Machine Learning-Based Calibrated Model for Forecast Vienna Mapping Function 3 Zenith Wet Delay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dataset Collection and Methodology of ZWD Calculation
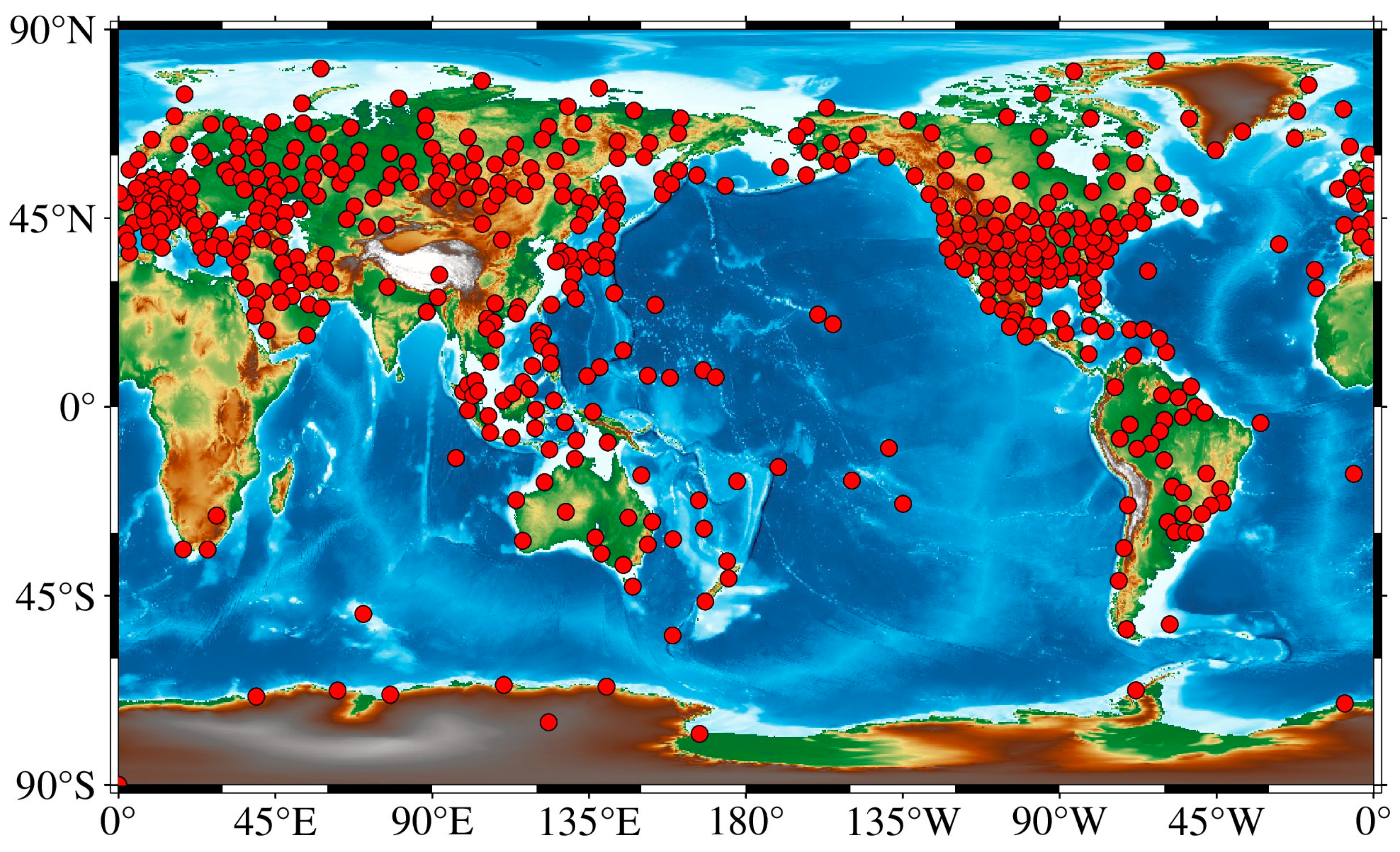
2.1. Radiosonde Data
2.2. VMF3-FC Data
2.3. Comparative Model
3. Methodology
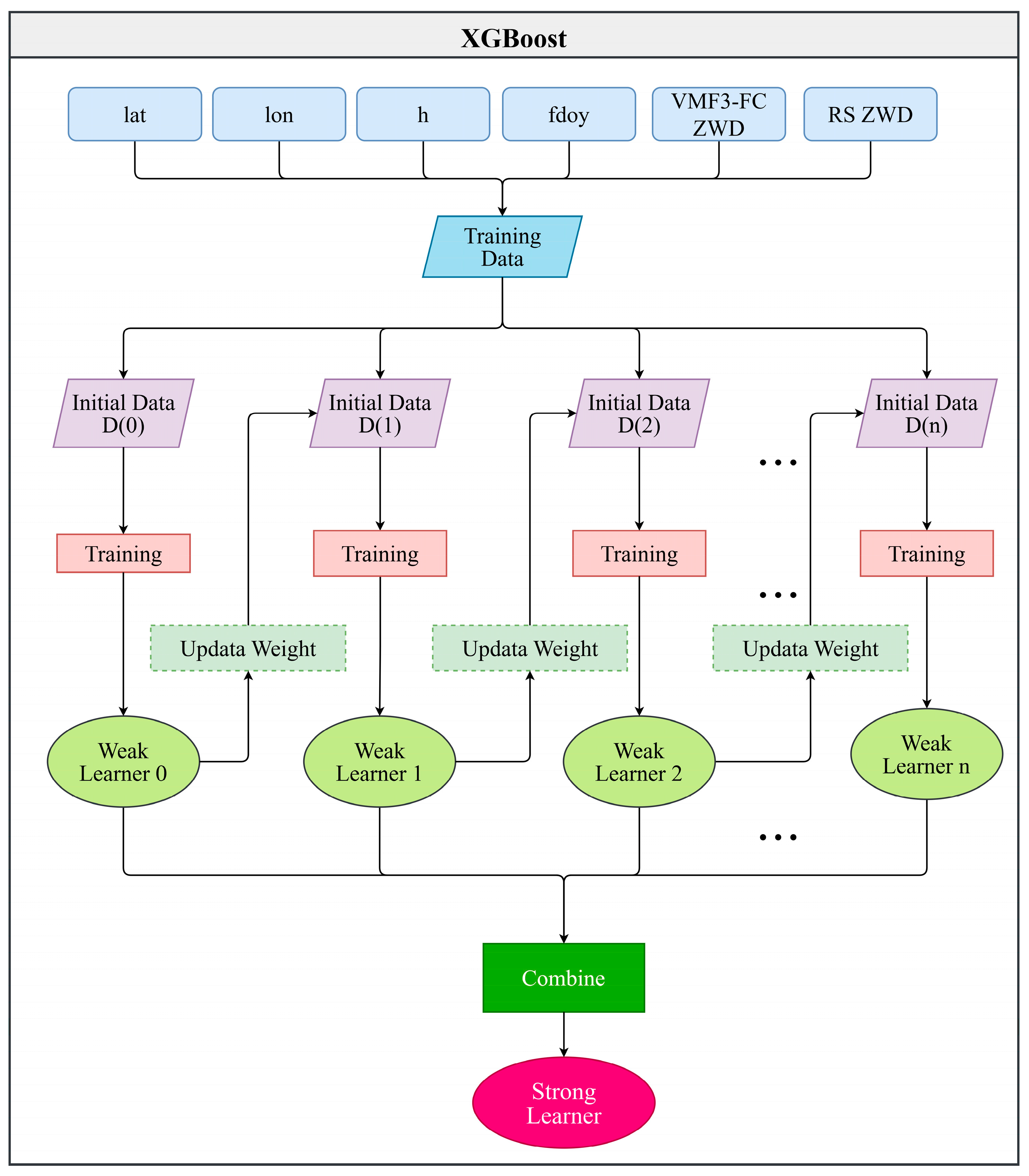
3.1. Construction of Calibrated Model
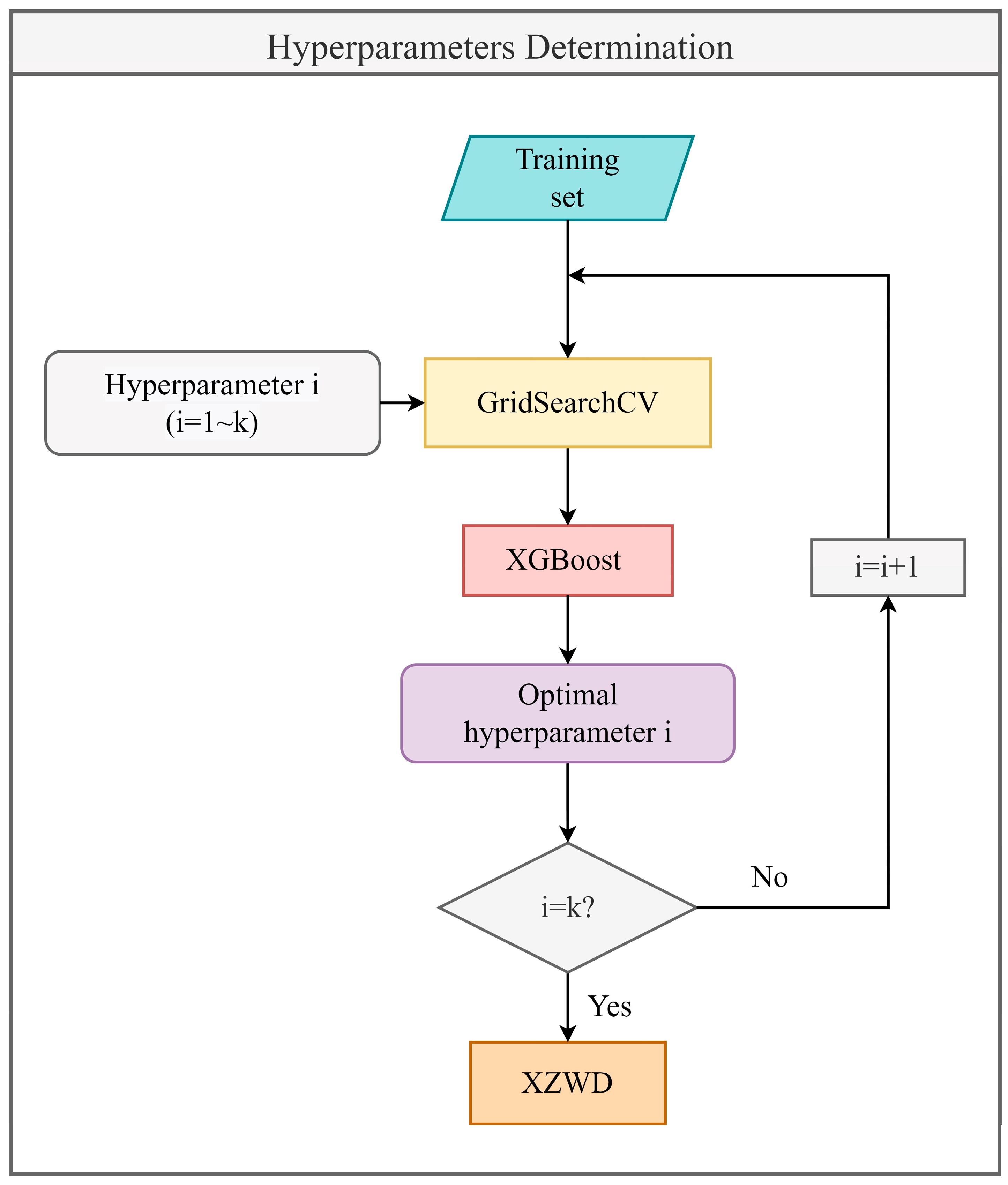
3.2. Hyperparameter Determination
3.3. Model Validation and Evaluation
4. Assessment of the Calibrated Model
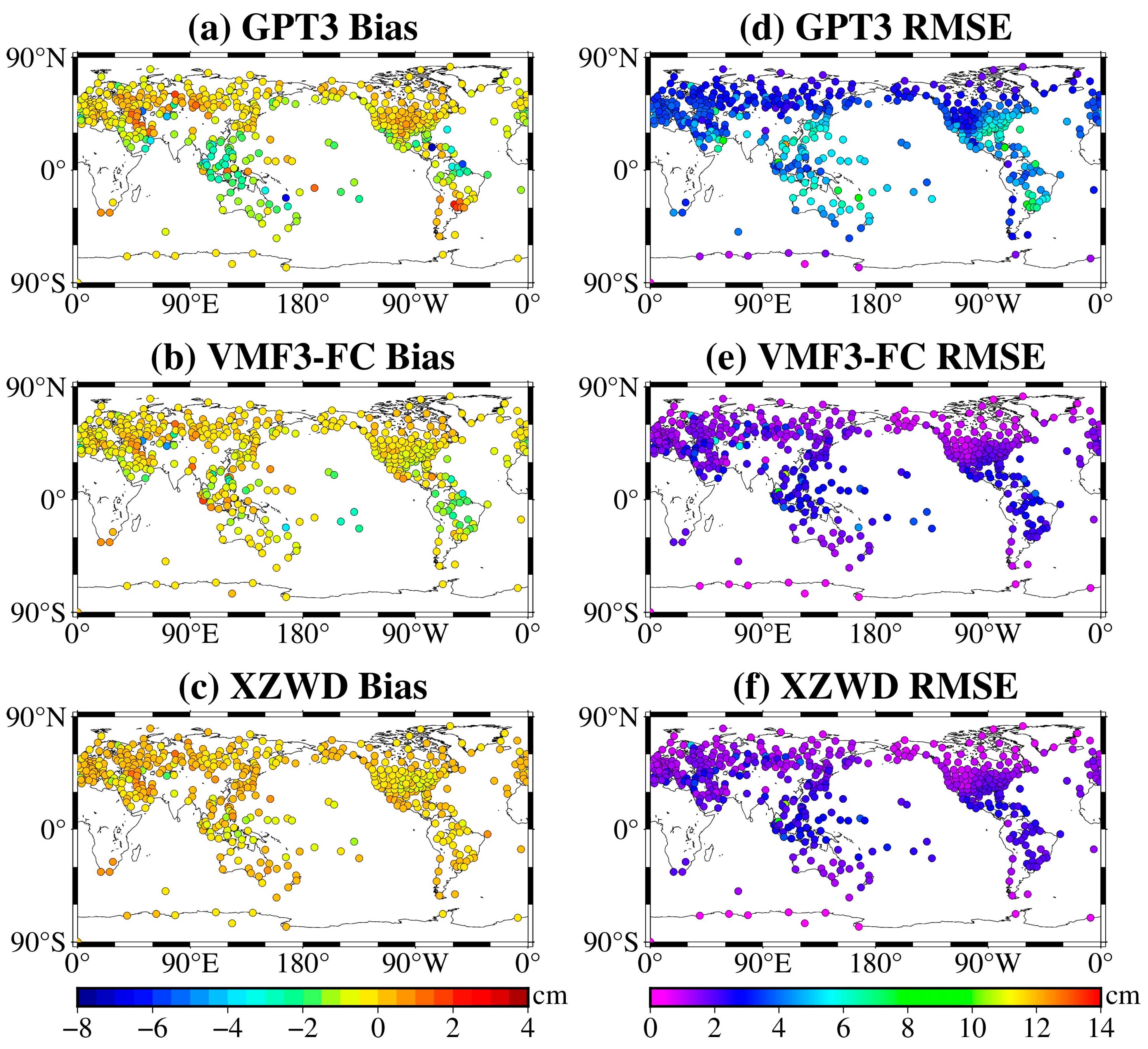
4.1. Global Accuracies
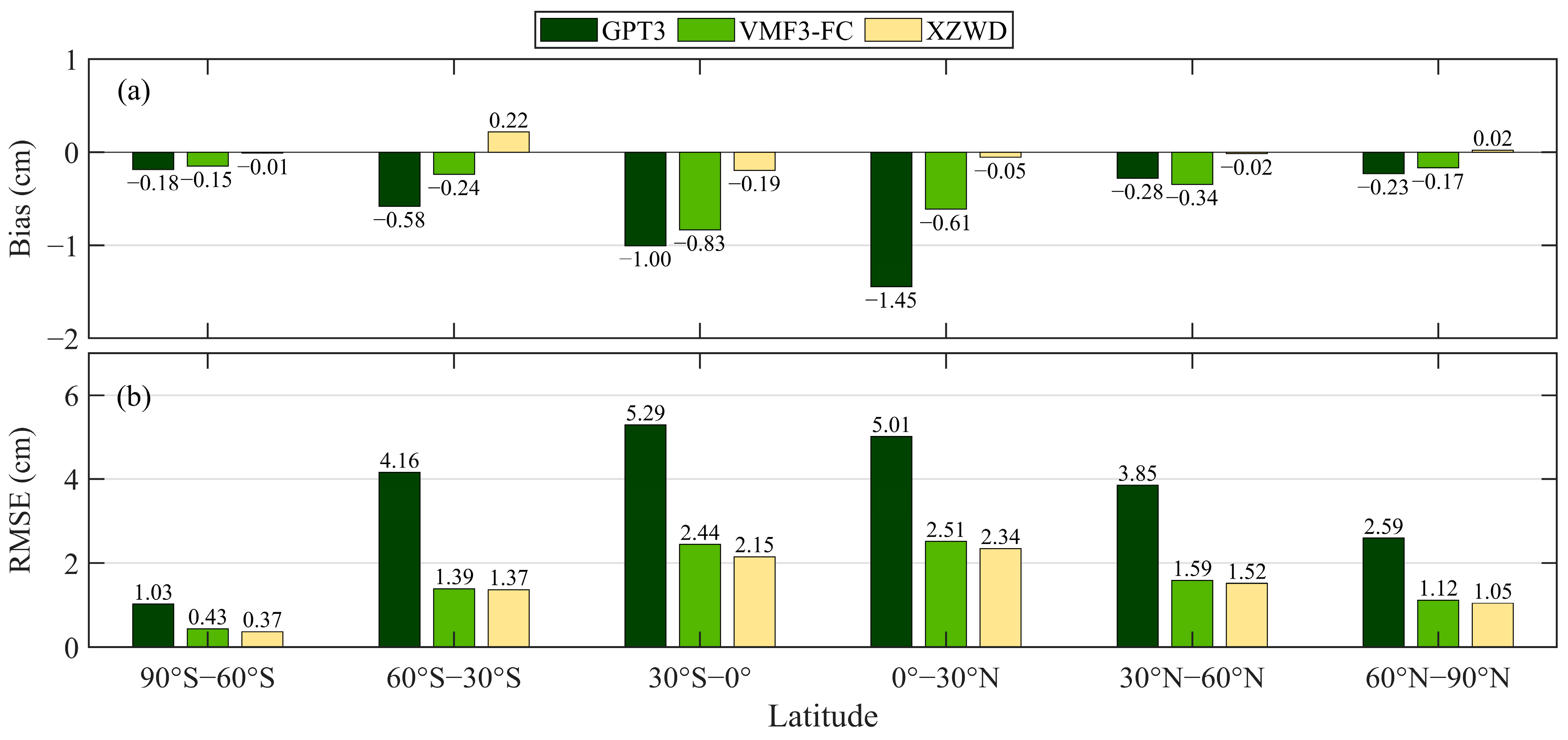
4.2. Accuracies in Different Latitude Belts
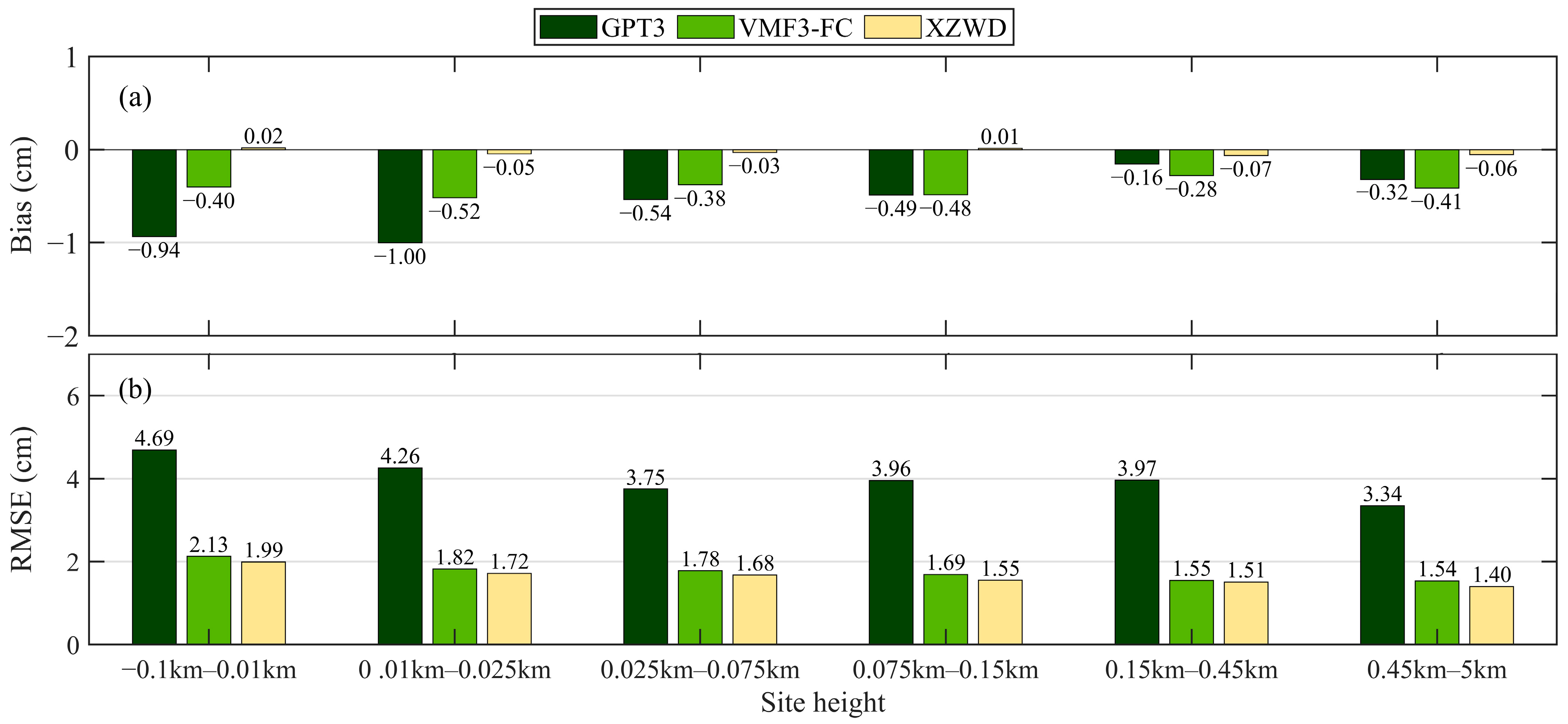
4.3. Accuracies in Different Height Ranges
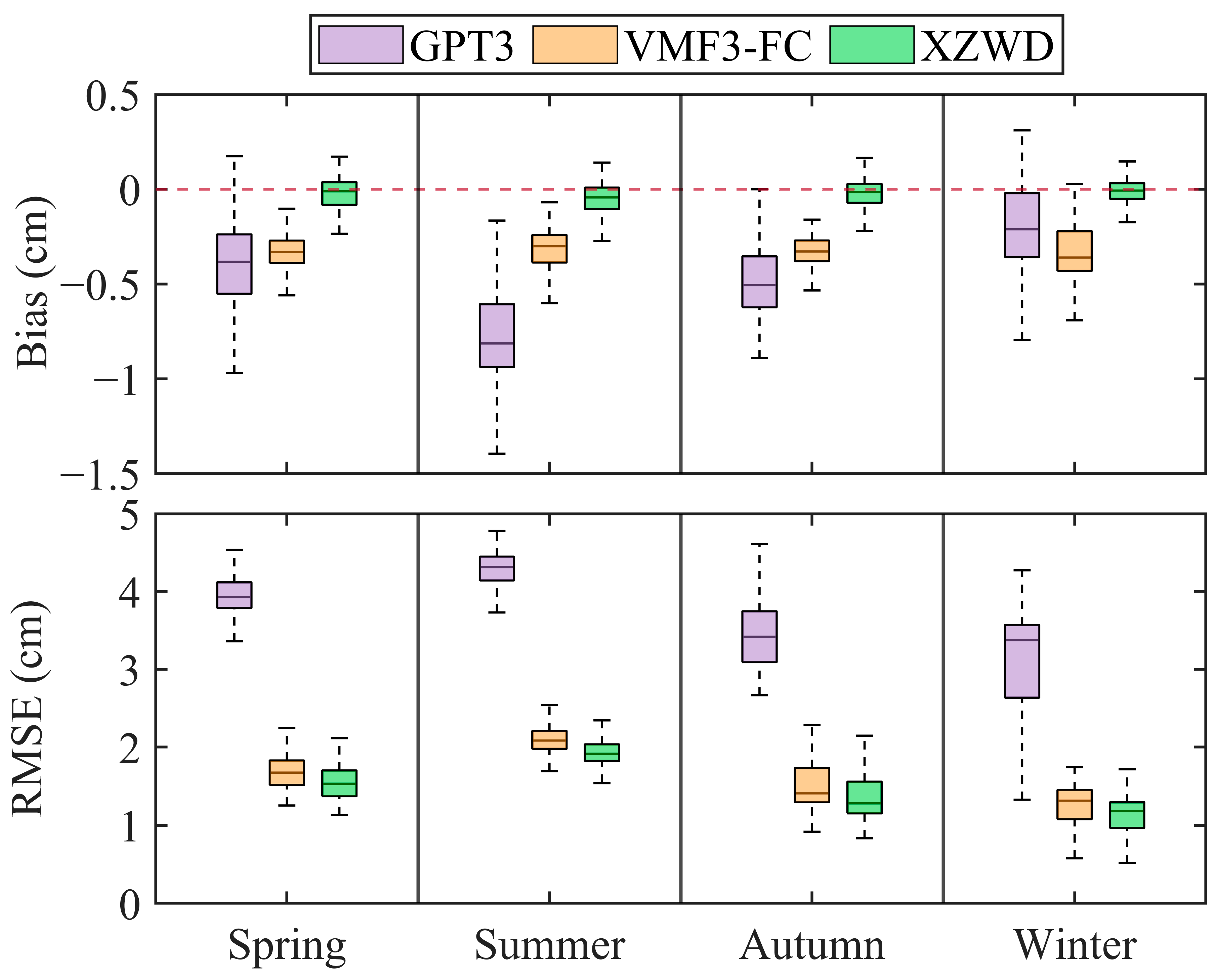
4.4. Accuracies in Different Seasons
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, F.; Guo, J.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Zou, J.; Xu, Y. Establishment and Assessment of a Zenith Wet Delay (ZWD) Augmentation Model. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Tong, M.; Ye, S.; Qian, J.; Fangxin, H. Establishing a High-Precision Real-Time ZTD Model of China with GPS and ERA5 Historical Data and Its Application in PPP. GPS Solut. 2022, 27, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, Y.; Hu, M.; Xu, C.; Su, X.; Che, D.; Peng, W. A Tropospheric Zenith Delay Forecasting Model Based on a Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network and Its Impact on Precise Point Positioning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Yao, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, F.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, B. A Refined Zenith Tropospheric Delay Model for Mainland China Based on the Global Pressure and Temperature 3 (GPT3) Model and Random Forest. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Su, J.; Xu, C.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J. High-Precision ZTD Model of Altitude-Related Correction. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, G.; Kang, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, H. A Global Zenith Tropospheric Delay Model with ERA5 and GNSS-Based ZTD Difference Correction. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W. An Analysis of Multisource Tropospheric Hydrostatic Delays and Their Implications for GPS/GLONASS PPP-Based Zenith Tropospheric Delay and Height Estimations. J. Geod. 2021, 95, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W. Real-Time Wide-Area Precise Tropospheric Corrections (WAPTCs) Jointly Using GNSS and NWP Forecasts for China. J. Geod. 2022, 96, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Yan, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, G.; Liu, F. A Regional NWP Tropospheric Delay Inversion Method Based on a General Regression Neural Network Model. Sensors 2020, 20, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Herring, T.A.; Shapiro, I.I.; Rogers, A.E.E.; Elgered, G. Geodesy by Radio Interferometry: Effects of Atmospheric Modeling Errors on Estimates of Baseline Length. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, S.Z.; Reuveni, Y. Flash Floods Prediction Using Precipitable Water Vapor Derived from GPS Tropospheric Path Delays over the Eastern Mediterranean. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5804017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liang, H.; Hu, H.; Liang, J.; Tu, M. Assimilation of GNSS PWV with NCAR-RTFDDA to Improve Prediction of a Landfall Typhoon. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, S.; Xu, T.; Bastos, L. Analyzing Correlations between GNSS Retrieved Precipitable Water Vapor and Land Surface Temperature after Earthquakes Occurrence. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawo, A.; Van Schaeybroeck, B.; Van Malderen, R.; Pottiaux, E. Precipitable Water Vapor in Regional Climate Models over Ethiopia: Model Evaluation and Climate Projections. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Choy, S.; Jiang, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, C.; Zhou, K.; Li, L.; Fu, E.; et al. Detecting Heavy Rainfall Using Anomaly-Based Percentile Thresholds of Predictors Derived from GNSS-PWV. Atmos. Res. 2022, 265, 105912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Herring, T.A.; Rocken, C.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R.H. GPS Meteorology: Remote Sensing of Atmospheric Water Vapor Using the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 15787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graffigna, V.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Azpilicueta, F.; Gende, M. Comprehensive Study on the Tropospheric Wet Delay and Horizontal Gradients during a Severe Weather Event. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, Z. A Comprehensive Evaluation and Analysis of the Performance of Multiple Tropospheric Models in China Region. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A. Accuracy Assessment of Reanalysis Datasets for GPS-PWV Estimation Using Indian IGS Stations Observations. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 9644–9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Heinkelmann, R.; Schuh, H. Short Note: A Global Model of Pressure and Temperature for Geodetic Applications. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagler, K.; Schindelegger, M.; Böhm, J.; Krásná, H.; Nilsson, T. GPT2: Empirical Slant Delay Model for Radio Space Geodetic Techniques. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Möller, G.; Schindelegger, M.; Pain, G.; Weber, R. Development of an Improved Empirical Model for Slant Delays in the Troposphere (GPT2w). GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landskron, D.; Böhm, J. VMF3/GPT3: Refined Discrete and Empirical Troposphere Mapping Functions. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.P.; Langley, R.B. A Tropospheric Delay Model for the User of the Wide Area Augmentation System; University of New Brunswick: Federiction, NB, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Leandro, R.F.; Langley, R.B.; Santos, M.C. UNB3m_pack: A Neutral Atmosphere Delay Package for Radiometric Space Techniques. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Holden, L.; Kealy, A.; Choy, S.; Hordyniec, P. Assessment of Forecast Vienna Mapping Function 1 for Real-Time Tropospheric Delay Modeling in GNSS. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1501–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liang, H.; Lou, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W. On the Suitability of ERA5 in Hourly GPS Precipitable Water Vapor Retrieval over China. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Wan, M.; Lin, Y. Retrieving Precipitable Water Vapor from Real-Time Precise Point Positioning Using VMF1/VMF3 Forecasting Products. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbesoglu, M.O. Prediction of Tropospheric Wet Delay by an Artificial Neural Network Model Based on Meteorological and GNSS Data. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2020, 23, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari Razin, M.-R.; Voosoghi, B. Modeling of Precipitable Water Vapor from GPS Observations Using Machine Learning and Tomography Methods. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 2671–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yu, X.; Sun, W. A Coalescent Grid Model of Weighted Mean Temperature for China Region Based on Feedforward Neural Network Algorithm. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lu, C.; Wu, Z.; Liao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. Machine Learning-Based Model for Real-Time GNSS Precipitable Water Vapor Sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Cao, M.; Wang, C.; Yu, N.; Qing, H. Research on Mining Maximum Subsidence Prediction Based on Genetic Algorithm Combined with XGBoost Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, M. Performance Augmentation Study on a Solar Flat Plate Water Collector System with Modified Absorber Flow Design and Its Performance Prediction Using the XGBoost Algorithm: A Machine Learning Approach. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Tan, Y.; Sun, W.; Ma, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, D. Study on the Prediction of the Uniaxial Compressive Strength of Rock Based on the SSA-XGBoost Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón Paz, J.M.; Mendoza, L.P.O.; Fernández, L.I. Near-Real-Time GNSS Tropospheric IWV Monitoring System for South America. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzcina, E.; Rohm, W.; Smolak, K. Parameterisation of the GNSS Troposphere Tomography Domain with Optimisation of the Nodes’ Distribution. J. Geod. 2022, 97, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W.; Ou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B. GPS PPP-Derived Precipitable Water Vapor Retrieval Based on Tm/Ps from Multiple Sources of Meteorological Data Sets in China: GPS-PWV Retrieval on Multiple Data Sets. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4165–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, W.; Mo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, L.; Jiang, W. A New Model for Vertical Adjustment of Precipitable Water Vapor with Consideration of the Time-Varying Lapse Rate. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhu, G.; Peng, H.; Liu, L.; Ren, C.; Jiang, W. An Improved Global Grid Model for Calibrating Zenith Tropospheric Delay for GNSS Applications. GPS Solut. 2022, 27, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, F.; Kenyon, S.C.; Factor, J.; Trimmer, R.; Pavlis, N.; Chinn, D.; Cox, C.; Klosko, S.; Luthcke, S.; Torrence, M.; et al. The Development of the Joint NASA GSFC and the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA) Geopotential Model EGM96; National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1998; Volume 206861.
- Xie, W.; Huang, G.; Fu, W.; Shu, B.; Cui, B.; Li, M.; Yue, F. A Quality Control Method Based on Improved IQR for Estimating Multi-GNSS Real-Time Satellite Clock Offset. Measurement 2022, 201, 111695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, X.; Yao, W.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y. A Drought Monitoring Method Based on Precipitable Water Vapor and Precipitation. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 10727–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J. Implementation and Testing of the Gridded Vienna Mapping Function 1 (VMF1). J. Geod. 2008, 82, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, M. Assessment of the Troposphere Products Derived from VMF Data Server with ERA5 and IGS Data Over China. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2021EA001815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.H. Stochastic Gradient Boosting. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2002, 38, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M. Developing a New Combined Model of Zenith Wet Delay by Using Neural Network. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yuan, L.; Jiang, Z. Modeling Tropospheric Zenith Wet Delays in the Chinese Mainland Based on Machine Learning. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Fu, X.; Zong, C. Short-Term Load Forecasting Method Based on Feature Preference Strategy and LightGBM-XGboost. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 75257–75268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Liang, C.-J. Prediction and Analysis of Atmospheric Visibility in Five Terrain Types with Artificial Intelligence. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, Y. TropNet: A Deep Spatiotemporal Neural Network for Tropospheric Delay Modeling and Forecasting. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, C.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X. Tibetan Zenith Wet Delay Model with Refined Vertical Correction. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Xia, J.; Ye, S.; Xu, C. A New Method for Estimating Tropospheric Zenith Wet-Component Delay of GNSS Signals from Surface Meteorology Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Term | Information |
|---|---|
| Production | VMF3-FC |
| Horizontal resolution | indir_VMF3_grid with 1° × 1° |
| Satellite altitude angle | 10° |
| Score | vmf3_grid.m https://vmf.geo.tuwien.ac.at/codes/ (accessed on 2 April 2023) |
| Gridded VMF3 files | orography_ell_1x1 http://vmf.geo.tuwien.ac.at/trop_products/GRID/ (accessed on 2 April 2023) |
| Input parameters | modified Julian date; ellipsoidal latitude (rad); ellipsoidal longitude (rad); ellipsoidal height (m); zenith distance (rad); grid resolution (°) (1) |
| Output parameters | zenith wet delay (m) |
| Order | Hyperparameters | Initial Value | Tried Value | Best Score | Best Hyperparameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | n_estimators | 500 | [100, 200, 300, 400, 500] | 0.97 | 300 |
| 2 | max_depth | 5 | [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] | 0.97 | 7 |
| 2 | min_child_weight | 1 | [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] | 0.97 | 5 |
| 3 | gamma | 0 | [0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5] | 0.97 | 0 |
| 4 | subsample | 0.8 | [0.6, 0.7,0.8, 0.9] | 0.97 | 0.9 |
| 4 | colsample_bytree | 0.8 | [0.6, 0.7,0.8, 0.9] | 0.97 | 0.8 |
| 5 | learning_rate | 0.1 | [0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5] | 0.97 | 0.2 |
| 6 | n_estimators | 500 | [100, 200, 300, 400, 500] | 0.97 | 300 |
| GPT3 | VMF3-FC | XZWD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bias (cm) | −0.56 | −0.41 | −0.03 |
| [−7.31, 2.20] | [−4.89, 1.55] | [−1.61 1.05] | |
| RMSE (cm) | 3.99 | 1.75 | 1.64 |
| [0.21, 12.24] | [0.19, 10.68] | [0.12, 10.44] |
| Site Height (km) | Number | Bias (cm) | RMSE (cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT3 | VMF3-FC | XZWD | GPT3 | VMF3-FC | XZWD | ||
| −0.10–0.010 | 85 | −0.94 | −0.40 | 0.02 | 4.69 | 2.13 | 1.99 |
| 0.010–0.025 | 72 | −1.00 | −0.52 | −0.05 | 4.26 | 1.82 | 1.72 |
| 0.025–0.075 | 83 | −0.54 | −0.38 | −0.03 | 3.75 | 1.78 | 1.68 |
| 0.075–0.150 | 84 | −0.49 | −0.48 | 0.01 | 3.96 | 1.69 | 1.55 |
| 0.150–0.450 | 85 | −0.16 | −0.28 | −0.07 | 3.97 | 1.55 | 1.51 |
| 0.450–5.00 | 83 | −0.32 | −0.41 | −0.06 | 3.34 | 1.54 | 1.40 |
| Bias (cm) | RMSE (cm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT3 | VMF3-FC | XZWD | GPT3 | VMF3-FC | XZWD | |
| Spring | −0.40 | −0.33 | −0.02 | 3.94 | 1.70 | 1.57 |
| Summer | −0.77 | −0.32 | −0.05 | 4.33 | 2.17 | 2.01 |
| Autumn | −0.48 | −0.33 | −0.02 | 3.44 | 1.53 | 1.39 |
| Winter | −0.21 | −0.33 | −0.01 | 3.12 | 1.31 | 1.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, L.; Zhou, L.; He, H. Machine Learning-Based Calibrated Model for Forecast Vienna Mapping Function 3 Zenith Wet Delay. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4824. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194824
Li F, Li J, Liu L, Huang L, Zhou L, He H. Machine Learning-Based Calibrated Model for Forecast Vienna Mapping Function 3 Zenith Wet Delay. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4824. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194824
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Feijuan, Junyu Li, Lilong Liu, Liangke Huang, Lv Zhou, and Hongchang He. 2023. "Machine Learning-Based Calibrated Model for Forecast Vienna Mapping Function 3 Zenith Wet Delay" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4824. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194824
APA StyleLi, F., Li, J., Liu, L., Huang, L., Zhou, L., & He, H. (2023). Machine Learning-Based Calibrated Model for Forecast Vienna Mapping Function 3 Zenith Wet Delay. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4824. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194824





