Assessing Rice Sheath Blight Disease Habitat Suitability at a Regional Scale through Multisource Data Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
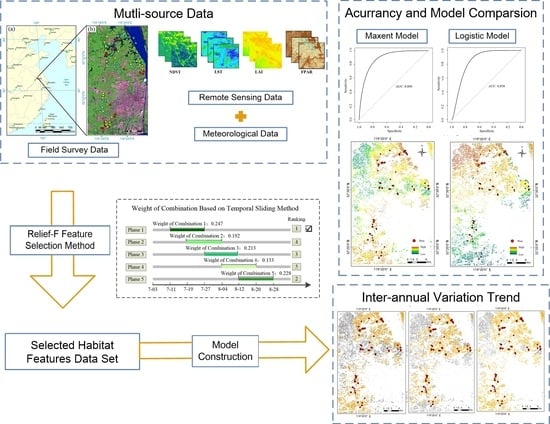
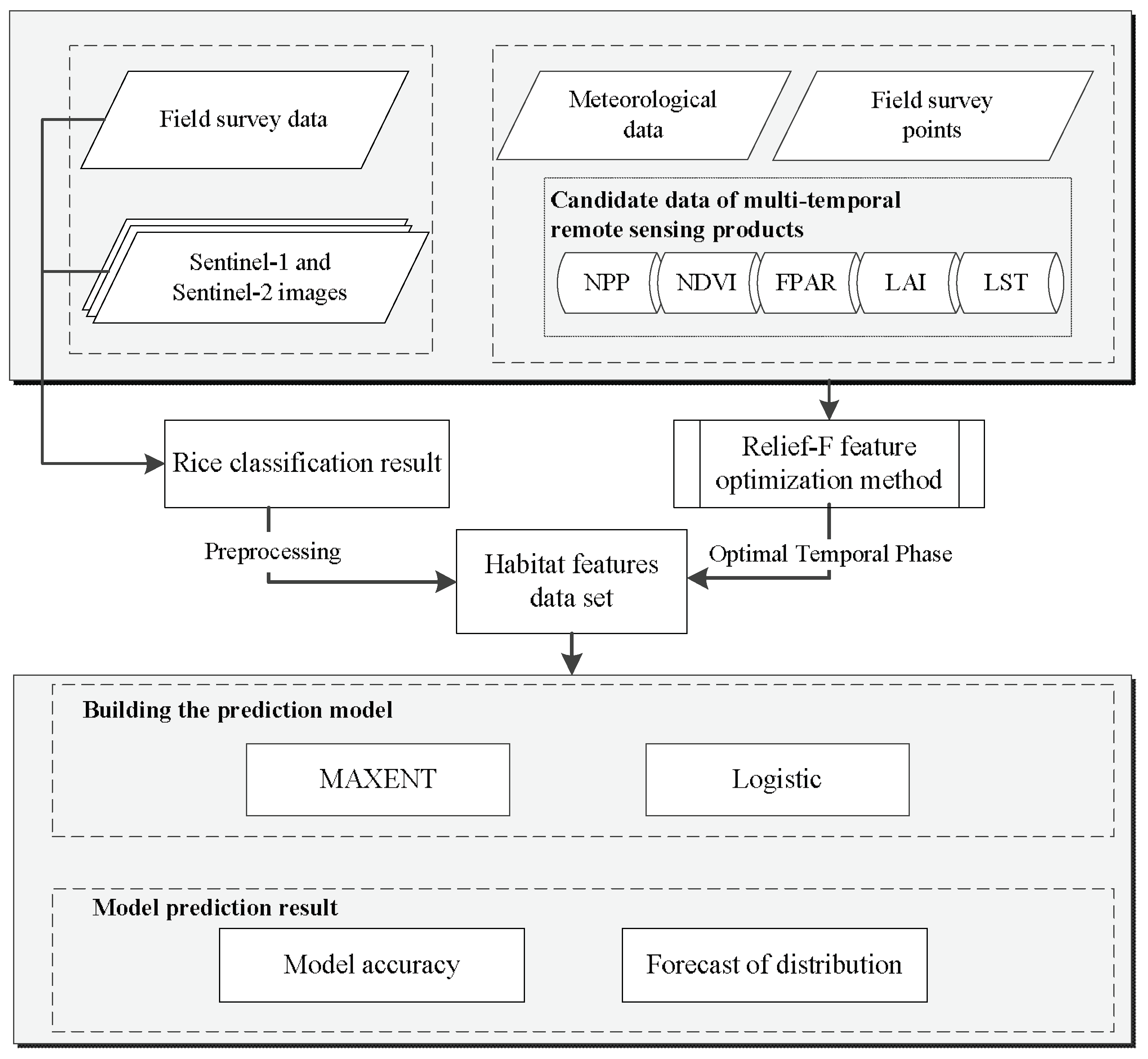
- To indicate the habitat characteristics of RSB, different types of satellite remote sensing data and meteorological data are used and analyzed. The Relief-F algorithm is adopted for feature selection, and a temporal optimization method is proposed.
- (2)
- Based on the optimized habitat features at appropriate stages, the habitat suitability assessment model for RSB is established at the regional level. The Maxent and logistic regression models are used and compared.
- (3)
- With the aid of the field survey data on disease occurrence, the accuracy and effectiveness of the established models are assessed. In addition, the spatial distribution patterns of the predicted risk areas in different years (2018–2020) are analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
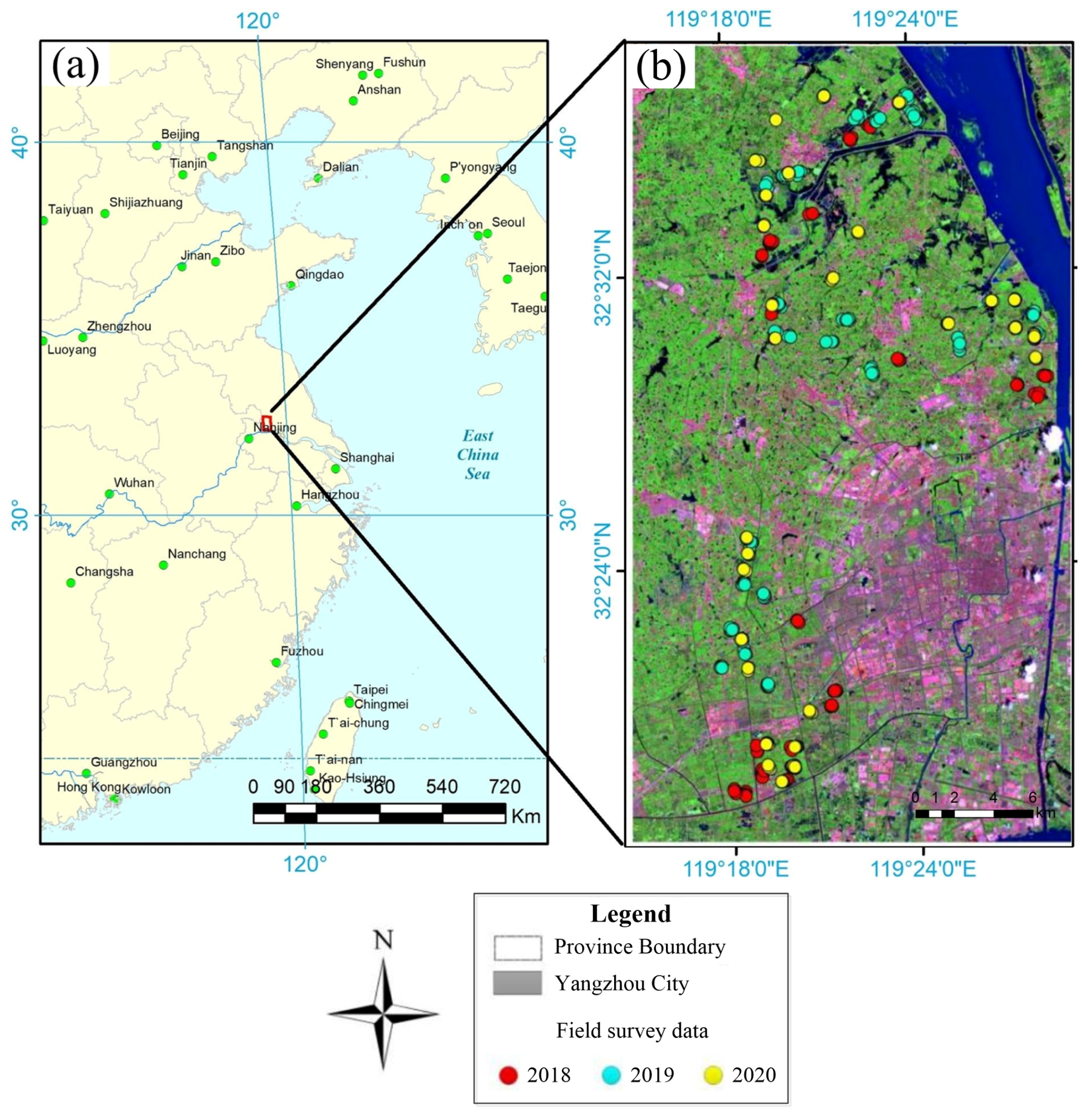
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Survey Data
2.2.1. Meteorological and Field Survey Data
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Data
2.3. Methods
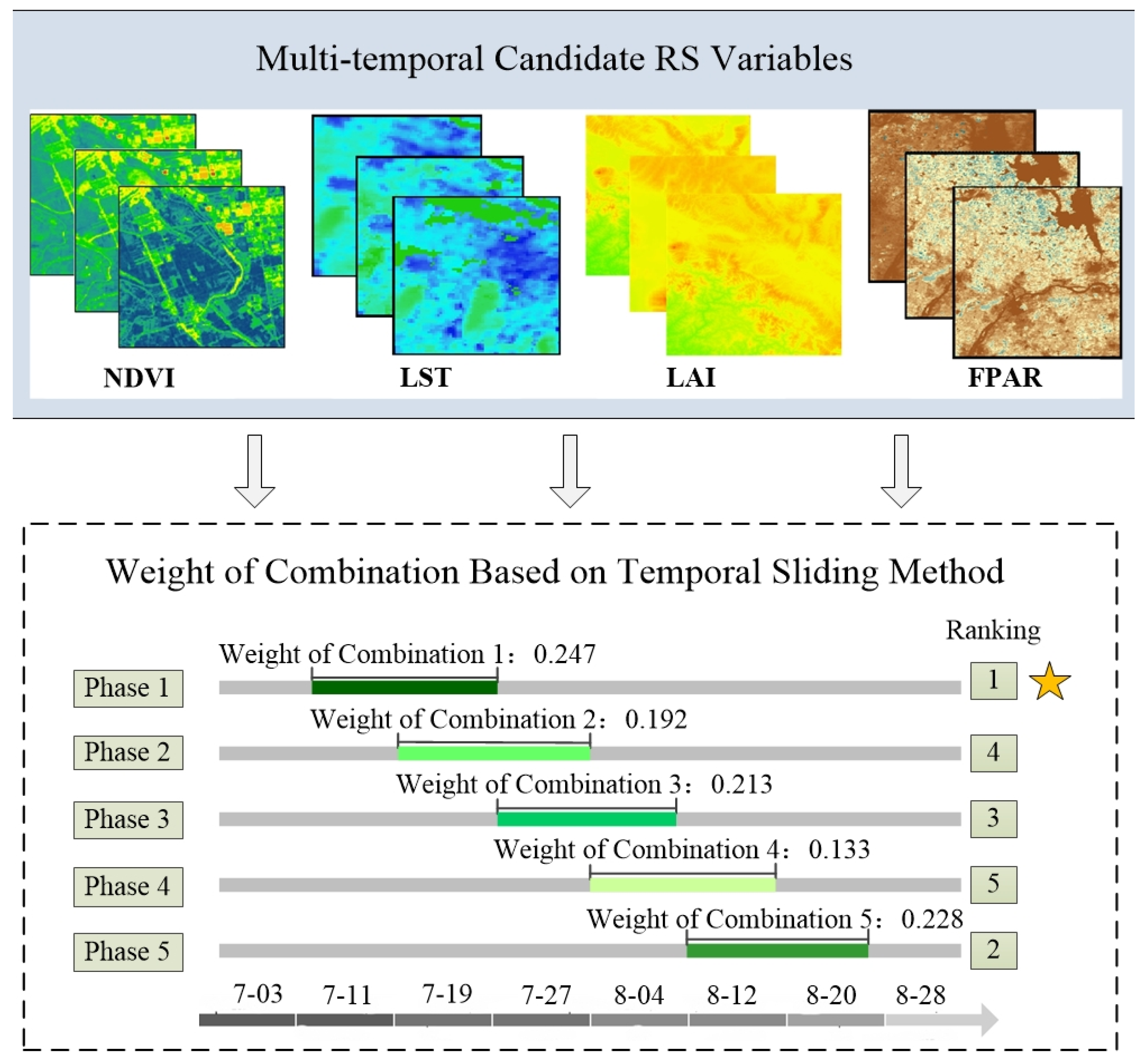
2.3.1. Selection of Remote Sensing Habitat Features
2.3.2. Extraction of Rice-Planting Area
2.3.3. RSB Habitat Suitability Modeling
2.3.4. Validation of the Disease Habitat Suitability Assessment Models
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of RSB Habitat Features
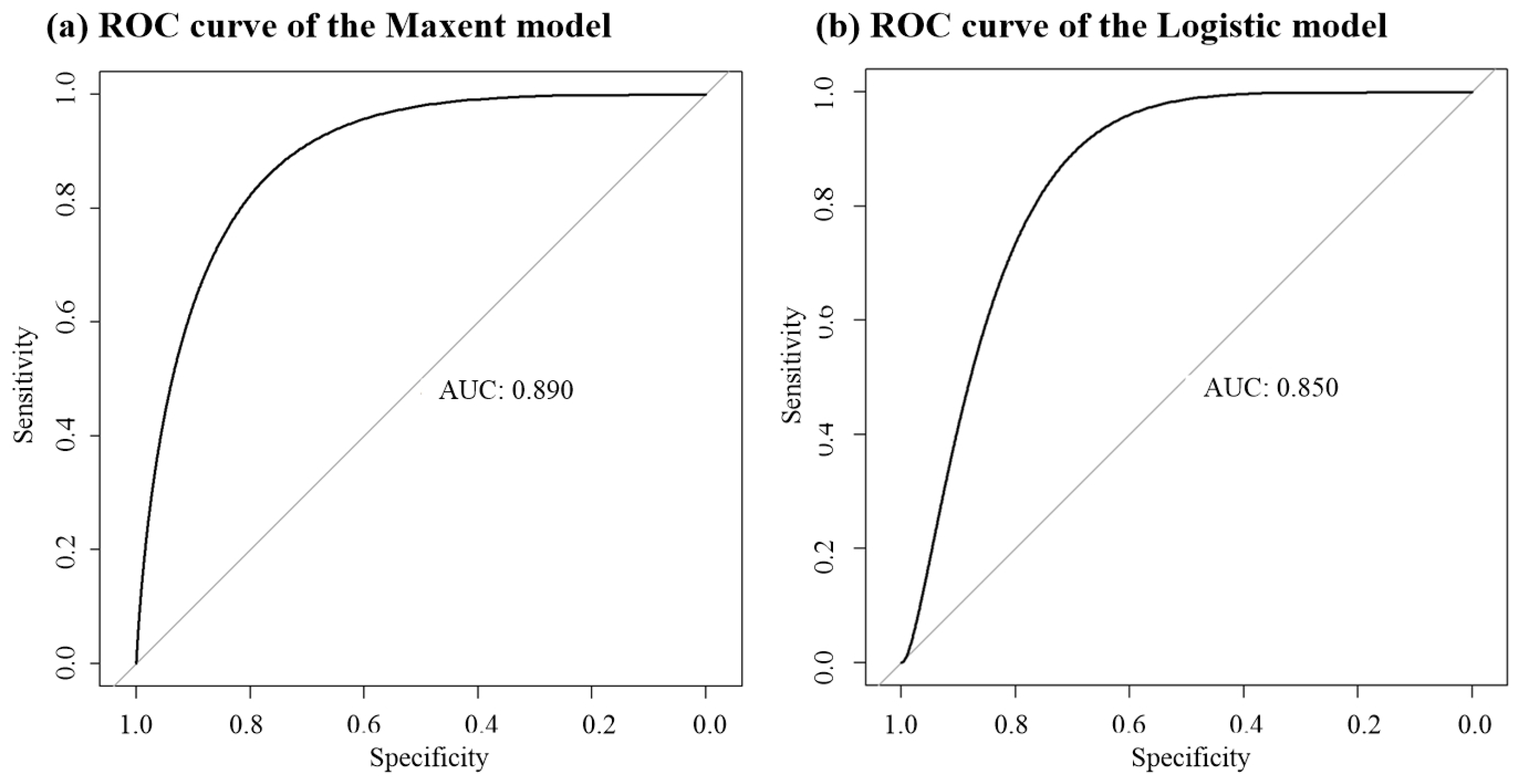
3.2. Evaluation of the Habitat Suitability Model for RSB
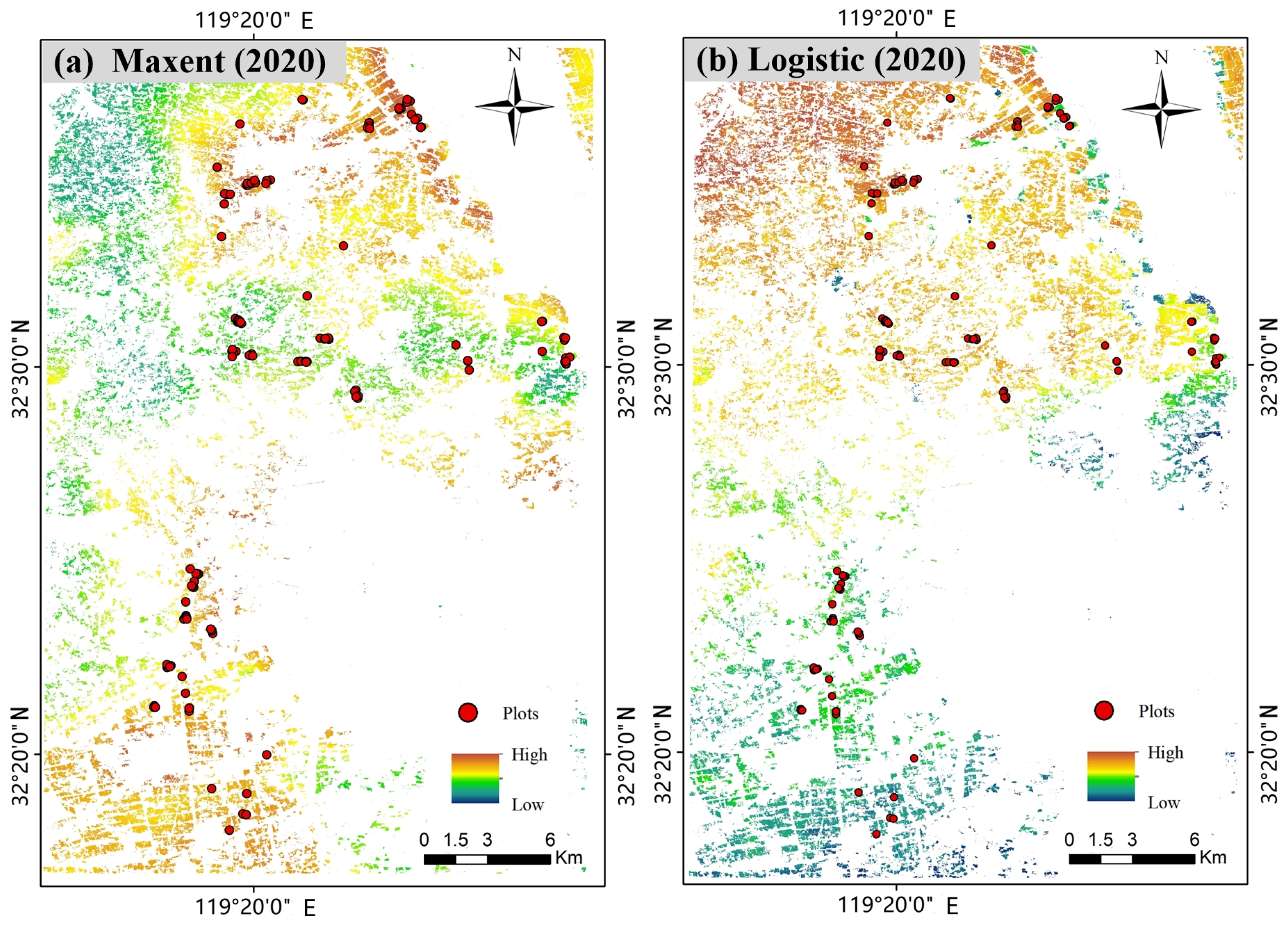
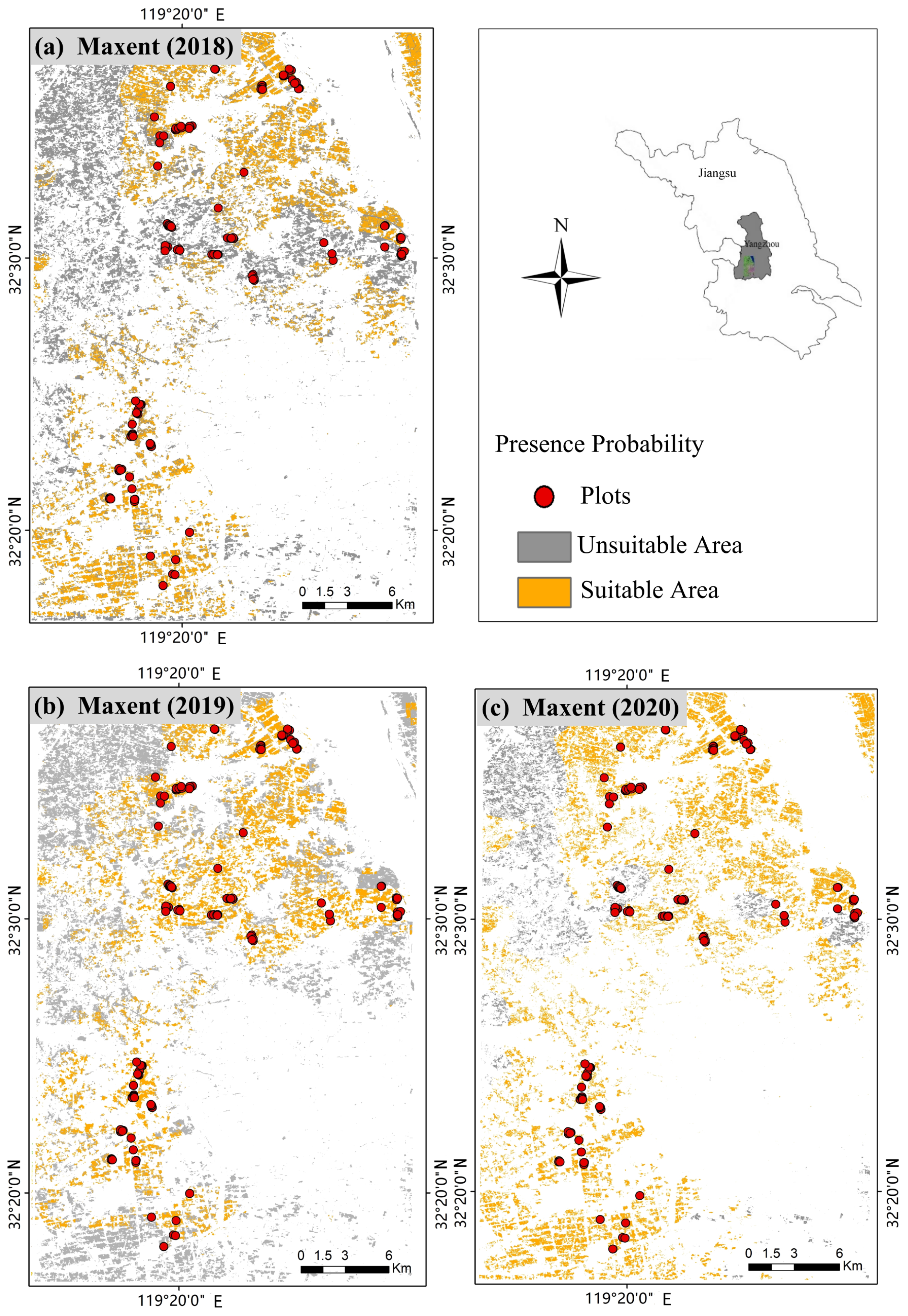
3.3. Distribution Pattern of the RSB Habitat Suitability Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The habitat features of RSB can be characterized by multisource remote sensing and meteorological data. The optimal habitat features with appropriate time windows were obtained according to the Relief-F algorithm.
- (2)
- The best habitat suitability assessment model for RSB was established using the Maxent algorithm, with an AUC value of 0.879 and a TSS value of 0.73. The heterogeneity of habitat suitability within a region can be reflected from the output of the model, which indicates the potential distribution of RSB in the region.
- (3)
- The established disease habitat suitability assessment model is able to generate reasonable predictions that are highly consistent with the actual spatial and temporal variation trends of RSB disease according to the field investigation records of the disease. Such information is essential for the forecasting, control, and management of RSB disease.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, K.H.; Cho, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, W. Predicting potential epidemics of rice leaf blast and sheath blight in South Korea under the RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 climate change scenarios using a rice disease epidemiology model, EPIRICE. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 203, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, S.; Castilla, N.P.; Willocquet, L. Analysis of the spatiotemporal structure of rice sheath blight epidemics in a farmer’s field. Plant Pathol. 2001, 50, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, N.P.; Leaño, R.M.; Elazhour, F.A. Effects of Plant Contact, Inoculation Pattern, Leaf Wetness Regime, and Nitrogen Supply on Inoculum Efficiency in Rice Sheath Blight. J. Phytopathol. 1996, 144, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellareddygari, S.K.R.; Reddy, M.S.; Kloepper, J.W. Rice Sheath Blight: A Review of Disease and Pathogen Management Approaches. J. Plant Pathol. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Su, P.; Liao, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H. Influencing factors on rice sheath blight epidemics in integrated rice-duck system. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Shen, D.; Tian, Y.Y.; Huang, W.J.; Yang, X.D. Research progress on habitat suitability assessment of crop diseases and pests by multi-source remote sensing information. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2023, 31, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.J.; Li, X.F.; Wu, S.; Jiang, L.Q. Prediction of potential distribution of soybean in the frigid region in China with Maxent modeling. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 72, 101834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, F.A.; Philipe, G.C.S.; Ricardo, S.S.; Paulo, A.S.J.; Marcelo, C.P.; Jonathan, O.O.; Mamoudou, S.; Sunday, E.; Christian, B. A machine learning algorithm-based approach (Maxent) for predicting invasive potential of Trioza erytreae on a global scale. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 71, 101792. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.Z.; Wang, W.G.; Ding, Y.M.; Liu, G.D.; Xing, W.Q.; Cao, X.C.; Chen, D. Assessment of climate change impact on the water footprint in rice production: Historical simulation and future projections at two representative rice cropping sites of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbogbo, A.Y.; Kouakou, B.K.; Dabo-Niang, S.; Zoueu, J.T. Predictive model for airborne insect abundance intercepted by a continuous wave Scheimpflug lidar in relation to meteorological parameters. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 68, 101528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.Q.; Huang, W.J.; Jing, Y.S.; Dong, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Nie, C.W.; Tang, C.C.; Zhao, J.L.; Huang, L.S. Wheat powdery mildew remote sensing monitoring based on the AdaBoost model and mRMR algorithm. J. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.C.; Liu, P.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.X.; Huang, W.J.; Wu, K.H. Analysis of spectral resolution impact in the inversion of plant physicochemical parameters based on continuous wavelet analysis. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2018, 37, 753–760. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, M.S.M.; Bavia, M.E.; Fonseca, E.O.L.; Cova, B.O.; Silva, M.M.N.; Carneiro, D.D.M.T.; Cardim, L.L.; Malone, J.B. Ecological niche models for sand fly species and predicted distribution of Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera: Psychodidae) and visceral leishmaniasis in Bahia state. Env. Monit Assess. 2019, 191 (Suppl. S2), 331. [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich, A.; Roilo, S.; Sonnenschein, R.; Cerrato, C.; Ewald, M.; Viterbi, R.; Cord, A.F. Modelling Distributions of Rove Beetles in Mountainous Areas Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancer, E.; Xue, B.; Zhang, M.J. Differential evolution for filter feature selection based on information theory and feature ranking. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2018, 140, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanowicz, R.J.; Meeker, M.; La Cava, W.; Olson, R.S.; Moore, J.H. Relief-based feature selection: Introduction and review. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 85, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.J.; Shi, Y.; Dong, Y.Y.; Ye, H.C.; Wu, M.Q.; Cui, B.; Liu, L.Y. Progress and prospects of crop diseases and pests monitoring by remote sensing. Smart Argric. 2019, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Solís-Montero, L.; Vega-Polanco, M.; Vázquez-Sánchez, M.; Suárez-Mota, M.E. Ecological niche modeling of interactions in a buzz-pollinated invasive weed. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 39, e02279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Store, R.; Jokimaki, J.A. GIS-based multi-scale approach to habitat suitability modeling. Ecol. Model. 2003, 169, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; Bao, Y.X.; Lu, M.H.; Liu, W.; Xie, X.Z.; Wang, C.Z.; Liu, W.C. A comparison of models for the short-term prediction of rice stripe virus disease and its association with biological and meteorological factors. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobek-Swant, S.; Kluza, D.A.; Cuddington, K.; Lyons, D.B. Potential distribution of emerald ash borer: What can we learn from ecological niche models using Maxent and GARP? For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 281, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.M.; Kumar, S.; Brown, C.S.; Stohlgren, T.J.; Bromberg, J. Field validation of an invasive species Maxent model. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 36, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.W.; Huang, J.F.; Guo, R.F.; Li, X.X.; Sun, W.B.; Wang, X.Z. Spatio-temporal reconstruction of air temperature maps and their application to estimate rice growing season heat accumulation using multi-temporal MODIS data. J. Zhejiang Univ. 2013, 14, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Mazumdar, P.; Harikrishna, J.A.; Babu, S. Sheath blight of rice: A review and identification of priorities for future research. Planta 2019, 250, 1387–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.Z.; Ding, Y.X.; Wen, Z.M.; Chen, Y.M.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J.Y. Spatiotemporal change and trend analysis of potential evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Sun, J.Q.; Shi, X.J.; Liu, D.L.; Sun, B.Y.; Deng, Y.J.; Zhang, D.L.; Liu, S.M. Evaluation of climate factors affecting the quality of red huajiao (Zanthoxylum bungeanum maxim.) based on UPLC-MS/MS and Maxent model. Food Chem. 2022, 16, 100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Roujean, J.L.; Cao, B.; Mallick, K.; Boulet, G.; Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Du, Y.; Liu, Q. Correction for LST directionality impact on the estimation of surface upwelling longwave radiation over vegetated surfaces at the satellite scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.B.; Ma, B.; Wang, C.G.; Li, Z.B. Identifying key landscape pattern indices influencing the NPP: A case study of the upper and middle reaches of the Yellow River. Ecol. Model. 2023, 484, 110457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machwitz, M.; Gessner, U.; Conrad, C.; Falk, U.; Richters, J.; Dech, S. Modelling the Gross Primary Productivity of West Africa with the Regional Biomass Model RBM+, using optimized 250m MODIS FPAR and fractional vegetation cover information. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 43, 177–194. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, G.; Palai, G.; Tozzini, L.; D’Onofrio, C.; Gucci, R. The role of LAI and leaf chlorophyll on NDVI estimated by UAV in grapevine canopies. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 322, 112398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, X.X.; Li, H.Z.; Zhou, X.J. A Novel Operational Rice Mapping Method Based on Multi-Source Satellite Images and Object-Oriented Classification. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Wei, J.; Lin, K.; Lu, L.; Ding, X.; Ye, H.; Huang, W.; Wang, N. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Grassland Grasshopper Habitat Suitability and Its Main Influencing Factors. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Kearney, M.; Phillips, S. The art of modelling range-shifting species. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariya, S.; Robert, P. Estimating optimal complexity for ecological niche models: A jackknife approach for species with small sample sizes. Ecol. Model. 2013, 269, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Allouche, O.; Tsoar, A.; Kadmon, R. Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: Prevalence, kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, J.M.; Jiménez-valverde, A.; Real, R. AUC: A Misleading Measure of the Performance of Predictive Distribution Models. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2008, 17, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, S.; Andres, F.; Timothy, G.G.; Adison, A.; Valeska, Y. A study on the effects of unbalanced data when fitting logistic regression models in ecology. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 502–508. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Q.J.; Zeng, A.C.; Su, Z.W.; Guo, F.T. Driving factors of forest fire in Zhejiang province based on Logistic regression model. J. Northwest A&F Univ. 2020, 48, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, D.; Singh, V. An Efficient Hybrid Feature Selection model for Dimensionality Reduction. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.F.; Meng, J.H.; Li, Q.Z. Review of overseas crop monitoring systems with remote sensing. Adv. Earth Sci. 2010, 25, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar]

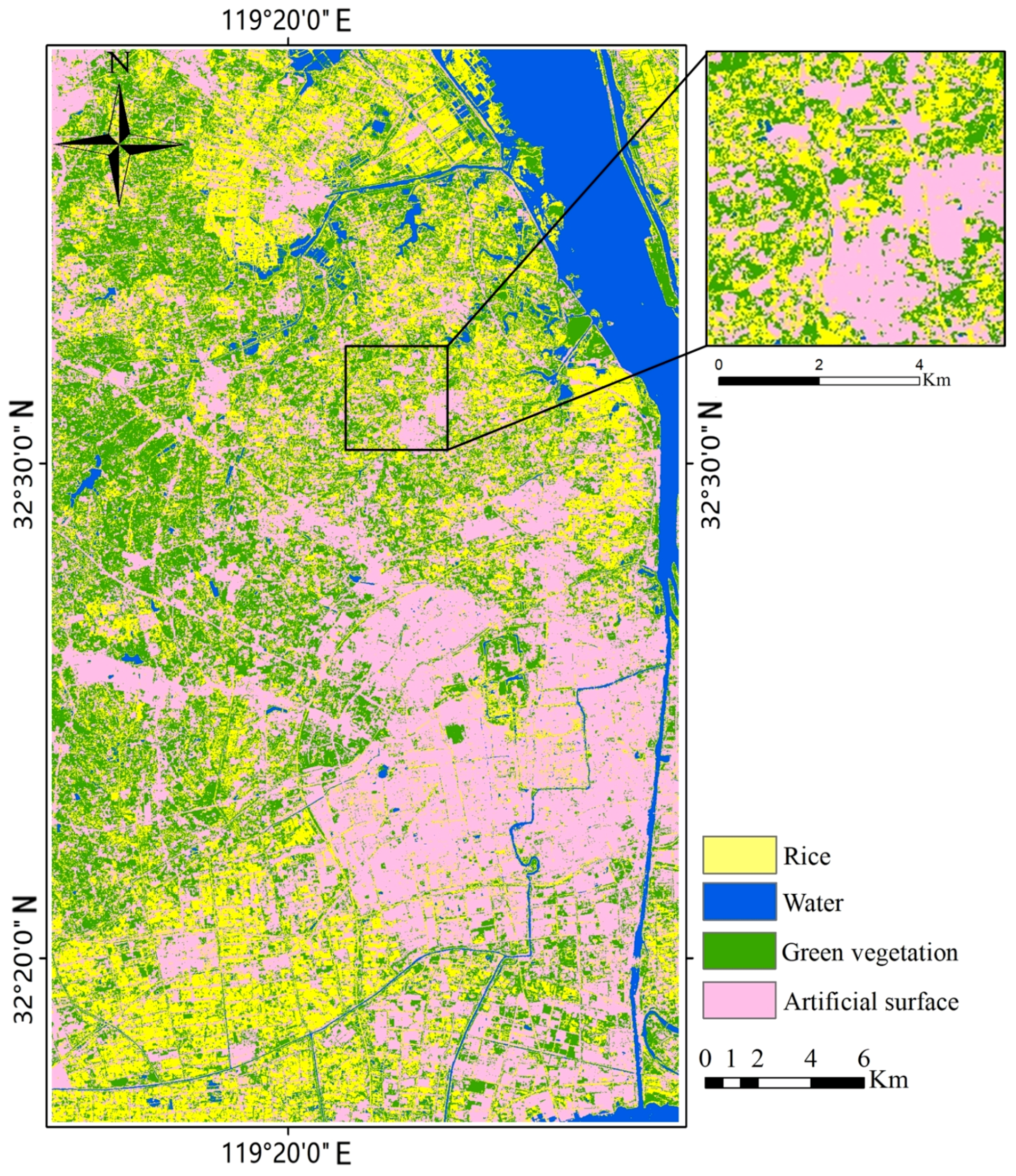
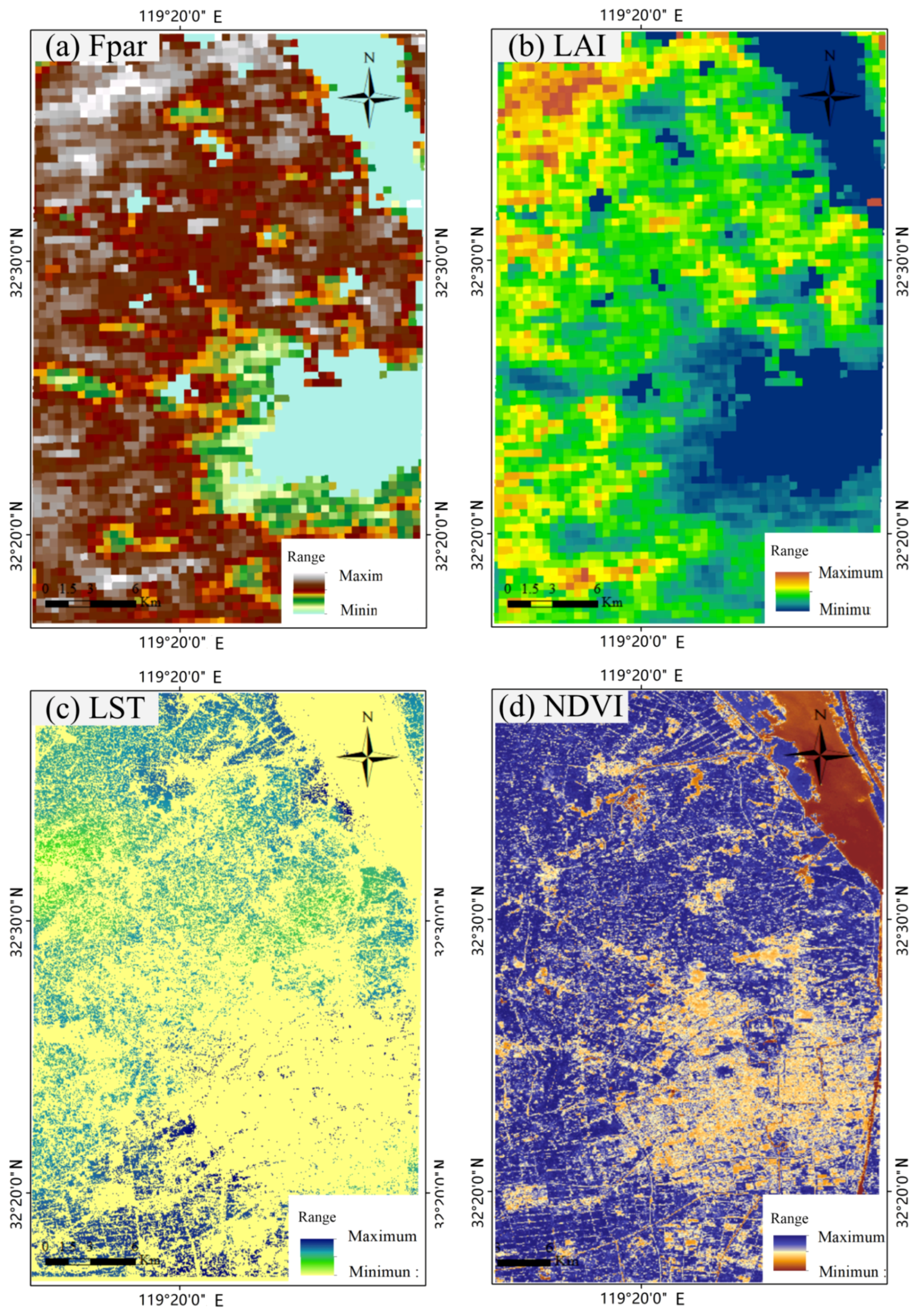
| Habitat Variable | Temporal Quantity | Data Source | Temporal Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf Area Index (LAI) | 12 (June–August) | MOD15A2 | 8 days |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | 6 (June–August) | MOD13Q1 | 16 days |
| Net Primary Productivity (NPP) | 1 | MOD15A2 | 1 year |
| Fraction of Photosynthetically Active Radiation (Fpar) | 12 | MOD15A2 | 8 days |
| Monthly Average Temperature | 3 (June–August) | The National Meteorological Administration of China | 1 month |
| Monthly Precipitation | 3 (June–August) | The National Meteorological Administration of China | 1 month |
| The Coldest Month Temperature | 1 | The National Meteorological Administration of China | 1 month |
| Land Surface Temperature (LST) | 8 (July–August) | MOD11A2/MYD11A2 | 8 days |
| Habitat Feature | Temporal Phase | Temporal Combination |
|---|---|---|
| LAI; FPAR | 0609, 0617, 0625 | C1 |
| 0617, 0625, 0703 | C2 | |
| 0625, 0703, 0711 | C3 | |
| 0703, 0711, 0719 | C4 | |
| 0711, 0719, 0727 | C5 | |
| 0719, 0727, 0804 | C6 | |
| 0727, 0804, 0812 | C7 | |
| 0804, 0812, 0820 | C8 | |
| 0812, 0820, 0828 | C9 | |
| NDVI | 0609, 0625 | C1 |
| 0625, 0711 | C2 | |
| 0711, 0727 | C3 | |
| 0727, 0812 | C4 | |
| 0812, 0828 | C5 | |
| LST | 0711, 0719, 0727 | C1 |
| 0719, 0727, 0804 | C2 | |
| 0727, 0804, 0812 | C3 | |
| 0804, 0812, 0820 | C4 | |
| 0812, 0820, 0828 | C5 |
| Years | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | OA | TSS | AUC | OA | TSS | AUC | OA | TSS | |
| Maxent | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.60 | 0.94 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.76 |
| Logistic | 0.70 | 0.77 | 0.64 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.59 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Tian, Y.; Qiu, H.; Zhou, X.; Ma, H.; Yuan, L. Assessing Rice Sheath Blight Disease Habitat Suitability at a Regional Scale through Multisource Data Analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235530
Zhang J, Li H, Tian Y, Qiu H, Zhou X, Ma H, Yuan L. Assessing Rice Sheath Blight Disease Habitat Suitability at a Regional Scale through Multisource Data Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(23):5530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235530
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingcheng, Huizi Li, Yangyang Tian, Hanxiao Qiu, Xuehe Zhou, Huiqin Ma, and Lin Yuan. 2023. "Assessing Rice Sheath Blight Disease Habitat Suitability at a Regional Scale through Multisource Data Analysis" Remote Sensing 15, no. 23: 5530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235530
APA StyleZhang, J., Li, H., Tian, Y., Qiu, H., Zhou, X., Ma, H., & Yuan, L. (2023). Assessing Rice Sheath Blight Disease Habitat Suitability at a Regional Scale through Multisource Data Analysis. Remote Sensing, 15(23), 5530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235530