The Creep-Sliding Deformation Mechanism of the Jiaju Ancient Landslide in the Upstream of Dadu River, Tibetan Plateau, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
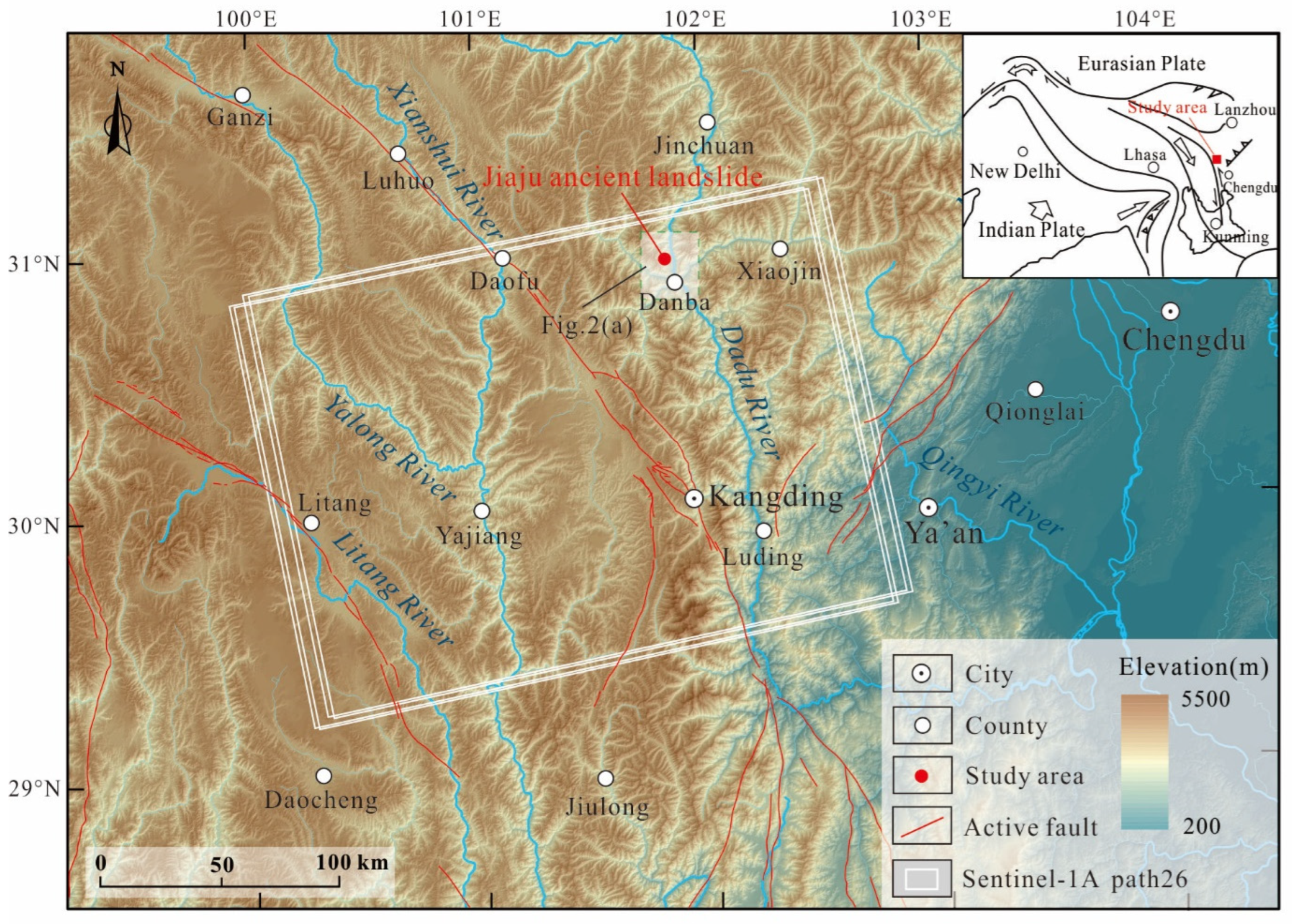
2. Geological Background
2.1. Geomorphology
2.2. Structure and Lithology

2.3. Geohazards
3. Methods and Data
3.1. Geological Survey
3.2. SAR Data
3.3. SBAS-InSAR Method
3.4. SAR Data Suitability Analysis
4. Results Analysis
4.1. Engineering Geological Characteristics
4.1.1. Spatial Development Characteristics
4.1.2. Development Characteristics of Five Secondary Landslides
- (1)
- Jiaju landslide (H01)
- (2)
- Niexiaping landslide (H02)
- (3)
- Xiaobawang landslide (H03)
- (4)
- Niela landslide (H04)
- (5)
- Mt.-peak landslide (H05)
4.2. Deformation Characteristics of the Jiaju Ancient Landslide
4.2.1. The Jiaju Ancient Landslide Deformation in the LOS
4.2.2. Two-Dimensional (2D) Deformation Rate Characteristics of the Jiaju Ancient Landslide
4.2.3. Typical Section Deformation Characteristics of the Jiaju Ancient Landslide
4.3. Deformation Characteristics of the Jiaju Landslide (H01)
4.4. Deformation Characteristics of the Niela Landslide (H04)
4.5. Deformation Characteristics of the Mt.-Peak Landslide (H05)
5. Discussion
5.1. Deformation Trend of the Jiaju Ancient Landslide
5.1.1. Landslide Creep Zone
5.1.2. Deformation Trend of the Jiaju Landslide (H01)
5.1.3. Deformation Trend of the Niela Landslide (H04)
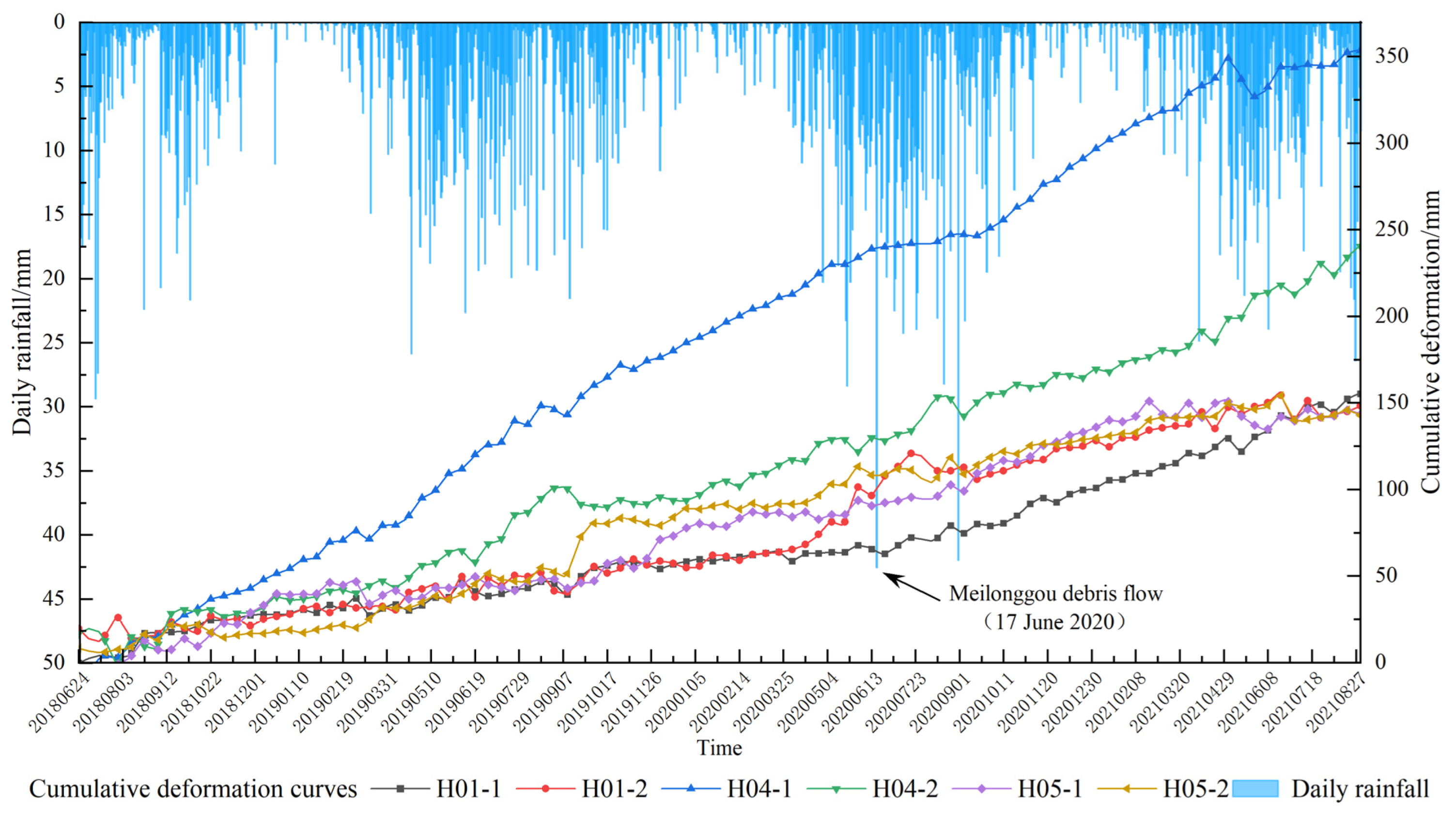
5.2. Impact of Extreme Rainfall on the Deformation
5.3. Stability Trend Analysis of the Jiaju Ancient Landslide
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melosh, H.J. The physics of very large landslides. Acta Mech. 1986, 64, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruden, D.M. A simple definition of a landslide. Bull. Int. Assoc. Eng. Geol. 1991, 43, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Lee, C.; Ngai, Y. Landslide risk assessment and management: An overview. Eng. Geol. 2002, 64, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.L.; Zhou, A.G.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.S.; Wu, J.B.; Liu, Z.H. Hydrological response characteristics of landslides under typhoon-triggered rainstorm conditions. China Geol. 2020, 3, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Soltanieh, A.; Macciotta, R. Updated Understanding of the Ripley Landslide Kinematics Using Satellite InSAR. Geosciences 2022, 12, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notti, D.; Wrzesniak, A.; Dematteis, N.; Lollino, P.; Fazio, N.L.; Zucca, F.; Giordan, D. A multidisciplinary investigation of deep-seated landslide reactivation triggered by an extreme rainfall event: A case study of the Monesi di Mendatica landslide, Ligurian Alps. Landslides 2021, 18, 2341–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Jain, K. Satellite based assessment of artificial reservoir induced landslides in data scarce environment: A case study of Baglihar reservoir in India. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 205, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.A.; Chen, Z.; Wang, R.; Shoaib, M. PS-InSAR-based Validated Landslide Susceptibility Mapping along Karakorum Highway, Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Montgomery, D.R.; Du, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S. How unusual is the long-runout of the earthquake-triggered giant Luanshibao landslide, Tibetan Plateau, China? Geomorphology 2016, 259, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhu, W.; Liu-Zeng, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, C. Integration of Sentinel-1 and ALOS/PALSAR-2 SAR datasets for mapping active landslides along the Jinsha River corridor, China. Eng. Geol. 2021, 284, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Ge, D.Q.; Deng, Y.K.; Wang, R. InSAR Study of Landslides: Early Detection, Three-Dimensional, and Long-Term Surface Displacement Estimation—A Case of Xiaojiang River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.M.; Yao, X.; Liu, X.H. Landslide Detection and Mapping Based on SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR: A Case Study in Gongjue County, Tibet, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J. Coupling of Earth’s Endogenic and Exogenic Geological Processes and Origins on Serious Geological Disasters Hazards. J. Eng. Geol. 2002, 10, 115–117, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.B.; Zhang, Y.S.; Jiang, L.W.; Shi, J.S.; Meng, W.; Du, Y.B.; Ma, C.T. Discussion on the Environmental and Engineering Geological Problems Along the Sichuan Tibet Railway and its Adjacent Area. Geoscience 2017, 31, 877–899, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Wu, R.A.; Guo, C.B.; Wang, L.C.; Yao, X.; Yang, Z.H. Research Progress and Prospect on Reactivation of Ancient Landslides. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 728–740, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.P. Rapid Huge Landslide and Hazard Reduction of Yigong River in the Bomi, Tibet. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2000, 27, 8–11, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Montgomery, D.R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, N.; Fan, C.; Wu, R.; Yang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Jin, J.; Yan, Y. Evidence for repeated failure of the giant Yigong landslide on the edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zheng, G.; Li, W.L.; He, C.Y.; Dong, X.J.; Guo, C.; Feng, W.K. Study on Successive Landslide Damming Events of Jinsha River in Baige Village on October 11 and November 3. J. Eng. Geol. 2018, 26, 129–146, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.C.; Wen, M.S.; Feng, Z.; Sun, W.F.; Wei, Y.J.; Li, J.F.; Wang, W.P. Researches on the Baige Landslide at Jinshajiang River, Tibet, China. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control. 2019, 30, 1–9, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, S.; Yang, Z.; Wu, R.; Jin, J. Reactivation of giant Jiangdingya ancient landslide in Zhouqu County, Gansu Province, China. Landslides 2019, 17, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Liu, D.; Yan, Y.; Hua, S.; Ren, S. Study of an ancient landslide reactivation mechanism based on centrifuge model testing: An example of the Jiangdingya ancient landslide reactivation in 2018, Gansu Province, China. Landslides 2023, 20, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. Research on the Stability and Controlling Engineering Effect of the Danba Landslide. Master’s Dissertation, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2006. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.B.; Hu, G.S.; He, N.; Li, R.Q.; Chen, N.S.; Ni, H.Y. Preliminary Analysis on the Characteristics and Causes of Landslide in “6·17” Aniangzhai Village in Danba County. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 21, 9243–9249, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.L.; Peng, J.H.; Zhang, D.X.; Li, S.H. Influence of Orbital Errors on InSAR Data Processing. J. Geomat. Sci. Technol. 2012, 29, 118–121+126, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wasowski, J.; Bovenga, F. Investigating landslides and unstable slopes with satellite Multi Temporal Interferometry: Current issues and future perspectives. Eng. Geol. 2014, 174, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carla, T.; Tofani, V.; Lombardi, L.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Bertolo, D.; Thuegaz, P.; Casagli, N. Combination of GNSS, Satellite InSAR, and GBInSAR Remote Sensing Monitoring to Improve the Understanding of a Large Landslide in High Alpine Environment. Geomorphology 2019, 335, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squarzoni, G.; Bayer, B.; Franceschini, S.; Simoni, A. Pre- and post-failure dynamics of landslides in the Northern Apennines revealed by space-borne synthetic aperture radar interferometry (InSAR). Geomorphology 2020, 369, 107353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.B.; Yan, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhang, X.J.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.H.; Wu, R.A. Study on the Creep-sliding Mechanism of the Giant Xiongba Ancient Landslide based on the SBAS-InSAR Method, Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achache, J.; Fruneau, B.; Delacourt, C. Applicability of SAR interferometry for operational monitoring of landslides. Proc. Second. ERS Appl. Workshop 1996, 383, 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novellino, A.; Cigna, F.; Sowter, A.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D. Exploitation of the Intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) Al-gorithm with COSMO-SkyMed Data for Landslide Inventory Mapping in North-Western Sicily, Italy. Geomorphology 2017, 280, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouali, E.H.; Oommen, T.; Escobar-Wolf, R. Mapping of slow landslides on the Palos Verdes Peninsula using the California landslide inventory and persistent scatterer interferometry. Landslides 2017, 15, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, A.; Tofani, V.; Tanteri, L.; Stefanelli, C.T.; Agostini, A.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. The New Landslide Inventory of Tuscany (Italy) Updated with PS-InSAR: Geomorphological Features and Landslide Distribution. Landslides 2018, 15, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.M.; Deng, G.S.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhang, Q.Z. GPS Monitoring on the Representative Landslides in Danba, Sichuan. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2008, 28, 30–34, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Zheng, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Integration of GPS with InSAR to monitoring of the Jiaju landslide in Sichuan, China. Landslides 2010, 7, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.J.; Zheng, W.M.; Deng, G.S.; Ning, H.Y.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Jia, J. Three-Dimensional System Monitoring and Nu-merical Simulation on the Dynamic Deformation Process of Jiaju Landslide in Danba, Sichuan. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2011, 30, 974–981, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Tang, M.; Liao, M.; Xu, Q.; Gong, J.; Ao, M. Mapping landslide surface displacements with time series SAR interferometry by combining persistent and distributed scatterers: A case study of Jiaju landslide in Danba, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Wu, R.A.; Guo, C.B.; Ren, S.S. Cognization, Characteristics, Age and Evolution of the Ancient Landslides Along the Deep-cut Valleys on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Earth Sci. Front. 2021, 28, 94–105, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.Y. Study on the Deformation Failure Model and Stability of the Abutment of Danba Hydroelectric Station in Dadu River. Master’s Dissertation, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2016. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.J. Research on Mesostructure and Evolution of Rock-soil Aggregate Landslides in Deeply Incised Valleys: A Case Study of Rock-soil Aggregate Landslides in the Danba Reach of the Dadu River. Ph.D. Dissertation, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2020. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.W.; Xie, Z.S.; Wang, J.C.; Zheng, W.M. Origin Mechanism Analysis and the Control Countermeasure of the Landslide in Jiaju of Danba County. Drill. Eng. 2008, 9, 59–62, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q. Understanding and Consideration of Related Issues in Early Identification of Potential Geohazards. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2020, 45, 1651–1659, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cascini, L.; Fornaro, G.; Peduto, D. Advanced Low-and Full-Resolution D-InSAR Map Generation for Slow-Moving Landslide Analysis at Different Scales. Eng. Geol. 2010, 112, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; García-Davalillo, J.C.; Guerrero, J.; Notti, D.; Galve, J.P.; Fernandez-Merodo, J.A.; Cooksley, G. Multi-sensor Advanced D-InSAR Monitoring of Very Slow landslides: The Tena Valley Case Study (Central Spanish Pyrenees). Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.K.; Dun, J.W.; Yi, X.Y.; Zhang, G.Q. Deformation Analysis of Woda Village Old Landslide in Jinsha River Basin Using SBAS-InSAR Technology. J. Eng. Geol. 2020, 28, 384–393, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.Y.; Liu, G.Q. An Improved CR-InSAR Technology Used for Deformation Monitoring in Jiaju Landslide, Sichuan. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2017, 42, 377–383, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Deng, G.S.; Zheng, W.M.; Yang, G.H.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Chen, Q.G.; Tang, Y.Q. GPS Monitoring of the Jiaju Landslide in Danba, Sichuan. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2011, 32, 99–104, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Liao, M.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Tang, M.; Gong, J. Detection and displacement characterization of landslides using multi-temporal satellite SAR interferometry: A case study of Danba County in the Dadu River Basin. Eng. Geol. 2018, 240, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intrieri, E.; Gigli, G.; Mugnai, F.; Fanti, R.; Casagli, N. Design and implementation of a landslide early warning system. Eng. Geol. 2012, 147-148, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allasia, P.; Manconi, A.; Giordan, D.; Baldo, M.; Lollino, G. ADVICE: A New Approach for Near-Real-Time Monitoring of Surface Displacements in Landslide Hazard Scenarios. Sensors 2013, 13, 8285–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Hack, R. Some new pre-warning criteria for creep slope failure. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhao, W.; Ju, N.; He, C.; Huang, H.; Cui, Q. Landslide evolution assessment based on InSAR and real-time monitoring of a large reactivated landslide, Wenchuan, China. Eng. Geol. 2020, 277, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Yao, X. InSAR-Based Method for Early Recognition of Ancient Landslide Reactivation in Dadu River, China. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2020, 51, 545–555, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]









| SAR Sensor | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Direction | Ascending |
| Path | 26 |
| Frame | 93 |
| Wave band | C |
| Radar wavelength/(cm) | 5.6 |
| Incident angle/(°) | 43.90 |
| Time interval/(day) | 12 |
| Image time | 24 June 2018 to 31 August 2021 |
| Quantity of SAR images | 96 |
| Progressing | Parameters |
|---|---|
| multi-look | 10 × 2 |
| temporal baselines | 150 m |
| spatial baselines | 24 days |
| DEM resolution | 30 m |
| masking threshold | 0.5 |
| interferograms | 96 |
| Name | Aspect (°) | Slope (°) | Area (km2) | Maximum LOS Rate (mm/a) | Maximum Slope Rate (mm/a) | Maximum Vertical Rate (mm/a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiaju landslide (H01-N) | 112 | 20~35 | 0.6 | −92 | −108 | −35 |
| Jiaju landslide (H01-S) | 67 | 20~35 | 0.8 | −42 | −50 | −16 |
| Niexiaping landslide (H02) | 120 | 20~35 | 2.1 | −44 | −52 | −17 |
| Xiaobawang landslide (H03) | 103 | 15~25 | 1.1 | −32 | −66 | −22 |
| Niela landslide (H04) | 87 | 15~30 | 1.3 | −170 | −211 | −180 |
| Mt.-peak landslide (H05) | 98 | 20~40 | 6.3 | −87 | −103 | −33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Guo, C.; Li, C.; Yuan, H.; Qiu, Z. The Creep-Sliding Deformation Mechanism of the Jiaju Ancient Landslide in the Upstream of Dadu River, Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030592
Yan Y, Guo C, Li C, Yuan H, Qiu Z. The Creep-Sliding Deformation Mechanism of the Jiaju Ancient Landslide in the Upstream of Dadu River, Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(3):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030592
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yiqiu, Changbao Guo, Caihong Li, Hao Yuan, and Zhendong Qiu. 2023. "The Creep-Sliding Deformation Mechanism of the Jiaju Ancient Landslide in the Upstream of Dadu River, Tibetan Plateau, China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 3: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030592
APA StyleYan, Y., Guo, C., Li, C., Yuan, H., & Qiu, Z. (2023). The Creep-Sliding Deformation Mechanism of the Jiaju Ancient Landslide in the Upstream of Dadu River, Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sensing, 15(3), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030592







