Abstract
Floods are severe natural disasters that are harmful and frequently occur across the world. From May to July 2022, the strongest, broadest, and longest rainfall event in recent years occurred in Guangdong Province, China. The flooding caused by continuous precipitation and a typhoon resulted in severe losses to local people and property. During flood events, there is an urgent need for timely and detailed flood inundation mapping for areas that have been severely affected. However, current satellite missions cannot provide sufficient information at a high enough spatio-temporal resolution for flooding applications. In contrast, spaceborne Global Navigation Satellite System reflectometry technology can be used to observe the Earth’s surface at a high spatio-temporal resolution without being affected by clouds or surface vegetation, providing a feasible scheme for flood disaster research. In this study, Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) L1 science data were processed to obtain the change in the delay-Doppler map and surface reflectivity (SR) during the flood event. Then, a flood inundation map of the extreme precipitation was drawn using the threshold method based on the CYGNSS SR. Additionally, the flooded areas that were calculated based on the soil moisture from the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) data were used as a reference. Furthermore, the daily Dry Wet Abrupt Alternation Index (DWAAI) was used to identify the occurrence of the flood events. The results showed good agreement between the flood inundation that was derived from the CYGNSS SR and SMAP soil moisture. Moreover, compared with the SMAP results, the CYGNSS SR can provide the daily flood inundation with higher accuracy due to its high spatio-temporal resolution. Furthermore, the DWAAI can identify the transformation from droughts to floods in a relatively short period. Consequently, the distributions of and variations in flood inundation under extreme weather conditions can be identified on a daily scale with good accuracy using the CYGNSS data.
1. Introduction
Floods are considered one of the most severe natural disasters in the world [1]. They are frequently distributed in places with dense populations, densely distributed lakes, and abundant rainfall, and they cause extensive damage to the natural and artificial environment [2,3]. China has a vast territory, complex terrain, and a remarkable monsoon climate. About 35% of the country’s cultivated land, 40% of the population, and 70% of the industry and agriculture are threatened by floods. Property loss due to floods ranks as the most frequent consequence in China, with China being one of the countries in the world with frequent floods and a wide range of impacts [4]. Recently, Guangdong Province suffered from extreme precipitation and a typhoon, which caused severe floods. Therefore, providing real-time flood detection plays an essential role in the decision-making, planning, and implementation of flood management schemes.
During floods, the Earth’s surface is usually covered by clouds. Thus, traditional optical remote sensing technology cannot penetrate the clouds and monitor the progress of the floods [5]. In contrast, microwave remote sensing is almost not affected by vegetation or clouds [6,7]. Consequently, it is considered to be an effective way to monitor flood disasters. Thus, microwave remote sensing data can be used to map flood inundation timeously and provide critical information for disaster relief agencies to make decisions.
Global Navigation Satellite System reflectometry (GNSS-R) is a new microwave remote sensing technology that is based on satellite navigation signals [8,9]. It can use remote geophysical parameters by receiving and processing GNSS signals reflected from the Earth’s surface [10]. The first spaceborne GNSS-R satellite was launched from the United Kingdom Disaster Monitoring Station in September 2003. The onboard GNSS-R equipment was used to obtain the physical coefficients of the Earth’s surface, such as sea surface roughness, which supported the feasibility of using the spaceborne GNSS-R signal for measuring the environmental parameters of the sea and land surface [11]. Therefore, the successful launches of satellites with GNSS-R equipment, including Britain’s Disaster Monitoring System-1 and Britain’s TechDemoSat-1, have ushered in a new era of spaceborne GNSS-R [12,13].
With the development of spaceborne GNSS-R, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched the Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) in December 2016, which is designed to mainly monitor ocean cyclones [14]. Further research has shown its data to be not only applicable to the study of ocean parameters but also to retrieving terrestrial physical properties, e.g., soil moisture [15,16,17,18], and vegetation biomass [19,20,21,22], especially for flood monitoring under extreme weather conditions as the signal can penetrate the clouds. Because of the sensitivity of the surface reflectivity (SR) of the CYGNSS to water, in 2018, Chew et al. used the CYGNSS data to draw a flood map of the Atlantic hurricane season during 2017. This was the first time that CYGNSS observations were applied to flood detection [23]. In 2019, Wan et al. [24] used CYGNSS data to verify the consistency between the SR and Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) soil moisture and surface brightness temperature. Furthermore, Zavorotny [25] found that the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the delay-Doppler map (DDM) was higher than that of the land due to the reflected GNSS signal of the water bodies in Qinghai Lake in China, indicating that DDM SNR can be used to identify inland water bodies. Then, Wang et al. [26] used DDM to distinguish permanent inland water bodies and land using the image segmentation method and refined power ratio. Moreover, Chew [27] proposed a flood monitoring theoretical model that is based on the change in the CYGNSS SR for different land cover types in 2020, indicating that CYGNSS SR is affected by surface roughness. When a flood occurred, the SR of the densely vegetated areas changed considerably before and after the flood, while that of the relatively smooth surfaces did not obviously change. Moreover, Song [28] proposed a dual-branch neural network method for flood detection based on the CYGNSS DDM and SMAP vegetation data and verified the use of the CYGNSS data for flood monitoring. In 2021, Yang and Zhang [5,7] both studied flood inundation in Henan Province during extreme precipitation events in 2020 using CYGNSS SR and the threshold method. It should be noted that Henan Province is located in the middle of mainland China, which belongs to a temperate monsoon climate with less precipitation and less moisture. In contrast, Guangdong Province is in South China and belongs to a subtropical monsoon climate with abundant precipitation and more soil moisture. Thus, it is not yet known whether the threshold method that was applied to detect flood inundation in Henan Province would be appropriate for Guangdong Province.
In 2022, Guangdong Province was affected by continuous heavy rainfall and typhoons from 11 May to 08 July, with frequent flooding and geological disasters. More than ten million people were affected, causing significant economic losses. To detect the flood inundation using CYGNSS observations in Guangdong Province, CYGNSS L1 V3.0 data were employed to obtain the sensitivity of the SR, the threshold values were selected according to different surface feature categories, and flood inundation maps were drawn for the flood events. In addition, the SMAP soil moisture was used to validate the use of CYGNSS SR for flood monitoring. Finally, the distributions of and variations in flood inundation were analyzed using the CYGNSS SR, SMAP soil moisture, and precipitation data. The results showed that there was a strong correlation between the CYGNSS SR and rainfall. The findings support that when the CYGNSS data are used, flood monitoring results with a high spatial and temporal resolution can be obtained, and flood inundation maps with high accuracy can be drawn. The findings can provide near-real-time data support for future flood monitoring and are of great significance for the study of changing flood behavior in a certain region.
Compared with traditional optical remote sensing monitoring, CYGNSS SR is less affected by the time–space resolution. Thus, using the threshold method to identify inundated areas has the advantage of being faster and more efficient. In addition, the results show that there was a strong correlation between CYGNSS SR and rainfall. This study verifies the capability of CYNGSS for detection the flood events as well as monitoring flood inundation dynamics with high spatial and temporal resolution. The results provide evidence for the further use of spaceborne GNSS-R to monitor environmental parameters of land surface.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Guangdong Province is located in the south of the Chinese mainland (20°09′N–25°31′N, 109°45′E–117°20′E), with Fujian in the east, Guangxi in the west, Jiangxi and Hunan in the north, and Hong Kong, Macao, and Hainan Island in the south, and a total area of 179,800 km2. From 11 May to 8 July 2022, most of southern China experienced heavy rainfall, especially in Guangdong Province. Guangdong Province experienced the strongest, widest-ranging, and longest heavy rainfall in recent years, with an average rainfall of more than 120 mm/d. The meteorological department termed the heavy rainfall process around the Dragon Boat Festival “Dragon Boat Water”, which lasted until 20 June. The conditions that led to the heavy rainfall were warm and humid airflow in the Western Pacific and cold air in the North meeting south of the Yangtze River and South China, and the cold and warm air mixed for a long time, resulting in a longer duration of rainfall. Additionally, the recent cyclone storm in the Bay of Bengal provided sufficient moisture conditions for the rainfall. On 30 June, Typhoon Siam Pa was generated in the South China Sea. Its cloud system circulated over a large area, moved slowly, and lasted for a long time. After landing, it brought strong winds, and the rain affected many places in Guangdong Province, causing substantial economic losses.
This study selected the continuous heavy rainfall from 11 May to 8 July 2022 in Guangdong as the research object. Considering the spatial distribution range of the CYGNSS data and the characteristics of rainstorm disasters, the period of rainfall was divided into three stages. Namely, the first stage was before the occurrence of heavy rainfall (1 April to 10 May), the second stage was during the heavy rainfall (11 May to 8 July), and the third stage was after the precipitation (9 July to 31 July). This was conducted to study the distribution and severity of the flood disaster due to continuous precipitation. Figure 1 shows the location of Guangdong Province in the Chinese mainland and the digital elevation model of Guangdong Province.
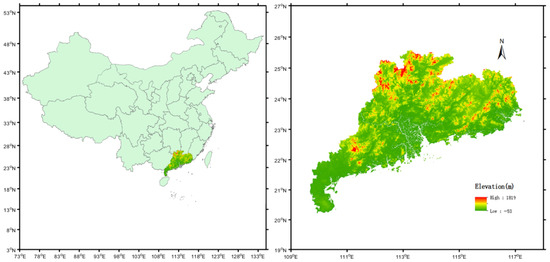
Figure 1.
Chinese mainland map and digital elevation model of Guangdong Province.
2.2. CYGNSS Data
The CYGNSS mission was launched in December 2016, it consists of eight small satellites that receive direct and reflected signals from Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites, and it has a spatial resolution of 7 × 0.5 km and revisiting time from 2.8 to 7 h for land applications [29]. The CYGNSS was initially designed to observe the wind speed on the ocean surface during hurricanes [30]. Therefore, it scans the tropical orbit at a 35° inclination, covering only 38°S and 38°N [31]. Although the CYGNSS is not a satellite system that is specially designed for land observation, the reflected GPS signals received from the land surface can be used to retrieve land geophysical parameters [27]. The emergence of these new satellite observations has important significance for the development of GNSS-R technology and the expansion of its application.
The CYGNSS Level 1 Version 3.0 data that were released by NASA in October 2020 were used, and can be downloaded from https://podaac-tools.jpl.nasa.gov/drive/files/allData/CYGNSS/L1/v3.0, accessed on 10 November 2022. Compared with the data that were contained in the previous generation, V2.1, the new version reassesses the effective isotropic radiated power using the direct signal power and antenna gain that is measured with a CYGNSS delay Doppler meter, thereby reducing the uncertainty caused by the antenna pattern [5].
2.3. Ancillary Data
The soil moisture data of the SMAP satellite L3 was selected as the comparative data for flood detection. The SMAP satellite was launched by NASA in January 2015 to obtain global soil moisture information by measuring brightness, temperature, and geophysical inversion [32,33]. Its revisiting time is 2–3 d with good space–time coverage of the world [34]. The signals received by the SMAP satellite and GNSS signal are both L-band signals. Therefore, the SMAP L3 radiometer was employed to measure the soil moisture (version 8) with a 36 × 36 km global daily grid. The data period was from 1 April to 31 July 2022. The SMAP data can be downloaded from the NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center website (https://nsidc.org/data/spl3smp/versions-/8, accessed on 10 November 2022). The daily precipitation data were used to study the temporal and spatial changes during the floods, which was downloaded from the China Land Data Assimilation System (CLDAS-v2.0) of the China Meteorological Administration (http://data.cma.cn/data/detail/dataCode/NAFP_CLDAS2.0_RT.html, accessed on 10 November 2022). This data combines the observation data of more than 2400 national stations and the precipitation data of more than 60,000 regional automatic stations to produce a set of multi-source fusion precipitation products with a spatial resolution of 6.25 × 6.25 km and time resolution of 1 h. Compared with similar international and domestic products, this product has a higher regional quality and accurate time–space distribution characteristics in China [35]. Then, to evaluate the impact of different land types, land uses, and precipitation on the results, the Sentinel-2 L2A data from 1 April to 1 July 2022 were used to classify the ground features in Guangdong Province, which had a spatial resolution of 60 m.
2.4. Data Processing
2.4.1. Quality Control
Since the original design intention for the CYGNSS was to use the on-board GNSS-R technology to retrieve the ocean surface wind field and monitor the activities of tropical cyclones, the CYGNSS raw data set contains a large number of ocean surface areas and other sampling points that cannot be used for soil moisture retrieval. Thus, to better retrieve the surface soil moisture, it was necessary to effectively control the quality of the original CYGNSS data set [36]. The main steps were as follows:
(1) Incident angle: Under the same dielectric constant, when the incident angle is about 65°, the reflectivity changes significantly, so the CYGNSS observations with an incident angle larger than 65° were not considered.
(2) Quality control flags: A set of quality flags in the data was used to indicate potential problems and make improvements, which was denoted as Quality_flags. The Quality_flags included the S-band transmitter startup error, Spacecraft attitude error, Blackbody DDM, and DDM test mode. The Quality_flags_2 included the wrong (port or starboard) antenna, the signal being off or very close to the top row of the complete DDM, and slight satellite orbit failure. The data with the above quality flags were removed.
(3) Additional correction and deletion: For the soil moisture extraction, the CYGNSS observations were filtered according to the following criteria: a signal-to-noise ratio less than 2 dB and greater than 14 dB, a receiver gain (GR) less than 0 dB, and the peak power of the reflected signal being greater than −147 dB [17,18,30].
Following the quality control strategy for incident angle selection, the quality control flags with potential problems were corrected or filtered, and a large amount of observation data were discarded. The remaining CYGNSS observations can provide enough data for soil moisture inversion.
2.4.2. Calculation of CYGNSS Surface Reflectivity
The CYGNSS receiver receives the surface forward scattering circular polarization signal that is transmitted by the GPS satellite and the characteristics and information of the underlying surface (ocean or land) are obtained. The main product parameter of the CYGNSS is the DDM, which consists of coherent components and incoherent components [7]. The most basic observation that was used in this study was the CYGNSS SR, which was calculated from the DDM observations and can reflect the physical parameters of the surface to a large extent. It was assumed that the CYGNSS land measurement is mainly specular point reflection, that is, the surface is relatively smooth and the reflected signal is coherent, so the coherent component can be expressed as [37,38]:
where is the transmission power of the signal, Gt and Gr are the gains of the transmitting antenna and the receiving antenna, respectively. Rts is the distance between the mirror reflection point and the GPS transmitter, Rsr is the distance between the mirror reflection point and the receiver, λ is the wavelength, and ΓRL is the SR. This is the basic measurement that was used in this study, and it can be calculated based on the DDM observations of the CYGNSS L1 data. Research has shown that reflectivity mainly depends on the physical parameters of the surface, such as the surface water, roughness, soil moisture, and vegetation coverage [39]. Generally, for the reflected signal of the navigation satellite L-band, a wetter surface produces stronger reflectivity, which is the basis of this study.
After quality control, the selected CYGNSS can be used for land applications.
The CYGNSS SR can be calculated from Equation (1), which was converted into dB form. Because the SR is also affected by the incident angle, the incident angle was corrected as follows [27]:
where θ is the incident angle. The details of the parameters are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The variables in Equation (1) and the corresponding CYGNSS data set parameters.
2.4.3. Drought to Flood Conversion
To quantify and identify drought-to-flood transformation, Wu et al. defined the Long-cycle Droughts–Floods Abrupt Alternation Index (LDFAI) [40]:
where is the standardized precipitation from May to June, is the standardized precipitation from July to August, is the intensity term of the rapid drought-to-flood transformation, is the intensity of the drought and flood, and is the weight coefficient, which is used to increase the weight of long-term drought or flood events and reduce the weight of total drought or flood events.
The LDFAI is the first index that was defined to quantify the sudden change that occurs with drought and flood events [41]. Its calculation process is simple and does not need artificial screening, which lays the foundation for the study of the basic characteristics and physical causes of sudden drought and flood events. However, due to its limitation of time resolution at a monthly scale, it is difficult to distinguish the precipitation in the early and late stages in a relatively short period.
Therefore, the Dry Wet Abrupt Alternation Index (DWAAI), which was improved by Sunnyvale in 2018, was used for the daily drought-to-flood conversion analysis [41]:
where and are the standardized precipitation anomaly in the early and late stages, respectively; and are the abnormal value of the standardized early precipitation index on the ith day of the later period and the last day of the earlier period, respectively. Thus, the Antecedent Precipitation Index of the ith day of the later period and the last day of the earlier period were standardized, and n is the number later days. In this study, we considered the process from a drought to a flood, that is, the early stage being the drought period and the later stage being the flood period; and the process from a flood to a drought, that is, the early stage being a flood period and the later stage being a drought period. Due to the different responses of the drought and flood events to time, the length of the drought and flood periods were considered separately. The flow framework of the study is shown in Figure 2.
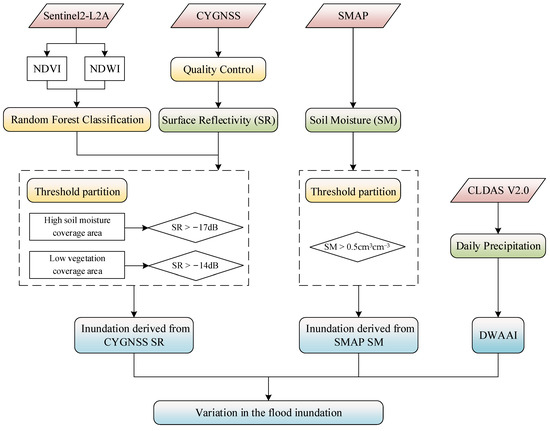
Figure 2.
Research flow framework.
3. Results
3.1. CYGNSS Observations
Figure 3 shows the distribution of the CYGNSS SR points in Guangdong Province in a single day (3 April 2022), including the CYGNSS SR that was calculated from the original data (Figure 3a) and that which was calculated from the quality control data (Figure 3b). Compared with Figure 3a, Figure 3b corrects the CYGNSS SR according to the incident angles of the transmitter and eliminates abnormal values in the CYGNSS L1 data by using quality control identification.
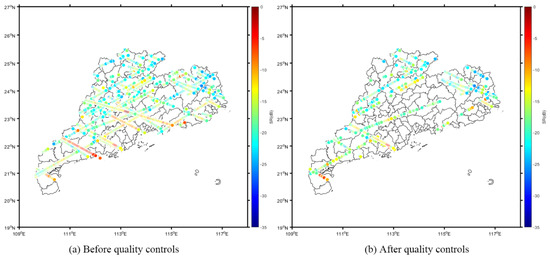
Figure 3.
Distribution of CYGNSS SR points along the satellite tracks (on 3 April 2022) before and after quality control.
To determine the extent of the flood caused by precipitation from the GYGNSS SR, the threshold detection method should be considered. That is, when the CYGNSS SR exceeds a preset threshold, it supports that the area has been flooded. This method has also been widely used in previous studies that used CYGNSS data to retrieve the submerged state of the water surface [5,7,24]. To analyze the distribution of and variation in the SR in the entire study area, radial basis function space interpolation [42] was applied to interpolate the SR points in all the areas of Guangdong Province. Figure 4 shows the CYGNSS SR distribution in Guangdong Province using the interpolation method after quality control on 15 April and 15 May 2022. The interpolation method can clearly display the difference between the distributions of the CYGNSS SR before and after the flood.
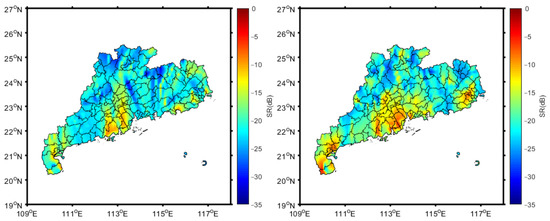
Figure 4.
Distribution of CYGNSS SR using the interpolation method after quality control. (Left: 15 April 2022; Right: 15 May 2022).
Due to the differences in the topography, vegetation coverage, and surface feature distribution in the study area, it was difficult to determine the threshold value for estimating the flood range. It would result in inaccurate estimates if the same threshold value was used to distinguish the flood inundation from areas that have moderate-density vegetation, high-density vegetation, and high soil moisture. Therefore, to make the results more accurate and reliable, the threshold should be carefully selected according to the surface conditions of the study area. Random Forest is a classification algorithm that is based on a decision tree, and it has a high calculation accuracy, short training time, and low sensitivity to the number and quality of training samples [43]. To confirm the land surface conditions through terrain classification, the Sentinel-2 L2A data were selected to extract the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI). Furthermore, the Random Forest algorithm was adopted to classify the land cover of Guangdong Province in 2022. Figure 5 shows the land cover and land use in Guangdong Province.
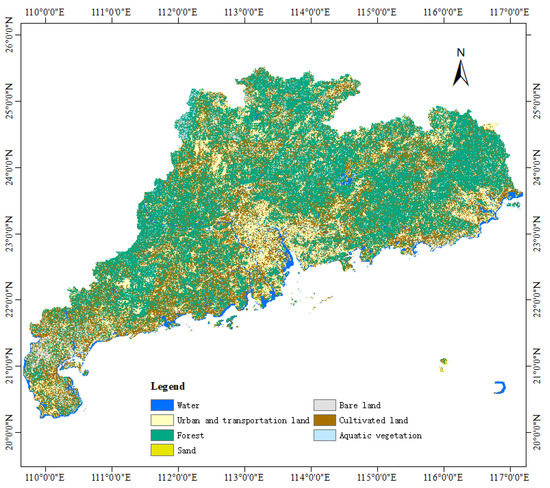
Figure 5.
Distribution map of the random forest classification features in Guangdong Province in 2022 based on Google Earth Engine and Sentinel-2 L2A data.
Through terrain classification, the land cover types of Guangdong Province were divided into water, urban and transportation land, forest, sand, bare land, cultivated land, and aquatic vegetation. When the CYGNSS signal passes through a water body, the SR value gets larger. Guangdong Province is in a subtropical and tropical climate zone with superior hydrothermal conditions and abundant rainfall. The kind of zonal forest vegetation is mainly evergreen broad-leaved forest, and the cultivated land is mainly rice with high annual humidity.
To study the differences in the SR and SNR values of the different land cover types, the CYGNSS L1 data with 65,053 DDMs from Guangdong Province between 1 April and 10 May were processed, as shown in Table 2. The SR and SNR values varied significantly. For example, the water and aquatic vegetation had the highest SR, at −12.31 dB and −14.43 dB, respectively. The SR values of the sand, bare land, and urban and transportation land were relatively high with values of about −18 dB; areas with high soil moisture (e.g., forest and cultivated land) had similar SR values of about −20 dB. In addition, the SNR values for the different land cover types had a similar trend of variation. To make the results more accurate and reliable, the threshold value was set at −14 dB for the low vegetation coverage areas and −17 dB for areas with high soil moisture coverage.

Table 2.
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and surface reflectivity (SR) of the different land covers in Guangdong Province (from 1 April to 10 May 2022).
3.2. Persistent Precipitation
To explore the feasibility of the SR changes for flood detection and analysis, the variation in precipitation in Guangdong Province was determined during the flood outbreak period. Figure 6 shows the precipitation changes on 9–15 May 2022; 3–9 June 2022; and 2–8 July 2022.
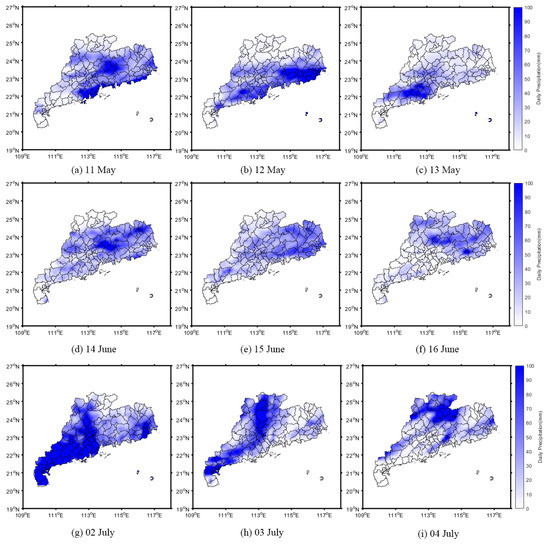
Figure 6.
Precipitation changes in Guangdong Province during the flood period.
Figure 6a–c show the occurrence of heavy precipitation during the flood period in May. Figure 6g–i show the continuous reduction in the precipitation before the flood receded in June, and Figure 6d–f show the common phenomenon during the flood period in early July. During the precipitation period, the daily precipitation ranged from 100 to 249.9 mm, which was at a heavy rain level (>100 mm/day), and it even reached an extremely heavy rain level (>200 mm/day). Heavy rain in a certain area often causes flash floods and inundation of farmland, which not only affects industrial and agricultural production but may also endanger people’s lives and cause severe economic losses. From 11 May to 8 July 2022, a total of 59 d, Guangdong Province continuously experienced heavy rainfall, and even some areas experienced continuous extremely heavy rainfall, which was the main reason for the flood period.
Since CYGNSS SR is sensitive to water bodies, a series of CYGNSS SR maps at different times were generated to show the evolution process of the floods. Figure 7 shows the daily change in the SR in the three stages of the flood period on 3 April, 21 May, and 15 July 2022.
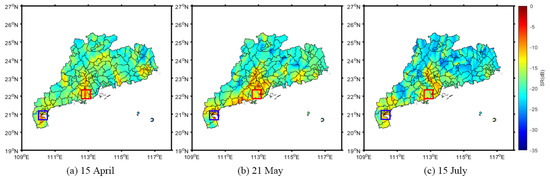
Figure 7.
Changes in surface reflectivity (SR) in the three stages of the flood period. The SR of the Xijiang River is indicated with a red box and that of the Tanjiang River is indicated with a blue box.
As demonstrated in Figure 7, CYGNSS data can accurately detect the existence of inland water bodies. The CYGNSS SR of the Xijiang River and Tanjiang River, which pass through the middle of Guangdong province, showed significantly higher SR than that of the other inland areas. In general, the CYGNSS SR first increased and then decreased, which is consistent with the occurrence of a flood, indicating the feasibility of CYGNSS reflectance for flood detection.
3.3. Flooded Area
To determine the flood inundation in the study area, the flood thresholds of the CYGNSS SR were selected as −14 dB and −17 dB for the low vegetation coverage area and high soil moisture coverage area, respectively. The maps of the flooded areas in May, June, and July are shown in Figure 8.
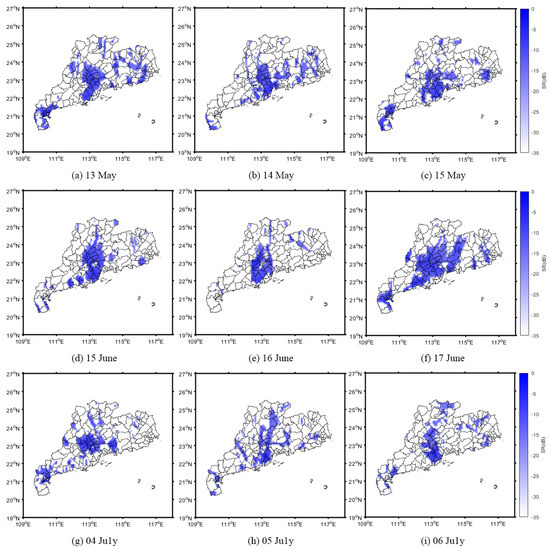
Figure 8.
Inundated areas that were extracted using Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System surface reflectivity (SR) and a threshold method.
As shown in Figure 8, the inundated areas always occurred 1 or 2 d after extreme precipitation (Figure 6). Although several parts of northern Guangdong Province have comprehensive vegetation coverage and a strong water storage capacity, they were flooded due to continuous heavy rainfall. Furthermore, in the central and western regions of the study area, the water levels of the rivers within the boundaries (e.g., Xijiang River and Tanjiang River) persistently increased due to continuous heavy rainfall, resulting in the persistently enhanced CYGNSS SR. In addition, the eastern part of the study area had low values of CYGNSS SR with less inundation due to the higher terrain.
3.4. DDM Changes before and after the Flooding
The DDM of the land reflection mainly depends on the dielectric constant, roughness, and vegetation coverage near the specular reflection point. Generally, when the reflection surface is coarser, the reflected signal energy gets weaker, and the reflected power that is received by the DDM becomes more scattered, having a typical or atypical horseshoe shape. Before and after the flood, as the conditions of the reflected surface change, the corresponding DDM change. Figure 9 shows the change in the DDM around 24.5°N and 112.0°E before, during, and after the flood. On 15 April, which was before the flood, the DDM had a typical horseshoe shape and the power distribution was relatively dispersed. During the flood (on 11 June), the area was flooded and the DDM changed significantly, while the reflected signal energy increased. After the flood, on 24 July, the DDM power distribution changed back to a horseshoe shape, which was similar to that before the flood. Table 3 shows the changes in the DDM parameters before and after the floods.
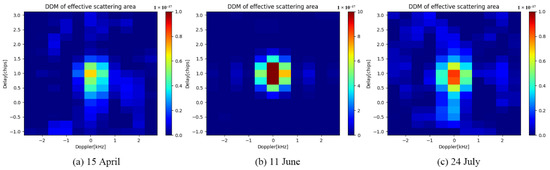
Figure 9.
DDM changes before, during, and after floods at 24.5°N and 112.0°E. (a) 15 April (before the floods); (b) 11 June (during the floods); (c) 24 July (after the floods).

Table 3.
Changes in DDM parameters before, during, and after the floods. The parameters include the effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP), surface reflectivity (SR), and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
Table 3 shows that during the flood, the SNR and SR in the study area increased significantly by 10 dB and 19 dB, respectively. After the flood receded, the SNR and SR decreased to the pre-flood level, increasing by 10 dB and 14 dB, respectively. The changes in these parameters confirm the effectiveness of using the SR threshold method to monitor flood distribution.
3.5. SMAP Flood-Monitoring Results
Considering that SMAP and CYGNSS are both L-band signals and their sensitivities to surface physical parameters are similar, the SMAP data were employed to extract the flooded area as a comparison with the results from the CYGNSS observations. Due to their low spatio-temporal resolutions, the SMAP soil moisture was averaged over 3 d and then interpolated in the entire Guangdong Province. Figure 10 shows the distributions of the soil moisture points in a single day in Guangdong Province from the SMAP data on 27 May and the three-day average soil moisture points from 27 to 29 May. The figure illustrates that the density of the soil moisture points increased for the three-day average SMAP observations. Thus, the spatial resolution improved. In contrast, the accuracy of the soil moisture points decreased with the use of the averaging process. Furthermore, although both of the quantity and density of the soil moisture points are increased after three-day averaging process, there are some areas without soil moisture points due to the low spatio-temporal resolutions of SMAP data, as shown in the red box near Guangdong City.
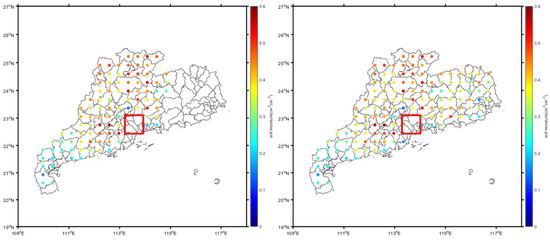
Figure 10.
Distributions of the soil moisture points from SMAP data in a single day on 27 May (left) and with three-day averaging from 27 to 29 May (right). The red box indicates the area without soil moisture points.
Figure 11 shows the changes in the SMAP three-day average soil moisture in the three stages of flood occurrence after interpolation in the entire Guangdong Province. The figure clearly depicts the variations in soil moisture during the flood event. For the first stage, before the flood, the soil moisture in most areas of Guangdong Province ranged between 0.05 and 0.3 cm3cm−3 (Figure 11a). Furthermore, it was found that the soil moisture was higher in the north of Guangdong Province than that in the other areas ranging between 0.3 and 0.5 cm3cm−3, and the area was dominated by mountain forests with generally high soil moisture. After the continuous heavy rainfall in the middle of May (Figure 11b), the soil moisture in most areas of northwest and north Guangdong Province increased rapidly, exceeding 0.5 cm3cm−3. Moreover, the soil moisture in the other areas such as the southwest and east also increased correspondingly. For the third stage, after the flood, in the first ten days of July, the reduction in precipitation led to a significant downward trend in the soil moisture in various parts of Guangdong Province (Figure 11c) while the flood was receding.
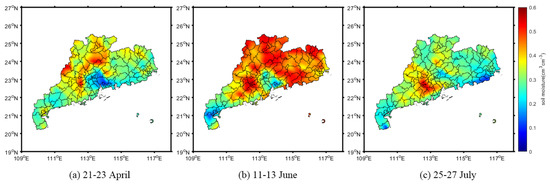
Figure 11.
SMAP soil moisture distributions after interpolation in the three stages of the flood period in Guangdong Province. (a) The soil moisture distribution before the flood; (b) the soil moisture distribution during the flood; (c) the soil moisture distribution after the flood.
To distinguish the inundated areas of the flood from the non-inundated areas using the soil moisture information, it was necessary to set proper thresholds according to the conditions of the study areas. Previous studies have used 0.38 cm3cm−3 and 0.4 cm3cm−3 as thresholds to extract inundated areas in Henan Province [7,26], which is located in Central China and belongs to a typical temperate monsoon climate with less precipitation and less soil moisture. In contrast, the study area of Guangdong Province is in South China and belongs to a subtropical monsoon climate with abundant precipitation and more soil moisture. Therefore, the values of the threshold needed to be larger. After analysis and verification, it was found that 0.5 cm3cm−3 as a threshold was more appropriate for identifying the inundated areas from no-inundated areas in this study, as shown in Figure 12.
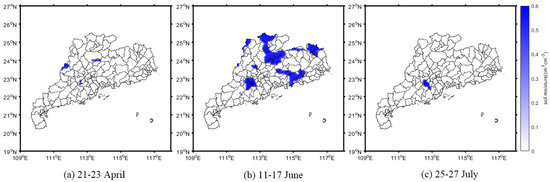
Figure 12.
Flood inundation extracted from the soil moisture distribution in the three stages of the flood period in Guangdong Province.
Through the threshold method, the flood inundation can be derived from the SMAP soil moisture, as shown in Figure 12. It can be seen in the first stage that before the continuous rainfall there was almost no flooded area in Guangdong Province (Figure 12a). While during the continuous rainfall period, flooded areas with high soil moisture emerged in several places in the study area (Figure 12b). In the third stage, after the heavy rainfall, the flood receded (Figure 12c). Although flood inundation can be identified using soil moisture SMAP data, it should be noted that Figure 10 and Figure 11 were both calculated based on three-day average data. Considering the low spatial resolution of 36 × 36 km and the long revisiting time of 2–3 d, there was less detail obtained for the short period of inundation that was derived from the SMAP soil moisture. In contrast, with a higher spatial resolution of 7 × 0.5 km and shorter revisiting time of 2.8–7 h, the inundation that was derived from the CYGNSS SR were more accurate and reliable than the inundation that was derived from the SMAP soil moisture.
To compare and evaluate the ability to extract the flood inundation extent when the data were derived from the CYGNSS SR and SMAP soil moisture, the two flood periods of June 8 and July 4 were selected, as shown in Figure 13 and Figure 14, where the first period was continuous rainfall, and the second was a typhoon period. Considering their spatial resolutions, the flood inundation extent that was derived from the CYGNSS SR was calculated using single-day data, while that from the SMAP soil moisture was calculated using three-day average data.
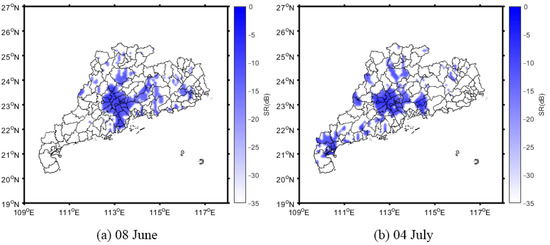
Figure 13.
Inundation maps that were derived from CYGNSS SR on 8 June (a) and 4 July (b).
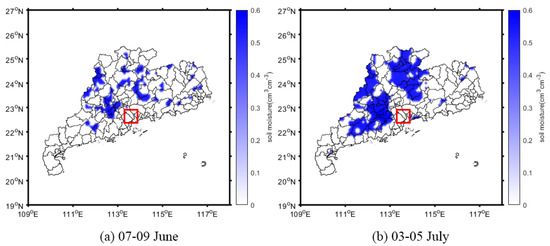
Figure 14.
Inundation maps that were derived from SMAP soil moisture with three-day averaging from 7–9 June (a) and 3–5 July (b). The red box indicates information that was lost from the flooded area when using this method.
The inundation maps can clearly display the distributions and variations in the flooded areas in the two flood periods, whether derived from the CYGNSS SR or SMAP soil moisture. During the continuous rainfall period, both the inundation maps of the CYGNSS and SMAP showed that the flooded areas were dispersed, while in the typhoon period, the flooded areas were larger and concentrated in the middle, west, and some areas north of Guangdong Province. Consequently, there was good agreement between the inundations that were derived from the CYGNSS SR and SMAP soil moisture. This indicates that both CYGNSS and SMAP can be used to detect flood inundation during extreme weather events. Nevertheless, the patches in Figure 14 were distributed closer together. In contrast, the patches in Figure 13 were more dispersed, which means that the inundation extent that was derived from the CYGNSS SR can reflect the flooded areas with more detail than that which was derived from the SMAP soil moisture, and the latter lost some information in the flooded areas (as shown with red solid line box). This is because the spatio-temporal resolution of the CYGNSS is much better than that of the SMAP.
3.6. Identification of the Flood Occurrence Using Multi-Source Data
To analyze the transfer node and severity of the drought and flood alternating events in Guangdong Province, the DWAAI was employed to distinguish the flood occurrence at a daily scale and quantify the transformation from a drought to a flood. In Equation (5) of Section 2.4, indicates the degree of “urgency”, and is the weight coefficient. A previous study [40] determined that parameter should be set at 1.3 to calculate the degree of “alternation” and identify whether the flood event occurred. The DWAAI was calculated based on the daily precipitation data of Guangdong Province.
Selecting 01 April to 31 May as the research period, the DWAAI was calculated for each day to find the most urgent day (abrupt alternation date) when it changed from a drought to a flood. The severity of the flood disasters in various regions of Guangdong Province was judged according to the degree of “urgency” and “alternation”. In addition, the daily precipitation, daily CYGNSS SR, and three-day average SMAP were calculated. Figure 15 shows the changes in the DWAAI, rainfall, SMAP soil moisture, and CYGNSS SR from 2 May to 14 May around 22.1°N and 112.5°E. The DWAAI reached its maximum value on 10 May, which indicates that this day was the most urgent day for this region to change from a drought to a flood. Additionally, the daily rainfall was 99.78 mm with the CYGNSS SR reaching up to −7.89 dB. They were the maximum values from 2 May to 14 May, and the correlation between the daily precipitation and SR was 0.89, verifying the high sensitivity of the CYGNSS SR to precipitation. Moreover, although there was good agreement between the CYGNSS SR and SMAP soil moisture, due to the limitation of the saptio-temporal resolution, the SMAP soil moisture cannot provide daily data such as the CYGNSS SR. Moreover, the day with the largest DWAAI value during the heavy rainfall period was selected as the abrupt alternation date for several areas in Guangdong Province, as shown in Table 4. The standardized precipitation anomaly showed a consistent growth trend. The abrupt alternation date was concentrated around 10 May 2022, and the continuous heavy rainfall on 10 May played an important role in the occurrence of flood events.
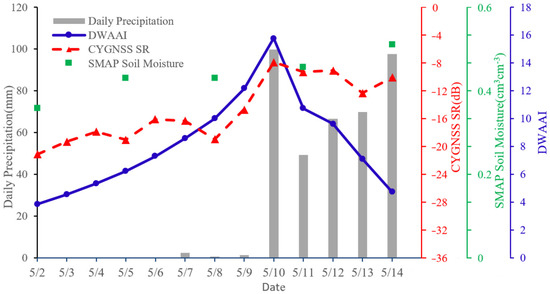
Figure 15.
Changes in DWAAI, rainfall, SMAP soil moisture, and CYGNSS SR from 2 May to 14 May in Jiangmen City, Guangdong Province (22.1°N, 112.5°E).

Table 4.
The degree of rapid change from a drought to a flood in Guangdong Province in 2022.
4. Discussions and Conclusions
The feasibility of detecting flood inundation using CYGNSS data was investigated and verified using the SMAP soil moisture and precipitation data. The temporal and spatial variations in the CYGNSS SR were illustrated during extreme precipitation over a relatively short period in Guangdong Province, China. Based on the CYGNSS SR, a threshold method was employed to extract and map the inundated areas. It was found that the threshold value should be selected according to the climatic characteristics and the surface conditions of the local area. Moreover, the flood inundation extent that was derived from the CYGNSS SR had good agreement with that which was derived from the SMAP soil moisture, indicating that both of them can be used to detect flood inundation in extreme weather conditions. However, some detailed information on the inundation extent was lost when it was derived from the SMAP soil moisture due to its low saptio-temporal resolution.
Consequently, this research indicates that CYGNSS SR can detect and evaluate flood inundation at a high spatio-temporal resolution. Considering the revisiting time ranges from 2.8 to 7 h for land applications, the flood inundation can be detected within 7 h after its occurrence when using CYGNSS observations. To obtain the flooded areas from the CYGNSS SR, the threshold should be selected according to the property of the surface cover, with −14 dB being used for low vegetation coverage and −17 dB being used for high soil moisture coverage. Nevertheless, there are some limitations to the application of this method: (1) the selection of threshold is relatively simple, so further research should be conducted under different weather conditions and at different locations; (2) the surface condition is one of the most important influencing factors for CYGNSS applications, e.g., the water, vegetation, soil, and urban areas with buildings and road networks which especially influence the surface condition parameters. Thus, for more accurate flood inundation derivation, additional corrections should be considered, and a more intelligent algorithm should be developed based on the CYGNSS data; (3) flood modeling and analysis is also an important research field for inundation monitoring. Therefore, three-dimensional floods should be simulated and visualized using Geographical Information System technology in combination with GNSS-R observations.
Author Contributions
H.W. supported the study, developed the algorithm and wrote the initial draft; T.Y. helped processing the CYGNSS data, SMAP data and wrote the initial draft; J.T. helped processing the CYGNSS data and writing; F.K. supervised the study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Fund (No. CX (21) 3068).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are sincerely thankful for the comments from anonymous reviewers and members of the editorial team. Thanks to NASA for providing CYGNSS and SMAP data products. Thanks to the China Meteorological Administration for providing the measured rainfall data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, P.; Wang, W.; Zhai, X.; Xia, J.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, N. Influence of Terrestrial Water Storage on Flood Potential Index in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, S.; Zin, W.W.; Kawasaki, A.; San, Z.M.L.T. Establishment of flood damage function models: A case study in the Bago River Basin, Myanmar. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 28, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Hu, K.H.; Hu, X.D. Rainfall occurrence and its relation to flood damage in China from 2000 to 2015. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 2492–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xue, W.; Xu, H.; Yan, D.; Wang, H.; Qi, W. Urban Flood Risk Assessment in Zhengzhou, China, Based on a D-Number-Improved Analytic Hierarchy Process and a Self-Organizing Map Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Gao, F.; Xu, T.; Wang, N.; Tu, J.; Jing, L.; Kong, Y. Daily Flood Monitoring Based on Spaceborne GNSS-R Data: A Case Study on Henan, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younos, T.; Parece, T.E. Advances in Watershed Science and Assessment; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Q.; Nan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, H. Using CYGNSS Data to Map Flood Inundation during the 2021 Extreme Precipitation in Henan Province, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, M.P.; Ruf, C.S.; Jales, P.; Gommenginger, C. Spaceborne GNSS-R Minimum Variance Wind Speed Estimator. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Yu, K.; Park, H.; Huang, W.; Han, S.; Yan, Q.; Qian, N.; Lin, Y. Estimation of Swell Height Using Spaceborne GNSS-R Data from Eight CYGNSS Satellites. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, W. Sea Ice Remote Sensing Using GNSS-R: A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.; Shah, R.; Zuffada, C.; Hajj, G.; Masters, D.; Mannucci, A.J. Demonstrating soil moisture remote sensing with observations from the UK TechDemoSat-1 satellite mission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, S.; Hodgart, S.; Sun, Y.; Gommenginger, C.; Mackin, S.; Adjrad, M.; Unwin, M. Detection and Processing of bistatically reflected GPS signals from low Earth orbit for the purpose of ocean remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Benson, C.; Park, H.; Camps, A.; Qiao, L.; Rizos, C. Detecting Targets above the Earth’s Surface Using GNSS-R Delay Doppler Maps: Results from TDS-1. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.S.; Atlas, R.; Chang, P.S.; Clarizia, M.P.; Garrison, J.L.; Gleason, S.; Katzberg, S.J.; Jelenak, Z.; Johnson, J.T.; Majumdar, S.J.; et al. New Ocean Winds Satellite Mission to Probe Hurricanes and Tropical Convection. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lakshmi, V. Use of Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CyGNSS) Observations for Estimation of Soil Moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 8272–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unwin, M.; Jales, P.; Blunt, P.; Duncan, S.; Brummitt, M.; Ruf, C. The SGR-ReSI and its application for GNSS reflectometry on the NASA EV-2 CYGNSS mission. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 02–09 March 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Carreno-Luengo, H.; Luzi, G.; Crosetto, M. Sensitivity of CyGNSS Bistatic Reflectivity and SMAP Microwave Radiometry Brightness Temperature to Geophysical Parameters Over Land Surfaces. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, O.; Kurum, M.; Boyd, D.; Gurbuz, A.C. High Spatio-Temporal Resolution CYGNSS Soil Moisture Estimates Using Artificial Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Small, E.E.; Gutmann, E.; Bilich, A.; Axelrad, P.; Braun, J. Using GPS multipath to measure soil moisture fluctuations: Initial results. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.E.; Larson, K.M.; Braun, J.J. Sensing vegetation growth with reflected GPS signals: SENSING VEGETATION WITH GPS REFLECTIONS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L12401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Won, D.; Akos, D.M.; Small, E.E. Vegetation Sensing Using GPS Interferometric Reflectometry: Experimental Results With a Horizontally Polarized Antenna. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4771–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrazzoli, P.; Guerriero, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Rahmoune, R. Forest biomass monitoring with GNSS-R: Theoretical simulations. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.; Reager, J.T.; Small, E. CYGNSS data map flood inundation during the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.; Liu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, G.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Hong, Y. Using CYGNSS Data to Monitor China’s Flood Inundation during Typhoon and Extreme Precipitation Events in 2017. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.; Loria, E.; O’Brien, A.; Downs, B.; Zuffada, C. Investigation of Coherent and Incoherent Scattering from Lakes Using Cygnss Observations. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020—2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–02 October 2020; pp. 5917–5920. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z. A New Coherence Detection Method for Mapping Inland Water Bodies Using CYGNSS Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.; Small, E. Estimating inundation extent using CYGNSS data: A conceptual modeling study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.; Yin, C.; Xia, J. A Novel Dual-Branch Neural Network Model for Flood Monitoring in South Asia Based on CYGNSS Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, D.; Clarizia, M.P.; Ruf, C.S. Improved CYGNSS Wind Speed Retrieval Using Significant Wave Height Correction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, M.P.; Pierdicca, N.; Costantini, F.; Floury, N. Analysis of CYGNSS Data for Soil Moisture Retrieval. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Jin, S. Evaluation of the Land GNSS-Reflected DDM Coherence on Soil Moisture Estimation from CYGNSS Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Xun, S.; Zhao, X. Validation of Multiple Soil Moisture Products over an Intensive Agricultural Region: Overall Accuracy and Diverse Responses to Precipitation and Irrigation Events. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azemati, A.; Melebari, A.; Campbell, J.D.; Walker, J.P.; Moghaddam, M. GNSS-R Soil Moisture Retrieval for Flat Vegetated Surfaces Using a Physics-Based Bistatic Scattering Model and Hybrid Global/Local Optimization. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.M.; Colwell, I.; Chew, C.; Lowe, S.; Shah, R. A Deep-Learning Approach to Soil Moisture Estimation with GNSS-R. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Shi, C.; Pan, Y.; Bai, L.; Xu, B.; Zhang, T.; Han, S.; Jiang, L. Applicability Assessment of the 1998–2018 CLDAS Multi-Source Precipitation Fusion Dataset over China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wan, W.; Sun, Z.; Liu, B.; Li, S.; Chen, X. Comprehensive Evaluation of Using TechDemoSat-1 and CYGNSS Data to Estimate Soil Moisture over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnithan, S.L.K.; Biswal, B.; Rüdiger, C. Flood Inundation Mapping by Combining GNSS-R Signals with Topographical Information. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Nahavandchi, H.; Hoseini, M. Evaluation of CYGNSS Observations for Flood Detection and Mapping during Sistan and Baluchestan Torrential Rain in 2020. Water 2020, 12, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xu, Y.; Ju, H.; Sun, Z. Monitoring and analysis of vegetation cover change in Changting County, Fujian Province based on remote sensing images. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 43, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Li, J.; He, J.; Jiang, Z. Occurrence of droughts and floods during the normal summer monsoons in the mid- and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L05813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Zhang, L.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; She, D.; Xia, J. Characteristics of dry-wet abrupt alternation events in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin and the relationship with ENSO. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1039–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazar, J.; Hosami, M. An interval for the shape parameter in radial basis function approximation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 315, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Jia, N.; Chen, R.; Guo, X.; Ge, J.; Zhou, F. High-Resolution Mapping of Seaweed Aquaculture along the Jiangsu Coast of China Using Google Earth Engine (2016–2022). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).