Abstract
Numerous riverbeds and floodplains in the Western Mediterranean Area (WMA) have been affected by anthropogenic modifications during the last centuries. In recent decades, an increase in floods in the coastal WMA has been observed. Variations in the rainfall regime and anthropisation have influenced the relevant geomorphological processes. The coastal floodplains analysed include those in Italy, France, and Spain. Geomorphological and land use changes that occurred in the last two centuries were examined using historical and recent maps, historical data, and European big data since the 1800s for 65 basins, for which over 670 flood events and more than 1300 victims were identified. Anthropogenic activities have changed the patterns of floodplains. In most cases, narrowing of the riverbeds, especially in the lower river sections, has been observed. The riverbeds have also changed from braided- to single-channel morphologies. GIS analysis shows reductions in the coastal watercourse widths ranging from 10% to 95%, with an average of 55%. Other changes are related to the deviation in the watercourses, with trends that did not respect the natural river flow. In some cases, the watercourses were covered and have vanished from recent maps. This aspect has reduced or eliminated the perception of the risk not only for the residents but also for land planners.
1. Introduction
Several authors [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] have assessed the increase in extreme precipitation and the associated increases in the frequency and magnitude of river floods. River flooding is strongly dependent upon complex catchment characteristics and land use patterns [9,10,11]. Indeed, the frequency and magnitude of river floods have changed in the past several decades in some regions, with impacts across human and natural systems [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Analyses of in situ streamflow measurements showed both increases and decreases in the frequency of river floods during 1960–2020 in Europe [24,25,26], as well decreases or variability in some areas in the Mediterranean [27,28].
Annually, floods affect 21 million people worldwide in different ways, and this number is expected to rise to 54 million by 2030 [29]. In the areas of central and southern Europe, climate change, in recent years, has led to an increase in extreme geohydrological events, with intense rainfall and damaging effects along river areas due to flooding. For example, in May 2014, a low-pressure cyclone affected a large area of Serbia and Bosnia–Herzegovina, which suffered the most severe damage. In total, 50 deaths occurred in Serbia alone, and around 32,000 people were evacuated [30]. The impacts of floods on humans are likely increasing, which can be seen when examining the figures for flood fatalities in the past decades. In the 30 years between 1980 and 2009, globally, floods led to over 540,000 casualties and injured over 360,000 people [31]. The flood frequency/intensity and associated damage are expected to increase because floods depend on both climate change and factors related to human activities, such as urban development in flood-prone areas and/or hazardous behaviours [32]. Coastal areas seem to be more sensitive to climate effects. All scenarios for climate change in the Mediterranean regions indicate warming and changes in rainfall [33,34], as well as ongoing warming of the sea and the atmosphere. The projected increases in climate hazards will impact large numbers of vulnerable natural systems and socio-economic sectors [35,36,37]. In addition, the temperature is generally expected to increase in the Mediterranean region up to 1.5 °C due to global warming. Groundwater recharge and soil water contents are also expected to consequently decline [38,39], in addition to the creation of high instability in marine ecosystems [36,38,40,41,42,43] and increased sea levels [1,42,44].
Global precipitation is projected to decrease by approximately 4% for warming levels above 2 °C for all seasons in the central and southern basin [45,46,47]. In addition, precipitation extremes are projected to increase for global warming levels above 2 °C, along with an increase in flash floods [48,49].
The Mediterranean basin is located in a transition zone for the circulation regimes [40]. This aspect has made the impacts of the observed climate change unbalanced between northern and southern EU countries, where the available time series often did not allow for the reconstruction of the past climate evolution on a sufficiently long time scale [41]. Future warming rates are anticipated to be higher, resulting in altered frequencies of flash and pluvial floods across the Mediterranean [16,24,37,41,42,43,44,45].
The length of the coastline for the EU member states with sea borders is estimated to be about 136,000 km. European coastal regions (about 1.5 × 106 km2) account for 43% of the total EU area and are occupied by 206 million citizens [46]. The EU public budget for protecting coastlines from the risk of erosion and flooding was expected to reach EUR 5.4 billion a year for the period of 1990–2020 [47], but no evidence to date confirms this intent.
Mediterranean coastal regions correspond to about 29% of European coastal regions and cover about 33% of European coastlines [47] (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Pie charts showing the following: (a) EU coastal area percentages by Mediterranean state; (b) EU coast length percentages by Mediterranean state. Slovenia and Malta were not considered because their percentages were lower than 1%.
The magnitude and impact of extreme floods vary significantly in Mediterranean areas, with differences in some sectors [48]. Usually, western areas are more prone to intense events with high impacts [49,50,51] due to oceanic climatic influences at latitudes where eastward atmospheric flows dominate [52,53], as well as the presence of reliefs close to the Western Mediterranean Area (WMA).
The WMA extends (from west to east) from the Strait of Gibraltar to the west coast of Sicily (Italy) (Figure 2).
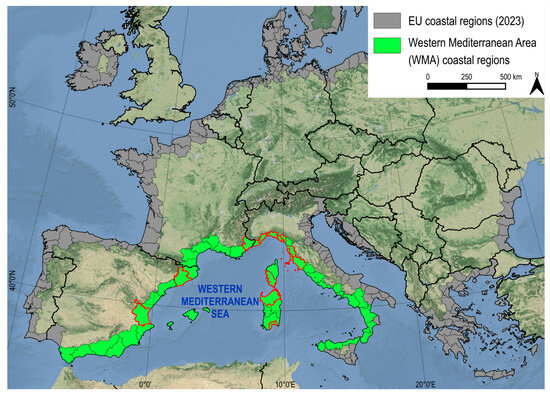
Figure 2.
EU Mediterranean coastal regions. Analysed floodplains on WMA coasts, including Spain, France, and Italy, are indicated in red, while the remaining WMA coasts are highlighted in green.
The coastal morphology induces the convergence of low-level atmospheric flows and the uplift of warm and humid air masses from the sea towards the interior of the coasts. Under these conditions, active convection is triggered and, as a result, short, intense rainfall occurs [51].
Since recorded history, powerful storms have unleashed torrential rain, resulting in widespread flooding in southern Spain, France, Italy, and western Greece [54,55,56,57,58,59]. This factor confirms the increased frequency of extreme flooding along the Mediterranean Sea coasts [59,60]. The 2019 Cecilia storm, named by Spain’s State Meteorological Agency, struck the Iberian Peninsula, southern France, and Italy, where deaths were reported. In recent years, intense rainfall has occurred across parts of Spain, south-eastern France, and north-western Italy, and has finally begun impacting southern Italy and Greece [61,62].
In Italy, an increase in geohydrological processes in small basins over the last 30–50 years has been confirmed [63,64]. If they are concentrated on reliefs close to the coasts, then these precipitations characterised by convective events (with cumulative rainfall greater than 100 mm in a few hours) can generate flash floods [59,65,66]. Affected areas are often limited to much-localised areas, measuring about a few square kilometres, with rapid hydrological responses between the peak rainfall intensity and peak downstream runoff [43].
Coastal urban flooding is a complex process that may be the result of high-intensity rainfall (pluvial flooding), inadequate drainage, and the overtopping of containable floods in channels or watercourses. A study of events in some Italian coastal urban cities showed that the most severe flood scenarios occurred due to a combination of surface flooding and the overtopping of watercourses [55]. For several parts of the world, urban flooding is a serious problem because it damages property and can cause casualties. Losses suffered due to flooding can be reduced with adequate knowledge of the expected processes and their impacts. Studies of past events make it possible to correctly estimate the extent of the flooding and flood risks under different flow conditions, enabling appropriate responses and intervention strategies to be prepared in advance.
The consequences of flash floods and ground effects in densely urbanised areas are amplified by the large number of vulnerable elements that may occur [67,68,69,70]. These areas are usually intersected by channelled watercourses that have been narrowed over time through infrastructure to acquire new urban spaces [71,72], making the river space inadequate for floodwater runoff.
Flash floods characterised by severe ground effects are generally triggered by intense and strongly convective rainfall events of short durations [73] over limited areas (<100 km2) and generate the local flooding of small watercourses that usually have areas of <40 km2 [74]. At the mesoscale, convective systems can produce stationary rainfall amounts of more than 200–300 mm in a few hours [75]. Significant examples of this phenomenon include three severe cloudbursts that impacted the Ligurian coasts (Italy) in recent years. Rainfall of 539.0 mm/24 h was recorded during the famous Cinque Terre flood event in October 2011 [76]; 556.0 mm/24 h was recorded near Genova in November, 2011 [55]; and 883.8 mm/24 h was recorded near Genova and Savona during the event that occurred in October, 2021. The 4 October 2021, event was one of the largest recorded flooding events in Europe in terms of the 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h rainfall data recorded [77]. On some occasions, heavy and prolonged rainfall may be part of large-scale perturbation lasting several days. In situations such as the Ligurian cases, extreme rainfall accumulation may be observed locally. Rainfall of 700 mm over 6 days (up to 1800 mm in October and November) caused floods and loss of life in the Liguria region during the events of 21–22 October 2019, and 23–24 November 2019 [78]. These events generally cover large areas from hundreds to thousands of km2.
Along the Italian coasts, the so-called “Meteorological Fall” is the main season for flash floods that cause severe damage, and often casualties, due to their suddenness. This season is particularly severe for mesoscale convective systems that produce long-lasting and stationary rainfall events, leading to strong responses by the corresponding watersheds (i.e., high runoff rates due to soil saturation) and substantial agreement between the peak rainfall and flood peaks in small hydrographic basins (<250 km2). The recent severe event of 15–17 May 2023, which affected the east coast of Italy (the Emilia Romagna region), is also an example of the Mediterranean area experiencing heavy rainfall. In this event, recorded rainfall peaks of 300 mm/48 h led to extensive flooding and more than 500 landslides on hilly areas [79]. This event followed an event a few days earlier in the same area. For 48 h, this event represented the most intense rainfall recorded in the entire region for two consecutive days since 1997, and the most intense in the spring season since 1961 (>200 mm and 150 mm/24 h, higher than the historical maximums recorded) [80].
In flood risk management, floodplains play an important role in relation to river discharge and protecting societies and economic activities from damage.
The structural measures put in place to protect properties and assets from the effects of catastrophic floods are often expensive and impracticable for the space available and, sometimes, inadequate.
The coastal regions of Spain, France, and Italy considered in this paper exemplify the whole WMA and thus represent a homogeneous field of investigation. The present re-search focuses on these areas, especially in relation to the large number and severity of geohydrological events that have occurred, the high number of people exposed, and the intense urbanisation processes that have affected and transformed the flood-prone land. In order to highlight the consistency of the changes induced on the territory, the anthropogenic activities over the past two centuries were considered in terms of the following: (i) the geomorphological patterns on streams, riverine areas, and floodplains; (ii) the urban sprawl; (iii) the sealed areas and land use; (iv) the distribution and frequency of flood events; (v) the reduction in riverbed widths in the lower sections; (vi) the evolutionary mechanism scheme; and (vii) the exposure of the population to flood risk over time (inhabitants and tourists).
2. General Settings
2.1. WMA Coasts
The WMA coasts, which include Spain, France, Italy (western coasts), and Malta, are permanently inhabited by 13 million people and visited by more than 23 million tourists per year [56] (figure based on the average pre-COVID-19-pandemic period).
The coastal regions of Spain, France, and Italy bordering the western Mediterranean cover an area of approximately 31 × 104 km2, for a linear developed coastline of approximately 11 × 103 km. Mediterranean basins are prone to geohydrological hazards due to their physical geographic characteristics [54,81], especially when the thermal contrast between air and seawater increases. The slopes are near to coasts and the Mediterranean Sea itself, which acts as a large source of moisture and heat. This context produces a rapid uplift of moist and unstable air that is responsible for triggering instability processes [81].
Therefore, the coastal regions of France, Spain, and the Italian Peninsula are exposed to severe geohydrological processes. These regions are surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea, with very urbanised coastal areas characterised by steep slopes and coastal complex lithology [22,82].
The stretch of coastline examined lies within the administrative territory of three neighbouring European states: Spain, France, and Italy. The study area consists of fourteen areas, defined as the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) by Regulation (EC) No. 1059/2003 of the European Parliament and the Council of 26 May 2003 for the European Office for Statistics [83]. The fourteen NUTS were chosen on the basis of the spatial distribution of representative coastal areas in the WMA. The selection was based on the homogeneity of the available statistical and spatial information (historical cartography, land use, riverine area changes, urbanisation, terrestrial and aerial images, etc.), and for which reports of historical flood events for a significant (at least 150 years) and homogeneous period were also available. Nine areas almost continuously cover the mainland coast from Cannes (France) to Grosseto (Italy), three NUTS cover a portion of the Corse (France) and Sardinia (Italy) coasts, and the remaining two NUTS are in Barcelona and Valencia (Spain). Thirty-eight major cities within these fourteen NUTS were chosen to analyse the urban sprawl and interactions between the cities and their major water streams (Figure 3).
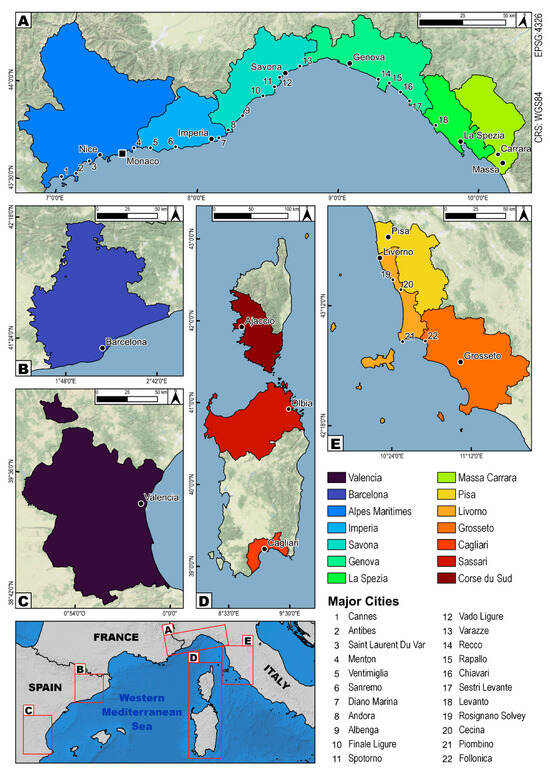
Figure 3.
Study areas with the main coastal cities identified. The names are based on the 14 NUTS (Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics) of the third level, created by the European Parliament (2003), in order to apply a common statistical standard [83]. The numbers from 1 to 22 indicate the additional major cities not explicated in the (A–E) boxes; (A–E) boxes location showed in the navigator (bottom left).
The main river courses flowing into the Mediterranean Sea were identified in these areas. In total, 65 watercourses were examined to analyse the development of the overall hydrographic network. This study focused particularly on the terminal sections of these watercourses in relation to the transformations over the last 150 years (Figure 4).
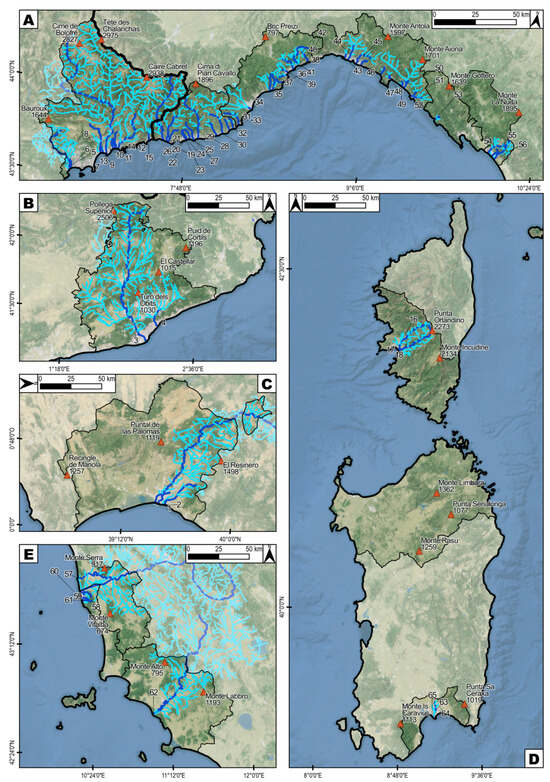
Figure 4.
Hydrographic network and morphological elements of the examined area. For the identification of (A–E) boxes, see Figure 3. The blue lines represent the major streams and the light-blue lines represent the river networks. the numbers 1–65 indicates the watercourses, numbered in Table 5. Some of the highest elevation points are indicated with brown triangles (the number indicates the peak elevation, in meters above sea level).
2.2. Population at Risk
The sectors connecting floodplains to coastal areas have been rapidly and intensively transformed over the past 150 years. Economic needs, with exchanges of goods by sea and summer tourism, and climatic–environmental conditions with mild temperatures all year round have facilitated the relocation of large numbers of people to coastal areas throughout the WMA. In particular, for the coastal areas analysed, the number of tourists has increased with the post-World War 2 economic recovery, while economic exchanges have intensified due to the presence of new ports, airports, and commercial areas along the coasts.
Increases in residents, tourists, and businesses have led to increased connections and services, such as dense networks of roads, highways, and railways. These intensely urbanised areas have become tourist destinations with population influxes that are 10-fold higher in the summer seasons (Figure 5). The tourism data in [83] take into account numerous possible accommodations (hotels, holiday, and other short-stay accommodations, as well as campsites, recreational vehicle parks, and caravan parks).

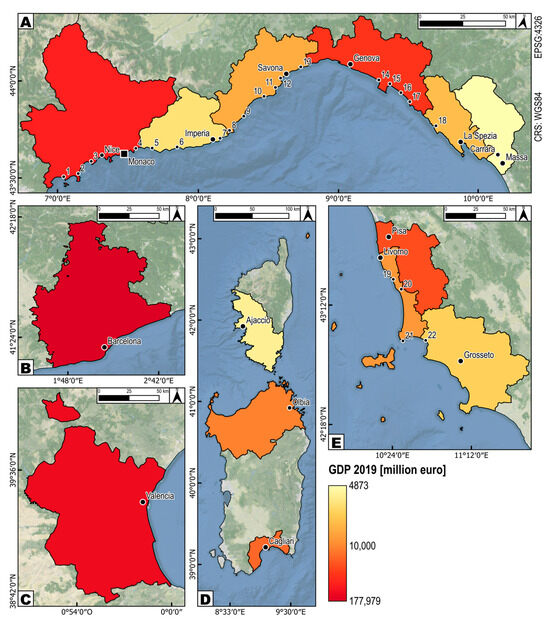
The increases in the tourist presence, relative to the resident populations in critical areas, aggravate the geohydrological risk conditions. There has been a reduction in tourists, largely connected to the COVID-19 pandemic. In some NUTS, decreases in the resident populations can also be observed. However, the percentages of people exposed to flood risks, both residents and tourists, are increasing. Figure 5 presents the current situations of the resident populations and tourism, which have oscillated considerably in the number of frequentations along the WMA coast since 1990. For example, in 1990, the city of Barcelona welcomed 1.7 million tourists; in 2012, it reached over 4.7 million tourists; and in 2017, it reached almost 32 million, increasing the actual population by 20 times [83]. The tourist presence in 2019 (considered to avoid pandemic-related variations) was up to 831% higher for Corse (France) and, on average, about 280% higher than the resident population. The areas examined are also important for their socio-economic aspects, particularly as sources of increased local welfare and economic resources. These increases translate into local GDPs, with a maximum of EUR 180 × 103 million among the Spanish NUTS (Barcelona and Valentia), followed by Nice, Genova, and Pisa (Figure 6).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Urban Impact Analysis
Numerous cartographic databases, aerial photos, and regional, national, and European databases were used to analyse the important transformations of the coastal areas, which allowed for the reconstruction of the Anthropocene evolution for all the NUTS areas from the 19th century to 2022 (Table 1). The possibility of using homogeneous territorial units (NUTS) for the analyses enabled an objective comparison of the parameters, including the growth of settlements within the NUTS.

Table 1.
Data sources for territorial analysis and urban transformations.
Cartographic analyses were carried out to assess the extent of the built-up areas from the middle of the 1800s onwards. For homogeneity, the analytical evaluations were undertaken using coeval maps via georeferencing in a GIS project, based on which transformations of the territory were reconstructed (Figure 7). In the GIS project, the historical documentation was georeferenced at a scale of 1:10,000 (by selecting cartographic documents that allowed this level of detail). For the measurement of the areas of urban transformations, land use, and the analysis of the extent of riverine areas (e.g., basin width and floodplain extent), the detail was increased to a scale of 1:500.
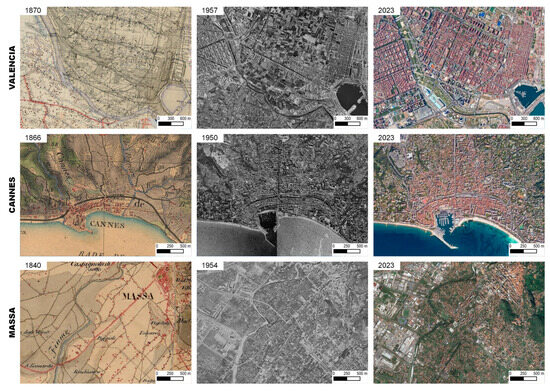
Figure 7.
Examples of diachronic built-up area mapping in three representative urban contexts of the study: Valencia (Spain; Box C, Figure 3), Cannes (France; Box A, Figure 3), and Massa (Italy; Box A, Figure 3). Anthropic growth was reconstructed through three periods: the mid-19th century, mid-20th century, and the present.
The CORINE Land Cover (CLC) categories were merged to highlight the main transformations of the territory. The NUTS considered are characterised by different land uses and divided into four macrocategories based on the degree of anthropisation and type of land management: anthropised areas, agricultural areas, natural areas, and water.
Anthropised areas include buildings, infrastructures, public and private adjacent areas, and roads (i.e., primary and secondary roads, helipads, and airports), harbour areas, port areas, commercial ports, and private and public docks. Agricultural areas consist of arable crops, agricultural woody crops (i.e., olive groves, vineyards, and orchards) (terraced or non-terraced), and heterogeneous agricultural areas (permanent crops, vegetable gardens, and agricultural areas with large natural spaces). Natural areas include wooded and semi-natural vegetated areas and permanent lawns (characterised by herbaceous vegetation, spontaneous grass emergence, and, commonly, unworked wooded and semi-natural vegetated areas, as well as semi-natural non-vegetated areas). Water areas consist of watercourses and rivers and streams, lakes, canals, and wet areas.
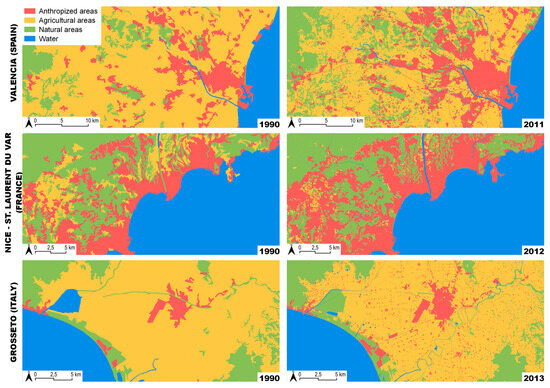
With regard to land use, we considered the CLC 2018 classes derived from the third level. The most accurate CLC data with a higher level of detail are the CLCs of the fourth level, which were available only until 2012. These more detailed CLCs (2012) made it possible to assess changes over an interval of approximately 22 years (yielding a comparison between 1990 and 2012) for each territorial unit for statistics, highlighting the various land use percentages and related transformations (Figure 8). The major processes of urbanisation occurred during the period prior to the first CLC considered (1990). In some cases, the primary transformation occurred after World War 2 (e.g., Olbia and Italy; see Box D, Figure 3). In other cases (e.g., Genova, Italy; see Box A, Figure 3), this transformation occurred immediately after industrialisation in the first decades of the 20th century. Therefore, the increase in anthropised areas in the floodplains shown in Figure 8 represents a residual evolution of a trend started well before the first CLC available at a European scale.
In some cases, it was possible to extend the period of analysis using historical maps highlighting the urbanised areas of the main cities from the mid-19th century onwards. For most coastal and riverine cities, the second post-war period was their moment of major expansion. However, an initial urban boom also occurred during industrialisation at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries. This analysis of historical maps enables us to better highlight anthropic impacts on the floodplains (Figure 9). The historical maps selected for relevance, quality, and original scale of representation, referring to the mid-19th century, were georeferenced via GIS. The maximum historical urbanised areas referable to the main cities of the NUTS considered were then drawn and compared with the current extent.
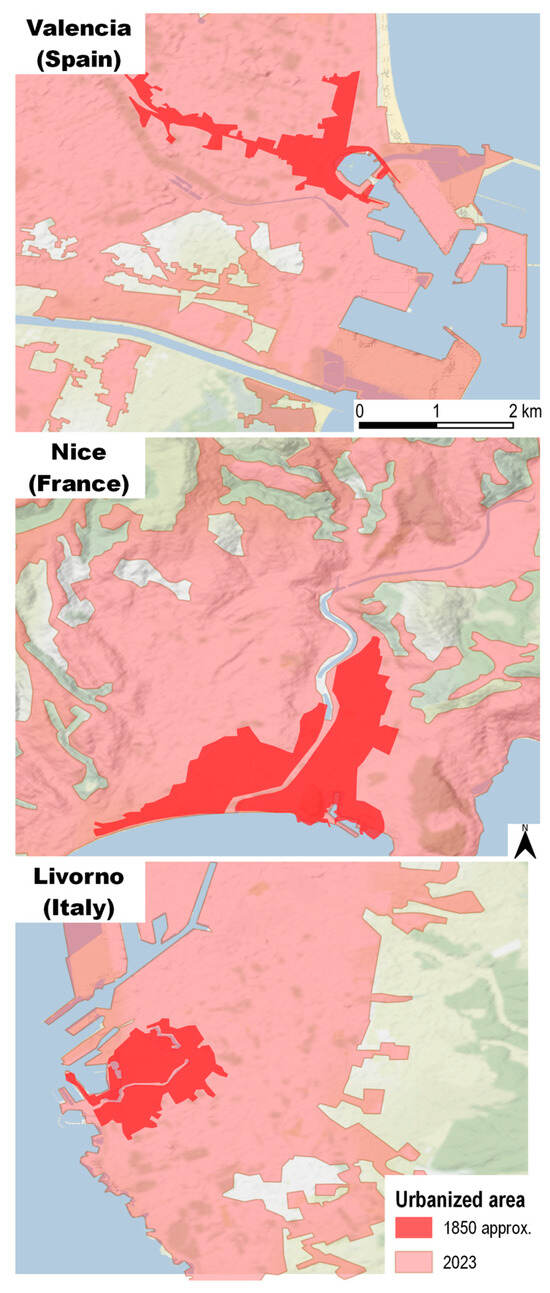
Figure 9.
Comparison of urbanised areas derived from old maps and recent cartography (see Figure 3 for localisation).
3.2. Hydro-Meteorological Hazards in Study Area
Several coastal regions of the western Mediterranean have suffered numerous flooding events affecting the corresponding river networks. The north-western coasts of Italy have been historically subject to flash floods, especially the Ligurian coasts, along with the Tuscan coasts and coasts in Sardinia [55,92]. For this research, the period between 1850 and 2022 was considered. Specific historical research based on unpublished documents, reports, monographs, newspapers, and online news reports (preferring official sources from competent bodies, technical–scientific reports and articles, and government databases) was used to uncover damaging geohydrological events that affected the various NUTS on a sub-basin scale. The events considered “major” and “main” floods are those that produced damaging effects, without considering the hydraulic characteristics (e.g., discharge, hydrometric levels, velocity, etc.) or associated solid transport.
At least 675 flood events have been recorded since 1850 (Table 2). In addition, torrential rain caused devastation in south-eastern Spain during the 25–26 September 2022 flood event. During this event, heavy rain triggered flooding and landslides. More than 29 mm of rain was recorded in just 10 min, and more than 86 mm was recorded in an hour [93]. Firefighters reported that one person died, and several were rescued, while emergency services responded to dozens of callouts, including flood rescues across 19 municipalities. Flooding and landslides caused damage to homes, streets, and vehicles and affected the regions of Catalonia, Barcelona, and Valencia in coastal eastern Spain on 16 September 2022. Furthermore, floods in south-east Spain left six dead and thousands evacuated on 16 September 2019.
On 3 October 2015, an exceptional rainfall event took place between Mandelieu-la-Napoule and Nice [94]. This rainfall event delivered approximately 200 mm/2 h and was comparable to a catastrophic event that occurred in 1966 in the same region [95], corresponding to an occurrence larger than the 100-year event [96]. Near Cannes city, rainfall of 175 mm/2 h was recorded, whereas the 100-year event was only 94.6 mm. This rainfall event caused the river discharge to rapidly increase (>250 m3/s—again, larger than the 100-year event) [95], and 20 people lost their lives during the event. Most of the urban areas bordering the Mediterranean developed along the terminal stretch of a coastal floodplain [97]. Since the early years of the twentieth century, anthropic activities have led to significant transformations in the territory, impacting most of the riverbeds and their floodplains [14,65,98,99,100]. The main consequences in watercourses are stream incision and channel narrowing, often with a significant reduction in the outflow section (Figure 10). In most cases, these alterations have also involved modifications of the river courses, which have more-or-less slowly passed from intertwined channels to braided channels to single channels.
All 675 identified flood events over the period of 1850–2022 are fully reported in the Supplementary Materials (Table S1) with an extensive supporting bibliography [55,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120].

Figure 10.
Recent floods in the study area, from left to right: (a) Livorno 2017 [121], (b) Valencia 2016 [122], and (c) Alpes-Maritimes 2010 [123].

Table 2.
Major geohydrological events in the examined areas, separated by each twenty-year interval and organised by NUTS, along with the numbers of victims, if known. The complete list of 675 flood events is given in the Supplementary Materials to this work.
Table 2.
Major geohydrological events in the examined areas, separated by each twenty-year interval and organised by NUTS, along with the numbers of victims, if known. The complete list of 675 flood events is given in the Supplementary Materials to this work.
| State | NUTS Name | Total Floods | No. of Victims | Before 1859 | 1860–1879 | 1880–1899 | 1900–1919 | 1920–1939 | 1940–1959 | 1960–1979 | 1980–1999 | After 2000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESP | Barcelona | 59 | 446 * | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 11 | 23 |
| Valencia | 33 | 83 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 17 | |
| FRA | Alpes Maritt. | 53 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 37 |
| Corse du Sud | 38 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 30 | |
| ITA | Cagliari | 35 | 268 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 10 |
| Genova | 54 | 126 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 12 | 17 | |
| Grosseto | 48 | 12 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 12 | 23 | 4 | |
| Imperia | 45 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 9 | |
| La Spezia | 57 | 11 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 8 | 16 | 18 | 3 | |
| Livorno | 62 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 9 | 21 | 20 | 6 | |
| Massa-Carrara | 38 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 9 | 19 | 6 | |
| Pisa | 35 | 35 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 22 | 8 | |
| Sassari | 65 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 20 | 18 | 6 | 11 | 7 | |
| Savona | 52 | 57 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 10 | 8 |
* According to other authors [108], the number of victims was 820.
3.3. Riverine Area Morphological Analysis
Urban transformations on the floodplains and in natural riverine areas [12] have been drastically reduced. To assess the incidence of the anthropogenic impact in each territorial NUTS, 65 watercourses (47 in Italy, 14 in France, and 4 in Spain) that have caused damaging geohydrological events, insisting on including densely urbanised areas, were selected.
For these watercourses, detailed analyses were carried out in a GIS project for the period of 1836–2023. In particular, changes to the riverbed widths in the terminal sectors on the floodplains were measured. In order to compare historical and recent river networks, it was necessary to georeference, with high precision, the oldest maps (approximately 1850) in which the hydrographic networks were represented with morphological detail (Figure 11).
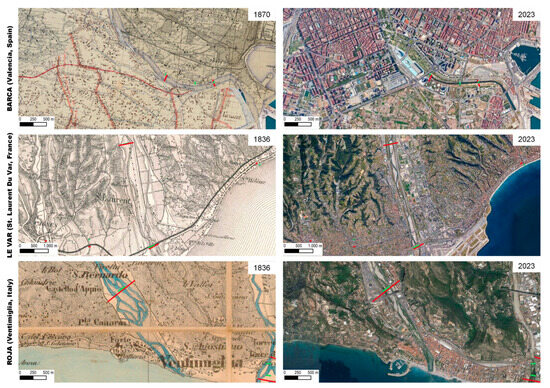
Figure 11.
Width reductions in the terminal stretches of watercourses in coastal plains measured via GIS using historical maps and current satellite images. Examples of three representative cases: Barca (Valencia, Spain; Box C in Figure 3), Le Var (St. Laurent du Var, France; Box A in Figure 3), and Roja (Ventimiglia, Italy; Box A in Figure 3).
The increase values of the urbanised areas in the lower sectors of the floodplains were compared through historical maps (19th century) and an analysis of recent satellite imagery (Google Earth). An area 1 km (the small coastal area is considered in relation to the homogenous extension of the overall floodplains (e.g., in Italy, where the floodplain is constrained between the sea and the mountains)) in width towards the inland, starting from the current coastline, was considered to evaluate the floodplain urbanisation.
For the morphological evolution of the floodplains, various evolutionary mechanisms for the watercourses were highlighted [12] (Figure 12). The morphological evolution of the WMA watercourses was affected by various evolutionary mechanisms (Figure 12). These are presented in Figure 12 in their dynamics: Originally, single-threaded waterways (A) were channelled (G), sometimes deleting certain riverbed paths (F). An initial braided morphology (B) often evolved towards a transitional morphology (G or H) or, more often, a single thread. Multi-thread catchments (C) were often deflected and lost a flow direction (E, L). Braided torrents followed various developmental lines that led them to evolve into narrow channels that were sometimes very culverted (M, P, or Q) and usually subject to techno-coasts (N or O). In some cases (e.g., Olbia and Cagliari, Italy), swamp areas (D) were drained via spread channelling (I). In many cases (e.g., N and P), a coastal sediment progradation was made.
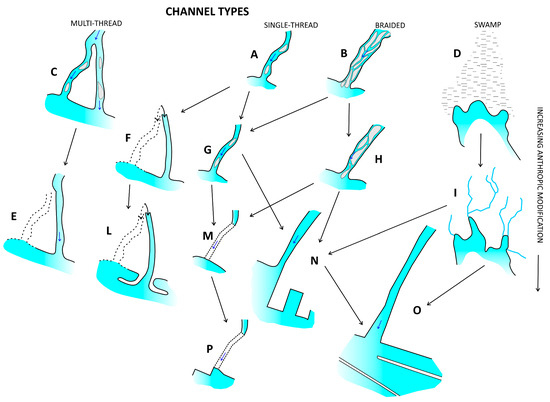
Figure 12.
Evolutionary mechanism scheme [12] based on incision and narrowing, as detected through the cartographic analysis.
4. Results
4.1. Urban Sprawl
The analysis of the urban sprawl in the period of 1950–2022 highlighted an increase in urbanised areas among the major cities of the NUTS. Normalising the data on the number of years yielded increases ranging from 0.04 km2/year (e.g., Ventimiglia, Italy) to 4.57 km2/year (Barcelona, Spain), with an overall increase rate of 0.5 km2/year. Over a period of about 60 years, the main cities of the NUTS grew by an average of 10.5 times, with a minimum increase of 1.4 times (San Remo, Italy) and a maximum increase of 51.8 times (Massa, Italy) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Growth rates of the urbanised areas of the main NUTS cities analysed. The abbreviations I (Italy), F (France), and S (Spain) refer to the EU states; for the locations of the cities, see Figure 3. The value Δarea represents the difference in the area in the period considered, and Δyears represents the interval of time considered.
The comparison of the 1990–2012 CLCs showed substantial growth in urbanised areas, with percentages ranging from 22% (Corse du Sud, France) to 284% (Grosseto, Italy), representing an average increase of about 91% when considering all the NUTS (Table 4). For Genova, the greatest increase took place following the 1930s. In the twentieth century, urbanisation began in the hillside area of the inland part of Genova, with a peak between the 1950s and 1980s; to date, this process remains ongoing [55,124]. For the same period, a comparison of the increase values of urbanised areas in the floodplain (coastal belts alone, identified by considering an area of 1 km in width towards the hinterland, starting from the current coastline) indicated general growth, with more anthropisation than the average value calculated for the entire NUTS. This result was especially evident for Cagliari (202%), La Spezia (93%), and Valencia (93%) (Table 4). This result indicates that, for several areas, the increase in urbanisation was concentrated in areas close to the coast.

Table 4.
Changes in urbanised areas based on a comparison of the 1990–2012 CLCs (fourth level).
4.2. Hydro-Meteorological Damaging Events
The temporal distribution of events (Table 2) shows a significant increase in damaging flood events for almost all the NUTS considered since the beginning of the 1980s. Among the NUTS considered alone, there were more than 1300 victims over the entire period of about 170 years. There were also other victims not specified by the documentary sources. In detail, 372 damaging flood events (over 55%) occurred after 1980, with one almost every 1.3 months and 27% in the last two decades (post-2000) (Figure 13).
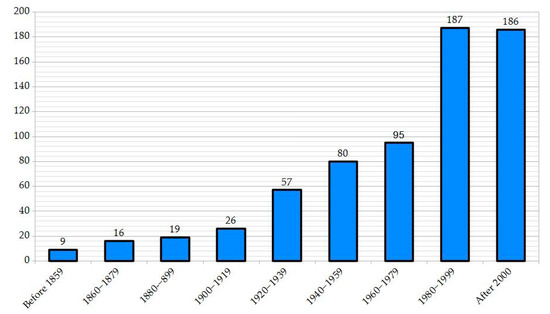
Figure 13.
Temporal distribution of the 675 flood events that affected the coastal areas of the NUTS analysed, broken down by 20-year periods starting in the middle of the 1800s [55,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121] (see Supplementary Materials).
The event data collection ended in the spring of 2022. However, recent flood events in 2023 show an increase in the frequency of heavy rainfall in all areas considered, even though these data are not included in the current analysis. Examples include the events in Spain, France, and Italy on 23–26 May 2023 [125,126], and in Barcelona and Valencia (Spain) on 30 May 2023 [127,128]. During the event on 23 May in the Murcia regions (Spain), 15 people were rescued from vehicles engulfed by floodwaters. Experts stated that the Mediterranean regions of the Iberian Peninsula, which are most often exposed to floods, receive 19% more rainfall during heavy rain periods compared to the 1960s [128].
The 30 April event in France and the 17 May 2023 event in Italy [129] are noteworthy. The delicate coastal situation in Italy is dramatically highlighted by the repeated flooding events that affected the Italian east coast (the Emilia Romagna and Marche regions) in May 2023, and produced 17 certain victims [130]. Flooding impacted about 30 watercourses and more than 1000 landslides surveyed.
4.3. Riverine Area Transformations
A comparison of 19th century maps with recent maps and images revealed a reduction in riverine areas, which were examined in comparable river stretches by measuring the riverbed widths and changes in the physical geography of the floodplains. The width measurements were replicated in significant stretches (generally at bridges or crossings). In many cases, it was possible to carry out at least two measurements and then give an average value for each watercourse. This value, expressed as a percentage, was extended to a NUTS scale, indicating an average reduction in the river spaces in the lower stretches of the watercourses in each NUTS.
Examining the morphological evolution of all the watercourses by adopting recent methodologies [12] indicates that the various evolutionary mechanisms for the watercourses often present an initial braided morphology that often evolved towards a transitional morphology or, more often, a single-thread morphology (Figure 12).
In the literature, the term “techno-coast” has been used to categorise stretches of artificial urban shores, modified to such an extent that the physical attributes of the original shore are no longer visible or preserved [131].
The measurements obtained for each watercourse are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Watercourses examined (shown in Figure 4) and their widths measured on historical (1800) and current (2020) maps, averaged over the number of measurements taken. The percentage reduction is reported. The average loss of useful discharge sections in the active riverbed is greater than 55%. The floodplain changes are shown in terms of pattern changes, diverting/culverting rivers, and the presence of techno-coasts [131]. The column “Type of pattern adjustment” refers to the evolutionary mechanism scheme in Figure 12.
The percentage reduction in the riverbed width from 1800 to today based on stream patterns varied between 11% and 96%. The average loss of useful discharge sections in the active riverbed was greater than 55%. Floodplain urbanisation was from high to very high for all watercourses, ranging from 12% to 81%. Additionally, 63% of the watercourses resulted in streams with paths that had been changed or covered.
5. Discussion
The study highlighted the critical nature of the Mediterranean areas subjected to considerable anthropic stress related to decades of uncontrolled urban sprawl, land use changes, and the soil sealing of extensive areas; these results sharply contrast with the geomorphological concept of floodplains and resilience. Such factors are especially influential when the drainage basin is closed between hilly and mountainous complexes and the sea, with areas constrained by the morphology itself.
The problems related to anthropic influence are extremely widespread and in danger of worsening due to the impacts of climate change [22] and the conditions of thermal increases in the sea level, which are responsible for disturbance processes associated with intense flooding events [12] that produce damage and casualties. The European coastal sectors bordering the Western Mediterranean Sea between Spain and Italy were considered for this study, as these areas exemplify the WMA. A natural continuation of the present research should also analyse the remaining Spanish, French, Greek, and Maltese coasts, for which data and historical documents are already being collected.
Increasingly frequent events, not only in number but also in magnitude and intensity, are leading to critical situations related to increasingly anthropised land. Indeed, the loss of natural areas over the past 20 years (1990–2012) is estimated to be 65% for the NUTS and over 90% in coastal areas alone (data obtained via CLC comparison).
Furthermore, if the same rainfall event had happened in an urbanised context at the beginning of the 20th century, it likely would have caused considerably less damage, referring to the damage that it would cause nowadays due to urbanisation. These considerations can be justified considering the lower vulnerability of the territory in terms of the resident population, a substantial absence of tourism, smaller impermeable areas, the low exposure of exposed movable and immovable goods, low socio-economic investments, and more adequate riverine spaces for the spreading of overflows.
A more in-depth study on this topic is also being considered. This study will represent each exposed factor in terms of its “vulnerability weight” in order to achieve a more precise flood risk calculation procedure.
The most significant factors related to the changes that have occurred during the Anthropocene in riverine areas include the following: (1) up to 81% of urbanised areas are located in floodplains; (2) a > 284% increase in urbanised areas was observed in the period of 1990–2018; (3) the main coastal cities increased by up to 51 times compared to the historical settlements; (4) flood events have increased in frequency; (5) physical geography changes compared to the situation in 1850 were found in all watercourses analysed, with the diversion and coverage of watercourses observed in more than 63% of the analysed cases, thereby narrowing up to 96% of the historical riverbed; and (6) the presence of techno-coasts was observed in more than 84% of the watercourses. These factors have dramatically influenced the physical geography of the floodplains, exposing coastal areas to increases in damaging floods. Additionally, the population exposed to this risk is constantly increasing, with an average touristic presence about 280% higher than the resident population and a peak of over 800% (Corse, France).
6. Conclusions
The drastic transformations of the physical geography of watercourses and floodplains are related to historical and intensive human settlements. Activities necessary to mitigate the harmful effects associated with geohydrological events must consider natural, economic, and social aspects.
The WMA coasts extend for nearly 3550 km between Spanish and Italian borders. This stretch of land contains several hundred catchments characterised by medium–small floodplains. In these sectors, the slopes are very steep, while the floodplains are typically narrow and elongated.
Mediterranean floodplains were historically characterised by floods that caused millions of euros in damage and hundreds of fatalities. Increases in geohydrological events have been observed since the 1980s due to variations in the rainfall regime and changes in land use, which have heavily influenced the geomorphological processes related to the dramatic increases in soil sealing.
The analyses performed in this study highlight some critical issues related to the territory and areas exposed to potential damage by river floods. About 650 floods related to 65 catchments were observed in only 14 NUTS out of the 51 WMA NUTS. These 14 NUTS represent almost 10% of the total Mediterranean coasts. In many cases, such disastrous floods can currently be identified as “exceptional”, but this term, in light of current climate change, could become “ordinary” in the near future. A 2 °C increase in global temperatures [22] would likely exacerbate this problem by significantly increasing the frequency [132] and severity of flooding, with a higher probability of coastal floods, storm surges, flash floods, and fluvial floods along the main rivers, as well as urban flooding in many cities [133].
Exposure is increasing rapidly, especially in terms of people who could be affected by damaging floods. The tourism factor is also extremely important in coastal areas due to the attractiveness of such sites. This aspect often aggravates the alert and response capabilities of the people involved. In many locations, the numbers of people exposed to flood events have increased by up to 10 times compared to the resident populations. It should be added that tourists are often unaware of the hydro-geological problems of holiday resorts or are very unconcerned about them. This aspect should lead to further sociological considerations and safeguard measures.
The various factors considered in this study should be part of an appropriate spatial planning process and expressed in terms of the resilience of the population.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs15194798/s1, Table S1: Complete list of flood events in WMA NUTS considered (period 1850–2022).
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation and methodology, L.T. and B.B.; validation, L.T. and B.B.; investigation, L.T. and B.B.; resources, L.T., B.B., F.L. and F.F.; data curation, L.T. and B.B.; writing—original draft preparation, L.T. and B.B.; writing—review and editing, L.T., B.B., F.L. and F.F.; supervision, L.T., B.B., F.L. and F.F.; project administration, F.L. and L.T.; funding acquisition, F.L. and L.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the FONTES Projects of Relevant National Interest (PRIN) Project (“Fonti geostoriche e sistemi informativi per la conoscenza del territorio e la gestione dei rischi ambientali e culturali”) (available online: https://fontes.univr.it/, accessed on 15 March 2023), supported by Government Funding (Project CNR Number DTA.AD003.737).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in the links reported as references.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Nicholls, N.; Easterling, D.; Goodess, C.M.; Kanae, S.; Kossin, J.; Luo, Y.; Marengo, J.; McInnes, K.; Rahimi, M.; et al. Changes in Impacts of Climate Extremes and Their Impacts on the Natural Physical Environment. In Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation; Field, C.B., Barros, V., Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Dokken, D.J., Ebi, K.L., Mastrandrea, M.D., Mach, K.J., Plattner, G.K., Allen, M., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 109–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messmer, M.; Simmonds, I. Global analysis of cyclone-induced compound precipitation and wind extreme events. Weather Clim. Extremes 2021, 32, 100324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.G.; Son, S.W.; Min, S.K. Possible impact of urbanization on extreme precipitation-temperature relationship in East Asian megacities. Weather Clim. Extremes 2021, 34, 100401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuel, O.; Martius, A. A climatology of sub-seasonal temporal clustering of extreme precipitation in Switzerland and its impacts. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 2949–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, B.; Cui, S.; Wang, L.; Shrestha, S. Post-Flood Resilience Assessment of July 2021 Flood in Western Germany and Henan, China. Land 2023, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, Y.; Giannakaki, P.; von Waldow, H.; Chevalier, C.; Pfahl, S.; Martius, O. Clustering of Regional-Scale Extreme Precipitation Events in Southern Switzerland. Monthly Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampa, F.; Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Kalantari, Z.; Ferreira, C.S.S. Flood Mitigation in Mediterranean Coastal Regions: Problems, Solutions, and Stakeholder Involvement. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.; Gil, S.; Olcina, J. Housing bubbles and the increase of flood exposure. Failures in flood risk management on the Spanish south-eastern coast (1975–2013). J. Flood Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijnissen, R.J.C.; Kok, M.; Kroeze, C.; van Loon-Steensma, M.J. Flood risk reduction by parallel flood defences—Case-study of a coastal multifunctional flood protection zone. Coast. Eng. 2021, 167, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornitz, V.; Oppenheimer, M.; Kopp, R.; Horton, R.; Orton, P.; Rosenzweig, C.; Solecki, W.; Patrick, L. Enhancing New York City’s resilience to sea level rise and increased coastal flooding. Urban Clim. 2020, 33, 100654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morucci, S.; Coraci, E.; Crosato, F.; Ferla, M. Extreme events in Venice and in the North Adriatic Sea: 28–29 October 2018. Rend. Lincei Sci. Fis. Nat. 2020, 31, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, F. Geohydrological hazards and urban development in the Mediterranean area: An example from Genoa (Ligu-ria, Italy). NHESS 2015, 15, 2631–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagnone, P.; Massazza, G.; Pezzoli, A.; Rosso, M. Hydrology of the Sirba River: Updating and Analysis of Discharge Time Series. Water 2019, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollero, A. Channel changes and floodplain management in the meandering middle Ebro River, Spain. Geomorphology 2010, 117, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, L.; Pianosi, F.; Woods, R. Event-based classification for global study of river flood generating processes. Hydr. Process. 2020, 34, 1514–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Viglione, A.; Perdigão, R.A.P.; Parajka, J.; Merz, B.; Lun, D.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; et al. Changing climate both increases and decreases European river floods. Nature 2019, 573, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramblay, Y.; Mimeau, L.; Neppel, L.; Freddy, V.; Sauquet, E. Detection and attribution of flood trends in Mediterranean basins. Hydr. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4419–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lompi, M.; Mediero, L.; Caporali, E. Future Flood Hazard Assessment for the City of Pamplona (Spain) Using an Ensemble of Climate Change Projections. Water 2021, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Coumou, D.; Frieler, K. Increased record-breaking precipitation events under global warming. Clim. Chang. 2015, 132, 517–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polomčić, D.; Bajić, D.; Ratković, J. Assessment of Historical Flood Risk to the Groundwater Regime: Case Study of the Kolubara Coal Basin, Serbia. Water 2018, 10, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doocy, S.; Daniels, A.; Murray, S.; Kirsch, T.D. The human impact of floods: A historical review of events 1980–2009 and systematic literature review. PLoS Curr. 2013, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.; Petersen, J.; Eggert, B.; Alias, A.; Christensen, O.B.; Bouwer, L.M.; Braun, A.; Colette, A.; Déqué, M.; Georgievski, G.; et al. EURO-CORDEX: New high-resolution climate change projections for European impact research. In IPCC—Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; Volume 14, pp. 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Alexander, L.V.; Allen, S.K.; Bindoff, N.L.; Bréon, F.-M.; Church, J.A.; Cubasch, U.; Emori, S.; et al. Technical summary. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Doschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 33–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, S.; Doblas-Miranda, E.; Lionello, P.; Borrego, C.; Giorgi, F.; Iglesias, A.; Jebari, S.; Mahmoudi, E.; Moriondo, M.; Pringault, O.; et al. Drivers of change. In Climate and Environmental Change in the Mediterranean Basin—Current Situation and Risks for the Future. First Mediterranean Assessment Report; Cramer, W., Guiot, J., Marini, K., Eds.; Union for the Mediterranean: Marseille, France, 2020; pp. 59–180. [Google Scholar]
- Field, C.B.; Barros, V.R.; Dokken, D.J.; Mach, K.J.; Mastrandrea, M.D.; Bilir, T.E. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Working Group II Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jacob, D.; Taylor, M.; Bindi, M.; Brown, S.; Camilloni, I.; Diedhiou, A.; Djalante, R.; Ebi, K.; Engelbrecht, F.; et al. Impacts of 1.5 °C Global Warming on Natural and Human Systems. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C: An IPCC Special Report; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pörtner, H.O., Roberts, D., Skea, J., Shukla, P.R., Pirani, A., Moufouma-Okia, W., Péan, C., Pidcock, R., et al., Eds.; IPCC Secretariat: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 175–311. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, W.; Guiot, J.; Marini, K. Climate and Environmental Change in the Mediterranean Basin—Current Situation and Risks for the Future; First Mediterranean Assessment Report; MedECC, Union for the Mediterranean: Marseille, France, 2020; 632p, ISBN 978-2-9577416-0-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovats, R.S.; Valentini, R.; Bouwer, L.; Georgopoulou, E.; Jacob, D.; Martin, E.; Rounsevell, M.; Soussana, J.-F. Europe. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1267–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niang, I.; Ruppel, O.C.; Abdrabo, M.A.; Essel, A.; Lennard, C.; Padgham, J.; Urquhart, P. Africa. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Barros, V.R., Field, C.B., Dokken, D.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Mach, K.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1199–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurse, L.A.; Mclean, R.; Agard, J.; Briguglio, L.; Duvat, V.; Pelesikoti, N.; Tompkins, E. Small islands. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Barros, V.R., Field, C.B., Dokken, D.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Mach, K.J., Bilir, T.E., Chatterjee, M., Ebi, K.L., Estrada, Y.O., Genova, R.C., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1613–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Karl, D.M.; Boyd, P.W.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Nojiri, Y.; Schmidt, D.N.; Zavialov, P.O. Ocean systems. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Field, C.B., Barros, V.R., Dokken, D.J., Mach, K.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Bilir, T.E., Chatterjee, M., Ebi, K.L., Estrada, Y.O., Genova, R.C., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 411–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.O.; Scholes, R.J.; Agard, J.; Archer, E.; Arneth, A.; Bai, X.; Barnes, D.; Burrows, M.; Chan, L.; Cheung, W.L.; et al. IPBES-IPCC Co-Sponsored Workshop Report on Biodiversity and Climate Change; IPBES and IPCC: Bonn, Germany, 2021; p. 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poloczanska, E.S.; Brown, C.J.; Sydeman, W.J.; Kiessling, W.; Schoeman, D.S.; Moore, P.J.; Brander, K.; Bruno, J.F.; Buckley, L.B.; Burrows, M.T.; et al. Global imprint of climate change on marine life. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzan, M.V.; Sadula, R.; Scalvenzi, L. Assessing Ecosystem Services Supplied by Agroecosystems in Mediterranean Europe: A Literature Review. Land 2020, 9, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, A.; Pan, Y.; Zeng, N.; Alessandri, A. Long-term climate change in the Mediterranean region in the midst of decadal variability. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 1437–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertig, E.; Tramblay, Y. Regional downscaling of Mediterranean droughts under past and future climatic conditions. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2017, 151, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P.; Scarascia, L. The relation of climate extremes with global warming in the Mediterranean region and its north versus south contrast. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2020, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llasat, M.C.; Marcos, R.; Turco, M.; Gilabert, J.; Llasat-Botija, M. Trends in flash flood events versus convective precipitation in the Mediterranean region: The case of Catalonia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 541, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramblay, Y.; Jarlan, L.; Hanich, L.; Somot, S. Future Scenarios of Surface Water Resources Availability in North African Dams. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, G.; Polverino, S. Nature-based solution for climate change adaptation and mitigation in urban areas with high natural risk. TeMA. J. Land Use Mobility Environ. 2023, 16, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediero, L.; Santillán, D.; Garrote, L.; Granados, A. Detection and attribution of trends in magnitude, frequency and timing of floods in Spain. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 1072–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baahmed, D.; Oudin, L.; Errih, M. Current runoff variations in the Macta catchment (Algeria): Is climate the sole factor? Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaume, E.; Borga, M.; Llasat, M.C.; Maouche, S.; Lang, M.; Diakakis, M. Mediterranean extreme floods and flash floods. In The Mediterranean Region under Climate Change; Thiébault, S., Moatti, J.P., Eds.; A Scientific Update Coll. Synthèses: Marseille, France, 2016; pp. 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Paprotny, D.; Sebastian, A.; Morales-Nápoles, O.; Jonkman, S.N. Trends in flood losses in Europe over the past 150 years. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Domínguez-Castro, F.; Murphy, C.; Hannaford, J.; Reig, F.; Peña-Angulo, D.; Tramblay, Y.; Trigo, R.M.; Mac Donald, N.; Luna, M.Y.; et al. Long-term variability and trends in meteorological droughts in Western Europe (1851–2018). Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 41, E690–E717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/ (accessed on 23 January 2022).
- European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/water/europes-seas-and-coasts (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Gohar, A.; Kondolf, G.M. Flash flooding as a threat to settlements even in remote areas. Environ. Urban. 2017, 29, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, O.; Papagiannaki, K.; Aceto, L.; Boissier, L.; Kotroni, V.; Grimalt, M. MEFF: The database of MEditerranean Flood Fatalities (1980 to 2015). J. Flood Risk Manag. 2019, 12, e12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Moral, A.; Llasat, M.C.; Rigo, T. Connecting flash flood events with radar-derived convective storm characteristics on the Northwestern Mediterranean coast: Knowing the present for better future scenarios adaptation. Atmos. Res. 2020, 238, 104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafnaoui, M.A.; Madi, M.; Hachemi, A.; Farhi, Y. El Bayadh city against flash floods: Case study. Urban Water J. 2020, 17, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaume, E.; Bain, V.; Bernardara, P.; Newinger, O.; Barbuc, M.; Bateman, A.; Blaškovičová, L.; Blöschl, G.; Borga, M.; Dumitrescu, A.; et al. A compilation of data on European flash floods. J. Hydrol. 2009, 367, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llasat, M.C.; Llasat-Botija, M.; Prat, M.A.; Porcú, F.; Price, C.; Mugnai, A.; Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V.; Katsanos, D.; Michaelides, S. High-impact floods and flash floods in Mediterranean countries: The FLASH preliminary database. Adv. Geosci. 2010, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; Davolio, S.; Furnari, L.; Mendicino, G. Reconstructing Flood Events in Mediterranean Coastal Areas Using Different Reanalyses and High-Resolution Meteorological Models. J. Hydrometeor. 2020, 21, 1865–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, F.; Luino, F.; Paliaga, G.; Roccati, A.; Turconi, L. Flash Flood Events along the West Mediterranean Coasts: Inundations of Urbanized Areas Conditioned by Anthropic Impacts. Land 2021, 10, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouaceur, Z.; Murarescu, O.; Muratoreanu, G. Statistical Analysis of Heavy Rains and Floods around the French Mediterranean Basin over One Half a Century of Observations. Geosciences 2022, 12, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinet, F.; Bigot, V.; Petrucci, O.; Papagiannaki, K.; Llasat, M.C.; Kotroni, V.; Boissier, L.; Aceto, L.; Grimalt, M.; Llasat-Botija, M.; et al. Mapping Flood-Related Mortality in the Mediterranean Basin. Results from the MEFF v2.0 DB. Water 2019, 11, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Díez, A.; Máyer Suárez, P.; Díaz Pacheco, J.; Dorta Antequera, P. Rainfall and Flooding in Coastal Tourist Areas of the Canary Islands (Spain). Atmosphere 2019, 10, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccati, A.; Paliaga, G.; Luino, F.; Faccini, F.; Turconi, L. Rainfall Threshold for Shallow Landslides Initiation and Analysis of Long-Term Rainfall Trends in a Mediterranean Area. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einfalt, T.; Hatzfeld, F.; Wagner, A.; Seltmann, J.; Castro, D.; Frerichs, S. URBAS: Forecasting and management of flash floods in urban areas. Urban Water J. 2009, 6, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Service Interministériel Régional de Défense et de Protection Civiles (SIRDPC) de la Préfecture de Corse-du-Sud. Available online: https://www.portivechju.corsica/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/DDRM_Corse-du-Sud_2021_2.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Accuweather. Available online: www.https://www.accuweather.com/en/severe-weather/deadly-flooding-wreaks-havoc-in-france-italy-and-greece/634338 (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- Luino, F.; Paliaga, G.; Roccati, A.; Sacchini, A.; Turconi, L.; Faccini, F. Anthropogenic changes in the alluvial plains of the Tyrrhenian Ligurian basins. Rend. Online Soc. Geol. Ital. 2019, 48, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, F.; Rebora, N.; Rossi, L.; Dolia, D.; Gabellani, S.; Pignone, F.; Trasforini, E.; Rudari, R.; De Angeli, S.; Masciulli, C. What if the 25 October 2011 event that struck Cinque Terre (Liguria) had happened in Genoa, Italy? Flooding scenarios, hazard mapping and damage estimation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, F.; Luino, F.; Sacchini, A.; Turconi, L. The 4th October 2010 flash flood event in Genoa Sestri Ponente (Liguria, Italy). Disaster Adv. 2015, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccati, A.; Faccini, F.; Luino, F.; De Graff, J.; Turconi, L. Morphological changes and human impact in the Entella River floodplain (Northern Italy) from the 17th century. Catena 2019, 182, 104122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audisio, C.; Turconi, L. Urban floods: A case study in the Savigliano area (North-Western Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 2951–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietz, G.J.; Walsh, C.J.; Fletche, T.D. Urban hydrogeomorphology and the urban stream syndrome: Treating the symptoms and causes of geomorphic change. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 40, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutter, S.L.; Emrich, C.T.; Gall, M.; Reeves, R. Flash Flood Risk and the Paradox of Urban Development. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2018, 19, 05017005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertan, S.; Çelik, R.N. The Assessment of Urbanization Effect and Sustainable Drainage Solutions on Flood Hazard by GIS. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliaga, G.; Faccini, F.; Luino, F.; Turconi, L. A spatial multicriteria prioritizing approach for geohydrological risk mitigation planning in small and densely urbanized Mediterranean basins. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccati, A.; Luino, F.; Turconi, L.; Piana, P.; Watkins, C.; Faccini, F. Historical Geomorphological Research of a Ligurian Coastal Floodplain (Italy) and Its Value for Management of Flood Risk and Environmental Sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassola, F.; Ferrari, F.; Mazzino, A.; Miglietta, M.M. The role of the sea on the flash floods events over Liguria (northwestern Italy). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3534–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimbus Hydrological Events. La Piena del Torrenta Genova del 26 Novembre 2002. Available online: http://www.nimbus.it/eventi/2002/021126genova.htm (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Faccini, F.; Luino, F.; Paliaga, G.; Sacchini, A.; Turconi, L.; Dejong, C. Role of rainfall intensity and urban sprawl in the 2014 flash flood in Genoa City, Bisagno catchment (Liguria, Italy). Appl. Geogr. 2018, 98, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevasco, A.; Brandolini, P.; Scopesi, C.; Rellini, I. Relationships between geo-hydrological processes induced by heavy rainfall and land-use: The case of 25 October 2011 in the Vernazza catchment (Cinque Terre, NW Italy). J. Maps 2013, 9, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The 4th October 2021 Event. Available online: https://www.greenlifeblog.it/2021/10/05/le-piogge-eccezionali-di-lunedi-4-ottobre-2021-in-liguria-e-piemonte/ (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Mandarino, A.; Luino, F.; Faccini, F. Flood-induced ground effects and flood-water dynamics for hydro-geomorphic hazard assessment: The 21–22 October 2019 extreme flood along the lower Orba River (Alessandria, NW Italy). J. Maps 2021, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISPRA 2023. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/files2023/notizie/nota-22maggio.pdf (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- ARPAE 2023. Available online: https://www.arpae.it/it/notizie/levento-meteo-idrogeologico-del-1-4-maggio (accessed on 8 July 2023).
- Flaounas, S.; Fita, L.; Lagouvardos, K.; Kotroni, V. Heavy rainfall in Mediterranean cyclones, Part II: Water budget, precipitation efficiency and remote water sources. Climate Dyn. 2019, 53, 2539–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dottori, F.; Alfieri, L.; Bianchi, A.; Skoien, J.; Salamon, P. A new dataset of river flood hazard maps for Europe and the Mediterranean Basin. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 1549–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Office for Statistics. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- Ministero dell’Ambiente, Geoportale Nazionale. Available online: http://www.pcn.minambiente.it/mattm/ (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- COPERNICUS, Land Monitoring Service. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- Regione Autonoma della Sardegna. Available online: www.sardegnageoportale.it (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- IGN. Catalogue Remonter le Temps. Available online: https://geoservices.ign.fr/remonter-le-temps (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Regione Toscana. Available online: www.regione.toscana.it/-/geoscopio (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Gobierno de España, Instituto Geográfico Nacional. Available online: https://www.ign.es/web/ign/portal (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Arcanum Maps. Available online: https://maps.arcanum.com/en/ (accessed on 7 May 2022).
- Regione Liguria. Available online: https://geoportal.regione.liguria.it/ (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Website 6 Aprile, Sardegna. Available online: http://www.6aprile.it/featured/2013/11/19/cronistoria-delle-alluvioni-in-sardegna.html (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- AEMET Spain’s State Meteorological Agency. Available online: https://floodlist.com/europe/spain-murcia-floods-september-2022 (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Météo-France. Available online: http://pluiesextremes.meteo.fr/france-metropole/Catastrophe-sur-la-Cote-d-Azur.html (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Kougkoulos, I.; Merad, M.; Cook, S.J.; Andredakis, I. Floods in Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur and lessons for French flood risk governance. Nat Hazards 2021, 109, 1959–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrega, P. Les inondations azuréennes du 3 octobre 2015: Un lourd bilan lié à un risque composite. Pollut Atmosphérique 2016, 228, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Marriner, N.; Morhange, C. Human influence and the changing geomorphology of Mediterranean deltas and coasts over the last 6000 years: From progradation to destruction phase? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 139, 336–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surian, N.; Rinaldi, M. Morphological response to river engineering and management in alluvial channels in Italy. Geomorphology 2003, 50, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarasa-Belmonte, A.M.; Soriano-Garcia, J. Flood risk assessment and mapping in peri-urban Mediterranean environments using hydrogeomorphology. Application to ephemeral streams in the Valencia region (eastern Spain). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 104, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolini, P.; Faccini, F.; Paliaga, G.; Piana, P. Urban Geomorphology in Coastal Environment: Man-Made Morphological Changes in a Seaside Tourist Resort (Rapallo, Eastern Liguria, Italy). Quaest. Geogr. 2017, 36, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriendos, M.; Rodrigo, F.S. Study of historical flood events on Spanish rivers using documentary data. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEDEC Climate and Environmental Change in the Mediterranean Basin—Current Situation and Risks for the Future. Available online: https://www.medecc.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/MedECC_MAR1_3_1_Water.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2022).
- First Mediterranean Assessment Report (MAR1) Gobierno de España, Dirección General de Protección Civil y Emergencias. Available online: https://www.proteccioncivil.es/ (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- Sardegna Clima APS. Available online: https://sardegna-clima.it/ (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- CNR IRPI Polaris Project. Available online: https://polaris.irpi.cnr.it/ (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- ADAPT Project (2014–2020) Assistere l’aDAttamento ai Cambiamenti Climatici dei Sistemi Urbani Dello sPazio Transfrontalier. Available online: http://interreg-maritime.eu/web/adapt (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- Wikipedia. Available online: https://it.wikipedia.org/ (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- Barrera, A.; Llasat, M.C.; Barriendos, M. Estimation of Extreme Flash Flood Evolution in Barcelona County from 1351 to 2005. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 6, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chelazzi, L.; Colombini, I.; Fallaci, M.; Gagnarli, E. La Memoria Dell’acqua Nella Pianura Grossetana. Wadi Project; C.N.R.: Florence, Italy, 2008; p. 205. [Google Scholar]
- CNR GNDCI AVI Archive. Available online: http://avi.gndci.cnr.it/ (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- Cecaro, R. I Giornali Sardi Dell’Ottocento. Quotidiani, Periodici e Riviste Delle Biblioteche Della Sardegna, Catalogo (1774–1899); Regione Autonoma Sella Sardegna: Cagliari, Italy, 2015; p. 369. [Google Scholar]
- ANSA. Available online: https://www.ansa.it/ (accessed on 17 March 2022).
- Martín-Vide, J.P.; Llasat, M.C. The 1962 flash flood in the Rubí stream (Barcelona, Spain). J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmundo. Available online: https://www.elmundo.es/ (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Préfet de la Corse-du-Sud. Service de l’État. Available online: https://www.corse-du-sud.gouv.fr/le-risque-inondation-a1983.html (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- PisaToday. Available online: https://www.pisatoday.it/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- L’Express. Available online: https://www.lexpress.fr/ (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- BBC. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/ (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- CatalanNews. Available online: https://www.catalannews.com/ (accessed on 19 March 2022).
- France3. Available online: https://france3-regions.francetvinfo.fr/ (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Toscana Notizie. Alluvione di Livorno: Le Foto Aeree. 2017. Available online: https://www.toscana-notizie.it/-/alluvione-di-livorno-le-foto-aeree (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- FloodList. Spain—Deadly Floods in Valencia and Murcia after Days of Torrential Rain. Available online: https://floodlist.com/europe/spain-deadly-floods-valencia-murcia-days-torrential-rain (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Var Matin. Il y a neuf ans, l’Est-Var était ravagé par les inondations. Available online: https://www.varmatin.com/environnement/photos-and-video-il-y-a-neuf-ans-lest-var-etait-ravage-par-les-inondations-57440 (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Faccini, F.; Paliaga, G.; Piana, P.; Sacchini, A.; Watkins, C. The Bisagno stream catchment (Genoa, Italy) and its major floods: Geomorphic and land use variations in the last three centuries. Geomorphology 2016, 273, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuters. Heavy Rains Turn Streets into Rivers on Spain’s Mediterranean Coast (Spain 25 May 2023 Flood Event). Available online: https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/heavy-rains-turn-streets-into-rivers-spains-mediterranean-coast-2023-05-26/ (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- The Connexion. Floods and Hail Hit Southern France as Stormy Spell Continues (France and Italy 25 May 2023 Flood Events). Available online: https://www.connexionfrance.com/article/French-news/Floods-and-hail-hit-southern-France-as-stormy-spell-continues (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- EuroNews.Travel. Barcelona, Ibiza, Madrid: Flash Floods Trigger Travel Warnings in Popular Holiday Destinations (Spain 30 May 2023 Flood Event). Available online: https://www.euronews.com/travel/2023/05/30/barcelona-ibiza-madrid-flash-floods-trigger-travel-warnings-in-popular-holiday-destination (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- AA. Heavy Rain Causes Flash Flooding across Southern Spain (Spain 23 May 2023 Flood Event). Available online: https://www.aa.com.tr/en/europe/heavy-rain-causes-flash-flooding-across-southern-spain/2906658 (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- SkyTg24. Allerta Maltempo Anche in Toscana: Frane a Marradi e Firenzuola (Italy 17 May Flood Event). Available online: https://tg24.sky.it/cronaca/2023/05/17/allerta-meteo-toscana-maltempo (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- RavennaeDintorni.it. Chi Sono le 17 Vittime Identificate Nell’alluvione in Emilia-Romagna (Italy Floods, May 2023). Available online: https://www.ravennaedintorni.it/cronaca/2023/05/26/chi-sono-vittime-ondate-alluvioni-emilia-romagna/ (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Anthony, E.J. The Human influence on the Mediterranean coast over the last 200 years: A brief appraisal from a geomorphological perspective. Géomorphologie Relief Process. Environ. 2014, 20, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudier, P.; Andersson, J.C.M.; Donnelly, C. Projections of future floods and hydrological droughts in Europe under a +2 °C global warming. Clim. Chang. 2016, 135, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrue, C.; Bruzzone, S.; Lévy, L.; Gralepois, M.; Schellenberger, T.; Trémorin, J.B.; Fournier, M.; Manson, C.; Thuilier, T. Analysing and evaluating Flood Risk Governance in France: From State Policy to Local Strategies. Halshs 2016, 01981420. Available online: https://shs.hal.science/halshs-01981420/document (accessed on 16 June 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).