability to provide a robust and strong relationship between SSM and other surface variables, as Im et al. [] found to downscale AMSR-E SM data, using MODIS products.
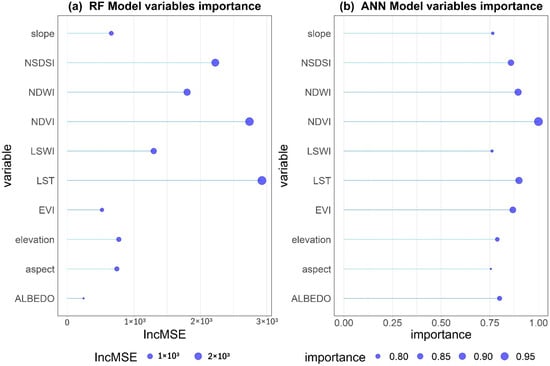
Figure 11.
Variables’ importance for the prediction of (a) RF+Terra model and (b) ANN+Terra model.
5.2. Spatial Distribution of Gap-Filled SM
SM features can be shown on large scales by using active and passive microwave satellite sensors; however, there are still gaps in these satellite-based SM products. Multiple variables, including radio-frequency interference and shifts in satellite-based sensors’ orbits and frozen state, contribute to this issue. Due to these issues, SMAP TB estimates are not available that are directly linked with dielectric constant associated with SM. Many efforts have been made to fill the missing values in the remotely sensed SM products. In this research work, for SMAP SM gap-filling, we first trained ML algorithms by using coarse-resolution (36 km) SMAP SM, along with coarse-resolution MODIS surface variables. During training, we selected those 36 km SMAP SM images that contain more than 90% pixels to cover the study area. Secondly, we applied these trained algorithms with high-resolution (1km) surface variables to fill the gaps in the SMAP SM images containing around 50% missing value. Finally, we validated gap-filled SMAP SM against in situ SM and temporally and spatially compared with CLDAS SM. We selected 20 images of SMAP SM for different dates during the whole study period from the year 2018 to 2019 at 36 km resolution and then predicted the missing values by applying the trained RF+Terra and ANN+Terra models. For gap-filing analysis, we neglected the RF+Aqua and ANN+Aqua based models due to their low predicting abilities in gap-filling compared to the downscaling of SMAP SM.
Figure 12 shows the spatial pattern distribution of gap-filled results from RF and ANN Terra models compared with SMAP SM, having about 50% missing pixels over the entire region of the SMN-SDR Basin. These gaps in the SMAP SM are due to the unavailability of TB because of paved areas, frozen states, or clouds during the capturing time of satellites. Overall, the southeastern part of the region is more humid than the northwestern part. The gap-filling results of the RF+Terra model are more consistent than the ANN+Terra model. Both models captured the humid and dry regions in the study area well. However, the ANN+Terra model gap-filling results are more humid than the RF+Terra model, as shown in Figure 12. However, the area having missing pixels in the original SMAP SM product was filled with very low SM values up to 0.15 / by RF+Terra model and up to 0.25 / by ANN+Terra model. Compared with CLDAS SM, RF+Terra showed a similar spatial pattern but was more relevant to the available pixels of the original SMAP SM. There is some mismatch in the CLDAS SM compared with SMAP SM. Most of the upper part of CLDAS SM showed the dry area having a minimum SM value of about 0.05 /, whereas the lower part showed a higher SM value of about 0.30 /, which presents a similar pattern related to SMAP SM. On the other hand, the spatial distribution results of ANN+Terra model were a little bit distorted, and the missing values were filled with high pixels values compared to the RF+Terra SM and CLDAS SM that can be due low efficiency of ANN model.
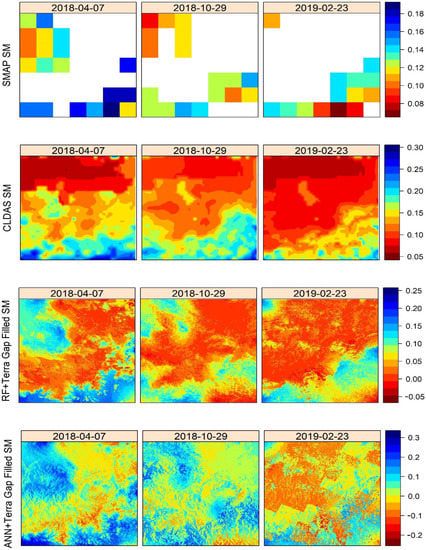
Figure 12.
Comparison of spatial distributions of gap-filled SM by RF+Terra model (3rd row) and ANN+Terra model (4th row) with CLDAS SM (2nd row) and original SMAP SM (1st row) at different dates 7 April 2018 (1st column), 29 August 2018 (2nd column), and 23 February 2019 (3rd column).
The time series of averaged SMAP SM, CLDAS SM, and gap-filled SM derived from RF+Terra and ANN+Terra SM are compared with in situ SM over the study area. Figure 13 describes the temporal dynamics of SM obtained from all the sources. In general, it can be observed that the SMAP and CLDAS SM show similar trends, and the gap-filled SM derived from the RF+Terra model shows a similar trend but is underestimated. However, the ANN+Terra model results show abrupt changes for some days and contain negative SM f-values, especially for the day 22 March 2019.
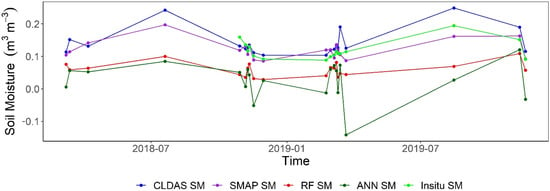
Figure 13.
The time series of averaged SM derived from RF+Terra model, ANN+Terra model, SMAP SM, and CLDAS SM against in situ SM over the SMN-SDR.
Figure 14 shows a scatter plot between SMAP SM, CLDAS SM, and gap-filled SM by RF and ANN models against in situ SM. To check the accuracy of CLDAS SM and gap-filled SM by RF and ANN models, the performance metrics (R and ubRMSE) were calculated against the in situ SM. The CLDAS SM showed good accuracy, with a high correlation (R) value of 0.76 and a lower ubRMSE value of 0.061 /. The correlation values for the gap-filled SM by RF+Terra and ANN+Terra models were 0.40 and 0.27, and the error (ubRMSE) values were 0.064 / and 0.066 /, respectively. These performance metrics are close enough to the Liu et al. [] findings. Overall, the RF+Terra-based gap-filled SM showed a reasonable accuracy, and the statistical results were almost close to the CLDAS SM results. It is acceptable since our approaches delivered acceptable results, significantly contributing to gap-filled time series and high-spatial-resolution SM and concentrating on widely used explanatory variables, such as Albedo, NDVI, and DEM. Our models, however, demonstrate excellent capability in defining sudden environmental changes since the variables utilized are daily [].
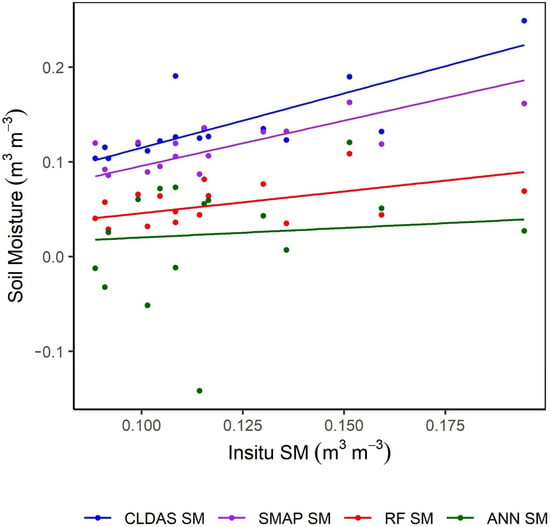
Figure 14.
Scatter plot between the average of gap-filled SM derived from RF and ANN models, SMAP SM, and CLDAS SM against the in situ SM for the selected number of days.
Overall, downscaling SMAP SM by using ML techniques and produce spatial–temporal gap-filled SMAP SM at a high resolution (1 km) rather than a coarse resolution (36 km) is a good way to obtain remotely sensed SM with good accuracy from the field to regional scale. Downscaled SM would be a realistic and significant achievement which is very useful in the fields that require fine-resolution SM, such as water resources management, agricultural processes (irrigation management, crop growth, and crop production). The downscaling factors are also very significant within the downscaling process since they determine the spatial variations within a coarse resolution SM. This study shows the effectiveness of RF to downscaling over ANN and can be implemented by using some additional surface variables (ET and LAI) that influence SSM condition.
6. Conclusions
To enhance the spatial resolution of low-resolution microwave SM, downscaling approaches based on ML techniques were proposed by using optical/TIR observation of surface variables (VIs, WIs, LST, albedo, and topographic factors). Two different ML algorithms (RF and ANN) were used to establish the relationship between low-resolution SMAP SSM and high-resolution surface variables. In this study, using MODIS (Aqua and Terra) datasets and two ML algorithms (RF and ANN), four downscaling combinations (RF+Aqua, RF+Terra, ANN+Aqua, and ANN+Terra) were introduced to compare downscaling results. The downscaled SMAP SM from all of these combinations was statistically validated with multi-scale (S-scale, M-scale, and L-scale) in situ SM measurements over the SMN-SDR Basin from 2018 to 2019. All the combinations performed well, but the RF+Terra model showed the best results statistically and with spatial visualization. The RF+Terra performed well at the L-scale, with a high correlation and less errors (R = 0.53, ubRMSE = 0.033 /) than at the M-scale (R = 0.58; ubRMSE = 0.034 /), and then S-scale (R = 0.52; ubRMSE = 0.037 /). The ANN+Aqua model showed the worst results in terms of ubRMSE values, but it had a slightly higher correlation compared to ANN+Terra against all multi-scale in situ SM observations. Furthermore, the vegetation impact on downscaled SM was analyzed against in situ SM from grassland, farmland, and woodland. The performance of all the RF and ANN models for farmland was good in terms of correlation (R) values, which ranged from 0.57 to 0.66, compared to grassland values, which ranged from 0.51 to 0.57, and for woodland R values, which ranged from 0.30 to 0.47. However, in terms of ubRMSE, the RF models (RF+Aqua and RF+Terra) showed satisfactory results, with values less than 0.034 / for all types of vegetation covers, but the ANN models contained higher error values, ranging from 0.038 / to 0.048/. The reason for the lower accuracy for woodland is due to the high vegetation attenuation of TB used to estimate the SSM. Moreover, the time-series comparison of downscaled SMAP SM from all the models showed a good trend with original SMAP SM and against all scales and all types of vegetation covered in situ SM observations. The spatial distribution of downscaled SM captured the original SMAP SM spatial distribution patterns well. At the end, the gaps in the original SMAP SM data due to clouds and frozen states in the study area were filled in at a high resolution (1 km) pixels resulted from RF+Terra and ANN+Terra models with acceptable accuracy. The gap-filled SM was statistically and spatially validated with in situ and CLDAS SM. The gap-filled SM results from RF+Terra model showed better accuracy (R = 0.40 and ubRMSE = 0.064 /) compared to the ANN+Terra models’ results (R = 0.27 and ubRMSE = 0.066/) and were almost close in term of errors to the CLDAS SM performance metrics (R = 0.76 and ubRMSE = 0.061/). The spatial patterns of gap-filled SM captured the wet and dry SM distribution over the study area very well. Overall, the algorithms provide encouraging results to obtain high-resolution SM from downscaling coarse-resolution SM products. Although the downscaling technique provided geographically detailed SM information, its utility was revised after the elimination of biasness in extreme values. For hydrological applications such as flood forecasting, bias correction in extreme readings, especially higher values, is crucial. Based on our study, future works will focus on reconstructing the missing SMAP SM at a high resolution and validating these methods in the regions covered with different vegetations types that were missing in this work.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. and A.A.N.; methodology, A.A.N. and Y.Z.; software, A.A.N., S.A. and X.W.; validation, A.A.N., Y.Z. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, A.A.N., S.A. and Z.A.; investigation, A.A.N. and X.W.; resources, Y.Z. and L.S.; data curation, A.A.N., M.A.U.R.T. and Z.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.N. and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, A.A.N., M.A.U.R.T. and Z.Z.; visualization, A.A.N. and S.A.; supervision, L.S.; project administration, L.S. and Y.Z.; funding acquisition, L.S. and Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (52279042) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFC3201204). Y.Z. also acknowledges the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2042021kf0200) and the Open Research Fund of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Water Engineering Materials and Structures, Guangxi Institute of Water Resources Research (GXHRI-WEMS-2022-01, GXHRI-WEMS-2022-07).
Data Availability Statement
All the dataset links are provided in the Section 2 (Material and Method) Section 2.2 (Data).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Corradini, C. Soil moisture in the development of hydrological processes and its determination at different spatial scales. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Camici, S.; Tarpanelli, A. Soil moisture for hydrological applications: Open questions and new opportunities. Water 2017, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detto, M.; Montaldo, N.; Albertson, J.D.; Mancini, M.; Katul, G. Soil moisture and vegetation controls on evapotranspiration in a heterogeneous Mediterranean ecosystem on Sardinia, Italy. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. Available online: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2005WR004693 (accessed on 27 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.A.; Zha, Y.; Mehmood, K.; Awais, M.; Afzal, M.M.; Hussain, H.; Shaheen, A.; Aslam, B. Quantification of temporal variations in groundwater level using satellite imagery technique: A case study of Rachna Doab, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13762-022-04162-3 (accessed on 27 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Sheffield, J. Soil moisture drought in China. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3257–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.A.; Wagner, W.; Hohensinn, R.; Hahn, S.; Paulik, C.; Xaver, A.; Gruber, A.; Drusch, M.; Mecklenburg, S.; Van Oevelen, P.; et al. The International Soil Moisture Network: A data hosting facility for global in situ soil moisture measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1675–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modeling, G.; Office, A. The Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications. J. Clim. 2002, 30, 5419–5454. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6999672/ (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Parinussa, R.M.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; van der Schalie, R.; Crow, W.T.; Lei, F.; Holmes, T.R.H. A quasi-global approach to improve day-time satellite surface soil moisture anomalies through the land surface temperature input. Climate 2016, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.P.; Li, X.; Frappart, F.; Fan, L.; Al-Yaari, A.; De Lannoy, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Le Masson, E.; Moisy, C. SMOS-IC data record of soil moisture and L-VOD: Historical development, applications and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 254, 112238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh-Bajgiran, P.; Berg, A.A.; Champagne, C.; Omasa, K. Estimation of soil moisture using optical/thermal infrared remote sensing in the Canadian Prairies. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 83, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, J.; Kędzior, M. Soil moisture variability over Odra watershed: Comparison between SMOS and GLDAS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.K.; Bindlish, R.; O’Neill, P.; Jackson, T.; Njoku, E.; Dunbar, S.; Chaubell, J.; Piepmeier, J.; Yueh, S.; Entekhabi, D.; et al. Development and assessment of the SMAP enhanced passive soil moisture product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chai, L.; Lu, Z.; Liu, S.; Qu, Y.; Geng, D.; Song, Y.; Guan, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Evaluation of SMAP, SMOS-IC, FY3B, JAXA, and LPRM Soil moisture products over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Its surrounding areas. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Albergel, C.; Balenzano, A.; Brocca, L.; Cartus, O.; Cosh, M.H.; Crow, W.T.; Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Dadson, S.; Davidson, M.W.J.; et al. A roadmap for high-resolution satellite soil moisture applications—Confronting product characteristics with user requirements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Yinglan, A.; Duan, L.; Xue, B.; Liu, T. A spatio-temporal cross comparison framework for the accuracies of remotely sensed soil moisture products in a climate-sensitive grassland region. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoest, N.E.C.; Lievens, H.; Wagner, W.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; Moran, M.S.; Mattia, F. On the soil roughness parameterization problem in soil moisture retrieval of bare surfaces from synthetic aperture radar. Sensors 2008, 8, 4213–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Hahn, S.; Kidd, R.; Melzer, T.; Bartalis, Z.; Hasenauer, S.; Figa-Saldaña, J.; De Rosnay, P.; Jann, A.; Schneider, S.; et al. The ASCAT soil moisture product: A review of its specifications, validation results, and emerging applications. Meteorol. Zeitschrift 2013, 22, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piles, M.; Sánchez, N.; Vall-Llossera, M.; Camps, A.; Martínez-Fernandez, J.; Martinez, J.; Gonzalez-Gambau, V. A downscaling approach for SMOS land observations: Evaluation of high-resolution soil moisture maps over the Iberian peninsula. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3845–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The soil moisture active passive (SMAP) mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molero, B.; Merlin, O.; Malbéteau, Y.; Al Bitar, A.; Cabot, F.; Stefan, V.; Kerr, Y.; Bacon, S.; Cosh, M.H.; Bindlish, R.; et al. SMOS disaggregated soil moisture product at 1 km resolution: Processor overview and first validation results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, M.; de Jeu, R.; Holmes, T. Multisensor historical climatology of satellite-derived global land surface moisture. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113. Available online: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2007JF000769 (accessed on 27 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, G.P.; Ireland, G.; Barrett, B. Surface soil moisture retrievals from remote sensing: Current status, products & future trends. Phys. Chem. Earth 2015, 83–84, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G. An algorithm for merging SMAP radiometer and radar data for high-resolution soil-moisture retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.K.; Bindlish, R.; O’Neill, P.E.; Njoku, E.; Jackson, T.; Colliander, A.; Chen, F.; Burgin, M.; Dunbar, S.; Piepmeier, J.; et al. Assessment of the SMAP Passive Soil Moisture Product. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4994–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Merlin, O.; Verhoest, N.E.C. A review of spatial downscaling of satellite remotely sensed soil moisture. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Walker, J.P.; Rüdiger, C.; Panciera, R.; Gao, Y. Medium-Resolution Soil Moisture Retrieval Using the Bayesian Merging Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6482–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaghy, S.; Walker, J.P.; Renzullo, L.J.; Jackson, T.J. Spatially enhanced passive microwave derived soil moisture: Capabilities and opportunities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 551–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Mao, K.; Xu, T.; Guo, J.; Zuo, Z.; Gao, C. A soil moisture estimation framework based on the CART algorithm and its application in China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.S.; Miller, S.; Ardanuy, P. Spaceborne soil moisture estimation at high resolution: A microwave-optical/IR synergistic approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4599–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hogue, T.S. Improving spatial soil moisture representation through integration of AMSR-E and MODIS products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V.; Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.J.; Cosh, M.; Basara, J. Passive Microwave Soil Moisture Downscaling Using Vegetation Index and Skin Surface Temperature. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, vzj2013.05.0089er. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzullo, L.J.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Perraud, J.M.; Collins, D.; Henderson, B.; Jin, H.; Smith, A.B.; McJannet, D.L. Continental satellite soil moisture data assimilation improves root-zone moisture analysis for water resources assessment. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2747–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piles, M.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Sánchez, N.; González-Zamora, Á.; Ireland, G. Towards improved spatio-temporal resolution soil moisture retrievals from the synergy of SMOS and MSG SEVIRI spaceborne observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.; Park, S.; Rhee, J.; Baik, J.; Choi, M. Downscaling of AMSR-E soil moisture with MODIS products using machine learning approaches. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbella, I.; Panciera, R.; Rudiger, C.; Walker, J.; Kerr, Y. Downscaling SMOS-Derived Soil Moisture Using MODIS Visible/Infrared Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3156–3166. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Niesel, J.; Loew, A.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Evaluation of satellite and reanalysis soil moisture products over southwest China using ground-based measurements. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15729–15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Niesel, J. Spatial Downscaling of Satellite Soil Moisture Data Using a Vegetation Temperature Condition Index. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, O.; Chehbouni, A.; Walker, J.P.; Panciera, R.; Kerr, Y.H. A simple method to disaggregate passive microwave-based soil moisture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, O.; Rüdiger, C.; Al Bitar, A.; Richaume, P.; Walker, J.P.; Kerr, Y.H. Disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture in Southeastern Australia. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1556–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbéteau, Y.; Merlin, O.; Molero, B.; Rüdiger, C.; Bacon, S. DisPATCh as a tool to evaluate coarse-scale remotely sensed soil moisture using localized in situ measurements: Application to SMOS and AMSR-E data in Southeastern Australia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V. Soil moisture at watershed scale: Remote sensing techniques. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, J.G.; Michalski, R.S.; Mitchell, T.M. An Overview of Machine Learning. In Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bouchefry, K.; de Souza, R.S. Learning in Big Data: Introduction to Machine Learning. In Knowledge Discovery in Big Data from Astronomy and Earth Observation. AstroGeoInformatics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 225–249. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128191545000230?via%3Dihub (accessed on 27 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Heuvelink, G.B.M. A Machine Learning-Based Geostatistical Downscaling Method for Coarse-Resolution Soil Moisture Products. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remesan, R.; Shamim, M.A.; Han, D.; Mathew, J. Runoff prediction using an integrated hybrid modelling scheme. J. Hydrol. 2009, 372, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Han, D.; Ramirez, M.R.; Islam, T. Machine Learning Techniques for Downscaling SMOS Satellite Soil Moisture Using MODIS Land Surface Temperature for Hydrological Application. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3127–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiong, W.; He, L.; Lv, F.; Fan, W.; Luo, Z.; Hong, Y. A soil moisture spatial and temporal resolution improving algorithm based on multi-source remote sensing data and GRNN model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jing, W.; Wang, Q.; Xia, X. Generating high-resolution daily soil moisture by using spatial downscaling techniques: A comparison of six machine learning algorithms. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 141, 103601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Liu, D.; Fu, Q.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Pham, Q.B.; Rahaman, M.M.; Dang, T.D.; Anh, D.T. Improving the resolution of grace data for spatio-temporal groundwater storage assessment. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Liu, D.; Fu, Q.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Pal, S.C.; Arshad, A.; Pham, Q.B.; Zhang, L. Constructing high-resolution groundwater drought at spatio-temporal scale using GRACE satellite data based on machine learning in the Indus Basin. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed Alemohammad, S.; Kolassa, J.; Prigent, C.; Aires, F.; Gentine, P. Global downscaling of remotely sensed soil moisture using neural networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5341–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, P.; Moradkhani, H.; Zhan, X. Downscaling SMAP Radiometer Soil Moisture Over the CONUS Using an Ensemble Learning Method. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 324–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Sánchez, N.; Lu, H.; Li, A. A spatial downscaling approach for the SMAP passive surface soil moisture product using random forest regression. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Lu, H.; Yue, S.; Yang, F.; Lyu, H.; Yang, K.; McColl, K.A.; Gianotti, D.; Entekhabi, D. Estimating Surface Soil Moisture from AMSR2 Tb with Artificial Neural Network Method and SMAP Products. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. 2019, 6998–7001. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8898152 (accessed on 27 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Miao, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.X.; Tang, Z.; Yang, L.; Qi, S. Downscaling of Satellite Remote Sensing Soil Moisture Products Over the Tibetan Plateau Based on the Random Forest Algorithm: Preliminary Results. Earth Sp. Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jing, W. Potential Applicability of SMAP in ECV Soil Moisture Gap-Filling: A Case Study in Europe. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 133114–133127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Teuling, A.J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, S.; Yang, X.; Wei, L.; Zhong, F.; Zheng, L. Reconstruction of ESA CCI satellite-derived soil moisture using an artificial neural network technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Wang, H.; Magagi, R.; Goita, K.; Wang, K. Spatial Gap-Filling of SMAP Soil Moisture Pixels over Tibetan Plateau via Machine Learning Versus Geostatistics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9899–9912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Shi, J.; Lv, L.; Xu, H.; Chen, D.; Cui, Q.; Jackson, T.J.; Yan, G.; Jia, L.; Chen, L.; et al. Soil moisture experiment in the Luan River supporting new satellite mission opportunities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.; Chan, S.; Njoku, E.; Jackson, T.; Bindlish, R. SMAP L3 Radiometer Global Daily 36 km EASE-Grid Soil Moisture. 2016. Available online: https://nsidc.org/sites/default/files/spl3smp-v008-userguide.pdf (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Cui, H.; Jiang, L.; Du, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, G.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J. Evaluation and analysis of AMSR-2, SMOS, and SMAP soil moisture products in the Genhe area of China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 8650–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, K.; Thurman, S.; Edelstein, W.; Spencer, M.; Chen, G.S.; Underwood, M.; Njoku, E.; Goodman, S.; Jai, B. NASA’s Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) observatory. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Yueh, S.; O’Neil, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Allen, A.; Bindlish, R.; Brown, M.; Chan, S.; Colliander, A.; Crow, W.; et al. SMAP Handbook—Soil Moisture Active Passive: Mapping Soil Moisture and Freeze/Thaw from Space; JPL Publication: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2014; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; She, D.; Zhang, L.; Guo, M.; Liu, X. Spatial downscaling methods of soil moisture based on multisource remote sensing data and its application. Water 2019, 11, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.A.; Zha, Y.; Shi, L.; Ran, G.; Ali, S.; Jahangir, Z.; Afzal, M.M.; Awais, M. Multi-Scale Assessment of SMAP Level 3 and Level 4 Soil Moisture Products over the Soil Moisture Network within the ShanDian River (SMN-SDR) Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChunXiang, S.; ZhengHui, X.; Hui, Q.; MiaoLing, L.; XiaoChun, Y. China land soil moisture EnKF data assimilation based on satellite remote sensing data. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar]
- Okut, H. Bayesian Regularized Neural Networks for Small n Big p Data. In Artificial Neural Networks. Model and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/50570 (accessed on 27 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Du, K.L.; Swamy, M.N.S. Neural networks and statistical learning, second edition. In Neural Networks and Statistical Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, Z.; Ling, F.; Zhou, D.; Wang, H.; Gui, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhang, X. A comparison of land surface water mapping using the normalized difference water index from TM, ETM+ and ALI. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5530–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Tian, J.; Tian, Q.; Xu, K.; Xu, N. Development of soil moisture indices from differences in water absorption between shortwave-infrared bands. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Berg, A.A.; Cosh, M.H.; Loew, A.; Mohanty, B.P.; Panciera, R.; De Rosnay, P.; Ryu, D.; Walker, J.P. Upscaling sparse ground-based soil moisture observations for the validation of coarse-resolution satellite soil moisture products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. Available online: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2011RG000372 (accessed on 27 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.A.; Xaver, A.; Vreugdenhil, M.; Gruber, A.; Hegyiová, A.; Sanchis-Dufau, A.D.; Zamojski, D.; Cordes, C.; Wagner, W.; Drusch, M. Global Automated Quality Control of In Situ Soil Moisture Data from the International Soil Moisture Network. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, vzj2012.0097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.; Vogel, G.K.; Rigon, R.; Entekhabi, D.; Castelli, F.; Rinaldo, A. On the spatial organization of soil moisture fields. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 2757–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D.; Crow, W.T. Performance metrics for soil moisture retrievals and application requirements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andy, L.; Matthew, W. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, W.; Meng, L. An approach for downscaling SMAP soil moisture by combining Sentinel-1 SAR and MODIS data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakigari, S.A.; Leconte, R. Enhancing Spatial Resolution of SMAP Soil Moisture Products through Spatial Downscaling over a Large Watershed: A Case Study for the Susquehanna River Basin in the Northeastern United States. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Shi, J.; Zhao, T.; Lu, H.; Al-Yaari, A. Rebuilding long time series global soil moisture products using the neural network adopting the microwave vegetation index. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, D.J. Artificial Neural Networks—Methods and Applications. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 53, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H. A neural-network based spatial resolution downscaling method for soil moisture: Case study of qinghai province. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.P.; Yeo, I.Y.; Walker, J.P.; Willgoose, G.R. Estimating catchment scale soil moisture at a high spatial resolution: Integrating remote sensing and machine learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadeusiewicz, R. Neural networks: A comprehensive foundation. Control Eng. Pract. 1995, 3, 746–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechelt, L. Early stopping—But when? In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7700, pp. 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H. Evaluating Downscaling Factors of Microwave Satellite Soil Moisture Based on Machine Learning Method. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. A robust gap-filling approach for ESA CCI soil moisture by integrating satellite observations, model-driven knowledge and spatiotemporal machine learning. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 1–40. Available online: https://hess.copernicus.org/articles/27/577/2023/hess-27-577-2023.html (accessed on 27 January 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).