Mapping Multi-Depth Soil Salinity Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Machine Learning in the Yellow River Delta, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
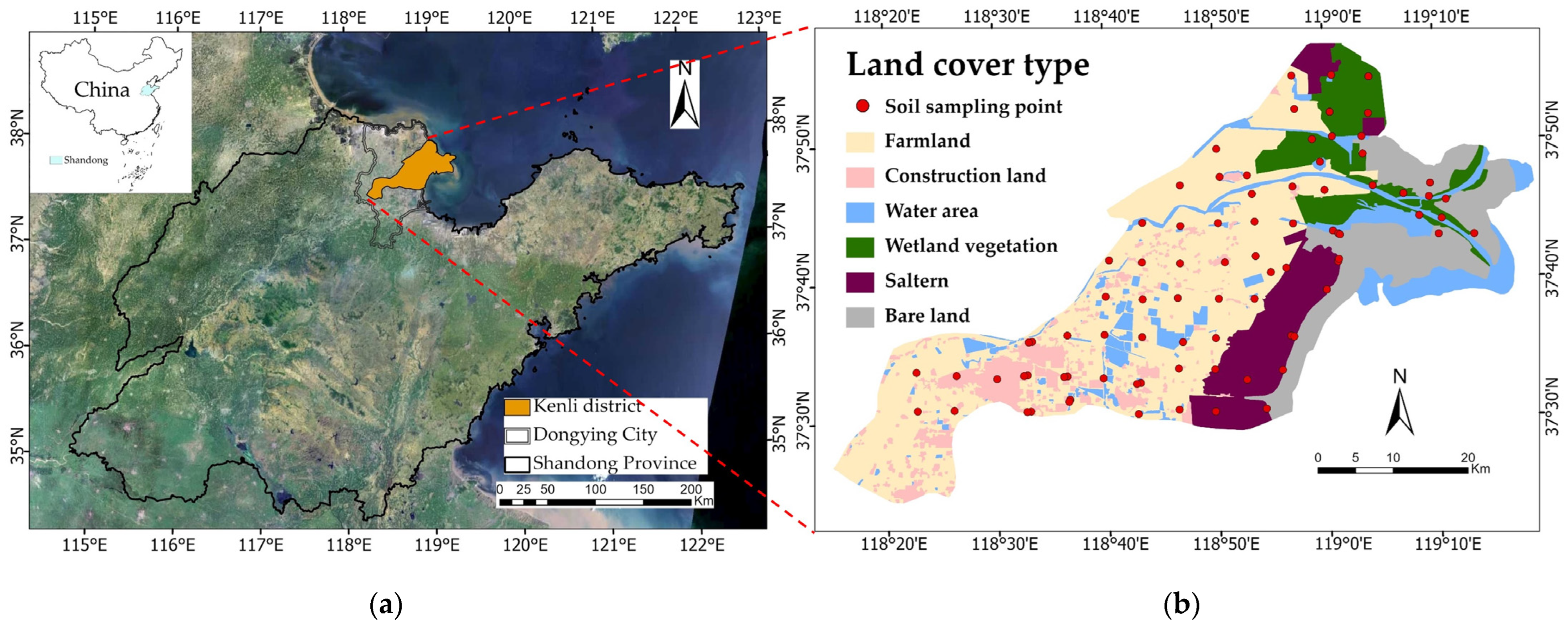
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Soil Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Data and Processing
2.3. Research Method
2.3.1. Environmental Variables
Spectral Value
Salinity Index
Vegetation Index
Heat and Moisture Indices
Spatial Location
2.3.2. Environmental Variable Selection
2.3.3. Estimating Algorithms
Backpropagation Neural Network
Support Vector Machine
Random Forest
2.3.4. Uncertainty and Accuracy Analysis
3. Results
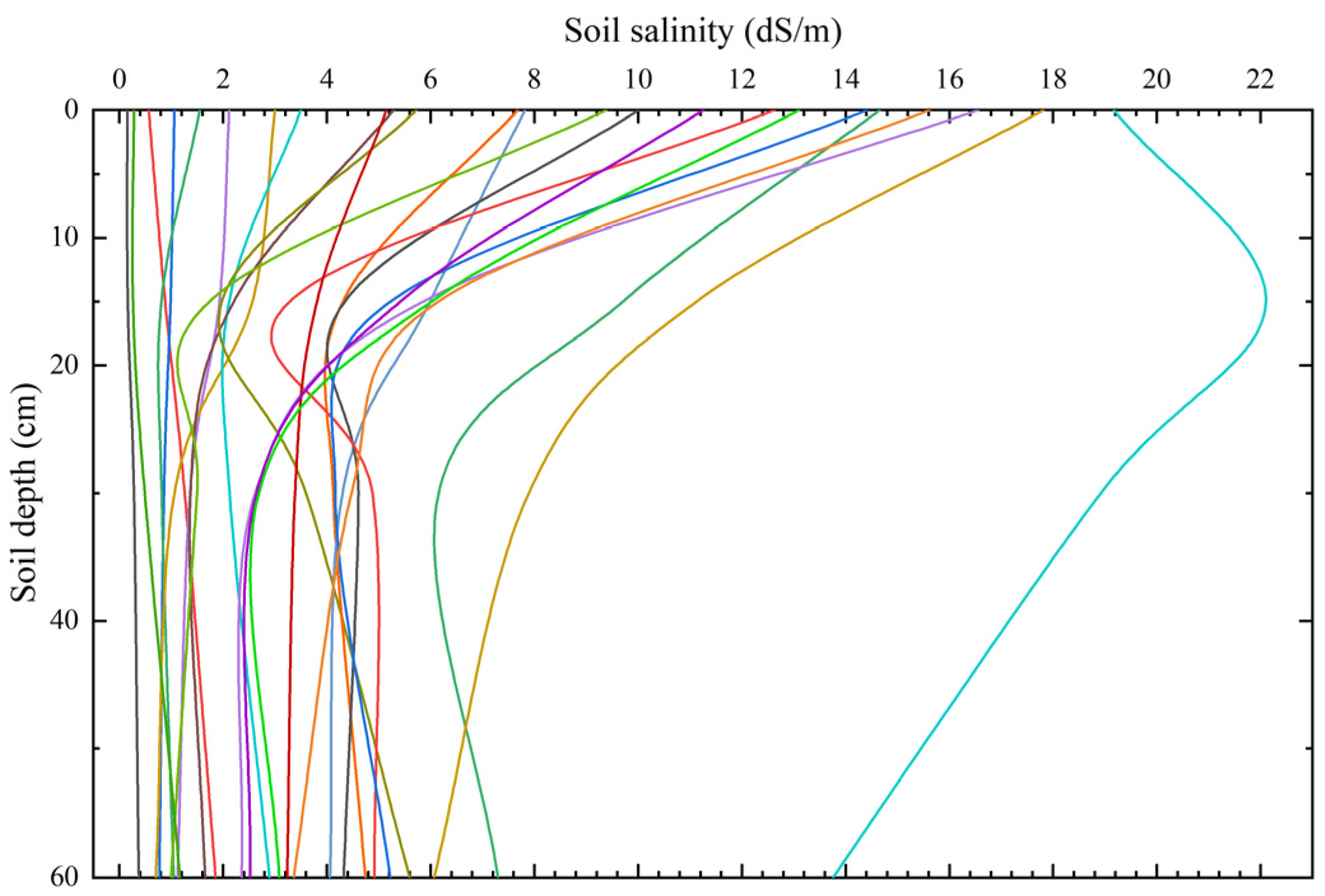
3.1. Statistical Analysis of Soil Salinity Data
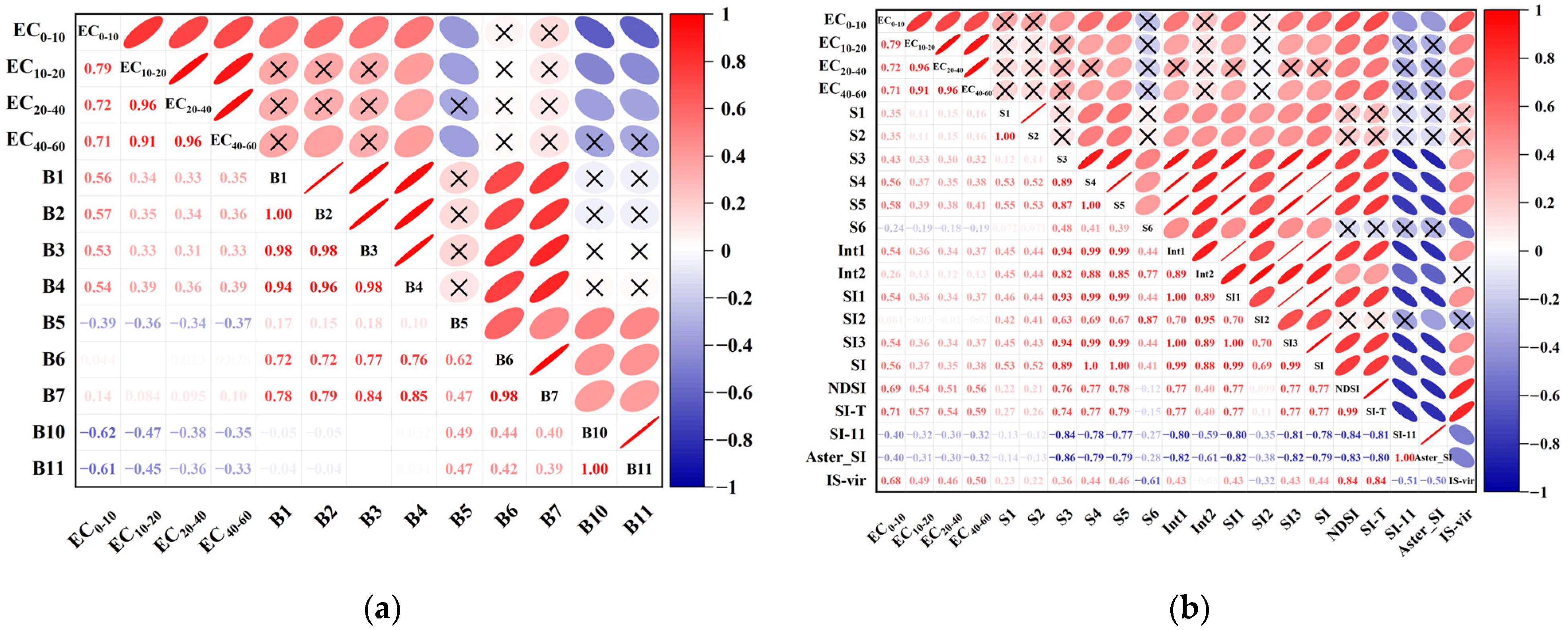
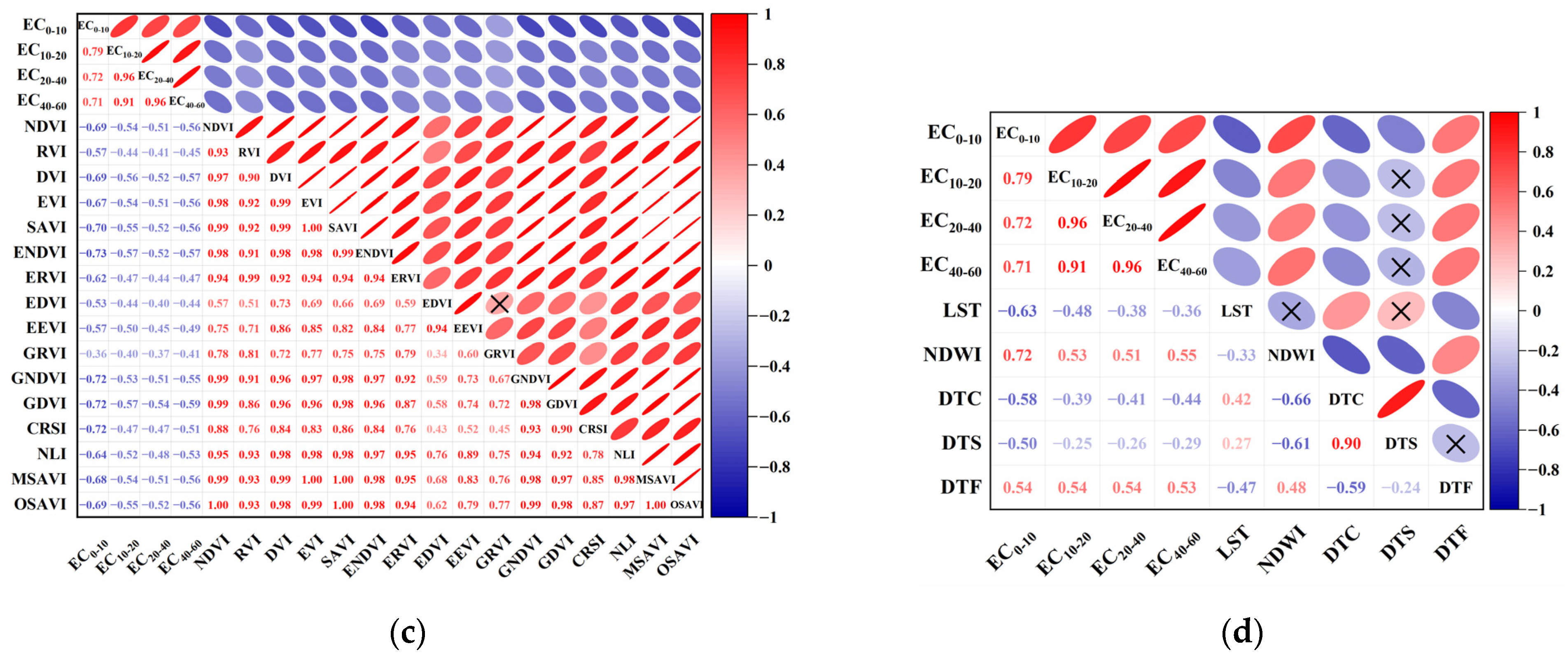
3.2. Correlation Analysis and Screening of Environmental Variables
3.3. Simulation Accuracy and Uncertainty Using Different Algorithms
3.4. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Salinity
3.4.1. Distribution Maps of Soil Salinity
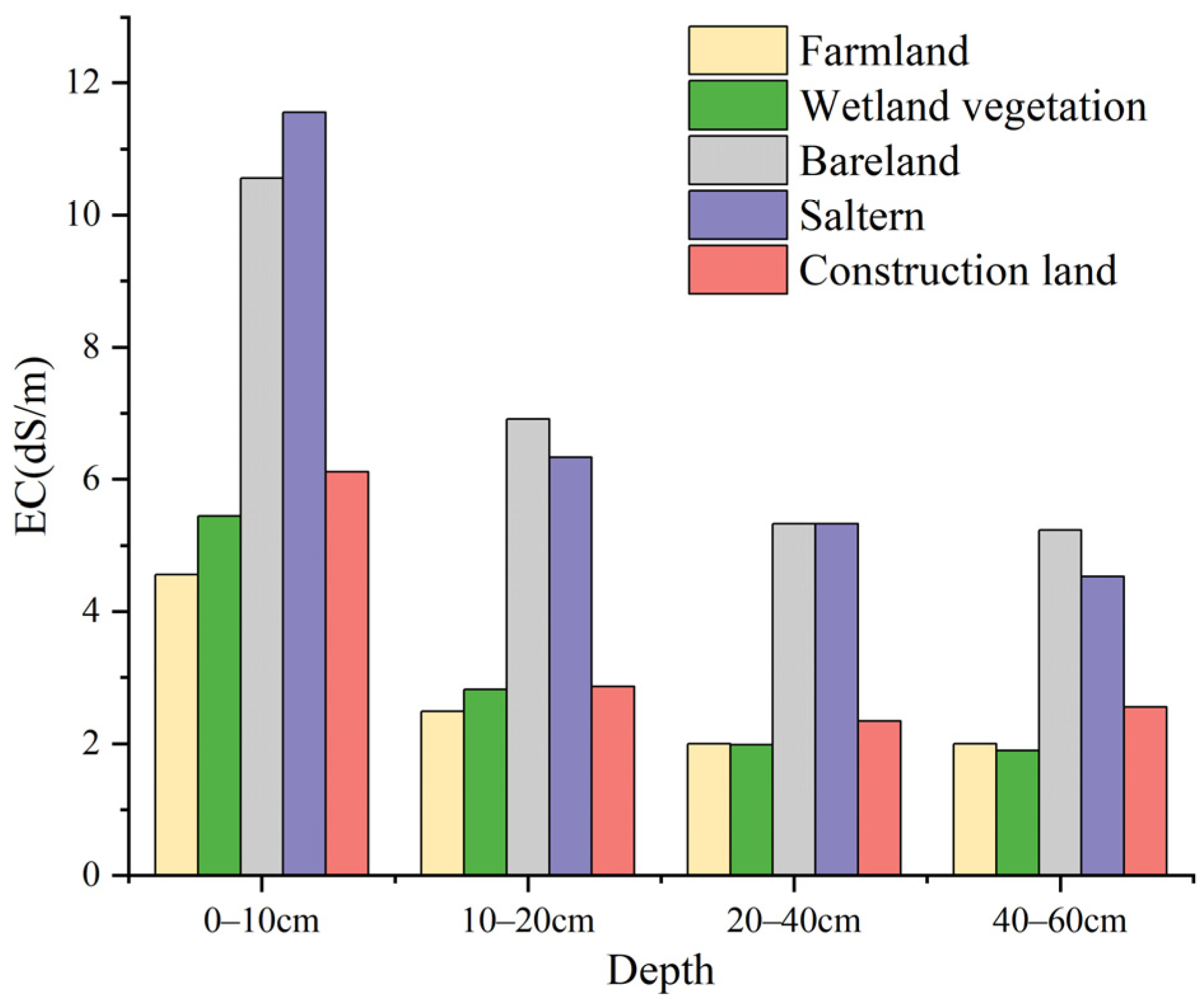
3.4.2. Soil Salinity for Different Land-Cover Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Environmental Variables on Soil Salinity
4.2. Model Accuracy, Uncertainty, and Applicability
4.3. Characterization of Soil Salinity Spatial Distribution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbas, A.; Khan, S.; Hussain, N.; Hanjra, M.A.; Akbar, S. Characterizing soil salinity in irrigated agriculture using a remote sensing approach. Phys. Chem. Earth 2013, 55–57, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqasemi, A.S.; Ibrahim, M.; Al-Quraishi, A.M.F.; Saibi, H.; Al-Fugara, A.K.; Kaplan, G. Detection and modeling of soil salinity variations in arid lands using remote sensing data. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstad, M.; Or, D.; Withers, P.J.; Shokri, N. Evaporation Dynamics and NaCl Precipitation on Capillarity-Coupled Heterogeneous Porous Surfaces. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 3876–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Guo, K.; Li, W.; Feng, X.; Liu, X. Changes in soil properties induced by pioneer vegetation patches in coastal ecosystem. CATENA 2021, 204, 105393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Pedroli, B.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Shu, L. Soil salinity development in the yellow river delta in relation to groundwater dynamics. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Zeng, S.L.; Gao, Y.; Ouyang, Z.T.; Li, B.; Fang, C.M.; Zhao, B. Assessing impact of land uses on land salinization in the Yellow River Delta, China using an integrated and spatial statistical model. Land Use Policy 2011, 28, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, U. Cropland Soil Salinization and Associated Hydrology: Trends, Processes and Examples. Water 2018, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, F.P.; Cutillas, P.P.; Cabañero, J.J.A.; Vivaldi, A.G. Use of remote sensing to evaluate the effects of environmental factors on soil salinity in a semi-arid area. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezketa, E. An integrated methodology for assessing soil salinization, a pre-condition for land desertification. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 67, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Li, H.; Yin, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H. Soil salinity mapping using machine learning algorithms with the Sentinel-2 MSI in arid areas, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Shi, Z.; Webster, R.; Triantafilis, J. Mapping the three-dimensional variation of soil salinity in a rice-paddy soil. Geoderma 2013, 195–196, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiee, M.; Ghazavi, R.; Pakparvar, M.; Vali, A. Mapping spatial variability of soil salinity in a coastal area located in an arid environment using geostatistical and correlation methods based on the satellite data. Desert 2018, 23, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, C.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Z.; Li, Y. Identifying change in spatial accumulation of soil salinity in an inland river watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, T.; Sertel, E.; Tanik, A. Monitoring soil salinity via remote sensing technology under data scarce conditions: A case study from Turkey. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G. Remote sensing prediction and characteristic analysis of cultivated land salinization in different seasons and multiple soil layers in the coastal area. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zovko, M.; Romić, D.; Colombo, C.; Di Iorio, E.; Romić, M.; Buttafuoco, G.; Castrignanò, A. A geostatistical Vis-NIR spectroscopy index to assess the incipient soil salinization in the Neretva River valley, Croatia. Geoderma 2018, 332, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, E.; Suryabhagavan, K.V.; Argaw, M. Soil salinity modeling and mapping using remote sensing and GIS: The case of Wonji sugar cane irrigation farm, Ethiopia. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Yu, D.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, X.; Teng, D.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Lizag, I.; et al. Capability of Sentinel-2 MSI data for monitoring and mapping of soil salinity in dry and wet seasons in the Ebinur Lake region, Xinjiang, China. Geoderma 2019, 353, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbeni, G.; Ngabire, M.; Musyimi, P.K.; Székely, B. Challenges and Opportunities in Remote Sensing for Soil Salinization Mapping and Monitoring: A Review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradipta, A.; Soupios, P.; Kourgialas, N.; Doula, M.; Dokou, Z.; Makkawi, M.; Alfarhan, M.; Tawabini, B.; Kirmizakis, P.; Yassin, M. Remote Sensing, Geophysics, and Modeling to Support Precision Agriculture—Part 1: Soil Applications. Water 2022, 14, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Ayoubi, S.; Jafari, A.; Tajik, S.; Finke, P. Digital mapping of soil properties using multiple machine learning in a semi-arid region, central Iran. Geoderma 2019, 338, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, D.; Van Niekerk, A. Machine learning performance for predicting soil salinity using different combinations of geomorphometric covariates. Geoderma 2017, 299, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokde, N.D.; Ali, Z.H.; Al-Hadidi, M.T.; Farooque, A.A.; Jamei, M.; Maliki, A.A.A.; Beyaztas, B.H.; Faris, H.; Yaseen, Z.M. Total Dissolved Salt Prediction Using Neurocomputing Models: Case Study of Gypsum Soil Within Iraq Region. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 53617–53635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.; Metwaly, M.M.; Metwalli, M.R.; AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; Badreldin, N. Integrating Active and Passive Remote Sensing Data for Mapping Soil Salinity Using Machine Learning and Feature Selection Approaches in Arid Regions. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farifteh, J.; Van der Meer, F.; Atzberger, C.; Carranza, E.J.M. Quantitative analysis of salt-affected soil reflectance spectra: A comparison of two adaptive methods (PLSR and ANN). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Ding, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, S. Digital mapping of soil salinization based on Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data combined with machine learning algorithms. Reg. Sustain. 2021, 2, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestani, M.; Mosleh Ghahfarokhi, Z.; Esfandiarpour-Boroujeni, I.; Shirani, H. Evaluating the spatiotemporal variations of soil salinity in Sirjan Playa, Iran using Sentinel-2A and Landsat-8 OLI imagery. CATENA 2023, 231, 107375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Shi, H.; Zheng, W.; Sun, J. Simulating spatial distribution of coastal soil carbon content using a comprehensive land surface factor system based on remote sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 384–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tian, J.; Lu, X.; Tian, Q. Temporal and spatial dynamics distribution of organic carbon content of surface soil in coastal wetlands of Yancheng, China from 2000 to 2022 based on Landsat images. CATENA 2023, 223, 106961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Sun, D.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J. Mapping soil salinity using a combination of vegetation index time series and single-temporal remote sensing images in the Yellow River Delta, China. CATENA 2023, 231, 107313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G. Upscaling remote sensing inversion and dynamic monitoring of soil salinization in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Yang, J.; Yu, S. Spatial variability of soil salinity based on multi-source data for typical zone of flood area of the Yellow river in central China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Cui, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Du, R.; Lao, C.; Zhou, Y. Soil salinity inversion at different depths using improved spectral index with UAV multispectral remote sensing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Chen, X.; Han, W.; Cui, X.; Ma, W.; Li, G. Estimation of Soil Salt Content at Different Depths Using UAV Multi-Spectral Remote Sensing Combined with Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.C.; de Souza, E.R.; de Melo, H.F.; Oliveira Pinto, J.G.; de Andrade Rego Junior, F.E.; de Souza Júnior, V.S.; Adriano Marques, F.; do Santos, M.A.; Schaffer, B.; Raj Gheyi, H. Comparison of solution extraction methods for estimating electrical conductivity in soils with contrasting mineralogical assemblages and textures. CATENA 2022, 218, 106581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeiry, A.A.; Garcia, L.A. Detecting Soil Salinity in Alfalfa Fields using Spatial Modeling and Remote Sensing. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Khan, S. Using remote sensing techniques for appraisal of irrigated soil salinity. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Modelling and Simulation (MODSIM), Christenchurch, New Zealand, 10–13 December 2007; pp. 2632–2638. [Google Scholar]
- Douaoui, A.E.K.; Nicolas, H.; Walter, C. Detecting salinity hazards within a semiarid context by means of combining soil and remote-sensing data. Geoderma 2006, 134, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Rastoskuev, V.V.; Shalina, E.V.; Sato, Y. Mapping salt-affected soils using remote sensing indicators—A simple approach with the use of GIS IDRISI. In Proceedings of the 22nd Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Singapore, 5–9 November 2001; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, N.; Rai, B.K.; Dwivedi, P. Spatial modeling of soil alkalinity in GIS environment using IRS data. In Proceedings of the 18th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, ACRS, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 20–24 October 1997; pp. 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fourati, H.T.; Bouaziz, M.; Benzina, M.; Bouaziz, S. Modeling of soil salinity within a semi-arid region using spectral analysis. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 11175–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ren, H.; Huang, C. Estimating Soil Salinity in the Yellow River Delta, Eastern China-An Integrated Approach Using Spectral and Terrain Indices with the Generalized Additive Model. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Merzlyak, M.N. Use of a green channel in remote sensing of global vegetation from EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Guyot, G. Potentials and limits of vegetation indices for LAI and APAR assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, J.G.P.W. The derivation of a simplified reflectance model for the estimation of leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Skaggs, T.H.; Corwin, D.L. Regional scale soil salinity evaluation using Landsat 7, western San Joaquin Valley, California, USA. Geoderma Reg. 2014, 2–3, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R. A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Gao, M. Remote sensing inversion of saline soil salinity based on modified vegetation index in estuary area of Yellow River. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farwell, L.S.; Gudex-Cross, D.; Anise, I.E.; Bosch, M.J.; Olah, A.M.; Radeloff, V.C.; Razenkova, E.; Rogova, N.; Silveira, E.M.O.; Smith, M.M.; et al. Satellite image texture captures vegetation heterogeneity and explains patterns of bird richness. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Al-Shafie, W.M.; Mhaimeed, A.S.; Ziadat, F.; Nangia, V.; Payne, W.B. Soil Salinity Mapping by Multiscale Remote Sensing in Mesopotamia, Iraq. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4442–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, N.S.; Qin, W. Influences of canopy architecture on relationships between various vegetation indices and LAI and Fpar: A computer simulation. Remote Sen. Rev. 1994, 10, 309–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.G.; Chehbouni, A.R.; Huete, A.R.; Kerr, Y.H.; Sorooshian, S. A modified soil adjusted vegetation index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, M.; Karnieli, A.; Berliner, P. Mono-window algorithm for retrieving land surface temperature from Landsat TM6 data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2001, 56, 456–466. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Brown, J.F.; Verdin, J.P.; Wardlow, B. A five-year analysis of MODIS NDVI and NDWI for grassland drought assessment over the central Great Plains of the United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L06407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Han, G.; Zhou, D.; Fu, Y.; Guan, B.; Wang, G.; Ning, K.; Wu, H.; Wang, J. The spatial distribution characteristics of soil salinity in coastal zone of the Yellow River Delta. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, Y. Soil structure and salinity effects of fish farming as compared to traditional farming in northeastern Egypt. Land Use Policy 2008, 25, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dongye, G.; Li, X. Countermeasure on sustainable utilization of saline soil in Yellow River Delta. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2003, 17, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xue, J.; Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; He, Y.; Shi, Z. Integrating Remote Sensing and Landscape Characteristics to Estimate Soil Salinity Using Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study from Southern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M. Mapping coastal wetland soil salinity in different seasons using an improved comprehensive land surface factor system. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Gašparović, M.; Alqasemi, A.S.; Aldhaheri, A.; Abuelgasim, A.; Ibrahim, M. Soil salinity prediction using Machine Learning and Sentinel—2 Remote Sensing Data in Hyper—Arid areas. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2023, 130, 103400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, B. Estimating soil salinity using Gaofen-2 imagery: A novel application of combined spectral and textural features. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Representations by Back Propagating Errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Ding, J.; Kung, H.-T.; Latif, A.; Johnson, V.C. Estimation of soil salt content (SSC) in the Ebinur Lake Wetland National Nature Reserve (ELWNNR), Northwest China, based on a Bootstrap-BP neural network model and optimal spectral indices. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Fan, Z.; Fu, Q.; Li, M.; Faiz, M.A.; Ali, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Khan, M.I. Random forest regression evaluation model of regional flood disaster resilience based on the whale optimization algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Wei, Y.; Shi, Q.; Ding, J. Characterizing soil salinity at multiple depth using electromagnetic induction and remote sensing data with random forests: A case study in Tarim River Basin of southern Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Feng, X.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Y.; Huang, J.; Cheng, J. A Framework for Soil Salinity Monitoring in Coastal Wetland Reclamation Areas Based on Combined Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Data and Satellite Data. Drones 2022, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Liu, J.; Shang, J.; Qian, B.; Ma, B.; Kovacs, J.M.; Walters, D.; Jiao, X.; Geng, X.; Shi, Y. Assessment of red-edge vegetation indices for crop leaf area index estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demattê, J.A.M.; Sayão, V.M.; Rizzo, R.; Fongaro, C.T. Soil class and attribute dynamics and their relationship with natural vegetation based on satellite remote sensing. Geoderma 2017, 302, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yao, R. Spatial variability of soil water and salt characteristics in the Yellow River Delta. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2007, 27, 348–353. [Google Scholar]
- Silatsa, F.B.T.; Kebede, F. A quarter century experience in soil salinity mapping and its contribution to sustainable soil management and food security in Morocco. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 34, e00695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xia, J.; Zhao, X.; Gao, F.; Zhao, W.; Xing, X.; Dong, M.; Chu, J. Enrichment of soil nutrients and salt ions with different salinities under Tamarix chinensis shrubs in the Yellow River Delta. CATENA 2023, 232, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Liu, D.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L. Spatial distribution and genesis of salt on the saline playa at Qehan Lake, Inner Mongolia, China. Catena 2019, 177, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Gao, M.; Chang, C. Spatial variability of soil salinity in coastal saline soil at different scales in the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, H. Evaluating the spatial distribution of soil salinity in the Yellow river delta based on Kriging and Cokriging Methods. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 0321–0327. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.; Shi, H.; Zheng, W.; Sun, J.; Fu, Z. Spatiotemporal characteristics and ecological effects of the human interference index of the Yellow River Delta in the last 30 years. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Salinity Index | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | B/R | [37] |
| S2 | (B − R)/(B + R) | |
| S3 | (G × R)/B | |
| S4 | (B × R)0.5 | |
| S5 | (B × R)/G | |
| S6 | (R × NIR)/G | |
| Int1 | (G + R)/2 | [38] |
| Int2 | (G + R + NIR)/2 | |
| SI1 | (G × R)0.5 | |
| SI2 | [(G)2 + (R)2 + (NIR)2]0.5 | |
| SI3 | [(R)2 + (G)2]0.5 | |
| SI | (B × R)0.5 | [39] |
| NDSI | (R − NIR)/(R + NIR) | |
| SI-T | (R/NIR) × 100 | [40] |
| SI-11 | SWIR1/SWIR2 | [41] |
| Aster-SI | (SWIR1 − SWIR2)/(SWIR1 + SWIR2) | |
| IS-vir | 2 × G − (R + NIR) |
| Vegetation Index | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| NDVI | (NIR − R)/(NIR + R) | [43] |
| RVI | NIR/R | [44] |
| DVI | NIR − R | [45] |
| EVI | 2.5 × (NIR − R)/(NIR + 6 × R − 7.5 × B + 1) | [46] |
| SAVI | 1.5((NIR − R)/(NIR + R + 0.5)) | [47] |
| ENDVI | (NIR + SWIR 2 − R)/(NIR + SWIR 2 + R) | [48] |
| ERVI | (NIR + SWIR 2)/R | |
| EDVI | NIR + SWIR 1 − R | |
| EEVI | 2.5 × (NIR + SWIR 1 − R)/(NIR+ SWIR 1 + 6 × R − 7.5 × B + 1) | |
| GRVI | (G − R)/(G + R) | [49] |
| GNDVI | (NIR − G)/(NIR + G) | [43] |
| GDVI | (NIR2 − R2)/(NIR2 + R2) | [50] |
| CRSI | ((NIR × R − G × B)/(NIR × R + G × B))0.5 | [30] |
| NLI | (NIR2 − R)/(NIR2 + R) | [51] |
| MSAVI | (2NIR + 1 − ((2NIR + 1) 2 − 8 (NIR − R))0.5)/2 | [52] |
| OSAVI | (1 + 0.16) (NIR − R)/(NIR + R + 0.16) |
| Soil Depths (cm) | BPNN | SVM | RF |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | Number of hidden layers = 2; Number of neurons = 13, 9; Activation functions = tanh, tanh | c = 1; g = 0.0625 | minleaf = 5; ntree = 500 |
| 10–20 | Number of hidden layers = 1; Number of neurons = 12; Activation functions = logistic | c = 1; g = 0.0625 | minleaf = 4; ntree = 300 |
| 20–40 | Number of hidden layers = 1; Number of neurons = 9; Activation functions = logistic | c = 0.3536; g = 0.0625 | minleaf = 4; ntree = 300 |
| 40–60 | Number of hidden layers = 2; Number of neurons = 16, 8; Activation functions = tanh, tanh | c = 1; g = 0.0625 | minleaf = 4; ntree = 200 |
| Soil Depths (cm) | Sample Number | Min | Max | Average | Median | SD | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | 89 | 0.154 | 19.170 | 6.084 | 3.330 | 5.917 | 0.973 |
| 10–20 | 89 | 0.149 | 22.100 | 2.821 | 1.633 | 3.734 | 1.324 |
| 20–40 | 89 | 0.169 | 18.920 | 2.231 | 1.366 | 2.988 | 1.339 |
| 40–60 | 89 | 0.120 | 13.760 | 2.216 | 1.248 | 2.418 | 1.091 |
| Soil Depths (cm) | Type | Predictive Factors |
|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | Spectral value | B10, B11, B2, B1, B4, B3, B5 |
| Salinity index | SI-T, NDSI, IS-vir, S5, S4, SI, Int1, SI1, SI3, S3, SI-11, Aster_SI | |
| Vegetation index | ENDVI, CRSI, GNDVI, GDVI, SAVI, DVI, OSAVI, NDVI, MSAVI, EVI, NLI, ERVI, RVI, EEVI, EDVI, GRVI | |
| Heat and moisture index | NDWI, LST | |
| Spatial location | DTC, DTF, DTS | |
| 10–20 | Spectral value | B10, B11, B4, B5 |
| Salinity index | SI-T, NDSI, IS-vir, S5, S4, SI, SI3, Int1, SI1 | |
| Vegetation index | GDVI, ENDVI, DVI, SAVI, OSAVI, EVI, MSAVI, NDVI, GNDVI, NLI, EEVI, ERVI, CRSI, EDVI, RVI, GRVI | |
| Heat and moisture index | NDWI, LST | |
| Spatial location | DTF, DTC | |
| 20–40 | Spectral value | B10, B11, B4 |
| Salinity index | SI-T, NDSI, IS-vir, S5 | |
| Vegetation index | GDVI, ENDVI, DVI, SAVI, OSAVI, NDVI, EVI, MSAVI, GNDVI, NLI, CRSI, EEVI, EVI, RVI, EDVI, GRVI | |
| Heat and moisture index | NDWI, LST | |
| Spatial location | DTF, DTC | |
| 40–60 | Spectral value | B4, B5, B2 |
| Salinity index | SI-T, NDSI, IS-vir, S5, S4, SI, SI3, Int1, SI1 | |
| Vegetation index | GDVI, DVI, ENDVI, SAVI, OSAVI, EVI, MSAVI, NDVI, GNDVI, NLI, CRSI, EEVI, ERVI, RVI, EDVI, GRVI | |
| Heat and moisture index | NDWI, LST | |
| Spatial location | DTF, DTC |
| Salinity Class | Soil Salinity (dS/m) | Soil Salinity Levels |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | <2 | non-saline |
| 2 | 2–4 | very slightly saline |
| 3 | 4–6 | slightly saline |
| 4 | 6–8 | |
| 5 | 8–10 | moderately saline |
| 6 | 10–12 | |
| 7 | 12–16 | |
| 8 | >16 | strongly saline |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. Mapping Multi-Depth Soil Salinity Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Machine Learning in the Yellow River Delta, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5640. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245640
Zhang H, Fu X, Zhang Y, Qi Z, Zhang H, Xu Z. Mapping Multi-Depth Soil Salinity Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Machine Learning in the Yellow River Delta, China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(24):5640. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245640
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haoran, Xin Fu, Yanna Zhang, Zhaishuo Qi, Hengcai Zhang, and Zhenghe Xu. 2023. "Mapping Multi-Depth Soil Salinity Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Machine Learning in the Yellow River Delta, China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 24: 5640. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245640
APA StyleZhang, H., Fu, X., Zhang, Y., Qi, Z., Zhang, H., & Xu, Z. (2023). Mapping Multi-Depth Soil Salinity Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Machine Learning in the Yellow River Delta, China. Remote Sensing, 15(24), 5640. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245640







