FuF-Det: An Early Forest Fire Detection Method under Fog
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Smoke Detection
1.2. Fire Point Detection
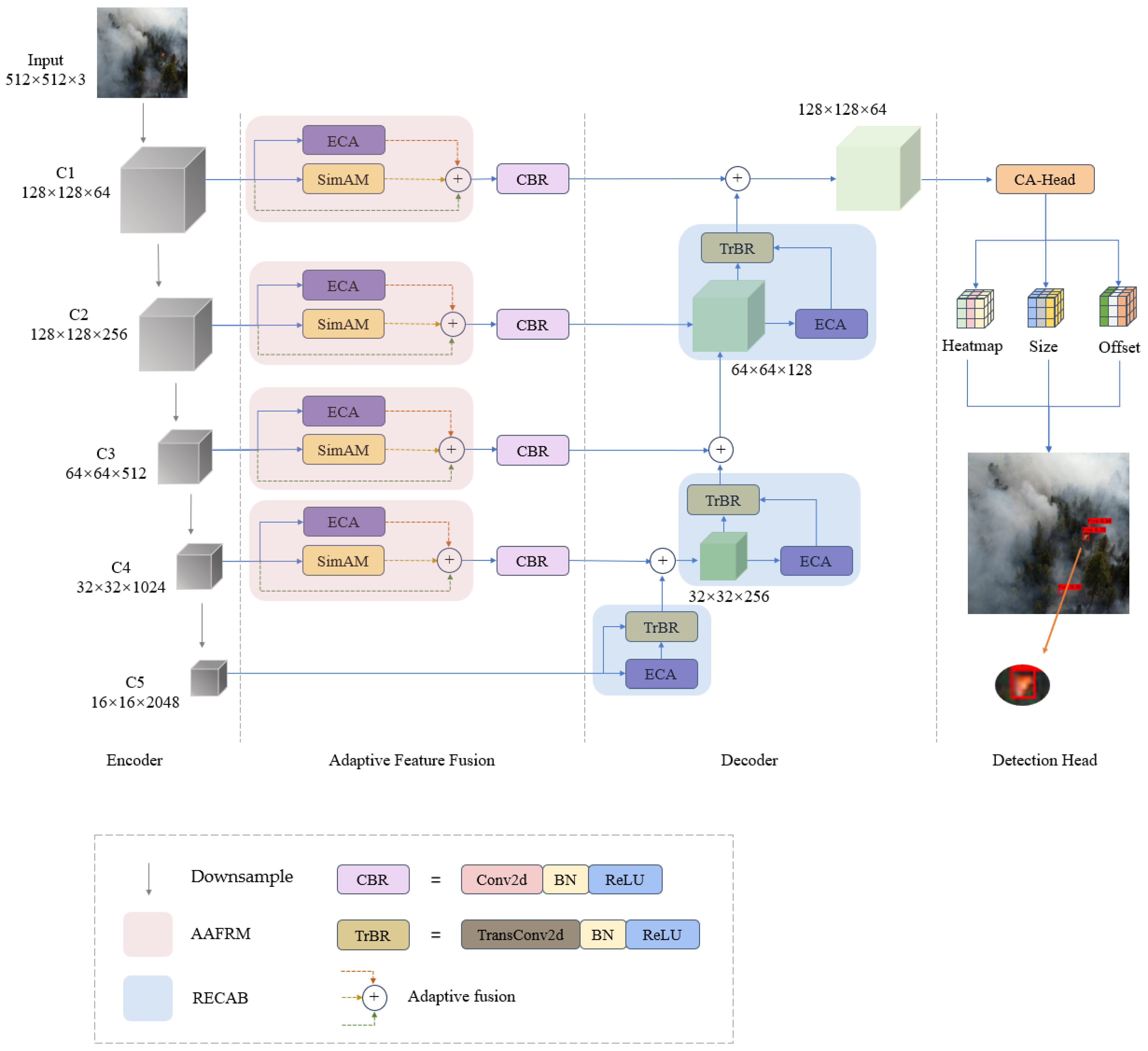
- The FuF-Det algorithm was proposed to enhance the detection accuracy of early forest fires in foggy scenes.
- To preserve the positional features of early fire points during the downsampling process of the encoder, AAFRM is designed as a feature fusion structure between the encoder and decoder.
- To address the issue of losing fine-grained fire point details in the presence of fog during upsampling, RECAB is constructed as the decoder unit.
- To enhance the accuracy of early forest fire localization, CA is introduced into the anchor-free detection head, resulting in the CA-Head.
2. Methods
2.1. FuF-Det Algorithm
2.2. Encoder
2.3. Attention-Based Adaptive Fusion Residual Module (AAFRM)
2.4. Residual Efficient Channel Attention Block (RECAB)
2.5. CA-Head and Loss Function
2.5.1. CA-Head
2.5.2. Loss Function
3. Experiment and Results
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Model Evaluation
3.3. Training
3.3.1. Experimental Environment
3.3.2. Training Parameter Settings
3.4. Experimental Results
3.4.1. Comparison with Other Target Detection Algorithms
3.4.2. Ablation Experiments
3.4.3. Missed Detection Analysis
4. The Detection Effect of FuF-Det in Different Scenes
4.1. Snowy Forest Scene
4.2. Non-Forest Fire Scenes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbrevations
| VAM | Value conversion-Attention mechanism Module |
| BiFPN | Bidirectional Feature Pyramid Network |
| YCbCr | Luminance, Colour-difference of blue, Colour-difference of red |
| HSV | Hue, Saturation, Value |
| HSL | Hue, Saturation, Lightness |
| HWB | Hue, Whiteness, Blackness |
| MS-FRCNN | Multi-Scale Faster RCNN Model |
| R-CNN | Region-CNN |
| MTL-FFDET | Multi-Task Learning-Based Model for Forest Fire Detection |
| GXLD | GhostNet-YOLOX-L-Light-Defog |
References
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. A Large and Persistent Carbon Sink in the World’s Forests. Science 2011, 333, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, K.; Short, K.; Xanthopoulos, G.; Viegas, D.; Ribeiro, L.M.; Blanchi, R. Wildfires and WUI fire fatalities. In Encyclopedia of Wildfires and WildlandUrban Interface (WUI) Fires; Manzello, S.L., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, J.; Handmer, J.; Mercer, D. Vulnerability to bushfires in rural Australia: A case study from East Gippsland, Victoria. J. Rural Stud. 2012, 28, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest Monitoring, Land Use & Deforestation Trends. Global Forest Watch. Available online: https://www.globalforestwatch.org/ (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Baijnath-Rodino, J.A.; Li, S.; Martinez, A.; Kumar, M.; Quinn-Davidson, L.N.; York, R.A.; Banerjee, T. Historical seasonal changes in prescribed burn windows in California. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, D.L.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Kolden, C.; Shive, K.; Kalashnikov, D.A.; Singh, D.; Smith, E. Climate change is narrowing and shifting prescribed fire windows in western United States. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dampage, U.; Bandaranayake, L.; Wanasinghe, R.; Kottahachchi, K.; Jayasanka, B. Forest fire detection system using wireless sensor networks and machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, D.; Kumari, R.; Tripathi, S. Semisupervised Classification Based Clustering Approach in WSN for Forest Fire Detection. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 109, 2561–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, N.; Meng, X. Real-time forest fire detection with wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Wuhan, China, 26 September 2005; pp. 1214–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.J.; Jang, E.; Im, J.; Kwon, C.G. A deep learning model using geostationary satellite data for forest fire detection with reduced detection latency. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 2019–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.M.; Utkin, E.; Lavrov, A.V.; Vilar, R.M. Development of neural network committee machines for automatic forest fire detection using lidar. Pattern Recognit. 2004, 37, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.K.; Cao, Y.C.; Feng, X.Q.; Lu, X.B. Global2Salient: Self-adaptive feature aggregation for remote sensing smoke detection. Neurocomputing 2021, 466, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tan, S.Q.; Yang, Z.G.; Wen, D.X.; Xiao, H.S. A forest fire smoke detection model combining convolutional neural network and vision transformer. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 6, 1136969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Song, W.G.; Lian, L.P.; Wei, X.G. Forest Fire Smoke Detection Using Back-Propagation Neural Network Based on MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4473–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, S.; Vijayakumar, V.; Sathiya Kumar, C.; Priya, V.; Ravi, L.; Subramaniyaswamy, V. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) based Forest Fire Detection and monitoring for reducing false alarms in forest-fires. Comput. Commun. 2020, 149, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.L.; Hu, Y.W.; Zhou, G.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Cai, W.W.; Li, L.J. A high-precision forest fire smoke detection approach based on ARGNet. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 196, 106874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, M.Y.; Ding, Y.H.; Bu, X.F. MS-FRCNN: A Multi-Scale Faster RCNN Model for Small Target Forest Fire Detection. Forests 2023, 14, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.T.; Dembélé, S.; Wu, Y.X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.L.; Zhang, Q.J. A lightweight algorithm capable of accurately identifying forest fires from UAV remote sensing imagery. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 6, 1134942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, A.A.A. A Review on Forest Fire Detection Techniques. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 10, 597368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpoutis, P.; Papaioannou, P.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Grammalidis, N. A Review on Early Forest Fire Detection Systems Using Optical Remote Sensing. Sensors 2020, 20, 6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, H.; Gualotuña, T.; Pinillos, M.; Marcillo, D.; Jácome, S. Machine Learning and Color Treatment for the Forest Fire and Smoke Detection Systems and Algorithms, a Recent Literature Review. In Artificial Intelligence, Computer and Software Engineering Advances: Proceedings of the CIT 2020, Quito, Ecuador, 26–30 October 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 109–120.
- Moulianitis, V.C.; Thanellas, G.; Xanthopoulos, N.; Aspragathos, N.A. Evaluation of UAV Based Schemes for Forest Fire Monitoring. In Advances in Service and Industrial Robotics: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Robotics in Alpe-Adria Danube Region (RAAD 2018), Patras, Greece, 6–8 June 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 143–150.
- Ko, B.C.; Kwak, J.Y.; Nam, J.Y. Wildfire smoke detection using temporospatial features and random forest classifiers. Opt. Eng. 2012, 51, 017208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prema, C.E.; Vinsley, S.S.; Suresh, S. Multi Feature Analysis of Smoke in YUV Color Space for Early Forest Fire Detection. Fire Technol. 2016, 52, 1319–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.S.; Wang, Y. Real-time Forest smoke detection using hand-designed features and deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 167, 105029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.F.; Sun, L.P.; Huang, Y.L. Forest fire smoke recognition based on convolutional neural network. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.S.; Huang, C.X.; Nogueira, F.G.; Bhatia, S.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C. EdgeFireSmoke: A Novel Lightweight CNN Model for Real-Time Video Fire–Smoke Detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7889–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, V.E.; Cho, J.; Subramanian, M.; Naren, O.S. Forest fire and smoke detection using deep learning-based learning without forgetting. Fire Ecol. 2023, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, R.L.; Xu, Z.Y.; Han, N. Forest fire smog feature extraction based on Pulse-Coupled neural network. In Proceedings of the 2011 6th IEEE Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference, Chongqing, China, 20–22 August 2011; pp. 186–189. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N. Dark convolutional neural network for forest smoke detection and localization based on single image. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 8647–8659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.J.; Gong, X.L.; Zhang, S.R.; Wang, L.J.; Li, F. Efficient attention based deep fusion CNN for smoke detection in fog environment. Neurocomputing 2021, 434, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Zhu, H.W.; Hu, C.H.; Zhang, J.G. An attention-based prototypical network for forest fire smoke few-shot detection. J. For. Res. 2022, 33, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.W.; Zhan, J.L.; Zhou, G.X.; Chen, A.B.; Cai, W.W. Fast forest fire smoke detection using MVMNet. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 241, 108219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Lu, C.; Xu, H.W.; Chen, A.B.; Li, L.J.; Zhou, G.X. MMFNet: Forest Fire Smoke Detection Using Multiscale Convergence Coordinated Pyramid Network with Mixed Attention and Fast-robust NMS. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 2023, 18168–18180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Smadi, Y.; Alauthman, M.; Al-Qerem, A.; Aldweesh, A.; Quaddoura, R. Early Wildfire Smoke Detection Using Different YOLO Models. Machines 2023, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, F.; Lou, L.M.; Cheng, P.L.; Huang, Y. Real-Time Detection of Full-Scale Forest Fire Smoke Based on Deep Convolution Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Zhou, G.X.; Chen, A.B.; Wang, Y.F.; Jiang, J.W.; Hu, Y.H.; Lu, C. Adaptive linear feature-reuse network for rapid forest fire smoke detection model. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 68, 101584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zheng, Z.X. Novel Recursive BiFPN Combining with Swin Transformer for Wildland Fire Smoke Detection. Forests 2022, 13, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.J.; Lin, J.; Bai, D.; Xu, R.J.; Lin, H.F. Omni-Dimensional Dynamic Convolution Meets Bottleneck Transformer: A Novel Improved High Accuracy Forest Fire Smoke Detection Model. Forests 2023, 14, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Fire detection using infrared images for UAV-based forest fire surveillance. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Miami, FL, USA, 13–16 June 2017; pp. 567–572. [Google Scholar]
- Ya’acob, N.; Najib, M.S.M.; Tajudin, N.; Yusof, A.L.; Kassim, M. Image Processing Based Forest Fire Detection using Infrared Camera. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1769, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.M. Aerial Images-Based Forest Fire Detection for Firefighting Using Optical Remote Sensing Techniques and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 88, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyono; Harjoko, A.; Dharmawan, A.; Adhinata, F.D.; Kosala, G.; Jo, K.H. Real-Time Forest Fire Detection Framework Based on Artificial Intelligence Using Color Probability Model and Motion Feature Analysis. Fire 2022, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.B.; Hua, Z.C.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X.J.; Zhang, F.Q.; Ye, Q.L.; Fu, L.Y. Preferred vector machine for forest fire detection. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 143, 109722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmy Prema, C.; Vinsley, S.S.; Suresh, S. Efficient Flame Detection Based on Static and Dynamic Texture Analysis in Forest Fire Detection. Fire Technol. 2018, 54, 255–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, K.; Ahmad, J.; Baik, S.W. Early fire detection using convolutional neural networks during surveillance for effective disaster management. Neurocomputing 2018, 288, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, C.Y.; Huang, S.Y. Research on the identification method for the forest fire based on deep learning. Optik 2020, 223, 165491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, K.; Ahmad, J.; Lv, Z.H.; Bellavista, P.; Yang, P.; Baik, S.W. Efficient Deep CNN-Based Fire Detection and Localization in Video Surveillance Applications. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 49, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.T.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xin, J.; Mu, L.X.; Yi, Y.M.; Liu, H.; Liu, D. A Deep Learning Based Forest Fire Detection Approach Using UAV and YOLOv3. In Proceedings of the 2019 1st International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence (IAI), Shenyang, China, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.Y.; Lin, H.F.; Wang, F. A Small Target Forest Fire Detection Model Based on YOLOv5 Improvement. Forests 2022, 13, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z.Y.; Gao, Y.C.; Bai, D.; Xu, R.J.; Lin, H.F. Multi-Scale Forest Fire Recognition Model Based on Improved YOLOv5s. Forests 2023, 14, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lin, H.F.; Wang, F. A Semi-Supervised Method for Real-Time Forest Fire Detection Algorithm Based on Adaptively Spatial Feature Fusion. Forests 2023, 14, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.L.; Lin, H.F.; Wang, F. FCDM: An Improved Forest Fire Classification and Detection Model Based on YOLOv5. Forests 2022, 13, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Xu, R.J.; Liu, Y.F. An Improved Forest Fire and Smoke Detection Model Based on YOLOv5. Forests 2023, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.J.; Huang, J.W.; Li, J.H.; Zhou, J.S.; Chen, X.L.; Liu, Y.F. MTL-FFDET: A Multi-Task Learning-Based Model for Forest Fire Detection. Forests 2022, 13, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; He, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, H. Real-Time Forest Fire Detection by Ensemble Lightweight YOLOX-L and Defogging Method. Sensors 2023, 23, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.; O’Neill, L.; Afghah, F.; Razi, A.; Rowell, E.; Watts, A.; Fule, P.; Coen, J. FLAME 2: Fire Detection and Modeling: Aerial Multi-Spectral Image Dataset. IEEE Dataport 2022. Available online: https://ieee-dataport.org/open-access/flame-2-fire-detection-and-modeling-aerial-multi-spectral-image-dataset (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.L.; Wu, B.G.; Zhu, P.F.; Li, P.H.; Zuo, W.M.; Hu, Q.H. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11531–11539. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.X.; Zhang, R.Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X.H. SimAM: A Simple, Parameter-Free Attention Module for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Shenzhen, China, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 11863–11874. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.B.; Zhou, D.Q.; Feng, J.S. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.M.; Dollar, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.Q.; He, K.M.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A.J. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y. Yolov4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. YOLOX: Exceeding Yolo Series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, D.; Kupec, J.; Hong, J.; Daoudi, A. Real-Time Flying Object Detection with YOLOv8. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.09972. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, K.W.; Bai, S.; Xie, L.X.; Qi, H.G.; Huang, Q.M.; Tian, Q. CenterNet: Keypoint Triplets for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019; pp. 6569–6578. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsoshoara, A.; Afghah, F.; Razi, A.; Zheng, L.; Fulé, P.Z.; Blasch, E. Aerial imagery pile burn detection using deep learning: The FLAME dataset. Comput. Netw. 2021, 193, 108001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
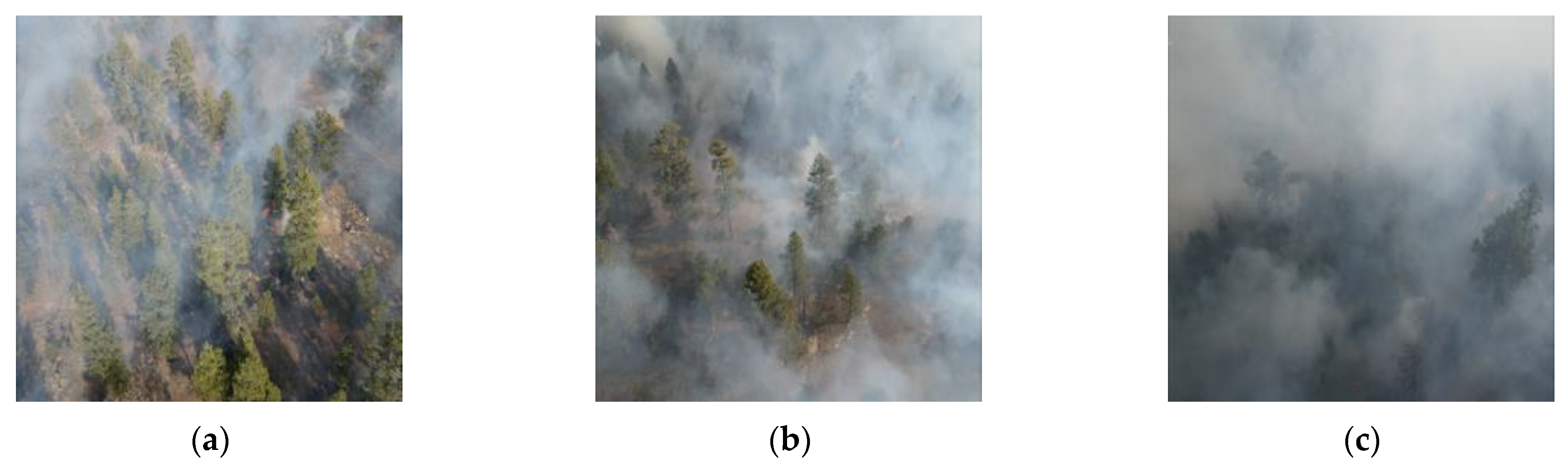















| Stage | Module | Module Numbers | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | Conv2d | 1 | 256 × 256 × 64 |
| BatchNorm | 1 | - | |
| Maxpool | 1 | 128 × 128 × 64 | |
| C2 | Conv Block | 1 | 128 × 128 × 256 |
| Identity Block | 2 | ||
| C3 | Conv Block | 1 | 64 × 64 × 512 |
| Identity Block | 3 | ||
| C4 | Conv Block | 1 | 32 × 32 × 1024 |
| Identity Block | 5 | ||
| C5 | Conv Block | 1 | 16 × 16 × 2048 |
| Identity Block | 2 |
| Training Epoch | Batch Size | Input Size | Optimizer | Momentum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freeze training | 1–50 | 16 | 512 × 512 | Adam | 0.9 |
| Unfreeze training | 51–200 | 8 |
| Method | AP@0.5 | Pre | Rec | F1 | FPS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anchor-based | Faster R-CNN (ResNet50) | 12.57% | 26.22% | 25.28% | 0.26 | 11 |
| YOLOv3 | 66.26% | 74.87% | 69.63% | 0.72 | 36 | |
| YOLOv4 | 64.05% | 81.87% | 50.84% | 0.63 | 32 | |
| YOLOv5_m | 80.25% | 87.66% | 69.02% | 0.77 | 33 | |
| YOLOv7 | 65.56% | 85.30% | 44.21% | 0.58 | 26 | |
| Anchor-free | YOLOX | 81.23% | 87.61% | 73.69% | 0.80 | 21 |
| YOLOv8_s | 86.46% | 92.46% | 73.36% | 0.82 | 58 | |
| CenterNet (ResNet50) | 76.72% | 87.58% | 68.55% | 0.77 | 30 | |
| FuF-Det (Ours) | 86.52% | 91.87% | 78.69% | 0.85 | 20 |
| Experiment | Data Augmentation | AAFRM | RECAB | CA-Head | AP@0.5 | Pre | Rec | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 70.08% | 87.43% | 46.78% | 26 | ||||
| 2 | √ | 76.72% | 87.58% | 68.55% | 30 | |||
| 3 | √ | √ | 83.48% | 89.81% | 77.80% | 21 | ||
| 4 | √ | √ | 82.50% | 90.62% | 74.07% | 30 | ||
| 5 | √ | √ | 82.73% | 90.40% | 73.79% | 30 | ||
| 6 | √ | √ | √ | 85.36% | 91.32% | 79.63% | 21 | |
| 7 | √ | √ | √ | 84.67% | 91.29% | 79.30% | 21 | |
| 8 | √ | √ | √ | 83.25% | 90.94% | 74.67% | 33 | |
| FuF-Det | √ | √ | √ | √ | 86.52% | 91.87% | 78.69% | 20 |
| Variable | Season | Obstructions | Scene | Fire Point Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The adaptability of FuF-Det | √ | √ | √ | × |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Y. FuF-Det: An Early Forest Fire Detection Method under Fog. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235435
Pang Y, Wu Y, Yuan Y. FuF-Det: An Early Forest Fire Detection Method under Fog. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(23):5435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235435
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Yaxuan, Yiquan Wu, and Yubin Yuan. 2023. "FuF-Det: An Early Forest Fire Detection Method under Fog" Remote Sensing 15, no. 23: 5435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235435
APA StylePang, Y., Wu, Y., & Yuan, Y. (2023). FuF-Det: An Early Forest Fire Detection Method under Fog. Remote Sensing, 15(23), 5435. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15235435






