Abstract
In remote sensing, the fusion of infrared and visible images is one of the common means of data processing. Its aim is to synthesize one fused image with abundant common and differential information from the source images. At present, the fusion methods based on deep learning are widely employed in this work. However, the existing fusion network with deep learning fails to effectively integrate common and differential information for source images. To alleviate the problem, we propose a dual-head fusion strategy and contextual information awareness fusion network (DCFusion) to preserve more meaningful information from source images. Firstly, we extract multi-scale features for the source images with multiple convolution and pooling layers. Then, we propose a dual-headed fusion strategy (DHFS) to fuse different modal features from the encoder. The DHFS can effectively preserve common and differential information for different modal features. Finally, we propose a contextual information awareness module (CIAM) to reconstruct the fused image. The CIAM can adequately exchange information from different scale features and improve fusion performance. Furthermore, the whole network was tested on MSRS and TNO datasets. The results of extensive experiments prove that our proposed network achieves good performance in target maintenance and texture preservation for fusion images.
1. Introduction
Due to certain limitations in the theory and technology of hardware devices [1], images obtained by a single sensor can not adequately display scene information. Therefore, image fusion technologies come into being and its purpose is to integrate the meaningful information for different modal images. Image fusion includes multi-modal image and digital photographic image fusion because of the existence of modal differences. Images from different sources of the same scene contain a wealth of complementary information. Moreover, image fusion has been widely applied in a wide range computer vision tasks, such as military operations, object detection [2], object tracking [3], pedestrian recognition [4] and semantic segmentation [5]. Due to the different imaging mechanisms of the sensors, the scene information for infrared and visible images has certain differences in contrast and texture. The infrared images can hold a certain level of sharpened thermal targets, but other targets that do not generate heat are easily overlooked. Conversely, visible images provide more texture detail and better visual performance. So, fusing the two type of images can obtain more all-round information compared with a single image, which is very meaningful for the previously mentioned tasks.
At present, many fusion methods already exist, both in traditional methods [6,7,8,9,10,11] and deep-learning-based methods. Through principles of mathematics, the traditional fusion method mainly transforms the source image to the transform domain. Further, it measures the activity level and designs fusion strategies in the domain to integrate information. The fusion methods include five categories, i.e., multi-scale decomposition-based methods [12,13], subspace clustering-based methods [14], sparse representation-based methods [15], optimization-based methods [16] and hybrid methods [17]. However, the development of traditional fusion algorithms has entered a bottleneck period. Firstly, the transformation or representations methods used by traditional methods are becoming increasingly complex, which does not meet the needs of real-time computer applications [18]. Secondly, the measurement of hand-crafted activity level and fusion methods cannot adapt complex scenarios. Moreover, the heat radiation information of infrared images is characterized with pixel intensity and the detail information of visible images is described by edges and gradients. Since different source images have different image characteristics, the traditional fusion method may lead to loss of feature diversity and the fused image may produce certain artifacts. These drawbacks make the design of fusion rules in the traditional way more difficult and complex.
To alleviate the shortcomings of traditional methods, fusion algorithms with deep learning are rapidly emerging. The methods include the three key elements: feature extraction, fusion strategy and data-driven training. In deep learning, feature extraction is used to obtain deep representations of the source image by multiple convolution layers. Different fusion strategies also have significant influence on the fused image. In [15,19], the decision map of the source images are acquired by sparse representation and neural network. The fused images are obtained by using the decision map and suitable post-processing. Although these methods have achieved certain effects, the design of fusion strategies and post-processing is relatively difficult. Therefore, some end-to-end convergence frameworks are proposed, i.e., FusionGAN [20], FusionGANv2 [8] and DDcGAN [21]. Based on adversarial learning, the framework overcomes shortcomings such as artificial features and fusion strategies. However, these methods fail to adequately preserve image details. To better protect the detail information of visible images, the RFN-Nest [22] was proposed. However, the multi-scale fusion method is simple and fails to adequately integrate complementary information for source images.
To alleviate the problems mentioned earlier, we propose the DCFusion that includes three parts: encoder module, fusion strategy and decoder module. The encoder module is employed to extract different scale features of source image. A dual-headed fusion strategy (DHFS) as the fusion module is provided to preserve common and differential information from intermediate features adequately. Furthermore, we propose a contextual information awareness module (CIAM) as the decoder to stack different scale features.
In general, our contributions are the following:
- (1)
- We propose the DCFusion can preserve more significant information by a suitable dual-headed fusion strategy and reconstruction method.
- (2)
- The dual-headed fusion strategy (DHFS) is designed to integrate different modal features. In addition to preserving common information, the fusion strategy also allows for the effective integration of complementary information for source images by differential information compensation.
- (3)
- We propose a contextual information awareness module (CIAM) to merge different scale features and generate result. The module achieve more competitive reconstruction performance by exchanging information for different scale feature.
2. Related Works
In the following, we present some existing fusion methods that are the most relevant to our work, including traditional image fusion algorithms, AE-based image fusion algorithms, CNN-based image fusion algorithms and GAN-based image fusion algorithms.
2.1. Traditional Image Fusion Algorithms
The fusion methods includes three main elements: feature extraction, feature fusion and feature reconstruction. The feature extraction and feature fusion are more important compared with feature reconstruction. To achieve more effective feature representation, many feature extraction methods was proposed such as multi-scale transforms, sparse representation and subspace clustering. In these feature extraction methods, the multi-scale transforms divide image features into different scales and combine the features in separated levels. So far, there are already classical multi-scale transforms such as discrete wavelet [23], shearlet [24], latent low-rank representation [12] and nonsubsampled contourlet transform [25]. Beyond multi-scale transforms, sparse representation [15] is embedded in fusion framework to extract features, which represent images using sparse encoding in a complete dictionary. Moreover, subspace clustering, such as independent component analysis [26], principal component analysis [27] and non-negative component matrix factorization [28], can extract mutually independent subcomponents by mapping high-dimensional images to low-dimensional subspace.
Moreover, optimization-based fusion methods also achieved a certain of development. Further, gradient transfer fusion drives the development of CNN-based fusion methods and GAN-based fusion methods, which defines overall intensity fidelity and texture structure preservation [16] as objective functions of image fusion. Moreover, some researchers improve fusion performance combining the advantages of different frameworks. Further, Liu et al. introduced a novel fusion algorithm and achieved better fusion performance by employing multi-scale transform and sparse representation [29].
2.2. AE-Based Image Fusion Algorithms
Since its powerful nonlinear fitting capability, deep learning was adequately employed in many computer vision tasks. In image fusion, data-driven methods have been explored such as the approach based on an auto-encoder. Similar to traditional fusion methods, AE-based methods also include three categories: feature extraction, feature fusion and feature reconstruction. Prabhakar et al. first finished feature extraction with a small number of convolutional layers in image fusion [30]. The reconstruction was also achieved with a few convolutional layers. In addition, the fused features for different modal images was generated by the element-wise addition.
However, a few convolution layers fail to extract deep features with semantic information. By introducing dense connection and the multi-scale encoder–decoder network, Li et al. had extracted deeper and more comprehensive features and achieved features reuse [31]. However, the fusion performance was influenced to some extent because of the handcrafted fusions rules.
2.3. CNN-Based Image Fusion Algorithms
To achieve better fusion performance, CNN-based image fusion networks have developed by some researchers. Zhang et al. designed a novel CNN-based fusion network that the ratio of gradient and intensity are maintained by intensity and gradient path [32]. The model was trained through a general loss function. In addition, Ma et al. introduced a salient target mask to enable its network extract and fuse more meaningful features [33]. Moreover, Xu et al. proposed a fusion network with elastic weight consolidation since the cross-fertilization of different image fusion tasks [34]. However, the framework fails to fully demonstrate its potential performance because of the missing of ground truth to the fusion results.
2.4. GAN-Based Image Fusion Algorithms
The image fusion is an unsupervised task because a lack of ground truth. Because the adversarial loss restricts the networks at the distribution level, GAN-based methods are relatively sensible for fusion tasks. Ma et al. first introduced the generator and the discriminator in fusion networks. Discriminators facilitate generators capable of generating images with more meaningful textures [20]. However, the use of a single discriminator is somewhat flawed. It may lead to an imbalance in the data distribution between different images. Further, Ma et al. also presented a new GAN-based image fusion network with a dual-discriminator to achieve the balance [21]. Moreover, Li et al. built the GAN-based fusion network through in on the attention regions with the dual-discriminator and the guidance of attention loss [35]. Subsequently, Ma et al. converted image fusion to multi-distribution simultaneous estimation. Moreover, they introduced a novel image fusion algorithm with multi-classification [36]. The fusion image have more significant contrast and plentiful texture with the multi-classifier.
3. Methodology
In the part, we illustrate implementation details of the overall proposed network. The fusion network is presented in Section 3.1 and the introduction of loss function of training is presented in Section 3.2.
3.1. Network Architecture
We propose an effective DCFusion network. The network includes three parts: encoder module, fusion strategy and decoder module. This overall network is described in Figure 1.
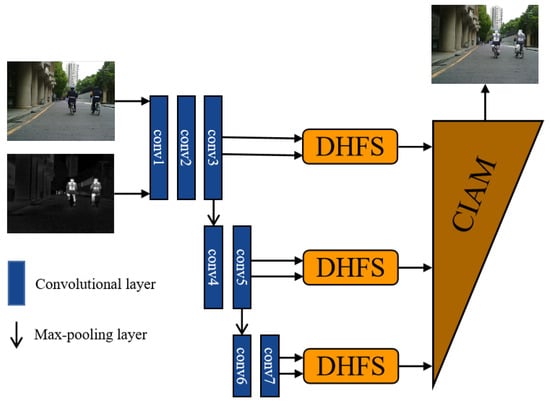
Figure 1.
The proposed DCFusion network (, represents source images and O indicate output image).
3.1.1. Encoder Module
The purpose of the encoder module is to obtain multi-scale features of source images. As shown in Figure 1, the encoder includes multiple convolutional layers and max-pooling layers. Combining convolution and pooling operations, we can obtain deep features at different scales. The description of the modules is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
The setting details of the encoder module.
3.1.2. Fusion Strategy
To compensate differential information, we design a dual-headed fusion strategy (DHFS) to merge two modal deep features from the encoder. Subsequently, the output of the module is fed into the reconstruction module to further integrate features. The fusion strategy is presented in Figure 2.
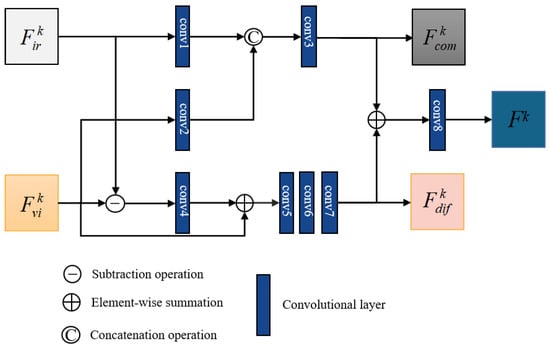
Figure 2.
The proposed DHFS module.
In Figure 2, and , respectively, denote the deep features of infrared and visible image. k indicates the level of different scale deep feature maps. The fusion module is to adequately merge common and differential information and the process can be divided into two heads. In Figure 2, the first head is to fully integrate common information from different modal features. are the output features of the first branch and contains rich common information. For example, some background information common to infrared images and visible images. Moreover, the can be defined as:
where concat indicates concatenation operation in channel dimension for different modal features and every conv indicates different convolutional layer. Furthermore, the second head is to compensate differential information of different modal features. are the output features for the second branch and contains abundant differential information. For example, thermal target information for infrared images and texture detail information for visible images. The can be defined as:
where + indicates element-wise summation operation and − indicates element-wise subtraction operation. conv indicates convolutional layer. Furthermore, the final fused features can be calculated as follows:
where + indicates element-wise summation operation and conv indicates different convolutional layer. Moreover, the more setting details of the convolutional layers are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
The setting details of the DHFS module.
3.1.3. Decoder Module
The fusion module output the multi-scale feature consisting of three features (, , ) corresponding to three resolution scale (×4, ×2, ×1). To further stack the fused multi-scale features, we proposed a contextual information awareness module (CIAM) based on multiple cross-scale feature integration module (CSFI). The decoder is shown in Figure 3. The CIAM can adequately exchange information for different scale feature maps. The low-scale feature is up-sampled to higher-scale feature and the high-scale feature is down-sample to lower feature while the cross-scale feature integration module (CSFI) is employed each time. Inside the CSFI, each scale feature receives exchanged information from other scale features by the up-sample, down-sample and concatenation operations. The channel number of features remains unchanged by convolution operation. Eventually, the channel number of the feature is recovered to one to achieve final fusion performance by three convolutional layers. The CIAM can further improve our fusion performance by combing cross-scale integration module (CSFI) and the setting description of the decoder module is presented in Table 3.
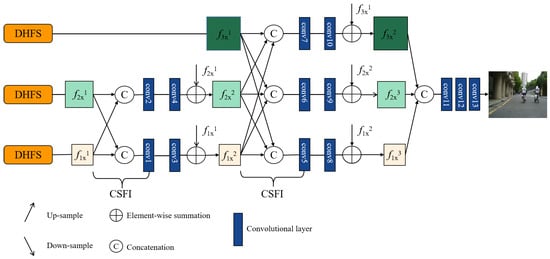
Figure 3.
The proposed CIAM.

Table 3.
The setting details of the CIAM network.
3.2. Loss Function
The proposed network architecture aims to obtain satisfactory fusion performance by training abundant visible and infrared images. To achieve the goal, we train the network with MSRS dataset [37] as the input images. In the training processing, a feature-preserving loss function is introduced to ensure that our fused result retains meaningfully common and complementary information. It is worth noting that our loss function mainly refer to proposed loss function of PIAFusion network [37]. The loss function includes three sub-loss function: illumination-aware loss, auxiliary intensity loss and texture loss. The illumination-aware loss is calculated as:
where and , respectively, refer to intensity loss function for infrared and visible image and be calculated as:
where h denotes the height and w denotes the width of the inputed images. refers to the -norm. Moreover, , and represent the output, the infrared and the visible images, respectively. and denote illumination-aware weights for infrared and visible images, respectively. The weights are defined as:
where and , respectively, represent the probability that the scene of the images belong to day or night. Moreover, and is calculated by a illumination-aware sub-network [37]. The illumination-aware loss can preserve intensity information but not keep the output in a best intensity distribution. Therefore, we introduce auxiliary intensity loss. The loss is illustrated as follows:
where stands of the element-wise maximum calculation. Furthermore, we introduce texture loss to retain optimal texture of the output and it is defined as follows:
where ∇ stands for the gradient operation and indicates the absolute operation. Therefore, the total loss function can be defined as follows:
where (i = 1, 2, 3) represents the weight of different sub-loss function.
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Details
The network architecture is trained by the MSRS training dataset [37] and the dataset consists of 26112 pairs images of training set. Before training the encoder-decoder network, we transform visible image into YCbCr color space. At the end of the training, we used the opposite operation again to recover the color image. Moreover, all images of training set are normalized to interval in [0, 1]. In the test processing, we test the validity on testing dataset MSRS, which selects 361 pairs of images as the testing images. Moreover, we test generalization performance for the method with 20 pairs of test images of the TNO [38] dataset.
To comprehensively test performance of the algorithm, we apply the mutual information (MI), the standard deviation (SD), the visual information fidelity (VIF), entropy (EN) and . The MI can measure the degree of similarity between two images. The larger the MI, the more source image information is retained in the fused image and the quality of the fused image is better. The SD takes stock of the contrast and distribution of the fused images from a statistical point of view. The VIF reflects the fused information fidelity from the human visual perspective. The EN is mainly an objective evaluation metric to measure the amount of information contained in an image. The evaluates the amount of fused edge information from the source images. Moreover, a fusion model with a better performance usually has more large MI, SD, VIF, EN and .
To further verify the role of the DCFusion, we compare the method with seven advanced algorithms on MFNet and TNO dataset, namely, MDLatLRR [12], FusionGAN [20], GANMcC [36], IFCNN [39], RFN-Nest [22], SDnet [40] and PIAFusion [37]. The fusion models for all comparisons are evaluated with public code where the relevant settings of the experiment remain unchanged. In the proposed network, the hyper-parameter , and are, respectively, set as 3, 7 and 50. The batch size and epoch are 80 and 30, respectively. The initial learning rate is 0.0001 and then decay after 15 epoch exponentially. In addition to comparative and generalization experiment, we verify the importance of our fusion strategy and decoder module by ablation experiments. Finally, we compared the running efficiency of our method with other methods. Related experiments for our method were conducted on the PyTorch platform. The MDLatLRR was run on a MATLAB R2017b with Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4460 CPU @ 3.20GHz. Then our DCFusion, RFN-Nest, IFCNN, SDNet and PIAFusion experiments were implemented by PyTorch with one GeForce GTX 1080 Ti GPU. The FusionGAN and GANMcC were implemented by TensorFlow with a GeForce GTX 1080 Ti GPU.
4.2. Comparative Experiment
4.2.1. Qualitative Analysis
Since the MSRS dataset consists of daytime scene and nighttime scene, we evaluate subjective performance with two daytime and two nighttime images. In daytime scenarios, thermal radiation information from infrared images is integrated into visible images as complementary information. A satisfactory fused result should include rich textural details and prominent targets. The daytime fused images are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. To show the subjective effect of the fused image more visually, we enlarge the area in the green box to show the texture details better and mark the highlighted targets with red box. It can be seen that the FusionGAN fails to adequately preserve texture details from the visible images, and there is a blurring of the edges of highlighted targets. Although the MDLatLRR can sharpen the edge of the highlighted target, the texture of visible images cannot also be protected fittingly. Moreover, the IFCNN, the GANMcC, the RFN-Nest and the SDnet can integrate meaningful information, but the fusion process is inevitably suffering some degree of interference of useless information. Only our DCFusion and PIAFusion can adequately integrate meaningful information for source images and avoid other distractions at the same time. In the nighttime scenes, the provided scene information for source images is limiting, so it is not easy to obtain a fused result with a wealth of information. The nighttime fused images are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. We find that all the algorithms can fuse the common and complementary information from source images to some degree. However, some differences are existing to the fused images of these methods. In addition to the PIAFusion and our DCFusion, other methods introduce contaminated detailed textures and weakened salient targets in the fused images. Moreover, our method achieve a better visual performance to some extent compared with PIAFusion. Therefore, our fusion network can better integrate meaningful information according to the fusion strategy and the proposed decoder.

Figure 4.
Comparative experiment for different fusion network of a typical daytime sample from the MSRS dataset.

Figure 5.
Comparative experiment for different fusion network of a typical daytime sample from the MSRS dataset.

Figure 6.
Comparative experiment for different fusion network of a typical nighttime sample from the MSRS dataset.

Figure 7.
Comparative experiment for different fusion network of a typical nighttime sample from the MSRS dataset.
4.2.2. Quantitative Analysis
To further verify the validity of the method more accurately, we select MI, SD, VIF and Qabf as evaluation metrics. The values of five objective metrics for the eight methods are given in Table 4. The values in the table indicate mean values of 361 pairs of images from MSRS dataset. We observe that our method obtains the best values in 5 metrics. The best MI Indicates that the fused image retains more source image information by the proposed network. The best SD represents the highest contrast for our fused results. The best VIF implies that the fused results own the highest information fidelity. The best EN means that fused images include the most information by our method. The best indicates that the edge information for fused results is effectively protected. Although our DCFusion is similar to the PIAFusion in subjective performance, our objective metrics are superior to the PIAFusion. Therefore, our fusion network can better integrate meaningful information such as thermal target information for infrared images and texture detail information for visible images.

Table 4.
The results of different metrics for the eight algorithms on the 361 MSRS dataset. The red value indicates the best result and the blue value indicates the second best result.
4.3. Generalization Experiment
As we all know, the generalization performance of a data-driven model is an important aspect to evaluate its goodness. Therefore, we select 20 pairs of images in the TNO dataset to evaluate generalizability of our DCFusion. The qualitative results for different models are provided in Figure 8 and Figure 9. To show the subjective effect of the fused image more visually, we enlarge the area in the green box to show the texture details better, and mark the highlighted targets with red box. We observe that the RFN-Nest and the MDLatLRR can weaken the salient targets. The FusionGAN and the GANMcC can blur the edge of thermal targets. All methods except our DCFusion and the PIAFusion suffer from some degree of spectral contamination. Moreover, we provide quantitative results for different methods in Table 5. We can notice that our DCFusion achieves the best results in SD and EN and obtains the second-best results in the rest of the metrics on the TNO dataset. Moreover, the other metrics are very close to the best values—unsurprising considering that our DCFusion is trained with the MSRS dataset and tested directly on the TNO dataset. Therefore, this proves that our DCFusion can preserve the texture details, sharpen the salient targets and maintain a comparatively good generalization performance effectively.
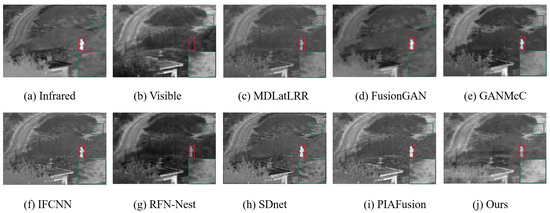
Figure 8.
Generalization experiment for different fusion network of a typical sample from the TNO dataset.

Figure 9.
Generalization experiment for different fusion network of a typical sample from the TNO dataset.

Table 5.
The results of different metrics for the eight algorithms on the 20 TNO dataset. The red value indicates the best result and the blue value indicates the second best result.
4.4. Ablation Experiment
In our DCFusion network, the DHFS is applied to fully merge the multi-modal deep features, the CSFI is utilized to adequately exchange information for different scale feature maps and the CIAM is employed to reconstruct the fusion result as a decoder of the network. In this section, we further analyze the role of the proposed DHFS, CSFI and CIAM for fusion performance by ablation experiments.
4.4.1. Ablation Study for the DHFS
It is worth noting that we replace the DHFS with three classical fusion strategies including of “add”, “max” and “RFN”. The “add” indicates that the fused features are acquired by adding the multi-modal features and the “max” means an element-wise choose-max method. In addition, the RFN module is utilized in RFN-Nest [22] fusion network as a fusion strategy based on the residual block. Except for the DHFS, the other modules of the proposed network remain unchanged. We select 361 pairs of images from the MSRS dataset as testing images to evaluate fused performance for different fusion strategy. Moreover, the objective metrics(MI, SD, VIF, EN, ) of different fusion strategies are shown in Table 6. We observe that the DHFS achieves the best values in MI, SD, VIF and the second best values in , EN. Moreover, the and EN of the DHFS is very close to the best values. Therefore, it powerfully proves that the DHFS can more effectively fuse common and differential information compared with other fusion strategies.

Table 6.
The results of ablation study for the DHFS on the 361 MSRS dataset. The red value indicates the best result and the blue value indicates the second-best result.
4.4.2. Ablation Study for the CSFI
In the part, we analysis the role of the CSFI in the decoder module. The decoder module without the CSFI is shown in Figure 10. The modified network is trained by the same training strategy with the DCFusion. The quantitative results of the five metrics are shown in Table 7. The “No-CSFI” means that the decoder does not have the CSFI module. Compared with “No-CSFI”, the DCFusion obtains the best values for all metrics. It indicates that the CSFI models plays an positive role to exchange information of different scale features and boost the reconstruction capacity for the decoder model.
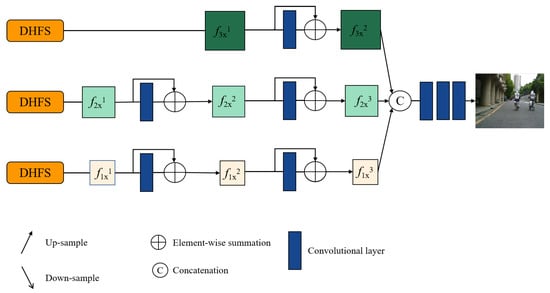
Figure 10.
Ablation study for the decoder without CSFI.

Table 7.
The results of ablation study for the CSFI on the 361 MSRS dataset. The red value indicates the best result and the blue value indicates the second-best result.
4.4.3. Ablation Study for the CIAM
In the paper, we introduce a completely new decoder module to integrate different scale features and obtain the final images. To verify the validity of the CIAM, we replace the CIAM with the decoder network of RFN-Nest [22]. The difference is that the decoder contains only three scales of feature fusion in our experiment. Apart from the decoder, all other settings remain unchanged compared with original experiment. We tested the performance of 361 pair images from the MSRS dataset to validate the role of the CIAM. Further, the object metrics of the different decoder are shown in Table 8. Compared with the decoder of RFN-Nest, the proposed CIAM achieves best values in MI, SD, VIF and EN and the second-best . Moreover, the of the CIAM is very close to the best value. Therefore, it validates that the CIAM can more effectively reconstruct the fused images.

Table 8.
The results of ablation study for the CSFI on the 361 MSRS dataset. The red value indicates the best result and the blue value indicates the second best result. The RFN-decoder indicates the decoder of the RFN-Nest.
4.5. Efficiency Comparison Experiment
To verify the execution efficiency of our method, we tested the processing time for each image pair on the 361 MSRS dataset and compared the time with other fusion methods. The final result is shown in Table 9. It can be seen that the efficiency of our method is higher compared to traditional methods. Because our method requires feature extraction at multiple scales, it is relatively time-consuming. Fortunately, the running efficiency of our method stays within an acceptable range.

Table 9.
The average processing time for each image pair on the 361 MSRS dataset. The red value indicates the best result and the blue value indicates the second best result (unit: s).
5. Conclusions
In the paper, we design a new image fusion network for infrared and visible images with a dual-headed fusion strategy and a contextual information awareness. First of all, the encoder is employed to extract different scale features of infrared and visible images. Secondly, the dual-headed fusion strategy (DHFS) is devised to sufficiently integrate common and differential information from different modal features. Thirdly, we introduce a contextual information awareness module (CIAM) to reconstruct fused images based on the CSFI model. Combined with three loss function of , and , the proposed DCFusion obtains the best performance in qualitative and quantitative evaluation compared with seven progressive fusion methods. Moreover, we prove a good generalization ability of the DCFusion in TNO dataset with a generalization experiment. Finally, the expanded ablation experiments validate that the proposed DHFS, CSFI and CIAM are beneficial to boost the fused performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.P.; methodology, Q.P.; software, Q.P. and A.C.; validation, Q.P., A.C. and G.J.; formal analysis, A.C.; investigation, G.J., L.Z.; resources, G.J., X.Y.; data curation, X.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.P.; writing—review and editing, Q.P.; visualization, Q.P. and L.Z.; supervision, G.J., X.Y.; project administration, X.Y.; funding acquisition, X.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research in our paper is sponsored by the funding from Sichuan University and Yibin Municipal People’s Government University and City strategic cooperation special fund project (Grant No. 2020CDYB-29); Science and Technology plan transfer payment project of Sichuan province (2021ZYSF007); The Key Research and Development Program of Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (No. 2020YFS0575, No.2021KJT0012-2021YFS0067).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the editors and reviewers in advance for their valuable comments that will improve the presentation of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Tian, X.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion meets deep learning: A survey and perspective. Inf. Fusion 2021, 76, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Guan, D.; Huang, W.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Qiao, Y. Pedestrian detection with unsupervised multispectral feature learning using deep neural networks. Inf. Fusion 2019, 46, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhu, C.; Huang, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, L. Cross-modal ranking with soft consistency and noisy labels for robust RGB-T tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 808–823. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, B.; Chu, Q.; Yu, N. Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13379–13389. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Q.; Watanabe, K.; Karasawa, T.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. MFNet: Towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5108–5115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, S.; Dong, M. Perceptual fusion of infrared and visible images through a hybrid multi-scale decomposition with Gaussian and bilateral filters. Inf. Fusion 2016, 30, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qi, X.; Xie, W. Fast infrared and visible image fusion with structural decomposition. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 204, 106182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Y. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradientlet filter. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2020, 197, 103016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, L.; Lu, L.; Ahmad, A.; Jeon, G.; Yang, X. Medical image fusion method by using Laplacian pyramid and convolutional sparse representation. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 32, e5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, L.; Lu, L.; Jeon, G.; Yang, X. Infrared and visible image fusion via rolling guidance filter and convolutional sparse representation. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 10603–10616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Liu, F.; Yan, H. Infrared and visible image fusion using dual-tree complex wavelet transform and convolutional sparse representation. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 39, 4617–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. MDLatLRR: A novel decomposition method for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4733–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Luo, L.; Mei, X.; Ma, J. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition. Inf. Sci. 2020, 508, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, F.; Xue, B. Fusion of infrared and visual images through region extraction by using multi scale center-surround top-hat transform. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 8444–8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, Z.J. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1882–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Huang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Inf. Fusion 2016, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Zong, H. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 82, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2017, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z. Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2017, 36, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Mei, X.; Zhang, X.P. DDcGAN: A dual-discriminator conditional generative adversarial network for multi-resolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4980–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images. Inf. Fusion 2021, 73, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Dong, X. Region level based multi-focus image fusion using quaternion wavelet and normalized cut. Signal Process. 2014, 97, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mei, W.; Du, H. Structure tensor and nonsubsampled shearlet transform based algorithm for CT and MRI image fusion. Neurocomputing 2017, 235, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Maldague, X. An adaptive fusion approach for infrared and visible images based on NSCT and compressed sensing. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 74, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvejic, N.; Bull, D.; Canagarajah, N. Region-based multimodal image fusion using ICA bases. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, Y. Infrared and visible images fusion based on RPCA and NSCT. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 77, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, J.; Gao, W.; Song, Z. Image fusion based on non-negative matrix factorization and infrared feature extraction. In Proceedings of the 2013 6th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing (CISP), Hangzhou, China, 16–18 December 2013; Volume 2, pp. 1046–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram Prabhakar, K.; Sai Srikar, V.; Venkatesh Babu, R. Deepfuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4714–4722. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Guo, X.; Ma, J. Rethinking the image fusion: A fast unified image fusion network based on proportional maintenance of gradient and intensity. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12797–12804. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huo, H.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Q. AttentionFGAN: Infrared and visible image fusion using attention-based generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Z.; Liang, P.; Xu, H. GANMcC: A generative adversarial network with multiclassification constraints for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Ma, J. PIAFusion: A progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware. Inf. Fusion 2022, 83, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A. TNO Image fusion dataset. Figshare Dataset 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Yan, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, J. SDNet: A versatile squeeze-and-decomposition network for real-time image fusion. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 2761–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).