A Multi-Domain Joint Novel Method for ISAR Imaging of Multi-Ship Targets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
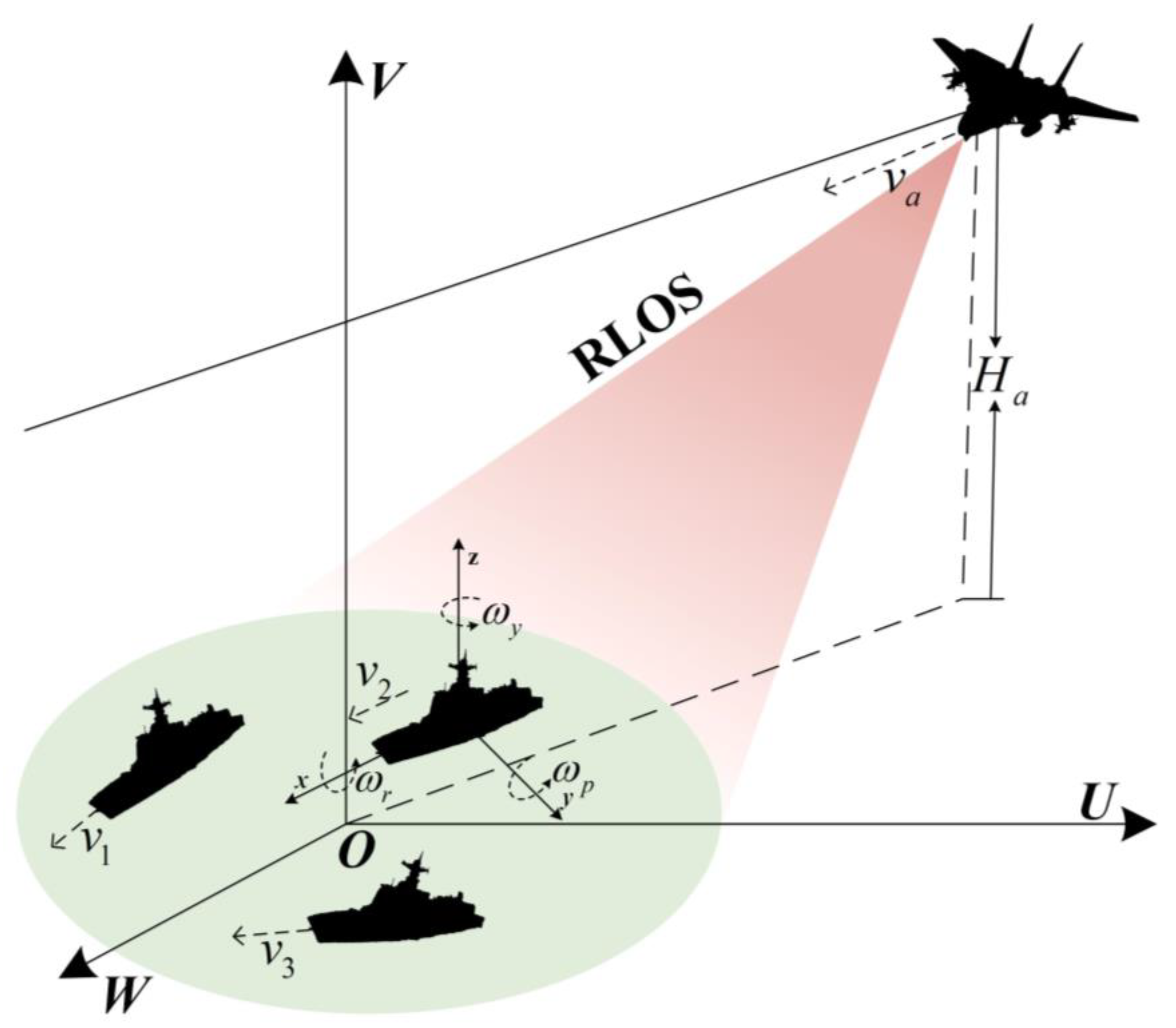
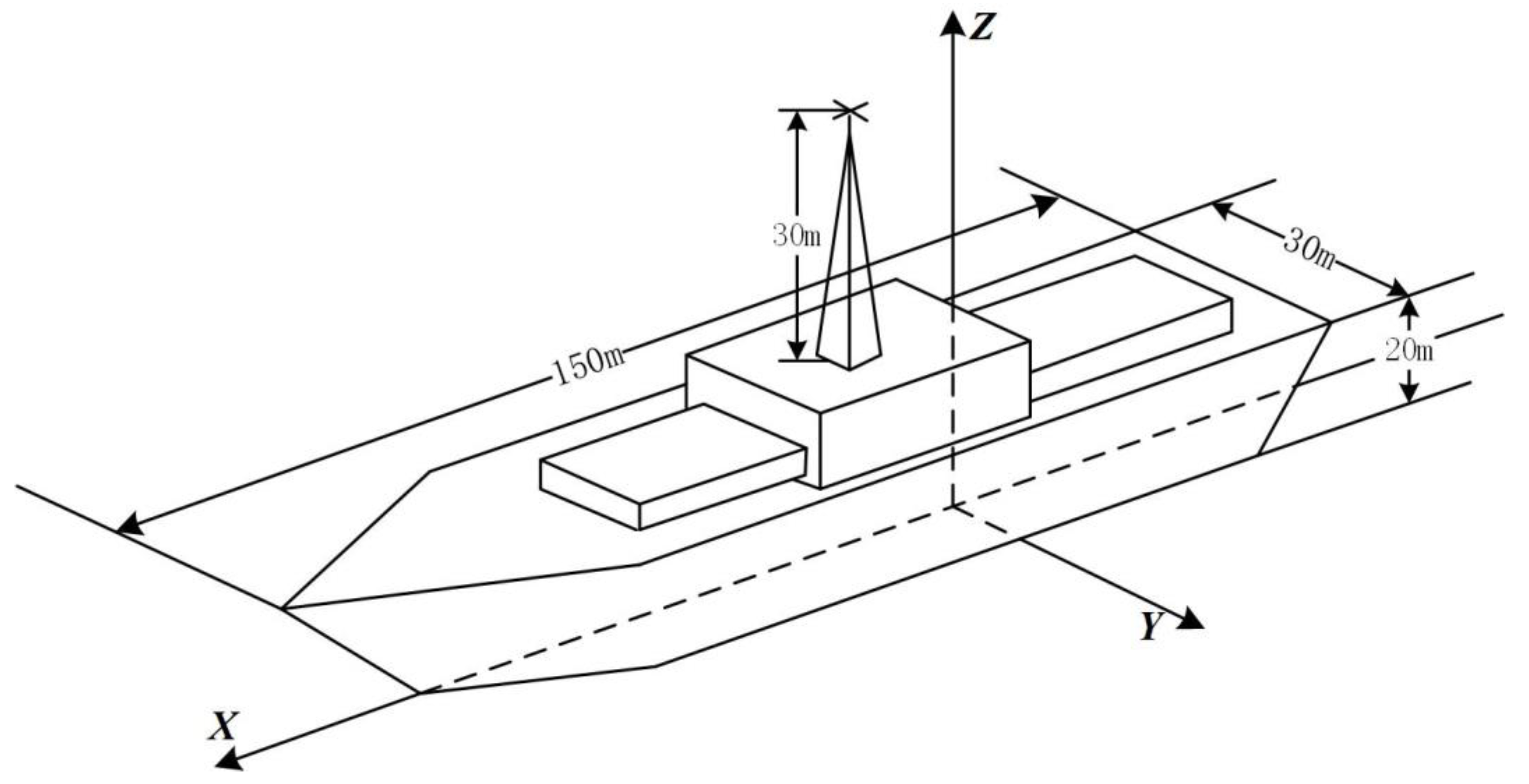
2. ISAR Imaging Geometry and Signal Model
2.1. Multi-Target ISAR Echo Signal
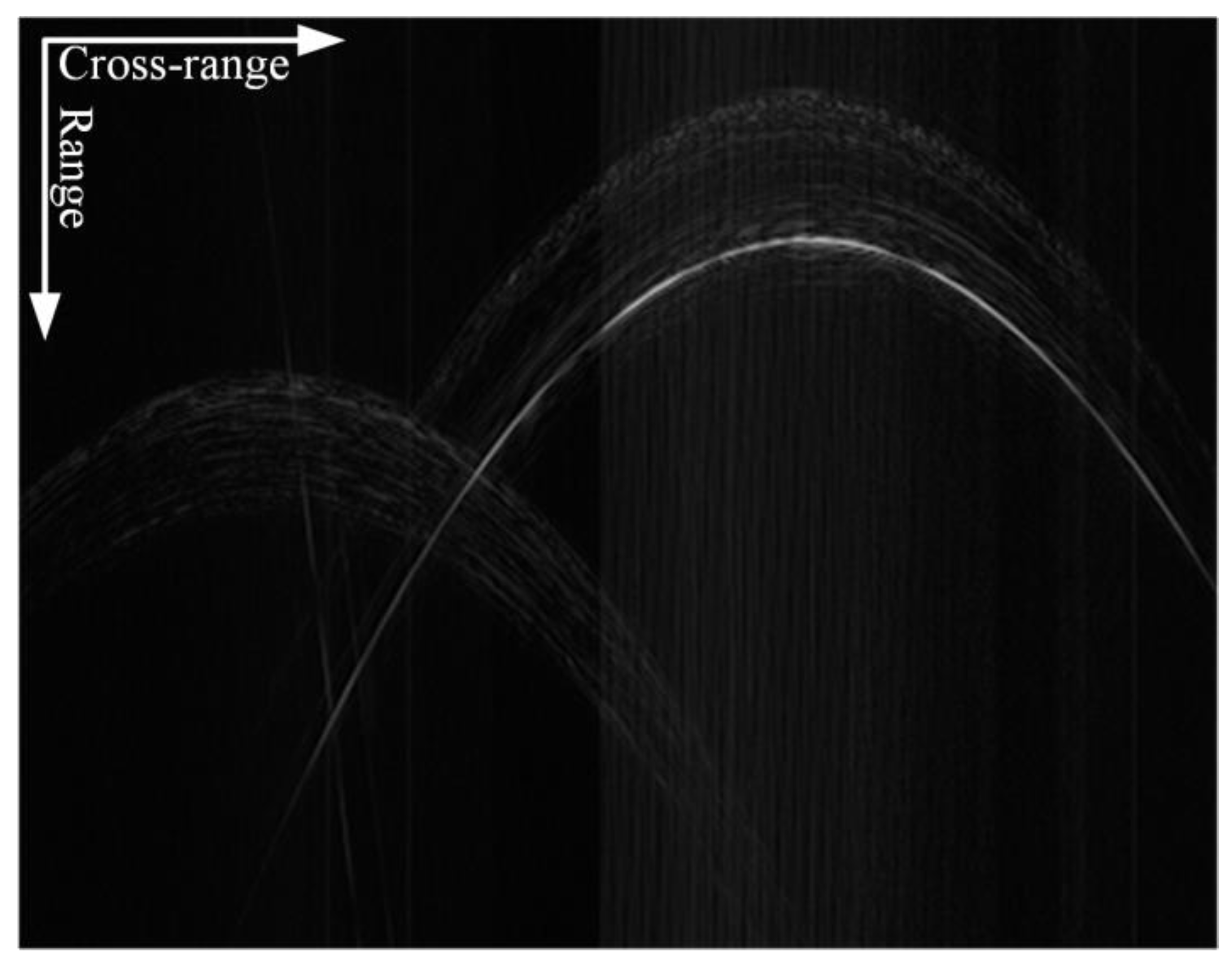
2.2. Principle of Multi-Target ISAR Echo Separation
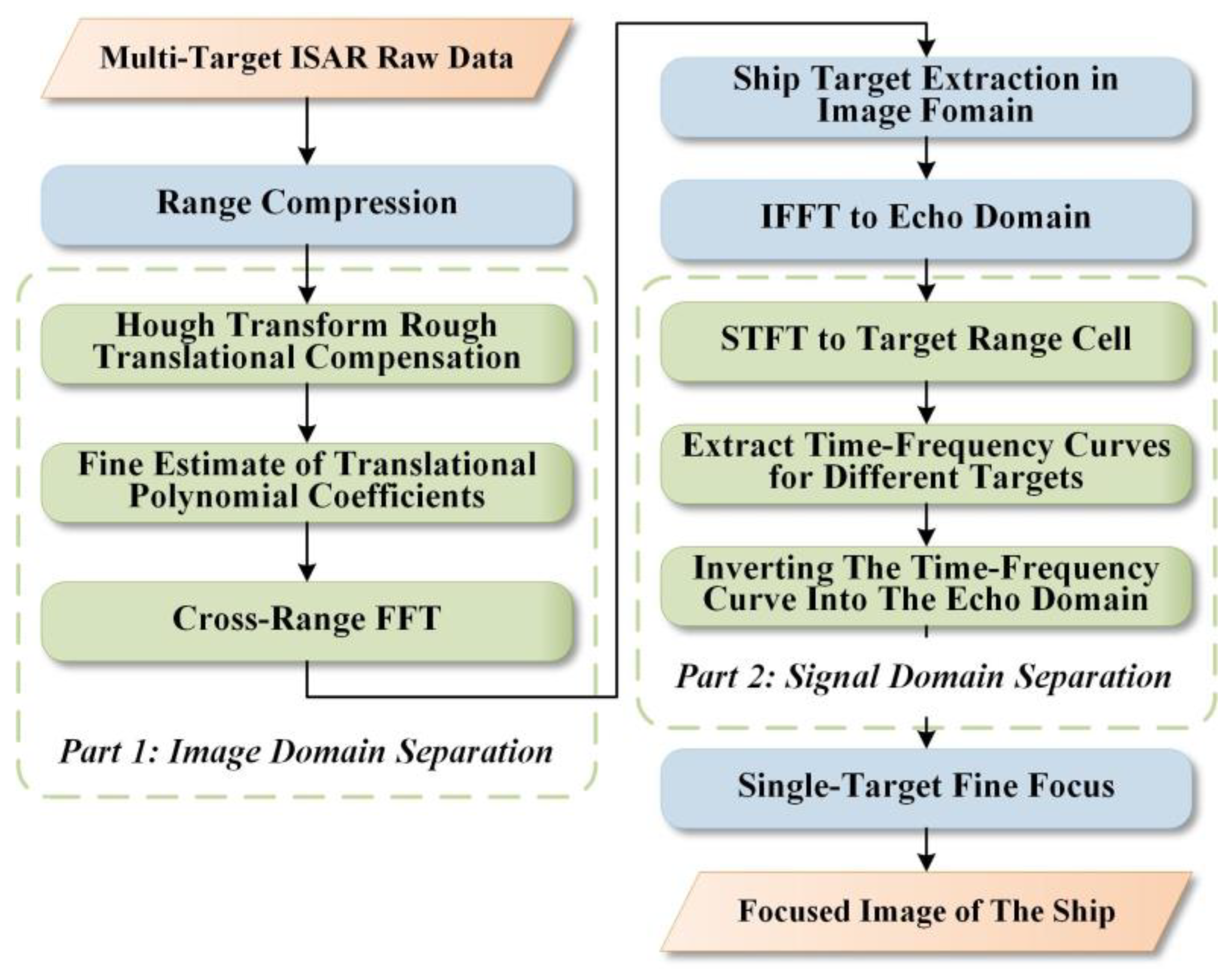
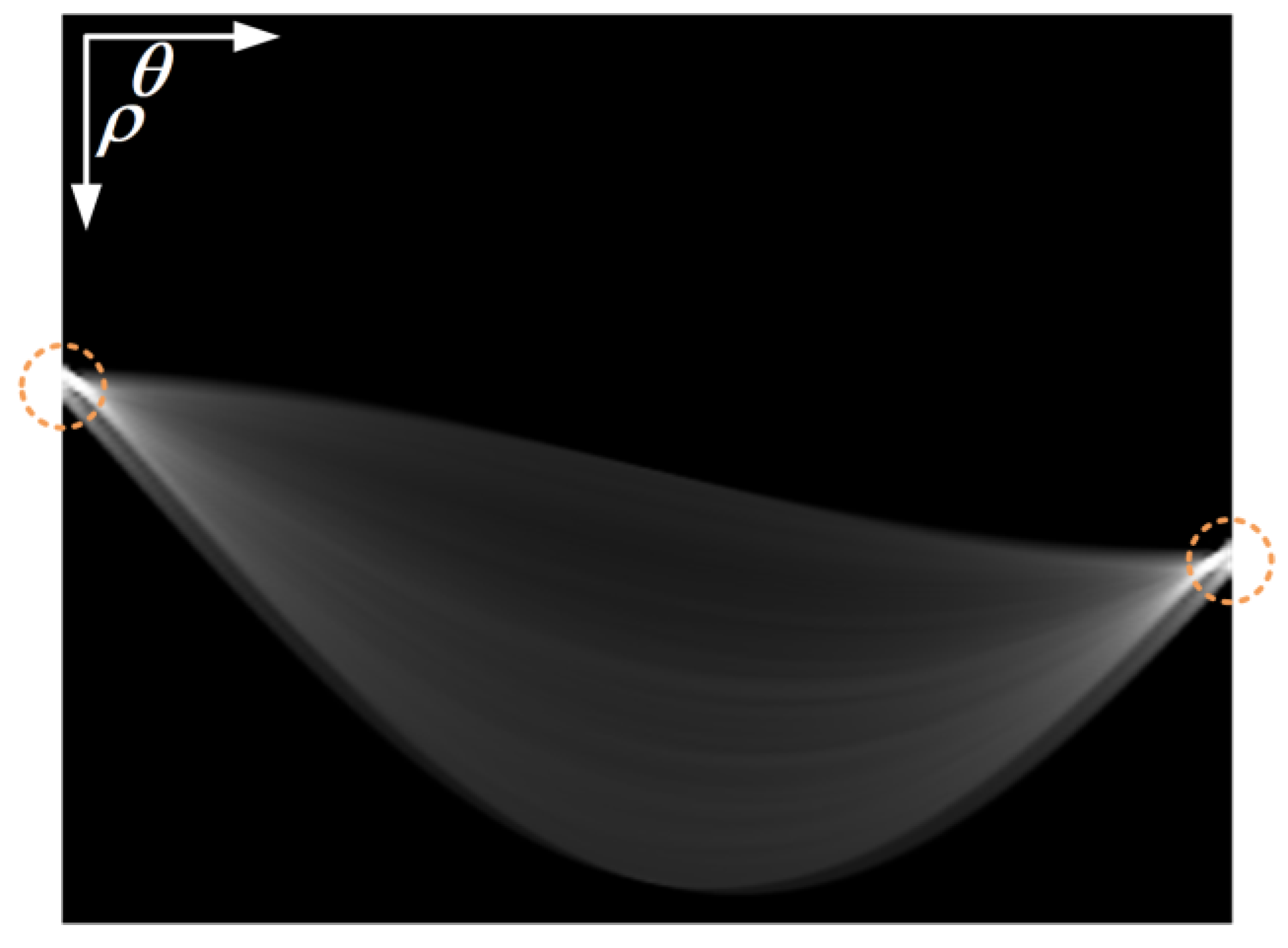
3. Multi-Ship Target ISAR Imaging Method Based on HT and STFT
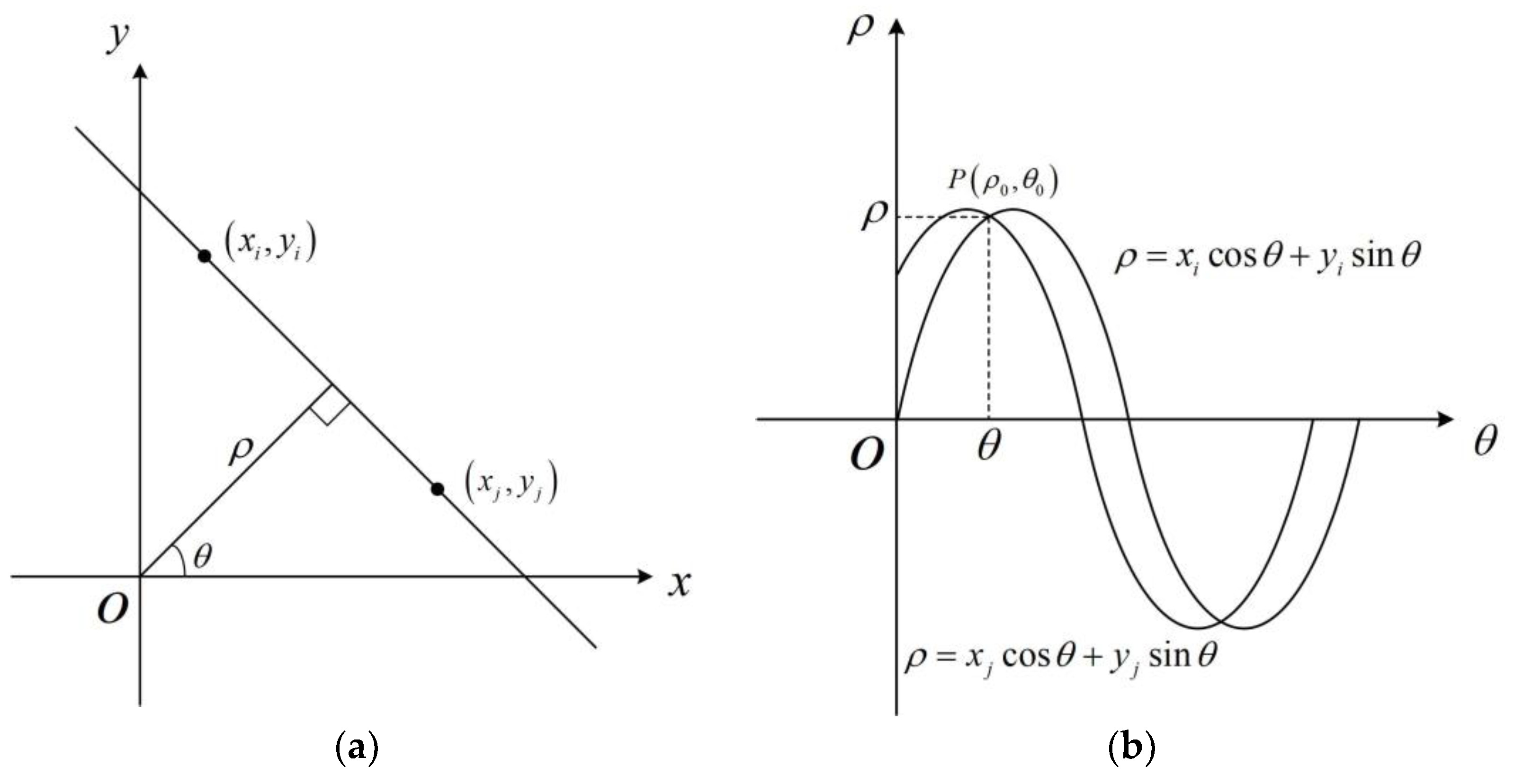
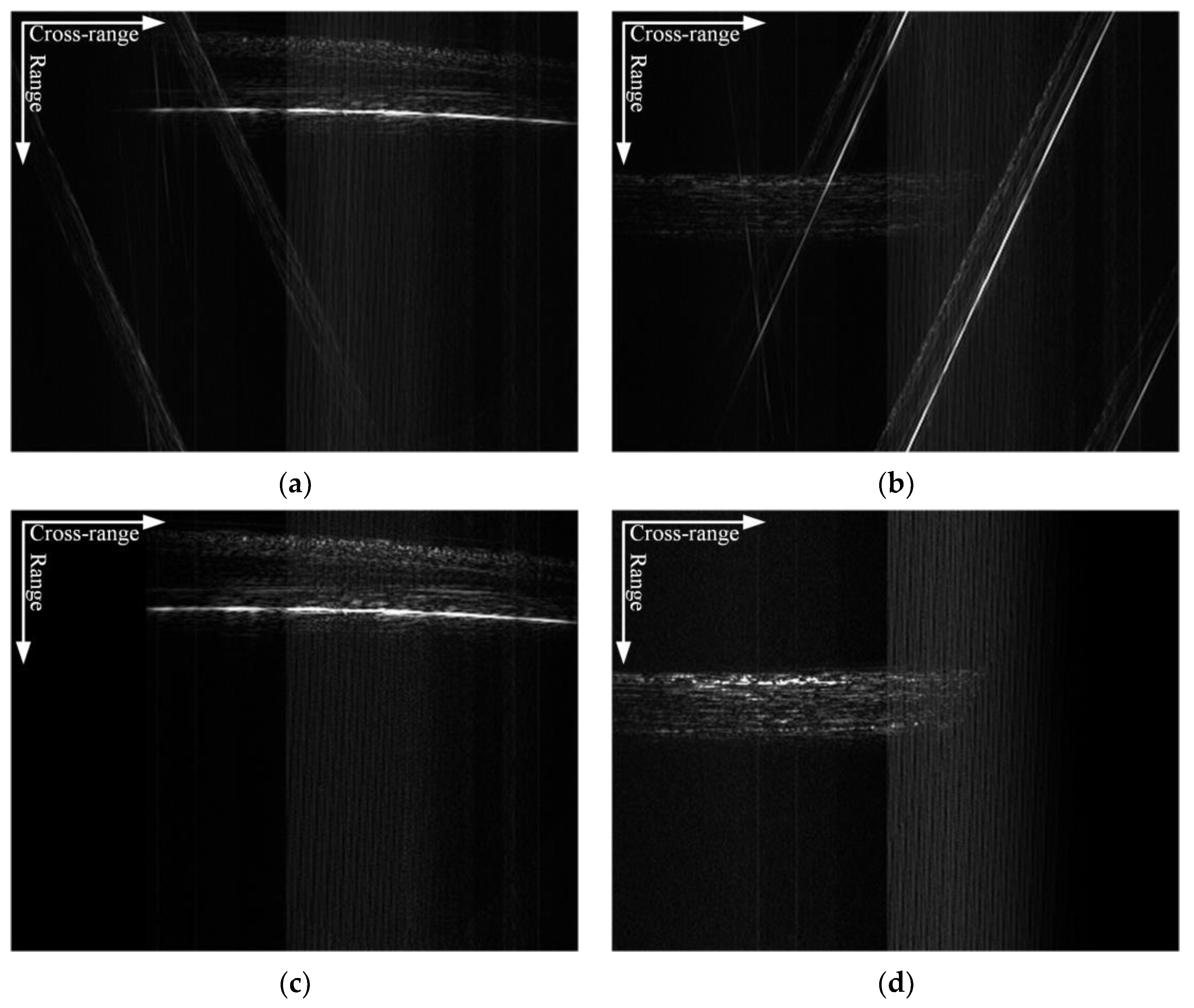
3.1. Image Domain Separation
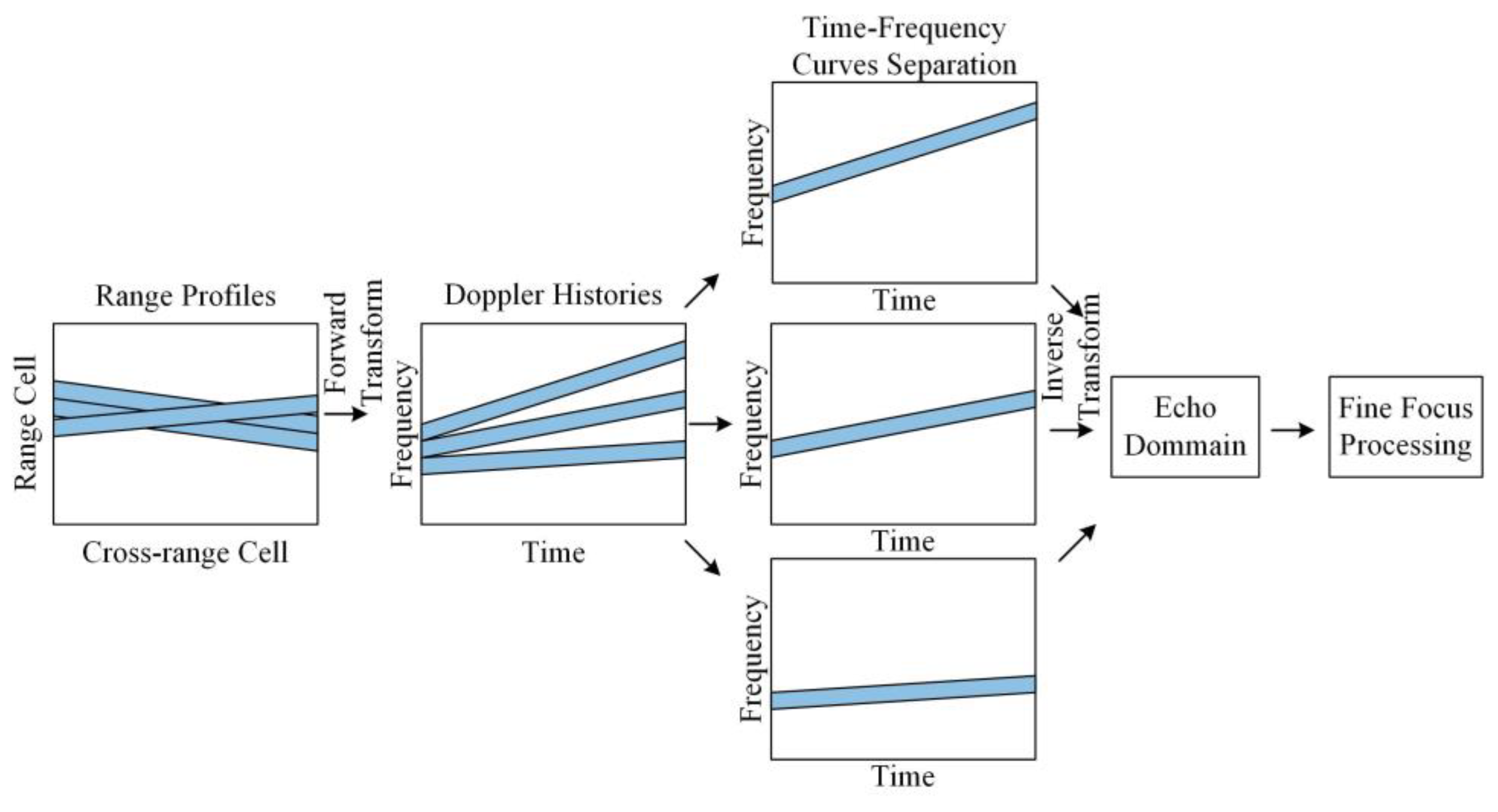
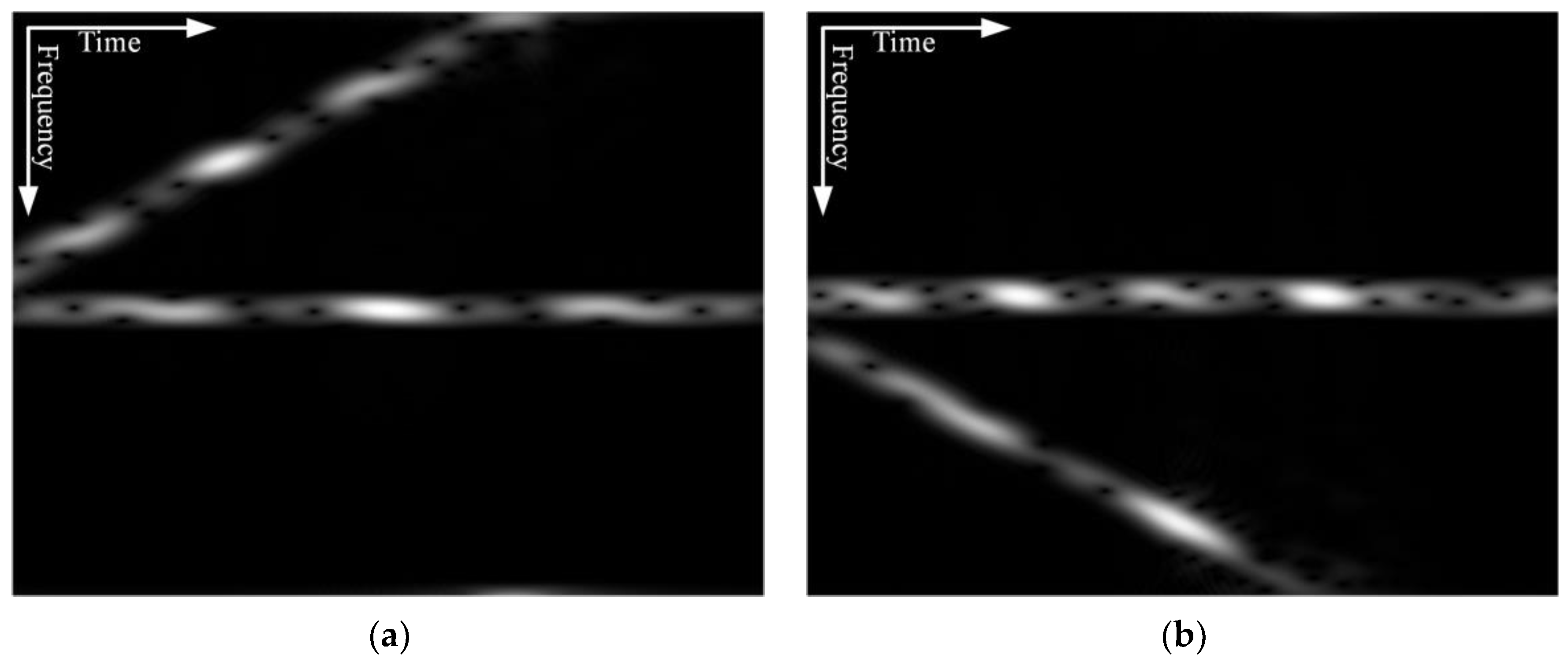
3.2. Signal Domain Separation
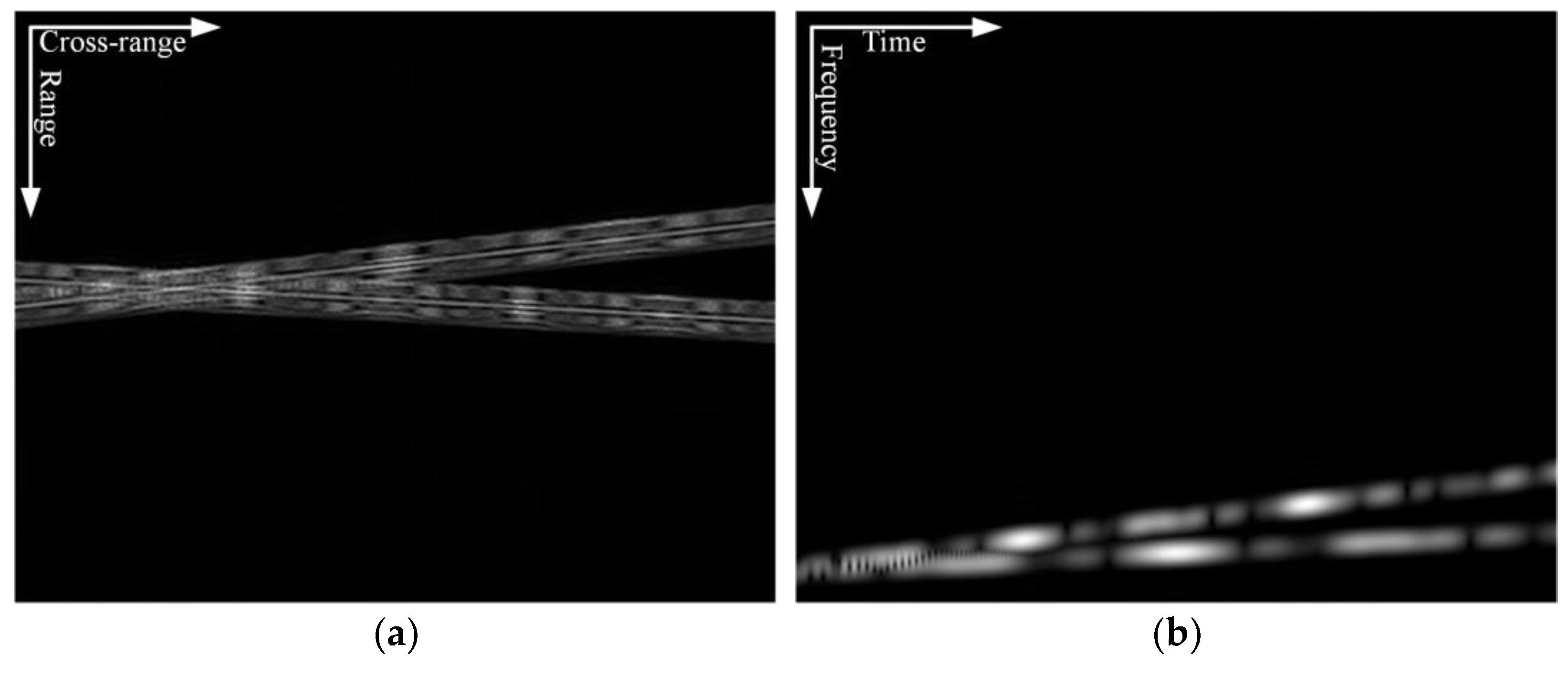
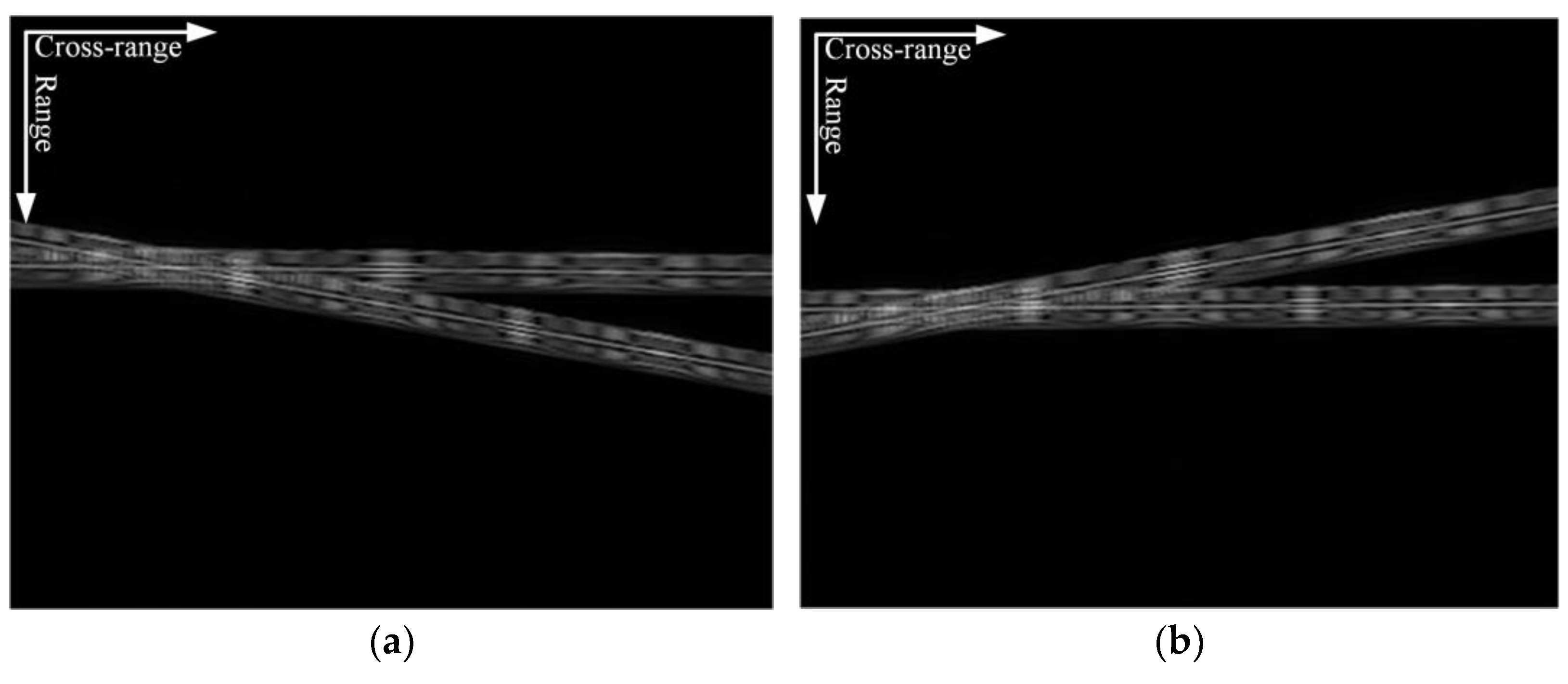
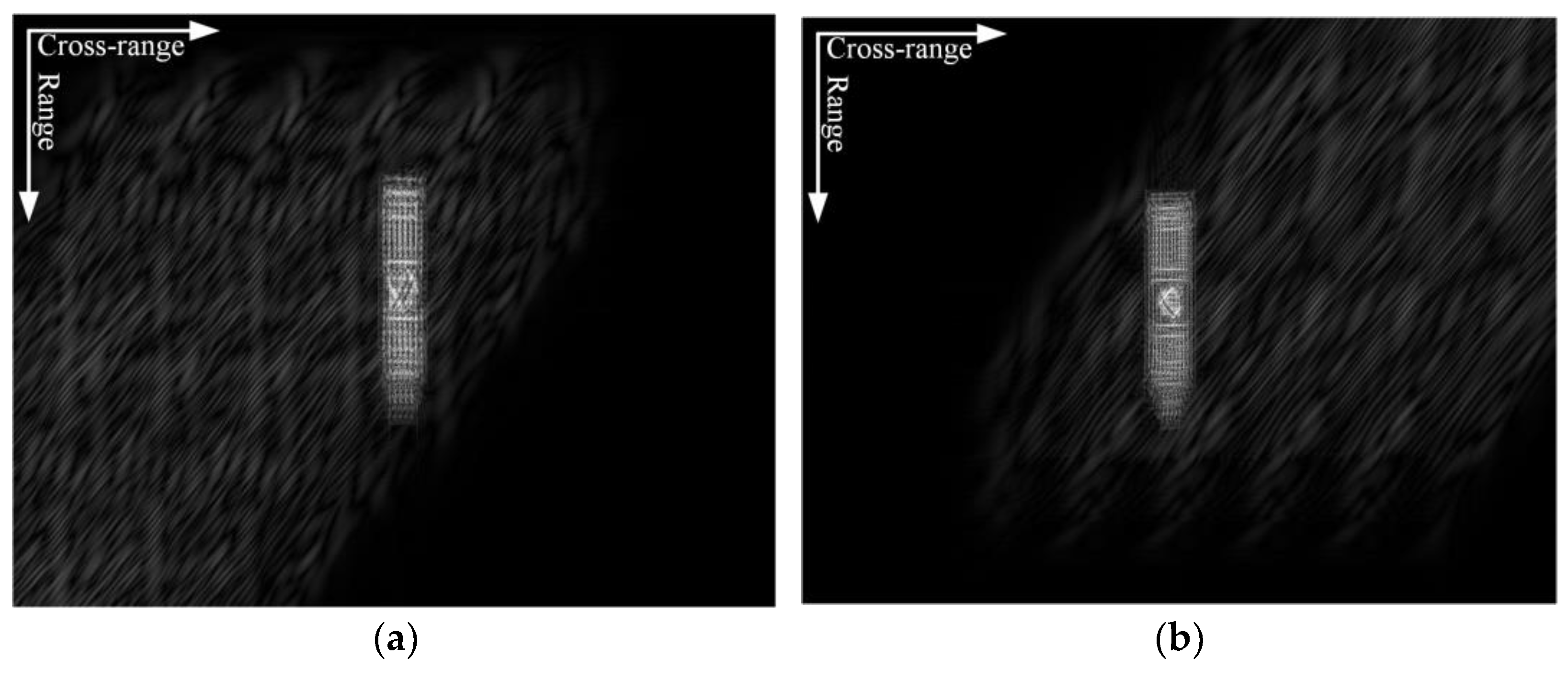
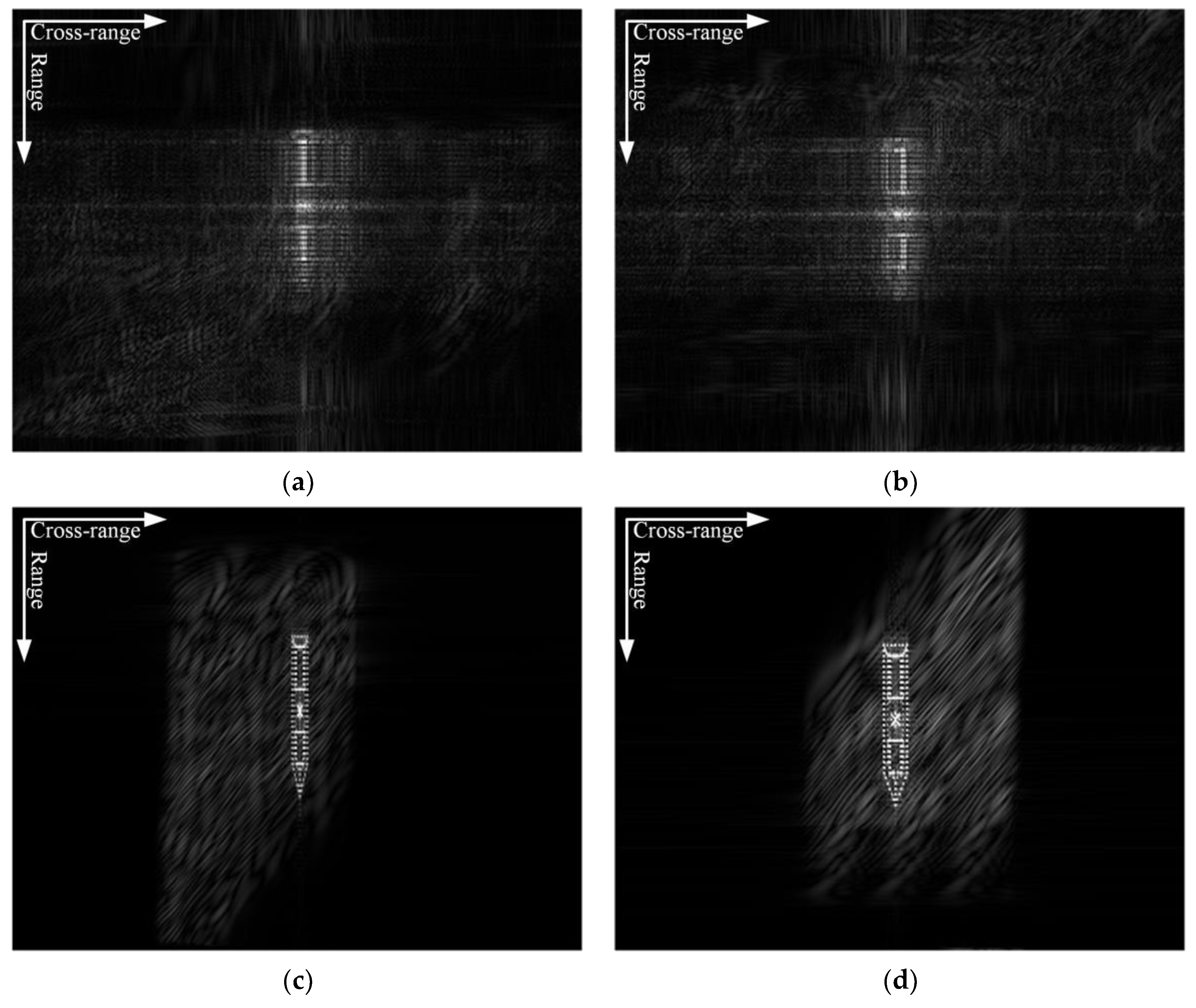
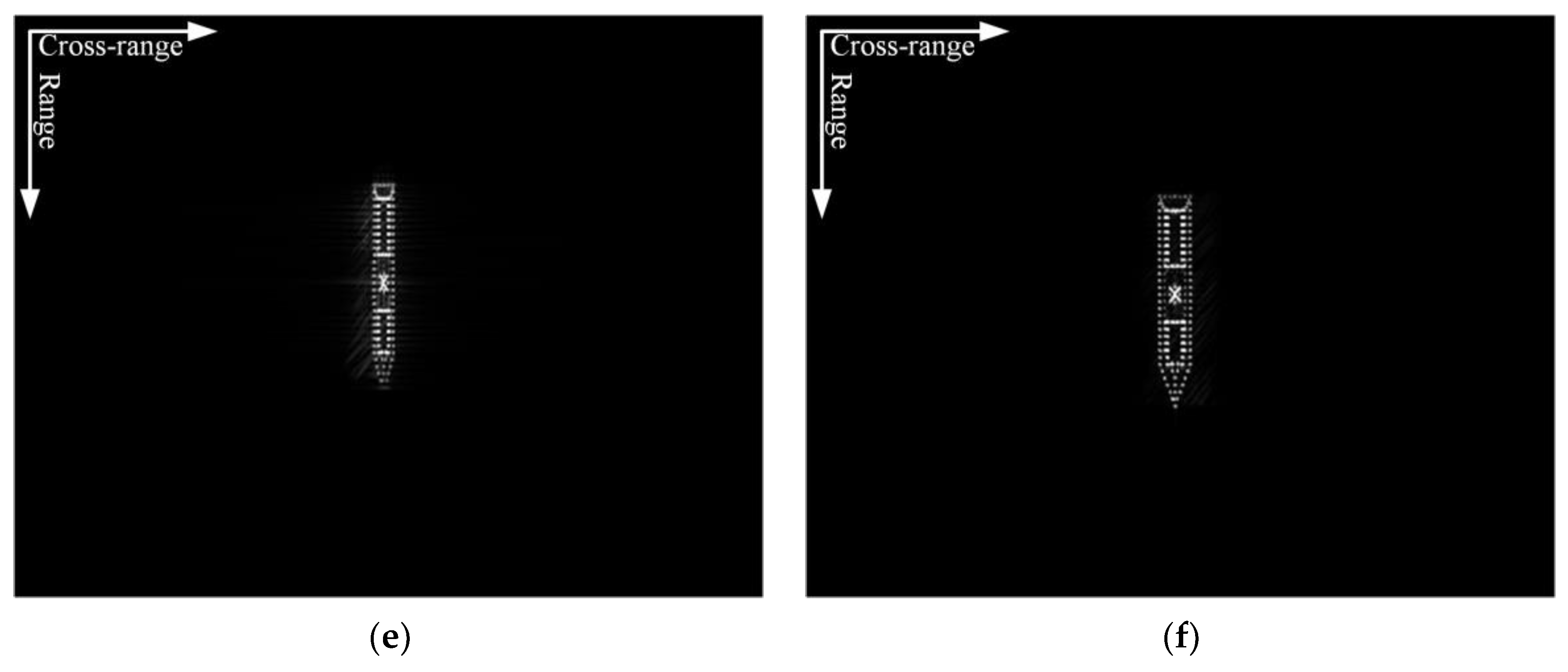
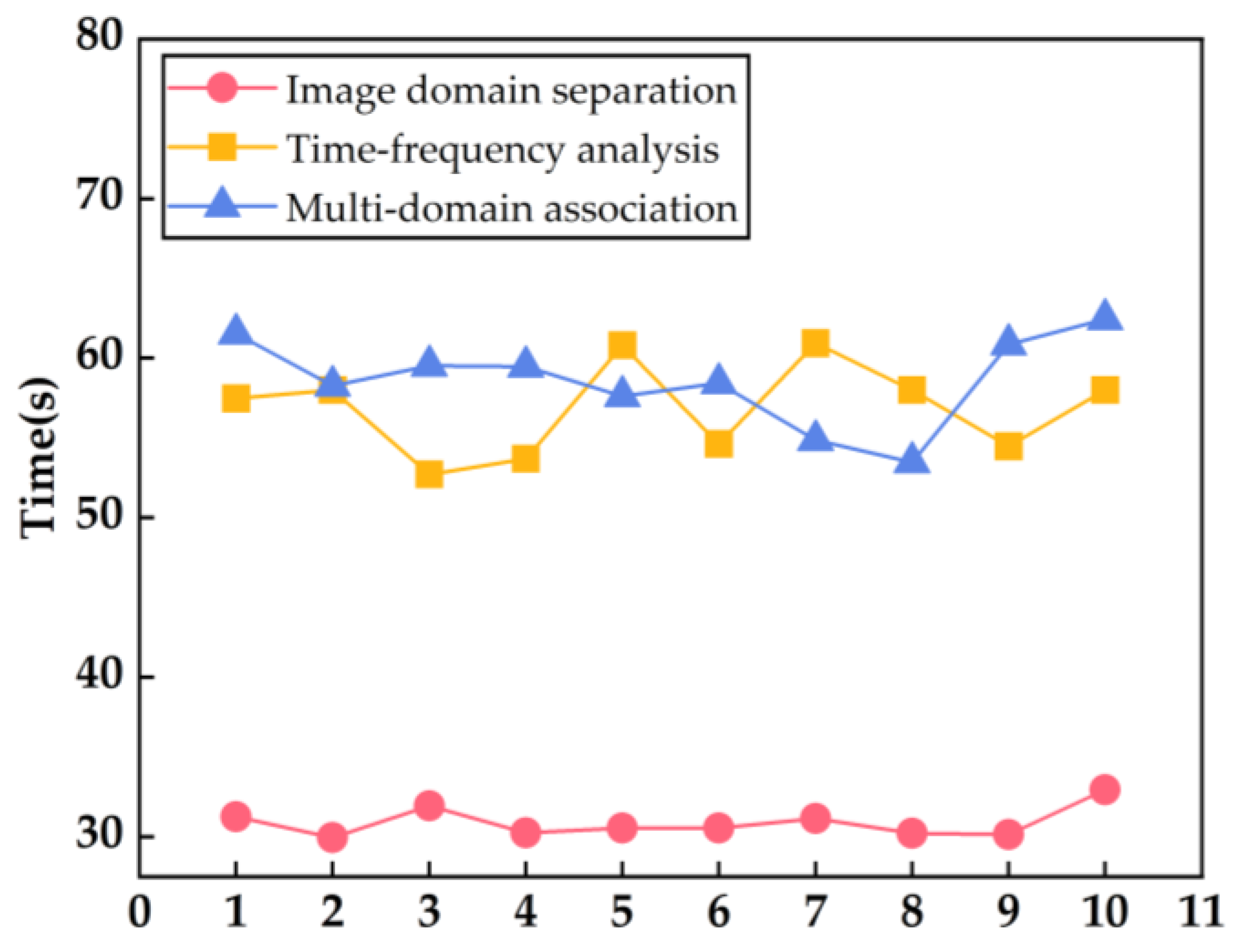
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
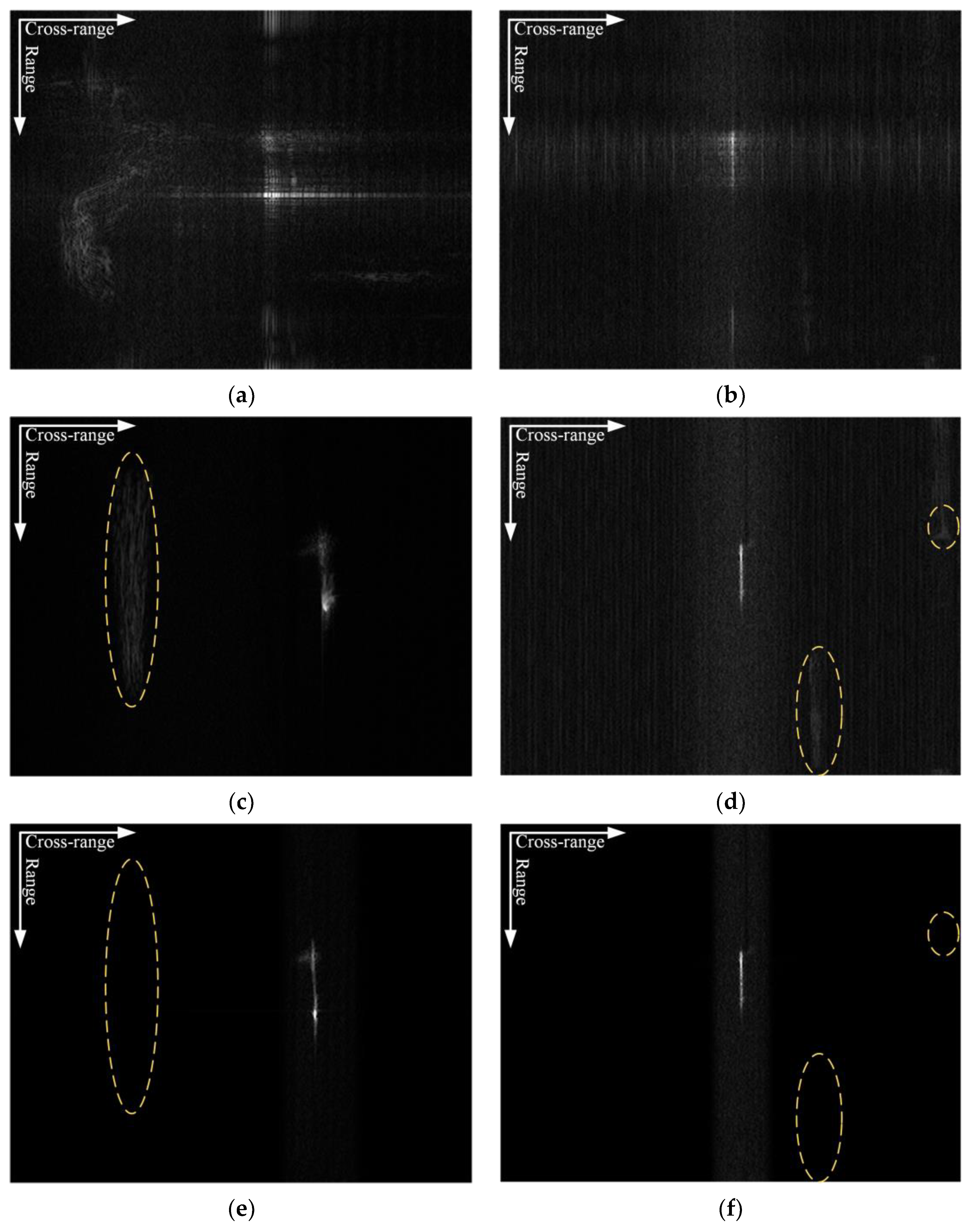
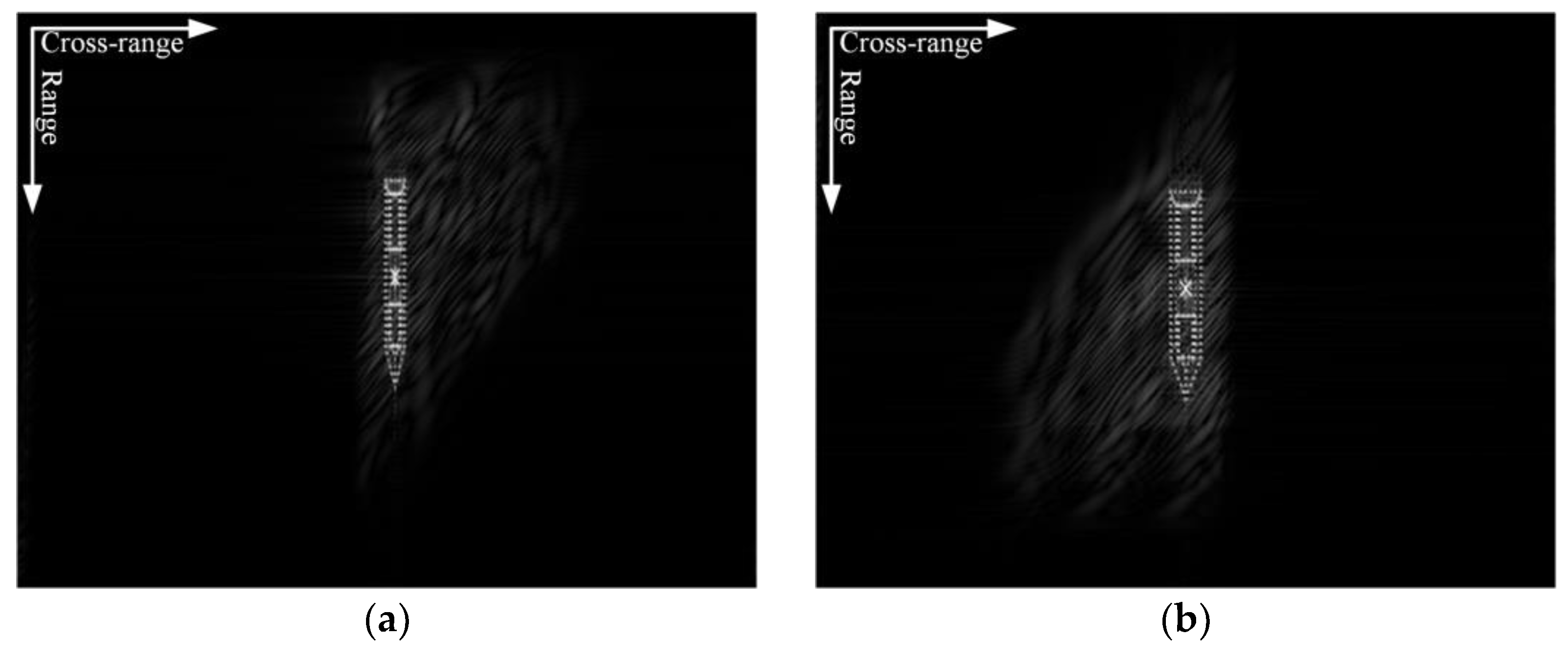
4.1. Simulated Data Processing Results
4.2. Measured Data Processing Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, Y.H.; Li, J.F.; Yang, Q.Y.; Liang, D.; Liu, K.Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, P.P.; Wang, R. First Demonstration of RFI Mitigation in the Phase Synchronization of LT-1 Bistatic SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, S.; Fan, H.; Li, H. An Effective Translational Motion Compensation Approach for High-Resolution ISAR Imaging with Time-Varying Amplitude. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 4007805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehmas, R.; Neuberger, N. Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging: A Historical Perspective and State-of-the-Art Survey. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 113917–113943. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Xing, M.; Guo, L.; Zhang, P. A modified range model and extended omega-k algorithm for high-speed-high-squint sar with curved trajectory. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5204515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wei, J. Joint motion compensation and distortion correction for maneuvering target bistatic isar imaging based on parametric minimum entropy optimization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zuo, L. Random frequency coded waveform optimization and signal coherent accumulation against compound deception jamming. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 4434–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Hu, J.; Sun, H.; Gao, Y. Resource allocation for target tracking in multiple radar architectures over lossy networks. Signal Process. 2023, 208, 108973. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Lu, X.F.; Li, Y.J. An approach of motion compensation and ISAR imaging for micro-motion targets. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2021, 32, 68–80. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.B.; Liang, G.L. ISAR Imaging of Targets with Complex Motions Based on the Keystone Time-Chirp Rate Distribution. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 1770–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Andrews, H.C. Target-motion induced radar imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1980, 16, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Du, L.; Yang, D.; Chen, B. Noise-Robust Motion Compensation for Aerial Maneuvering Target ISAR Imaging by Parametric Minimum Entropy Optimization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4202–4217. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, D.E.; Eichel, P.H.; Ghiglia, D.C.; Jakowatz, C.V. Phase gradient autofocus–A robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Sueda, H.; Watanabe, Y. Motion compensation for ISAR via centroid tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1996, 32, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H. High-Resolution ISAR Imaging and Motion Compensation with 2-D Joint Sparse Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6791–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xing, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Z. Joint Translational Motion Compensation Method for ISAR Imagery Under Low SNR Condition Using Dynamic Image Sharpness Metric Optimization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5108515. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liang, B.; Yang, D.-G.; Zhao, D.-J.; Xing, M.; Sun, G.-C. Two-Step Accuracy Improvement of Motion Compensation for Airborne SAR With Ultrahigh Resolution and Wide Swath. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7148–7160. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, A.F. Research on ISAR Imaging of Multiple Moving Targets. J. Astronaut. 2005, 26, 450–454. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.N.; Fu, Y.W.; Li, X. The Summarization of Multiple Target ISAR Imaging. Signal Process. 2009, 25, 1092–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Ding, J.; Zhang, P.; Xing, M. Joint Translational Motion Compensation for Multi-target ISAR Imaging Based on Integrated Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5108716. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z.; Sun, C.Y.; Xing, M.D. Time-frequency approaches to ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets and their limitations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2001, 37, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Berizzi, F.; Mese, E.D.; Diani, M.; Martorella, M. High-resolution ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets by means of the range instantaneous Doppler technique: Modeling and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZZhu, D.; Yin, J.; Wu, X.Q.; Zhou, J.J. ISAR Imaging of Multiple Moving Targets Using Time-Frequency Representations. Mod. Radar 1993, 15, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.W. ISAR Imaging of Multi-Target; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, V.C.; Qian, S. Joint time-frequency transform for radar range-Doppler imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1998, 34, 486–499. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, H.T.; Song, Z.Y.; Fan, H.Q. Simultaneous ISAR imaging of group targets flying in formation. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, M.S.; Bao, Z. A Real-time Implementation Technique of Multi-target ISAR Imaging. Acta Electron. Sin. 1995, 23, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.C.; Xing, M.D. An ISAR Imaging Algorithm for Multiple Targets Based on Keystone Transformation. Mod. Radar 2005, 27, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Park, K.K.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, H.T.; Kim, K.T. ISAR Imaging of Multiple Targets Using Edge Detection and Hough Transform. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2008, 22, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, H.T.; Kim, K.T. Segmentation of ISAR Images of Targets Moving in Formation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.R.; Zhou, F.; Xing, M.D.; Bao, Z. A Novel Method for Imaging of Group Targets Moving in a Formation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 50, 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.Q.; Zhu, Z.D. Simultaneous imaging of multiple targets in an inverse synthetic aperture radar. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Aerospace and Electronics, Dayton, OH, USA, 21–25 May 1990; pp. 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.D.; She, Z.S.; Zhou, J.J. Multiple moving target resolution and imaging based on ISAR principle. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1995 National Aerospace and Electronics Conference, NAECON 1995, Dayton, OH, USA, 22–26 May 1995; pp. 982–987. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, V.C.; Lu, Z.Z. Radar imaging of multiple moving targets. In Radar Processing Technology and Applications II; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1997; Volume 3161, pp. 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, V.C. Radar detection of multiple moving targets in clutter using time-frequency radon transform. In Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 2002; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2002; Volume 4728, pp. 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.C. An Implementation Method of ISAR Imaging for Multiple Targets in Formation. Acta Electron. Sin. 2006, 34, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, H.T.; Fan, H.Q.; Song, Z.Y. ISAR Imaging of Multiple Moving Targets Using Signals Separation. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Mechatronic Sciences, Electric Engineering and Computer (MEC), Shenyang, China, 20–22 December 2013; pp. 1156–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Gu, X.; Zhai, W.S. ISAR imaging of multiple targets based on sparse representations. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Communications, Antennas and Electronic Systems (COMCAS), Tel Aviv, Israel, 2–4 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Feng, C.Q.; He, S.S.; Luo, Y.Z.; Luo, X. Multi Targets Echo Signal Separation Algorithm Based on Joint Time-frequency Filtering. Fire Control Command Control 2015, 40, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Bai, X.; Xing, M.; Bao, Z. Analysis of wide-angle radar imaging. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, F.; Tao, M.; Zhang, Z. A Novel Method for Multi-Targets ISAR Imaging Based on Particle Swarm Optimization and Modified CLEAN Technique. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, S. Ground-Based Radar Detection for High-Speed Maneuvering Target via Fast Discrete Chirp-Fourier Transform. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 12097–12113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.G.; Zhang, Z.F. Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1993, 41, 3397–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.-H.; Lee, I.-H.; Kang, B.-S.; Kim, K.-T. Frame Selection Method for ISAR Imaging of 3-D Rotating Target Based on Time–Frequency Analysis and Radon Transform. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 19953–19964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-J.; Kang, B.-S.; Kang, M.-S.; Kim, K.-T. ISAR Cross-Range Scaling Using Radon Transform and its Projection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 2590–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, B. Radon transform and the modified envelope correlation method for ISAR imaging of multi-target. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 10–14 May 2010; pp. 637–641. [Google Scholar]
- Hongyin, S.; Yue, L.; Jianwen, G.; Mingxin, L. ISAR autofocus imaging algorithm for maneuvering targets based on deep learning and keystone transform. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2020, 31, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.D.; Evans, E.D.; Wilson, S.L. Search radar detection and track with the Hough transform. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Bai, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, X.P.; Wang, M. Analysis and extraction of micro-doppler features in FMCW-ISAR using a Modified Extended Hough Transform. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 24–27 October 2011; pp. 1652–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, L.; Bo, J.; Hong-Wei, L.; Bo, F. Cross-range scaling of interferometric ISAR based on Randomized Hough Transform. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Xi’an, China, 25–27 October 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.J.; Guo, M.G. ISAR imaging for multiple targets based on randomized Hough transform. In Proceedings of the 2008 Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Sanya, China, 27–30 May 2008; pp. 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.A.; Zhang, D.C.; Chen, W.D.; Wang, D.J. ISAR imaging of multiple moving targets based on RSPWVD-Hough transform. In Proceedings of the 2008 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Hong Kong, China, 16–20 December 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Martorella, M.; Berizzi, F.; Haywood, B. Contrast Maximisation based technique for 2-D ISAR autofocusing. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2005, 152, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L. Time-frequency distributions—A review. Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 941–981. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.A.; Zulfiqar, S.; Irfan, M. An Efficient ISAR Image Enrichment and Feature Abstraction of Moving Targets using Time-Frequency Transforms. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Business Analytics for Technology and Security (ICBATS), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 7–8 March 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sejdić, E.; Djurović, I.; Jiang, J. Time-frequency feature representation using energy concentration: An overview of recent advances. Digit. Signal Process. 2009, 19, 153–183. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H. Time–Frequency Feature Enhancement of Moving Target Based on Adaptive Short-Time Sparse Representation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4026205. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, S.C.; Huang, S.G. STFT with Adaptive Window Width Based on the Chirp Rate. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 4065–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.G.; Huang, Y. Time-Frequency Representation Based on an Adaptive Short-Time Fourier Transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 5118–5128. [Google Scholar]
- Martorella, M.; Berizzi, F.; Giusti, E.; Bacci, A. Refocussing of moving targets in SAR images based on inversion mapping and ISAR processing. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE RadarCon (RADAR), Kansas City, MO, USA, 23–27 May 2011; pp. 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Shang, F. A Novel Method for ISAR Imaging of Multiple Maneuvering Targets. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2019, 81, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.D.; Wu, R.B.; Lan, J.Q.; Bao, Z. Migration through resolution cell compensation in ISAR imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.L.; Xing, M.D.; Zhang, S.H.; Bao, Z. Keystone transformation of the Wigner-Ville distribution for analysis of multicomponent LFM signals. Signal Process. 2009, 89, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Radar Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 10 GHz |
| Bandwidth | 210 MHz |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 400 Hz |
| Pulse width | 10 |
| Airborne velocity | 120 m/s |
| Ship1 velocity | 18 Kn |
| Ship2 velocity | 23 Kn |
| Radar height | 2000 m |
| Straight-line distance betweenship targets | 120 m |
| Target | Method | IC | IE | IP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-ship target 1 | Based on image domain | 2.9128 | 6.1450 | 3.3464 × 105 |
| Based on time–frequency analysis | 6.5186 | 6.0113 | 3.5459 × 105 | |
| Based on multi-domain association | 7.9994 | 5.1444 | 1.1803 × 106 | |
| Sub-ship target 2 | Based on image domain | 2.8358 | 6.1988 | 1.2049 × 106 |
| Based on time–frequency analysis | 5.9921 | 5.9540 | 1.2574 × 106 | |
| Based on multi-domain association | 7.1528 | 5.1597 | 1.6022 × 106 |
| Target | Method | IC | IE | IP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-ship target 1 | Based on image domain | 2.1233 | 5.8923 | 2.8353 × 104 |
| Based on time–frequency analysis | 3.6108 | 5.7162 | 1.1138 × 104 | |
| Based on multi-domain association | 11.4638 | 5.6643 | 3.1239 × 104 | |
| Sub-ship target 2 | Based on image domain | 2.3459 | 5.7641 | 1.6443 × 104 |
| Based on time–frequency analysis | 4.6659 | 5.7390 | 1.8430 × 104 | |
| Based on multi-domain association | 10.6554 | 5.7152 | 1.9326 × 104 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Xu, N.; Li, N.; Guo, Z. A Multi-Domain Joint Novel Method for ISAR Imaging of Multi-Ship Targets. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194878
Zhang Y, Xu N, Li N, Guo Z. A Multi-Domain Joint Novel Method for ISAR Imaging of Multi-Ship Targets. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194878
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yangyang, Ning Xu, Ning Li, and Zhengwei Guo. 2023. "A Multi-Domain Joint Novel Method for ISAR Imaging of Multi-Ship Targets" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194878
APA StyleZhang, Y., Xu, N., Li, N., & Guo, Z. (2023). A Multi-Domain Joint Novel Method for ISAR Imaging of Multi-Ship Targets. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194878







