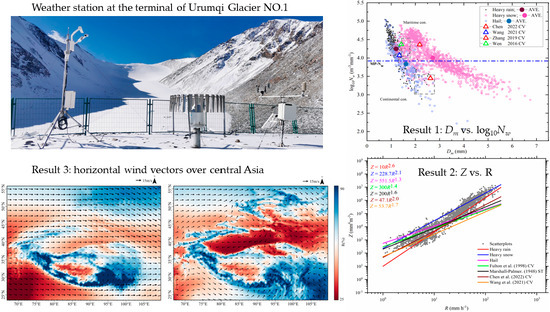
Raindrop Size Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events Based on a PWS100 Disdrometer in the Alpine Mountains, Eastern Tianshan, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Methodology
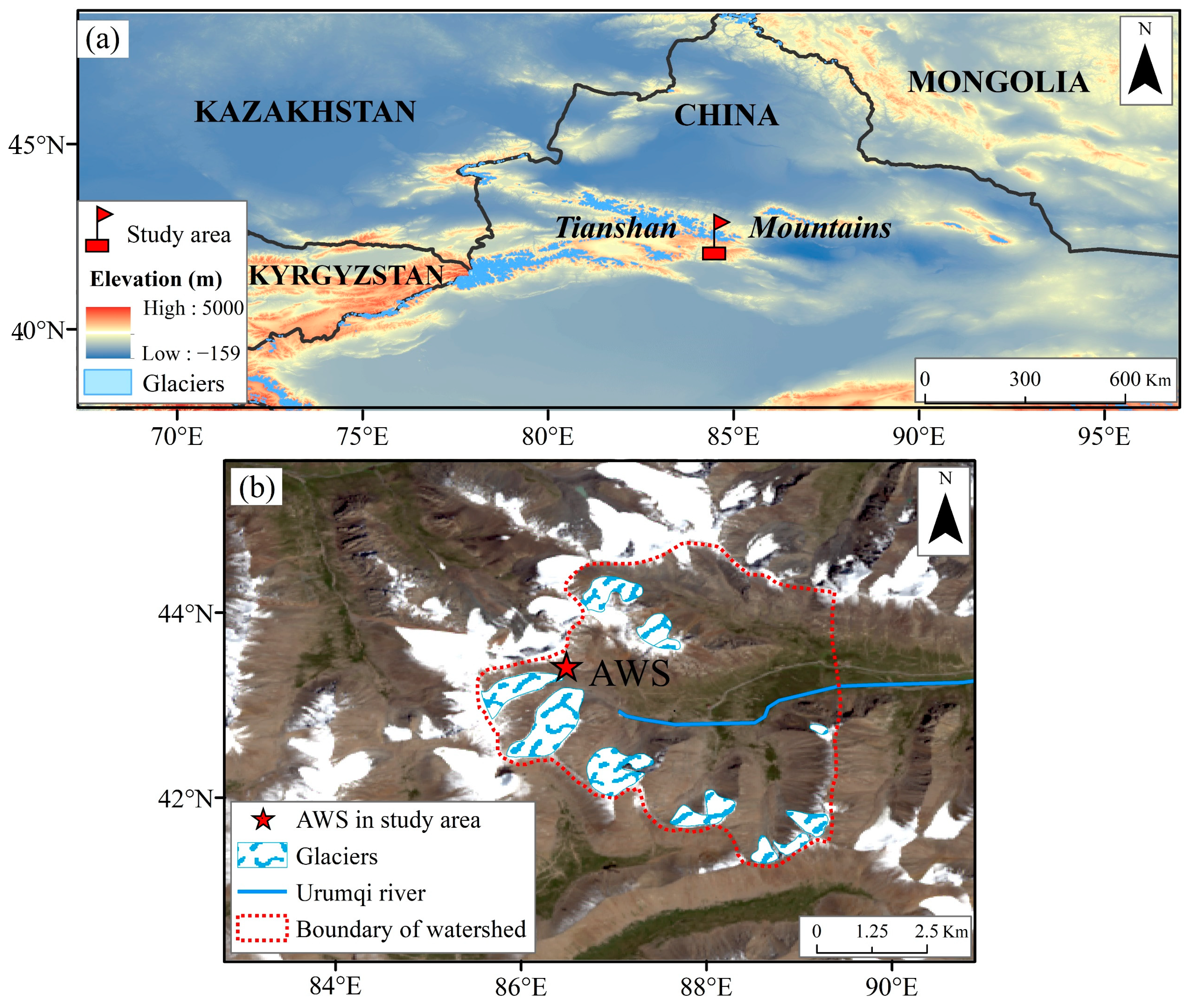
2.1. PWS100 Disdrometer and Dataset
2.2. Methodology
2.3. Quality Control
3. Results and Analyses
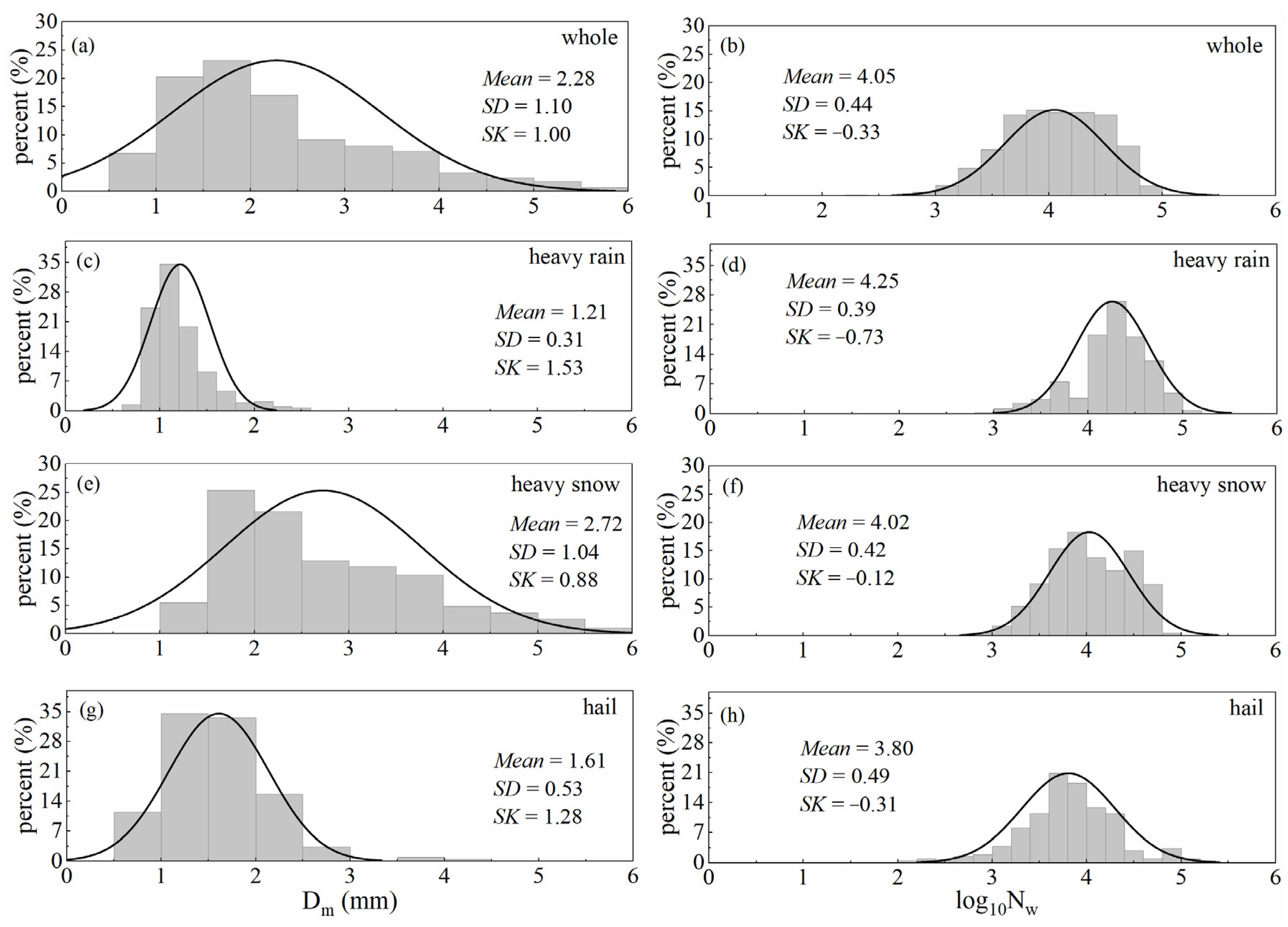
3.1. Characteristics of Dm and Nw
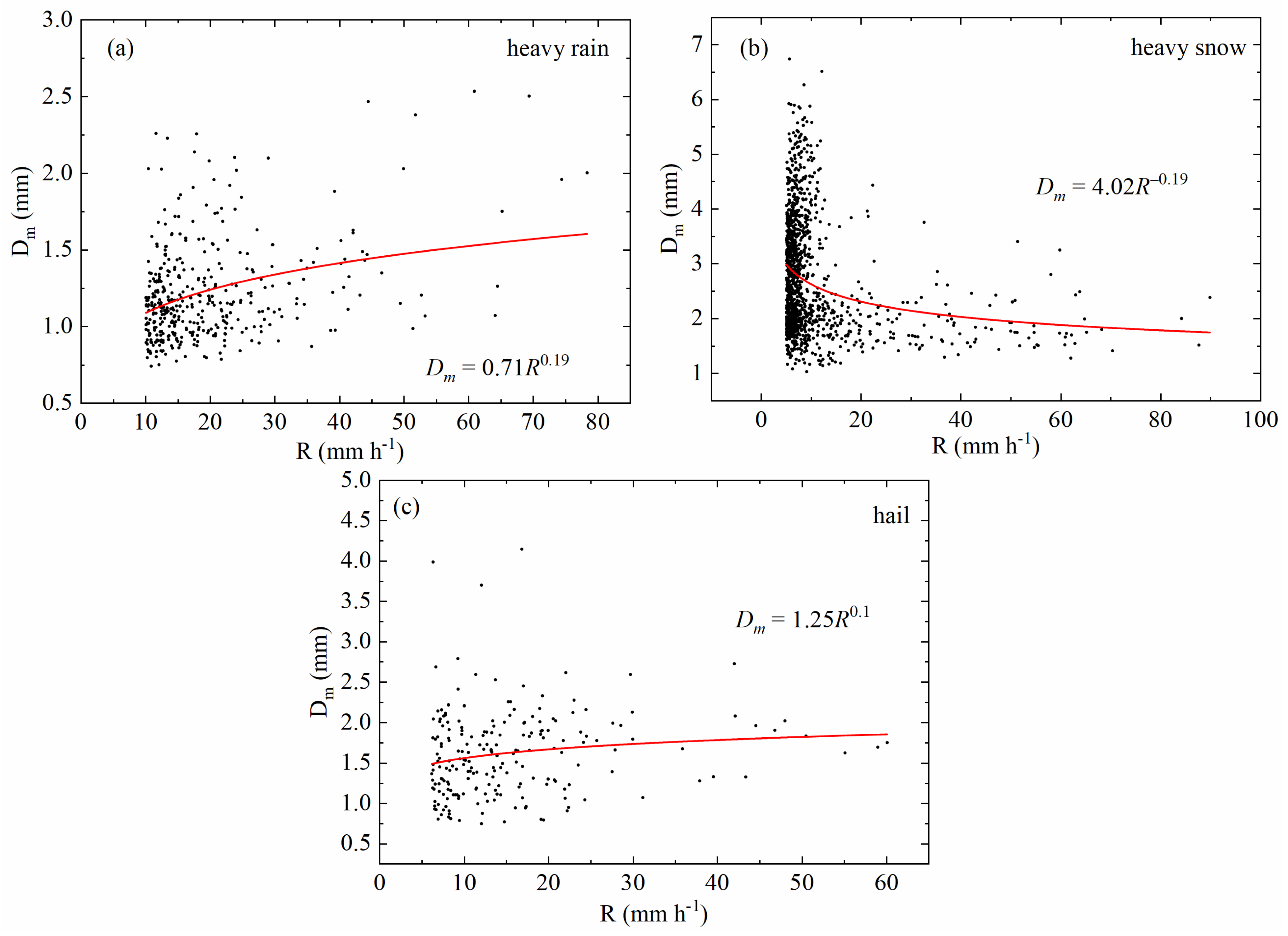
3.2. Characteristics of the DSD for Different Precipitation Patterns
3.3. Z-R Relationship
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rincon, R.F.; Lang, R.H. Microwave link dual-wavelength measurements of path-average attenuation for the estimation of drop size distributions and rainfall. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, C.; Prodi, F.; Battaglia, A.; Porcu, F. Analysis of the moments and parameters of a gamma DSD to infer precipitation properties: A convective stratiform discrimination algorithm. Atmos. Res. 2006, 80, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Sun, J.; Brandes, E.A. Improving parameterization of rain microphysics with disdrometer and radar observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adirosi, E.; Baldini, L.; Lombardo, F.; Russo, F.; Napolitano, F.; Volpi, E.; Tokay, A. Comparison of different fittings of drop spectra for rainfall retrievals. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 83, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Martínez, M.; Barros, A.P. Measurement uncertainty in rainfall kinetic energy and intensity relationships for soil erosion studies: An evaluation using PARSIVEL disdrometers in the Southern Appalachian Mountains. Geomorphology 2015, 228, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanko, K.; Moskalski, S.M.; Torres, R. Rainfall erosivity–intensity relationships for normal rainfall events and a tropical cyclone on the US southeast coast. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhao, K.; Huang, H.; Zhou, B.; Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, M.; Wen, L.; Dai, H.; Xu, L.; et al. Evolution of microphysical structure of a subtropical squall line observed by a polarimetric radar and a disdrometer during OPACC in Eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 8033–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavian, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Cerda, A.; Fallah, M.; Abdollahi, Z. Simulated raindrop’s characteristic measurements. A new approach of image processing tested under laboratory rainfall simulation. Catena 2018, 167, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, K.; Lee, W.C.; Zhang, F. Microphysical and kinematic structure of convective-scale elements in the inner rainband of Typhoon Matmo (2014) after landfall. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6549–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, K.V.; Johnson, D.B.; Baumgardner, D. Aircraft observations of large raindrops in warm, shallow, convective clouds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1986, 13, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Zrnić, D.S. Comparison of dual-polarization radar estimators of rain. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Chen, B.; Xiao, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, G. Raindrop size distributions and rain characteristics observed by a PARSIVEL disdrometer in Beijing, Northern China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarquhar, G.M.; Hsieh, T.L.; Freer, M.; Mascio, J.; Jewett, B.F. The characterization of ice hydrometeor gamma size distributions as volumes in N0–λ–μ phase space: Implications for microphysical process modeling. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 892–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, C.; Napoli, M.; Porcù, F.; Prodi, F.; Dietrich, S.; Zanchi, C.; Orlandini, S. Raindrop size distribution and soil erosion. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygin, S.D.; Erpul, G. Modeling aggregate size distribution of eroded sediment resulting from rain-splash and raindrop impacted flow processes. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2019, 34, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janapati, J.; Seela, B.K.; Lin, P.L.; Wang, P.K.; Kumar, U. An assessment of tropical cyclones rainfall erosivity for Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.L.; Schoenhuber, M. Raindrop size distribution in different climatic regimes from disdrometer and dual-polarized radar analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna UV, M.; Reddy, K.K.; Seela, B.K.; Shirooka, R.; Lin, P.L.; Pan, C.J. Raindrop size distribution of easterly and westerly monsoon precipitation observed over Palau islands in the Western Pacific Ocean. Atmos. Res. 2016, 174, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janapati, J.; Reddy, V.; Reddy, K.; Lin, P.L.; Liu, C.Y. A study on raindrop size distribution variability in before and after landfall precipitations of tropical cyclones observed over southern India. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2017, 159, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seela, B.K.; Janapati, J.; Lin, P.L.; Reddy, K.K.; Shirooka, R.; Wang, P.K. A comparison study of summer season raindrop size distribution between Palau and Taiwan, two islands in western Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 787-11,805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumesh, R.K.; Resmi, E.A.; Unnikrishnan, C.K.; Jash, D.; Sreekanth, T.S.; Resmi, M.M.; Rajeevan, k.; Nita, S.; Ramachandran, K.K. Microphysical aspects of tropical rainfall during Bright Band events at mid and high-altitude regions over Southern Western Ghats, India. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 178–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, H.; Kang, X.; Tian, J.; Guo, S. Characteristics of Raindrop Size Distribution for Different Precipitation Clouds in Longbao Area of the Three-River Source Region. Plateau Mt. Meteorol. Res. 2022, 42, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, P. Characteristics of orographic raindrop size distribution in the Tianshan Mountains, China. Atmos. Res. 2022, 278, 106332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Sun, Y.; Feng, L. Raindrop size distribution and microphysical characteristics of a great rainstorm in 2016 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 239, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.; Sun, J.H.; Lu, R.; Fu, S. Analysis of the 20 July 2016 unusual heavy rainfall in North China and Beijing. Meteorol. Mon. 2018, 44, 351–360. [Google Scholar]
- Min, A.; Liao, Y.; Deng, W. The analysis of the distribution and trend for heavy rainfall based on the precipitation data from 2008 to 2013 in China. Torrential Rain Disasters 2016, 35, 576–584. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Lu, Y.; Hua, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X. Evaluating the Variability of Simulated Raindrop Size Distributions in the “21· 7” Henan Extremely Heavy Rainfall Event. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL102849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarquhar, G.M. Raindrop size distribution and evolution. Rainfall State Sci. 2010, 191, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Tian, W.; Xiao, H.; Cheng, B.; Liu, L.; Sha, X.; Song, C.; Sun, Y.; Shu, W. Raindrop size distribution and microphysical features of the extremely severe rainstorm on 20 July 2021 in Zhengzhou, China. Atmos. Res. 2023, 289, 106739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, B.; Fuchs, B.; Rutledge, S.A.; Barnes, E.A.; Thompson, E.J. Primary modes of global drop size distributions. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 1453–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, A.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Liu, C.; Zipser, E.J. Weak linkage between the heaviest rainfall and tallest storms. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, F.; Terao, T.; Chakravarty, K.; Syiemlieh, H.J.; Cajee, L. Characteristics of orographic rain drop-size distribution at Cherrapunji, Northeast India. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chen, H.; Wei, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, T. Extreme precipitation produced by relatively weak convective systems in the tropics and subtropics. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, A.; Bolch, T.; Stoffel, M.; Solomina, O.; Beniston, M. Climate change impacts on glaciers and runoff in Tien Shan (Central Asia). Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Fang, G.; Li, Z. Changes in Central Asia’s water tower: Past, present and future. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, E.F.; Zawadzki, I.; Petitdidier, M.; Fernandez, W. Measurement of raindrop size distributions in tropical rain at Costa Rica. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, S.; Han, D.; Lv, G. Estimation of rainfall erosivity based on WRF-derived raindrop size distributions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 5407–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, L.; Tong, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, J. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution during rainy seasons in Northwest China. Adv. Meteorol. 2021, 2021, 6667786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Guo, L.; Duan, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Lou, X.; Chen, B. Characteristics of raindrop size distributions during Meiyu season in Mount Lushan, eastern China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2022, 100, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jung, W.; Suh, S.H.; Lee, D.I.; You, C.H. The characteristics of raindrop size distribution at windward and leeward side over mountain area. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhang, W.; Kou, M. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution during rainy seasons in Complicated Mountain Terrain. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Yang, M.; Jia, Y.; Peng, J. Raindrop size distribution characteristics in summer of a nival glacial zone in eastern Tianshan, Central Asia. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 976732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tstsuo, O.; Bai, Z.; Ding, L. Development of Local Climate in the Glaciated Area in the Head of Urumqi River. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 1989, 11, 325–335. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, S. Quantitative Analysis of the Glacial Effect on Precipitation of Glacier No.1 at the Headwaters of the Urumqi River, Tianshan Mountains. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2000, 22, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Ming, J.; Wei, W. Microclimate measurements related to glacier cooling effect at No. 1 glacier, headwater of Urumqi River, Tianshan Mountains. Arid. Land Geo 2011, 34, 449–457. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, F.; Li, H. Observed changes in streamflow at the headwaters of the Urumqi River, eastern Tianshan, central Asia. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2010, 24, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, L.L.; Zambon, N.; Strauss, P.; Dostal, T.; Neumann, M.; Zumr, D.; Cochrane, T.A.; Blöschl, G.; Klik, A. Comparison of three types of laser optical disdrometers under natural rainfall conditions. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.A.; Sandford, A.P.; Jones, G.E.; Richards, J.; Petzing, J.; Coupland, J.M. New laser technology to determine present weather parameters. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, C.W. Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribution. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, C.W.; Atlas, D. Rainfall microphysics and radar properties: Analysis methods for drop size spectra. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1998, 37, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Vivekanandan, J.; Brandes, E.A.; Meneghini, R.; Kozu, T. The shape–slope relation in observed gamma raindrop size distributions: Statistical error or useful information? J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Martínez, G.; Gómez-Balvás, S.S.; García-García, F. Study of rain classification and the tendency of gamma DSD parameterizations in Mexico. Atmos. Res. 2021, 252, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, P.T. Functional fits to some observed drop size distributions and parameterization of rain. J. Atmos. Sci. 1984, 41, 1648–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testud, J.; Oury, S.; Black, R.A.; Amayenc, P.; Dou, X. The concept of “normalized” distribution to describe raindrop spectra: A tool for cloud physics and cloud remote sensing. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2001, 40, 1118–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell Scientific, Inc. PWS100 Present Weather Sensor; Instruction Manual. Revision 9/15; Campbell Scientific, Inc.: Logan, UT, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Pu, J. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the Meiyu season observed in eastern China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2013, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, R.A.; Breidenbach, J.P.; Seo, D.J.; Miller, D.A.; O’Bannon, T. The WSR-88D rainfall algorithm. Weather. Forecast. 1998, 13, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, R.; Zhaxi, S.; Liu, S. Raindrop size distribution measurements on the Southeast Tibetan Plateau during the STEP project. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, D.; Liang, Z.; Huang, C.; Xiao, L.; Min, C.; Li, H. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the monsoon season observed in southern China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W.M.K. The distribution of raindrops with size. J. Atmos. Sci. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, L.; Tong, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhou, Y. Characteristics and Applications of Summer Season Raindrop Size Distributions Based on a PARSIVEL2 Disdrometer in the Western Tianshan Mountains (China). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, Z.; Jiang, Y. Statistical Characteristics of Summer Season Raindrop Size Distribution in the Western and Central Tianshan Mountains in China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2022, 100, 855–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G. Raindrop size distribution measurements at 4,500 m on the Tibetan Plateau during TIPEX-III. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 11092–11106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcù, F.; D’adderio, L.P.; Prodi, F.; Caracciolo, C. Effects of altitude on maximum raindrop size and fall velocity as limited by collisional breakup. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

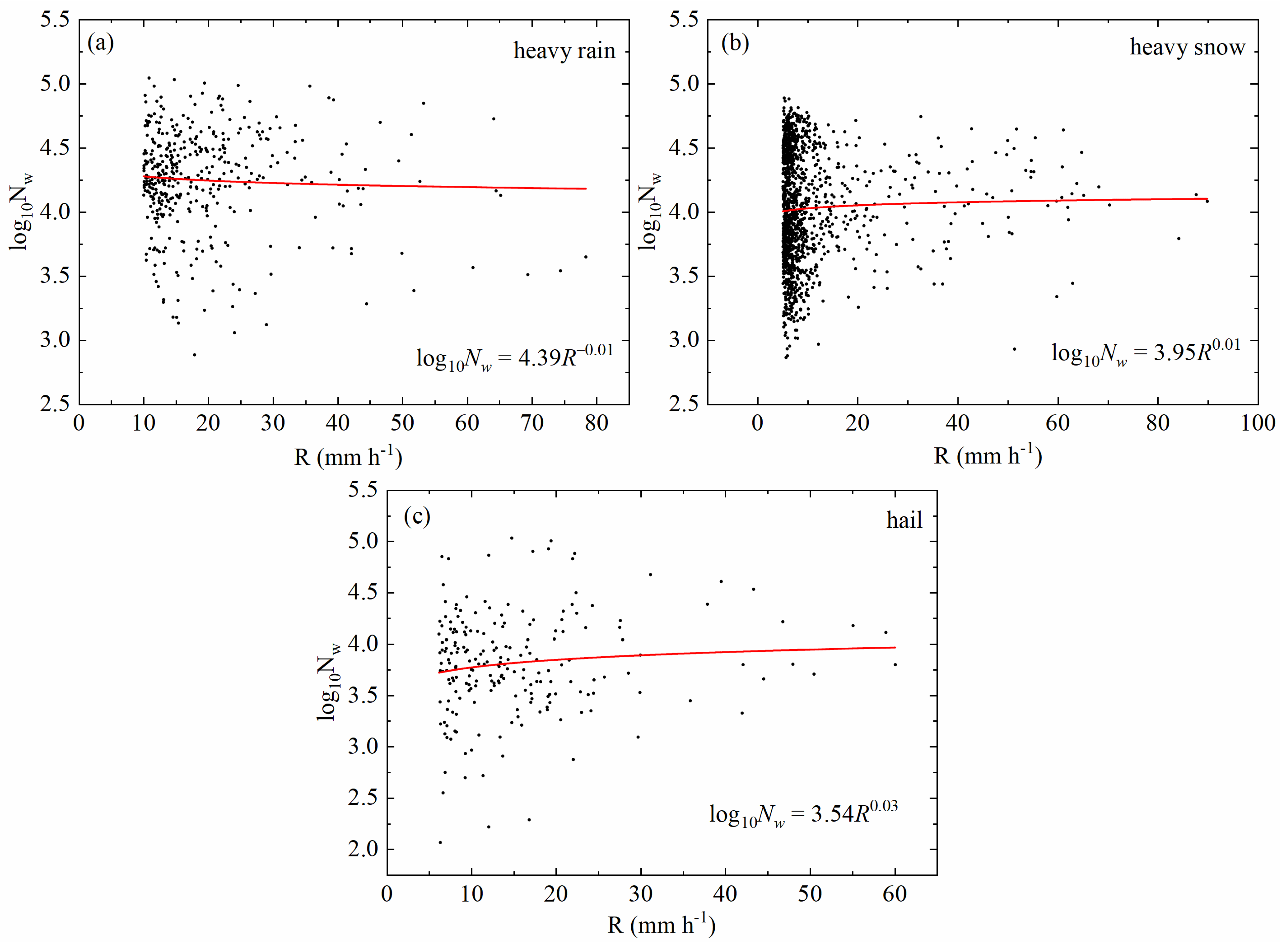
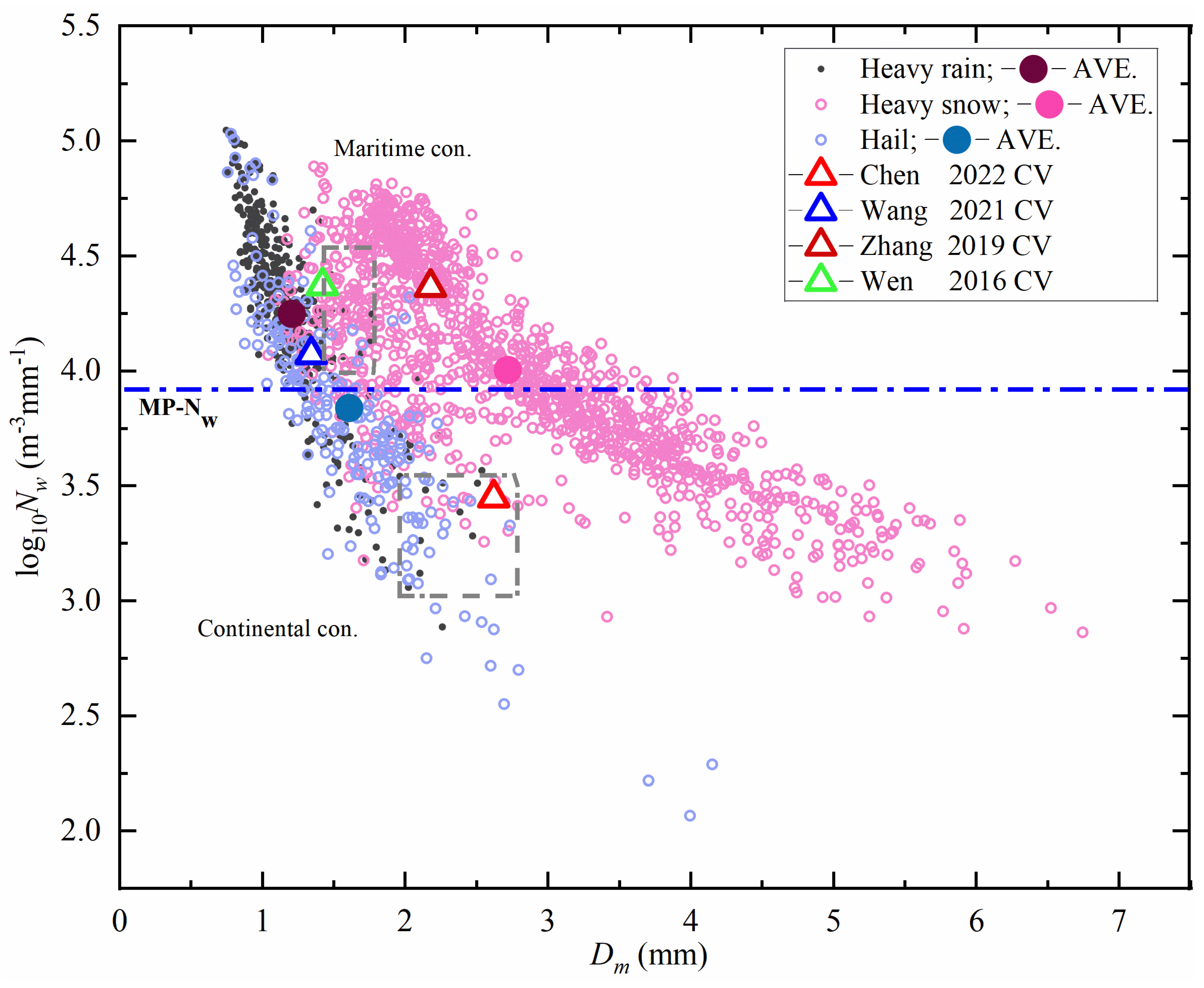


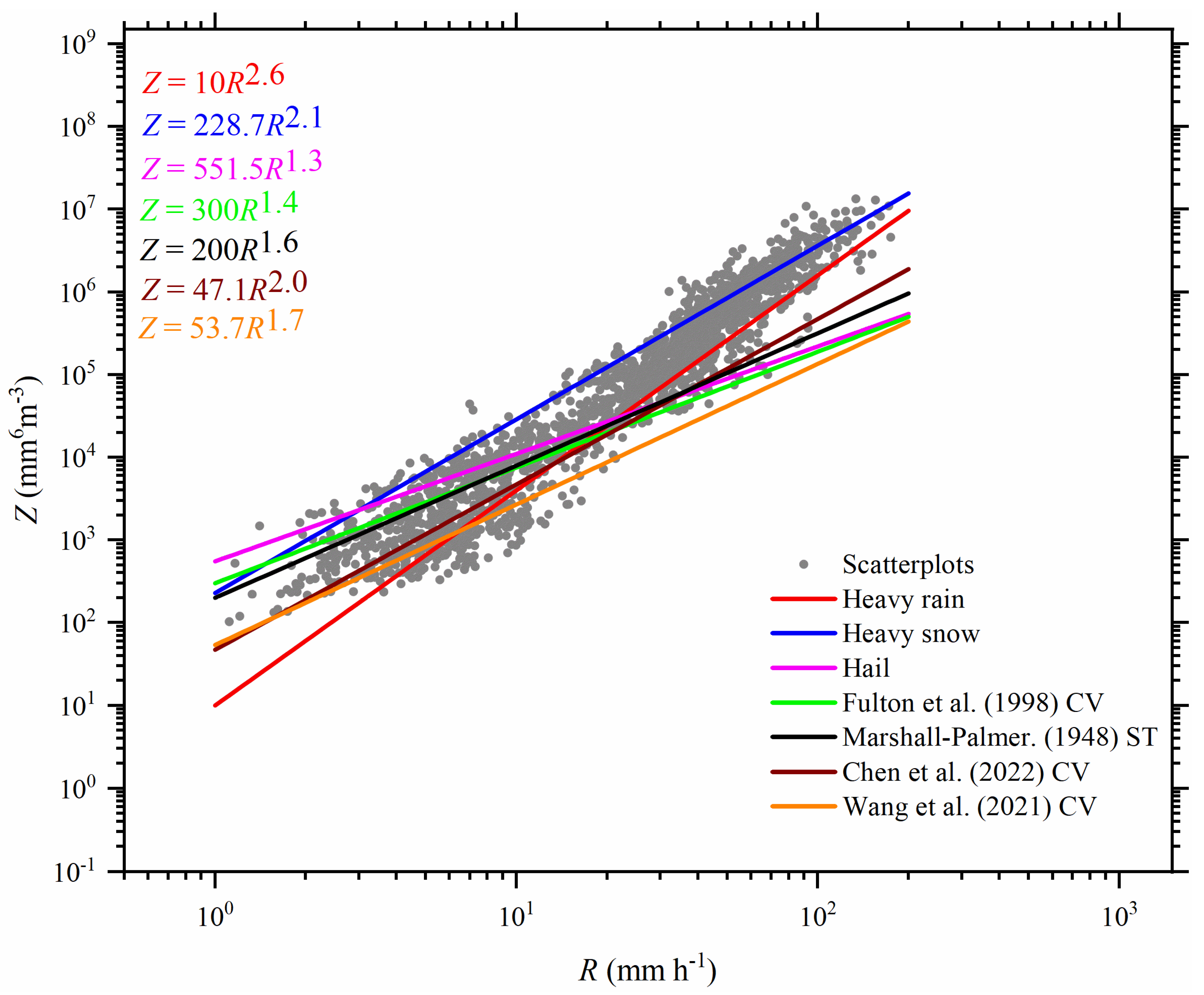
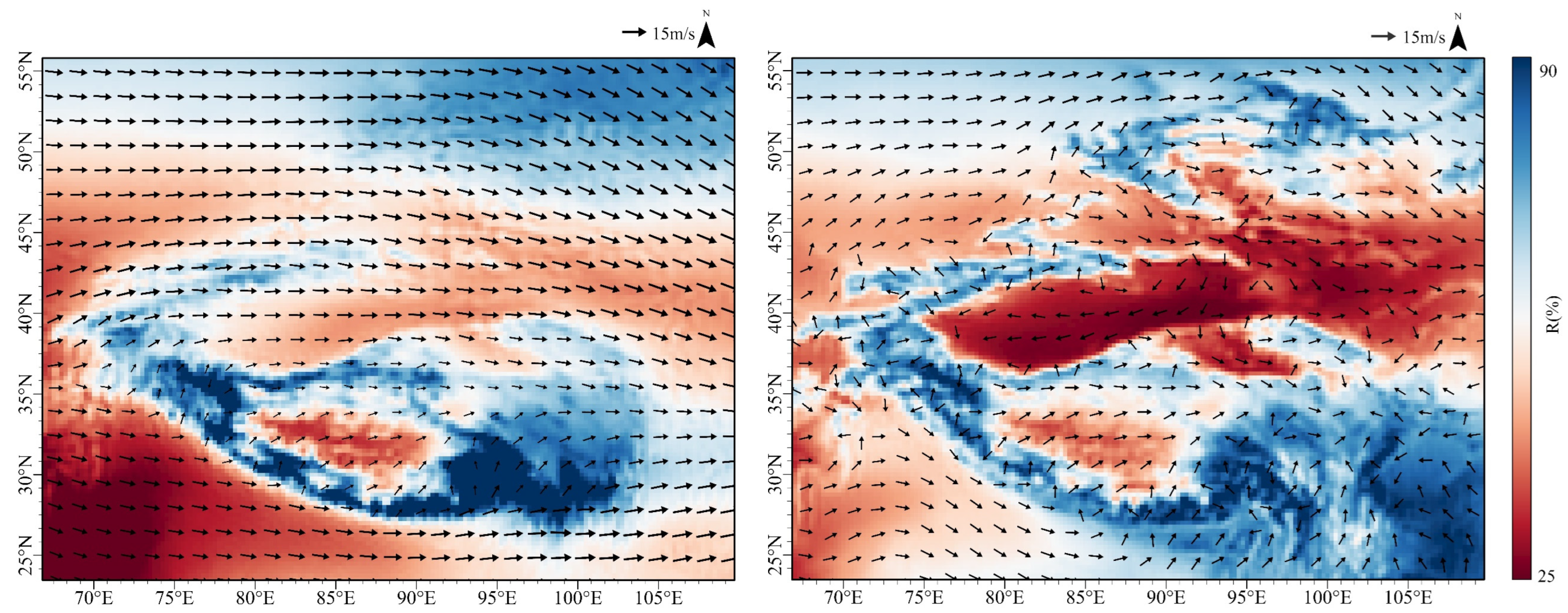
| Precipitation Pattern | No. of Rain Events | No. of Minute Spectra | Rain Accumulation (mm) | Rain Rate (mm h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy rainfall | 43 | 931 | 176.6 | 19.4 |
| Heavy snow | 69 | 2266 | 277.4 | 10.6 |
| Hail | 31 | 651 | 67.4 | 15.4 |
| Precipitation Pattern | Intensity Bounds of Rain, Snow and Hail (mm h−1) |
|---|---|
| Heavy rainfall | R ≥ 10.0 |
| Heavy snow | R ≥ 5.0 |
| Hail | R ≥ 6.7 |
| Rain Type | Nt | W | Z | Dm | Log10Nw | N0 | μ | Λ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m−3 | g m−3 | dBZ | mm | Nw in m−3mm−1 | m−3mm−(1+μ) | mm−1 | ||
| Heavy rain | 615 | 0.49 | 31.3 | 1.21 | 4.25 | 3,845,043 | 6.90 | 8.39 |
| Heavy snow | 815 | 7.67 | 52.3 | 2.72 | 4.02 | 3079 | 4.84 | 2.67 |
| Hail | 331 | 0.54 | 34.7 | 1.61 | 3.80 | 272,287 | 7.88 | 6.80 |
| Whole | 719 | 5.34 | 45.8 | 2.28 | 4.05 | - | - | - |
| Location | Cloud | R | Nt | W | Z | Dm | Log10Nw | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm h−1 | m−3 | g m−3 | dBZ | mm | Nw in m−3mm−1 | |||
| Zhuhai, Guangdong | Zhang et al. (2019) [59] | CV | 32.6 | 758 | 8.07 | - | 2.21 | 4.36 |
| Shunyi, Beijing | Wen et al. (2017) [7] | CV | 17.6 | 1522 | 0.86 | 42.1 | 1.78 | - |
| Zhaosu, Xinjiang | Zeng et al. (2022) [61] | CV | 13.6 | - | 0.56 | 40.2 | 2.11 | 3.44 |
| Urumqi, Xinjiang | Zeng et al. (2022) [62] | CV | - | - | 0.69 | 38.1 | 1.56 | 3.97 |
| Nilek, Xinjiang | Zeng et al. (2022) [62] | CV | - | - | 0.54 | 40.2 | 2.08 | 3.36 |
| Naqu, Xizang | Chen et al. (2017) [63] | CV | - | 451 | 0.36 | 39.8 | 1.87 | 3.4 |
| Motuo, Xizang | Wang et al. (2021) [58] | CV | - | 793 | 0.47 | 36.0 | 1.42 | 3.98 |
| Urumqi River source area | This study | - | 29.6 | 719 | 5.34 | 45.8 | 2.28 | 4.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Yang, M.; Peng, J.; Li, H. Raindrop Size Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events Based on a PWS100 Disdrometer in the Alpine Mountains, Eastern Tianshan, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5068. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15205068
Chen P, Wang P, Li Z, Yang Y, Jia Y, Yang M, Peng J, Li H. Raindrop Size Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events Based on a PWS100 Disdrometer in the Alpine Mountains, Eastern Tianshan, China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(20):5068. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15205068
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Puchen, Puyu Wang, Zhongqin Li, Yefei Yang, Yufeng Jia, Min Yang, Jiajia Peng, and Hongliang Li. 2023. "Raindrop Size Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events Based on a PWS100 Disdrometer in the Alpine Mountains, Eastern Tianshan, China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 20: 5068. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15205068
APA StyleChen, P., Wang, P., Li, Z., Yang, Y., Jia, Y., Yang, M., Peng, J., & Li, H. (2023). Raindrop Size Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Precipitation Events Based on a PWS100 Disdrometer in the Alpine Mountains, Eastern Tianshan, China. Remote Sensing, 15(20), 5068. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15205068