Abstract
Recent years have witnessed contrasting trends in summer total rainfall (STR) over the Tibetan Plateau (TP), with an increase in the northern and a decrease in the southern TP. This study identifies four significant centers of rainfall trends: eastern TP (“region A”), Qiangtang Plateau (“B”), Qaidam Basin (“C”), and the northern foothills of the Himalayas (“D”). Heavy rainfall dominates STR trends in regions A and D, accounting for 55.6% and 52.0%, respectively. In region B, moderate and light rainfall contribute almost equally, accounting for 37.3% and 44.8% of the STR trend, respectively. Region C is primarily influenced by light rainfall, explaining 71.2% of the STR trend. Notably, the contributions of different rainfall intensities to STR in each region vary annually, with region A experiencing more heavy rainfall, region B having moderate dominance but less light rainfall, and region C and D showing reduced and increased light rainfall contributions, respectively. Mechanistically, the strengthening of the upper-level westerly jet and the South Asian High, coupled with changes in moisture transport and convective available potential energy, collectively cause variations in rainfall intensity, characterizing the spatial heterogeneity in STR in the TP.
1. Introduction
The Tibetan Plateau (TP), with an average elevation above 4000 m (Figure S1), stands as the world’s highest plateau. Its dynamic and thermal forcing has long been recognized for its critical impact on the onset and establishment of the Asian summer monsoon and even climate changes across the entire Northern Hemisphere [1,2,3,4,5,6].
Functioning as the “Water Tower of Asia” [7], the rainfall of the TP significantly shapes ecosystems, the carbon cycle, and water resources in both local and surrounding regions [8,9,10,11,12]. Moreover, it plays a pivotal role in regulating weather and climate changes across various time scales in Asia through the simultaneously released latent heat of condensation [13,14,15,16,17,18]. Therefore, it is of great significance to comprehensively understand the characteristics of rainfall over the TP.
Global rainfall patterns have dramatically shifted under greenhouse warming, adhering to the trend of “dry gets drier, and wet gets wetter” [19]. The TP, experiencing warming surpassing the global average [20,21], has witnessed substantial alterations in its rainfall on multiple timescales, sparking intense research interest. Some studies have unveiled significant regional disparities in TP rainfall trends, often with distinct mechanisms and characteristics. Xu et al. [8] highlighted increased rainfall in most TP regions, particularly in the east and central areas, whereas the western TP experienced a decline during 1961–2001. Later, studies indicated increased wetness over the western-central TP since the mid-1990s, partly attributed to the rapid lake expansion [22,23,24]. And weaker surface sensible heating from 1980 to 2008 led to reduced rainfall along the TP’s southern and eastern slopes [25]. Recent decades showcased intensified rainfall over northern TP but not in the south [26,27,28]. Yue et al. [29] reported decreased summer rainfall and lake shrinkage in the southern TP post 1998, linked to a dipolar sea surface temperature pattern between the equatorial central Pacific and Indo-Pacific warm pool. In contrast, Wang et al. [28] attributed drying tendencies in the southern TP’s rainfall to an anticyclonic trend over the northeastern TP associated with a circumglobal teleconnection (CGT)-like pattern. Meanwhile, the upward rainfall trend over northern TP might be linked to the genesis of TP vortices [27].
Various aspects of rainfall, encompassing intensity, quantity, and frequency, are undergoing transformations under greenhouse warming. These alterations have far-reaching consequences, notably affecting plant species diversity and essential terrestrial carbon processes [30,31,32] and contributing to recent droughts in arid and semi-arid regions [33,34]. Heavy rainfall is projected to become more frequent and intense with continued warming [35]. Westra et al. [36] highlighted a noticeable global increase in average maximum daily rainfall from 1900 to 2009. Since 2000, a substantial shift has occurred in many elements—such as temperature, winds, and surface sensible heating—over the TP [37,38]. However, it remains unclear how different levels of rainfall intensities change across different TP regions and their respective contributions to the summer (June–July–August, JJA) total rainfall (STR). Therefore, our study endeavors to elucidate the spatial characteristics of trends in STR and different levels of rainfall intensities over the TP during the past two decades by using multi-source rainfall products. Further, we investigate the potential relationship between changes in different levels of rainfall intensities and the STR trend. This analysis delves into the nature of this relationship, its stability, and whether it has undergone changes in time. Crucially, we suggest the underlying physical mechanisms driving these observed trends. Furthermore, we examine the ability of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) models to accurately simulate the trends in STR and different levels of rainfall intensities over the TP, providing insights for future predictions. Our objective is to enhance our understanding of the specific nuances in TP rainfall patterns within the context of greenhouse warming.
2. Data and Methods
We collected observational daily rainfall data from 293 stations spanning the central and eastern TP (see their locations in Figure 1b) from 1950 to 2021 through the China Meteorological Administration (CMA). Additionally, the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM), succeeding the TRMM satellite mission [39], provided a robust dataset with over 20 years of data, offering high spatial (0.1° × 0.1°) and temporal (30-min) resolution from 2000 to 2021. This dataset is widely recognized for its good applicability across multiple time scales [40]. Supplementary Materials contain results from other widely used datasets. The reanalysis meteorological rainfall dataset CN05.1 is interpolated from more than 2400 stations over China from CMA, with a resolution of 0.25° × 0.25° [41]. The Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) pentad precipitation is a merged analysis derived from satellite and gauge observations during 1979–2023, with a spatial resolution of 2.5° × 2.5° [42]. Daily rainfall dataset can also be extracted from a variety of reanalysis datasets, including the Japanese 55-year Reanalysis (JRA-55) [43] and the fifth-generation ECMWF reanalysis for 1979–2023 (ERA5) [44]. These datasets have horizontal resolutions of 1.25° × 1.25° and 0.25° × 0.25°, respectively. To maintain consistency, this study focused on the common time frame of 2000–2021.
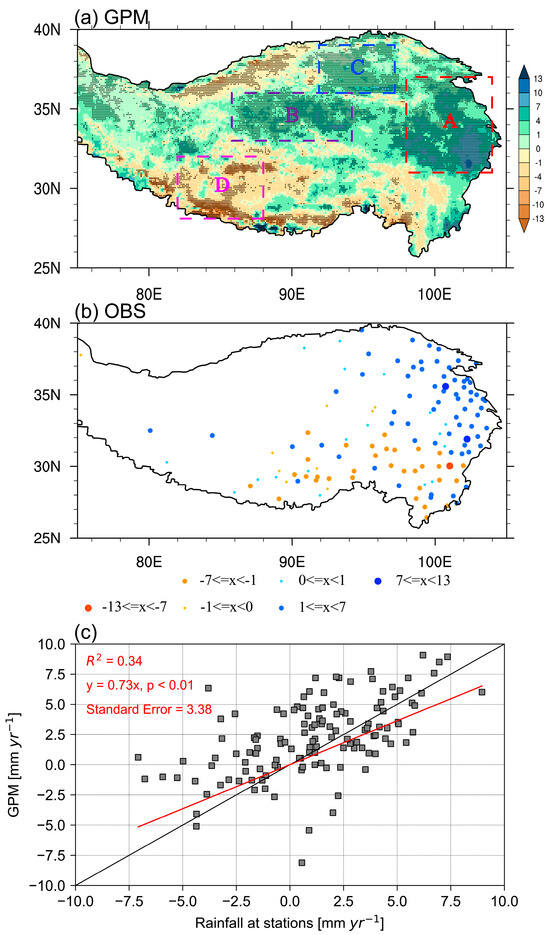
Figure 1.
Spatial distributions of the trend in summer total rainfall (STR, mm yr−1) over the Tibetan Plateau (TP) for the period of 2000–2021 based on (a) GPM and (b) station observations, respectively. (c) Comparison of STR trends between GPM and station observations (red line) and the black line presents the 1:1 slope. Dotted areas in (a) represent the significance above the 90% level as estimated using the Student’s t-test. Colored boxes represent the four key regions (A, B, C, and D and the same below) focused on in this study, where rainfall trends are predominantly significant.
Additionally, various variables from JRA-55, including zonal and meridional wind fields, geopotential height, vertical velocity, specific humidity, convective, and large-scale rainfall, were also employed in this study for the underlying physical mechanism analysis.
For CMIP6 multi-model simulations (available at https://esgf-node.llnl.gov/projects/cmip6/ accessed on 14 June 2023 ), six models (BCC-CSM2-MR, CMCC-CM2-SR5, CMCC-ESM2, INM-CM5-0, KACE-1-0-G, and MRI-ESM2-0) were incorporated. These models provide historical simulations from 1850 to 2014. To evaluate the performance of CMIP6 in simulating the rainfall trends over the TP from 2000 to 2021, it is imperative to integrate both historical and future data of the model simulations (specifically, the future scenario SSP126 was adopted). This allows for the extraction of model data during this specific period, facilitating the comparison with the observed results.
According to the CMA classification, rainfall intensity can be categorized into three levels: light rainfall (0.1–10 mm d−1), moderate rainfall (10–25 mm d−1), and heavy rainfall (exceeding 25 mm d−1).
The linear trend represents the overall upward or downward changes, and the linear trendline is a straight line characterized by the function
where represents a climate variable with a sample size of n, and is the corresponding time period. “b” is the slope of the trendline and “a” is an intercept, which can be calculated by using the least-squares method:
where , . And the spatial distribution of the trends is obtained by calculating the trend at each grid point over the TP. And to assess the statistical significance of the linear trends, a two-tailed Student’s t-test is applied.
3. Results
The TP predominantly comprises arid and semi-arid regions, where the average annual rainfall is 621.6 mm. Notably, summer rainfall constitutes around 55.8% of this total (Figure S2). This summertime rainfall, intertwined with the release of condensation latent heat, exerts a significant influence on the local and surrounding ecosystems, water resources, and climate change. It is therefore crucial to unravel the characteristics of the summer rainfall of the TP.
3.1. Trends in Summer Total Rainfall over the TP
Figure 1 and Figure S3 show the spatial distributions of linear trends in STR over the TP from 2000 to 2021 using the station observations, station-based upscaled products, the satellite-based dataset, and reanalysis rainfall products. The five gridded datasets in general show robust increases in rainfall over the northeastern TP and decreases over the southeastern TP, closely aligning with direct station observations (Figure 1b). Notably, magnitudes of these trends are comparable, with the exception of ERA5, whose trends are obviously underestimated (Figure S3c). In the western TP, the rainfall in CN05.1, despite being station-based [41], faces uncertainties due to the sparse meteorological station coverage there (Figure 1b). This scarcity similarly affects the quality of the reanalysis product’s regional climate representation. Notably, both ERA5 and JRA-55 depict significant decreases in rainfall over the northwestern TP, a trend inconsistent with the increases observed in CN05.1 and the two satellite-based products (GPM and GPCP) (Figure 1 and Figure S3). These two satellite-based rainfall products appear to have a high degree of consistency, albeit in different spatial resolutions (Figure 1a and Figure S3b). Considering factors such as spatial resolution, uncertainty, and trend strength, our study focuses on the state-of-the-art high-resolution GPM dataset for a detailed analysis of the trends in STR over the TP, providing a comprehensive understanding of the changing rainfall patterns.
Quantitatively, we interpolated the gridded GPM rainfall onto the locations of the meteorological stations to compare trend magnitudes with station observations. While GPM appears to slightly underestimate the decreasing trends over the southeastern TP, it exhibits good overall performance, showing a slope of 0.73 (p < 0.01), a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.34, and a standard error of 3.38 in comparison with the station observations (Figure 1c). This verified the results of Lin et al. [40].
Furthermore, we can clearly see that there are three significant wetting centers: the eastern TP (defined here as region A, 31°–37°N, 98°–104°E), Qiangtang Plateau (region B, 33°–36°N, 86°–94°E), and Qaidam Basin (region C, 36°–39°N, 92°–97°E). Conversely, a drying center is observed in the northern foothills of the Himalayas (region D, 28°~32°N, 82°~88°E). Hereafter, the four centers are mainly concerned in this study (Figure 1a).
3.2. Contributions of Various Rainfall Intensities to Regional STR Trends
3.2.1. Spatial Distributions
Changes in STR are primarily attributed to shifts in both rainfall frequency and intensity. We can find that there is a significant increase in rainfall frequency over the wetting centers, with region A experiencing increased frequencies of heavy and moderate rainfall, region B mainly observing an increase in moderate rainfall, and region C witnessing a rise in light rainfall. In contrast, the frequency of moderate and light rainfall over region D significantly decreases (Figure S4). Taking the changes in frequency and mean intensity into account, here, we comprehensively investigate the accumulated summer rainfall in different levels of intensities.
Clearly, contributions from different levels of rainfall intensities to STR changes exhibit obvious spatial heterogeneity (Figure 1a and Figure 2a–c). Heavy rainfall demonstrates an overall east–west contrasting pattern, with increasing trends over the eastern TP and decreasing trends over the western TP. The high-value centers of wetting and drying of the heavy rainfall are mainly concentrated in the eastern and southwestern TP, corresponding to regions A and D (Figure 2a). Furthermore, in regions A and D, heavy rainfall trends contribute to more than 60% of the STR trends in most significant grids, even reaching over 90% in certain areas (Figure 2d). This dominance of heavy rainfall suggests its pivotal role in shaping the STR trends in these regions, accounting for 80% and 60% of the total area of the significant grids in regions A and D, respectively. Regarding moderate rainfall, remarkably, two wetting centers and one drying center are exactly located in regions A, B, and D, respectively (Figure 2b). Obviously, the area where moderate rainfall contributes more than 60% to the STR trends occupies almost the entire area of B except for some northern parts with contributions below 40%, indicating that the variation in moderate rainfall may be foremost in the long-term rainfall changes in this region. In regions A and D, moderate rainfall also accounts for above 60% of the STR trend in some parts but less than 50% in more parts (Figure 2e). In addition, it should be noted that areas with significant changes of heavy and moderate rainfall are also different in regions A and D. For instance, heavy and moderate rainfall mainly contribute to the southern part and northwest–southeast direction in region A, respectively, whereas moderate rainfall significantly contributes to the southeastern region of D (Figure 2d,e).
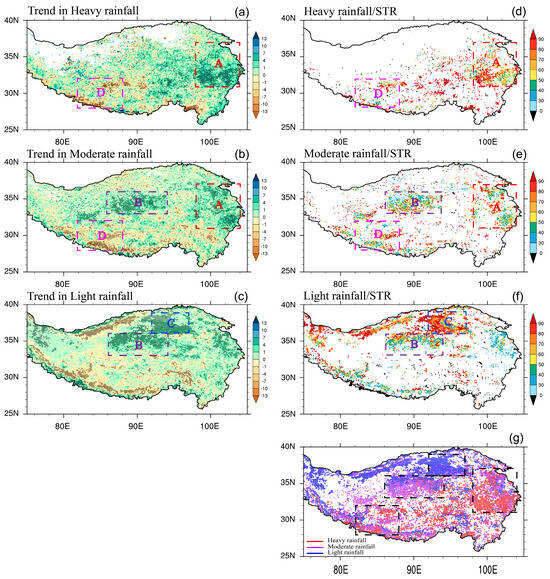
Figure 2.
Spatial distributions of trends in (a) heavy rainfall (mm yr−1), (b) moderate rainfall (mm yr−1), and (c) light rainfall (mm yr−1) for the period of 2000–2021 (left panel). The percentage of trends in (d) heavy rainfall, (e) moderate rainfall, and (f) light rainfall to trends in STR over the significantly varying grids, and (g) significant areas with the largest proportions of rainfall intensities (right panel). Dotted areas in (a–f) represent the significance above the 90% level. The red, purple, and blue dots in (g) represent the heavy, moderate, and light rain, respectively.
In the case of light rainfall, an increasing trend is predominantly observed over the northern TP, contrasting with a decreasing trend over the southern TP (Figure 2c). Notably, two significant centers of rainfall intensification occur in the northern part of region B and the entire region of C, highlighting the importance of light rainfall in long-term changes. Examining the percentage of the light rainfall trend to the STR trend (Figure 2f) reveals that it exceeds 60% in specific grids but falls below 40% in many parts of region B. However, in region C, light rainfall accounts for over 80% of the STR in most areas. It is worth mentioning that the light rainfall is almost the only type of rainfall in region C, making its trend a representative indicator of the overall STR trend in this area.
To identify the primary contributor to the STR trend in these four key regions, we aggregate the contributions of heavy, moderate, and light rainfall (Figure 2g). Clearly, in region A, heavy rainfall covers the largest area, constituting 56% of its total significant area, followed by moderate rainfall at 36%. In region B, moderate rainfall predominantly influences most areas, while light rainfall dominates the northernmost part, accounting for approximately 51% and 41% of the dominant areas, respectively. Region C is entirely dominated by light rainfall with a significant area of approximately 93%. And in region D, the situation is complicated with moderate, heavy, and light rainfall contributing areas of 42%, 38%, and 20%, respectively.
It is well known that the climatological STR over the TP typically decreases from southeast to northwest, with most parts of the TP being predominantly characterized by light rainfall, followed by moderate and heavy rainfall (Figure 3a–c). Specifically, the climatological percentage of light rainfall to STR is generally above 50% in most TP areas (Figure 3c). In contrast, the proportions of heavy and moderate rainfall are considerably smaller, typically falling below 50% (Figure 3a,b). A comparison between the spatial patterns of dominant contributors to climatological rainfall and rainfall trends reveals significant disparities (Figure 2g and Figure 3d), indicating that the trend variations in different levels of rainfall intensities are gradually altering the pattern of their original climate states.
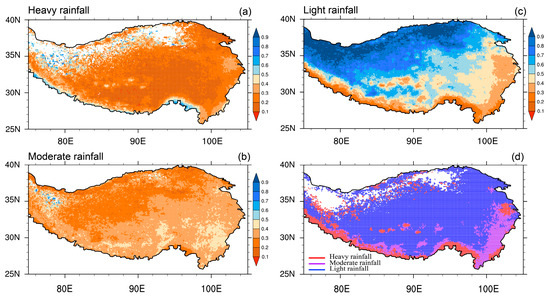
Figure 3.
Spatial distributions of the climatological proportion of (a) heavy rainfall, (b) moderate rainfall, (c) light rainfall to STR during 2000–2021. (d) the largest proportion of rainfall intensities. The red, purple, and blue dots in (d) represent the heavy, moderate, and light rainfall, respectively.
3.2.2. Temporal Evolution
Based on the regional average STR and different levels of rainfall intensities in the four key regions (Figure 4a–d and Table 1), we can see that the change in STR shows a significant increasing trend of 48.6 mm 10 yr–1 in region A. The heavy rainfall here, with values below 100 mm before 2018, is much less than moderate and light rainfall, which is well consistent with the manifestation in Figure 3a. However, heavy rainfall experienced the strongest upward trend in recent decades, increasing at a rate of 27.0 mm 10 yr–1 and contributing to a 55.6% rise in STR (Table 1). The growth rate of moderate rainfall (15.3 mm 10 yr–1) in this region is also prominent and conductive to the upward trend in STR. In contrast, light rainfall has high values but a weak trend (6.3 mm 10 yr–1). It is interesting that the most rapid increase in STR and different levels of rainfall intensities all occurred after 2016 in region A. Observations in region A also show similar results to GPM, but with a larger trend in moderate rainfall than that in heavy rainfall which may be related to the limited stations in the southwest of region A (Figure 1b), where heavy rainfall predominantly occurs (Figure 2d).
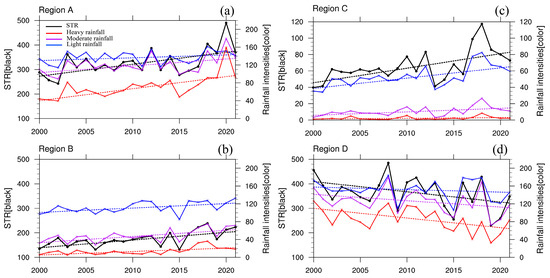
Figure 4.
Time series of STR (black lines, mm), heavy rainfall (red lines, mm), moderate rainfall (purple lines, mm), and light rainfall (blue lines, mm) averaged over regions (a) A, (b) B, (c) C, and (d) D. The dotted lines represent the trends in each variable during 2000–2020. Left and right axis represent the STR and three levels of rainfall intensities, respectively.

Table 1.
Trend (mm 10 yr–1) in STR and three levels of rainfall intensities over the TP. The symbols *, **, ***, and **** indicate the statistical significance above the 90%, 95%, 99%, and 99.9% confidence level, respectively. The numbers in brackets represent the explaining percentages of trend in dominant rainfall intensities to STR trend in four key regions.
In region B, the temporal variations in STR and three levels of rainfall intensities all have robust strengthening trends (p < 0.05) (Figure 4b and Table 1). Obviously, light rainfall exhibits a trend almost twice that of moderate rainfall, with a robust increase of approximately 20.9 mm 10 yr–1, contributing about 44.8% to the STR trend. Moderate rainfall, with a trend of 17.4 mm 10 yr–1, contributes 37.3% to the STR trend (Table 1). Heavy rainfall, with values below 40 mm yr–1 in this region, displays a relatively weak increasing trend of 8.4 mm 10 yr–1 (p < 0.001). Hence, quantitatively, light rainfall and moderate rainfall indeed are the main contributors to the long-term change in STR in region B.
For region C, light rainfall is clearly the dominant rainfall intensity, with comparable magnitude and trend to the STR (about 71.2%) (Figure 4c and Table 1). Meanwhile, in region D, heavy rainfall exhibits the lowest magnitude, and although all three levels of rainfall intensities have similar interannual variabilities with STR (Figure 4d), only the decreasing trend in heavy rainfall is significant with a rate of 21.7 mm 10 yr–1 (Table 1). This decrease accounts for 52.0% of the STR trend, marking heavy rainfall as the dominant rainfall intensity driving the weakening of STR (–41.7 mm 10 yr–1), and a sudden decline appeared after 2011. Moderate rainfall follows, but with a statistically non-significant trend. Similar to region A, the trend changes of STR here caused by light rainfall are also weak.
3.2.3. Trend in Proportions of Different Levels of Rainfall Intensities to STR
From the above analysis, we have known that in the different regions of concern, the contributions of three levels of rainfall intensities are different. Additionally, it is also worth paying attention to whether this kind of relationship remains steady along with climate change.
Figure 5a–c show the trends in the proportion of three levels of rainfall intensities to STR in the period of 2000–2021. Clearly, the proportion of heavy rainfall exhibits a consistent increasing trend in the eastern TP (Figure 5a), well consistent with its own trends (Figure 2a). Conversely, the proportion of moderate rainfall demonstrates an opposing trend to that of heavy rainfall over the entire TP (Figure 5b). Additionally, the trend in the proportion of light rainfall weakens in most TP regions, except for region D and north of region B (Figure 5c).
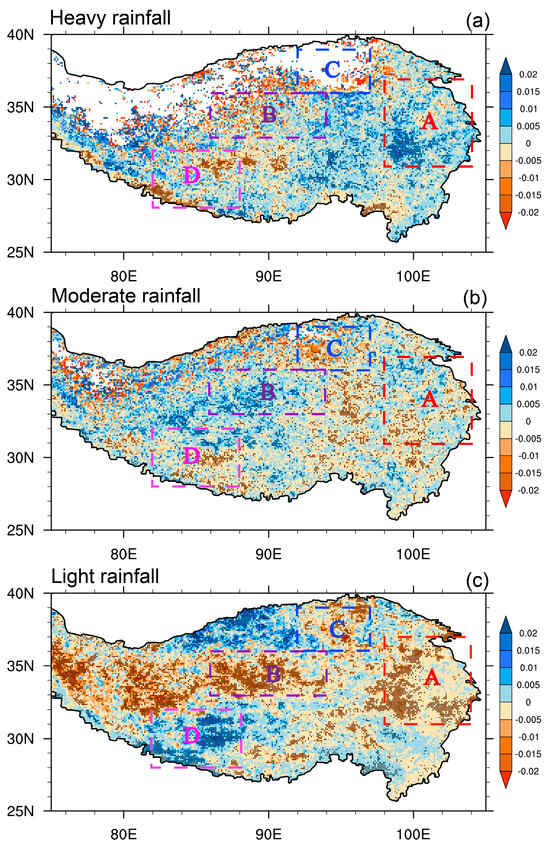
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of linear trends of percentage contribution of rainfall intensities to STR from 2000 to 2021: (a) heavy rainfall, (b) moderate rainfall, and (c) light rainfall. Dotted areas represent the significance levels above 90%.
Specifically, the increasing trend in STR in Region A is mainly attributed to heavy and moderate rainfall (Figure 2 and Table 1). The increasing proportion of heavy rainfall, coupled with decreasing moderate and light rainfall (Figure 5), highlights the paramount importance and stability of heavy rainfall in influencing the STR trend in region A. And in region B, the increasing trends in light and moderate rainfall make comparable contributions to the strengthened STR trend (Table 1). But it is worth noting that the steady rise in the proportion of moderate rainfall, coupled with a weakening trend in light rainfall in region B, underscores the growing prominence of moderate rainfall here (Figure 5b,c). Region C witnessed a robust increase in STR primarily due to light rainfall (Figure 2 and Table 1). However, the weakening proportion of light rainfall (Figure 5c) suggests a shift in dynamics. And this change might be linked to the increasing proportion of moderate rainfall in this region (Figure 5b). The situation is more complicated in region D. Similar to the heavy and moderate rainfall trends (Figure 2a,b), their proportions are decreasing in most parts in region D, especially where rainfall has substantially weakened. On the contrary, light rainfall, while exhibiting the weakest trend, exhibits a robust increase in proportion in recent years in region D (Figure 5c). This implies that the variation in STR in this region is gradually becoming reliant on changes in light rainfall.
3.3. Possible Physical Mechanisms
Using the JRA55 reanalysis, which demonstrates consistent STR trends over regions A, C, and D (Figure 1a and Figure S3d), we proceeded with further mechanism analysis. Figure 6 shows the trends in relevant large-scale circulations and various element fields. Evidently, the subtropical westerly jet north of the TP has significantly strengthened in response to recent climate change (Figure 6a). A direct comparison between the first (2000–2004) and last (2017–2021) five years of this period reveals an eastward extension and widening of the jet stream. A similar intensification is observed in potential height at 200 hPa along the northeastern edge of the South Asian High (Figure 6b), promoting upper-level divergence in the northeastern TP under the influence of this anomalous height center (Figure 6c).
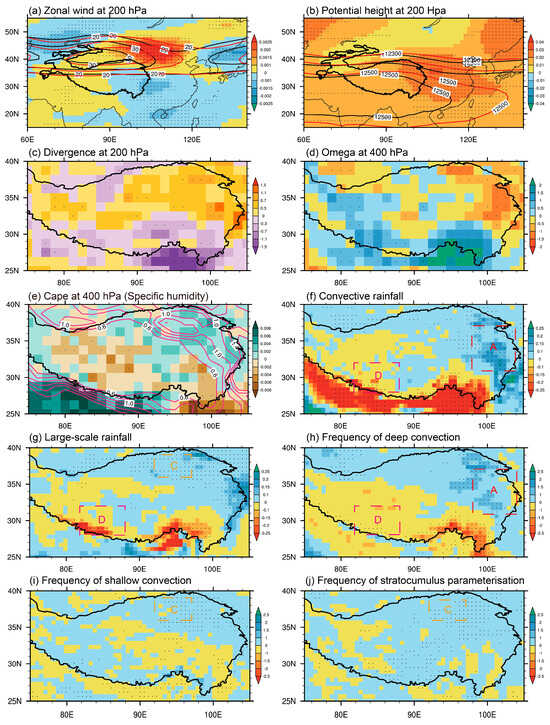
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of the linear trends in (a) zonal wind (shaded, m s−1 yr−1), (b) potential height (shaded, gpm yr−1), and (c) divergence (10–9 s−1 yr−1) at 200 hPa. The black contours in (a) and (b) represent the averaged zonal wind and potential height for the first 5 years from 2000 to 2004, while the red contours are the last 5 years from 2017 to 2021, respectively. Panels (d,e) show vertical velocity (10–5 Pa s−1 yr−1) and convective available potential energy (CAPE) (shaded, J kg–1 yr−1) at 400 hPa, and vertical integrated specific humidity (contours, 10–5 kg kg−1 yr−1) during 2000–2021, respectively. Trends in (f) convective rainfall (mm yr−1), (g) large-scale rainfall (mm yr−1), the frequency (% yr−1) of (h) deep convection and (i) shallow convection, and (j) stratocumulus parameterization during the period of 2000–2021 are also shown. The dotted areas represent significant values above the 90% confidence level.
Conversely, the southern TP, especially the southeastern TP, experiences easterly anomalies, contrary to the climatological status, which suppresses the upper-level divergence (Figure 6c). Consequently, the combined effects of the jet stream and South Asian High due to climate change lead to a strengthening of upper-level divergence in the north and a weakening in the south of the TP (Figure 6c). This divergence pattern fosters upward motion in the northern parts and downward motion in the southern parts. Notably, regions A and C exhibit a highly significant upward motion trend at 400 hPa (Figure 6d). Concurrently, moisture increasingly accumulates in the northeastern TP, and the convective available potential energy (CAPE) consistently rises in this area (Figure 6e). These conditions align well with the observed increasing rainfall trends in these regions.
Further analysis found that the upward motion in region A extends from the surface to nearly 100 hPa over the TP, while it only occurs below 300 hPa in region C, which indicates that deep convection and shallow convection are more likely to occur in these two regions, respectively. Indeed, in region A, heavy rainfall is the primary contributor to the STR trend, which may be mainly due to the significant enhancement in convective rainfall in recent years, particularly the increase in the frequency of deep convection (Figure 6f,h). In region C, the increasing light rainfall is mainly related to the enhancement in large-scale rainfall and the rise in the frequency of shallow convective and stratocumulus processes (Figure 6g,i,j). And this condition is almost opposite in region D. The decreasing rainfall trend here seems to be closely related to the weakening trend of convective and large-scale rainfall (Figure 6f,g).
4. Conclusions
In this study, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of the spatial trends in STR over the TP from 2000 to 2021, based on the station observations and satellite products. We find that the STR overall presents a pattern of drying in the south and wetting in the north. Notably, significant changes are concentrated in four key regions: the eastern TP (referred to as “region A”), Qiangtang Plateau (“region B”), Qaidam Basin (“region C”), and the northern foothills of the Himalayas (“region D”). Further analysis shows that the increasing STR trend in regions A and C is mainly driven by variations in heavy and light rainfall, respectively, and the enhanced STR in region B can be attributed to the combined contribution of moderate and light rainfall. Conversely, the decreasing STR trend in region D is largely due to the changes in heavy rainfall.
Specifically, heavy rainfall changes account for over 55.6% and 52.0% of the STR trend in regions A and D, respectively. In region B, moderate and light rainfall contributions are comparable, making up 37.3% and 44.8% of the STR trend, respectively. Furthermore, light rainfall, as the dominant rainfall intensity in region C, can explain 71.2% of the STR trend. Obviously, the variations in the different rainfall intensities largely shape the spatial heterogeneity in the STR trend. Moreover, our analysis reveals dynamic shifts in the contributions of these rainfall intensities to STR magnitude within each year over these four key regions, showcasing evolving patterns such as increased heavy rainfall contributions in region A, augmented moderate rainfall but decreased light rainfall contributions in region B, reduced light rainfall but enhanced moderate rainfall contributions in region C, and more light rainfall in region D.
In response to the recent climate change, the subtropical westerly jet north of the TP and the northeast edge of the South Asian High become significantly strengthened, which further enhance (reduce) the upper-level divergence, resulting in the upward (downward) movement tendency in the north (south) parts of the TP. Consequently, more instances of deep convection in region A and shallow convection in region C likely contribute to the increasing trends in heavy rainfall and light rainfall, respectively.
Rainfall intensity trends across different TP regions vary significantly. Apart from large-scale circulation, these differences are intricately linked to various factors, including the activity of intraseasonal oscillation [45], the development of the small- and medium-scale systems [27], and atmospheric aerosols [46]. A more in-depth mechanism analysis needs to be further studied in the future.
The simulations of the trends in STR and different levels of rainfall intensities in the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) models did not meet expectations. Six models, evaluated for the period of 2000–2021, failed to reproduce the observed spatial trends in STR over the TP, even displaying patterns contrary to both observations and GPM data (Figure S5). Moreover, the models struggled to accurately simulate different levels of rainfall intensities (Figures S6–S8). And the possible reasons for the serious rainfall deviation over the TP region in climate models may be attributed to the inadequate representation of the underlying surface and cloud physical processes [47]. Given the complex terrain of the TP, these disparities in CMIP6 models highlight the pressing need for improved convection and large-scale rainfall parameterization, as well as enhancements in model resolution, to improve their accuracy.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs15235587/s1: Figure S1. Terrain height (units: m) over the Tibetan Plateau (TP). Figure S2. Annual cycle of the total rainfall (mm) at 293 meteorological stations over the Tibetan Plateau (TP) during the period of 2000–2021. Figure S3. Spatial distributions of the trends in summer total rainfall (STR, mm yr−1) over the TP during the period of 2000–2021 based on (a) CN05.1, (b) GPCP, (c) ERA5, and (d) JRA-55. The dotted areas represent significance above the 90% level estimated through the Student’s t-test. Figure S4. Spatial distributions of the trends in frequency (days yr−1) of (a) STR, (b) heavy rainfall, (c) moderate rainfall, and (d) light rainfall during the period of 2000–2021. The dotted areas represent significance above the 90% level estimated through the Student’s t-test. Figure S5. Spatial distributions of the STR trends (mm yr−1) over the TP during the period of 2000–2021 in six CMIP6 models. The dotted areas represent significance above the 90% level estimated through Student’s t-test. Figure S6. Same as Figure S5, but for heavy rainfall (mm yr−1). Figure S7. Same as Figure S5, but for moderate rainfall (mm yr−1). Figure S8. Same as Figure S5, but for light rainfall (mm yr−1).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Y.; formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, M.W.; writing—review and editing, J.W. and B.L.; visualization, J.Y., Z.Z. and S.Z.; supervision, X.Y. and J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42030611), the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research (STEP) Program (2019QZKK0105), Fengyun Satellite Application Pilot Program (2022) (FY-APP-2022.0102),the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (grant no. BK20221449), the Open Grants of the State Key Laboratory of Severe Weather (2023LASW-B06, 2023LASW-B14), and the open project of Key Laboratory of Meteorological Disaster (KLME), Ministry of Education & Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters (CIC-FEMD), Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology (grant no. KLME202203).
Data Availability Statement
Observational daily rainfall data from the China Meteorological Administration (CMA) are available at http://data.cma.cn/en/?r=data/detail&dataCode=A.0012.0001 accessed on 15 June 2022. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) is available at https://pmm.nasa.gov/GPM accessed on 12 December 2022. Pentad Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) is available at https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/metadata/landing-page/bin/iso?id=gov.noaa.ncdc:C00933 accessed on 19 March 2022. Daily Japanese 55-year Reanalysis can be accessed at https://data.diasjp.net/dl/storages/filelist/dataset:204 accessed on 26 February 2023 (registration is required) and ERA5 hourly data on single levels are provided at https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-single-levels?tab=form accessed on 20 February 2023.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the China Meteorological Administration for access to the observational daily rainfall data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Flohn, H. 1957 Large-scale aspects of the summer monsoon in South and East Asia. J. Meteoroligical Soc. Jpn. 1957, 35, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohn, H. Recent investigations on the mechanism of the “summer monsoon” of southern and eastern Asia. Monsoons World N Delhi Ed Hindu Union Press 1960, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.Y.; Ding, Y.H. Observational evidence of the influence of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau on the occurrence of heavy rain and severe convective storms in China. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1981, 62, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.B.; Yanai, M. The large-scale circulation and heat sources over Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas during the early summer of 1979. Part I: Precipitation and kinematic analyses. Mon. Weather Rev. 1983, 111, 922–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.X.; Zhang, Y.S. Tibetan Plateau Forcing and the Timing of the Monsoon Onset over South Asia and the South China Sea. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.X.; Zhou, X.J.; Xu, X.D.; Huang, J.P.; Duan, A.M.; Yang, S.; Hu, W.T.; Ma, Y.M.; Liu, Y.M.; Bian, J.C.; et al. An integrated research plan for the Tibetan Plateau land-air coupled system and its impacts on the global climate. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2023, 104, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yu, G.; Xie, G. Tibetan Plateau serves as a water tower. IEEE Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. 2005, 5, 3120–3123. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.X.; Gong, T.L.; Li, J.Y. Decadal trend of climate in the Tibetan Plateau-Regional temperature and precipitation. Hydrol. Process 2008, 22, 3056–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; Pu, J.C.; Shen, Y.P.; Lu, A.X. Recent glacial retreat in high Asia in China and its impact on water resource in northwest China. Sci. China Ser. A D 2004, 47, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.C. Climatic characteristics of heavy rainfall in the northeast Tibetan Plateau. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2006, 17, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.D.; Zhao, T.L.; Lu, C.G.; Shi, X.H. Characteristics of the water cycle in the atmosphere over the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2014, 72, 1079–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J.; Pang, G.J.; Yang, M.X. Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades: A review based on observations and simulations. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 1116–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, M.; Li, C.F.; Song, Z.S. Seasonal heating of the Tibetan Plateau and its effects on the evolution of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 1992, 70, 319–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.M.; Wu, G.X. Role of the Tibetan Plateau thermal forcing in the summer climate patterns over subtropical Asia. Clim. Dyn. 2005, 24, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.Q.; Guo, P.W.; Xue, R.K.; Min, Y.Q. Relationship between Summer Latent Heat in the Eastern Qinghai- Tibet Plateau and Intensity of Western North Pacific Typhoon. J. Meteorol. Res. Appl. 2010, 31, 16–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duan, A.M.; Wu, G.X.; Liu, Y.M.; Ma, Y.M.; Zhao, P. Weather and climate effects of the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Yang, S.; Li, Z.; He, B.; He, S.; Wang, Z. Possible effect of the Tibetan Plateau on the “upstream” climate over West Asia, North Africa, South Europe and the North Atlantic. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.R.; Wang, J.; Duan, A.M.; Yang, J. Quasi-biweekly impact of the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau on summer rainfall in Eastern China. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 4489–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, M. Global land moisture trends: Drier in dry and wetter in wet over land. Sci. Rep. 2016, 5, 18018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Chen, B.D. Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 1729–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.W.; Zhang, R.H. Decadal variations of temperature and geopotential height over the Tibetan Plateau and their relations with Tibetan Ozone depletion. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L18705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, K.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Lu, H. Why has the inner Tibetan Plateau become wetter since the mid-1990s? J. Clim. 2020, 33, 8507–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, H.; Qin, J.; Lin, C.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: A review. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 112, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Luo, W.; Chen, W.; Zheng, G. A robust but variable lake expansion on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 1306–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Wu, G. Persistent weakening trend in the spring sensible heat source over the Tibetan Plateau and its impact on the Asian summer monsoon. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 5671–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.D.; Liu, C.L.; Lin, H. Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation maxima during 1960–2005 in the Yangtze River basin and possible association with large-scale circulation. J. Hydrol. 2008, 353, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Wen, M.; Lv, J. Regionally different precipitation trends over the Tibetan Plateau in the warming context: A perspective of the Tibetan Plateau vortices. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, S.; Luo, H.L.; Li, J.D. Drying tendency over the southern slope of the Tibetan Plateau in recent decades: Role of a CGT-like atmospheric change. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 59, 2801–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Wang, B.; Yang, K.; Xie, Z.; Lu, H.; He, J. Mechanisms of the decadal variability of monsoon rainfall in the southern Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 16, 014011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, A.K.; Fay, P.A.; Blair, J.M.; Collins, S.L.; Smith, M.D.; Carlisle, J.D.; Harper, C.W.; Danner, B.T.; Lett, M.S.; McCarron, J.K. Rainfall Variability, Carbon Cycling and Plant Species Diversity in a Mesic Grassland. Science 2002, 298, 2202–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Shi, H. Effects of Precipitation Intensity and Temperature on NDVI-Based Grass Change over Northern China during the Period from 1982 to 2011. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10164–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Cai, Q.; Zeng, N.; Lu, X.; Yang, R.; Jiang, F.; Wang, H.; Ju, W. Considerable uncertainties in simulating land carbon sinks induced by different precipitation products. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2021JG006524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, C. Geographic patterns of extreme climate changes in China during 1951–1997. Clim. Environ. Res. 2000, 5, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, Q.; Gong, D.; Fan, J.; Ruby, L.L.; Ralf, B.; Chen, D.; Wang, W. Heavy pollution suppresses light rain in China: Observations and modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, 4427–4433. [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Zhang, X.; Adnan, M.; Badi, W.; Dereczynski, C.; Di Luca, A.; Ghosh, S.; Iskandar, I.; Kossin, J.; Lewis, S.; et al. Weather and Climate Extreme Events in a Changing Climate. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Pe, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1513–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Westra, S.; Alexander, L.V.; Zwiers, F.W. Global Increasing Trends in Annual Maximum Daily Precipitation. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 3904–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.R.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.L.; Duan, A.M.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhou, S.W.; Guo, D.; Wang, H.M.; Ju, W.M. Recent recovery of the boreal spring sensible heating over the Tibetan Plateau will continue in CMIP6 future projections. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Shi, X.D.; Li, D.L. Some New Changes of the Regional Climate on the Tibetan Plateau Since 2000. Adv. Earth Sci. 2021, 36, 785–796. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.-L.; Joyce, R.J.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Stocker, E.F.; Tan, J. Integrated multi-satellite retrievals for the global precipitation measurement (GPM) mission (IMERG). Adv. Glob. Chang. Res. 2020, 1, 343–353. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.Q.; Yao, X.P.; Du, J.; Zhou, Z.B. Refined evaluation of satellite precipitation products against rain gauge observations along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway. J. Meteorol. Res. 2022, 36, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.J. A gridded daily observation dataset over China region and comparison with the other datasets. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 1102–1111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Arkin, P.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Gruber, A.; Janowiak, J.; McNab, A.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U. The Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) combined precipitation dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Ota, Y.; Harada, Y.; Ebita, A.; Moriya, M.; Onoda, H.; Onogi, K.; Kamahori, H.; Kobayashi, C.; Endo, H.; et al. The JRA-55 reanalysis: General specifications and basic characteristics. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 93, 5–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Royal Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jiang, G.; Ren, X.; Yang, X.Q. Role of intraseasonal oscillation in the persistent extreme precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin during June 1998. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 10453–10469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.B.; Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, R.R.Y.; Zhu, Q.Z.; Tan, Z.Y.; Luo, R. Role of anthropogenic aerosols in affecting different-grade precipitation over eastern China: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, K.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Prein, A. Added value of kilometer-scale modeling over the third pole region: A CORDEX-CPTP pilot study. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).