Machine Learning in the Hyperspectral Classification of Glycaspis brimblecombei (Hemiptera Psyllidae) Attack Severity in Eucalyptus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Machine Learning Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analyses
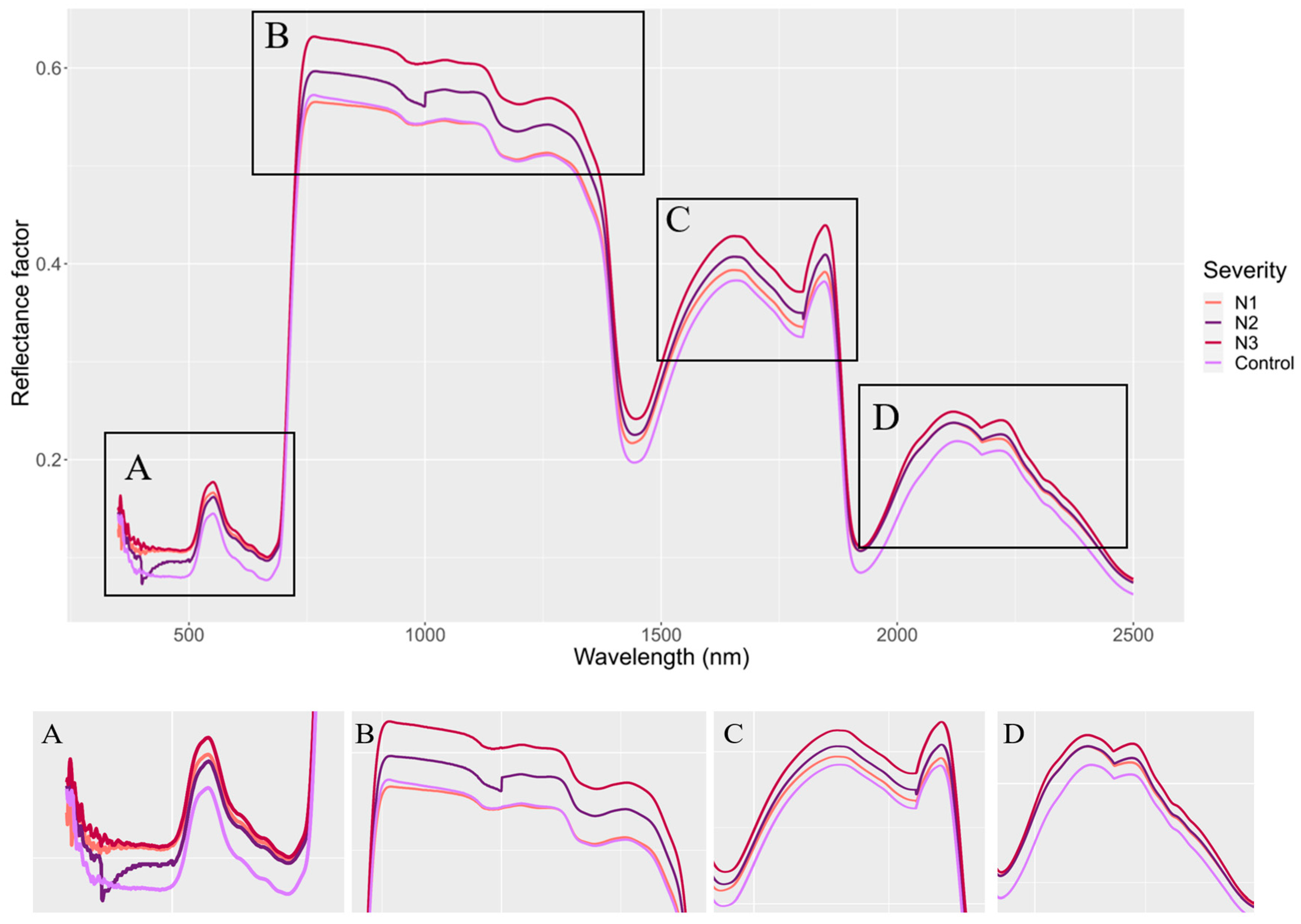
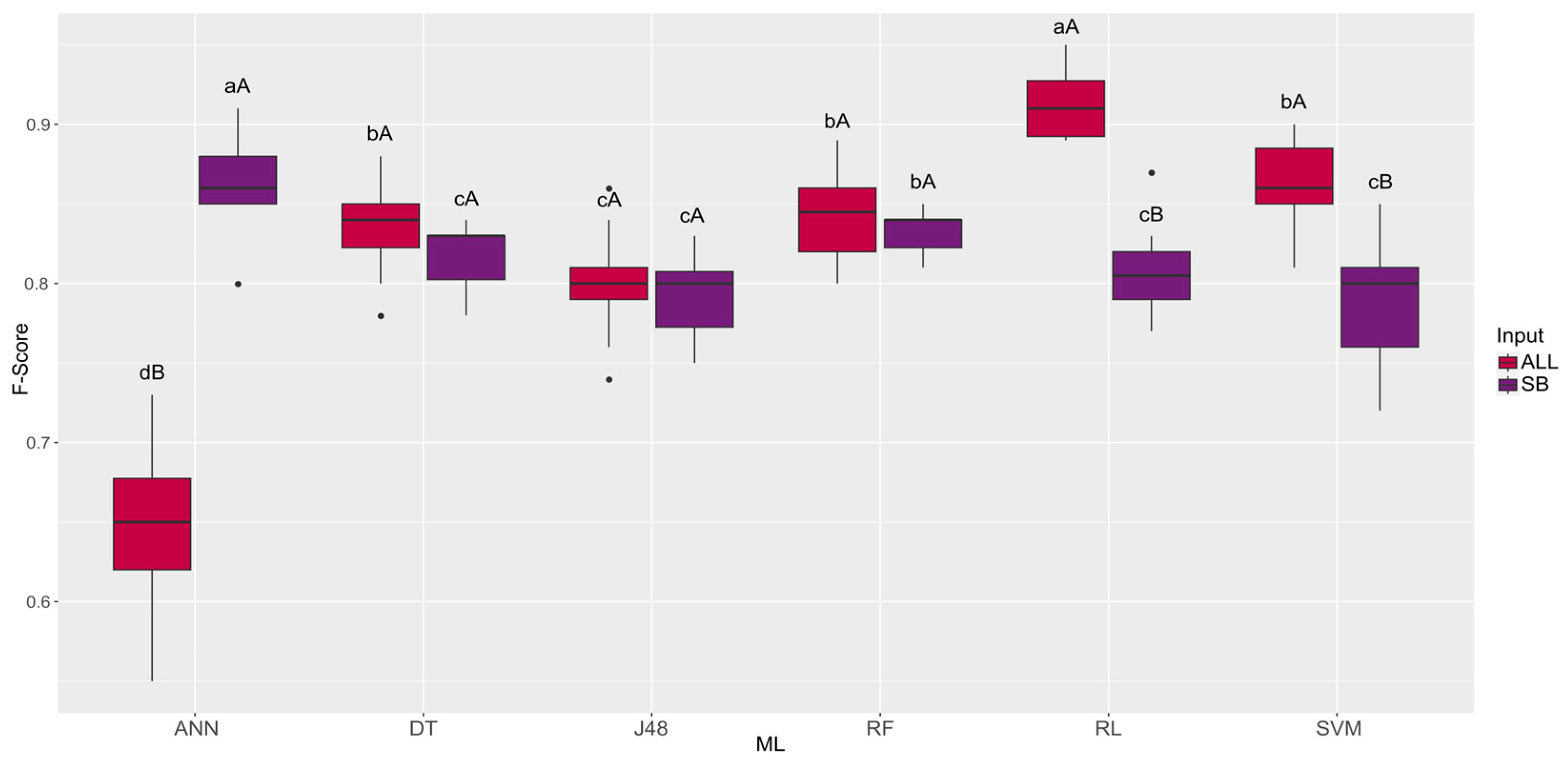
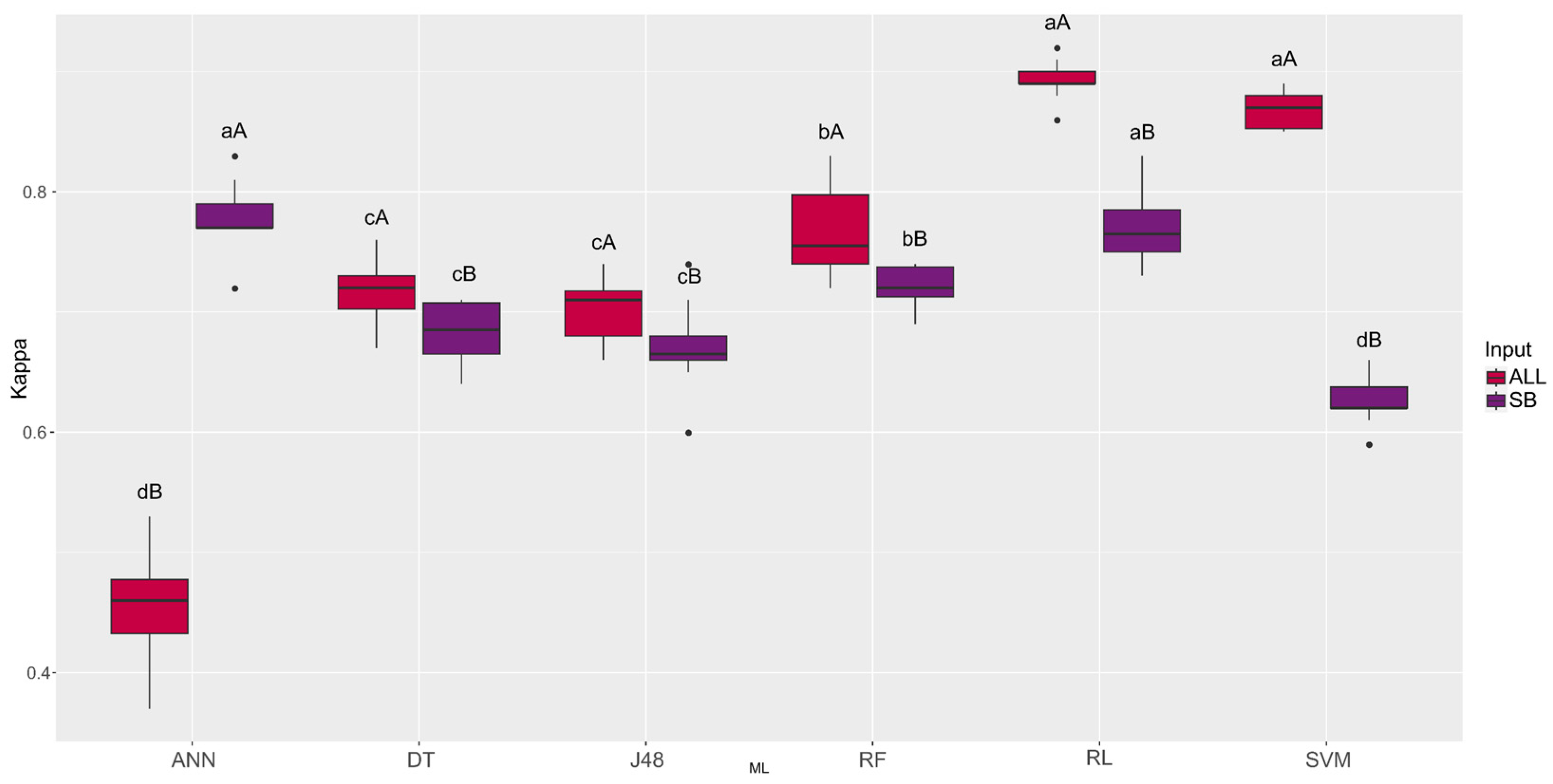
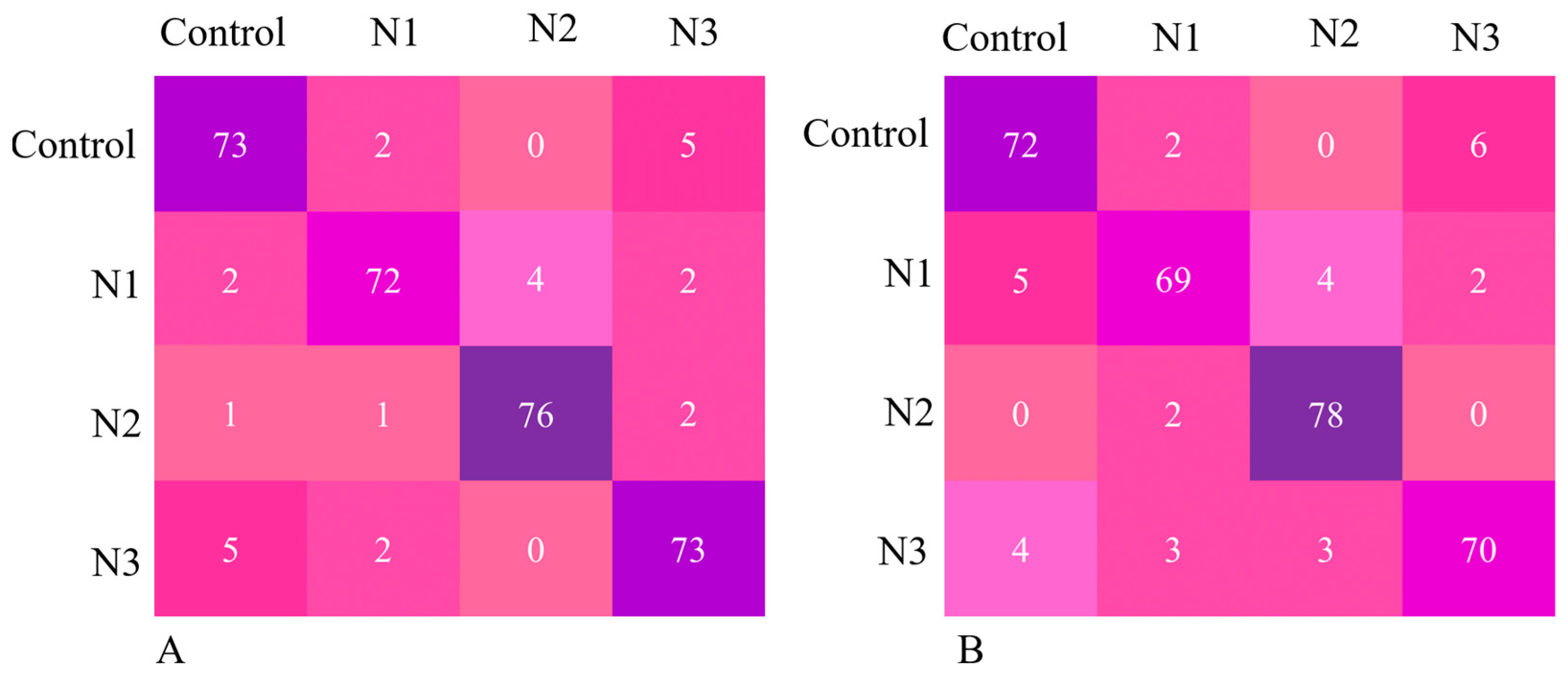
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reguia, K.; Peris-Felipo, F.J. Glycaspis Brimblecombei Moore, 1964 (Hemiptera Psyllidae) Invasion and New Records in the Mediterranean Area. Biodivers. J. 2013, 4, 501–506. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira-Filho, P.J.; Wilcken, C.F.; Masson, M.V.; de Souza Tavares, W.; Guerreiro, J.C.; Do Carmo, J.B.; Prado, E.P.; Zanuncio, J.C. Influence of Temperature and Rainfall on the Population Dynamics of Glycaspis Brimblecombei and Psyllaephagus Bliteus in Eucalyptus Camaldulensis Plantations. Rev. Colomb. Entomol. 2017, 43, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannu, R.; Buffa, F.; Pinna, C.; Deiana, V.; Satta, A.; Floris, I. Preliminary Results on the Spatio-Temporal Variability of Glycaspis Brimblecombei (Hemiptera Psyllidae) Populations from a Three-Year Monitoring Program in Sardinia (Italy). Redia 2018, 101, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, F.R.; Speight, M.R. Insect Pests in Tropical Forestry; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2012; ISBN 1845936361. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, A.H.; Faúndez, M.; Araya, J.E. Susceptibility of Eucafyptus Spp. to an Induced Infestation of Red Gum Lerp Psyllid Glycaspis Brimblecombei Moore (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) in Santiago, Chile. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. Rev. Latinoam. Cienc. Agric. 2010, 37, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- do Amaral Dal, M.H.F.; Wilcken, C.F.; Gimenes, M.J.; de Souza Christovam, R.; Prado, E.P. Control of Red-Gum Lerp Psyllid with Formulated Mycoinsecticides under Semi-Field Conditions. Int. J. Trop. Insect. Sci. 2011, 31, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcken, C.F.; do Couto, E.B.; Orlato, C.; Ferreira-Filho, P.J.; Firmino, D.C. Ocorrência Do Psilídeo-de-Concha (Glycaspis Brimblecombei) Em Florestas de Eucalipto No Brasil. Circ. Téc. IPEF 2003, 201, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcken, C.F.; Firmino-Winckler, D.C.; Dal Pogetto, M.; Dias, T.K.R.; Lima, A.C.V.; de SÁ, L.A.N.; Ferreira Filho, P.J. Psilídeo-de-Concha-Do-Eucalipto, Glycaspis Brimblecombei Moore. In Pragas Introduzidas No Brasil: Insetos e Ácaros; FEALQ: Piracicaba, Brazil, 2015; pp. 883–897. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, R.J. New State Record: Redgum Lerp Psyllid, Glycaspis Brimblecombei. Calif. Plant Pest Dis. Rep. 1998, 17, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- de Lima Vieira, R.; Pessoa, L.G.A.; de Souza Loureiro, E.; Poersh, N.L. Ocorrência de Glycaspis Brimblecombei Sobre Eucalyptus Em Chapadão Do Sul, Mato Grosso Do Sul. Rev. Agric. Neotrop. 2018, 5, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jere, V.; Mhango, J.; Njera, D.; Jenya, H. Infestation of Glycaspis Brimblecombei (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) on Three Eucalyptus Species in Selected Ecological Zones in Malawi. Afr. J. Ecol. 2020, 58, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Mishra, A.; Ehsani, R.; Davis, C. A Review of Advanced Techniques for Detecting Plant Diseases. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante-Ramirez, B. Remote Sensing-Applications; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; ISBN 9535106511. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, P.; Prabhakar, R. An Analysis of Machine Learning Techniques (J48 & AdaBoost)-for Classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 1st India International Conference on Information Processing (IICIP), Delhi, India, 12–14 August 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.B.; Naiker, M. Seeing Red: A Review of the Use of near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) in Entomology. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2020, 55, 810–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, D.E.G.; Ma, L.; Pinheiro, M.M.F.; Gomes, F.D.G.; Gonçalvez, W.N.; Junior, J.M.; de Castro Rodrigues, D.; Blassioli-Moraes, M.C.; Michereff, M.F.F.; Borges, M.; et al. Prediction of Insect-Herbivory-Damage and Insect-Type Attack in Maize Plants Using Hyperspectral Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102608. [Google Scholar]
- Mahlein, A.-K.; Kuska, M.T.; Behmann, J.; Polder, G.; Walter, A. Hyperspectral Sensors and Imaging Technologies in Phytopathology: State of the Art. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 535–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.M.; Bachik, N.A.; Muhadi, N.; Yusof, T.N.T.; Gomes, C. Non-Destructive Techniques of Detecting Plant Diseases: A Review. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 108, 101426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Reddy, B.; Neeraja, S. Plant Leaf Disease Classification and Damage Detection System Using Deep Learning Models. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 24021–24040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelabu, S.; Mutanga, O.; Adam, E. Evaluating the Impact of Red-Edge Band from Rapideye Image for Classifying Insect Defoliation Levels. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 95, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Junior, C.A.; Nanni, M.R.; Shakir, M.; Teodoro, P.E.; de Oliveira-Júnior, J.F.; Cezar, E.; de Gois, G.; Lima, M.; Wojciechowski, J.C.; Shiratsuchi, L.S. Soybean Varieties Discrimination Using Non-Imaging Hyperspectral Sensor. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 89, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.R.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Holmes, G.; Pfahringer, B.; Reutemann, P.; Witten, I.H. WEKA—Experiences with a Java Open-Source Project. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 2533–2541. [Google Scholar]
- Al Snousy, M.B.; El-Deeb, H.M.; Badran, K.; Al Khlil, I.A. Suite of Decision Tree-Based Classification Algorithms on Cancer Gene Expression Data. Egypt. Inform. J. 2011, 12, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajvanshi, N.; Chowdhary, K.R. Comparison of SVM and Naïve Bayes Text Classification Algorithms Using WEKA. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2017, 6, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.-J. LIBSVM: A Library for Support Vector Machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2001, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhering, L.L. Rbio: A Tool for Biometric and Statistical Analysis Using the R Platform. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2017, 17, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; pp. 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Semeraro, T.; Mastroleo, G.; Pomes, A.; Luvisi, A.; Gissi, E.; Aretano, R. Modelling Fuzzy Combination of Remote Sensing Vegetation Index for Durum Wheat Crop Analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulridha, J.; Ampatzidis, Y.; Roberts, P.; Kakarla, S.C. Detecting Powdery Mildew Disease in Squash at Different Stages Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Imaging and Artificial Intelligence. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 197, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.A. Fundamentos Do Sensoriamento Remoto e Metodologias de Aplicação, 3rd ed.; UFV: Viçosa, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Qi, J.-G.; Wang, N.-N.; Zhu, Z.-R.; Luo, J.; Liu, L.-J.; Tang, J.; Cheng, J.-A. Hyperspectral Discrimination of Foliar Biotic Damages in Rice Using Principal Component Analysis and Probabilistic Neural Network. Precis. Agric. 2018, 19, 973–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, S.A.D.M.; Omar, A.F.; Jamlos, M.F.; Azmi, M.A.M.; Muncan, J. A Review of Visible and Near-Infrared (Vis-NIR) Spectroscopy Application in Plant Stress Detection. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 338, 113468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, E.; Ma, J.; Collins, G.S.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Verbakel, J.Y.; Van Calster, B. A Systematic Review Shows No Performance Benefit of Machine Learning over Logistic Regression for Clinical Prediction Models. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 110, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikanth, L.; Jayas, D.S.; White, N.D.G.; Fields, P.G.; Sun, D.-W. Extraction of Spectral Information from Hyperspectral Data and Application of Hyperspectral Imaging for Food and Agricultural Products. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, W.; Huang, W.; Zhao, J.; Song, F. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Winter Wheat Powdery Mildew Based on Wavelet Analysis and Support Vector Machine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, L. Detection and Discrimination of Disease and Insect Stress of Tea Plants Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Wavelet Analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairunniza-Bejo, S.; Shahibullah, M.S.; Azmi, A.N.N.; Jahari, M. Non-Destructive Detection of Asymptomatic Ganoderma Boninense Infection of Oil Palm Seedlings Using NIR-Hyperspectral Data and Support Vector Machine. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, D.C.; Teodoro, L.P.R.; Baio, F.H.R.; dos Santos, R.G.; Coradi, P.C.; Biduski, B.; da Silva Junior, C.A.; Teodoro, P.E.; Shiratsuchi, L.S. Classification of Soybean Genotypes for Industrial Traits Using UAV Multispectral Imagery and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. Appl. 2023, 29, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gava, R.; Santana, D.C.; Cotrim, M.F.; Rossi, F.S.; Teodoro, L.P.R.; da Silva Junior, C.A.; Teodoro, P.E. Soybean Cultivars Identification Using Remotely Sensed Image and Machine Learning Models. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Machine Learning | ALL | SB |
|---|---|---|
| ANN | 59.11 dB | 83.38 aA |
| DT | 78.88 cA | 76.22 cB |
| J48 | 77.61 cA | 75.35 cB |
| RF | 82.38 bA | 79.00 bB |
| RL | 91.93 aA | 82.69 aB |
| SVM | 90.18 aA | 72.03 dB |
| Machine Learning | ALL | SB |
|---|---|---|
| ANN | 0.65 dB | 0.86 aA |
| DT | 0.84 bA | 0.82 cA |
| J48 | 0.80 cA | 0.79 cA |
| RF | 0.84 bA | 0.83 bA |
| RL | 0.91 aA | 0.81 cB |
| SVM | 0.86 bA | 0.79 cB |
| Machine Learning | ALL | SB |
|---|---|---|
| ANN | 0.45 dB | 0.78 aA |
| DT | 0.72 cA | 0.68 cB |
| J48 | 0.70 cA | 0.67 cB |
| RF | 0.77 bA | 0.72 bB |
| RL | 0.89 aA | 0. 77 aB |
| SVM | 0.87 aA | 0.63 dB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gregori, G.S.d.; de Souza Loureiro, E.; Amorim Pessoa, L.G.; Azevedo, G.B.d.; Azevedo, G.T.d.O.S.; Santana, D.C.; Oliveira, I.C.d.; Oliveira, J.L.G.d.; Teodoro, L.P.R.; Baio, F.H.R.; et al. Machine Learning in the Hyperspectral Classification of Glycaspis brimblecombei (Hemiptera Psyllidae) Attack Severity in Eucalyptus. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5657. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245657
Gregori GSd, de Souza Loureiro E, Amorim Pessoa LG, Azevedo GBd, Azevedo GTdOS, Santana DC, Oliveira ICd, Oliveira JLGd, Teodoro LPR, Baio FHR, et al. Machine Learning in the Hyperspectral Classification of Glycaspis brimblecombei (Hemiptera Psyllidae) Attack Severity in Eucalyptus. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(24):5657. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245657
Chicago/Turabian StyleGregori, Gabriella Silva de, Elisângela de Souza Loureiro, Luis Gustavo Amorim Pessoa, Gileno Brito de Azevedo, Glauce Taís de Oliveira Sousa Azevedo, Dthenifer Cordeiro Santana, Izabela Cristina de Oliveira, João Lucas Gouveia de Oliveira, Larissa Pereira Ribeiro Teodoro, Fábio Henrique Rojo Baio, and et al. 2023. "Machine Learning in the Hyperspectral Classification of Glycaspis brimblecombei (Hemiptera Psyllidae) Attack Severity in Eucalyptus" Remote Sensing 15, no. 24: 5657. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245657
APA StyleGregori, G. S. d., de Souza Loureiro, E., Amorim Pessoa, L. G., Azevedo, G. B. d., Azevedo, G. T. d. O. S., Santana, D. C., Oliveira, I. C. d., Oliveira, J. L. G. d., Teodoro, L. P. R., Baio, F. H. R., Silva Junior, C. A. d., Teodoro, P. E., & Shiratsuchi, L. S. (2023). Machine Learning in the Hyperspectral Classification of Glycaspis brimblecombei (Hemiptera Psyllidae) Attack Severity in Eucalyptus. Remote Sensing, 15(24), 5657. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245657











