ADAfinder Tool Applied to EGMS Data for the Structural Health Monitoring of Urban Settlements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. EGMS Data
2.2. ADAfinder Tool
2.3. Proposed Methodology
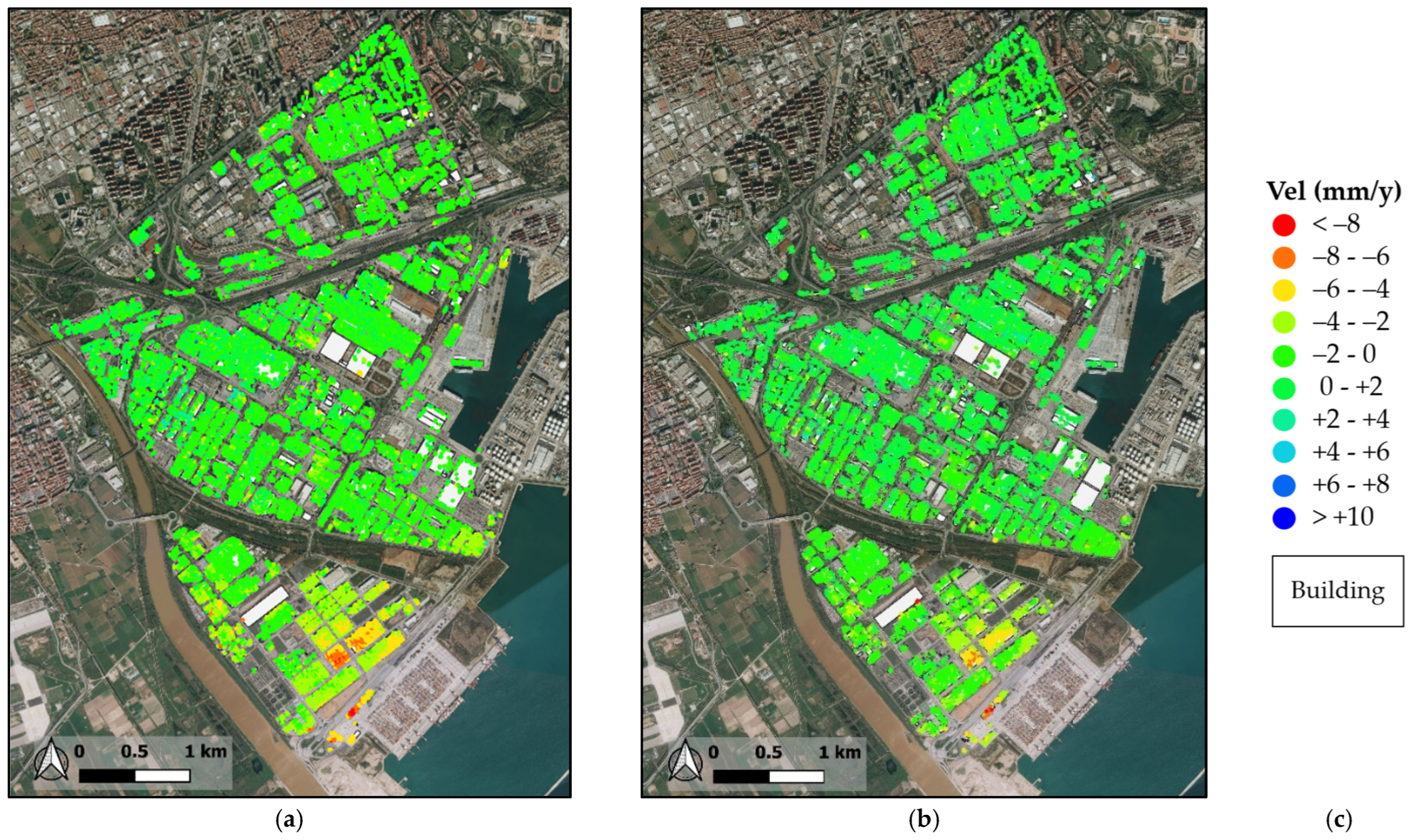
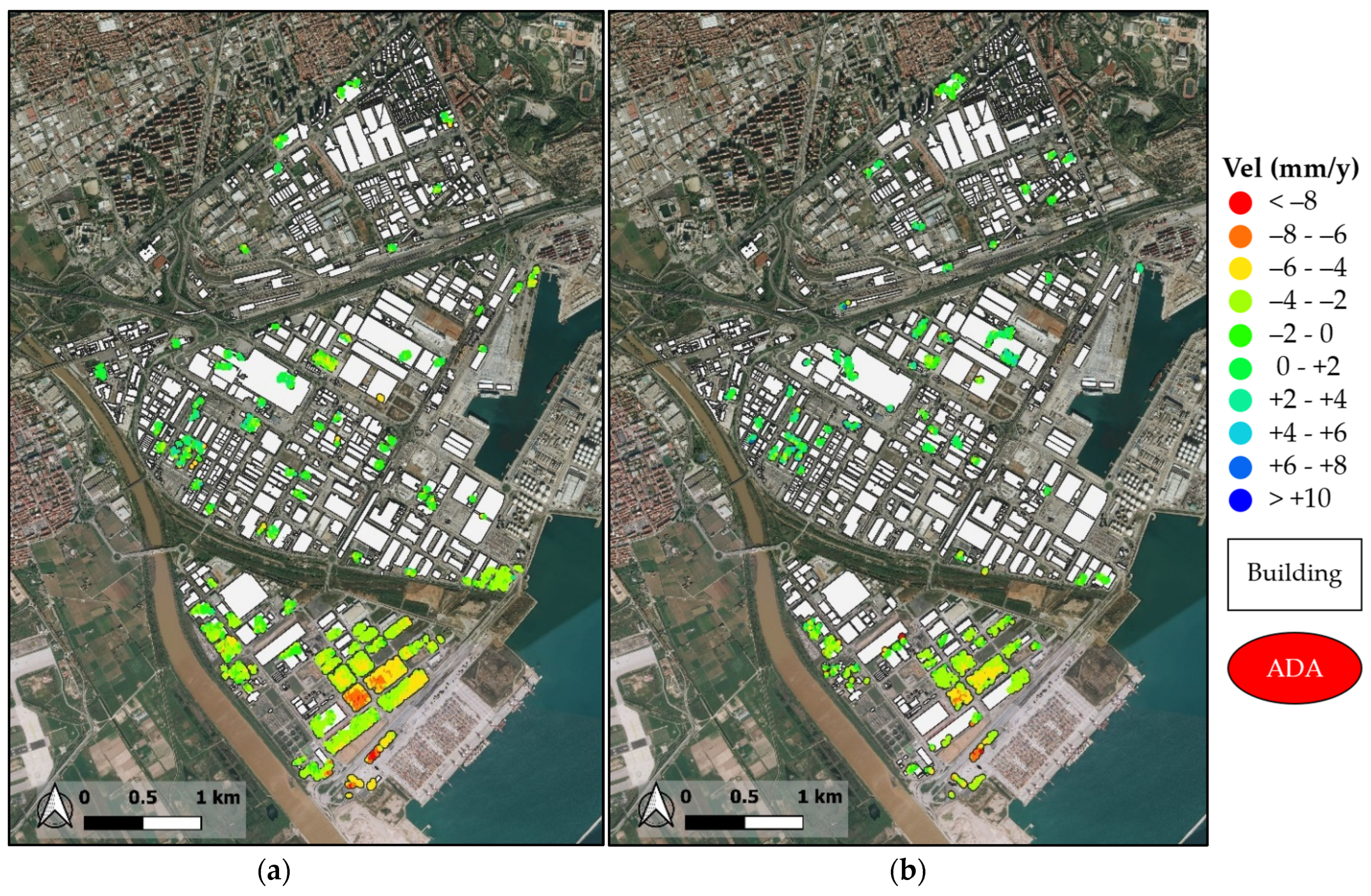
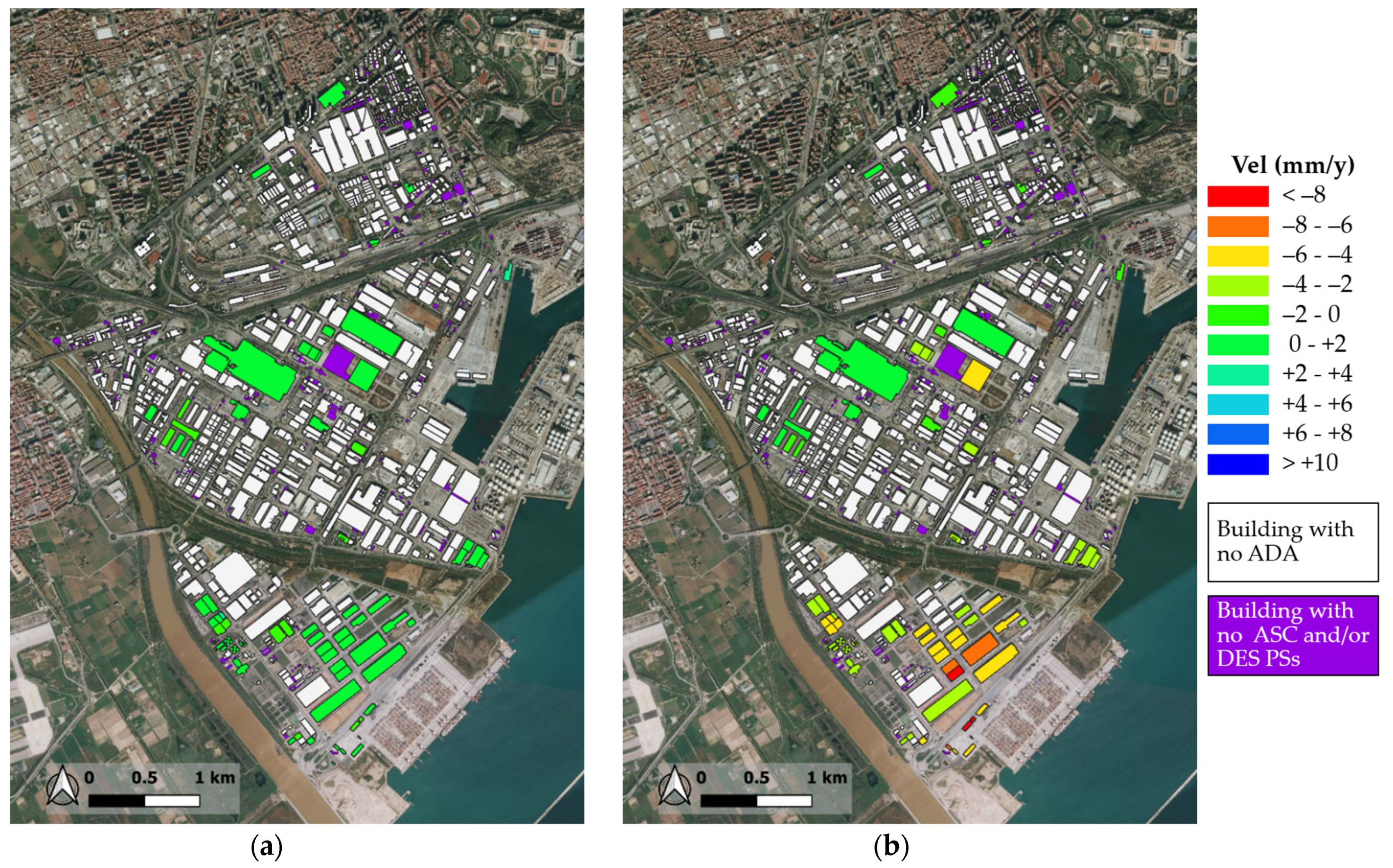
3. Experimental Results
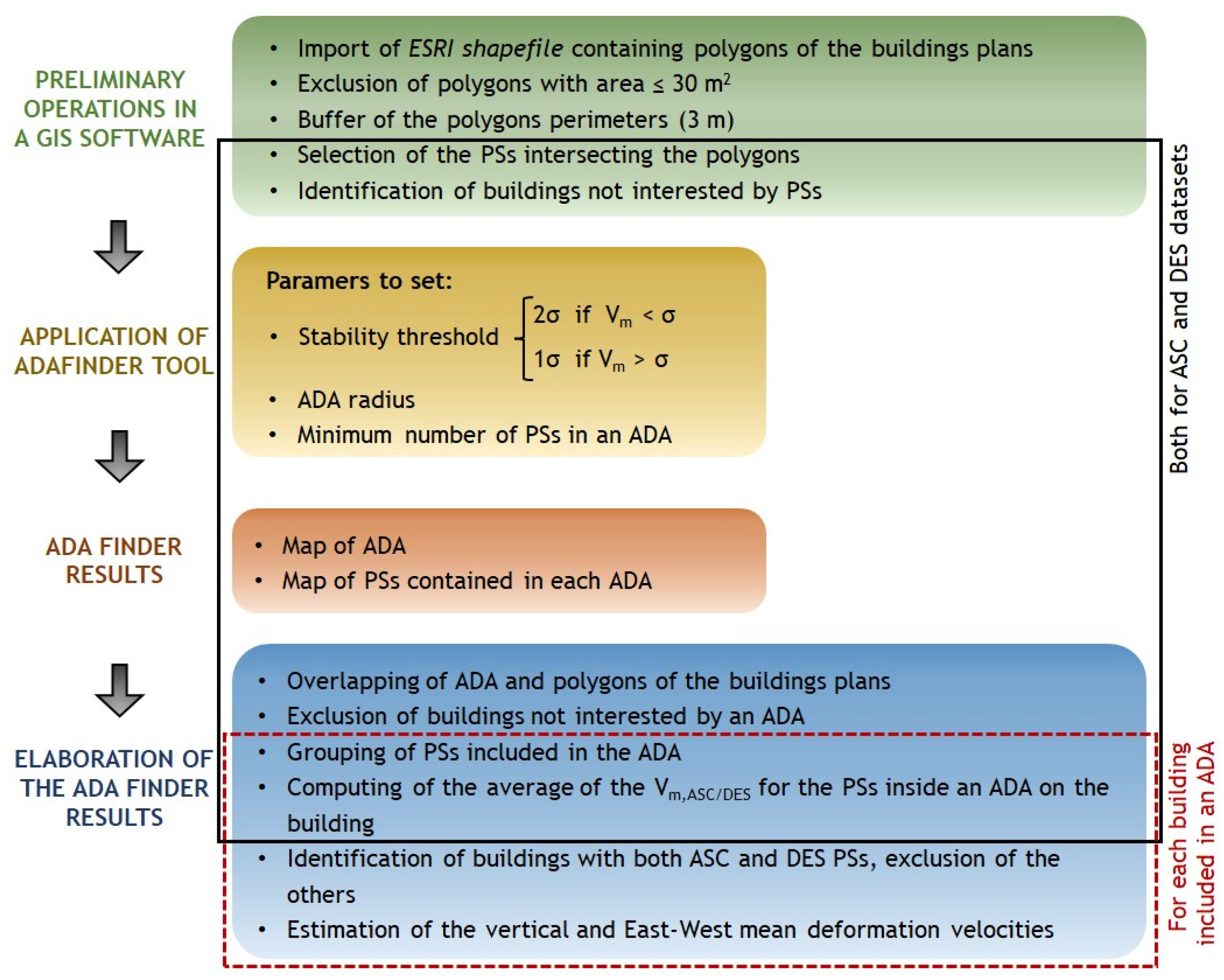
3.1. Preliminary Operations
3.2. Application of ADAfinder Tool and Results
3.3. Elaboration of the ADAfinder Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomás, R.; Li, Z. Earth Observations for Geohazards: Present and Future Challenges. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Raspini, F.; Solari, L.; Del Soldato, M.; Ciampalini, A.; Rosi, A.; Casagli, N. From Picture to Movie: Twenty Years of Ground Deformation Recording Over Tuscany Region (Italy) with Satellite InSAR. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucoules, D.; Colesanti, C.; Carnec, C. Use of SAR interferometry for detecting and assessing ground subsidence. C. R. Geosci. 2007, 339, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Ferretti, A.; Minati, F.; Falco, S.; Trillo, F.; Colombo, D.; Novali, F.; Malvarosa, F.; Mammone, C.; Vecchioli, F.; et al. Analysis of surface deformations over the whole Italian territory by interferometric processing of ERS, Envisat and COSMO-SkyMed radar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 250–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Romero, R.; Mulas, J.; Marturià, J.J.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; González, P.J.; Fernández, J.; et al. Radar interferometry techniques for the study of ground subsidence phenomena: A review of practical issues through cases in Spain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 71, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, D.; Fornaro, G.; Pauciullo, A.; Zhu, X.; Bamler, R. Tomographic imaging and monitoring of buildings with very high resolution SAR data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arangio, S.; Calò, F.; Di Mauro, M.; Bonano, M.; Marsella, M.; Manunta, M. An application of the SBAS-DInSAR technique for the assessment of structural damage in the city of Rome. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2013, 10, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Pratesi, F.; Nolesini, T.; Casagli, N. Building deformation assessment by means of persistent scatterer interferometry analysis on a landslide affected area: The Volterra (Italy) case study. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4678–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhou, W.; Chen, C.; Ma, P. Extended D-TomoSAR Displacement Monitoring for Nanjing (China) City Built Structure Using High-Resolution TerraSAR/TanDEM-X and Cosmo SkyMed SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusson, D.; Rossi, C.; Ozkan, I.F. Early warning system for the detection of unexpected bridge displacements from radar satellite data. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 11, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, F.; Miano, A.; Giannetti, I.; Mele, A.; Bonano, M.; Lanari, R.; Meda, A.; Prota, A. On the integration of multi-temporal synthetic aperture radar interferometry products and historical surveys data for buildings structural monitoring. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, A.; Mele, A.; Calcaterra, D.; Di Martire, D.; Infante, D.; Prota, A.; Ramondini, M. The use of satellite data to support the structural health monitoring in areas affected by slow-moving landslides: A potential application to reinforced concrete buildings. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 20, 3265–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, A.; Miano, A.; Di Martire, D.; Infante, D.; Ramondini, M.; Prota, A. Potential of remote sensing data to support the seismic safety assessment of reinforced concrete buildings affected by slow-moving landslides. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2022, 22, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, A.; Di Carlo, F.; Mele, A.; Giannetti, I.; Nappo, N.; Rompato, M.; Striano, P.; Bonano, M.; Bozzano, F.; Lanari, R.; et al. GIS Integration of DInSAR Measurements, Geological Investigation and Historical Surveys for the Structural Monitoring of Buildings and Infrastructures: An Application to the Valco San Paolo Urban Area of Rome. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talledo, D.A.; Miano, A.; Bonano, M.; Di Carlo, F.; Lanari, R.; Manunta, M.; Meda, A.; Mele, A.; Saeta, A.; Stella, A. Satellite radar interferometry: Potential and limitations for structural assessment and monitoring. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Wasowski, J. Satellite interferometry for monitoring ground deformations in the urban environment. In Proceedings of the 10th IAEG Congress, Nottingham, UK, 6–10 September 2006; pp. 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Manunta, M.; Marsella, M.; Zeni, G.; Sciotti, M.; Atzori, S.; Lanari, R. Two-scale surface deformation analysis using the SBAS-DInSAR technique: A case study of the city of Rome, Italy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1665–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Bozzano, F.; Marra, F.; Wegmuller, U.; Cinti, F.R.; Moro, M.; Saroli, M. Subsidence induced by urbanisation in the city of Rome detected by advanced InSAR technique and geotechnical investigations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3160–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, D.; Confuorto, P.; Di Martire, D.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D. Use of DInSAR data for multi-level vulnerability assessment of urban settings affected by slow-moving and intermittent landslides. Procedia Eng. 2016, 158, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduto, D.; Nicodemo, G.; Maccabiani, J.; Ferlisi, S. Multi-scale analysis of settlement-induced building damage using damage surveys and DInSAR data: A case study in the Netherlands. Eng. Geol. 2017, 218, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchiarulo, V.; Milillo, P.; DeJong, M.J.; González Martí, J.; Sánchez, J.; Giardina, G. Integrated InSAR monitoring and structural assessment of tunnelling-induced building deformations. Struct. Control Health 2021, 28, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehls, J.F.; Larsen, Y.; Marinkovic, P.; Lauknes, T.R.; Stødle, D.; Moldestad, D.A. INSAR. No: A National Insar Deformation Mapping/Monitoring Service in Norway-From Concept to Operations. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 5461–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, A.C.; Frei, M.; Lege, T. A Copernicus downstream-service for the nationwide monitoring of surface displacements in Germany. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Del Soldato, M.; Solari, L.; Novali, F.; Del Conte, S.; Rucci, A.; Ferretti, A.; Casagli, N. Continuous, semi-automatic monitoring of ground deformation using Sentinel-1 satellites. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Soldato, M.; Solari, L.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Montalti, R.; Ferretti, A.; Pellegrineschi, V.; Casagli, N. Monitoring Ground Instabilities Using SAR Satellite Data: A Practical Approach. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Del Soldato, M.; Montalti, R.; Bianchini, S.; Raspini, F.; Thuegaz, P.; Bertolo, D.; Tofani, V.; Casagli, N. A Sentinel-1 based hot-spot analysis: Landslide mapping in north-western Italy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 7898–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Solari, L.; Mróz, M.; Balasis-Levinsen, J.; Casagli, N.; Frei, M.; Oyen, A.; Moldestad, D.A.; Bateson, L.; Guerrieri, L.; et al. The evolution of wide-area DInSAR: From regional and national services to the European Ground Motion Service. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Solari, L.; Balasis-Levinsen, J.; Casagli, N.; Frei, M.; Oyen, A.; Moldestad, D.A. Ground deformation monitoring at continental scale: The European Ground Motion Service. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 43, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Minati, F.; Trillo, F.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Passera, E.; Dehls, J.; Larsen, Y.; Marinkovic, P.; Eineder, M.; et al. European Ground Motion Service (EGMS). In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 3293–3296. [Google Scholar]
- Crosetto, M.; Solari, L.; Balasis-Levinsen, J.; Bateson, L.; Casagli, N.; Frei, M.; Oyen, A.; Moldestad, D.A.; Mróz, M. Deformation Monitoring at European Scale: The Copernicus Ground Motion Service. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 43, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisina, C.; Zucca, F.; Notti, D.; Colombo, A.; Cucchi, A.; Savio, G.; Giannico, C.; Bianchi, M. Geological Interpretation of PSInSAR Data at Regional Scale. Sensors 2008, 8, 7469–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Cigna, F.; Righini, G.; Proietti, C.; Casagli, N. Landslide HotSpot Mapping by means of Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 1155–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Barra, A.; Herrera, G.; Bianchini, S.; Monserrat, O.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Crosetto, M.; Sarro, R.; Moretti, S. Fast detection of ground motions on vulnerable elements using Sentinel-1 InSAR data. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk. 2018, 9, 152–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, A.; Vitiello, A.; Bonano, M.; Miano, A.; Lanari, R.; Acampora, G.; Prota, A. On the Joint Exploitation of Satellite DInSAR Measurements and DBSCAN-Based Techniques for Preliminary Identification and Ranking of Critical Constructions in a Built Environment. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A.; Solari, L.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Monserrat, O.; Bianchini, S.; Herrera, G.; Crosseto, M.; Sarro, R.; Gonzales-Alonso, E.; Mateos, R.M.; et al. A methodology to detect and update active deformation areas based on sentinel-1 SAR images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.A.; Tomás, R.; Barra, A.; Pagán, J.I.; Reyes-Carmona, C.; Solari, L.; Vinielles, J.L.; Falco, S.; Crosetto, M. ADAtools: Automatic detection and classification of active deformation areas from PSI displacement maps. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EGMS White Paper. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/egms-white-paper (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- CLSM. Available online: https://www.copernicus.eu/en/copernicus-services/land (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Passera, E.; Capes, R. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document. EGMS Documentation. 2021. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/egms-algorithm-theoretical-basis-document (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Kotzerke, P.; Siegmund, R.; Langenwalter, J. Product User Manual. EGMS Documentation. 2022. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/egms-product-user-manual (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Tomás, R.; Pagán, J.I.; Navarro, J.A.; Cano, M.; Pastor, J.L.; Riquelme, A.; Cuevas-Gonzales, M.; Crosseto, M.; Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; et al. Semi-automatic identification and pre-screening of geological–geotechnical deformational processes using persistent scatterer interferometry datasets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Monti-Guarnieri, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Massonet, D. InSAR Principles-Guidelines for SAR Interferometry Processing and Interpretation, TM-19; ESA Publications: Auckland, New Zealand, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- OpenStreetMap. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org/ (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Miano, A.; Mele, A.; Prota, A. Fragility curves for different classes of existing RC buildings under ground differential settlements. Eng. Struct. 2022, 257, 114077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Y.; Wong, D.W. An adaptive inverse-distance weighting spatial interpolation technique. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Count | Minimum Vm | Maximum Vm | Average Vm | σ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending | 6389 | −7.30 | 6.60 | 0.11 | 0.82 |
| Descending | 4347 | −6.20 | 7.30 | 0.15 | 0.94 |
| Count | Minimum Vm | Maximum Vm | Average Vm | σ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending | 33,965 | −10.50 | 6.90 | −0.90 | 1.54 |
| Descending | 19,333 | −8.60 | 7.70 | −0.12 | 1.35 |
| Eixample | Zona Franca | |
|---|---|---|
| Total number of buildings | 540 | 1358 |
| % of buildings with no ASC PSs | 3% | 12% |
| % of buildings with no DESC PSs | 1% | 18% |
| % of monitorable buildings | 96% | 77% |
| Count | Minimum Vm | Maximum Vm | Average Vm | σ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending | 4800 | −7.30 | 6.90 | 0.12 | 1.06 |
| Descending | 1624 | −6.20 | 7.30 | 0.15 | 1.28 |
| Count | Minimum Vm | Maximum Vm | Average Vm | σ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending | 6333 | −10.50 | 6.80 | −2.82 | 2.15 |
| Descending | 2248 | −8.60 | 7.70 | −1.50 | 2.49 |
| Eixample | Zona Franca | |
|---|---|---|
| Total number of buildings | 540 | 1358 |
| % of buildings included in an ASC ADA | 54% | 13% |
| % of buildings included in a DES ADA | 53% | 10% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mele, A.; Crosetto, M.; Miano, A.; Prota, A. ADAfinder Tool Applied to EGMS Data for the Structural Health Monitoring of Urban Settlements. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020324
Mele A, Crosetto M, Miano A, Prota A. ADAfinder Tool Applied to EGMS Data for the Structural Health Monitoring of Urban Settlements. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(2):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020324
Chicago/Turabian StyleMele, Annalisa, Michele Crosetto, Andrea Miano, and Andrea Prota. 2023. "ADAfinder Tool Applied to EGMS Data for the Structural Health Monitoring of Urban Settlements" Remote Sensing 15, no. 2: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020324
APA StyleMele, A., Crosetto, M., Miano, A., & Prota, A. (2023). ADAfinder Tool Applied to EGMS Data for the Structural Health Monitoring of Urban Settlements. Remote Sensing, 15(2), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020324







