Abstract
Satellite observations have provided global and regional soil-moisture estimates in the last four decades. However, the accuracy of these observations largely depends on reducing uncertainties in the retrieval algorithms. In this study, we address two challenges affecting the quality of soil-moisture estimates from a widely used soil-moisture-retrieval model, the land parameter retrieval model (LPRM). We studied two improvement schemes that were aimed at reducing uncertainties in open water signals (the LPRMv6_OWF) and vegetation signals (the LPRMv6_Veg), as well as a scheme to reduce their combined impacts (the LPRMv6_OWFVeg) on LPRM-retrieved soil moisture using the FengYun-3B (FY-3B) satellite observations. To assess the impacts of the improvement schemes, we utilized in situ soil moisture from the Jiangsu and Jiangxi provinces in China. We found that the retrievals (Rs) of the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg were mainly in the range of 0.2 to 0.5 in Jiangsu and Jiangxi, with increases of 0.1 compared to those of the LPRMv6. The standard deviation (SD) of the LPRMv6_OWFVeg increased in Jiangsu, while the R of the LPRMv6_OWF increased in Jiangsu by 0.05–0.1 compared to that of the LPRMv6, but the SD tended to become worse. In Jiangxi, there was an increase of 0.1 in R. The results show that each of these algorithms improved the accuracy of soil-moisture inversion to some extent, compared to the original algorithm, with the LPRMv6_OWFVeg showing the greatest improvement, followed by the LPRMv6_Veg. The accuracy of both the LPRMv6_OWF and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg decreased to some extent when the open-water fraction (OWF) was greater than 0.2. Full areal extent analyses based on triple collocation showed significant improvements in correlations and minimized errors across different vegetation scenarios over the entire region of China in both the LPRMv6_OWF and the LPRMv6_Veg. However, reduced qualities were found in arid regions in northern China because of the nonlinear relationships between land-surface temperature, vegetation, and soil moisture in the LPRM. These results highlight important lessons for developing comprehensive improvement schemes for soil-moisture retrievals from passive microwave satellite observations.
1. Introduction
Soil moisture (SM), or soil-moisture content, is usually expressed as the dimensionless soil-to-water ratio per unit volume [1]. Although SM is a small fraction of the Earth’s water-cycle components, it is an important basis for many hydrological, biological, and biogeochemical processes [2,3,4]. The effort to obtain soil-moisture data with continuous spatial and temporal characteristics is important for understanding the system of the whole Earth [4].
Commonly used methods for obtaining soil moisture include practical measurements at the site, estimates from remote-sensing techniques, and simulations from land-surface or hydrological models [5,6]. However, each method comes with its strengths and limitations. Station measurements can accurately measure soil moisture at the surface and subsoil layers at close temporal intervals (~15–60 min) at a particular location. Although the measurements via this approach are considered to be the closest to the “true value”, its point-scale representativeness makes it most suitable for small-scale studies in the observation field. Over medium-to-large scales, these point-scale datasets have limited applications and become useful mainly for evaluating other datasets [7].
In the last four decades, satellite remote-sensing technologies have consistently provided global grid average soil-moisture estimates, which prove valuable for medium- to large-scale applications. Among the commonly used sensors, microwave sensors have often been preferred, due to their ability to penetrate clouds and capture land-surface observations [8,9,10]. As a result, numerous studies have made continuous efforts to enhance retrieval schemes for obtaining soil-moisture estimates. Among the widely used retrieval algorithms for passive microwave observations (PMVs), the land parameter retrieval model (LPRM) [8,11,12,13] has been applied to several satellite observations and is currently used by both the European Space Agency (ESA) Climate Change Initiative (CCI) essential climate variables and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) to obtain long-term soil-moisture estimates [14,15].
While the retrieval algorithms of the LPRM and other relevant PMVs have proven useful, several factors hamper the performance of their soil-moisture retrievals, including proximity to open water, dense vegetation, and proximity to urban areas [16]. Studies have shown that when signals from open water and vegetation in PMVs are usually not well isolated in the retrieval schemes, they can impact the quality of the soil-moisture estimates [17,18]. For instance, Holmes et al. noted that open-water signals could increase the biases of the soil-moisture products by about 4 K through the land-surface temperature (LST) inputs [19]. Mladenova et al. showed this same impact when the LPRM-retrieved soil moisture demonstrated overestimations across the global mid-to-high latitudes in the northern hemisphere and regions with open water [20]. PMVs are usually characterized by large spatial coverage and high temporal resolution; however, compared to active microwave observations, their spatial resolution is coarse [21].
Nonetheless, a study showed that nighttime PMV observations have higher qualities [19]. Compared to thermal infrared observations, microwave sensors are able to obtain observations under most weather conditions, since they can penetrate directly through clouds and vegetation cover. This is particularly important for obtaining consistent spatial and temporal land-surface information.
Several challenges still linger when retrieving satellite soil-moisture estimates from PMVs. Studies have shown that factors such as physical temperatures, soil wetness conditions or inland open water, vegetation, surface roughness, and urbanization introduce biases and uncertainties in the temporal and spatial variability in PMV observations. As a result, other studies have been dedicated to minimizing these uncertainties by developing improvement schemes for soil-moisture-retrieval algorithms. For instance, in the development of the LPRM, Parinussa et al. proposed a nonlinear method for improving soil moisture by recalibrating the LST input of the LPRM by leveraging lessons from a reanalyzed LST product to optimize the daytime and nighttime soil-moisture retrievals [22]. Following that study, Van der Schalie et al. improved the single-scattering albedo and roughness parameters in the LPRM using soil moisture and ocean salinity (SMOS) data [23]. Here, this updated version of the LPRM is referred to as the LPRMv6. Furthermore, Parinussa et al. proposed a data-driven scheme for minimizing biases in the LPRMv6 soil-moisture retrievals by recalibrating the single-scattering albedo and roughness parameters using high-temporal soil-moisture measurements from the Jiangxi province of China, due to the complex vegetation distribution in the region (hereafter, referred to as the LPRMv6_Veg) [24].
More recently, Song et al. proposed an approach to minimize the impact of the open-water fraction on the LST input of the LPRM using the Ku-band instead of the traditionally used Ka-band from AMSR-E [25]. While the study by Song et al. demonstrated improved soil-moisture qualities, some challenges persisted with their approach for generic applications. First, in 2019, Song et al. relied on the Ku-band instead of the Ka-band, as the Ku-band is known to have higher sensitivity than the Ka-band, thus making it more challenging to separate the impact of LST, vegetation, and other land features on the soil-moisture output [19]. Second, Song et al. treated the relationship between soil moisture and LST in the LPRM as a direct linear relationship, suggesting that a 1% improvement of the LST input would result in a 1% improvement in soil-moisture retrieval. However, several studies demonstrated that the relationship is nonlinear and complex, as it is intermediated by vegetation, surface roughness, and other soil properties [16,19,26]. Finally, the Song et al. approach assumed that one freezing value of LST could be used for the entire globe. However, where the impact of open water is dynamically considered per pixel, a dynamic frozen point for each pixel would also be required.
A similar study by Hagan et al. proposed a step-by-step, more generic approach to correct the impact of the open-water fraction (OWF) on LST retrieved from PMV brightness temperatures (HG19) [27]. In their approach, Hagan et al. [27] performed a pixel-wise linear regression using Ka-band brightness temperature from FY-3B and MERRA-2 LST to derive functional relationships for slope and intercept with the open-water fraction, using the Jiangsu province as a testbed due to the abundance of inland freshwater. Additionally, the HG19 assumes a dynamic frozen point per pixel and calculates the open-water fraction per pixel.
In this study, we extend the approach of Hagan et al. to soil-moisture retrievals (LPRMv6_OWF) by using a nonlinear approach, and we assume that soil moisture is indirectly linked to LST. [22]. Following that, we attempt to isolate the impact of the added value of the LPRMv6_OWF and the LPRMv6_Veg, as well as their combined impact on soil-moisture retrievals from the LPRM, using the region of China as a testbed through sensitivity experiments in the LPRM. This study aims to identify the potential impacts of these improvement schemes in sensitivity experiments; all other parameters are held constant to first isolate their initial impacts in the LPRM. The selected region comprises the major global climate regions without the added noise of global signals [28].
By conducting a soil-moisture site comparison between the Jiangsu and Jiangxi regions, our objective was to assess the applicability of different algorithms in these two locations. Simultaneously, we utilized triple collocation analysis (TCA) to evaluate the overall performance of these algorithms at a national level. All retrievals were based on brightness temperatures from the FengYun-3B observations, which have been pivotal for the recent advances in the LPRM algorithm [24,27]. The implications of the added value of these improvement schemes are necessary to inform the careful improvement of the LPRM and soil-moisture retrievals from PMVs, especially for developing long-term soil-moisture products.
In the rest of the paper, Section 2 presents the study area, the data, and the research methodology used and introduces the different improvement schemes. Section 3 compares the soil-moisture datasets retrieved from different improved schemes in different surface scenarios. Section 4 provides a summary and the conclusion.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
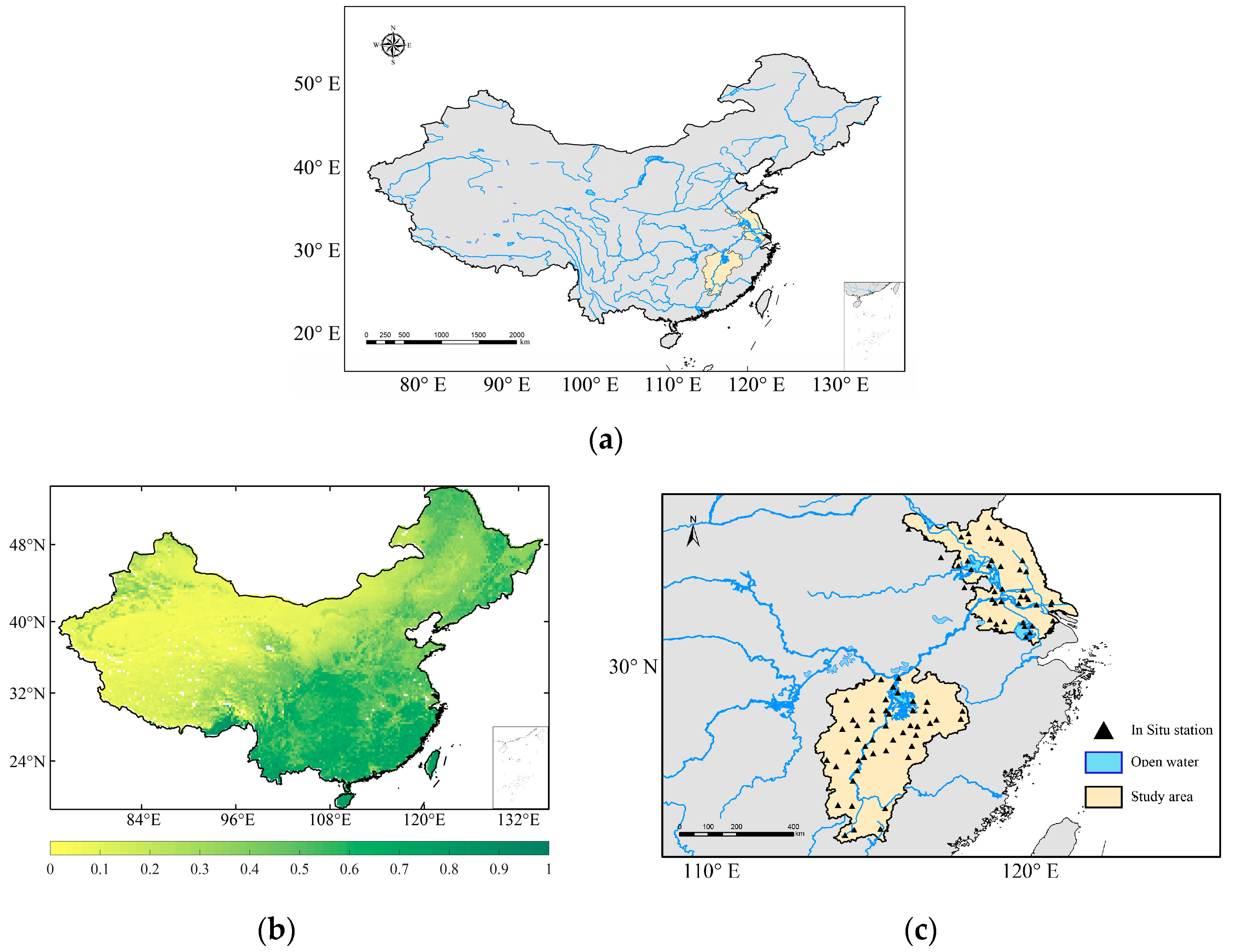
China is a vast country, spanning a wide range of latitudes from north to south, bordering the Pacific Ocean in the east with deep inland regions in the west. This geography allows China to have most of the major climatic divisions. Rivers and lakes in China are widely distributed, due to abundant rainfall and high mountain glacier meltwater (Figure 1a). Southern China is in a subtropical and tropical monsoon climate zone, where abundant heat and precipitation make for lush vegetation (Figure 1b). Jiangsu Province is located on the eastern coast of mainland China, spanning latitudes 30°45′–35°08′ north and longitudes 116°21′–121°56′ east. Jiangsu has a flat topography consisting of plains, water areas, and low hills; it is bordered by the Yellow Sea to the east and straddles two major water systems, the Yangtze River and the Huai River. Geographically, Jiangsu straddles north and south, and its climate and vegetation have both southern and northern characteristics. The western part of Jiangsu Province is dominated by inland water systems, the north by major lakes, and the south by the Yangtze River, which stretches from west to east. The presence of large amounts of open water, which strongly influences passive microwave signals, makes it difficult to obtain accurate land-surface temperatures in this region.
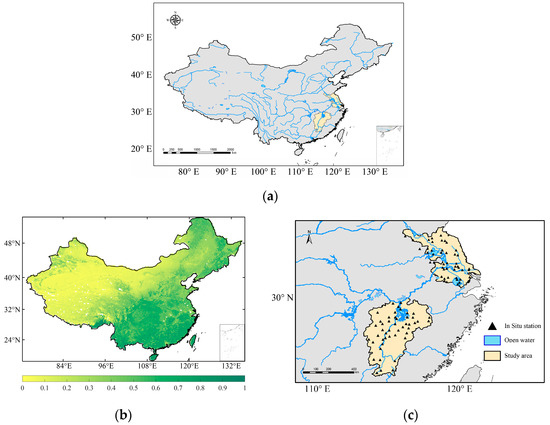
Figure 1.
Overview maps of the study region showing (a) the water distribution, (b) the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) distribution, and (c) the soil-moisture ground observations over China.
In contrast, the vegetation conditions in Jiangsu Province are relatively moderate, without much spatial variability, so the effect of open water on passive microwave signals can be isolated [27]. Jiangxi Province is another area included in this study. It is located in southeastern China, on the south bank of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, between 24°29′14″ and 30°04′43″ north latitude and 113°34′18″ and 118°28′56″ east longitude. Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China, is located in the northern part of Jiangxi, and its water area varies with the amount of precipitation. Around Poyang Lake, there is a large amount of agricultural land, while most other areas are covered by forests. The complex topographic features, dense vegetation, and open water in Jiangxi have a strong influence on the quality of soil-moisture inversion results, and this mutual influence is not direct [24]. The soil-moisture observation sites in Jiangxi and Jiangsu are used for calibration and evaluation (Figure 1c).
2.2. Materials
This article involves various comparison, validation, and auxiliary datasets. The table below provides an overview of the information regarding the data used. Detailed descriptions are provided after Table 1.

Table 1.
The list of datasets used in this paper.
2.2.1. FY-3B Brightness Temperature
This study uses descending 2:00 am microwave-brightness-temperature data observed by the microwave radiation imager (MWRI) that was onboard the Chinese meteorological satellite FY-3B from 2012–2015. The choice to use descending data was made because soil-moisture retrievals using FY-3B descending data yield better results than ascending data, due to a higher thermal equilibrium at nighttime [22]. Thus, using nighttime LST data is advantageous, due to their smaller variations than those of daytime data, which enhances the accuracy of soil-moisture retrieval. The FY-3 is a second-generation polar-orbiting meteorological satellite developed by China to obtain all-weather, multispectral, three-dimensional, quantitative, and high-precision information on global atmospheric and geophysical elements. The FY-3B was launched on 5 November 2010 with a local equatorial. The upper-air descent time was 01:40, and the rise time was 13:40. The MWRI provides horizontally and vertically polarized TB from 10.65 GHz to 89.00 GHz. In the LPRM, Ka-band (36.50 GHz) vertically polarized TB data are linked to the LST [19], while X-band (10.65 GHz) vertically and horizontally polarized TB data are used for inversion SM.
2.2.2. ESA CCI Soil Moisture
In order to understand the fundamental role of soil moisture in the long-term variations of the water, energy, and carbon cycles over land, the European Space Agency (ESA) released the first long-term, global, satellite-observed soil moisture dataset through its Climate Change Initiative (CCI) program [29]. Three CCI global soil-moisture products were created by merging soil-moisture data from multiple satellite microwave observations: one from passive microwave observations, one from active microwave observations, and another where the active and passive observations were combined (the combined observations) [30]. In this study, active CCI SM data were used for triple collocation analysis (TCA). The data covered the years from 2012 to 2015 at an 0.25° spatial resolution and a daily time resolution.
2.2.3. GLDAS-Noah Soil Moisture
The global land data assimilation system (GLDAS) was jointly developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the National Centers for Environment Prediction (NCEP) [30]. The new-generation GLDAS-2.1 product provides high-quality global land-surface variables from 2000 to the present, composed of three land surface models—the catchment, VIC, and NOAH models [31,32]. In this study, the NOAH2.1 active soil-moisture datasets at 3:00 each day from 2012 to 2015 were used for TCA and correlation analysis at an 0.25° spatial resolution.
2.2.4. LPRMv5
Holmes et al. [19] proposed an alternative to thermal infrared sensors for measuring LST. LST is measured using the 37 GHz vertically polarized bright temperature to retrieve the LST. A linear regression of the ground station surface temperature against the satellite-observed bright temperature reveals a strong relationship between the surface temperature and the brightness temperature, as shown in Equation (1).
where Ts and TB,37V represent the land surface temperature and the satellite observed bright temperature, respectively. Accurate Ts values can be obtained from this frequency by a simple linear relationship. In order to distinguish between frozen and unfrozen conditions, a brightness-temperature threshold of 259.8 K was set at a physical temperature of 273.15 K (0 °C). When the brightness-temperature value was less than 259.8 K, there was no soil-moisture output.
Ts = 1.11 ∗ TB,37V + 15.2 for TB,37V > 259.8
This method allowed the land-surface temperature to be obtained, except for permafrost and land with open-water grid points. Of these, 60% of the LST deviations were within 1 K, which increased to 69% if areas with sparse vegetation or bare soil were excluded. This LST-acquisition method is referred to in this paper as H09, and the SM data obtained by using the H09 LSTs as input to the LPRM are referred to as the LPRMv5.
2.2.5. LPRMv6
The single-scattering albedo and roughness parameters in the LPRM were improved by Van der Schalie et al., using soil-moisture and ocean-salinity (SMOS) data [23,33]. The SMOS LPRM soil-moisture retrieval was used as a baseline for optimizing the internal parameterization (i.e., surface roughness and single-scattering albedo) of the AMSR-E LPRM retrieval. To overcome the uniqueness of these datasets, a linear scaling approach was used to form consistent soil-moisture datasets. Internal parameterizations (single-scattering albedo and roughness) were empirically adjusted globally to match the dynamics of SMOS soil moisture retrievals (i.e., long-term mean and amplitude ranges). While the best results (in space and time) were found through fixed values of single-scattering albedo, the roughness parameterization performed best when dependence on soil moisture was introduced. In addition, to further correct the effects of vegetation and roughness, the roughness parameterization was also updated with a vegetation correction. This vegetation correction was based on the optical depth of vegetation in the initial run and further corrected for the effects of roughness in the final run. In this article, this updated version of the LPRM will be referred to as the LPRMv06.
2.2.6. LPRMv6_OWF
A previously utilized linear method for the inversion of LST from the Ka-band was based on masking out the water-column conditions [27]. Based on H09, the LST derived from the FY-3B passive microwave observations was recalibrated using a data-driven approach that considered the effect of open water on the signal received by satellite.
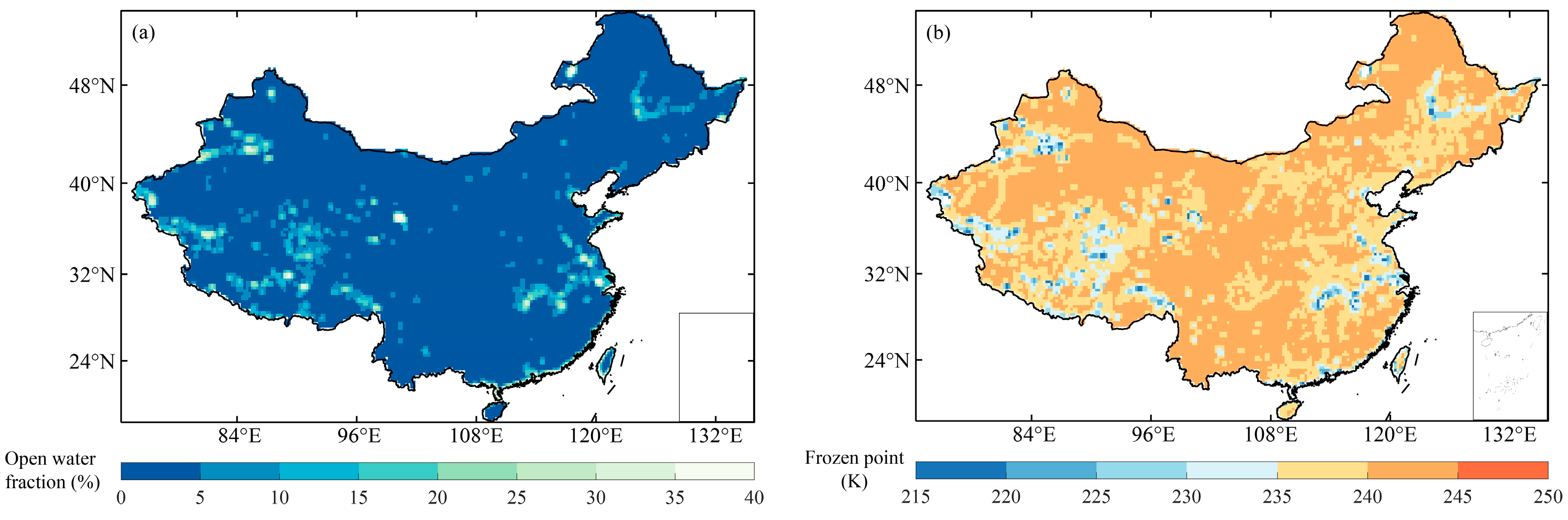
To quantify the open-water impact, Hagan et al. [27] defined an index—the open water fraction (OWF)—that describes the proportion of a gridded area covered by open water (Figure 2a). For every 0.25° pixel, the percentage covered by open-water features was computed by overlaying with the higher-resolution land cover map. The OWF is the percentage of pixels representing open water in the land-cover maps within the coverage of an 0.25°pixel and its surrounding eight pixels. The land-cover dataset used in this study was provided by the Institute of Geographical Sciences and Natural Resources Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. It contains several detailed natural and man-made features over the entire country at a spatial resolution of about 800 m [27]. The slope and intercept of the linear relationship between the LST and the brightness temperature were obtained for each grid point by linearly regressing the MERRA LST and the FY-3B Ka-band bright temperature, based on each grid point. The slope and intercept were fitted linearly to the open-water fraction to obtain an optimized functional relationship based on the open-water fraction (HG19).
where γ stands for the intercept, α represents the slope, and OWF represents the open-water fraction. The LST, hereafter λ, is estimated by Equation (4).
where ρ represents the frozen point based on the HG19 method, which considers the fraction of open water. The H09 method uses a fixed frozen-point threshold (259.8 K) and excludes pixels with open water more than 4% in the pixel, while the HG19 method provides pixel-wise freezing points based on open-water information for the TB,37V observations that are derived for the LST, equal to 273.15 K.
γ = (4.391 ∗ OWF) + 24.98
α = (−0.015 ∗ OWF) + 1.03
λi,j = αi,j ∗ TB,37V + γi,j for TB,37V > ρi,j
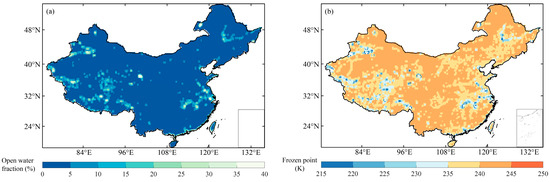
Figure 2.
The distribution of (a) the open-water fraction and (b) the spatially dynamic TB,37V frozen-point threshold over China.
After obtaining the LST derived by the HG19 method, we imposed 10 scenarios of biases on the obtained HG19 LST. These 10 LST scenarios were used as input for the LPRM to retrieve 10 scenarios of SM corresponding to the LST scenarios. Positive biases were not used, because they produced degraded SM retrievals.
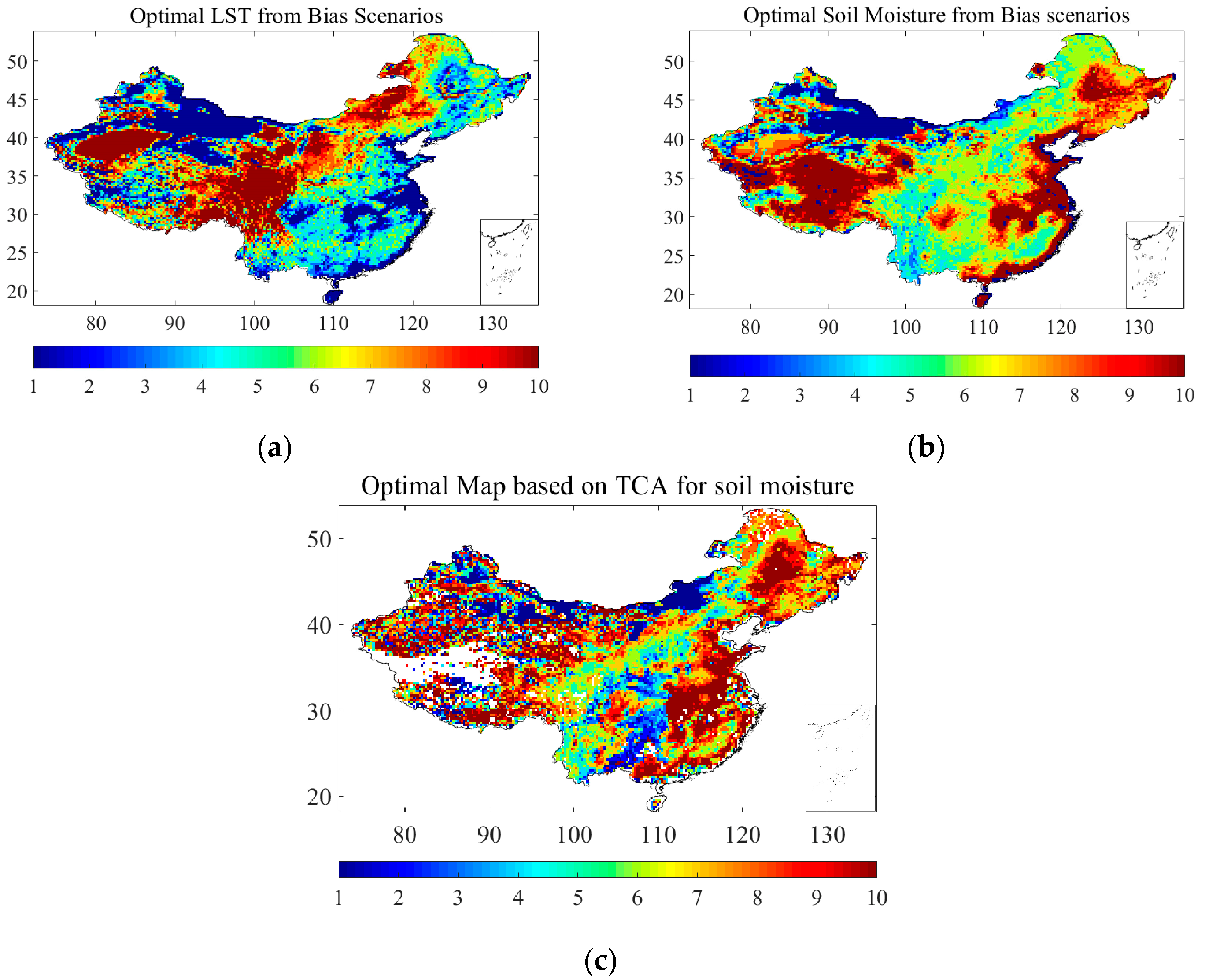
Figure 3 shows optimal maps for the LST and the SM from the 10 retrieval scenarios and the unimposed HG19 scenario for each pixel. Each color represents a specific LST bias scenario, ranging from 0 K to 10 K, for both the SM and the LST. Through this approach, we aimed to show that a 1% improvement in the LST input would not result in a 1% improvement in the SM, since these two are nonlinearly linked in the LPRM. Figure 3a,b shows the optimal solutions for the LST and the SM, respectively, for each pixel, where we find the bias scenario with the lowest bias. Generally, the results demonstrate that the optimal solutions for the two variables are distinct. For instance, in eastern China, along the coast and in areas with large open water, the optimal LST corresponds mainly to the LST case of −1 K bias, while the optimal SM corresponds mainly to the LST case of −10 K bias. In the Tibetan Plateau region, the optimal LST corresponds to the LST case of −10 K bias in the eastern part of the Tibetan Plateau. In comparison, the optimal SM corresponds to the LST case of −10 K bias in the western part of the Tibetan Plateau. This fully illustrates that improvement in the LST does not necessarily lead to a direct increase in the accuracy of the retrieval SM. Figure 3c shows an independent validation of the optimal soil-moisture scenario based on the TCA of the optimal soil moisture, CCI active-soil moisture, and NOAH2.1 soil moisture. Each pixel comprises 11 soil-moisture values, corresponding to 11 LST scenarios (including one original LST and 10 additional LST scenarios). Among these soil-moisture values, the one with the lowest TCA RMSE was considered the optimal soil moisture. Figure 3c illustrates the LST scenarios associated with the minimum TCA RMSE for each pixel’s soil moisture. Here, the agreement with Figure 3b demonstrates the reliability of the optimal scenario.
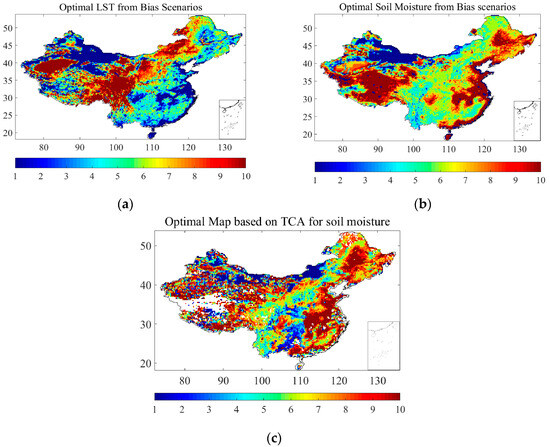
Figure 3.
Optimal scenarios for (a) LST and (b) soil moisture from RMSE validations (c) soil moisture based on TCA RMSE (white areas are not taken into consideration, due to limited observations for TCA computations).
Based on the above, the best scenario for soil-moisture retrieval should be developed considering the best-case scenarios for the LST and how these scenarios vary across vegetation situations. This is important because the SM and VOD outputs of the LPRM rely on the input of the LST. This requires improved methods that focus on soil moisture, along with changes in other variables and their interactions. Here, within the Jiangsu province, we utilized the LST scenario corresponding to the optimal soil-moisture TCA RMSE. We performed a linear regression between this LST and FY-3B brightness temperature and, subsequently, applied the HG19 method once again, resulting in a new soil-moisture product, LPRMv6_OWF.
2.2.7. LPRMv6_Veg
Parinussa et al. [24] proposed a data-driven scheme for improving the soil-moisture inversion algorithm. The development of this new scheme consisted of two steps. In the first step, the LPRM algorithm was applied, based on a wide range of single-scattering albedo (ω). The corresponding optimal ω value with the highest correlation coefficient with site-soil moisture was empirically determined. In the second step, the optimal ω value was fitted to the mean vegetation-optical-depth (τ) condition to obtain a fitted equation for ω versus τ to determine the vegetation density-dependent single-scattering albedo, which was based entirely on observed data and was used as the final algorithm configuration for our study area. The method was applied to Jiangxi Province, China, where the previous algorithm configuration showed a significant improvement (up to 30%) in soil-moisture data, using the newly developed configuration, compared to the previous algorithm configuration. The existing LPRMv5 and LPRMv6 algorithm configurations were also evaluated for all grid cells, and all results showed consistent improvements between successive algorithm versions. This improved soil-moisture product, the LPRMv6_Veg, is based on a single-scattering albedo related to vegetation density.
2.2.8. LPRMv6_OWFVeg
The LPRMv6_OWFVeg is an improved algorithm that considers both vegetation and water bodies. LPRMv6_OWFVeg soil moisture is obtained by combining the approach described in Section 2.2.6, which uses a linear method and incorporates an open water fraction to refit the LST to bright temperature, with a data-driven approach to improve the soil moisture inversion algorithm as briefly described in Section 2.2.7.
2.2.9. In Situ Soil Moisture
Site-based soil-moisture observations are generally considered the closest to representing actual soil-moisture conditions and are often used as the “ground truth” to validate data from other sources [34].
The ground observation data used in this study were obtained from automatic stations at the Jiangsu and Jiangxi meteorological agencies. These automatic stations are located in the eastern and southeastern regions of China, and they record soil-moisture conditions at hourly intervals. These two provinces represent regions with humid to moderately dense vegetation. Here, we used data from 2012 to 2015, at 2:00 am each day, to align with the timeframe of the satellite remote-sensing data.
2.2.10. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index
A surface’s vegetation cover can influence the signals received by satellite sensors [35,36,37,38]. As vegetation density increases, the signal attenuation by vegetation intensifies, making it more difficult for the sensor to capture surface signals that cannot penetrate the vegetation canopy. The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) is used to quantify the surface vegetation-cover conditions. This study utilized NDVI data obtained from a moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) and resampled it from 0.05° resolution to 0.25° resolution to match the satellite remote-sensing data.
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Land Parameter Retrieval Model
The land parameter retrieval model (LPRM) is one of the most widely used soil-moisture retrieval algorithms that are suitable for multiple microwave frequencies, including the C, X, and Ka bands [39,40]. The LPRM links soil moisture and LST to microwave brightness temperature through radiative transfer equations and acquires the vegetation optical depth (VOD) derived from the microwave polarization difference index (MPDI) [39]. A unique advantage of the LPRM is that it minimizes the use of ancillary external data, such as model-based LST, SM ground observations, or vegetation information inputs that are commonly used in other retrieval methods, thereby reducing external errors [22,41]. In this study, we used the LPRM to link brightness-temperature observations from the microwave radiation imager that was onboard the FY-3B satellite to soil moisture. The LSTs were derived from vertically polarized Ka-band observations [19,42] and as input variables for the inversion of the SM and the VOD in the LPRM. This publicly available version, from NASA, is referred to here as the LPRM version 5 (LPRMv5).
Van der Schalie et al. performed a global recalibration of the LPRM and successfully introduced a dynamic vegetation correction [23]. Their study obtained a new global dataset of RTM fixed parameters, based on the international soil moisture network [43] determined from publicly available in situ observations, and showed good soil-moisture inversion results in the assessment. The new set of global fixed input parameters contributed to the LPRM version 6 (LPRMv6). The details of the LPRMv5 and the LPRMv6 are described in Section 2.3. Based on the LPRM version 5 and the LPRM version 6, we added improved soil-moisture inversion algorithms that consider different water and vegetation conditions and compare them with in situ observations to determine the strengths and weaknesses of the different improved algorithms under different conditions.
2.3.2. Triple Collocation Analysis
Triple collocation analysis (TCA) is an analytical technique used to compare three separate geophysical products with each other. The data products are objectively assessed and analyzed by quantifying their error magnitudes [44]. The method was initially used to study winds [45] and was subsequently developed to evaluate satellite remote sensing of soil moisture [46,47], soil temperature [48] and other datasets. The use of TCA requires the satisfaction of at least four assumptions. First, only three datasets are allowed. As described below, we conducted TCA using multiple remote-sensing retrieval datasets, ESA CCI soil moisture and NOAH2.1 active soil moisture. Second, the errors from all three datasets were mutually uncorrelated. Among the datasets we used, multiple retrieval datasets were based on passive remote sensing; the ESA CCI soil-moisture dataset was reanalysis data; and the NOAH2.1 active soil-moisture dataset included model data. The three datasets originated from different sources, thus meeting this assumption. Third, zero-error cross-correlation was assumed. To satisfy this assumption, we employed data anomalies in our TCA, eliminating any temporal offsets or errors. Finally, the data were analyzed at the same time. We used data spanning the years from 2012 to 2015 to fulfill this assumption [44,49,50,51,52].
A brief description of the TCA is as follows: three estimates—θ FY-3B, θ CCI, and θ NOAH2.1—represent SM data from optimal soil moisture, CCI active-soil moisture, and NOAH2.1 soil moisture, respectively. According to Scipal et al. [51], the error-variance formula of the SM is as follows:
where σ2FY-3B represents the error variance of FY-3B data and <·> represents the time series mean, based on at least 100 overlapping observation points.
σ2FY-3B = < (θCCI − θFY-3B) (θNOAH2.1 − θFY-3B) >
In addition, we employed an extended triple collocation analysis (ETC) technique. It utilized the same assumptions as TCA and yielded an additional performance metric—namely, the coefficient (R2) between the measurement system and the unknown target. R2 is a proportionate, unbiased signal-to-noise ratio that, in comparison to the RMSE, provides a complementary analysis [45].
3. Results
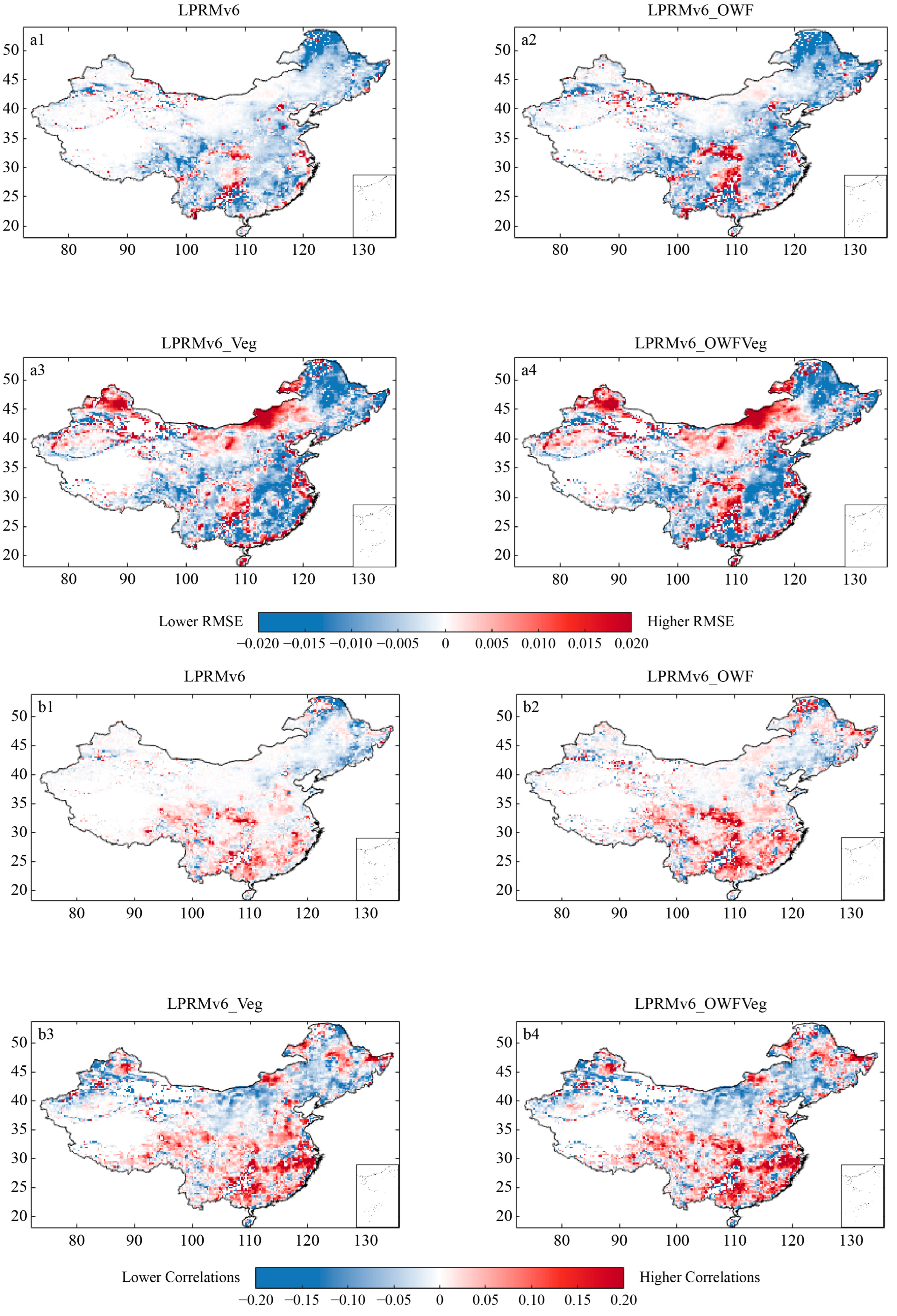
Figure 4 shows the difference between the RMSE and R of all the retrieval schemes and the LPRMv5. The goal was to understand the relative merits and demerits of various improved algorithms of the LPRMv6 in comparison to the LPRMv5 in different geographical regions. The comparison between the LPRMv5 and the LPRMv6 is already quite well-documented [23,24,47]. Nonetheless, we included it as a benchmark. Figure 4(a1,b1) generally shows improvements across most parts of the region for reduced errors (Figure 4(a1)) and increased correlations (Figure 4(b1)), especially for the eastern and southern parts of China. We also found decreased performance in the temporal variations over the northern parts of China, linked to changes in the single-scattering albedo and roughness parameters. The regions with decreased performances were generally less vegetated and dominated by bare lands. Thus, the roughness values used in the LPRMv6 may have overcompensated for the land-surface features.
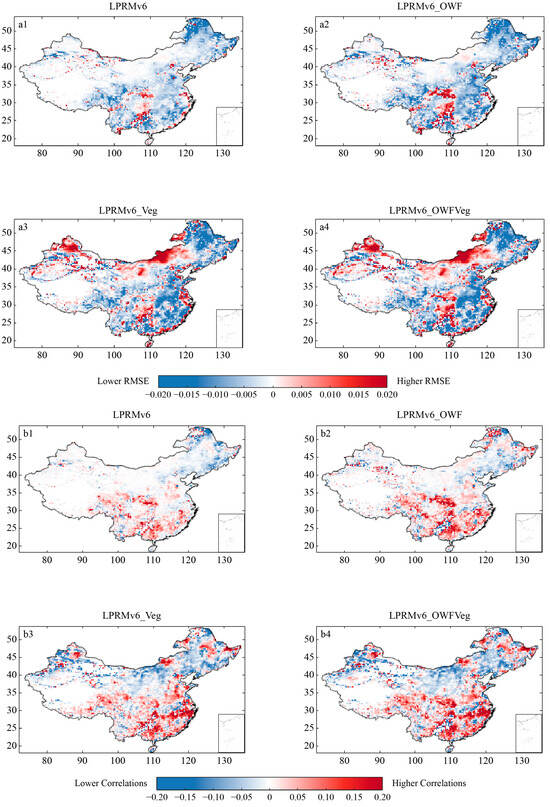
Figure 4.
Maps of China showing the differences between the multiple datasets and the LPRMv5 based on RMSE and R. (a1,b1) show the differences in RMSE and R between the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv5. (a2,b2) show the differences in RMSE and R between the LPRMv6_OWF and the LPRMv5. (a3,b3) show the differences in RMSE and R between the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv5. (a4,b4) show the differences in RMSE and R between the LPRMv6_OWFVeg and the LPRMv5. For RMSE, a negative (positive) value (blue) indicates that reduced error, compared to the LPRMv5 algorithm, works better. The opposite is true for R.
The three proposed improvement schemes all showed substantial magnitudes of improvements in reduced errors and increased correlations, although these came at some cost. Figure 4(a2,b2) shows the results for the LPRMv6, which accounts for open-water impacts on the microwave signals (LPRMv6_OWF). We found reduced RMSEs dominating the eastern region of China, except for the mountainous areas to the north and south of the Sichuan basin, where the difference with the LPRMv5 mostly ranged between −0.02 and −0.015 (Figure 4(a2)). We also found increased Rs in most parts of the region, with more substantial improvements over the southeastern region (Figure 4(b2)), concentrated in the mountainous, hilly areas of central and western China and in the south. These highlighted the importance of quantifying open-water impacts on microwave observations, as most of these improvements were over the wet regions, where rainfall is more frequent, following the precipitation distribution. Nonetheless, we also found some deterioration in R over the northeastern part of the region.
Vegetation density also affects the quality of soil-moisture anomalies from passive microwave observations [47]. Dense vegetation affects the penetration of the satellite signal into the canopy, resulting in large deviations in the ground signal received by the sensor [19,20]. Figure 4(a3,b3) shows the results when we accounted for spatial vegetation dynamics using a vegetation-density-based scattering-albedo scheme in the LPRM (LPRMv6_Veg). Thus, the difference in the RMSE and the R of the SM obtained, compared to the LPRMv5, indicated the potential sensitivity of the retrieval model to vegetation corrections (Figure 4(a3,b3)). The distribution of RMSE reductions was not distinctly different from the open-water correction potential, due to soil wetness and the vegetation having very similar distributions over the region. However, the improvements shown in Figure 4(a3,b3) were more substantial than in the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv6_OWF. Regions of higher RMSE and lower R difference occurred most strongly at the northern border and in the Inner Mongolia Plateau. This was because the area is inherently a drier region, away from water bodies, with sparse vegetation; therefore, overcompensating for these features could easily lead to deterioration in quality. We also noted that since this improved algorithm calibrated the use of vegetation information from the densely vegetated Jiangxi province of China, the improved algorithm was less effective than the LPRMv5 in the arid regions of northern China and in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River plain, where the water network is dense and there are fewer areas of tall, dense, mature vegetation, reducing the accuracy of the improved algorithm to some extent. In the hilly regions of southern China and the northeast, where vegetation cover is high, the improved algorithm had a significant advantage over the LPRMv5, with an RMSE difference of −0.02.
Finally, Figure 4(a4,b4) shows differences in the RMSE and the R of the satellite soil-moisture time series, where we account for the impacts of both water bodies and vegetation. We found that both the merits and demerits of the LPRMv6_OWF and the LPRMv6_Veg had propagated into the combined scheme (Figure 4(a4,b4)). As a result, we still had qualities decreasing at the northern border and in the Inner Mongolia Plateau. However, we also found the most substantial improvements in the eastern and southern parts of the region, showing reduced RMSEs and increased Rs. The results shown in Figure 4 highlight the need to properly calibrate the parameters over different vegetation and soil-wetness ranges, especially where there are strikingly distinct differences between the climate zones, like those between the eastern and western parts of our study region.
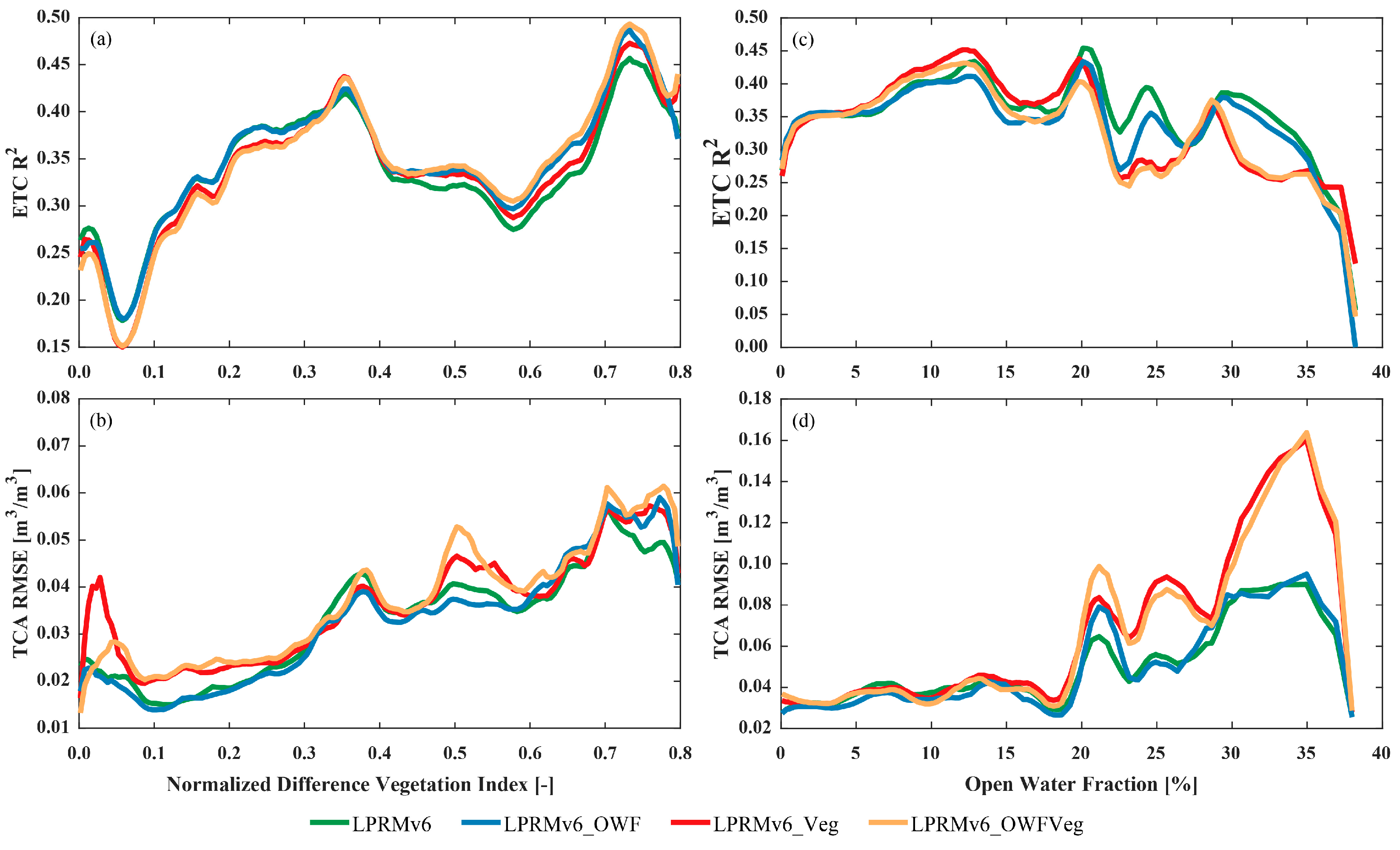
Based on the TC analysis conducted, we analyzed the relationship between our results and the patterns of the OWF and the NDVI. Figure 5a shows that in low-vegetation regions (NDVI< 0.35), the R² of each dataset was on an overall increase from a minimum NDVI value of 0.05. Under low-to-medium vegetation densities (0.01 to 0.33), we found that the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv6_OWF had the highest correlations, followed by the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg (Figure 5a). From mid-to-high NDVI densities, the LPRMv6_OWFVeg showed the highest qualities (highest R2), harnessing the open-water and vegetation corrections to outperform the LPRMv6_OWF and the LPRMv6_Veg. This was followed by the LPRMv6_OWF, the LPRMv6_Veg, and, eventually, the LPRMv6. The temporal correlation improvements, although not intended in these schemes, were possible because of (1) the dynamic frozen conditions used for the input LST improvements, which changed the sample sizes of the time series for each pixel, and (2) the dynamic scattering albedo used in the LPRMv6_Veg, which also affected the length of the time series obtained for the soil-moisture estimates. Generally, we expected R to be higher under low-vegetation conditions and to drop with increasing vegetation density [38]. However, Figure 5a shows that R2 increased with increasing vegetation density, highlighting the important added value of these schemes to improve temporal consistency.
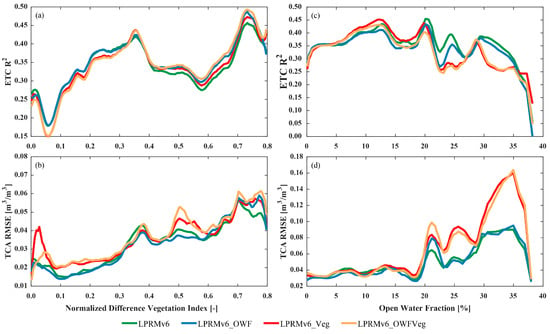
Figure 5.
Full areal validation results for the time series anomalies of the retrieved soil moisture from the different retrieval schemes based on (a,c) ETC (R2) analysis and (b,d) RMSE results from the triple collocation analysis as a function of (a,b) vegetation density, using the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and (c,d) the open-water fraction.
Figure 5b shows the results for the TCA RMSE of the retrieved soil-moisture estimates as a function of the NDVI. As expected, the RMSE of all the soil-moisture estimates increased with increasing vegetation density [24]. The LPRMv6 had a steady performance, with generally lower RMSEs; however, this scheme would benefit from open-water information, which reduces the RMSE even more for most parts of the region. The results of the two schemes that account for vegetation (the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg) suggest that much of the benefit is found over high vegetation regions (NDVI > 0.5). We also note that the seemingly higher RMSEs in the latter two soil-moisture estimates might have resulted from averaging, which included regions of increased errors, as shown in Figure 4. Nonetheless, all three improvement variations of the LPRMv6 demonstrated the need to isolate and account for open-water and vegetation information for soil-moisture estimation.
Figure 5c,d demonstrates that as the OWF increased, the overall correlation of various datasets decreased, and the RMSE generally rose. This reaffirmed the impact of open water on remote-sensing soil-moisture retrieval. As shown in Figure 5c, when the OWF was less than 5%, there was no significant difference in the correlation among the various datasets. When the OWF was greater than 5% but less than 20%, the LPRM_Veg showed a slightly better correlation. When the OWF exceeded 20%, the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv6_OWF outperformed the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg, with the LPRMv6 slightly superior to the LPRMv6_OWF. In Figure 5d, it can be observed that when the OWF exceeded 20%, both the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg exhibited higher RMSE values than those of the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv6_OWF.
Through complete areal TC validation, we discovered that two algorithms incorporating open-water information consistently improved the R2. However, it is worth noting that when the OWF was relatively high, these algorithms tended to perform less favorably than the LPRMv6. Furthermore, when the OWF exceeded 20%, notable differences in the performance of these two open-water-inclusive algorithms emerged. The LPRM_OWF yielded results that were reasonably close to those of the LPRMv6, while the LPRMv6_OWFVeg was notably inferior to the LPRMv6. This observation implies that in regions characterized by higher OWFs, the parameter calibration conducted in Jiangxi province no longer contributed positively to data quality but, instead, resulted in a decline in data quality. Moreover, with regard to the RMSE, the performance of both the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg lagged behind those of the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv6_OWF, further corroborating the aforementioned findings.
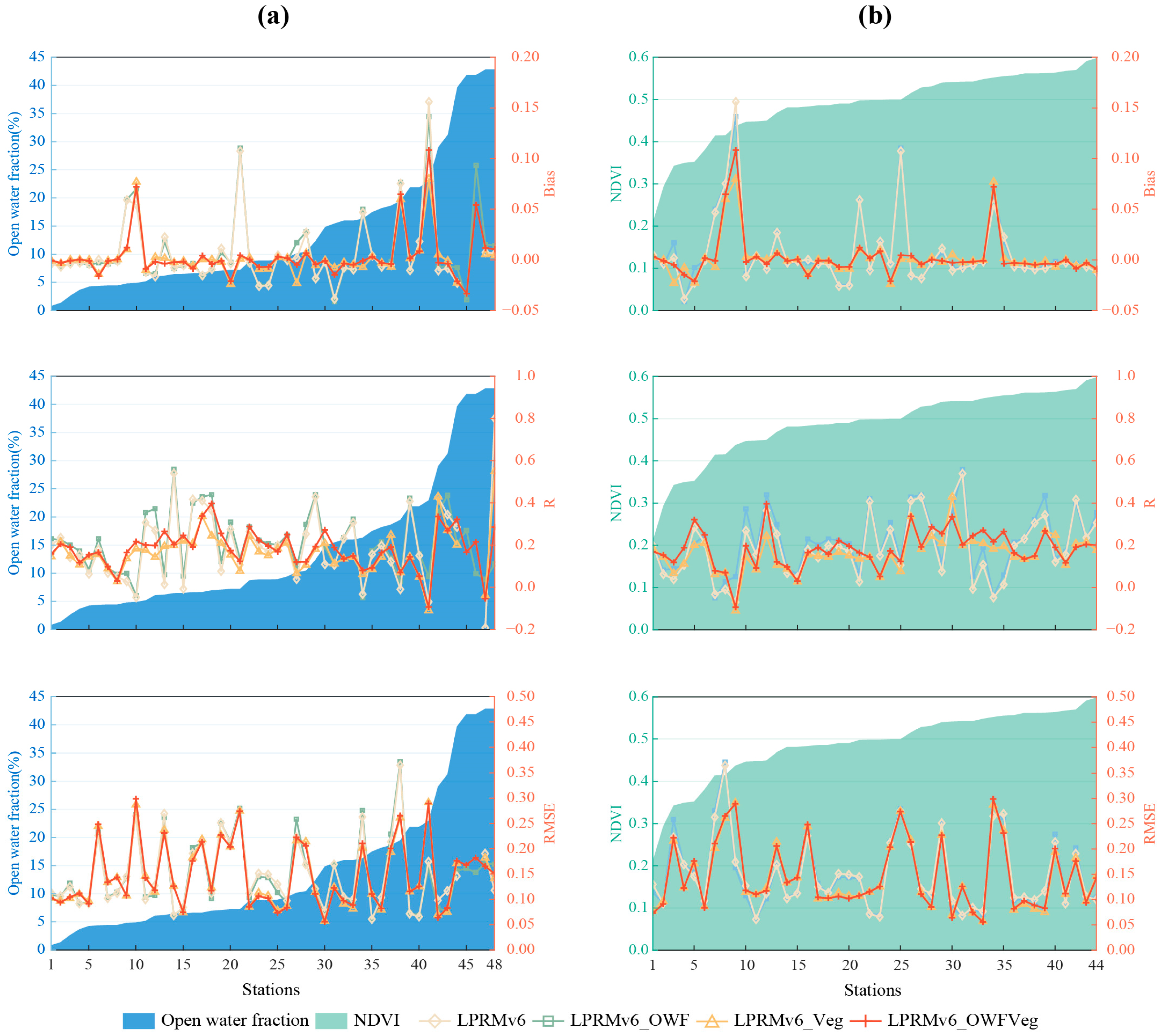
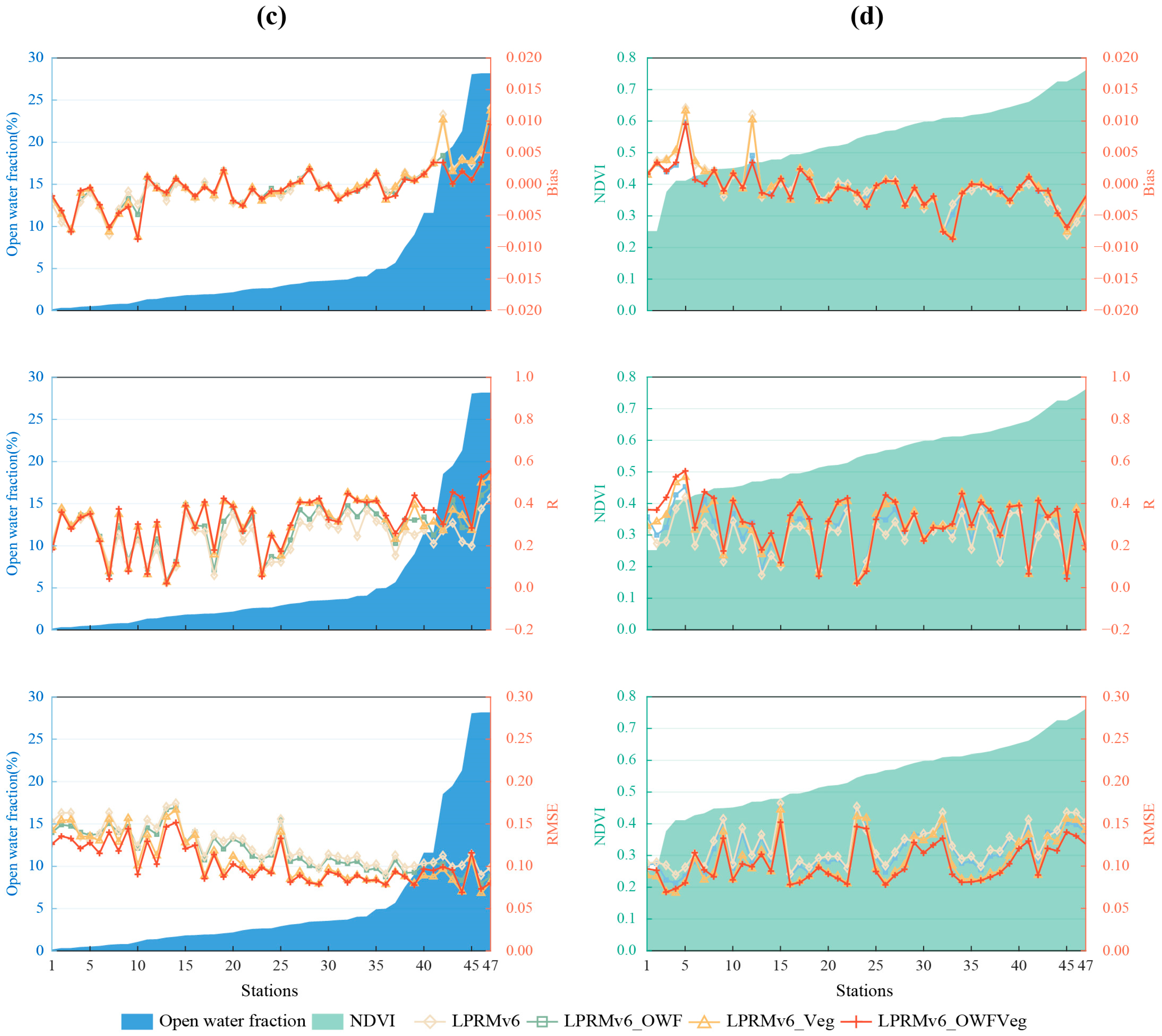
Figure 6 compares multiple datasets against in situ observations, using different metrics. The 48 stations in Jiangsu (Figure 6a,b) and the 47 stations in Jiangxi (Figure 6c,d) were arranged from left to right, based on the magnitude of the open-water fraction or the NDVI values. Four Jiangsu stations are not listed in Figure 6b, due to the absence of corresponding NDVI values. The size of the left values and the background represent the levels of the open-water fraction (Figure 6a,c) and the NDVI (Figure 6b,d). The values on the right represent bias, correlation (R), and RMSE, respectively. The shapes of the dots represent the results from the different improvement schemes, where diamonds represent the LPRMv6, squares represent the LPRMv6_OWF, triangles represent the LPRMv6_Veg, and crosses represent the LPRMv6_OWFVeg.
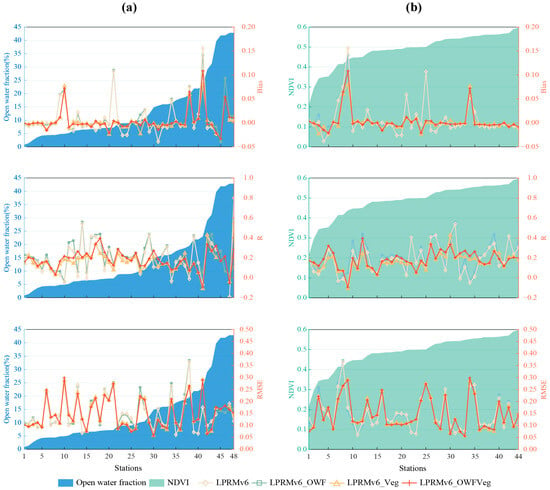
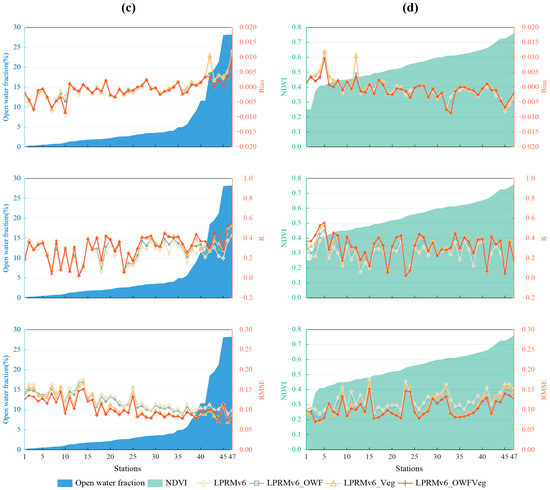
Figure 6.
The comparisons between in situ observations and multiple datasets to show bias (unit: m3m−3), R, RMSE (unit: m3m−3) in Jiangsu (a,b) and Jiangxi (c,d) under different open-water fractions and different NDVI scenarios, respectively.
Figure 6a,b presents the comparisons of multiple datasets with the Jiangsu stations. From the metric R, it can be observed that out of the 48 stations, 26 stations showed that the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv6_OWF performed better than the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg. Among these 26 stations, 90% indicated that the LPRMv6_OWF slightly outperformed the LPRMv6. However, based on bias and the RMSE, 30 sites indicated that the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg performed better than the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv6_OWF. Among the 22 sites with open-water fractions greater than 10%, approximately 16 sites indicated that the LPRMv6_OWF did not provide a significant improvement over the LPRMv6. We found that in Jiangsu Province, which is predominantly plain terrain with some hills and a significant presence of open-water area, the LPRMv6_OWF performed better in terms of correlation metrics than the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg, but the advantage over the LPRMv6 was not substantial. This may have been due to the fact that temporally invariant open-water and vegetation metrics were used; therefore, the R improvements were not expected. Nonetheless, due to the pixel-wise frozen conditions that were used, there could have been differences in R, due to the differences in time series lengths. On the other hand, the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg performed better than the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv6_OWF in terms of error reduction, indicating that algorithm improvements that consider vegetation factors have some applicability in reducing errors.
Figure 6c,d shows that all three improved algorithms performed better than the LPRMv6 overall in the Jiangxi province. Despite NDVI values ranging from 0.25 to 0.75 across the 47 sites, there was no clear trend shown in the metrics. Furthermore, in terms of bias, there was not a significant difference between the algorithms. However, in the metrics of the R and the RMSE, the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg outperformed the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv6_OWF. When the open-water fraction was greater than 10%, the R of the LPRMv6_OWFVeg was better than that of the LPRMv6_Veg, while the opposite was observed in the RMSE. Although the number of sites was limited, this finding is consistent with the observation shown in Figure 6a where, when the open-water fraction was greater than 10%, there was at least a slight improvement in the R but an increase in error.
Additionally, Figure S1 illustrates the comparisons between each dataset and the stations without considering the OWF and the NDVI. Figure S1a,b summarizes the performances, based on Taylor diagrams of the different soil-moisture time series and their anomalies obtained from the four improvement algorithms against in situ observed soil moisture, respectively, with red representing the Jiangsu site and blue representing the Jiangxi site.
Figure S1a shows the Taylor diagrams for the time series anomalies. The results in Jiangxi appeared to be better than the results in Jiangsu, especially where vegetation was accounted for. The correlations over the Jiangxi sites were generally higher than those in the Jiangsu site (Figure 7a).
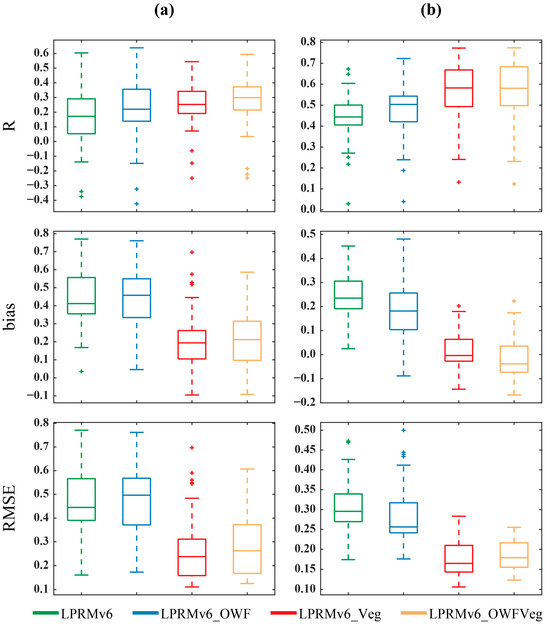
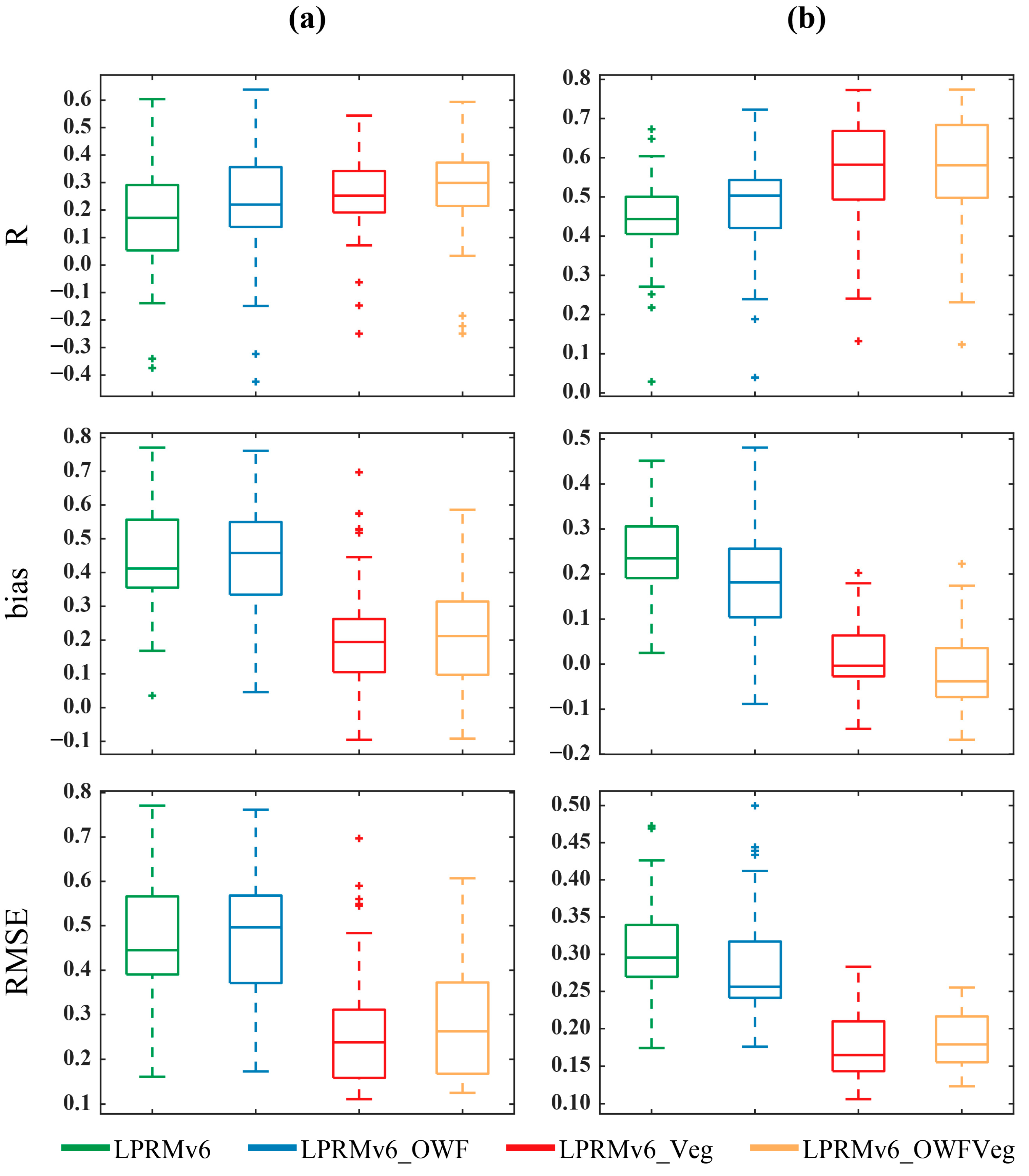
Figure 7.
Box plot of evaluation metrics for multiple datasets at the (a) Jiangsu and (b) Jiangxi sites.
Figure S1b shows that the improvement schemes also impacted the original time series. In the Jiangsu province, the three improved algorithms reduced the extremely low correlation values (0–0.1), compared to the original LPRMv6 algorithm, while the scatter-of-correlation values greater than 0.4 increased significantly. Analysis of the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg Taylor plots showed that the scatter-distribution-of-correlation between Jiangsu Province and the site calculation was concentrated in the region of 0.2–0.4, while the concentration region of the LPRMv6 algorithm was 0–0.3. Among these three algorithms, the LPRMv6_OWFVeg performed the best in terms of R, while the LPRMv6_Veg excelled in standard deviation. In the Jiangxi province, although there was no significant improvement in correlation, more than half of the standard deviation ratio of the two improved algorithms that considered vegetation was below 2. In contrast, the original LPRMv6 algorithm and the LPRMv6_OWF were mostly concentrated in 2–3. This indicated that, although the two improved algorithms that considered vegetation showed little improvement in temporal consistency, there was a significant reduction in standard deviation.
It should be noted that our research indicates that the progress of anomalies is not significantly greater than that in the original time series, as was expected. The greater progress in the original time series was due to our primary focus on bias minimizations.
4. Discussions
This study has shown, through sensitivity experiments, potential implications for open water in the LST inputs and vegetation corrections in the LPRM for SM retrievals. We routinely demonstrated that direct improvements in the retrieval inputs may not directly improve SM retrievals.
Here, we began from the LST-retrieval algorithm developed by Holmes et al. [19] which linked the Ka-band brightness temperatures to land-surface temperature through a linear relationship for passive microwave observations (H09). However, this approach did not account for corrections related to open-water fractions, resulting in biases in the SM retrieved from earlier versions of the LPRM (the LPRMv5). Following that, a number of studies evaluated the assumptions in the LPRMv5, and even attempted to improve the SM retrievals in the LPRM by directly linking LST adjustments to the SM [26] and indirectly linking them [22]. A more recent study attempted to isolate the impact of open-water fractions on LST by using the Ku-band and accounting for open-water fraction [25]; however, directly linking their corrections in the LST to the SM did not yield significant global improvements, as was expected. As noted earlier, this was because the SM and the LST were not directly related within the LPRM. Other recent studies also relied on vegetation corrections using ground-based SM measurements to improve SM retrievals from the LPRM [23,24].
This study built on these earlier studies by attempting to learn just how much we might improve the SM from the LPRM by routinely accounting for open-water corrections in H09, using the approach proposed by Hagan et al. [27] and, eventually, linking it to the SM, as well as including a vegetation correction from Parinussa et al. [24]. By keeping other parameters in the LPRM constant, we assessed regions that may benefit or degrade in SM qualities when these adjustments are applied over a wide range of climate conditions.
Figure 7 provides an overview of the performance of various algorithms in Jiangsu and Jiangxi. In the Jiangsu province, it was evident that the LPRMv6_OWF exhibited greater variability in terms of correlation. When considering both Figure 7a and Figure S1, the LPRMv6 showed a higher number of relatively high correlations (R > 0.4). This aligned with the conclusions drawn in Figure 5, supporting the notion that considering open-water information has a positive impact on enhancing correlation.
Simultaneously, the LPRMv6_OWF also generated more negative correlations compared to the LPRMv6. This can be attributed to the scale effect of the data comparison. In theory, the values at a single site can only represent an extremely small area. During the calibration of parameters related to vegetation density, variations within an 0.25° pixel related to vegetation density were relatively minor. Consequently, using site data for comparison resulted in relatively low errors. However, when considering open-water areas, the situation was different. Within a single pixel, if a site was located far from open water, the open water had minimal influence on the actual measurements. Still, open-water areas can have a noticeable impact on remote-sensing-received data. As a result, the comparison of indicators in the Jiangsu province exhibited substantial fluctuations.
In the Jiangxi province (Figure 7b), the algorithms that accounted for vegetation factors demonstrated a superior correlation performance, as these algorithms were initially calibrated for this specific region. In terms of bias and RMSE metrics, both the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg outperformed the LPRMv6 and the LPRMv6_OWF.This indicated that considering vegetation factors has a positive effect on reducing errors in the retrieved data.
Several challenges in this study made it difficult to adequately understand the performances of the various improvement schemes. For instance, there was a lack of an extensive publicly available network of in situ datasets, which would have been helpful to optimize the vegetation correction, as well as to validate the results more comprehensively. As a result, the TC analysis and the in situ data validations did not cover the same areal extents, resulting in some inconsistent results. Additionally, the open-water metric used here is a static-based one that does not consider seasonal changes in open-water areas to the extent necessary for adequately isolating the impact of open water on SM retrievals. Finally, a study of global extent may be more beneficial to properly optimize the LPRM to cover all climate conditions. Future studies will be able to consider these possibilities.
5. Conclusions
This paper aimed to learn lessons for some improvement schemes for soil moisture (SM) retrieved from the land parameter retrieval model (LPRM) by routinely considering the impacts of open-water conditions and vegetation dynamics. We relied on in situ datasets from two typical regions in China—Jiangsu Province, which has an abundance of fresh water, and Jiangxi Province, which is dominated by complex vegetation cover. Additionally, we used triple collocation analysis (TC) to evaluate the improvements for the entire region of China, which we used as a testbed without the added noise of global signals such as the Sahara desert and the Amazon basin.
Our conclusions are as follows.
- The algorithm used to quantitatively account for the influence of open water to enhance LST inputs can improve the correlation metrics of retrieved soil-moisture data. However, when the OWF exceeds 10%, the correlation of the LPRMv6_OWF became uncertain. In comparison with the Jiangsu site, despite the significant fluctuations in the R metric, an improvement in the correlation of the LPRMv6_OWF could still be observed. Nevertheless, the performance of this approach fell short of expectations, in terms of errors.
- In comparison with the Jiangxi site, the LPRMv6_Veg performed best across all metrics, primarily because its parameters were calibrated specifically for Jiangxi. However, in comparison with the Jiangsu site, considering the vegetation effects reduces data errors. Nevertheless, in the TC comparisons, both the LPRMv6_Veg and the LPRMv6_OWFVeg exhibited suboptimal performance. This suggested that a single-scattering albedo calibration, based on vegetation density conducted in Jiangxi, may not be universally applicable in the full area, as other vegetation-cover or climatic-zone effects need to be taken into account. Although in Jiangsu, the LPRMv6_Veg reduced bias and RMSE, it cannot be assumed that this algorithm is universally suitable for the Jiangsu province. This is because both Jiangsu and Jiangxi share a subtropical monsoon climate, and their vegetation exhibits certain similar characteristics.
- The LPRMv6_OWFVeg outperformed the LPRMv6_Veg in correlation, albeit the advantage was not very pronounced. However, the LPRMv6_OWFVeg exhibited notable inferiority in bias and RMSE compared to the LPRMv6_Veg. From this, we concluded that the impact of calibrating single-scattering albedo for soil-moisture retrieval based on vegetation density is more significant than the approach of enhancing LST input for soil-moisture retrieval. The LPRMv6_OWFVeg tended to perform better in regions with vegetation characteristics that were similar to Jiangxi and with an OWF below 20%.
These lessons add to existing knowledge to better understand how to improve SM retrievals from the LPRM more effectively. The lessons learned here can be extended to global applications as well as to other passive microwave satellite observations, where the LPRM can be applied.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs15215108/s1, Figure S1: Taylor diagrams of multiple datasets against the in situ observations of Jiangsu and Jiangxi stations based on (a) soil moisture anomalies and (b) soil moisture original time series.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.W., H.L. and D.F.T.H.; methodology, G.W. and D.F.T.H.; software, D.F.T.H.; validation, G.W., Y.H. and D.F.T.H.; formal analysis, G.W. and H.L.; investigation, G.W. and H.L.; resources, G.W.; data curation, H.L. and D.F.T.H.; writing—original draft preparation, G.W. and H.L.; writing—review and editing, D.F.T.H., I.K.N., F.Z. and E.Y.; visualization, G.W., D.F.T.H., H.L. and Y.H.; project administration, G.W.; funding acquisition, G.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 42275028; the Sino-German Cooperation Group Program, grant number GZ1447; and the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, grant number KYCX23_1343.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to developers, managers, and funding agencies of the ESA, CCI, and NASA for granting access to these datasets under citation policies. We are also grateful to all data providers who made their data available for use in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Petropoulos, G.P.; Ireland, G.; Barrett, B. Surface soil moisture retrievals from remote sensing: Current status, products & future trends. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 83, 36–56. [Google Scholar]
- Guillod, B.P.; Orlowsky, B.; Miralles, D.G.; Teuling, A.J.; Seneviratne, S.I. Reconciling spatial and temporal soil moisture effects on afternoon rainfall. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, R.; Seneviratne, S.I. Propagation of soil moisture memory to streamflow and evapotranspiration in Europe. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 3895–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, J.J. Satellite remote sensing applications for surface soil moisture monitoring: A review. Front. Earth Sci. China 2009, 3, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhu, S. Subseasonal variabilities of surface soil moisture in reanalysis datasets and CESM simulations. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2020, 13, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergel, C.; de Rosnay, P.; Gruhier, C.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Hasenauer, S.; Isaksen, L.; Kerr, Y.; Wagner, W. Evaluation of remotely sensed and modelled soil moisture products using global ground-based in situ observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jeu, R.A.M.; Owe, M. Further validation of a new methodology for surface moisture and vegetation optical depth retrieval. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4559–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fily, M.; Royer, A.; Goıta, K.; Prigent, C. A simple retrieval method for land surface temperature and fraction of water surface determination from satellite microwave brightness temperatures in sub-arctic areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinussa, R.M.; de Jeu, R.A.; Holmes, T.R.; Walker, J.P. Comparison of microwave and infrared land surface temperature products over the NAFE’06 research sites. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Li, L. Retrieval of land surface parameters using passive microwave measurements at 6-18 GHz. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Wilson, W.J.; Yueh, S.H.; Dinardo, S.J.; Li, F.K.; Jackson, T.J.; Lakshmi, V.; Bolten, J. Observations of soil moisture using a passive and active low-frequency microwave airborne sensor during SGP99. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2659–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, M.; de Jeu, R.; Walker, J. A methodology for surface soil moisture and vegetation optical depth retrieval using the microwave polarization difference index. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Dorigo, W.A.; Parinussa, R.; de Jeu, R.A.; Wagner, W.; McCabe, M.F.; Evans, J.; Van Dijk, A. Trend-preserving blending of passive and active microwave soil moisture retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Parinussa, R.; Dorigo, W.A.; De Jeu, R.A.; Wagner, W.; Van Dijk, A.; McCabe, M.F.; Evans, J. Developing an improved soil moisture dataset by blending passive and active microwave satellite-based retrievals. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouweleeuw, B.; Van Dijk, A.; Guerschman, J.P.; Dyce, P.; Owe, M. Space-based passive microwave soil moisture retrievals and the correction for a dynamic open water fraction. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew, A. Impact of surface heterogeneity on surface soil moisture retrievals from passive microwave data at the regional scale: The Upper Danube case. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, I.J.; Sandells, M.J.; Gurney, R.J. The effects of scene heterogeneity on soil moisture retrieval from passive microwave data. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, T.; De Jeu, R.; Owe, M.; Dolman, A. Land surface temperature from Ka band (37 GHz) passive microwave observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D04113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, I.; Jackson, T.; Njoku, E.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Cosh, M.; Holmes, T.; De Jeu, R.; Jones, L.; Kimball, J. Remote monitoring of soil moisture using passive microwave-based techniques—Theoretical basis and overview of selected algorithms for AMSR-E. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.S.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Watts, J.M.; McElroy, S. Estimating soil moisture at the watershed scale with satellite-based radar and land surface models. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 805–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinussa, R.M.; De Jeu, R.A.; Van der Schalie, R.; Crow, W.T.; Lei, F.; Holmes, T.R. A quasi-global approach to improve day-time satellite surface soil moisture anomalies through the land surface temperature input. Climate 2016, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schalie, R.; de Jeu, R.A.; Kerr, Y.H.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Rodríguez-Fernández, N.J.; Al-Yaari, A.; Parinussa, R.M.; Mecklenburg, S.; Drusch, M. The merging of radiative transfer based surface soil moisture data from SMOS and AMSR-E. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 189, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinussa, R.M.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Lou, D.; Hagan, D.F.T.; Zhan, M.; Su, B.; Jiang, T. Improved surface soil moisture anomalies from Fengyun-3B over the Jiangxi province of the People’s Republic of China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 8950–8962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Huang, J.; Mansaray, L.R.; Wen, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X. An Improved Soil Moisture Retrieval Algorithm Based on the Land Parameter Retrieval Model for Water–Land Mixed Pixels Using AMSR-E Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7643–7657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinussa, R.; Holmes, T.; Yilmaz, M.; Crow, W. The impact of land surface temperature on soil moisture anomaly detection from passive microwave observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 3135–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, D.F.; Wang, G.; Parinussa, R.; Shi, X. Inter-comparing and improving land surface temperature estimates from passive microwaves over the Jiangsu province of the People’s Republic of China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 5563–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, D.F.T.; Parinussa, R.M.; Wang, G.; Draper, C.S. An evaluation of soil moisture anomalies from global model-based datasets over the people’s republic of China. Water 2019, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Albergel, C.; Albrecht, F.; Balsamo, G.; Brocca, L.; Chung, D.; Ertl, M.; Forkel, M.; Gruber, A. ESA CCI Soil Moisture for improved Earth system understanding: State-of-the art and future directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 203, 185–215. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ma, X.; Hagan, D.F.T.; van der Schalie, R.; Kattel, G.; Ullah, W.; Tao, L.; Miao, L.; Liu, Y. Towards Consistent Soil Moisture Records from China’s FengYun-3 Microwave Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Feng, H.; He, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of soil moisture climatology and anomaly components derived from ERA5-land and GLDAS-2.1 in China. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Inter-comparison of satellite-retrieved and Global Land Data Assimilation System-simulated soil moisture datasets for global drought analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Schalie, R.; Kerr, Y.H.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Rodríguez-Fernández, N.J.; Al-Yaari, A.; de Jeu, R.A. Global SMOS soil moisture retrievals from the land parameter retrieval model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, W.T.; Berg, A.A.; Cosh, M.H.; Loew, A.; Mohanty, B.P.; Panciera, R.; de Rosnay, P.; Ryu, D.; Walker, J.P. Upscaling sparse ground-based soil moisture observations for the validation of coarse-resolution satellite soil moisture products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Wood, E.F.; Jackson, T.J. Vegetative and atmospheric corrections for the soil moisture retrieval from passive microwave remote sensing data: Results from the Southern Great Plains Hydrology Experiment 1997. J. Hydrometeorol. 2001, 2, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D.; Dong, J.; Berg, A.A. Global soil moisture from satellite observations, land surface models, and ground data: Implications for data assimilation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Blöschl, G.; Pampaloni, P.; Calvet, J.-C.; Bizzarri, B.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Kerr, Y. Operational readiness of microwave remote sensing of soil moisture for hydrologic applications. Hydrol. Res. 2007, 38, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jeu, R.A.; Wagner, W.; Holmes, T.; Dolman, A.; Van De Giesen, N.; Friesen, J. Global soil moisture patterns observed by space borne microwave radiometers and scatterometers. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesters, A.G.; De Jeu, R.A.; Owe, M. Analytical derivation of the vegetation optical depth from the microwave polarization difference index. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 2, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, M.; de Jeu, R.; Holmes, T. Multisensor historical climatology of satellite-derived global land surface moisture. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113, F01002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Kerr, Y.; Waldteufel, P.; Saleh, K.; Escorihuela, M.-J.; Richaume, P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; De Rosnay, P.; Gurney, R.; Calvet, J.-C. L-band Microwave Emission of the Biosphere (L-MEB) Model: Description and calibration against experimental data sets over crop fields. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinussa, R.M.; Holmes, T.R.; de Jeu, R.A. Soil moisture retrievals from the WindSat spaceborne polarimetric microwave radiometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 50, 2683–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.; Xaver, A.; Vreugdenhil, M.; Gruber, A.; Hegyiova, A.; Sanchis-Dufau, A.; Zamojski, D.; Cordes, C.; Wagner, W.; Drusch, M. Global automated quality control of in situ soil moisture data from the International Soil Moisture Network. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.T.; Crow, W.T. Evaluation of assumptions in soil moisture triple collocation analysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Vogelzang, J.; Konings, A.G.; Entekhabi, D.; Piles, M.; Stoffelen, A. Extended triple collocation: Estimating errors and correlation coefficients with respect to an unknown target. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6229–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.; Reichle, R.; de Jeu, R.; Naeimi, V.; Parinussa, R.; Wagner, W. Estimating root mean square errors in remotely sensed soil moisture over continental scale domains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinussa, R.M.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.Y.; Hagan, D.F.; Lin, F.; Van der Schalie, R.; De Jeu, R.A. The Evaluation of Single-Sensor Surface Soil Moisture Anomalies over the Mainland of the People’s Republic of China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Roy, A.; Derksen, C.; Konings, A.G.; Alemohammed, S.H.; Entekhabi, D. Triple collocation for binary and categorical variables: Application to validating landscape freeze/thaw retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Fisher, C.K.; Chaney, N.W.; Zhan, W.; Crow, W.T.; Aires, F.; Entekhabi, D.; Wood, E.F. Triple collocation: Beyond three estimates and separation of structural/non-structural errors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Crow, W.T.; Shen, H.; Parinussa, R.M.; Holmes, T.R. The impact of local acquisition time on the accuracy of microwave surface soil moisture retrievals over the contiguous United States. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13448–13465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scipal, K.; Dorigo, W.; deJeu, R. Triple collocation—A new tool to determine the error structure of global soil moisture products. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 4426–4429. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, A.; Su, C.-H.; Zwieback, S.; Crow, W.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W. Recent advances in (soil moisture) triple collocation analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).