Associating Anomaly Detection Strategy Based on Kittler’s Taxonomy with Image Editing to Extend the Mapping of Polluted Water Bodies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
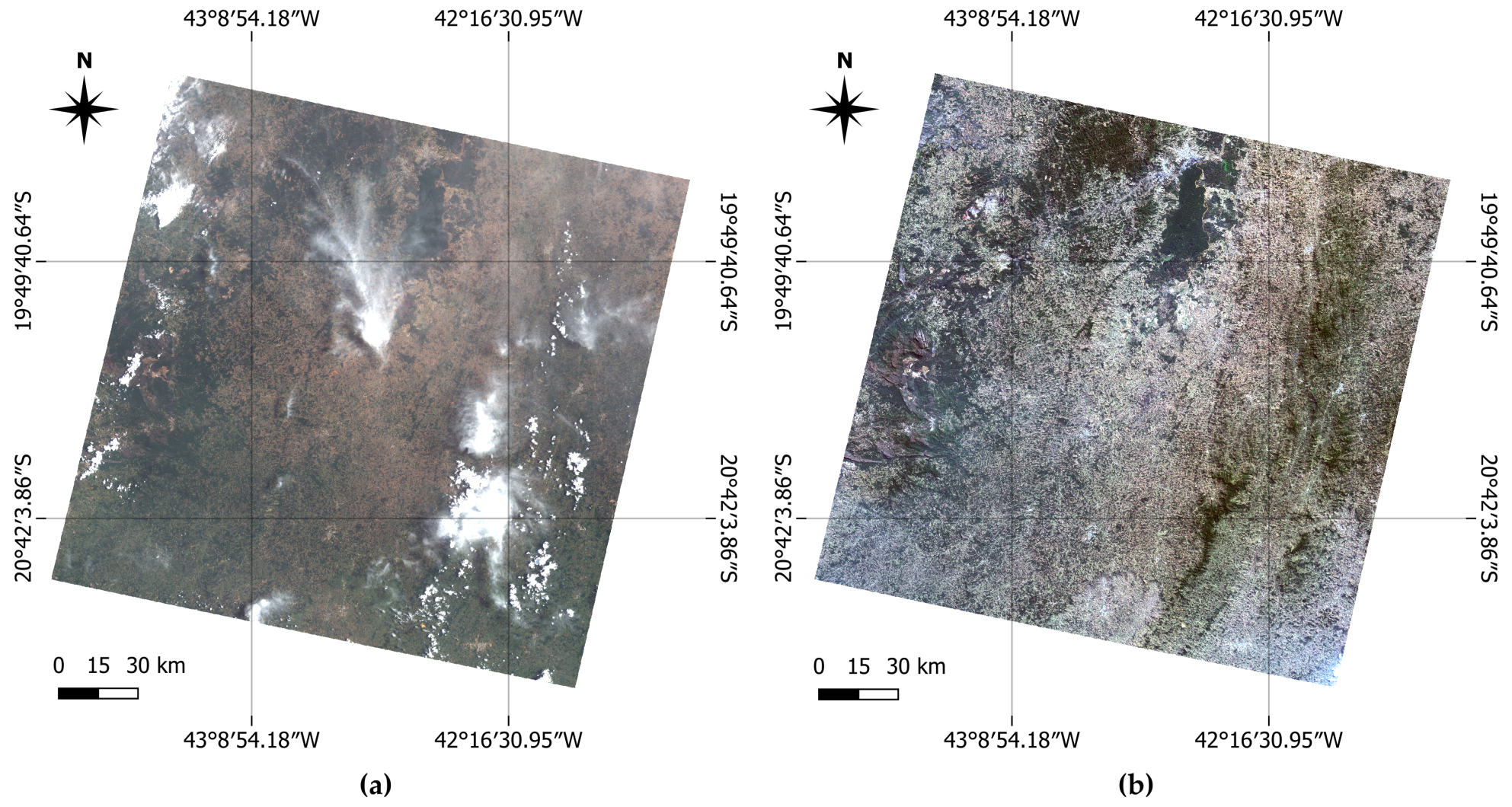
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Materials
3.3. Conceptualization
3.3.1. Contextual and Non-Contextual Classification
3.3.2. Incongruences and Congruences
3.3.3. Anomaly Detection
3.3.4. Kittler’s Taxonomy
3.3.5. Cloud Removal
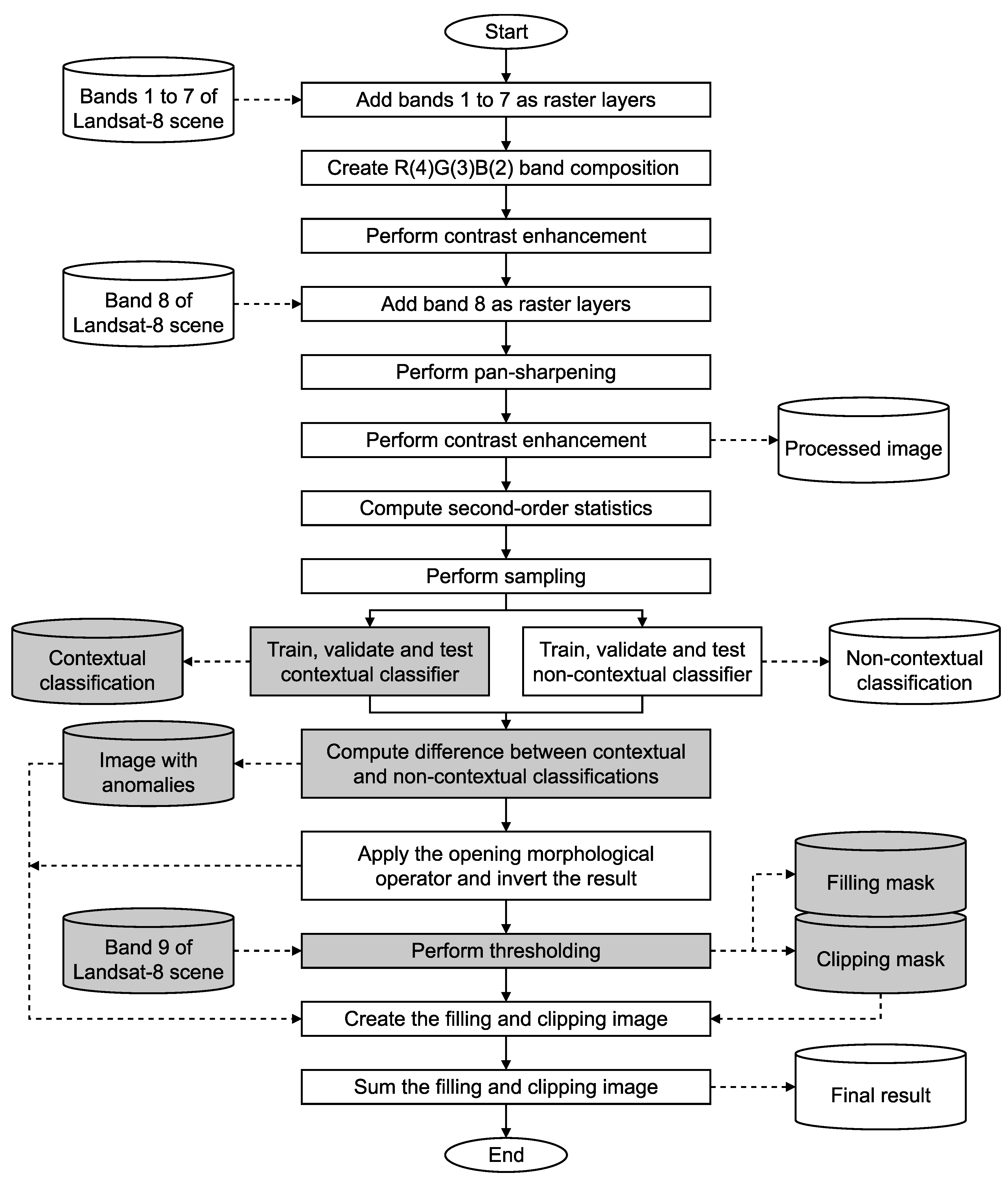
3.4. Summary of the Methodology
3.5. Data Processing
3.6. Training, Validation, and Testing
3.7. Image Editing
4. Results
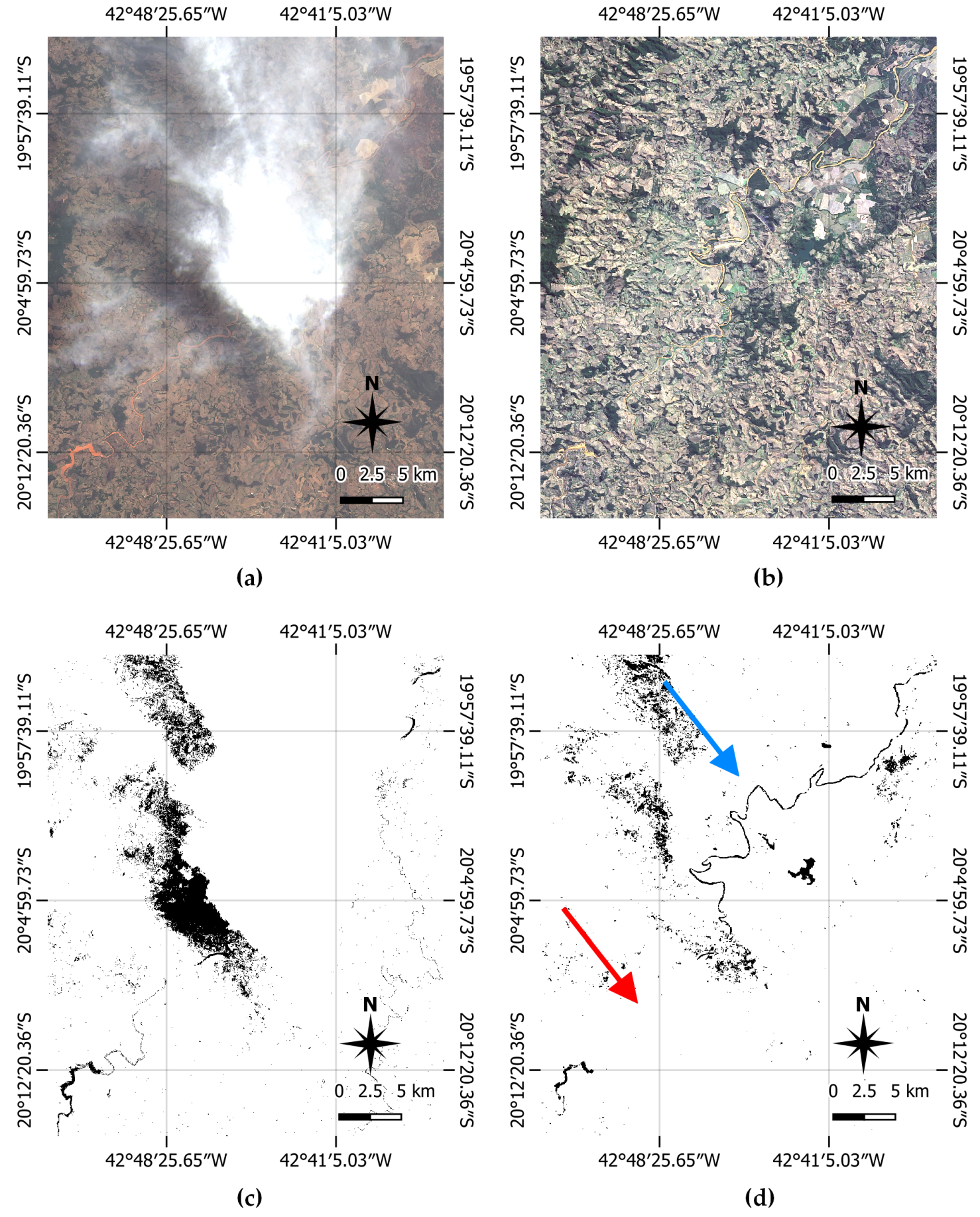
4.1. First Validation
4.2. Second Validation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Parameter Values
| Step | Tool | Param Name | Param Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual raster | QGIS—Build Virtual Raster (Catalog) | Use visible raster layers for input Separate | True (set) True (set) |
| Band composition and contrast enhancement | QGIS—Raster Style Properties | Red band Green band Blue band Mean standard deviation x Clip extent to canvas | Band 4 Band 3 Band 2 True (set) True (set) |
| Pan-sharpening—first part | Orfeo Toolbox—Superimpose sensor | Reference input The image to reproject Default elevation Spacing of the deformation field Mode Interpolation | Panchromatic image Multiespectral image 0 4 Default nn |
| Pan-sharpening—second part | Orfeo Toolbox—Pan-sharpening (RCS—Ratio Component Substitution) | Input PAN image Input XS image Algorithm | Panchromatic image Superimpose sensor result rcs |
| Second-order statistics | Orfeo Toolbox—Compute images’ second-order statistics | Input images | The processed image |
| Classifier training | Orfeo Toolbox—TrainImagesClassifier | Default elevation Maximum training sample size per class Maximum validation sample size per class Bound sample number by minimum Training and validation sample ratio Name of the discrimination field Random seed On-edge pixel inclusion | 0 1000 1000 1 0.5 Class 0 False (not set) |
| Classifier training | Orfeo Toolbox—TrainImagesClassifier (dt) | Maximum depth of the tree Minimum number of samples in each node Termination criteria for regression tree Cluster possible values of a categorical variable into K ≤ cat clusters to find a suboptimal split K-fold cross-validations Set Use1seRule flag to false Set TruncatePrunedTree flag to false | 65,535 10 0.01 10 10 True (set) True (set) |
| Classifier training | Orfeo Toolbox—TrainImagesClassifier (boost) | Boost type Weak count Weight trim rate Maximum depth of the tree | real 100 0.95 1 |
| Image classification | Orfeo Toolbox—Image Classification | Input image Model file Statistics file | The processed image The classifier model The statistics file |
| Difference between classifications | QGis—Raster Calculator | Raster calculator expression | (raster_A OR raster_B) - (raster_A AND raster_B)) |
| Morphological operator | SAGA—Morphological filter | Structuring element Radius Method | Square 1 Opening |
| Result inversion | QGis—Raster Calculator | Raster calculator expression | ifelse(eq(a, 1), 0, 1) |
| Thresholding | QGis—Raster Calculator | Raster calculator expression | ifelse(it(a, 8000), 1, 0) |
| Multiplication | QGis—Raster Calculator | Raster calculator expression | raster_A × raster_B |
| Sum | QGis—Raster Calculator | Raster calculator expression | raster_A + raster_B |
References
- Richards, J.; Jia, X. Remote Sensing Digital Image Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schowengerdt, R.A. Remote Sensing: Models and Methods for Image Processing, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanzieri, E.; Melgani, F. Nearest Neighbor Classification of Remote Sensing Images with the Maximal Margin Principle. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Crawford, M.M.; Tian, J. Local Manifold Learning-Based k -Nearest-Neighbor for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 4099–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Li, C. Water body extraction from Landsat ETM+ imagery using adaboost algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Luo, C.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Xiong, Z. Industrial Wastewater Discharge Retrieval Based on Stable Nighttime Light Imagery in China from 1992 to 2010. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7566–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J.E. Combining Landsat TM/ETM+ and HJ-1 A/B CCD Sensors for Monitoring Coastal Water Quality in Hong Kong. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1898–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.G.; Tang, P.; Zhou, M. Detecting anomaly regions in satellite image time series based on seasonal autocorrelation analysis. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, III-3, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sublime, J.; Kalinicheva, E. Automatic Post-Disaster Damage Mapping Using Deep-Learning Techniques for Change Detection: Case Study of the Tohoku Tsunami. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.A.; Silva, E.A.d.; Azevedo, S.C.d.; Casaca, W.; Statella, T.; Negri, R.G. An Incongruence-Based Anomaly Detection Strategy for Analyzing Water Pollution in Images from Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.B.; Vannah, B.; Jeffrey Yang, Y. Comparative Sensor Fusion Between Hyperspectral and Multispectral Satellite Sensors for Monitoring Microcystin Distribution in Lake Erie. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2426–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotchi, S.O.; Brazeau, S.; Turgeon, P.; Pelcat, Y.; Légaré, J.; Lavigne, M.P.; Essono, F.N.; Fournier, R.A.; Michel, P. Evaluation of Earth Observation Systems for Estimating Environmental Determinants of Microbial Contamination in Recreational Waters. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3730–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W.N.; Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q. Estimation of Colored Dissolved Organic Matter From Landsat-8 Imagery for Complex Inland Water: Case Study of Lake Huron. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.T.T.; Koike, K.; Nhuan, M.T.; Canh, B.D.; Thao, N.T.P.; Parsons, M. Landsat 8/OLI Two Bands Ratio Algorithm for Chlorophyll-A Concentration Mapping in Hypertrophic Waters: An Application to West Lake in Hanoi (Vietnam). IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4919–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.A.; Marinho, G.C.; Negri, R.G.; Casaca, W.; Muñoz, I.B.; Eler, D.M. A Machine Learning Strategy Based on Kittler’s Taxonomy to Detect Anomalies and Recognize Contexts Applied to Monitor Water Bodies in Environments. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, G.C.; Júnior, W.E.M.; Dias, M.A.; Eler, D.M.; Negri, R.G.; Casaca, W. Dimensionality Reduction and Anomaly Detection Based on Kittler’s Taxonomy: Analyzing Water Bodies in Two Dimensional Spaces. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittler, J.; Christmas, W.; De Campos, T.; Windridge, D.; Yan, F.; Illingworth, J.; Osman, M. Domain Anomaly Detection in Machine Perception: A System Architecture and Taxonomy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bransford, J.D.; Brown, A.L.; Cocking, R.R. How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School: Expanded Edition; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Huo, L.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, P. Multi-Temporal Landsat Data Automatic Cloud Removal Using Poisson Blending. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 46151–46161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Tsai, P.H.; Lai, K.H.; Chen, J.Y. Cloud Removal From Multitemporal Satellite Images Using Information Cloning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, W.; Li, R. Cloud Removal From Optical Satellite Imagery With SAR Imagery Using Sparse Representation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Jia, X.; Pickering, M.; Plaza, A.J. Cloud Removal Based on Sparse Representation via Multitemporal Dictionary Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2998–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, F.; Gao, Z.; Ling, X. A Coarse-to-Fine Framework for Cloud Removal in Remote Sensing Image Sequence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5963–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Pickering, M.; Plaza, A.J.; Jia, X. Thin Cloud Removal Based on Signal Transmission Principles and Spectral Mixture Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, L.; Yang, X.; Fan, R.; Bilal, M.; Li, Q. Thick Clouds Removal From Multitemporal ZY-3 Satellite Images Using Deep Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmer, E.; Ruefenacht, B. Cloud-Free Satellite Image Mosaics with Regression Trees and Histogram Matching. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning (Information Science and Statistics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Weinshall, D.; Zweig, A.; Hermansky, H.; Kombrink, S.; Ohl, F.W.; Anemüller, J.; Bach, J.H.; Van Gool, L.; Nater, F.; Pajdla, T.; et al. Beyond Novelty Detection: Incongruent Events, When General and Specific Classifiers Disagree. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1886–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yang, B.; Song, S.; Peng, X.; Huang, R. Automatic Clearance Anomaly Detection for Transmission Line Corridors Utilizing UAV-Borne LIDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, F.; Shao, Z.; Sun, T.; Wu, L.; Xu, Y. DSformer: A Double Sampling Transformer for Multivariate Time Series Long-Term Prediction. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Birmingham, UK, 21–25 October 2023; pp. 3062–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorgtabar, B.; Mahapatra, D. Attention-Conditioned Augmentations for Self-Supervised Anomaly Detection and Localization. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirty-Fifth Conference on Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Thirteenth Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; AAAI Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Klucik, R.; Chen, C.; Grant, G.; Gallaher, D.; Lv, Q.; Shang, L. Unsupervised detection of contextual anomaly in remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, K.J.; McCabe, M.F.; Evans, J.P. Satellite based observations for seasonal snow cover detection and characterisation in Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.J.; Qiao, W.; Chuanqing, W.; Xiaoling, C.; Wandong, M.; Mao, H. A robust anomaly based change detection method for time-series remote sensing images. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 17, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, K.; Das, K.; Votava, P. Distributed Anomaly Detection using Satellite Data From Multiple Modalitie. In Proceedings of the 2010 Conference on Intelligent Data Understanding (CIDU), Mountain View, CA, USA, 5–6 October 2010; pp. 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Chandola, V.; Vatsavai, R.R. A Gaussian Process Based Online Change Detection Algorithm for Monitoring Periodic Time Series. In Proceedings of the 2011 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), Mesa, AZ, USA, 28–30 April 2011; pp. 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayot, N.; D’Ortenzio, F.; Ribera d’Alcalà, M.; Lavigne, H.; Claustre, H. Interannual variability of the Mediterranean trophic regimes from ocean color satellites. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 1901–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciancia, E.; Lacava, T.; Pergola, N.; Vellucci, V.; Antoine, D.; Satriano, V.; Tramutoli, V. Quantifying the Variability of Phytoplankton Blooms in the NW Mediterranean Sea with the Robust Satellite Techniques (RST). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Documentation for QGIS 2.18. Available online: https://docs.qgis.org/2.18/en/docs/ (accessed on 11 March 2023).
- Documentation for Orfeo ToolBox 6.4. Available online: https://www.orfeo-toolbox.org/CookBook-6.4/ (accessed on 11 March 2023).
- United States Geological Survey. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 11 March 2023).
- Kittler, J.; Zor, C. A measure of surprise for incongruence detection. In Proceedings of the 2nd IET International Conference on Intelligent Signal Processing 2015 (ISP), London, UK, 1–2 December 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, M.; Kittler, J.; Riva, M.; De Campos, T.; Zor, C. A decision cognizant Kullback–Leibler divergence. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittler, J.; Zor, C. Delta Divergence: A Novel Decision Cognizant Measure of Classifier Incongruence. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 2331–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, V.; Austin, J. A Survey of Outlier Detection Methodologies. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2004, 22, 85–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandola, V.; Kumar, V. Outlier Detection: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2009, 41, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, P.; Bhattacharyya, D.K.; Borah, B.; Kalita, J. A Survey of Outlier Detection Methods in Network Anomaly Identification. Comput. J. 2011, 54, 570–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Shi, S.; Sun, J.; He, X. A Survey of Outlier Detection Methodologies and Their Applications. In Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence; Deng, H., Miao, D., Lei, J., Wang, F.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 380–387. [Google Scholar]
- Zimek, A.; Schubert, E.; Kriegel, H.P. A survey on unsupervised outlier detection in high-dimensional numerical data. Stat. Anal. Data Min. 2012, 5, 363–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Gao, J.; Aggarwal, C.C.; Han, J. Outlier Detection for Temporal Data: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2014, 26, 2250–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalouf, A.; Carre, P.; Augereau, B.; Fernandez-Maloigne, C. A Bandelet-Based Inpainting Technique for Clouds Removal From Remotely Sensed Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Alparone, L.; Chanussot, J.; Dalla Mura, M.; Garzelli, A.; Licciardi, G.A.; Restaino, R.; Wald, L. A Critical Comparison Among Pansharpening Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2565–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, E.; Shirley, P.; Ashikhmin, M.; Troscianko, T. Second Order Image Statistics in Computer Graphics. In Proceedings of the 1st Symposium on Applied Perception in Graphics and Visualization, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 7–8 August 2004; pp. 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuia, D.; Persello, C.; Bruzzone, L. Domain Adaptation for the Classification of Remote Sensing Data: An Overview of Recent Advances. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soille, P. Morphological Image Analysis-Principles and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goal 6: Ensure Access to Water and Sanitation for All. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/water-and-sanitation/ (accessed on 20 September 2023).

| Identifier | UTM | Latitude | Longitude | Date of Acquisition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 | 201348.07S | 424347.24W | 12 November 2015 | |
| 23 | 201348.07S | 424347.24W | 10 August 2016 |
| Band | Wavelength (Micrometers) | Spatial Resolution (Meters) |
|---|---|---|
| Band 1—Coastal Aerosol | 0.43–0.45 µm | 30 m |
| Band 2—Blue | 0.45–0.51 µm | 30 m |
| Band 3—Green | 0.53–0.59 µm | 30 m |
| Band 4—Red | 0.64–0.67 µm | 30 m |
| Band 5—Near-Infrared (NIR) | 0.85–0.88 µm | 30 m |
| Band 6—SWIR 1 | 1.57–1.65 µm | 30 m |
| Band 7—SWIR 2 | 2.11–2.29 µm | 30 m |
| Band 8—Panchromatic (PAN) | 0.50–0.68 µm | 15 m |
| Band 9—Cirrus | 1.36–1.38 µm | 30 m |
| Incongruent Event | Congruent Event | |
|---|---|---|
| Incongruent detection | TP = 79 | FP = 27 |
| Congruent detection | FN = 5 | TN = 8289 |
| Incongruent Event | Congruent Event | |
|---|---|---|
| Incongruent detection | TP = 63 | FP = 4 |
| Congruent detection | FN = 5 | TN = 8328 |
| Study | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Validation 2 | 99.89% | 94.03% | 92.65% | 93.33% |
| [11] | 99.78% | 73.96% | 100.00% | 85.04% |
| [33] | 91.20% | 98.10% | 95.7% | 96.88% |
| [30] | - | 96.50% | 94.8% | 95.64% |
| Validation 1 | 99.62% | 74.53% | 94.05% | 83.16% |
| [34] | 99.20% | 91.85% | 53.55% | 67.66% |
| [9] | 88.68% | 90.62% | 79.62% | 84.76% |
| [35] | 98.49% | 83.84% | 83.66% | 83.76% |
| [36] | 98.00% | - | - | - |
| [37] | 78.00% | 82.00% | 75.00% | 78.34% |
| [10] | 84.00% | 63.00% | 81.00% | 70.88% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marinho, G.C.; Júnior, W.E.M.; Dias, M.A.; Eler, D.M.; Artero, A.O.; Casaca, W.; Negri, R.G. Associating Anomaly Detection Strategy Based on Kittler’s Taxonomy with Image Editing to Extend the Mapping of Polluted Water Bodies. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245760
Marinho GC, Júnior WEM, Dias MA, Eler DM, Artero AO, Casaca W, Negri RG. Associating Anomaly Detection Strategy Based on Kittler’s Taxonomy with Image Editing to Extend the Mapping of Polluted Water Bodies. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(24):5760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245760
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarinho, Giovanna Carreira, Wilson Estécio Marcílio Júnior, Mauricio Araujo Dias, Danilo Medeiros Eler, Almir Olivette Artero, Wallace Casaca, and Rogério Galante Negri. 2023. "Associating Anomaly Detection Strategy Based on Kittler’s Taxonomy with Image Editing to Extend the Mapping of Polluted Water Bodies" Remote Sensing 15, no. 24: 5760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245760
APA StyleMarinho, G. C., Júnior, W. E. M., Dias, M. A., Eler, D. M., Artero, A. O., Casaca, W., & Negri, R. G. (2023). Associating Anomaly Detection Strategy Based on Kittler’s Taxonomy with Image Editing to Extend the Mapping of Polluted Water Bodies. Remote Sensing, 15(24), 5760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245760








