Abstract
Vegetation change and ecological quality of the Loess Plateau (LP) are directly related to ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin. Based on LP ecological zoning and multisource remote sensing data, we analyzed vegetation change and its relationship with climate, terrestrial water storage (TWS), and land use/cover change from 2000 to 2020, using the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), fraction of vegetation cover (FVC), and net primary productivity (NPP). And ecological environmental quality was evaluated based on the remote sensing ecological index (RSEI). The results showed that the spatial distribution pattern of NDVI, FVC and NPP decreased from southeast to northwest in the LP as a whole. Vegetation in the LP recovered significantly, and NDVI, FVC, and NPP showed significant increases of 35.66%, 34%, and 54.69%, respectively. The average NDVI and FVC in the earth–rocky mountainous region and river valley plain region (Area D) were the highest, but the growth rate was the slowest. The average NDVI, FVC, and growth rates in the loess hilly and gully regions (Area B) were slightly higher than those in the loess sorghum gully region (Area A). The average NDVI, FVC, and NPP in the sandy land and agricultural irrigation regions (Area C) were the lowest but showed significant increase. RSEI in most LP areas changed from poor to medium, increasing by 43.45%. Precipitation is the basic factor affecting vegetation cover pattern, with the increase (40.79 mm/10a) promoting vegetation restoration in the LP. Vegetation restoration lost much TWS (−0.6 mm/month), and Area D had the highest average NDVI, FVC, and NPP but the largest TWS loss. Anthropogenic land use/cover change (LUCC) (decrease in cultivated land and unused land; increase in forest, grassland, and construction land) is the primary factor affecting LP vegetation change. This study provides a scientific reference for further vegetation restoration in the LP.
1. Introduction
The response of terrestrial ecosystems to global change and research concerning ecological environment quality are major scientific issues related to the sustainable development of human society. Vegetation is an important part of terrestrial ecosystems that connects the atmosphere, soil, hydrology, and other ecological elements. It is also an important ecological environmental indicator, playing an important role in maintaining ecological balance, regulating climate, conserving water sources, combating desertification, conserving water and soil, and regulating carbon sources and sinks [1,2,3,4]. Since the 1980s, global vegetation has generally become greener, and photosynthesis and productivity of vegetation have increased significantly [5,6]. From 2000 to 2017, one-third of the global vegetation area showed a greening trend (mainly distributed in East and South Asia, southern Europe, central North America, central Africa, and southeast South America [7]), whereas 5% showed a browning trend [8]. From 1982 to 2018, the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) of China gradually increased at a rate of 0.005/10a, becoming a major contributor to global greening [8,9]. Climate change, CO2 fertilization, nitrogen deposition, population growth, agricultural and land-use measures have become important factors affecting global vegetation change [8,10,11,12,13].
The Loess Plateau (LP) is an important birthplace of Chinese civilization, with a total population of 108 million and a gross national product of 1.85 trillion yuan [14]. It is an important economic region in China; however, it has a fragile ecological environment. It was once renowned for extensive and severe soil erosion [15,16,17]. In recent decades, the warming range in the plateau has reached 0.29 °C/10a [18], which is significantly higher than the national (0.23 °C/10a) and global (0.19 °C/10a) averages [19]; as such, it is also a sensitive area of climate change. To improve the ecological environment of the LP, since 1999, the Chinese government has implemented a large-scale vegetation restoration project called Grain for Green. Under the combined influence of climate change and human activity, what changes have occurred in the vegetation of the LP? What is the quality of the environment? These problems are directly related to the ecological security and sustainable social and economic development of the region and even wider regions. They have attracted the attention of local governments and relevant investigators and have extremely important scientific research value and practical significance.
At present, in terms of the characteristics and attributes of vegetation change on the LP, numerous studies have found that NDVI on the LP has shown a gradually increasing trend since 1980, especially since 1999 [2,20,21]. Kou et al. [22] pointed out that nearly 80% of the land fraction of vegetation cover (FVC) in the LP increased from 1998 to 2018, especially in the Shaanxi and Gansu provinces, and that climate, irrigation, urban expansion, land-use management, and various protection schemes are the main factors that lead to vegetation change in the LP. Ni et al. [23] found that the net primary productivity (NPP) of vegetation in the LP has increased significantly during the past 20 years, and the contribution rates of human activity and climate change to the increase in NPP were 64.2% and 35.8%, respectively. In terms of the impact of vegetation change, Zhang et al. [24] found that vegetation restoration significantly enhanced the carbon fixation services of the LP ecosystem, improved soil conservation services, and stabilized water production services. Zhang et al. [25] found that the current vegetation coverage (average: 0.48) in most areas of the LP exceeded the balanced vegetation coverage (average: 0.43) defined by climate. Overplanting has become the main cause of soil dryness in this region, particularly in the central and eastern regions. In addition, large-scale vegetation restoration has been found to have had an impact on the climate of the LP, such as cooling, humidifying, and increasing evapotranspiration [13,26,27,28,29]. In terms of eco-environmental quality assessment, Yang et al. [30] analyzed the spatiotemporal pattern and evolutionary trend of eco-environmental quality in the Yellow River Basin for 1990 to 2019 by constructing the remote sensing ecological index (RSEI). Based on the conceptual framework of “pattern–process–service–sustainability”, Fu et al. [16] analyzed the ecological changes and problems in the LP in recent decades and proposed social-ecological sustainability measures. At present, most studies have only analyzed vegetation change in the LP based on a single NDVI, FVC, or NPP index, and there is a lack of comprehensive analysis combining multiple indices, particularly concerning regional differences in vegetation change and ecological environmental quality evaluation in the LP.
There may be uncertainty in analyzing vegetation change and eco-environmental quality only by a single remote sensing index [7], so it is necessary to comprehensive analyze multiple indicators. By comparing the related indexes, it is found that NDVI, FVC and NPP are the most commonly used vegetation indices and are more suitable for the LP [2,22,31,32]. Among them, NDVI reflects the change in vegetation growth state [33]. FVC focuses on vegetation coverage, and NPP lay emphasis on biomass, that is, vegetation growth and quality [22,34]. The three indexes prove each other and can fully reflect the evolution of vegetation activity in the LP. The new RSEI was coupled with four important evaluation indicators of the natural ecological environment: greenness (NDVI), humidity (WET), heat (LST), and dryness (NDSI). This method can reflect the regional ecological environment quality comprehensively, quickly, and objectively [35]. It has been widely used to evaluate the quality of regional ecosystems [36,37,38]. In view of this, based on the ecological zoning and multisource remote sensing data of the LP, this study selected multiple indices including NDVI, FVC, and NPP to conduct the interannual and zonal research on vegetation changes in the LP, and analyzed the main reasons for the changes from the aspects of climate change, terrestrial water storage (TWS) and land use/cover change (LUCC). At the same time, RSEI was constructed to evaluate the eco-environmental quality of the LP, in order to provide a scientific reference for the formulation of the Grain for Green national policy, the construction of ecological civilization and sustainable development on the LP, and the national strategy of ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The LP is one of the four plateaus in China and the largest loess distribution area in the world [18]. It is located in the middle and upper reaches of the Yellow River in northern China (100°54′–114°33′E, 33°43′–41°16′N) (Figure 1). It starts from Taihang Mountain in the east, reaches Riyue Mountain in Qinghai in the west, borders the Qinling Mountains in the south, and reaches Yin Mountain in the north. The total area of the LP is approximately 64 × 104 km2, including 341 counties (cities) in 7 provinces (autonomous regions) [39]. This area has a continental monsoon climate, with semihumid, semiarid, and arid regions from southeast to northwest. The average annual temperature is 3.6–14.3 °C, and the precipitation is 150–750 mm [40]. Typical landform types are loess Yuan, Liang, and Mao, along with various valleys containing different degrees of erosion [18]. Because loess is loose, porous, homogeneous, and easy to cultivate, LP has become an important dry-farming area in China [41]. The natural annual runoff of the Yellow River, which irrigates the Hetao Plain and other areas, is 58 billion m3. Other rivers with annual runoff exceeding 3 billion m3 in this area include the Weihe, Taohe, Huangshui, and Yiluo Rivers. The LP is an important water-producing area of the Yellow River and is the source area of most sediment. It is one of the most concentrated areas in terms of population, resources, and environmental conflicts in China. It is also a key area for soil and water conservation and ecological construction in China [42]. Based on regional characteristics and differences, the LP is divided into four ecological zones: (A) loess sorghum gully region (218,000 km2), (B) loess hilly and gully region (129,000 km2), (C) sandy land and agricultural irrigation region (135,000 km2), and (D) earth–rocky mountainous and river valley plain region (179,000 km2) [43].
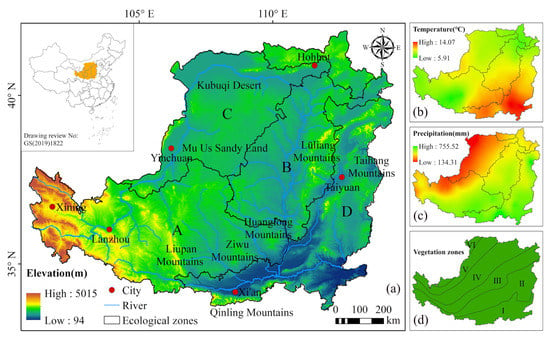
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the LP: (a) ecological zoning of the LP: (A) loess sorghum gully region; (B) loess hilly and gully region; (C) sandy land and agricultural irrigation region; (D) earth–rocky mountainous and river valley plain region. (b) spatial distribution of average temperature on the LP from 2000 to 2020. (c) Spatial distribution of mean precipitation on LP from 2000 to 2020. (d) vegetation zoning in the LP: I, sub-belt of deciduous oak forest in southern warm temperate zone; II, subzone of deciduous oak forest in northern warm temperate zone; III, temperate forest grassland sub zone; IV, temperate typical grassland sub-zone; V, temperate desert grassland sub-belt; VI, temperate steppe desert sub-belt.
2.2. Materials
In this study, ecological zoning data of the LP and vegetation zoning data were obtained from the National Earth System Science Data Center, and the remote sensing data comprised the MODIS series product dataset from 2000 to 2020. Among them, NDVI uses MOD13Q1/MOD13A1 V6 product data. The algorithm selects the best available pixel value from all the collected data during a 16-day period, using the criteria of low cloud, low-view angle, and the highest NDVI value. NPP was calculated using the Carnegie–Ames–Stanford approach (CASA) model based on MCD15A3H, MOD15A2H, MCD12Q1, Terraclimate, Gladas/T3H, and the NOAA Climate Data Record of AVHRR and NDVI data. MOD09A1, MOD11A2, and MOD13A1 data were also used to calculate the RSEI. These data were downloaded, processed, and calculated using the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform. To ensure the accuracy of geometric matching between different data sources, this study adopted data format conversion, projection coordinate conversion, data resampling, spatial registration, and other technical means to collate the data at the same scale. The final data were projected using the GCS_WGS_1984 geographic coordinate system with a spatial resolution of 500 m. Temperature and precipitation observations were obtained from the China Meteorological Science Data Sharing Service Network. TWS data were obtained by inverting the GRACE Level-2 RL06 gravity field model, provided by the Space Research Center of Texas State University. The highest order is 60, and the spatial resolution was 0.25° × 0.25°. The study period was from January 2003 to December 2020. The missing data during this period were replaced by the accumulated average of the missing months or average of the adjacent months. Land-use data with a resolution of 300 m were obtained from the European Space Agency for the period 2000 to 2020. In this study, land-use types were verified by field investigation, comprising six first-class categories: farmland, forest, grassland, built-up areas, water bodies, and unused land. The data used in this study and their sources are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Data types and sources used in this article.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Calculation of FVC
FVC refers to the percentage of the vertical projection area of vegetation (including leaves, stems, and branches) on the ground relative to total area of interest. It is an important indicator of surface vegetation coverage and has a strong positive correlation with NDVI. Based on the pixel dichotomy model, the FVC of the LP was calculated using an inversion model based on the NDVI data. The calculation formula is [22,24]:
where FVC is the vegetation coverage (%), NDVIi is the NDVI value of a pixel in this period, and NDVImax and NDVImin are the maximum and minimum NDVI values of all pixels in the study area, respectively.
FVC = (NDVIi − NDVImin)/(NDVImax − NDVImin),
According to the field situation, the vegetation in the LP is divided into areas characterized by high vegetation coverage (FVC > 80%), medium-high vegetation coverage (60% < FVC ≤ 80%), medium vegetation coverage (40% < FVC ≤ 60%), medium-low vegetation coverage (20% < FVC ≤ 40%), and low vegetation coverage (20% ≤ FVC).
2.3.2. Estimation of NPP
The NPP of vegetation refers to the amount of organic matter accumulated by vegetation through photosynthesis per unit time and unit area. It is an important factor in determining the carbon source/sink of ecosystems [32]. In this study, based on the improved light-energy utilization model, the CASA model, the vegetation NPP of the LP was calculated using the GEE. The CASA model is a classic model for estimating the NPP of terrestrial ecosystem vegetation that has been widely applied to the estimation of vegetation NPP for large-scale areas and is currently one of the models with the highest estimation accuracy. Its basic formula is the product of the photosynthetic active radiation absorbed by vegetation (APAR) and the light-energy utilization ratio ε. The calculation formula is as follows [24,32,34]:
where NPP is the net primary productivity of vegetation (g C/m2); APAR is the photosynthetic active radiation (MJ/m2); SOL is the total solar radiation (MJ/m2); FPAR is the ratio of the absorption of vegetation to APAR; the constant 0.5 represents the ratio of the effective solar radiation (wavelength of 0.4–0.7 μm) available to vegetation from the total solar radiation; ε is the efficiency for plants to convert absorbed APAR into organic carbon (gC/MJ); Tε1 is the degree to which plants weaken photosynthesis under high and low temperatures owing to their own physiological effects; Tε2 is the trend in which the utilization rate of light energy gradually decreases when the optimum temperature for plant growth changes to high and low temperatures; Wε is the limit degree of water condition to light-energy utilization efficiency; and εmax is the maximum light-energy utilization efficiency under ideal conditions (gC/MJ).
NPP(x,t) = APAR(x,t) × ε(x,t),
APAR(x,t) = SOL(x,t) × FPAR(x,t) × 0.5,
ε(x,t) = Tε1(x,t) × Tε2(x,t) × Wε(x,t) × εmax,
2.3.3. Construction of RSEI
RSEI is a quantitative evaluation method for regional ecological quality based on remote sensing information and natural factors. It is coupled with four evaluation indexes, including vegetation index, humidity component, surface temperature, and soil index, representing four ecological factors: greenness, humidity, heat, and dryness. It has the advantages of easy index acquisition, no artificial weights, and visualization of results [35]. At present, it has been widely used in the evaluation of regional ecological environment quality at the municipal [44,45], provincial [36] and watershed levels [30], and achieved good results. RSEI ranges between 0 and 1, in which a larger value indicates a better ecological environment. The calculation formula is as follows [35]:
where RSEI0 is the initial value of the remote sensing ecological index, PC1 is the first principal component value obtained after PCA, NDVI is the greenness index, WET is the humidity index, LST is the heat index, NDSI is the dryness index, RSEI is the remote sensing ecological index, and RSEI0min and RSEI0max are the minimum and maximum values of RSEI0, respectively.
RSEI0 = 1 − PC1[f(NDVI,WET,LST,NDSI)],
RSEI = (RSEI0 − RSEI0min)/(RSEI0max − RSEI0min),
RSEI was divided into five ecological classes: poor [0, 0.2], relatively poor [0.2, 0.4), medium [0.4, 0.6), good [0.6, 0.8) and excellent [0.8, 1).
2.3.4. Change Trend and Inspection
In this study, the univariate linear regression method was used to analyze the interannual variation trends of the variables. The Mann-Kendall trend test was used to test the trends of the research variables. Pearson’s correlation analysis method is used to analyze the correlations between the variables. The Hurst index (H) method was used to predict future change trends in the vegetation NPP. The judgment criteria were as follows: 0.5 < H < 1 indicates that the future trend is consistent with the past trend, and the closer H is to 1, the stronger the persistence; H = 0.5 indicates that the future change is random and has no relation with the past trend; 0 < H < 0.5 means that the future trend is opposite that of the past, and H to 0 represents stronger antipersistence [39,46].
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Vegetation Changes in the LP
3.1.1. Changes in the NDVI
From the perspective of spatial distribution characteristics, the NDVI of the LP generally showed a spatial pattern of decrease from southeast to northwest (Figure 2a–c). Taking 2020 as an example, the NDVI of most areas in Area D was higher, mostly above 0.6. The NDVI of Ziwu Mountain, Huanglong Mountain in the east, Liupan Mountain in the middle, and mountainous areas west of Area A were higher, reaching greater than 0.8; however, it was lower in the northern area, mostly 0.2–0.4. The NDVI of Lüliang Mountain in the east and mountainous areas south of Area B was relatively high and gradually decreased to the west and north, mostly 0.4–0.6 in the west. Area C had a low NDVI of 0.2–0.4 in most areas because it is close to the inland and far from the water vapor source, containing the areas of Mu Us Sandy Land and Kubuqi Desert. Only the irrigated areas along the Yellow River (Hetao Plain) had a higher NDVI, mostly 0.6–0.8. From 2000 to 2020, the average NDVI values in districts A, B, C, and D were 0.55, 0.56, 0.35, and 0.68, respectively, indicating that the vegetation coverage in Area D was the largest. In terms of dynamic changes, NDVI has increased in most areas of the LP during the past 21 years, especially in Area B (Figure 2d).
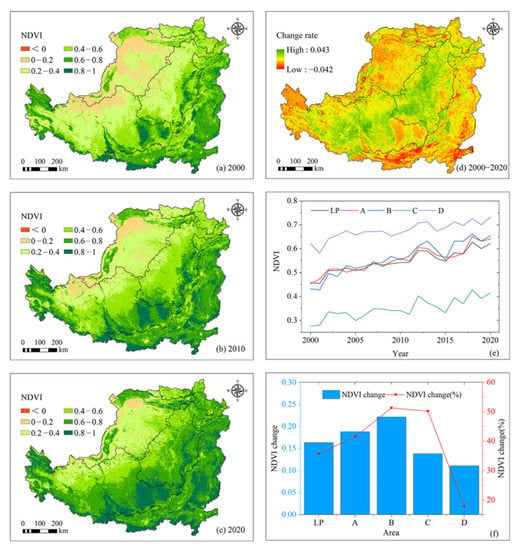
Figure 2.
Characteristics of NDVI in the LP from 2000 to 2020: (a) spatial distribution of NDVI in 2000; (b) spatial distribution of NDVI in 2010; (c) spatial distribution of NDVI in 2020; (d) spatial variation trend of NDVI; (e) interannual variation in NDVI; (f) NDVI change value and rate.
From the perspective of variation through time, the NDVI of the LP showed a fluctuating upward trend from 2000 to 2020, ranging from 0.45 to 0.62, rising by 0.007/a (p < 0.01) with a multiyear average of 0.55. In 21 years, the NDVI increased by 35.66% (Figure 2e). From the perspective of each partition, the NDVI of partitions A, B, C, and D showed a significant increase from 2000 to 2020, at 0.008/a, 0.01/a, 0.006/a, and 0.005/a, respectively, rising by 41.57% (0.188), 51.29% (0.222), 50.2% (0.138), and 17.89% (0.111) during 21 years (Figure 2e,f). This shows that the vegetation in Area B increased the fastest, whereas that in Area D exhibited the smallest rate of increase.
Further comparing NDVI from different periods, we found that the average NDVI of the LP from 2000 to 2010 was 0.51, an increase of 18.28% (0.08). Districts A, B, C, and D rose by 23.47% (0.106), 27.77% (0.120), 23.43% (0.065), and 7.3% (0.045), respectively. The average NDVI of the LP from 2010 to 2020 was 0.58, an increase of 14.69% (0.08), with districts A, B, C, and D rising by 14.66% (0.08), 18.41% (0.1), 21.69% (0.07), and 9.87% (0.066), respectively. Although the NDVI of the LP in 2010–2020 was 0.07 higher than that in 2000–2010, the increase was significantly reduced, and the vegetation restoration rate in the LP was slightly slowed during the last 10 years.
3.1.2. Changes in FVC
From 2000 to 2020, the average FVC of the LP was 58.73%, showing a decrease from southeast to northwest and a spatial distribution pattern similar to that of the NDVI (Figure 3a–c). In terms of each subarea, the annual FVC in Areas A, B, C, and D was 59.37%, 60.1%, 40.77%, and 70.64%, respectively, indicating that Area D had the highest vegetation coverage, followed by Areas B, A, and C. The FVC in the northern part of Area A and western part of Area B were also relatively low. In the past 21 years, FVC in most areas of the LP has increased, especially in Areas A and B, as well as the irrigated areas along the Yellow River in Area C. Meanwhile, the regions with a significant reduction in FVC were mainly distributed in areas with strong human activity, such as the urbanization in the Guanzhong Plain, Taiyuan City, and Yinchuan City (Figure 3d).
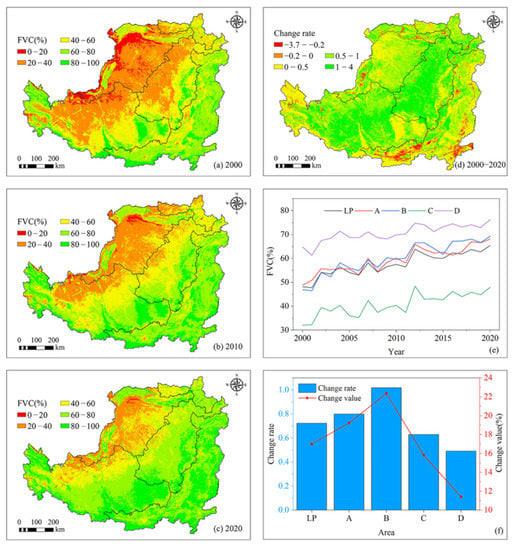
Figure 3.
Characteristics of FVC in the LP from 2000 to 2020: (a) spatial distribution of FVC in 2000; (b) spatial distribution of FVC in 2010; (c) spatial distribution of FVC in 2020; (d) FVC spatial variation trend; (e) interannual variation in FVC; (f) FVC change rate and change value.
Through time, the FVC of the LP increased significantly at a rate of 0.723%/a (p < 0.01) from 2000 to 2020 and expanded by 34.44% in 21 years (Figure 3e). A, B, C, and D all showed significant expansion (p < 0.01), with rising rates of 0.8%/a, 1.017%/a, 0.63%/a, and 0.492%/a, respectively, adding values of 19.24%, 22.36%, 15.82%, and 11.41%, respectively, and change rates of 39.36%, 47.62%, 49.35%, and 17.6%, respectively (Figure 3e,f). This shows that the increase rate and value of FVC in Area B are the largest, and the increase rate, added value, and change rate in Area A are slightly lower than those in Area B. The change rate in Area C is the largest, whereas the increase rate, added value, and change rate in Area D are the smallest.
According to the changes in FVC of various grades (Table 2), the average FVC value at all grades in the LP from 2000 to 2020 showed a significant increase (p < 0.01), except for low-grade FVC. Among them, medium-low FVC had the fastest rate of increase (0.107%/a) and largest added value (2.53%). This was followed by high FVC, with an increase rate of 0.077%/a and added value of 1.43%. Low FVC increased at the lowest rate of 0.02%/a. This shows that all grades of FVC are improving, and vegetation in the LP is gradually recovering. Besides Area B, in which the average growth rate of medium FVC was the fastest (0.236%/a), all districts had medium-low FVC as having the fastest average growth rate. It is worth noting that low FVC in Areas A and B and high FVC in Area C showed a downward trend.

Table 2.
FVC of different grades on the LP from 2000 to 2020.
3.1.3. Changes in the NPP
The NPP of vegetation in the LP was high in the southeast (especially in the Qinling Mountains, Liupan Mountains, and Ziwu Mountains) and low in the northwest (especially in the Kubuqi Desert) (Figure 4a–c). The annual average NPP values of districts A, B, C, and D were 332.58, 282.73, 143.85, and 381.92 g C/m2, respectively, indicating that the NPP of vegetation in Area D was the highest, followed by that in Area A (especially in the southeast), and the lowest was in Area C. From the perspective of dynamic changes, the NPP of vegetation in most areas of the LP increased from 2000 to 2020, especially in the center and eastern region of Area A and the southern and eastern regions of Area B. The area where NPP decreased was mainly distributed in the northwestern region of Area C (Kubuqi Desert) (Figure 4d).
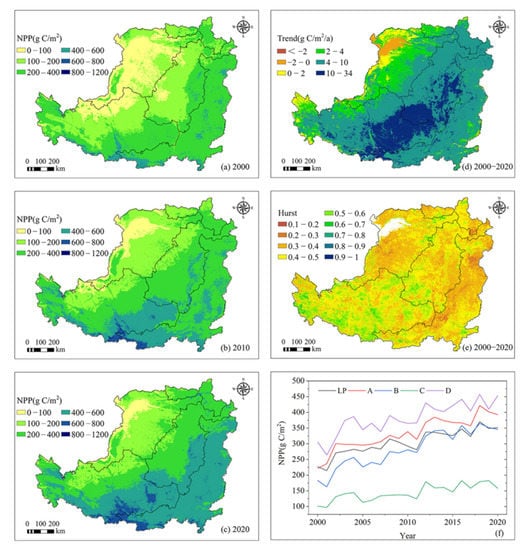
Figure 4.
NPP changes in the LP from 2000 to 2020: (a) spatial distribution of NPP in 2000; (b) spatial distribution of NPP in 2010; (c) spatial distribution of NPP in 2020; (d) spatial trend of NPP; (e) Hurst exponential spatial distribution of NPP; (f) interannual variation in NPP.
Regarding interannual change, the vegetation NPP of the LP showed significant increase from 2000 to 2020, rising by 5.9 g C/m2/a (p < 0.1). The NPP increased from 227.04 g C/m2 in 2000 to 351.22 g C/m2 in 2020, with an increase of 54.69% (Figure 4f). Districts A, B, C, and D all showed a significant upward trend (p < 0.1), increasing by 7.8 g C/m2/a, 9 g C/m2/a, 3.3 g C/m2/a, and 6.9 g C/m2/a, respectively. During the past 21 years, the NPP in the four districts increased by 77.31% (171.21 g C/m2), 89.05% (162.87 g C/m2), 56.27% (56.87 g C/m2), and 48.33% (147.7 g C/m2), respectively, indicating that the carbon sequestration capacity of vegetation in the LP gradually increased during this time period.
The Hurst index of the vegetation NPP in the LP varied from 0.15 to 0.96, with a mean value of 0.42 (Figure 4e). This shows that although the NPP of vegetation in the LP has increased in the past 21 years, it is likely not to be sustainable in the future; that is, the carbon fixation capacity of vegetation will decrease. Specifically, the Hurst index of Area A was 0.46, and the vegetation NPP may decrease in most regions in this area in the future; the regions of increase were mainly distributed in the southwest, Liupan Mountain, Ziwu Mountain, and other sparse areas. The Hurst index of Area B was 0.42. In the future, the NPP of vegetation in the southwestern region of Area B may increase; however, the vegetation NPP in most other regions will decrease. The Hurst index in Area C was 0.404; the vegetation NPP there may decrease in the future, especially in Mu Us Sandy Land. The Hurst index in Area D was only 0.397, indicating that the NPP of vegetation will decrease significantly in the future.
3.2. Ecological Environment Quality Evaluation of the LP
The changes in the RSEI on the LP from 2000 to 2020 are shown in Figure 5, from which it can be seen that the ecological environment of the LP has gradually improved during the past 21 years, with the RSEI increasing from 0.32 in 2000 to 0.46 in 2020, an increase of 43.45%. At present, the eco-environmental quality of the LP is generally at a medium level. In detail, the RSEI in most areas of the LP was at a poor level in 2000; however, in 2020, most regions had evolved to a moderate level, whereby the regions of poor levels in Area D were significantly reduced. In particular, the vast majority of areas in northern Inner Mongolia had reached a good level. On the whole, from 2000 to 2020, the RSEI in Areas A, B, C, and D increased from 0.344, 0.336, 0.27, and 0.32 to 0.469, 0.47, 0.495, and 0.41, respectively, with increases of 36.49%, 40.46%, 82.78%, and 29.84, respectively. From 2000 to 2010, the RSEI in the LP and Areas A, B, C, and D were 0.03 (9.23%), 0.03 (9.96%), 0.08 (22.5%), 0.1 (35.69%), and 0.02 (7.33%), respectively. From 2010 to 2020, RSEI in the LP and Areas A, B, C, and D were 0.11 (31.33%), 0.16 (51.59%), 0.06 (14.66%), 0.13 (34.7%), and 0.07 (20.97%), respectively. The eco-environmental quality of the LP has improved rapidly during the last 10 years.
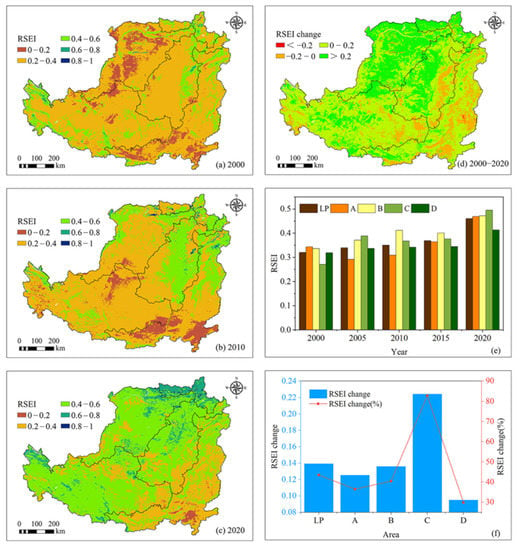
Figure 5.
Variation characteristics of RSEI on the LP from 2000 to 2020: (a) spatial distribution of RSEI in 2000; (b) spatial distribution of RSEI in 2010; (c) spatial distribution of RSEI in 2020; (d) spatial variation in RSEI; (e) interannual variation in RSEI; (f) RSEI change value and change rate.
3.3. Analysis on the Causes of Vegetation Change
3.3.1. Climatic Factors
Climate is a basic factor affecting vegetation change. From 2000 to 2020, the average temperature and precipitation on the LP were 9.8 °C and 446.87 mm, respectively. The overall warming rate was 0.26 °C/10a, and the precipitation increased significantly at a rate of 40.79 mm/10a (p < 0.01) (Figure 6a). During this period, 85.07% of the stations showed a warming trend and 89.33% of the stations showed increasing precipitation (Figure 6b,c). Pearson’s correlation analysis showed that precipitation in the LP was positively correlated with NDVI and FVC, with correlation coefficients of 0.577 and 0.553, respectively (p < 0.01). There was significant positive correlation with NPP, with a correlation coefficient of 0.506 (p < 0.05). There were no significant positive correlations between temperature and NDVI, FVC, or NPP, with correlation coefficients of 0.32, 0.317, and 0.34, respectively. The results show that the increase in NDVI, FVC, and NPP is closely related to the increase in precipitation in the LP from 2000 to 2020, whereas the effect of the temperature increase is weak.
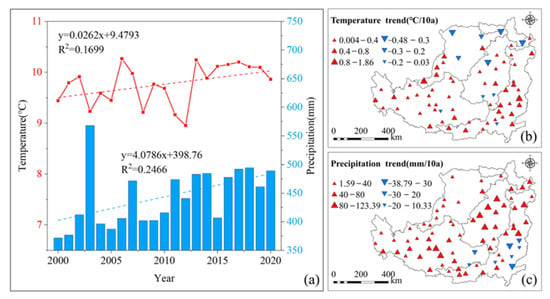
Figure 6.
Characteristics of climate change on the LP from 2000 to 2020: (a) changes in average annual temperature and precipitation; (b) spatial variations in temperature; (c) spatial variation in precipitation.
3.3.2. TWS Factor
In arid and semiarid areas, water resources are key natural factors that restrict construction in the ecological environment. It can be seen from the spatial change in TWS in the LP from 2003 to 2020 (Figure 7a) that the TWS east of the LP, especially in the central and eastern region of Area D, has the most serious deficit, and the rate of deficit gradually decreases toward the west. Only the southwest portion of the entire area shows a slight increase through time, but the absolute value of the increase rate (0–2.92 mm/a) is far lower than the absolute value of the loss rate (−34.22 to 0 mm/a) in other regions. Specifically, the annual average TWS changes in the LP and Areas A, B, C, and D are −38.70, −9.54, −51.70, −28.59, and −72.66 mm/a, respectively, indicating that Area D has the largest TWS loss, followed by Areas B, C, and A. From the perspective of interannual change, the rates of change in TWS in the LP and Areas A, B, C, and D from 2003 to 2020 were −0.60, −0.12, −0.86, −0.44, and −1.13 mm/month (p < 0.1), respectively (Figure 7b), which also indicates that the loss rate of TWS in Area D of the LP was the largest. From 2003 to 2020, the TWS of the LP and Areas A, B, C, and D changed by −121.91, −0.93, −212.49, −103.39, and −218.06 mm, respectively, indicating that Area D has the largest TWS deficit. Through Pearson’s correlation analysis (Table 3), the TWS of the LP and its subregions was found to be negatively correlated with all vegetation indicators, with all reaching a very significant level, except Area A. This shows that large-scale vegetation restoration in the LP is likely at the cost of serious loss of TWS.
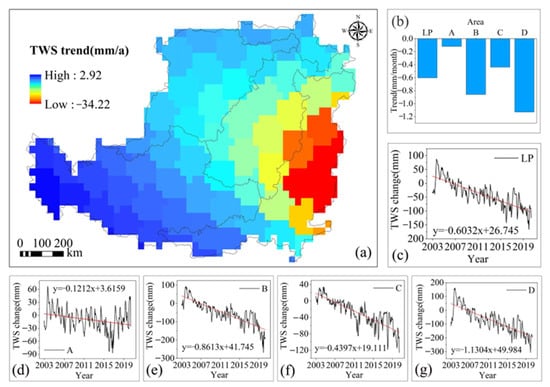
Figure 7.
Changes in TWS in the LP from 2003 to 2020: (a) spatial changes in TWS in the LP during 2003–2020; (b) change rate of TWS in the LP and its subregions; (c–g) monthly variation in TWS in the LP and its subregions.

Table 3.
Pearson correlation coefficient of TWS and vegetation indexes in the LP.
3.3.3. LUCC Factors
By comparing the land use/cover maps of the LP for 2000 and 2020 (Figure 8, Table 4), it was found that in Area A, except for the decrease in the area of farmland (−5298.76 km2), the area of all types of land use increased, for instance, the area of grassland increased by 3288.89 km2, and the area of forest increased by 382.56 km2. The farmland, forest, and unused land in Area C decreased, shrinking by 372.37, 1020.38, and 3934.8 km2, respectively; the grassland and built-up areas increased by 2976.93 and 2277.08 km2, respectively. The areas of farmland and grassland in Area D decreased by 5955.09 and 1524.23 km2, respectively. The areas of forest, built-up areas, and water bodies increased by 1692.21, 6016.67, and 87.12 km2, respectively. Overall, the LUCC of the LP from 2000 to 2020 was mainly characterized by a decrease in farmland and unused land area and an increase in forest, grassland, and built-up areas. Specifically, the area of farmland and unused land decreased by 14,693 and 4284.49 km2, respectively, and the area of forest, grassland, built-up areas, and water bodies increased by 1584.65, 6059.2, 11,140.51, and 193.05 km2, respectively. The significant decrease in farmland area and increase in forest and grassland area in the LP during the 21 years indicates that ecological protection projects such as Grain for Green and Three–North Shelterbelt have promoted vegetation restoration in the LP, and LUCC has played an important role in driving vegetation change in the LP.
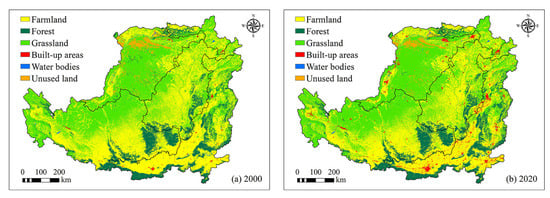
Figure 8.
LUCC of the LP for 2000 and 2020: (a) land use/cover in the loess plateau in 2000; (b) land use/cover in the loess plateau in 2020.

Table 4.
LUCC in the LP from 2000 to 2020.
With the restoration of vegetation, the eco-environmental quality of the LP has also changed accordingly. Pearson correlation analysis shows that there is a positive correlation between RSEI and NDVI, FVC and NPP changes in the LP and its subregions, especially in the LP and Areas B, C, and D. Additionally, RSEI have reached a significant or extremely significant level with NDVI and FVC (Table 5). It shows that vegetation is an important factor affecting the ecological environment quality of the LP, and vegetation restoration has greatly promoted the improvement of the ecological environment quality of the LP.

Table 5.
Pearson correlation coefficient between RSEI and vegetation index for the Loess Plateau.
4. Discussion
Most areas of the LP have arid and semiarid climates, and vegetation is sensitive to changes in precipitation [28,33,47,48]. On the one hand, with the gradual decrease in precipitation from southeast to northwest, the vegetation presents a regular distribution pattern of forest, forest grassland, typical grassland, desert grassland, and grassland desert (Figure 1c) [49]. According to meteorological observation data, the average annual precipitation in Area D is 527.11 mm, and that in Area C is 239.75 mm. This explains the fundamental reason why the average NDVI, FVC, and NPP in Area D were the highest and the average NDVI, FVC, and NPP in Area C were the lowest. Chen et al. [50] also found that the average annual rainfall had a strong interpretation of the spatial distribution of NDVI and was the main restriction factor for vegetation growth in 85.2% of the LP region. On the other hand, increased precipitation directly strengthens the physiological and biochemical activities of plants, supplementing soil moisture and promoting plant growth. Temperature has both positive and negative effects on plant growth. A positive effect is that the growing season is prolonged, the photosynthetic and water-use efficiency of plants is improved, and plant growth is promoted. For example, the annual average temperature in Area D is 11.64 °C, and that in Area C is 9.15 °C, which is one of the main reasons that Area D has the highest NPP and Area C has the lowest NPP. A negative effect is that an increase in temperature accelerates the transpiration of vegetation, reduces soil moisture, and leads to an increase in evapotranspiration, which is not conducive to the growth of vegetation [33,48]. Some researchers have also pointed out that in the LP, vegetation growth in arid areas is mainly affected by rainfall, vegetation in semihumid areas is more closely related to temperature, and vegetation growth in semiarid areas is affected by both temperature and rainfall [51]. In addition, some studies have found that the potential evapotranspiration of the LP has increased at a rate of 13.5 mm/10a during the last 40 years [52], especially in the east, which may also cause to some extent the slow growth rate of average NDVI and FVC in Area D. From an interannual point of view, the increase in precipitation has been the main meteorological factor for the increase in NDVI, FVC, and NPP in the LP since 2000, whereas the influence of the temperature rise is weak [20,53,54]. However, in the long run, the negative effects of the rise in temperature should not be underestimated.
In this study, it is believed that vegetation restoration on the LP has lost a large amount of TWS, and the variation of TWS is not only related to the vegetation restoration rate, but also related to the vegetation covering the basement, regional water use (such as agriculture) and other factors (Figure 7a,b). Han et al. [55] also found that the groundwater water consumption caused by vegetation dynamic significant area in the LP was higher than that in non-significant area. Li et al. [56] found that the significant increase of leaf area index in forest and farmland areas of the LP was the largest contributing factor for the increase of ET and the decrease of TWS in the Yellow River Basin. According to Feng et al. [14], vegetation restoration in the LP during 2000–2010 resulted in an annual loss of 2.4 ± 0.9 mm of soil moisture and 0.5 ± 0.3 mm of runoff. Guo et al. divided TWS in the LP into shallow- and deep-water storage. Shallow-water storage represents 0–2 m of soil water storage, and deep-water storage includes soil water reserves below 2 m and groundwater storage. Deep soil water has been found to be an extremely important source of water for vegetation in the LP, especially in the Grain for Green project. A large number of newly added plantations belong to deep-rooted vegetation, which can absorb deep soil water below 10 m, the main factor leading to the serious decline in TWS in the LP [56,57,58]. Fu et al. [18] have also suggested that the guidance of ecohydrological theory has been neglected in the construction of the Three–North Shelterbelt Forest Program. On the one hand, the vegetation has used soil moisture excessively, resulting in a dry soil layer; on the other hand, the growth of vegetation has also been restricted, resulting in “the little old man trees”. In arid and semiarid areas, soil water availability controls the degree of vegetation restoration [39]. Currently, the scale of vegetation restoration in the LP is close to the threshold of the sustainable carrying capacity of regional water resources, and the blind afforestation will inevitably affect the human water demand [14]. Therefore, further vegetation restoration must be based on the carrying capacity of water resources, especially the maintenance of ecosystem stability and improvement of ecosystem quality should be considered in Areas D and B.
In order to improve the fragile ecological environment of the LP, the Chinese government has successively implemented ecological environment protection projects such as building terraces, constructing silt dams, planting trees, restoring natural vegetation, returning farmland to forests, controlling gullies, and reclaiming land since 1949. Numerous studies have shown that the LUCC resulting from climate change, especially human activity such as the Grain for Green Project, the construction of the Three–North Shelterbelt Forest Project, natural forest protection projects, socioeconomic development, and urbanization, is the main factor affecting vegetation change in the LP [16,29,59,60,61]. Zheng et al. [13] also found that a series of land-use management measures (ecological restoration projects) were the dominant factors in vegetation greening in China. In the LP, it is noteworthy that the decrease in forest area in Area C may be related to factors such as the increase in other types of land use/cover (e.g., increase of 2277.08 km2 in built-up areas and 2976.93 km2 in grassland) or government policy adjustments (arid and semiarid water-scarce areas are not considered suitable for extensive afforestation [17,27]). Areas B and A are the zones with the largest rates of increase in forest and grassland areas, respectively, in the four zones. Overall, the sum of the increase rates of forest and grassland in Area B (7.73%) was the largest, followed by Area A (4.83%), which explains why the average growth rates of NDVI, FVC, and NPP in Area B were the fastest, followed by Area A. Relevant research also found that Yan’an City and Yulin City in Shaanxi Province experienced the most significant afforestation in the LP, followed by the eastern part of Gansu Province [15,22].
With the restoration of vegetation in the LP and the implementation of a series of other eco-environmental protection measures, soil erosion in the LP has been weakened [62,63], and sediment input to the Yellow River has been reduced [18], soil erosion has been effectively curbed, and ecosystem services and carrying capacity have been gradually enhanced [24,64]. For example, the monitoring data from the Tongguan hydrological station show that the average annual sand transport of the Yellow River has decreased from 790 million tons in the 1990s to less than 200 million tons in the 2010s [65]. Therefore, in general, from 2000 to 2020, the eco-environmental quality of the LP gradually improved, and the RSEI in the LP also showed a gradual increase.
Based on multisource remote sensing data, this study analyzed the changes in NDVI, FVC, NPP, and RSEI in the LP. It should be pointed out that although high-quality remote sensing data and classical analysis models are used in this study, there may be errors in the research results due to the displacement of remote sensing sensors, complex meteorology, topography, and model selection [31,66], but it still has important reference significance for revealing the vegetation and ecological environment quality of the LP. In the research that will follow, the region can be further refined and appropriate analysis indexes can be selected, and adopting the latest remote sensing data, research methods, and analysis models that are gradually improved to further improve the accuracy. At the same time, this study found that there are temporal and spatial differences between NPP, NDVI, and FVC changes in the LP, which may be related to different vegetation characteristics reflected by different indices, natural disturbance, influence of climate change and human activities, vegetation types, data quality, research methods, and other factors. Ding et al. [7] also found that 45.6% of the world’s vegetation area experienced inconsistent trends in vegetation greenness, coverage, and productivity. Its specific mechanism needs further study. Furthermore, it also shows that it is uncertain to only rely on a single index to analyze vegetation changes, and it is necessary to comprehensively analyze vegetation dynamic changes from various indexes reflecting biophysical characteristics. This study holds that in the future climate change scenario, vegetation restoration in the LP must be based on local natural conditions and social and economic development; consider the risks brought by climate change; coordinate ecological water use with human water use; adopt reasonable restoration methods; select suitable vegetation types, scales, and densities; predict vegetation restoration effects; and coordinate water resources security, food security, and ecological security with the national “carbon neutral” strategy, so as to achieve regional sustainable development.
5. Conclusions
Based on the ecological zoning of the LP and multisource remote sensing data, this study focused on analyzed the interannual and zoning changes in NDVI, FVC, and NPP in the LP from 2000 to 2020 and dissected the main reasons for these changes. Additionally, the changes in eco-environmental quality in the LP were evaluated based on RSEI, which provides a scientific reference for ecological civilization construction and sustainable development in the LP, ecological protection, and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin. The results show that the NDVI, FVC, and NPP in the LP all generally decrease from southeast to northwest in the LP. During the study period, NDVI, FVC, and NPP showed a significant upward trend in the LP, rising by 0.007/a, 0.722%/a, and 5.9 g C/m2/a, respectively. In Area D, the average NDVI and FVC were the highest, but the growth rate was the lowest at 0.005/a and 0.492%/a, respectively. The average NDVI and FVC in Area B and their growth rates (0.01/a, 1.017%/a) were slightly higher than those in Area A (0.008/a, 0.8%/a). The average NDVI, FVC, and NPP in Area C were the lowest but also showed a significant increase through time, with growth rates of 0.006/a, 0.63%/a, and 3.3 g C/m2/a, respectively. With the restoration of vegetation, the RSEI of the LP increased by 43.45% during the past 21 years, and the ecological environmental quality has gradually improved and is generally at a medium level. The rate of increase in RSEI in Area C was the largest (82.78%), Area D had the smallest (29.84%), and Area B had a slightly higher RSEI rate of increase (40.46%) than Area A (36.49%). Climate affects the basic distribution of the vegetation coverage patterns, and the increase in precipitation (40.79 mm/10a) is the main meteorological factor for vegetation restoration in the LP. Vegetation restoration most likely comes at the cost of serious TWS loss (−0.6 mm/month). The average NDVI, FVC, and NPP in Area D were the highest, and the TWS loss was also the largest. LUCC caused by human activity (mainly characterized by a decrease in farmland and increase in forest, grassland, and built-up areas) is the main factor for spatiotemporal changes and differences in vegetation in the LP.
Author Contributions
Q.Z. conceived the framework for this paper and processed the data; S.C. wrote the paper; Y.C. and H.Z. revised the paper; Y.X., Z.L. and Y.H. assisted in data processing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (20210302123265).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Yang YF from Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Northwest A&F University, and “National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science and Technology Infrastructure of China (http://www.geodata.cn (accessed on 15 May 2022))” for providing the ecological regionalization data for the Loess Plateau.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, Y.P.; Chen, Y.N.; Sun, F.; Li, Z. Recent vegetation browning and its drivers on Tianshan Mountain, Central Asia. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Y.; Song, X.Y.; Mu, X.M.; Gao, P.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G.J. Spatiotemporal vegetation cover variations associated with climate change and ecological restoration in the Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 209, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.D.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.Y.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. A Large and Persistent Carbon Sink in the World’s Forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Cong, N.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Ecological Engi-neering Projects Shifted the Dominance of Human Activity and Climate Variability on Vegetation Dynamics. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.M.; Fu, B.J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, N.Q.; Zeng, Z.Z.; Tian, H.Q.; Lyu, Y.H.; Chen, Y.Z.; Ciais, P.; Wang, Y.P. Recent leveling off of vegetation greenness and primary production reveals the increasing soil water limitations on the greening Earth. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Song, C.H.; Band, L.E.; Sun, G.; Li, J.X. Reanalysis of global terrestrial vegetation trends from MODIS products: Browning or greening? Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Peng, J.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, Y. Nearly Half of Global Vegetated Area Experienced Inconsistent Vegetation Growth in Terms of Greenness, Cover, and Productivity. Earths Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.H.; Piao, S.L.; Xu, B.D.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R.; et al. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xi, M.; Wang, L.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Qin, F. Vegetation responses to climate change and anthropogenic activity in China, 1982 to 2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.L.; Baret, F.; Plummer, S.; Schaepman-Strub, G. An Overview of Global Leaf Area Index (LAI): Methods, Products, Validation, and Applications. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 739–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Huang, X.R. Human disturbance caused stronger influences on global vegetation change than climate change. Peerj 2019, 7, e7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.C.; Piao, S.L.; Myneni, R.B.; Huang, M.T.; Zeng, Z.Z.; Canadell, J.G.; Ciais, P.; Sitch, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; Arneth, A.; et al. Greening of the earth and its drivers. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Miao, C.; Li, X.; Kong, D.; Gou, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S. Effects of vegetation changes and multiple environmental factors on evapotranspiration across China over the past 34 years. Earths Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.F.; Dao, R.N.; Hu, Y. Vegetation change and driving factors: Contribution analysis in the Loess Plateau of China during 2000–2015. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Wu, X.T.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wu, X.L.; Wang, S. Coupling human and natural systems for sustainability: Experience from China’s Loess Plateau. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2022, 13, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yue, D.X.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Huo, F.B.; Bao, Q.; Li, K. Drought resistance of vegetation and its change characteristics before and after the implementation of the Grain for Green Program on the Loess Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.B.; Liang, W.; Miao, C.Y. Hydrogeomorphic ecosystem responses to natural and anthropogenic changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 45, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Ma, C.M.; Chen, G. Introduction to Global Change Science, 4th ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 415–416. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, S.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Z.; Tian, J.; Abbas, S.; Luo, L.L.; Meresa, H.K. Both climate and socioeconomic drivers contribute to vegetation greening of the Loess Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1160–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J. Satellite evidence for significant biophysical consequences of the “Grain for Green” Program on the Loess Plateau in China. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2014, 119, 2261–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, P.L.; Xu, Q.; Jin, Z.; Yunus, A.P.; Luo, X.B.; Liu, M.H. Complex anthropogenic interaction on vegetation greening in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.N.; Guo, W.; Li, X.T.; Li, S.H. Heterogeneity of increases in net primary production under intensified human activity and climate variability on the Loess Plateau of China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lu, Y.H.; Fu, B.J.; Yin, L.C.; Yu, D.D. Impact of vegetation cover change on ecosystem services in the Loess Plateau and its threshold. J. Geogr. 2020, 75, 949–960. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.L.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y.T.; Piao, S.; Yang, H.B.; Lei, H.M.; Fu, B.J. Excessive afforestation and soil drying on China’s Loess Plateau. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, Z.F.; Song, S.F. Modulation of vegetation restoration on outdoor thermal comfort over the Loess Plateau, China from 1982 to 2015. Environ. Res. Commun. 2021, 3, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Wang, F.; Zong, Q.L.; Qin, P.; Liu, C.X. Impact of variations in vegetation on surface air temperature change over the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.Q.; Tian, L.; Zhao, X.N.; Wu, P. Feedbacks between vegetation restoration and local precipitation over the Loess Plateau in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.R.; Fu, M.C.; Sun, Y.F.; Bao, W.K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wu, J.J. How large-scale anthropogenic activities influence vegetation cover change in China? A review. Forests 2021, 12, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.K.; Tian, J.; Li, W.Y.; Su, W.R.; Guo, R.Y.; Liu, W.J. Spatio-temporal pattern and evolution trend of eco-environmental quality in the Yellow River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 7627–7636. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, N.; Srivastava, A.; Dumka, U.C. A Long-Term Spatiotemporal Analysis of Vegetation Greenness over the Himalayan Region Using Google Earth Engine. Climate 2021, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.D.; Shen, W.; Bai, X.Y. Response of net primary productivity to vegetation restoration in Chinese Loess Plateau during 1986–2015. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e219270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yin, D.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Su, W.; Li, X.; Wang, H. Spatial–Temporal Evolution of Vegetation NDVI in Association with Climatic, Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors in the Loess Plateau, China during 2000–2015: Quantitative Analysis Based on Geographical Detector Model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, C.C.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.R.; Wen, Z.M. The impacts of land conversion and management measures on the grassland net primary productivity over the Loess Plateau, Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. A remote sensing index for assessment of regional ecological changes. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Q.; Wang, Y.F.; Guan, H.D.; Shi, T.T.; Hu, X.S. Detecting Ecological Changes with a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI) Produced Time Series and Change Vector Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, F.; Kou, W. Assessment of spatial–temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE: A case study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, J.Y.; Qin, F. The improvement of ecological environment index model RSEI. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 403. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Cui, C.; Dai, Q. Contributions of Vegetation Greening and Climate Change to Evapotranspiration Trend after Large-Scale Vegetation Restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. Water 2021, 13, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Xie, B.; Shao, M.A.; Zhao, C. Primary Productivity and Precipitation-Use Efficiency in Temperate Grassland in the Loess Plateau of China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e135490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Wen, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Soil erosion, conservation, and eco- environment changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.J.; Wu, X.T.; Wang, Y.P. Dynamics and sustainability of social-ecological systems in the Loess Plateau. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Wang, B.; Wang, G.L.; Li, Z.S. Ecological regionalization and overview of the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7389–7397. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.S.; Xu, H.Q. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, R.K.; Zhao, J. Eco-Environmental Quality Monitoring in Beijing, China, Using an RSEI-Based Approach Combined With Random Forest Algorithms. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 196657–196666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Fu, M.; Feng, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhai, G. Spatiotemporal Changes in Vegetation Cover and Its Influencing Factors in the Loess Plateau of China Based on the Geographically Weighted Regression Model. Forests 2021, 12, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.J.; Jia, L.; Guo, Y.J.; Li, H.; Yao, S.B.; Chu, L.Q.; Lu, W.N.; Hou, M.Y.; Mo, B.B.; Wang, Y.M.; et al. Evaluation of the ecological effects of ecological restoration programs: A case study of the sloping land conversion program on the Loess Plateau, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.Y.; Deng, L.Q.; Wang, F.; Han, J.Q. Quantifying the contributions of human activities and climate change to vegetation net primary productivity dynamics in China from 2001 to 2016. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Peng, S.Z.; Li, Z. Detecting and attributing vegetation changes on China’s Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 247, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Jiao, J.Y.; Tian, H.W.; Xu, Q.; Feng, L.Q.; Wang, N.; Bai, L.C.; Yang, X. Spatial correlation analysis between vegetation NDVI and natural environmental factors based on geographical detector on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 3569–3580. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Jia, X.; Qin, Z.; Shen, J.; Chang, Q. Vegetation dynamics and climate change on the Loess Plateau, China: 1982–2011. Reg. Environ. Change 2016, 16, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Huang, W.J.; Cao, M.; Qi, W.; Li, J.S. Potential Evapotranspiration and Influence Factors of Vegetation in the Loess Plateau. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 5, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Sun, S.B.; Han, J.C.; Yan, J.W.; Liu, W.B.; Wei, Y.; Lu, N.; Sun, Y.Y. Impacts of Chinese Grain for Green program and climate change on vegetation in the Loess Plateau during 1982–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.B. Comparative Assessment of Vegetation Dynamics under the Influence of Climate Change and Human Activities in Five Ecologically Vulnerable Regions of China from 2000 to 2015. Forests 2015, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.M.; Huang, S.Z.; Huang, Q.; Bai, Q.J.; Leng, G.Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Wei, X.T.; Zheng, X.D. Effects of vegetation restoration on groundwater drought in the Loess Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Shen, Y.J.; Yu, Q. Decadal water storage decrease driven by vegetation changes in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, S2095927320304771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Q. Attribution Analysis of Vegetation Coverage Change and Its Impact on Water Storage on the Loess Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, Q.P.; Zhu, Q.K. Response of deep soil moisture to different vegetation types in the Loess Plateau of northern Shannxi, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Understanding the impacts of ‘Grain for Green’ land management practice on land greening dynamics over the Loess Plateau of China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.G.; Wang, Z.H.; Wei, F.Y.; Xiao, P.Q.; Shen, Z.Z.; Lv, X.Z.; Shi, Y.L. Determining the Contributions of Vegetation and Climate Change to Ecosystem WUE Variation over the Last Two Decades on the Loess Plateau, China. Forests 2021, 12, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.F.; He, H.M.; Wang, J.J.; Bai, C.Y.; Zhang, C.J. Vegetation Restoration and Its Environmental Effects on the Loess Plateau. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.J.; Piao, S.L.; Lü, Y.H.; Ciais, P.; Feng, X.M.; Wang, Y.F. Reduced sediment transport in the Yellow River due to anthropogenic changes. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Gao, G.Y.; Fu, B.J.; Gupta, H.V. Formulating an elasticity approach to quantify the effects of climate variability and ecological restoration on sediment discharge change in the Loess Plateau, China. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 9604–9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.X.; Cui, X.M.; Wang, D.C.; Wang, S.D.; Wang, H.S.; Yao, X.J.; Li, S.S. Spatial and temporal characteristics of water use efficiency in typical ecosystems on the Loess Plateau in the last 20 years, with drivers and implications for ecological restoration. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.B.; Deng, L.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Chen, Y.P.; Lin, X. Sustainability of eco-environment in semi-arid regions: Lessons from the Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 125, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Ortega, P.; García-Montero, L.G.; Sibelet, N. Temporal Patterns in Illumination Conditions and Its Effect on Vegetation Indices Using Landsat on Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).