Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Total Suspended Sediments in the Belize Coastal Lagoon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Ecological Significance of the Belize Coastal Lagoon
1.2. Economic Importance of the Belize Coastal Lagoon
1.3. Sedimentation Issues and the BCL’s Water Quality
1.4. Remote Sensing of TSS
1.5. Summary and Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
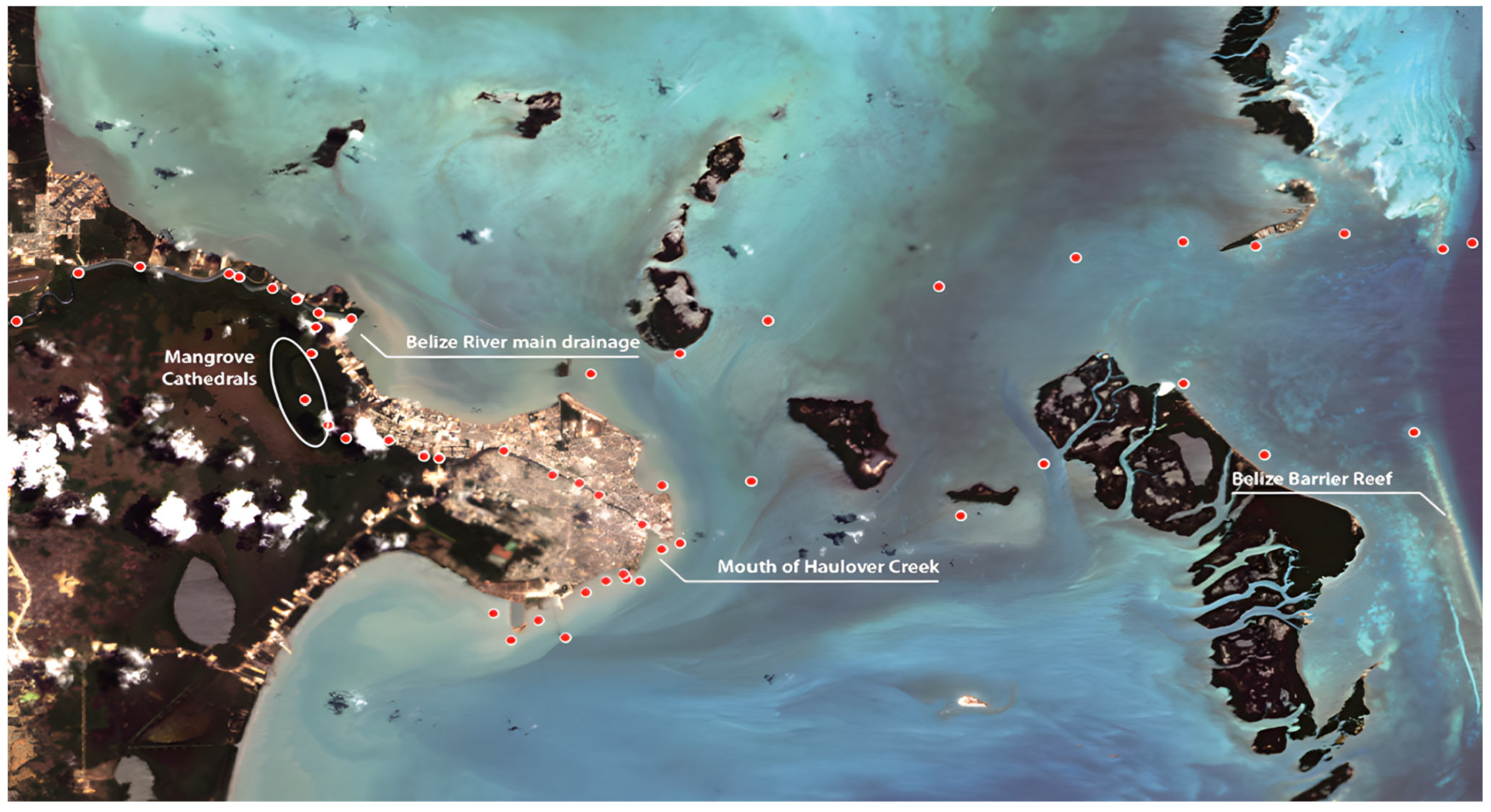
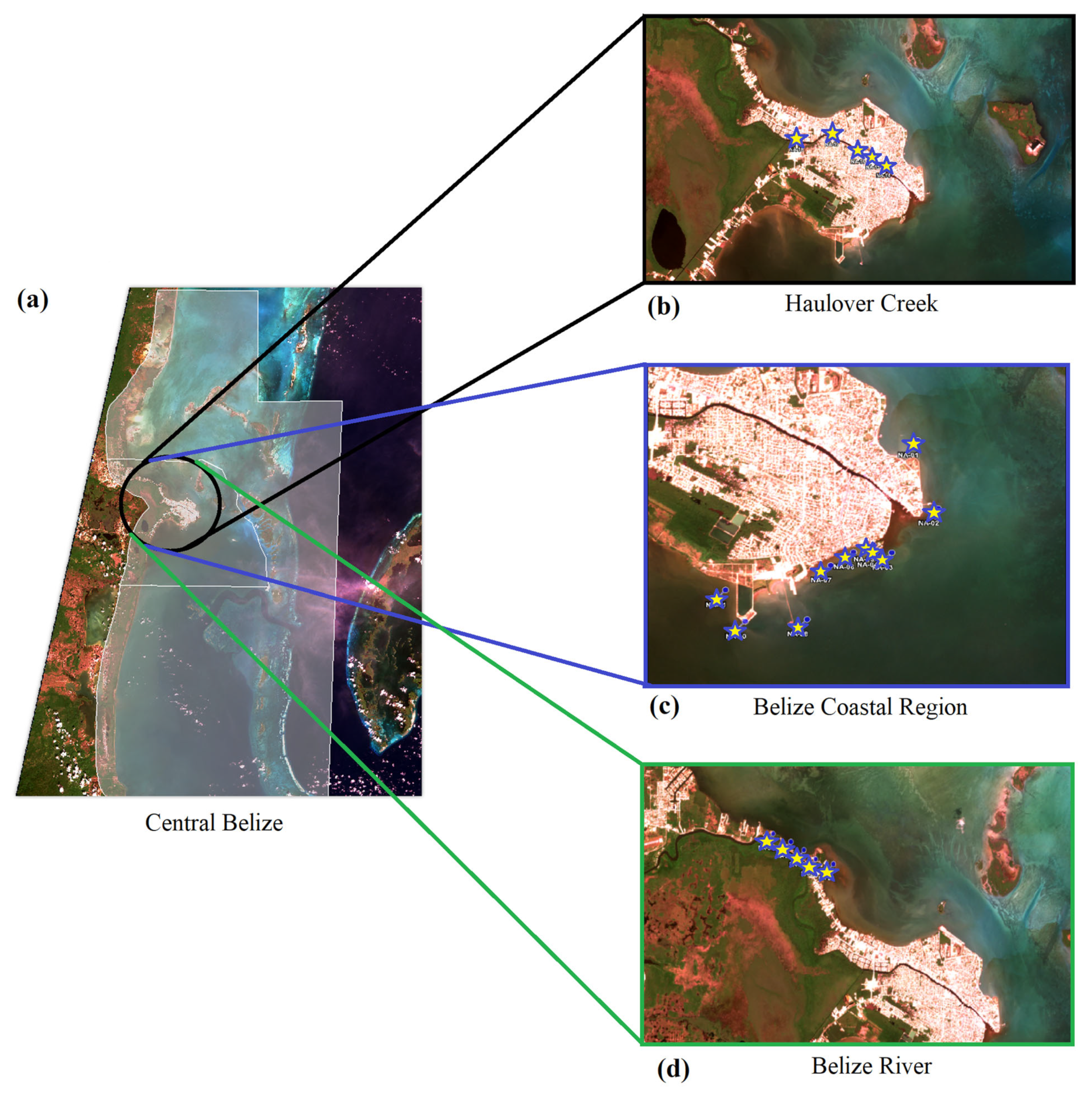
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Field Data
2.2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Covariables Selection
2.3.2. Model Training
2.3.3. Time-Series Analysis
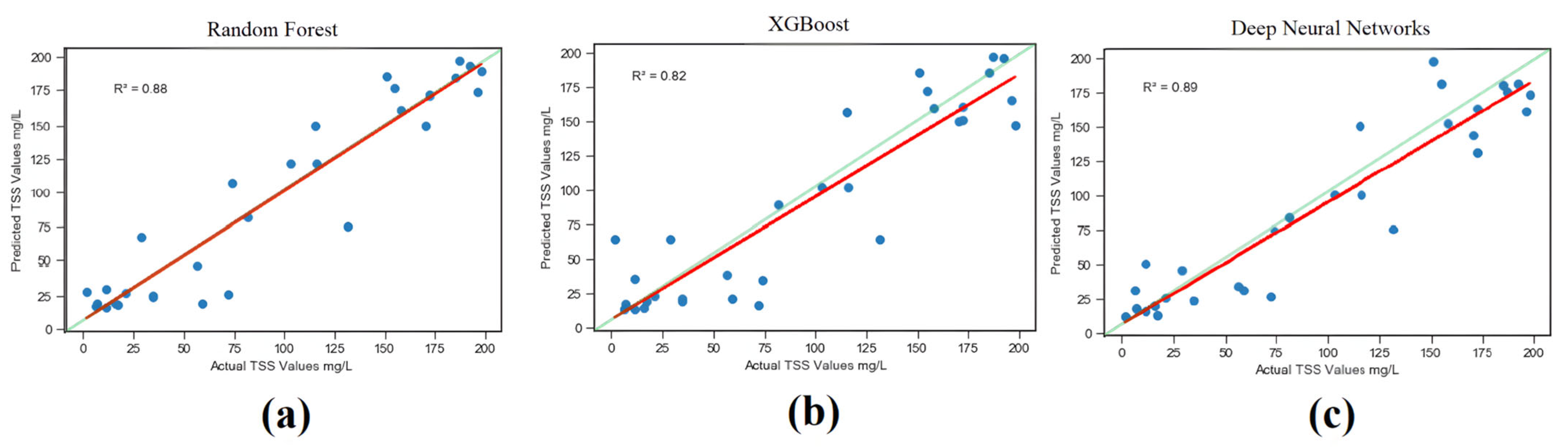
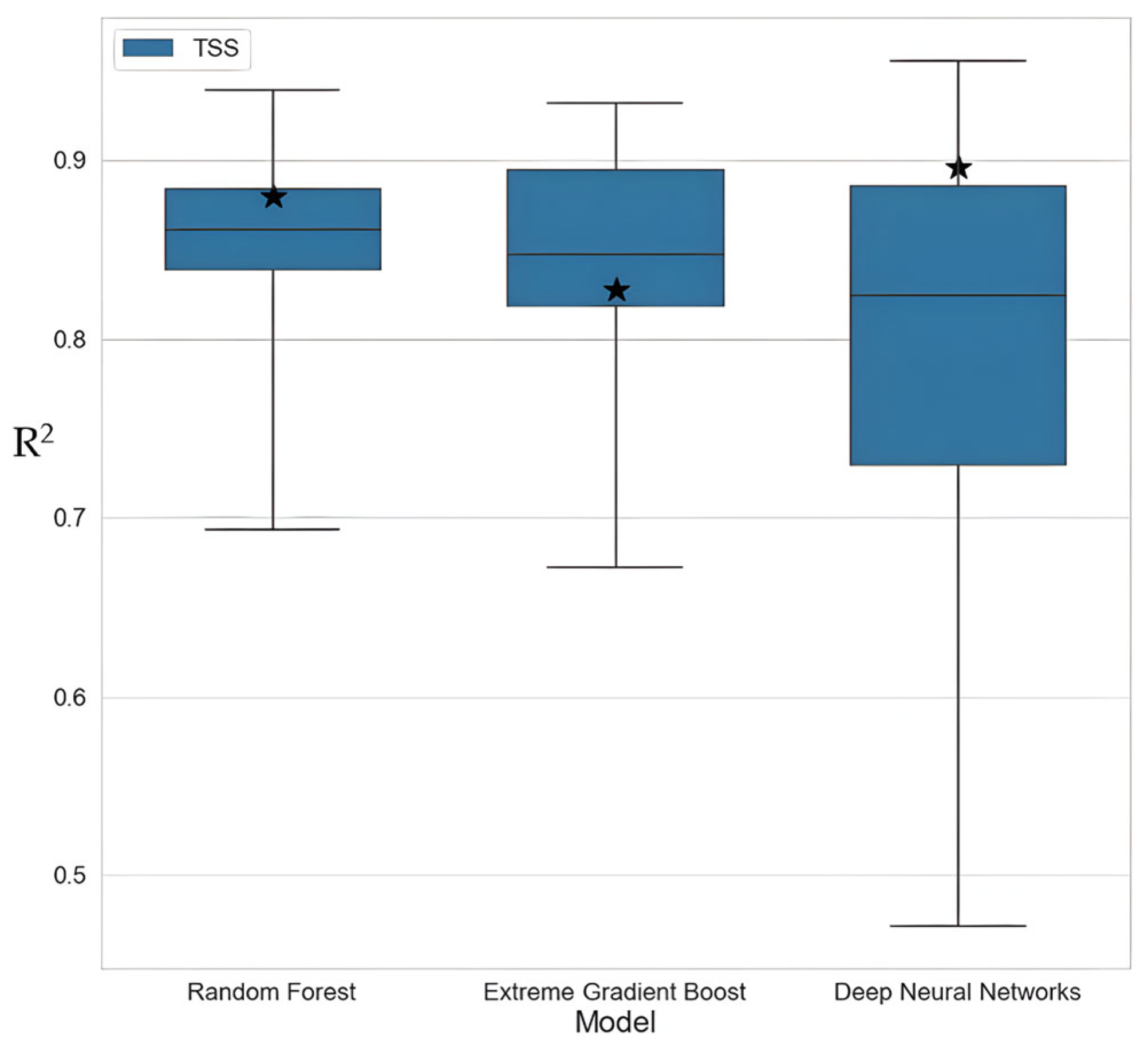
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Remote Sensing of TSS in BCL Using ML Algorithms
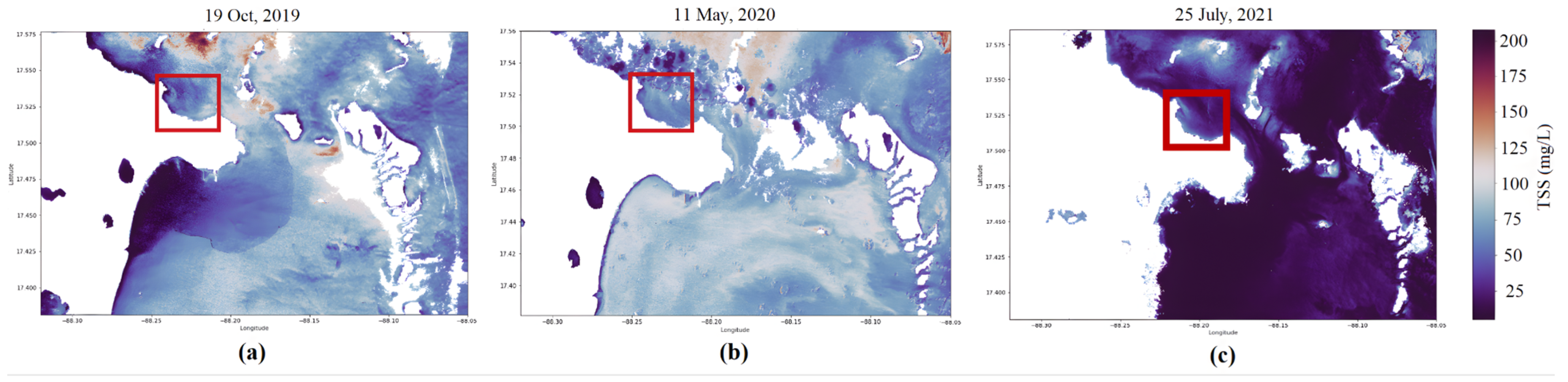
4.2. Time-Series Analysis of TSS Concentration Trends in Central Belize
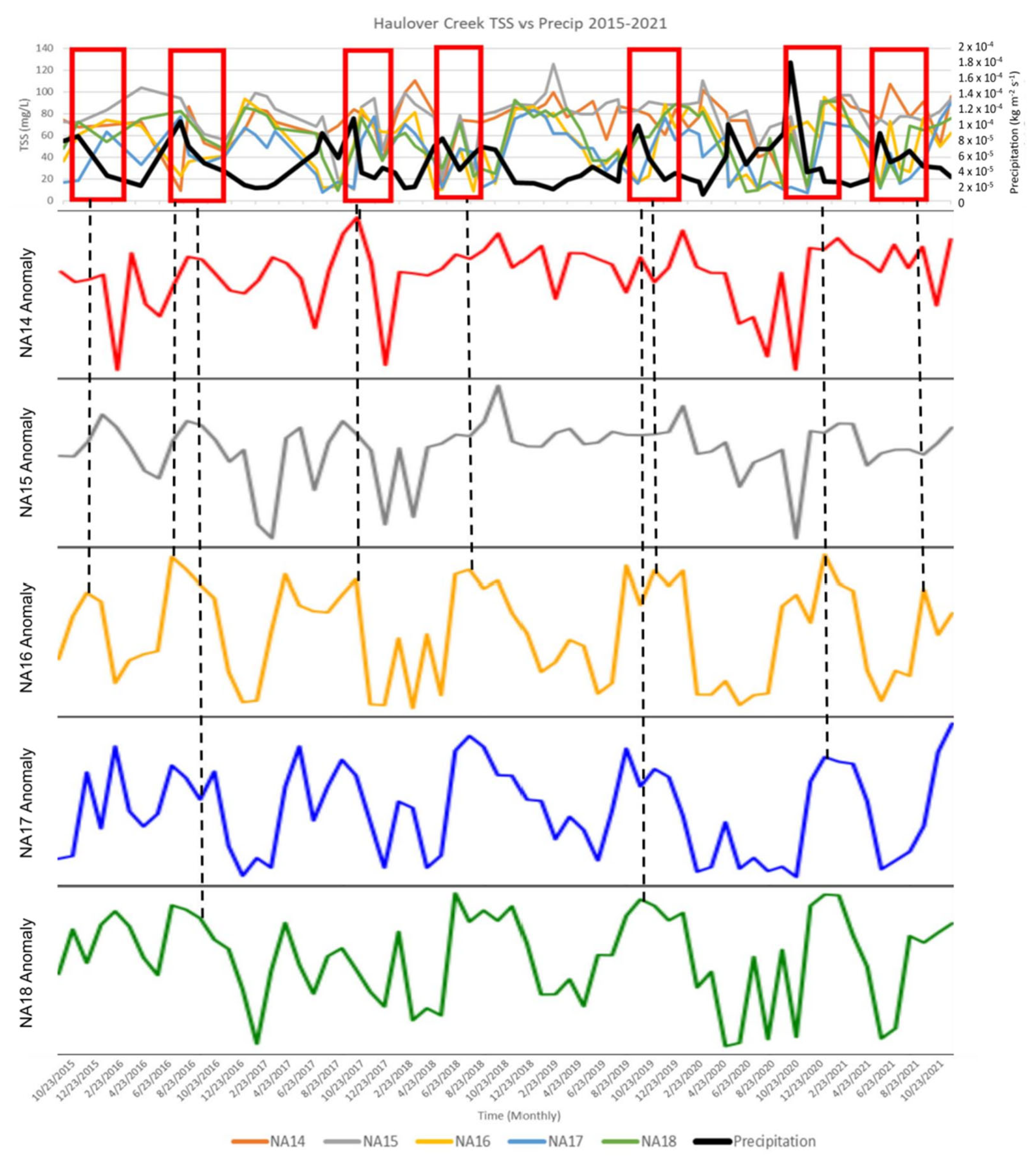
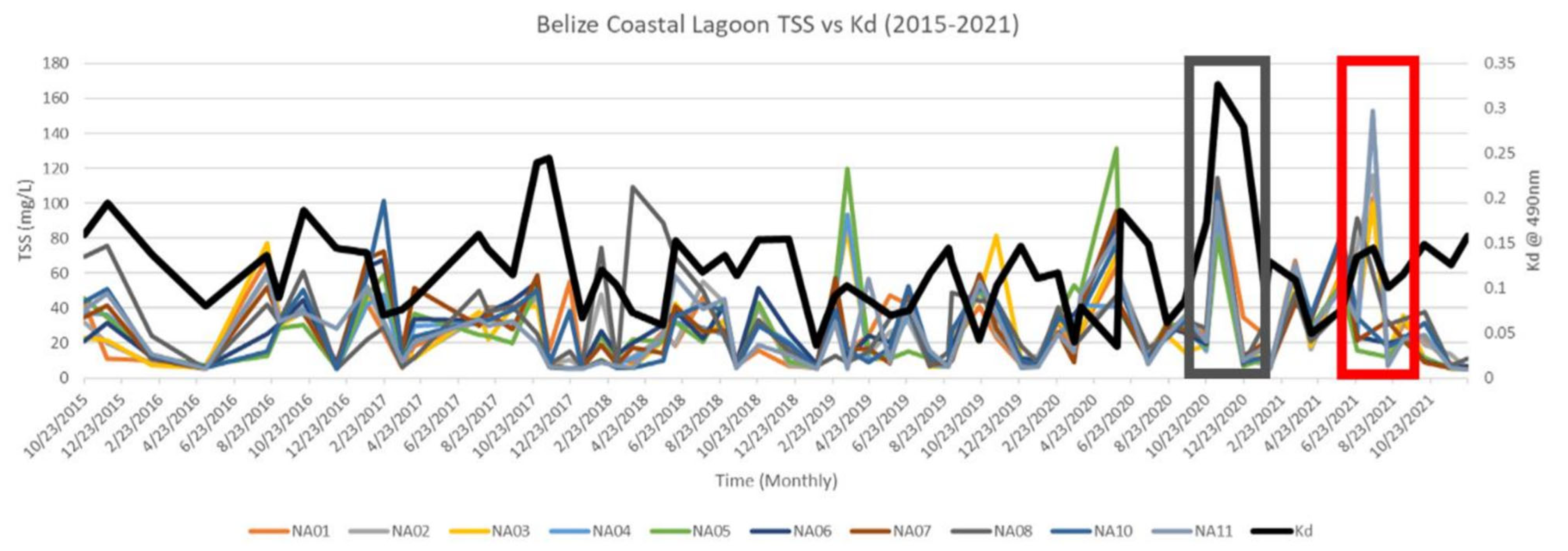
4.2.1. Haulover Creek and Belize Coastal Region Time-Series Analysis
4.2.2. Belize River Time-Series Analysis
4.3. Water Quality in Belize Coastal Lagoon (BCL)—Towards Sustainable Development Goals
4.4. Effectiveness of TSS Monitoring in BCL, Limitations and Future Scope
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waight, K.; Ake, J.; Romero, J.; Thiagarajan, T. A Preliminary Study of Water Quality in Rural Belize. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 5, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- WRI. WRI Annual Report 2009; WRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.D.; Stednick, J.D.; Gilbert, D.M. Environmental Water Quality Monitoring Program: Final Report and Annexes; For Belize Department of Environment by NARMAP, United States Agency for International Development: Belize City, Belize, 1995; 172p. [Google Scholar]
- Azueta, J.; Enriquez-Hernández, G.; García-Flores, F.; Torres-Rodríguez, V.; Libertad, A.; Cisneros, G. State of the Belize Coastal Zone Report 2014–2018; Coastal Zone Management Authority and Institute: Belize City, Belize, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wear, S.L.; Thurber, R.V. Sewage Pollution: Mitigation Is Key for Coral Reef Stewardship. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1355, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.; O’Leary, R.A.; Low-Choy, S.; Mengersen, K.; Knowlton, N.; Brainard, R.E.; Caley, M.J. Species Richness on Coral Reefs and the Pursuit of Convergent Global Estimates. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.V.; Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Binding, C.; Schalles, J.; Loisel, H.; Gurlin, D.; Greb, S.; Alikas, K.; Randla, M.; et al. Robust Algorithm for Estimating Total Suspended Solids (TSS) in Inland and Nearshore Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; McKee, B.A. Using MODIS Terra 250 m Imagery to Map Concentrations of Total Suspended Matter in Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Millward, G.E. Suspended Particles: Their Role in Estuarine Biogeochemical Cycles. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 55, 857–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupssinskü, L.S.; Guimarães, T.T.; De Souza, E.M.; Zanotta, D.C.; Veronez, M.R.; Gonzaga, L.; Mauad, F.F. A Method for Chlorophyll-a and Suspended Solids Prediction through Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, R.P.M. Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Dredging on Reef Corals. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1978, 9, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, R.E.; Vaisnys, J.R. Coral Populations and Growth Patterns: Responses to Sedimentation and Turbidity Associated with Dredging. J. Mar. Res. 1977, 35, 715. [Google Scholar]
- Erftemeijer, P.L.A.; Riegl, B.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Todd, P.A. Environmental Impacts of Dredging and Other Sediment Disturbances on Corals: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1737–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricius, K.E. Effects of Terrestrial Runoff on the Ecology of Corals and Coral Reefs: Review and Synthesis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.; Ricardo, G.F.; Negri, A.P. Effects of Sediments on the Reproductive Cycle of Corals. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, C.S. Responses of Coral Reefs and Reef Organisms to Sedimentation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 62, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessell-Browne, P.; Negri, A.P.; Fisher, R.; Clode, P.L.; Duckworth, A.; Jones, R. Impacts of Turbidity on Corals: The Relative Importance of Light Limitation and Suspended Sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humanes, A.; Ricardo, G.F.; Willis, B.L.; Fabricius, K.E.; Negri, A.P. Cumulative Effects of Suspended Sediments, Organic Nutrients and Temperature Stress on Early Life History Stages of the Coral Acropora Tenuis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riegl, B. Effects of Sand Deposition on Scleractinian and Alcyonacean Corals. Mar. Biol. 1995, 121, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford-Smith, M.G.; Ormond, R.F.G. Sediment-Rejection Mechanisms of 42 Species of Australian Scleractinian Corals. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1992, 43, 683–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, P.J.; Davies, P.S. An Energy Budget for Porites Porites (Scleractinia), Growing in a Stressed Environment. Coral Reefs 1989, 8, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junjie, R.K.; Browne, N.K.; Erftemeijer, P.L.A.; Todd, P.A. Impacts of Sediments on Coral Energetics: Partitioning the Effects of Turbidity and Settling Particles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, F.; Hoogenboom, M.O.; Smith, L.D.; Cooper, T.F.; Abrego, D.; Negri, A.P. Chronic Exposure of Corals to Fine Sediments: Lethal and Sub-Lethal Impacts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirman, D.; Orlando, B.; Maciá, S.; Manzello, D.; Kaufman, L.; Biber, P.; Jones, T. Coral Communities of Biscayne Bay, Florida and Adjacent Offshore Areas: Diversity, Abundance, Distribution, and Environmental Correlates. Aquat. Conserv. 2003, 13, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.W.; Karazsia, J.; Groves, C.E.; Griffin, S.; Moore, T.; Wilber, P.; Gregg, K. Detecting Sedimentation Impacts to Coral Reefs Resulting from Dredging the Port of Miami, Florida USA. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, M.; Nietzer, S.; Schils, T.; Schupp, P.J. Low Sediment Loads Affect Survival of Coral Recruits: The First Weeks Are Crucial. Coral Reefs 2017, 36, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouillon, S.; Douillet, P.; Andréfouët, S. Coupling Satellite Data with in Situ Measurements and Numerical Modeling to Study Fine Suspended-Sediment Transport: A Study for the Lagoon of New Caledonia. Coral Reefs 2004, 23, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Md Equeenuddin, S.; Mishra, D.R.; Acharya, B.C.; Kumar, A.; Equeenuddin, S.M.; Mishra, D.R.; Acharya, B.C. Remote Monitoring of Sediment Dynamics in a Coastal Lagoon: Long-Term Spatio-Temporal Variability of Suspended Sediment in Chilika. ECSS 2016, 170, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrusek, M.; Stengel, E.; Kinkade, C.S.; Vogel, R.L.; Keegstra, P.; Hunter, C.; Kim, C. The Development of a New Optical Total Suspended Matter Algorithm for the Chesapeake Bay. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Song, Q. Influence of the Three Gorges Dam on Total Suspended Matters in the Yangtze Estuary and Its Adjacent Coastal Waters: Observations from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Doxaran, D.; Ruddick, K.; Shen, F.; Gentili, B.; Yan, L.; Huang, H.; Gordon, H.R.; Brown, O.B.; Evans, R.H.; et al. Saturation of Water Reflectance in Extremely Turbid Media Based on Field Measurements, Satellite Data and Bio-Optical Modelling. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 10435–10451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Zimba, P.V.; Everitt, J.H. Remote Sensing Techniques to Assess Water Quality. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. An Assessment of the Black Ocean Pixel Assumption for MODIS SWIR Bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejas, I.A.; Lee, C.M.; Mishra, D.R.; Felgate, S.L.; Evans, C.; Carrias, A.; Rosado, A.; Griffin, R.; Cherrington, E.A.; Ayad, M.; et al. Effect of COVID-19 Anthropause on Water Clarity in the Belize Coastal Lagoon. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 490. [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Tewfik, A.; Phillips, M. Macroalgae Reveal Nitrogen Enrichment and Elevated N:P Ratios on the Belize Barrier Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Laas, A.; Sepp, M.; Paavel, B.; Nõges, T. First Experiences in Mapping Lakewater Quality Parameters with Sentinel-2 MSI Imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grendaitė, D.; Stonevičius, E.; Karosienė, J.; Savadova, K.; Kasperovičienė, J. Chlorophyll-a Concentration Retrieval in Eutrophic Lakes in Lithuania from Sentinel-2 Data. Geol. Geogr. 2018, 4, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric Correction of Metre-Scale Optical Satellite Data for Inland and Coastal Water Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.T.O. Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.C. NDWI—A Normalized Difference Water Index for Remote Sensing of Vegetation Liquid Water from Space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of Normalised Difference Water Index (NDWI) to Enhance Open Water Features in Remotely Sensed Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, N.R.; Samuel, C. Assessment of the temporal variations of surface water bodies in and around Chennai using Landsat imagery. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A New Technique for Surface Water Mapping Using Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacaux, J.P.; Tourre, Y.M.; Vignolles, C.; Ndione, J.A.; Lafaye, M. Classification of Ponds from High-Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing: Application to Rift Valley Fever Epidemics in Senegal. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birth, G.S.; McVey, G.R. Measuring the Color of Growing Turf with a Reflectance Spectrophotometer1. Agron. J. 1968, 60, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Ustin, S.L. Modeling Canopy Water Content for Carbon Estimates from MODIS Data at Land EOS Validation Sites. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. 2001, 1, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.R.; Glysson, G.D.; Turcios, L.M.; Schwarz, G.E. Comparability of Suspended-Sediment Concentration and Total Suspended Solids Data. Water-Resources Investigations Report; 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, H. Sediment and Suspended Sediment. The USGS Water Science School. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, K.; Wu, X.; Qin, Y.; Du, P. Comparison of Surface Water Extraction Performances of Different Classic Water Indices Using OLI and TM Imageries in Different Situations. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 18, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberioon, M.; Brom, J.; Nedbal, V.; Souček, P.; Císař, P. Chlorophyll-a and Total Suspended Solids Retrieval and Mapping Using Sentinel-2A and Machine Learning for Inland Waters. Ecol. Indic 2020, 113, 106236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernez, P.; Lafon, V.; Lerouxel, A.; Curti, C.; Lubac, B.; Cerisier, S.; Barillé, L. Toward Sentinel-2 High Resolution Remote Sensing of Suspended Particulate Matter in Very Turbid Waters: SPOT4 (Take5) Experiment in the Loire and Gironde Estuaries. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9507–9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Steinmetz, F.; Navarro, G. Evaluation of the First Year of Operational Sentinel-2A Data for Retrieval of Suspended Solids in Medium- to High-Turbidity Waters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.; Sugg, Z.; Cherubin, L.; Kuchinke, C.; Paris, C.; Kool, J. Hydrologic Modeling of Watersheds Discharging Adjacent to the Mesoamerican Reef; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lary, D.J.; Alavi, A.H.; Gandomi, A.H.; Walker, A.L. Machine Learning in Geosciences and Remote Sensing. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H. Machine Learning Applications in Oceanography. Rev. Artic. Aquat. Res. 2019, 2, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, O. Scikit-Learn. Stud. Big Data 2016, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Domingos, P. A Few Useful Things to Know about Machine Learning. Commun. ACM 2012, 55, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Acolite for Sentinel-2: Aquatic Applications of MSI Imagery. European Space Agency. In Proceedings of the 2016 ESA Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zuhlke, M.; Fomferra, N.; Brockmann, C.; Peters, M.; Veci, L.; Malik, J.; Regner, P. SNAP (Sentinel Application Platform) and the ESA Sentinel 3 Toolbox. In Sentinel-3 for Science Workshop; 2015; Volume 734, p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Hu, T.; Li, Y. Rbeast: Bayesian Change-Point Detection and Time Series Decomposition. R package version 0.2 2019, Volume 2. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/Rbeast/Rbeast.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2023).
- Sagerman, J.; Hansen, J.P.; Wikström, S.A. Effects of Boat Traffic and Mooring Infrastructure on Aquatic Vegetation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ambio 2020, 49, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubon, W.F. Belize River Water Quality—A Baseline Chemical Assessment; University of Belize: Belmopan, Belize, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McNally, W.H.; Mehta, A.J. Sediment Transport and Deposition in Estuaries (Sample Chapter). In Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS): Coastal Zones and Estuaries; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cruise Passenger Arrivals in Belize 2022|Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/387145/cruise-tourism-volume-belize/ (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Burke, L.; Maidens, J. Belize Coastal Threat Atlas; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 9 January 2005. Available online: https://www.wri.org/belize-coastal-threat-atlas (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Statistics|Belize Tourism Board. Available online: https://www.belizetourismboard.org/belize-tourism/statistics/ (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Cunning, R.; Silverstein, R.N.; Barnes, B.B.; Baker, A.C. Extensive Coral Mortality and Critical Habitat Loss Following Dredging and Their Association with Remotely-Sensed Sediment Plumes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saussaye, L.; van Veen, E.; Rollinson, G.; Boutouil, M.; Andersen, J.; Coggan, J. Geotechnical and Mineralogical Characterisations of Marine-Dredged Sediments before and after Stabilisation to Optimise Their Use as a Road Material. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 3034–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swart, P.K. Report on the Mineralogy and the Stable Carbon and Oxygen Isotopic Composition of Samples Supplied by NOAA. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.J. Spatial Patterns of Chemical Contamination (Metals, PAHs, PCBs, PCDDs/PCDFS) in Sediments of a Non-Industrialized but Densely Populated Coral Atoll/Small Island State (Bermuda). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1362–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrington, E.; Kay, E.; Waight-Cho, I. Modelling the Impacts of Climate Change and Land. Use Change on Belize’s Water Resources: Potential. Effects on Erosion and Runoff. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Peng, C.; Dai, P.; Lai, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal Variation, Composition of DIN and Its Contribution to Eutrophication in Coastal Waters Adjacent to Hainan Island, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 37, 101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrington, E.A.; Ek, E.; Cho, P.; Howell, B.F.; Hernandez, B.E.; Anderson, E.R.; Flores, A.I.; Garcia, B.C.; Sempris, E.; Irwin, D.E. Forest Cover and Deforestation in Belize: 1980–2010. SERVIR, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Belizean. Belize Country Report on the Protection of Coral Reef as It Relates to the un Secretary General Report. 2021.
- Government’s Response to Wildfire Situation—Government of Belize Press Office. Available online: https://www.pressoffice.gov.bz/governments-response-to-wildfire-situation/ (accessed on 14 September 2023).


| In Situ TSS Concentrations (mg/L)—Statistical Description | |
|---|---|
| No. of Samples | 203 |
| Mean | 70.51 |
| Min | 1.5 |
| Max | 199.5 |
| Standard Deviation | 64.3 |
| No. of Field Samples | Field Sampling Dates | Sentinel-2 Image Dates |
|---|---|---|
| 39 | 5 November 2018–11 November 2018 | 6 November 2018; 8 November 2018; 11 November 2018; 13 November 2018 |
| 32 | 14 May 2019–15 May 2019 | 17 May 2019 |
| 48 | 30 May 2020 | 24 May 2020 |
| 42 | 10 May 2021–11 May 2021 | 11 May 2021 |
| 22 | 30 April 2021 | 29 April 2021 |
| 20 | 21 July 2021 | 25 July 2021 |
| From Satellite-based Reflectance Measurements | ||
|---|---|---|
| Spectral Index | Definition Based on Sentinel-2 Bands | Reference |
| NDWI | (B3−B8)/(B3 + B8) | Gao, 1996 [40] |
| MNDWI | (B3−B11)/(B3 + B11) | Xu, 2007 [41] |
| WRI | (B3 + B4)/(B8 + B11) | Mukherjee and Samuel, 2016 [42] |
| AWEI | 4 × (B3−B11)−(0.25 × B8 + 2.75 × B11) | Feyisa et al., 2014 [43] |
| NDTI | (B4−B3)/(B4 + B3) | Lacaux et al., 2007 [44] |
| SR | B4/B8 | Birth & McVey, 1968 [45] |
| SRWC | B4/B2 | Zarco-Tejada and Ustin, 2001 [46] |
| From NASA MERRA Products | ||
| Parameter | Product | Reference |
| Precipitation (kg m−2 s−1) | M2TMNXFLX v5.12.4 via NASA MERRA 2.0 | Gray et al., 2000 [47] |
| Runoff (kg m−2 s−1) | M2TMNXLND v5.12.4 via NASA MERRA 2.0 | Perlman, 2014 [48] |
| Training Set | Testing Set | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | R2 | MSE | R2 | MSE |
| RF | 0.87 | 0.011 | 0.88 | 0.014 |
| XGBoost | 0.85 | 0.015 | 0.82 | 0.0211 |
| DNN | 0.83 | 0.027 | 0.89 | 0.0127 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maniyar, C.B.; Rudresh, M.; Callejas, I.A.; Osborn, K.; Lee, C.M.; Jay, J.; Phillips, M.; Auil Gomez, N.; Cherrington, E.A.; Griffin, R.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Total Suspended Sediments in the Belize Coastal Lagoon. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235625
Maniyar CB, Rudresh M, Callejas IA, Osborn K, Lee CM, Jay J, Phillips M, Auil Gomez N, Cherrington EA, Griffin R, et al. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Total Suspended Sediments in the Belize Coastal Lagoon. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(23):5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235625
Chicago/Turabian StyleManiyar, Chintan B., Megha Rudresh, Ileana A. Callejas, Katie Osborn, Christine M. Lee, Jennifer Jay, Myles Phillips, Nicole Auil Gomez, Emil A. Cherrington, Robert Griffin, and et al. 2023. "Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Total Suspended Sediments in the Belize Coastal Lagoon" Remote Sensing 15, no. 23: 5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235625
APA StyleManiyar, C. B., Rudresh, M., Callejas, I. A., Osborn, K., Lee, C. M., Jay, J., Phillips, M., Auil Gomez, N., Cherrington, E. A., Griffin, R., Evans, C., Rosado, A., Rosado, S., Felgate, S. L., Evans, C., Martín-Arias, V., & Mishra, D. R. (2023). Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Total Suspended Sediments in the Belize Coastal Lagoon. Remote Sensing, 15(23), 5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235625










