A Multi-Band Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for Deriving Water Leaving Reflectances over Turbid Waters from VIIRS Data
Abstract
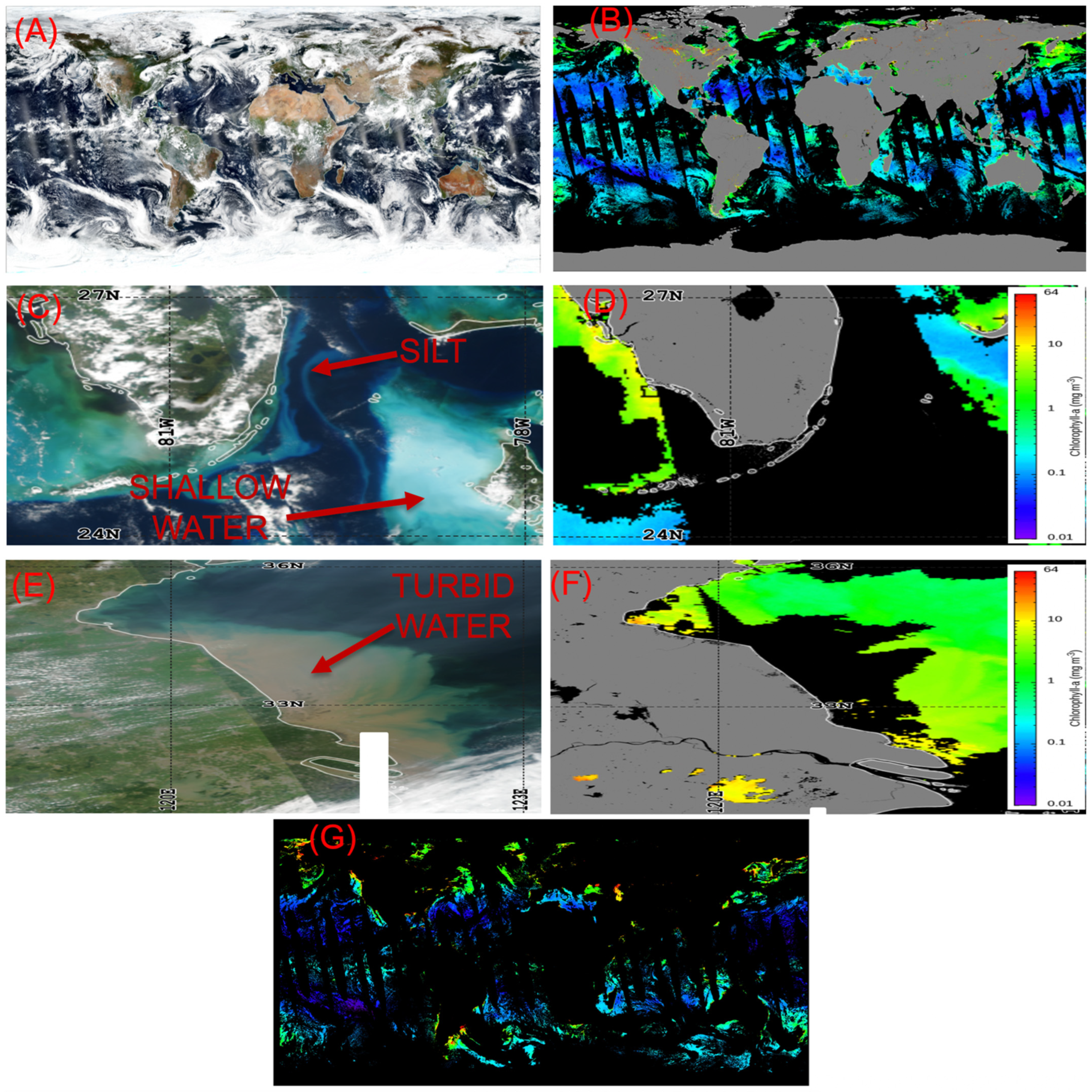
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. VIIRS Instrument
2.2. Atmospheric Corrections for VIIRS Data
3. Results
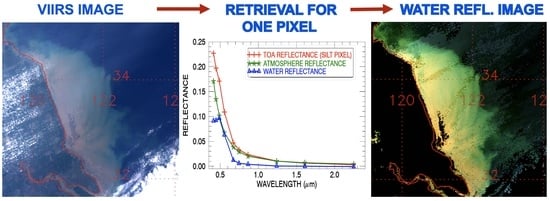
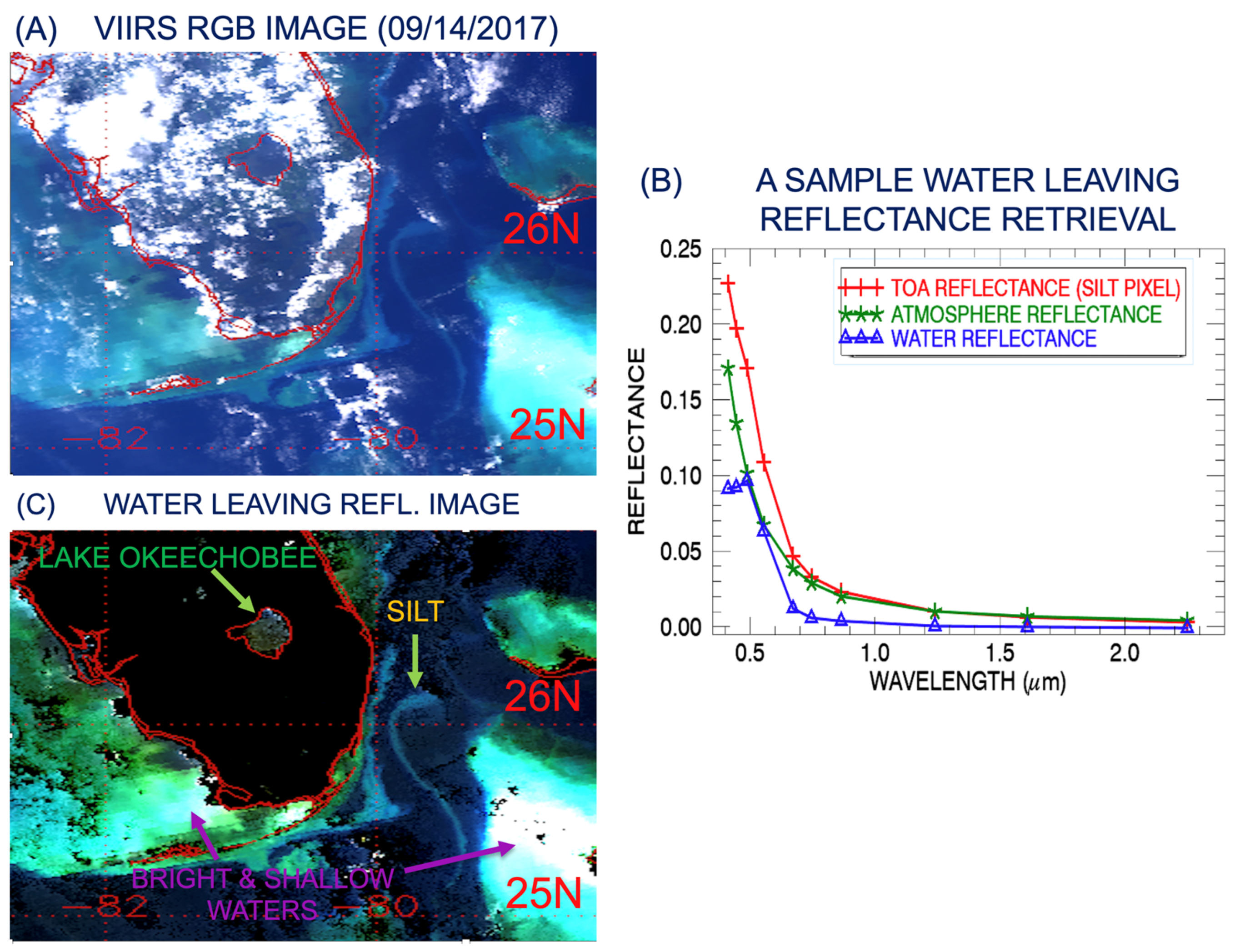
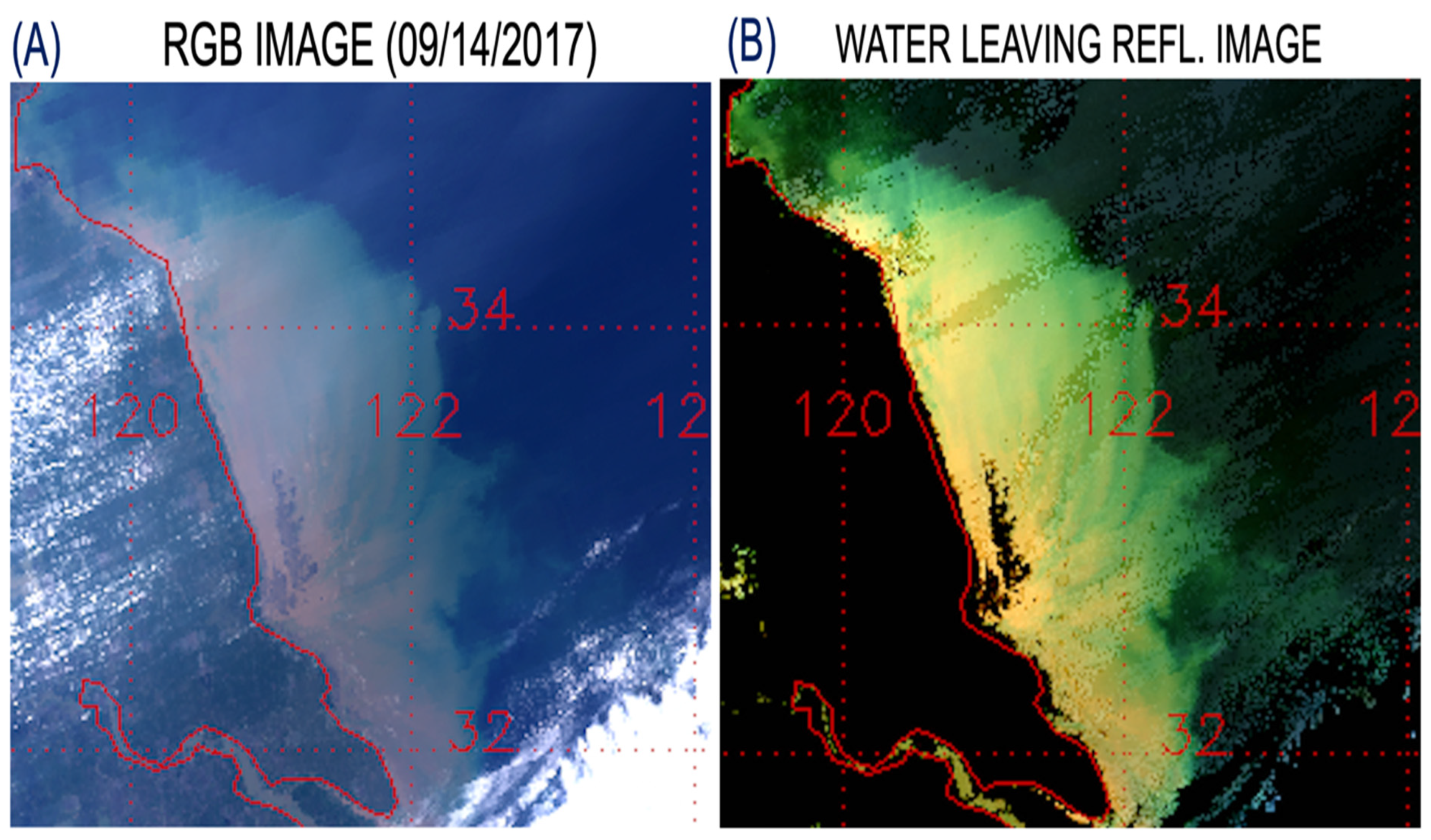
3.1. VIIRS Scene over Southern Florida Area, 14 September 2017
3.2. VIIRS Scene over Eastern Coastal Area of China, 14 September 2017
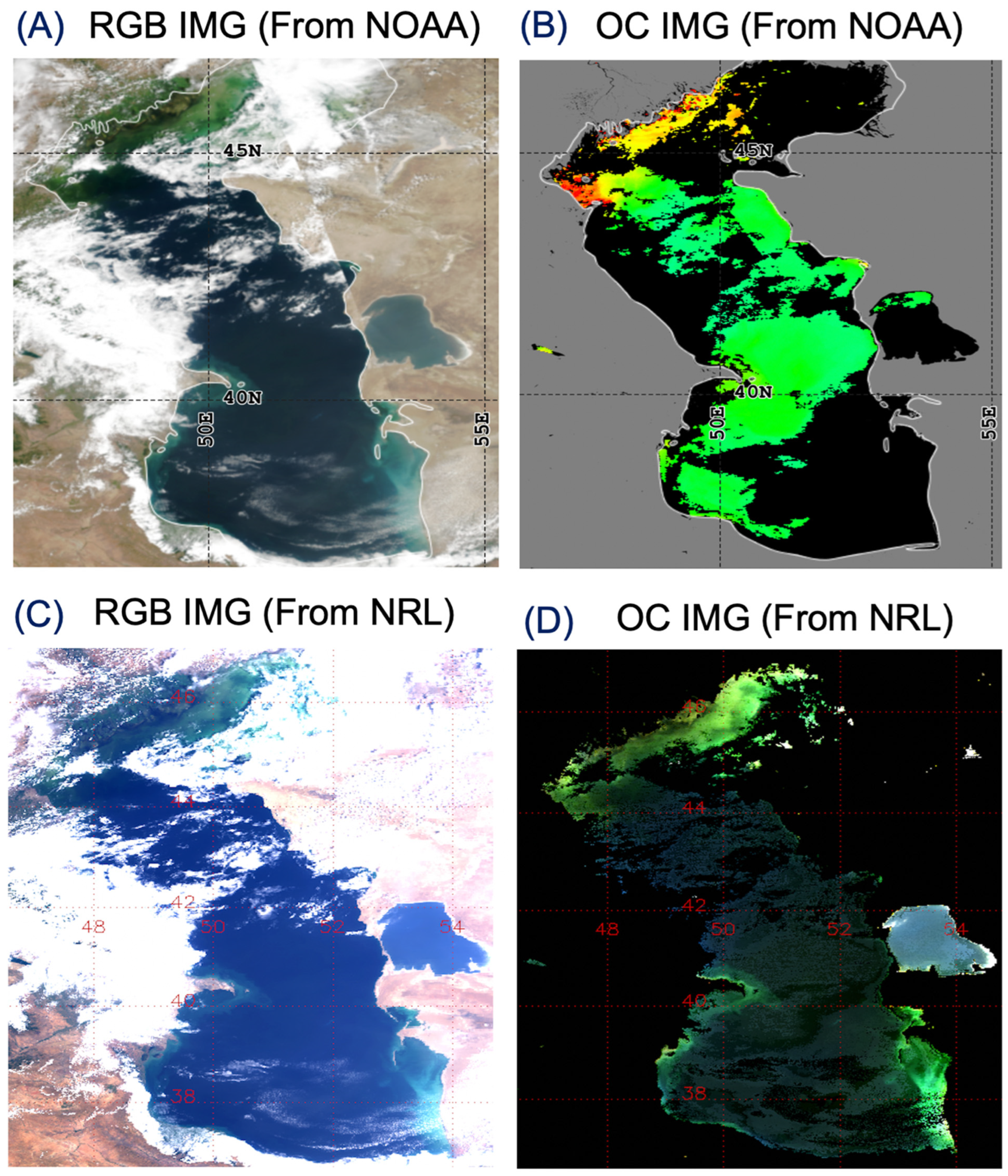
3.3. VIIRS Scene over Caspian Sea, 23 July 2022
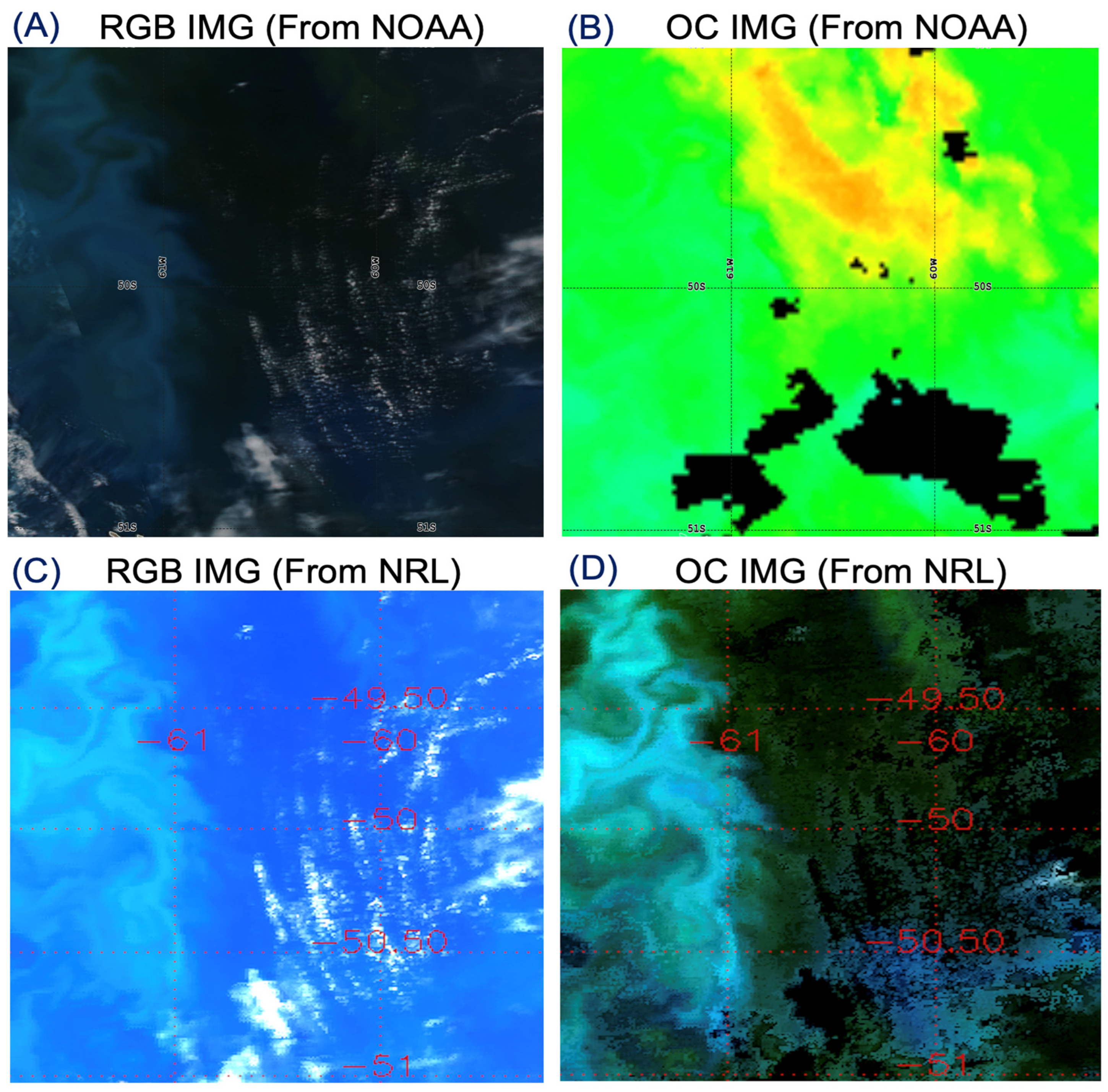
3.4. VIIRS Scene off the Eastern Coastal Area of Argentina, 8 December 2017
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordon, H.R. Removal of atmospheric effects from satellite imagery of the oceans. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooker, S.B.; Esaias, W.E.; Feldman, G.C.; Gregg, W.W.; McClain, C.R. An overview of SeaWiFS and ocean color, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD. SewWiFS Tech. Rep. NASA Tech. Memo. 1992, 1, 104566. [Google Scholar]
- Salomonson, V.V.; Barnes, W.L.; Maymon, P.W.; Montgomery, H.E.; Ostrow, H. MODIS: Advanced facility instrument for studies of the earth as a system. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1989, 27, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Menzel, W.P.; Tanre, D. Remote sensing of cloud, aerosol, and water vapor properties from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.E.; Barnes, W.L.; Lyapustin, A.; Privette, J.; Welsch, C.; DeLuccia, F.; Swenson, H.; Schueler, C.F.; Ardanuy, P.E.; Kealy, P.S.M. Using VIIRS to provide data continuity with MODIS. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 9–13 July 2001; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=976795 (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- McClain, C.R.; Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J. Genesis and evolution of NASA’s satellite ocean color program. Front. Remote Sens. 2022, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R. Evolution of ocean color atmospheric correction: 1970–2005. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.; Wang, M. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS: A preliminary algorithm. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, C.D.; Werdell, J.; Franz, B.; Ahmad, Z.; Bailey, S. Atmospheric Correction for Satellite Ocean Color Radiometry; NASA T/M-2016-217551; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, Maryland, 2016; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Barnes, B.; Feng, L.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L. On the interplay between ocean color data quality and data quantity: Impacts of quality control flags. IEEE Geosci. Rem. Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C. Comparison of valid ocean observations between MODIS Terra and Aqua over the global oceans. IEEE. Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C.; Kaufman, Y.J. Selection of the 1.375-µm MODIS channel for remote sensing of cirrus clouds and stratospheric aerosols from space. J. Atm. Sci. 1995, 52, 4231–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C.; Yang, P.; Han, W.; Li, R.-R.; Wiscombe, W.J. An algorithm using visible and 1.38-micron channels to retrieve cirrus cloud reflectances from aircraft and satellite data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.-C.; Montes, M.J.; Ahmad, Z.; Davis, C.O. Atmospheric correction algorithm for hyperspectral remote sensing of ocean color from space. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.; Davis, C. Naval EarthMap Observer (NEMO) Satellite. 1999. Available online: https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie/3753/0000/Naval-EarthMap-Observer-NEMO-satellite/10.1117/12.366268.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Fraser, R.S.; Mattoo, S.; Yeh, E.-N.; McClain, C.R. Algorithm for atmospheric and glint corrections of satellite measurements of ocean pigment. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 17107–17118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.; Ferrare, R.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Mattoo, S. Algorithm for atmospheric corrections of aircraft and satellite imagery. NASA Tech. Memo. 1989, 13, 100751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanre, D.; Deroo, C.; Duhaut, P.; Herman, M.; Morcrette, J.J.; Perbos, J.; Deschamps, P.Y. Description of a computer code to simulate the satellite signal in the solar spectrum: The 5S code. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1990, 11, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Fraser, R.S. An iterative radiative transfer code for ocean-atmosphere systems. J. Atmos. Sci. 1982, 39, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.W.; Hu, Y. An improved pseudo spherical shell algorithm for vector radiative transfer. J. Quant. Spectr. Rad. Transf. 2022, 282, 108132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, G.; Green, R.O.; Chrien, T.G.; Enmark, H.T.; Hansen, E.G.; Porter, W.M. The Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer. Remote Sens. Env. 1993, 44, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, C.; Esaias, W.; Feldman, G.; Frouin, R.; Gregg, W.; Hooker, S. The proposal for the NASA Sensor Intercalibration and Merger for Biological and Interdisciplinary Oceanic Studies (SIMBIOS) Program; NASA Tech. Memo. 2002-210008; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, Maryland, 2002; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.-C.; Montes, M.J.; Li, R.-R.; Dierssen, H.M.; Davis, C.O. An atmospheric correction algorithm for remote sensing of bright coastal waters using MODIS land and ocean channels in the solar spectral region. IEEE Trans. Geosc. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
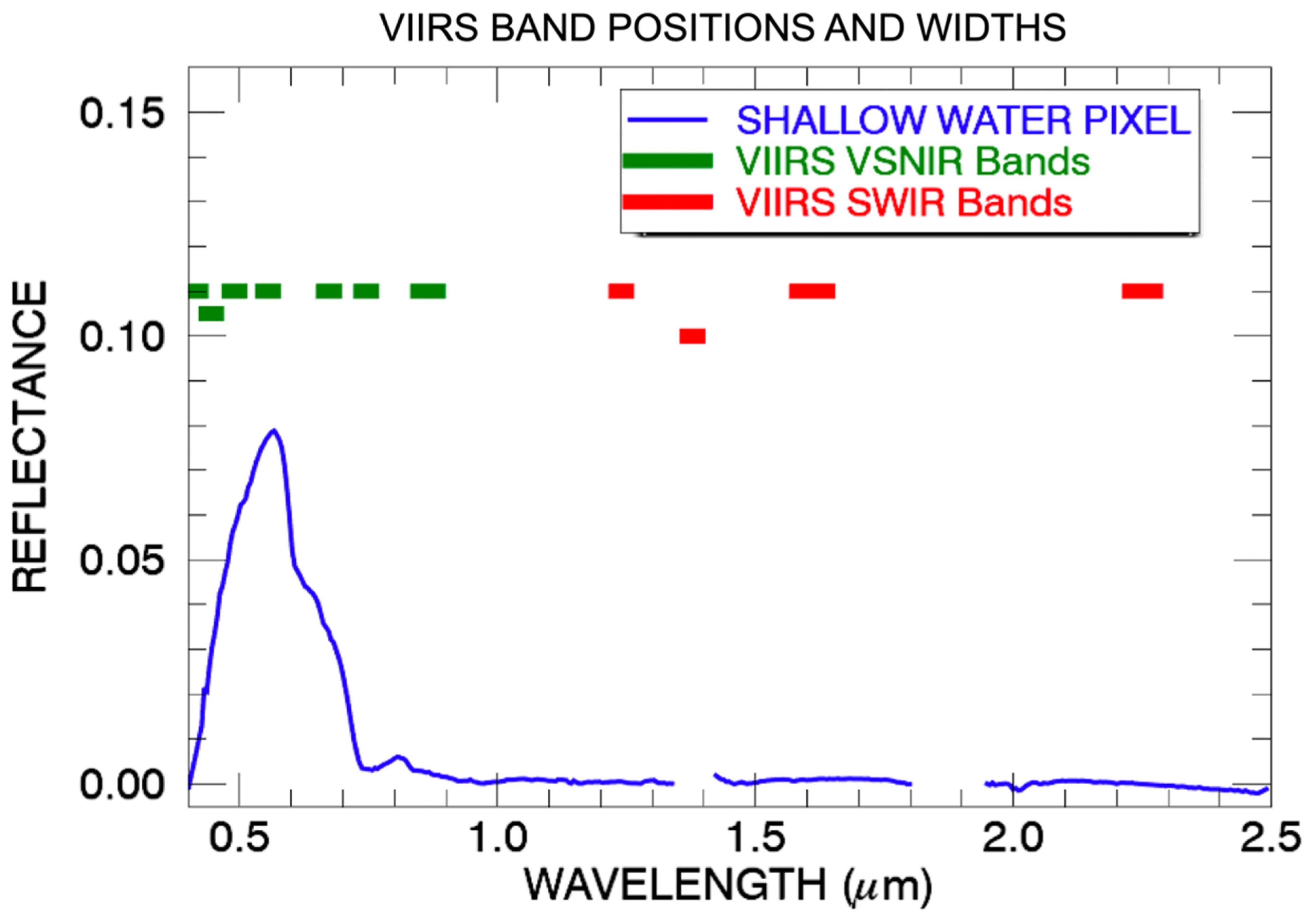
| Bands | Wavelength (μm) | Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | 0.405–0.425 | 750 |
| M2 | 0.435–0.455 | 750 |
| M3 | 0.480–0.500 | 750 |
| M4 | 0.545–0.565 | 750 |
| M5 | 0.663–0.684 | 750 |
| M6 | 0.736–0.756 | 750 |
| M7 | 0.846–0.885 | 750 |
| M8 | 1.230–1.250 | 750 |
| M9 (Cirrus Band) | 1.368–1.388 | 750 |
| M10 | 1.580–1.640 | 750 |
| M11 | 2.225–2.275 | 750 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, B.-C.; Li, R.-R. A Multi-Band Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for Deriving Water Leaving Reflectances over Turbid Waters from VIIRS Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020425
Gao B-C, Li R-R. A Multi-Band Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for Deriving Water Leaving Reflectances over Turbid Waters from VIIRS Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(2):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020425
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Bo-Cai, and Rong-Rong Li. 2023. "A Multi-Band Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for Deriving Water Leaving Reflectances over Turbid Waters from VIIRS Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 2: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020425
APA StyleGao, B.-C., & Li, R.-R. (2023). A Multi-Band Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for Deriving Water Leaving Reflectances over Turbid Waters from VIIRS Data. Remote Sensing, 15(2), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020425