Remote Sensing of Planetary Boundary Layer Thermodynamic and Material Structures over a Large Steel Plant, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Site, Instrumentations and Methodology
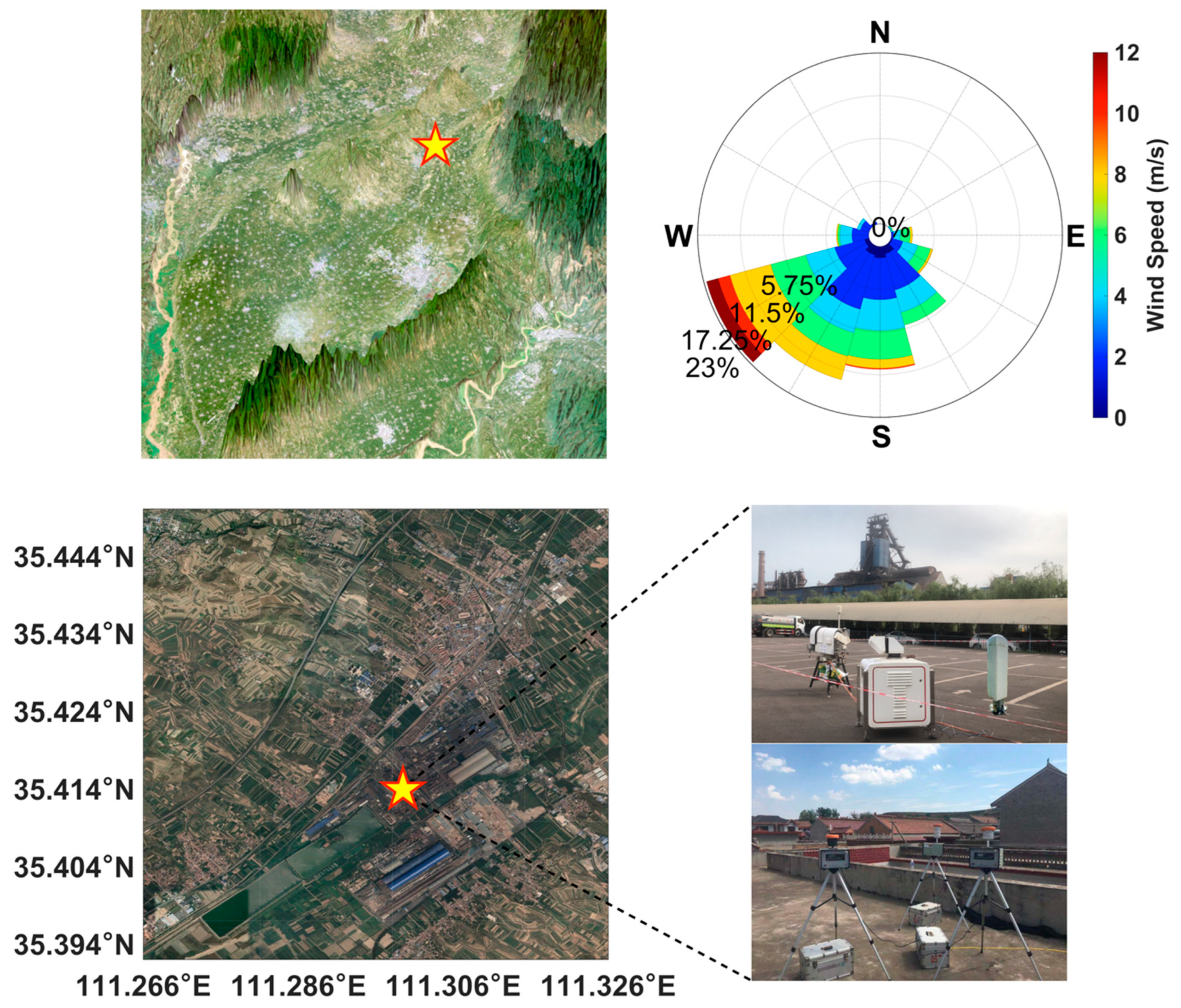
2.1. Observation Site
2.2. Instrumentations
2.2.1. Microwave Radiometer
2.2.2. Doppler Wind Lidar
2.2.3. CL51 Ceilometer
2.3. Methodology
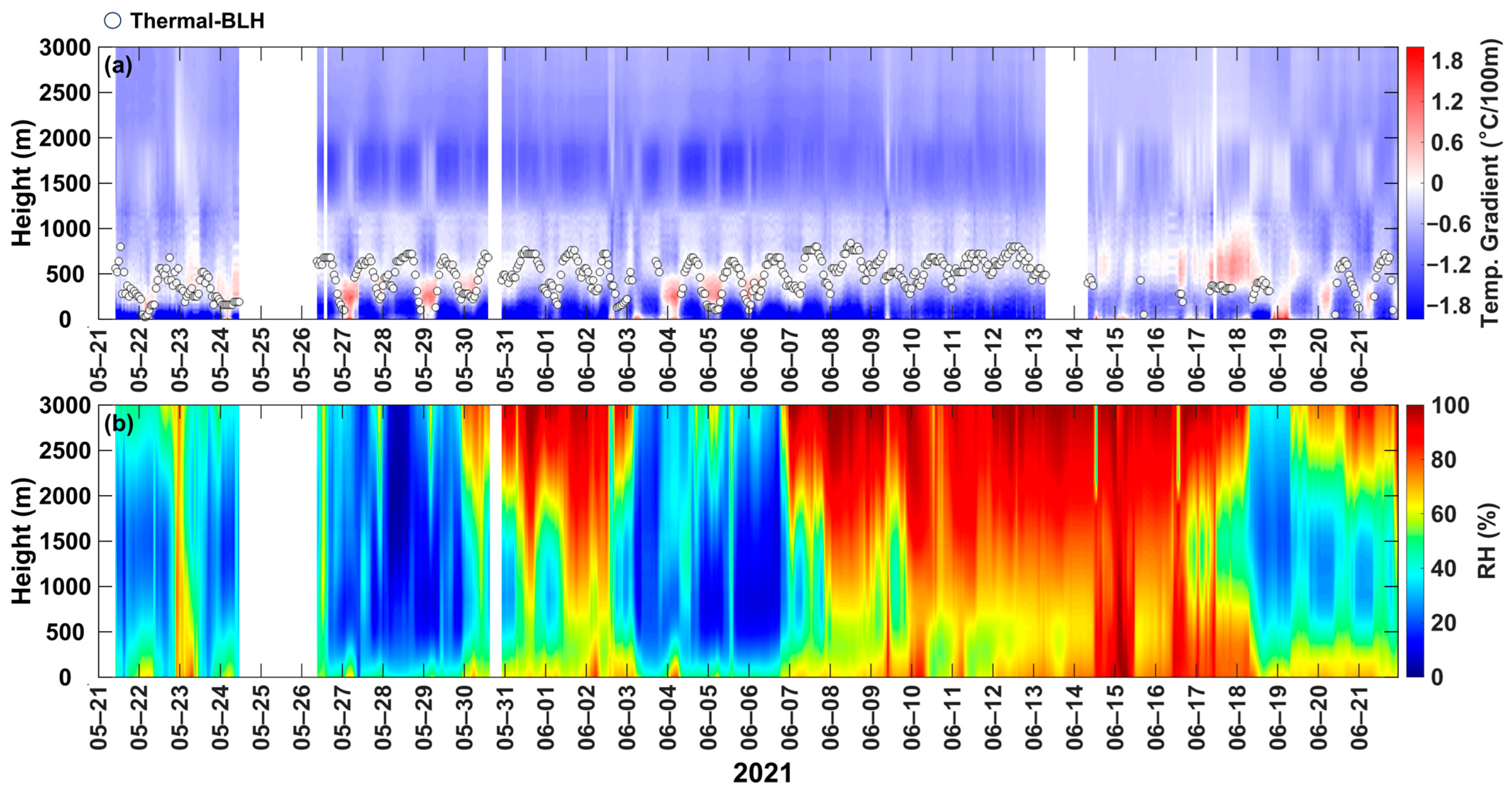
2.3.1. Temperature Inversion
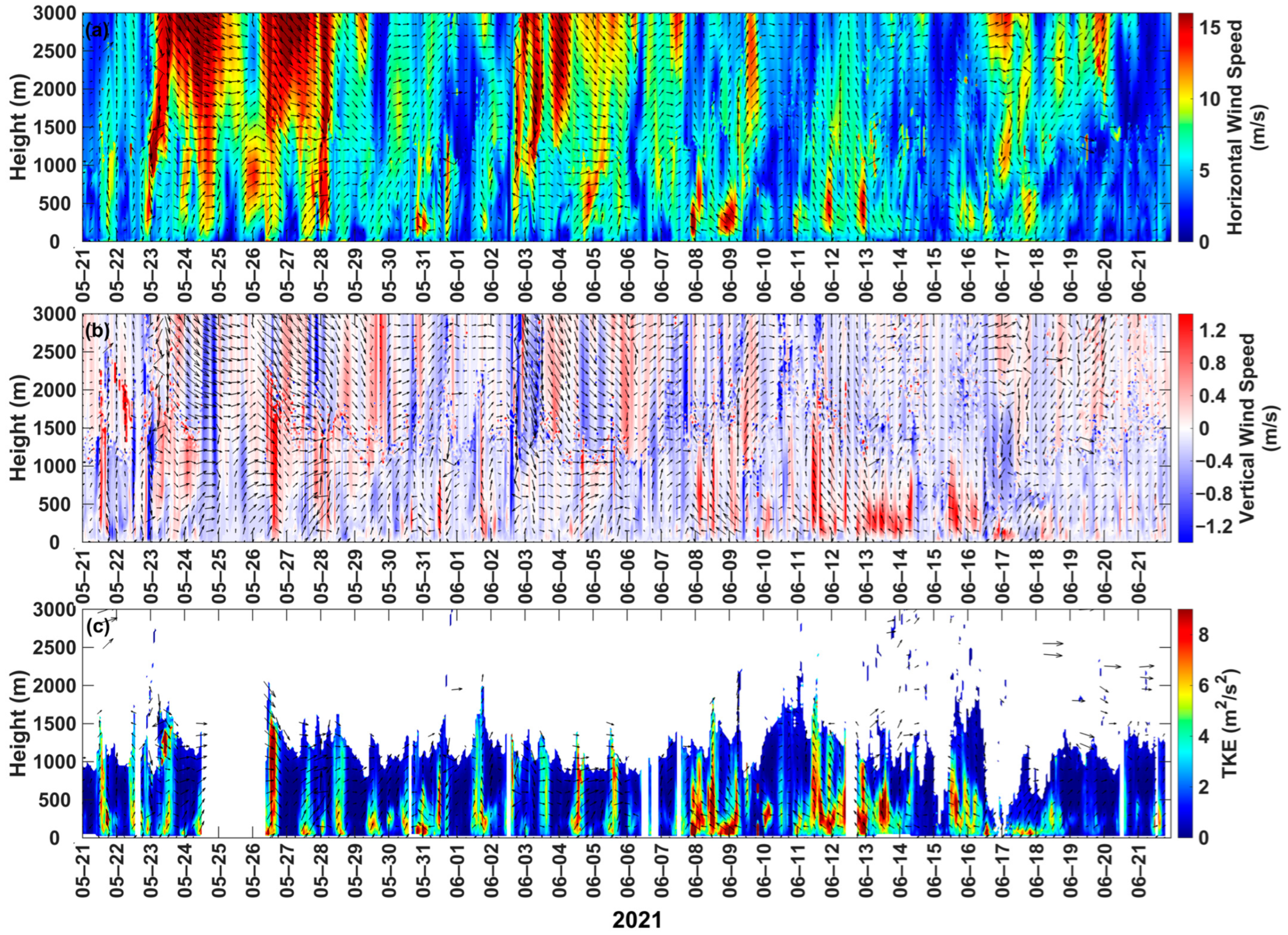
2.3.2. Turbulent Kinetic Energy (TKE)
2.3.3. Gradient Richard Number
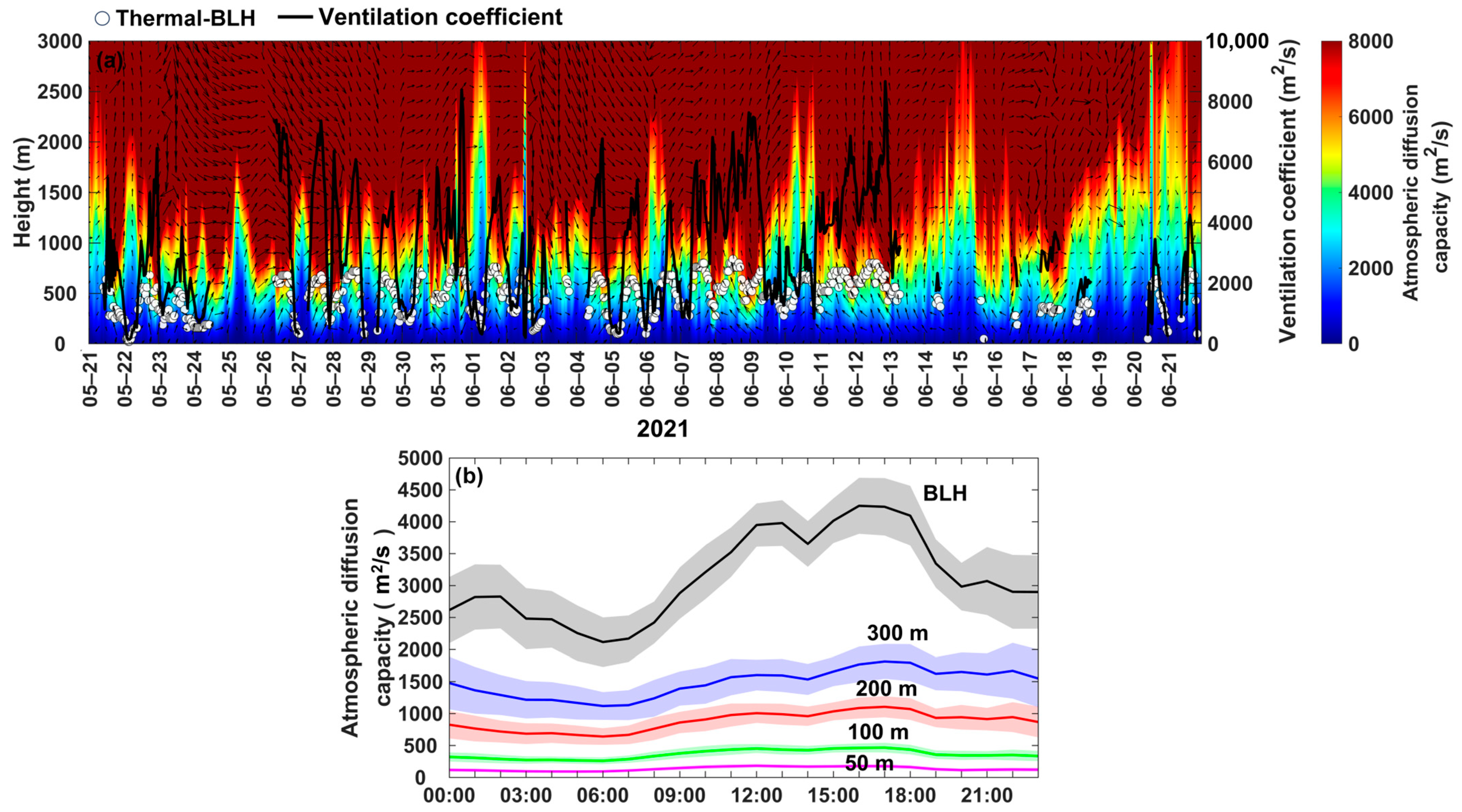
2.3.4. Ventilation Coefficient
2.3.5. Calculations of Different Types of BLH
3. Results
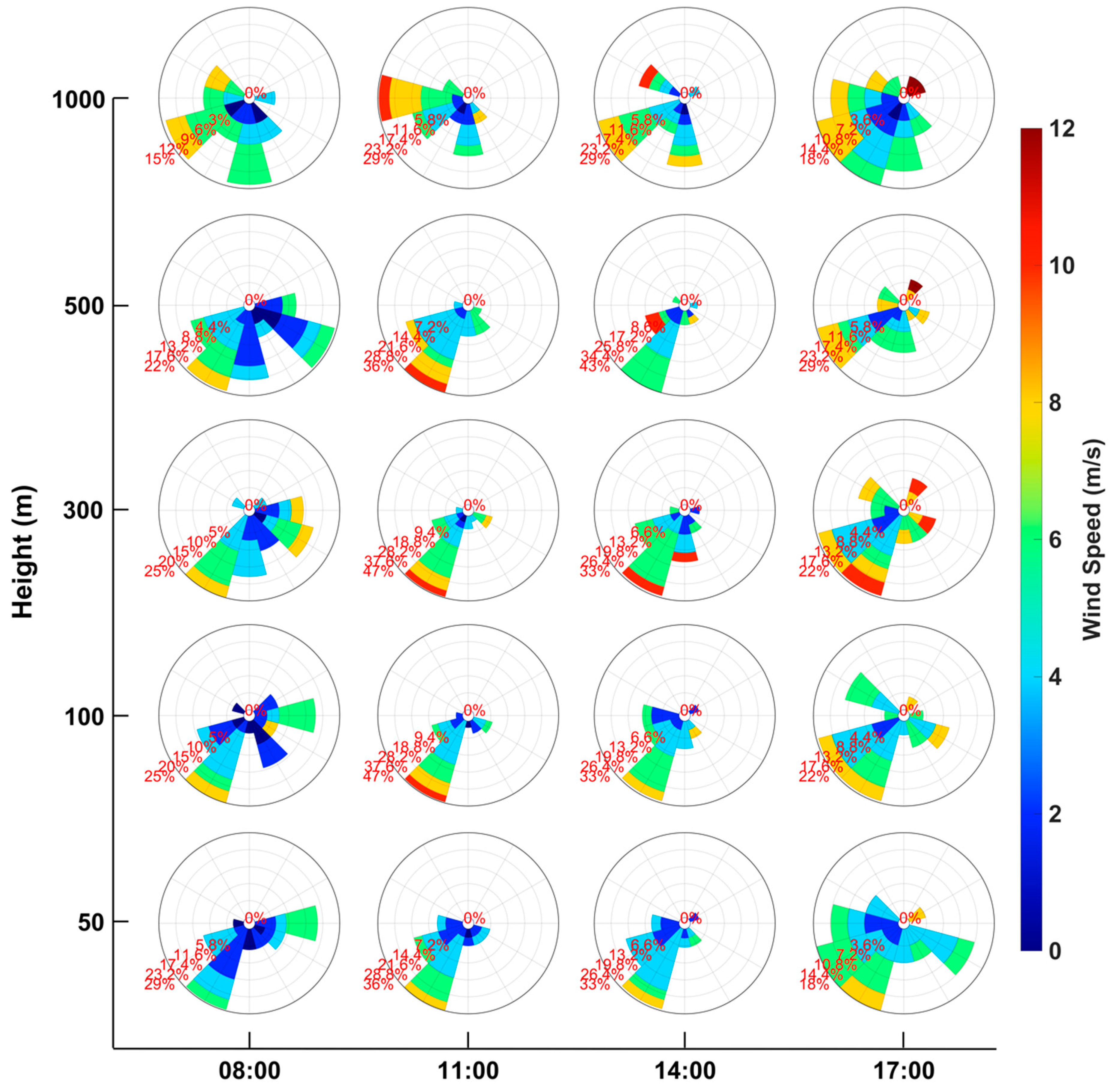
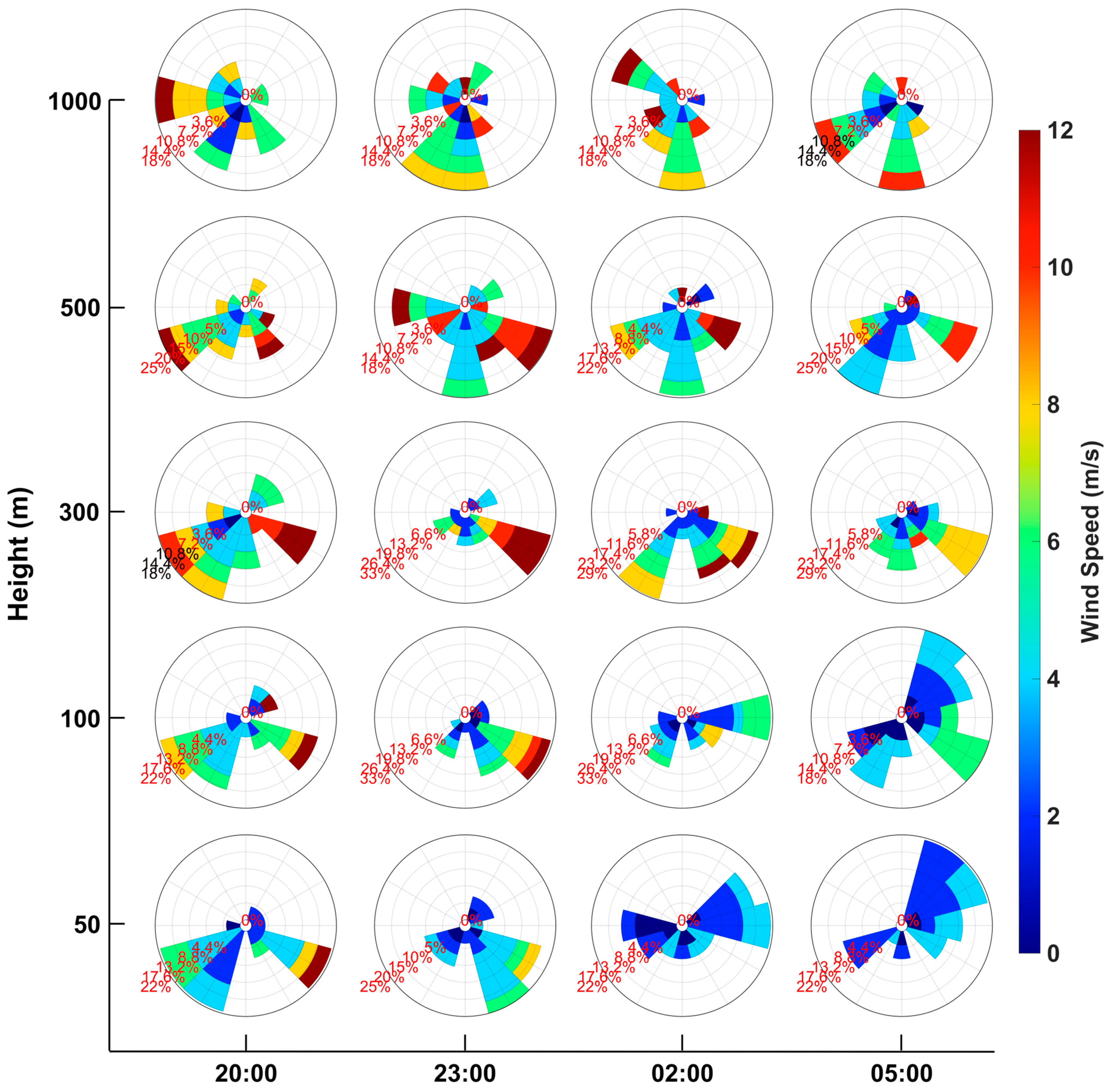
3.1. Variation of Different Types of Boundary Layer Structures
3.1.1. Thermal Boundary Layer
3.1.2. Dynamic Boundary Layer
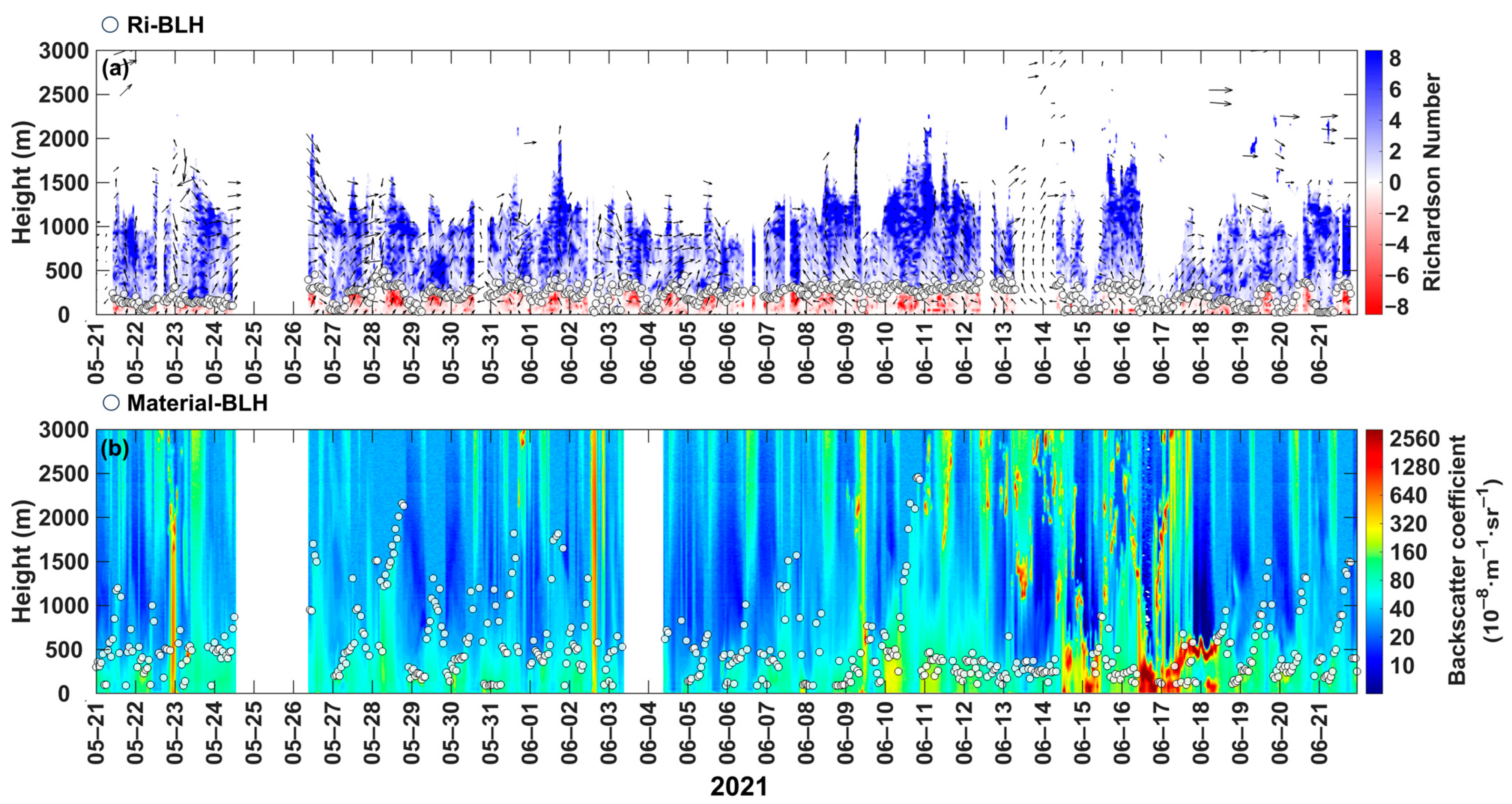
3.1.3. Material Boundary Layer
3.2. Ventilation Coefficient
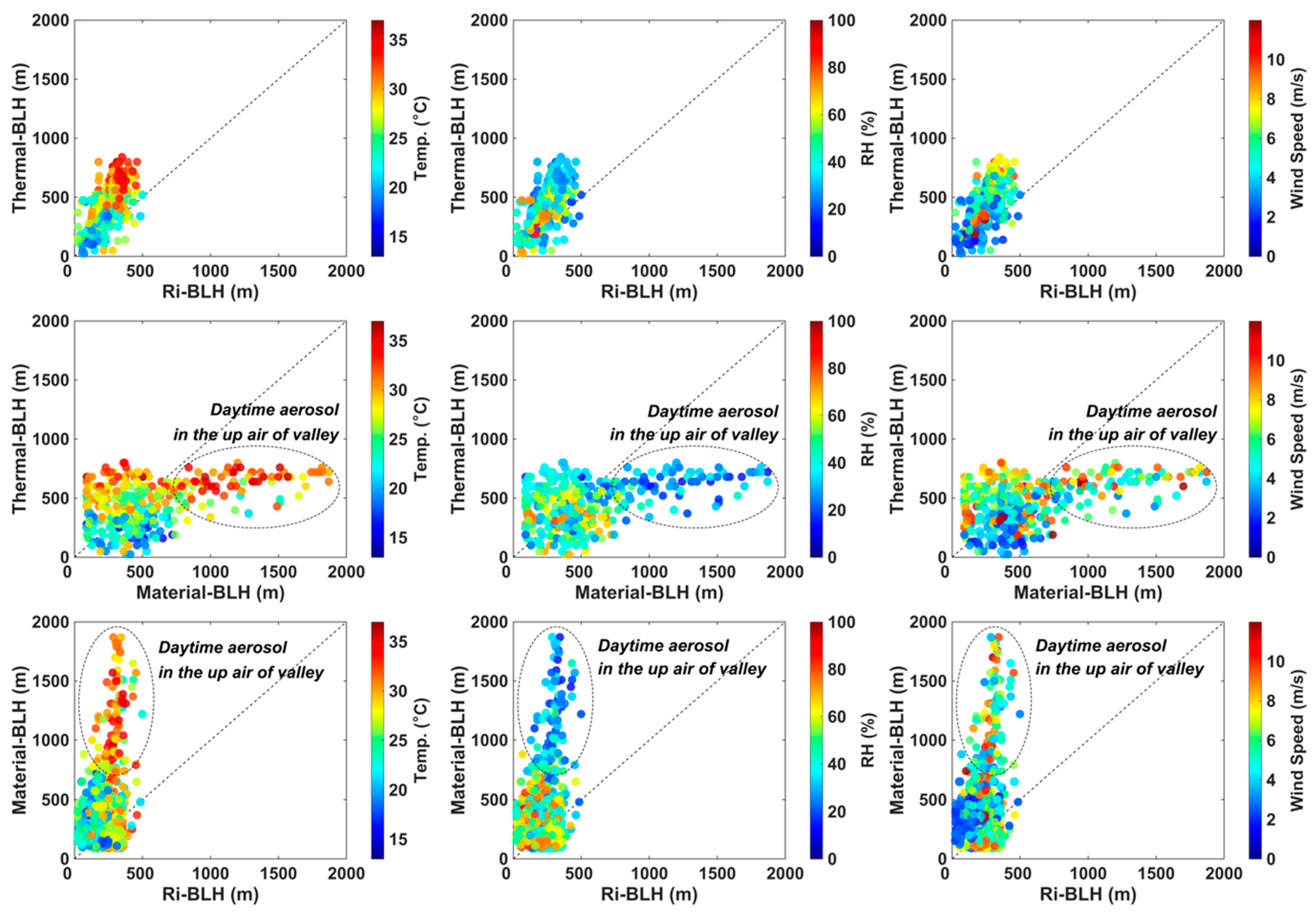
3.3. Inter-Comparison of Thermal-BLH, Ri-BLH, and Material-BLH
4. Conclusions and Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Xin, J.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Tang, G.; Ren, Y.; Wu, L.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, D.; et al. The dynamic multi-box algorithm of atmospheric environmental capacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, S.; Wang, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, H.; Miao, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Yim, S.H.L.; et al. Diurnal Evolution of the Wintertime Boundary Layer in Urban Beijing, China: Insights from Doppler Lidar and a 325-m Meteorological Tower. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, M.; Ren, G.; Liu, S.; Zong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Modulation of Wintertime Canopy Urban Heat Island (CUHI) Intensity in Beijing by Synoptic Weather Pattern in Planetary Boundary Layer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xin, J.; Yin, Y.; Chang, W.; Xue, M.; Jia, D.; Ma, Y. Understanding the Major Impact of Planetary Boundary Layer Schemes on Simulation of Vertical Wind Structure. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, G.; Xin, J.; Quan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, L.; Gao, W.; Tang, G.; Hu, B.; et al. Haze pollution under a high atmospheric oxidization capacity in summer in Beijing: Insights into formation mechanism of atmospheric physicochemical processes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 4575–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xin, J.; Gong, C.; Quan, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Dai, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, G.; et al. The impact threshold of the aerosol radiative forcing on the boundary layer structure in the pollution region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5739–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ye, J.; Xin, J.; Zhang, W.; Vilà-Guerau de Arellano, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, D.; Dai, L.; Ma, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. The Stove, Dome, and Umbrella Effects of Atmospheric Aerosol on the Development of the Planetary Boundary Layer in Hazy Regions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Pan, X.; Ma, Y.; Xin, J. Long-Term (2017–2020) Aerosol Optical Depth Observations in Hohhot City in Mongolian Plateau and the Impacts from Different Types of Aerosol. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, D.; Gong, C.; Ren, X.; Tang, G.; Xia, X.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; de Arellano, J.V.-G.; et al. The feedback effects of aerosols from different sources on the urban boundary layer in Beijing China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 325, 121440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Stanič, S.; Bergant, K.; Eichinger, W.; Močnik, G.; Drinovec, L.; Vaupotič, J.; Miler, M.; Gosar, M.; Gregorič, A. Retrieval of Vertical Mass Concentration Distributions—Vipava Valley Case Study. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Stanič, S.; Eichinger, W.; Song, X.; Zavrtanik, M. Development of an Automatic Polarization Raman LiDAR for Aerosol Monitoring over Complex Terrain. Sensors 2019, 19, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Z.; Bu, Z.; Wang, A.; Mao, S.; Yi, Y.; Müller, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Quality assessment of aerosol lidars at 1064nm in the framework of the MEMO campaign. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 4307–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, G.d.A.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Foyo-Moreno, I.; Cazorla, A.; Alados, I.; Lyamani, H.; Landulfo, E.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Study of the planetary boundary layer height in an urban environment using a combination of microwave radiometer and ceilometer. Atmos. Res. 2020, 240, 104932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, D.; Zhao, D.; Wang, M.; Dai, L.; Wang, L.; et al. The thermodynamic structures of the planetary boundary layer dominated by synoptic circulations and the regular effect on air pollution in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 6111–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Wang, Q.; Kalogiros, J.A.; Lenschow, D.H.; Gao, Z.; Zhou, M. Determining Boundary-Layer Height from Aircraft Measurements. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2014, 152, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münkel, C.; Eresmaa, N.; Räsänen, J.; Karppinen, A. Retrieval of mixing height and dust concentration with lidar ceilometer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2007, 124, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, S.; Schäfer, K. Remote Sensing Methods to Investigate Boundary-layer Structures relevant to Air Pollution in Cities. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2006, 121, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, A.M. A Prognostic Parameterization for the Subgrid-Scale Variability of Water Vapor and Clouds in Large-Scale Models and Its Use to Diagnose Cloud Cover. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 1917–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xin, J.; Wang, X.; Si, R.; Ma, Y.; Wen, T.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W. Impact of the coal banning zone on visibility in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Xin, J.; Wang, W.; Jia, D.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Tong, L.; Ma, Y.; et al. Effects of the sea-land breeze on coastal ozone pollution in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, S.; Fan, R.; Gong, W. The relationship between atmospheric boundary layer and temperature inversion layer and their aerosol capture capabilities. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271, 106121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.F.; Cao, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, N.X.; Sun, L.; Logan, T.; Shi, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Y.M.; Lin, Y.; et al. Aerosol vertical distribution and optical properties over China from long-term satellite and ground-based remote sensing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2509–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.F.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.M.; Tang, K.; Xu, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.J.; Liang, J.N.; Ji, Y.M.; Jiang, J.H.; et al. Radiative absorption enhancement of dust mixed with anthropogenic pollution over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7815–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.F.; Yu, Z.R.; Cui, C.; Huang, J.P.; Kang, C.L.; Shi, J.S.; Cao, X.J.; Zhang, L. Atmospheric aerosol size distribution impacts radiative effects over the Himalayas via modulating aerosol single-scattering albedo. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.H.; Won, H.Y.; Han, D.; Kim, Y.H.; Ha, J.C. Characterization of downwelling radiance measured from a ground-based microwave radiometer using numerical weather prediction model data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xin, J.; Gong, C.; Quan, J.; Liu, G.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Song, T. The formation mechanism of air pollution episodes in Beijing city: Insights into the measured feedback between aerosol radiative forcing and the atmospheric boundary layer stability. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadillas, B.A.; Bégué, A.; Neumann, T. Comparison of turbulence spectra derived from LiDAR and sonic measurements at the offshore platform FINO1. In Proceedings of the 10th German Wind Energy Conference 2010, Bremen, Germany, 17–18 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Xin, J.; Zuo, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Ma, Y.; Jia, D.; Wu, F. Multilevel Validation of Doppler Wind Lidar by the 325 m Meteorological Tower in the Planetary Boundary Layer of Beijing. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zhu, X.; Hu, B.; Xin, J.; Wang, L.; Münkel, C.; Mao, G.; Wang, Y. Impact of emission controls on air quality in Beijing during APEC 2014: Lidar ceilometer observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12667–12680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Song, T.; Münkel, C.; Hu, B.; Schäfer, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Mixing layer height and its implications for air pollution over Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2459–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M.; Pichugina, Y.L.; Brewer, W.A. Turbulent Velocity-Variance Profiles in the Stable Boundary Layer Generated by a Nocturnal Low-Level Jet. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 2700–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Fan, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Miao, S.; Zou, H.; et al. Vertical observations of the atmospheric boundary layer structure over Beijing urban area during air pollution episodes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6949–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakh, V.A.; Smalikho, I.N.; Falits, A.V. Wind–Temperature Regime and Wind Turbulence in a Stable Boundary Layer of the Atmosphere: Case Study. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. A Simulation Study on the Structure of the Urban Boundary Layer and the Diffusion of SO2 Pollutants over Shenyang; Peking University: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Tang, G.; Lv, F.; Hu, B.; Cheng, M.; Münkel, C.; Schäfer, K.; Xin, J.; An, X.; Wang, G.; et al. The spatial representativeness of mixing layer height observations in the North China Plain. Atmos. Res. 2018, 209, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, F.; Jia, D.; Zhao, D.; Xin, J. Remote Sensing of Planetary Boundary Layer Thermodynamic and Material Structures over a Large Steel Plant, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15215104
Ren X, Zhao L, Ma Y, Wu J, Zhou F, Jia D, Zhao D, Xin J. Remote Sensing of Planetary Boundary Layer Thermodynamic and Material Structures over a Large Steel Plant, China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(21):5104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15215104
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xinbing, Liping Zhao, Yongjing Ma, Junsong Wu, Fentao Zhou, Danjie Jia, Dandan Zhao, and Jinyuan Xin. 2023. "Remote Sensing of Planetary Boundary Layer Thermodynamic and Material Structures over a Large Steel Plant, China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 21: 5104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15215104
APA StyleRen, X., Zhao, L., Ma, Y., Wu, J., Zhou, F., Jia, D., Zhao, D., & Xin, J. (2023). Remote Sensing of Planetary Boundary Layer Thermodynamic and Material Structures over a Large Steel Plant, China. Remote Sensing, 15(21), 5104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15215104







