Thermodynamics-Inspired Multi-Feature Network for Infrared Small Target Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We introduce an innovative IRSTD model, TMNet, which leverages an innovative super-resolution branch for assisted feature learning and explores and fuses multi-scale features through full-link connections, demonstrating outstanding performance on the NUAA-SIRST dataset.
- We reconstruct the encoder and propose a new AFCE structure, which utilizes generated depth vectors to induce multi-scale feature image fusion, enabling the comprehensive exploration of spatial detail information features.
- We introduce a thermodynamics-inspired cooperative mechanism by creating the TSB, which combines the Hamming equation of the thermodynamic and super-resolution to enhance the high-resolution representation under low-resolution input.
2. Related Work
2.1. Infrared Small Target Detection
2.2. Cross-Layer Feature Fusion
2.3. Image Super-Resolution
3. Method
3.1. Network Overview
3.2. Attention-Directed Feature Cross-Aggregation Encoder (AFCE)
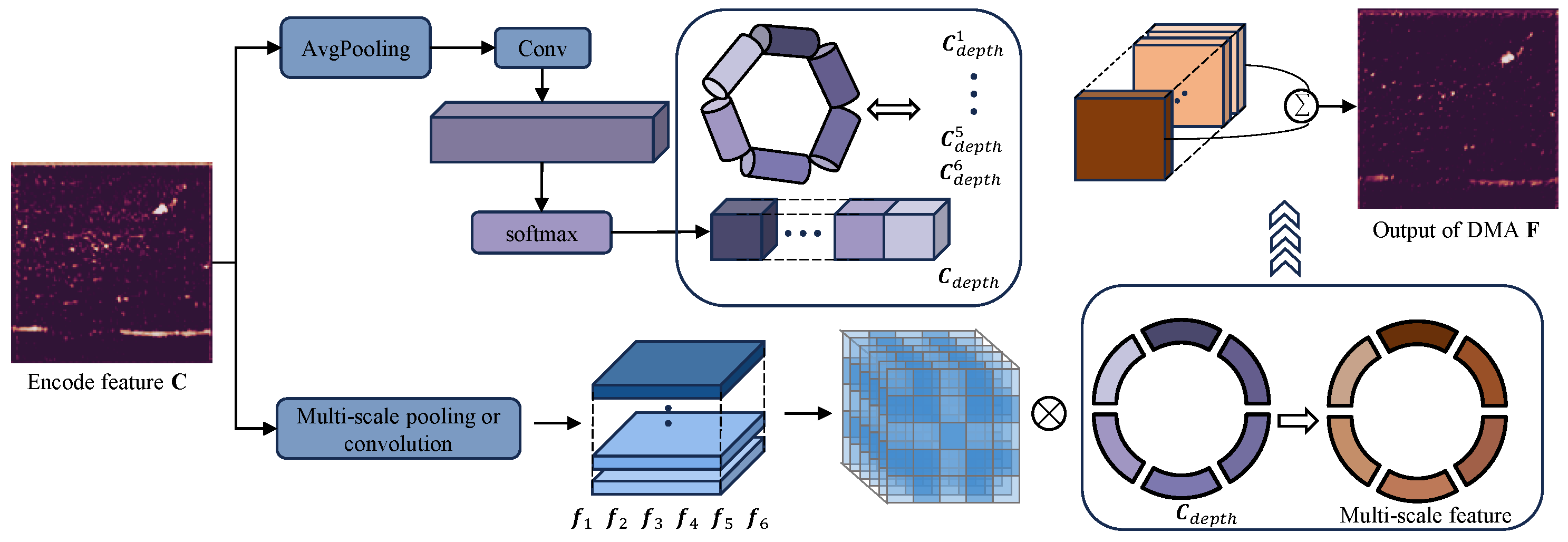
3.2.1. Depth-Weighted Multi-Scale Attention Module (DMA)
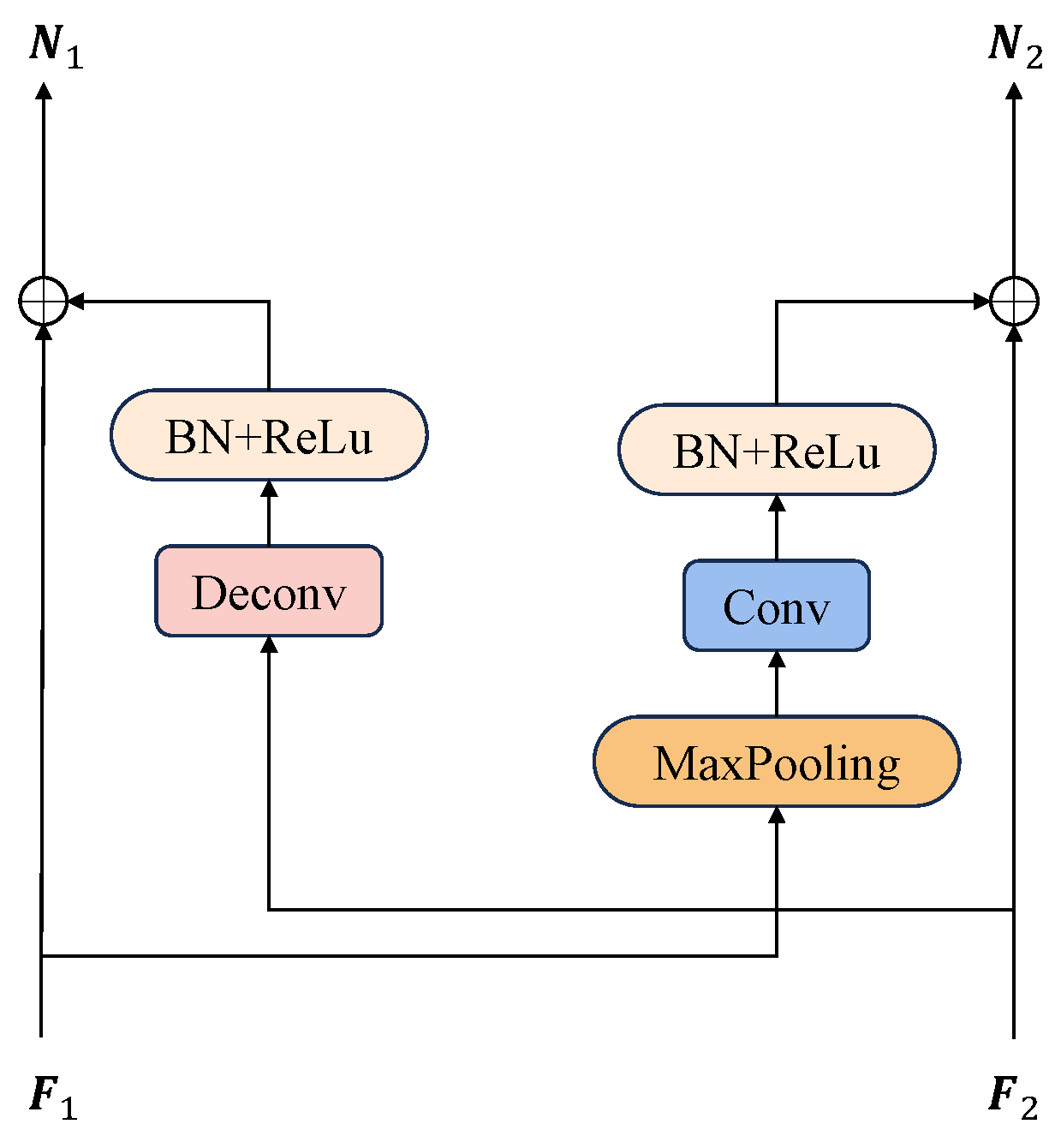
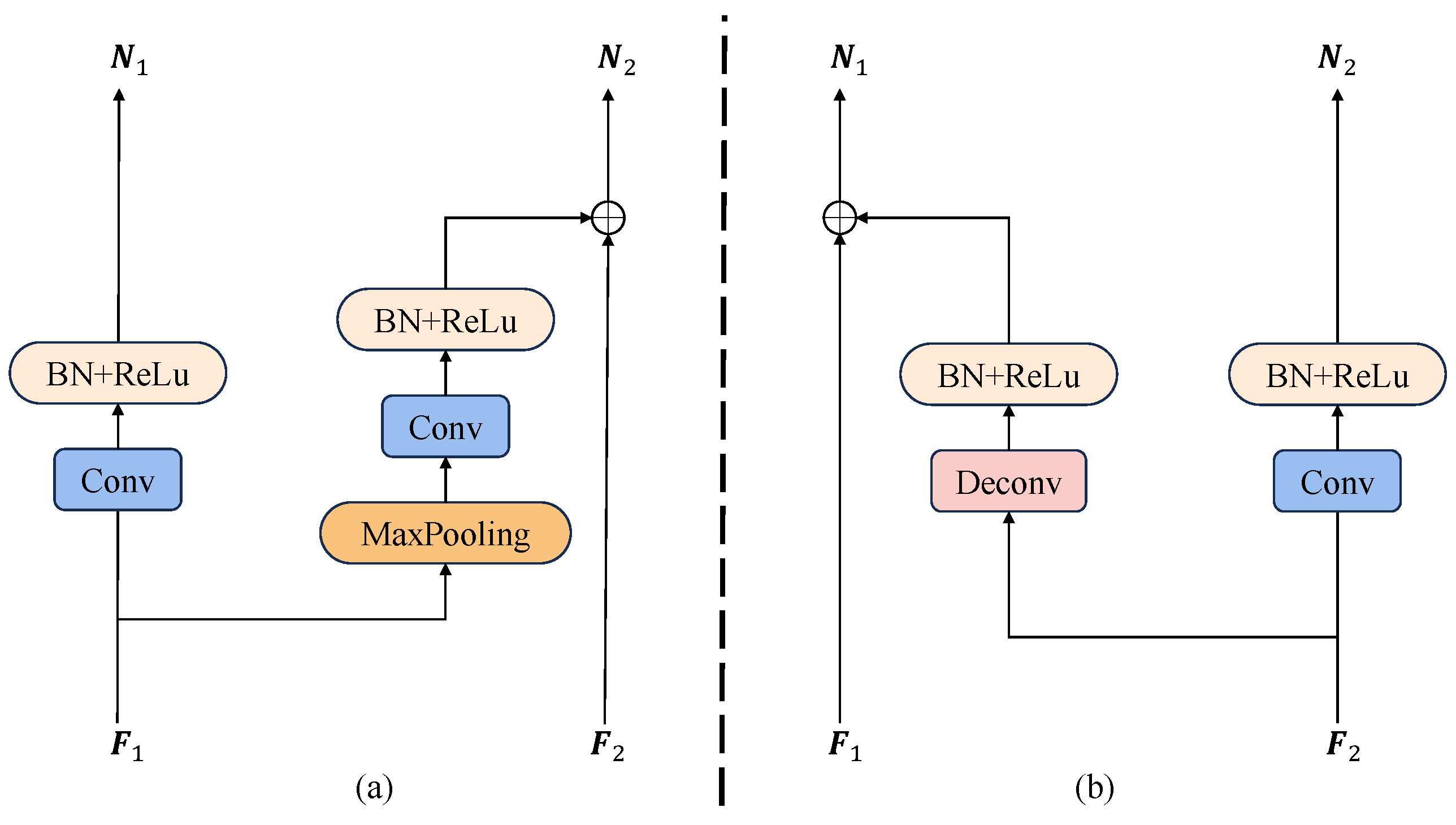
3.2.2. Cross-Layer Feature Fusion Module (Cff)
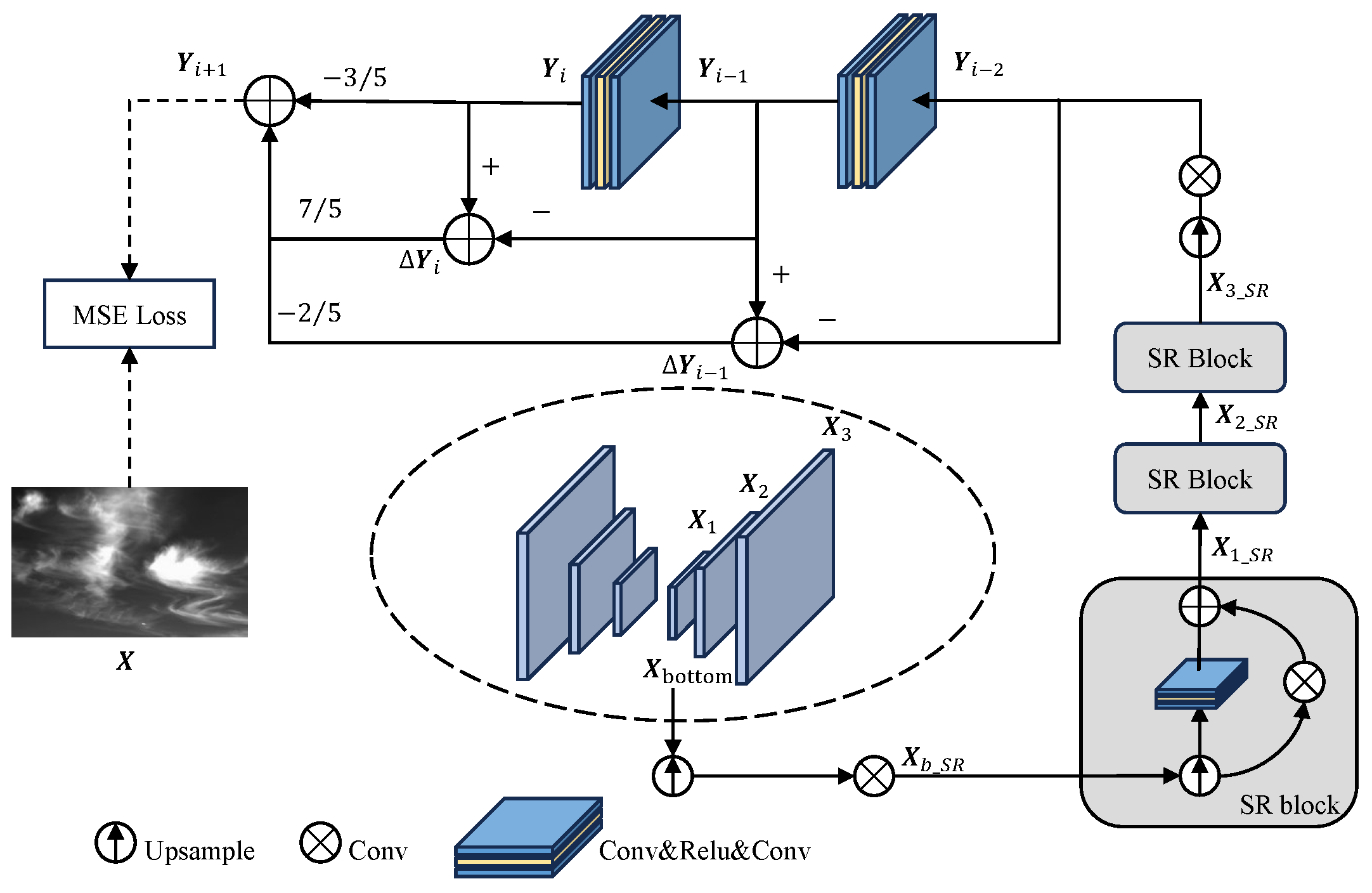
3.3. Thermodynamic Super-Resolution Branch (TSB)
3.4. Loss Functions
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.1.1. Dataset
4.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
- Intersection over union (IoU): IoU is designed to gauge the precision of detecting the corresponding object within a given dataset. It can be defined as follows:where T, P, and represent true, positive, and true positive target messages, respectively.
- Normalized intersection over union (nIoU): nIoU is the normalization of IoU, which is a metric specifically designed for IRSTD. It effectively strikes a balance between the structural similarity and pixel accuracy, especially for small infrared targets. It can be calculated as follows:where M indicates the overall target messages.
- Probability of detection (): can be computed by dividing the count of correctly predicted targets by the total number of targets, i.e.,where and stand for the amount of accurately detected targets and the total amount of targets, respectively.
- False alarm rate (): represents the proportion of falsely predicted target pixels in the infrared image relative to all the pixels present, i.e.,where stands for the amount of incorrectly detected pixels.
4.1.3. Implementation Details
4.2. Comparison Results with Sota Methods
4.2.1. Quantitative Results
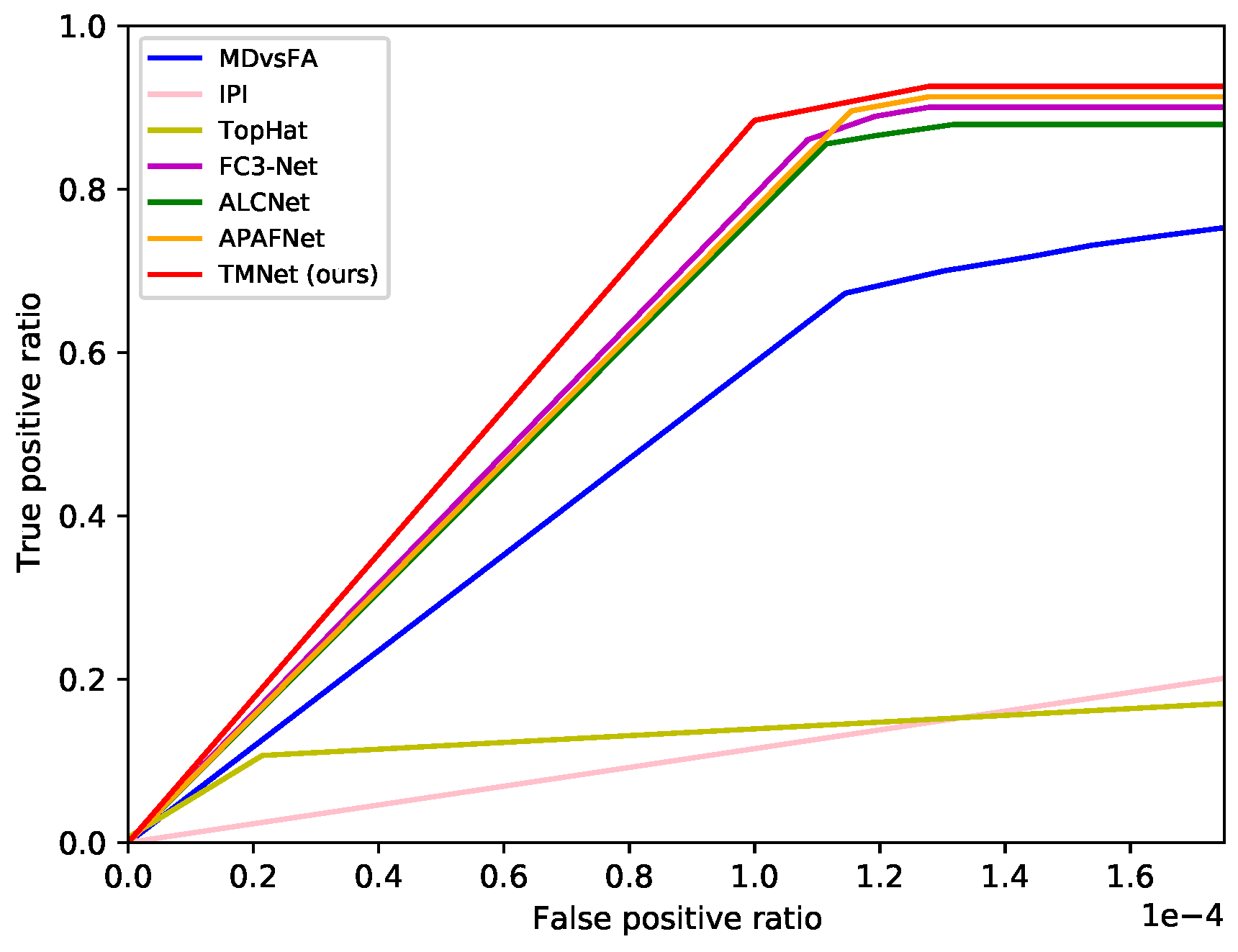
4.2.2. Roc Results
4.2.3. Visual Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of Attention-Directed Feature Cross-Aggregation Encoder (AFCE)
5.1.1. Analysis of Depth-Weighted Multi-Scale Attention (DMA)
5.1.2. Analysis of Cross-Layer Feature Fusion (Cff)
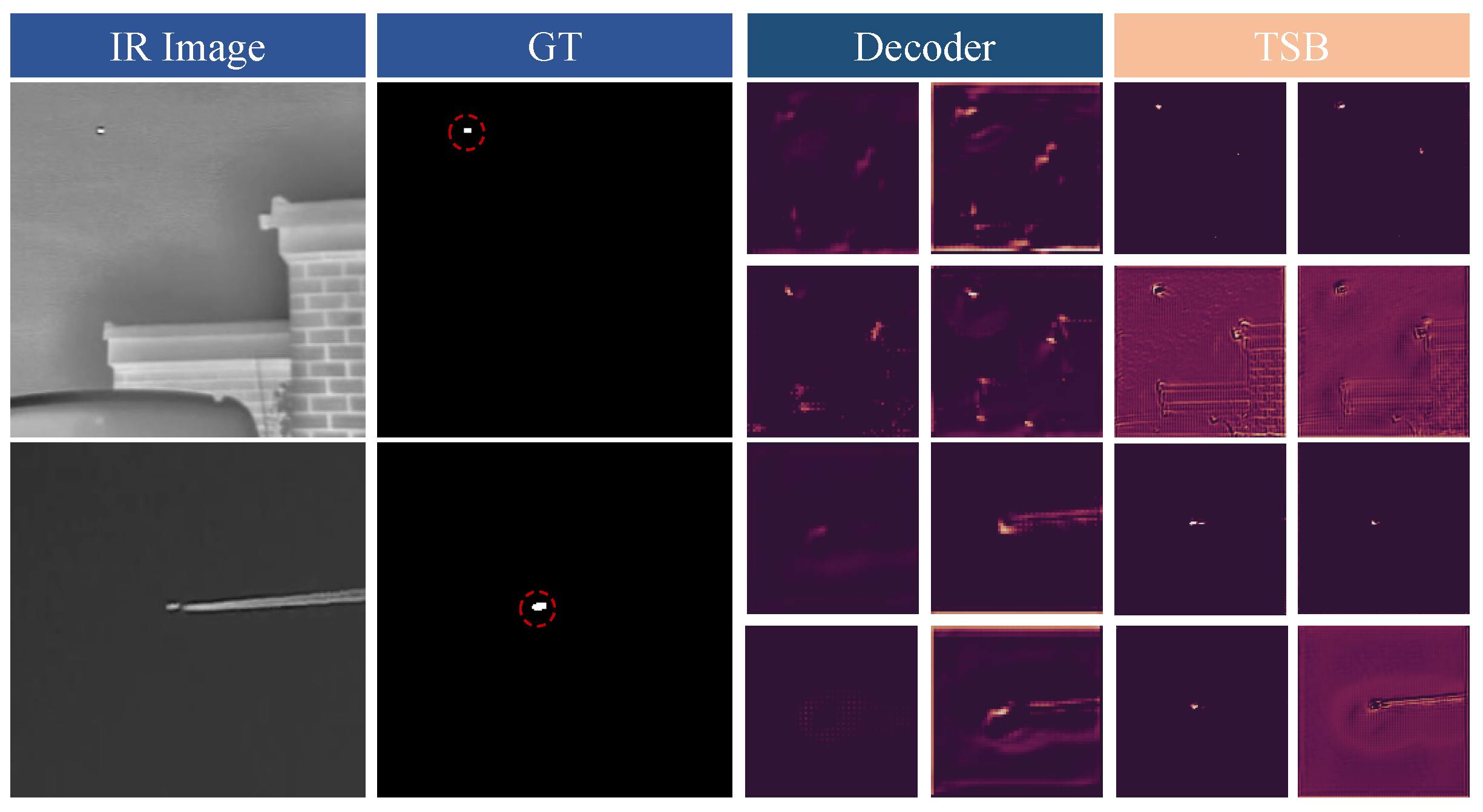
5.2. Analysis on Thermodynamic Super-Resolution Branch (TSB)
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Law, W.C.; Xu, Z.; Yong, K.T.; Liu, X.; Swihart, M.T.; Seshadri, M.; Prasad, P.N. Manganese-doped near-infrared emitting nanocrystals for in vivo biomedical imaging. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 17553–17561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teutsch, M.; Krüger, W. Classification of small boats in infrared images for maritime surveillance. In Proceedings of the 2010 International WaterSide Security Conference, Carrara, Italy, 3–5 November 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Empowering things with intelligence: A survey of the progress, challenges, and opportunities in artificial intelligence of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 7789–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, X. Heat transfer-inspired network for image super-resolution reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; He, C.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Peng, X.; Guo, J. SAR-to-Optical Image Translation via Neural Partial Differential Equations. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-22), Vienna, Austria, 23–29 July 2022; pp. 1644–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, L.; Zhang, T.; Cao, S.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection via non-convex rank approximation minimization joint l 2, 1 norm. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, T.; Peng, Z. Structure-adaptive clutter suppression for infrared small target detection: Chain-growth filtering. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection via non-convex tensor rank surrogate joint local contrast energy. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Guo, J.; Tao, D. Fluid micelle network for image super-resolution reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; He, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Song, B. Edge-preserving convolutional generative adversarial networks for SAR-to-optical image translation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.D.; Er, M.H.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Chan, P. Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small targets. In Proceedings of the Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets, Denver, CO, USA, 18–23 July 1999; SPIE: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1999; Volume 3809, pp. 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, S.; Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Xiao, F. Infrared small target detection via low-rank tensor completion with top-hat regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, L. Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Moradi, S.; Faramarzi, I.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, N. Infrared small target detection based on the weighted strengthened local contrast measure. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 21078718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.P.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xia, T.; Tang, Y.Y. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, F. Analysis of new top-hat transformation and the application for infrared dim small target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L. Miss detection vs. false alarm: Adversarial learning for small object segmentation in infrared images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8509–8518. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Barnard, K. Asymmetric contextual modulation for infrared small target detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 950–959. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Barnard, K. Attentional local contrast networks for infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 9813–9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, X. Dim2Clear network for infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Gao, X. RKformer: Runge-Kutta Transformer with Random-Connection Attention for Infrared Small Target Detection. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 1730–1738. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Mo, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Cheng, J. Ode-inspired network design for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1732–1741. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhong, A.; Li, Q.; Dong, B. Beyond finite layer neural networks: Bridging deep architectures and numerical differential equations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 3276–3285. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Yue, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, X. Exploring Feature Compensation and Cross-level Correlation for Infrared Small Target Detection. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 1857–1865. [Google Scholar]
- Song, I.; Kim, S. AVILNet: A new pliable network with a novel metric for small-object segmentation and detection in infrared images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourure, D.; Emonet, R.; Fromont, E.; Muselet, D.; Tremeau, A.; Wolf, C. Residual conv-deconv grid network for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.07958. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Shen, Y. YOLOSR-IST: A deep learning method for small target detection in infrared remote sensing images based on super-resolution and YOLO. Signal Process. 2023, 208, 108962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, C. Dual-Domain Prior-Driven Deep Network for Infrared Small-Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Pan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lei, B.; Hu, Y. APAFNet: Single-Frame Infrared Small Target Detection by Asymmetric Patch Attention Fusion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadhoud, M.M.; Thomas, D.W. The two-dimensional adaptive LMS (TDLMS) algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1988, 35, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantin, D.; Zosso, D. Two-dimensional variational mode decomposition. In Proceedings of the Energy Minimization Methods in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hong Kong, China, 13–16 January 2015; Volume 8932, pp. 197–208. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Meng, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hauptmann, A.G. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 4996–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Volume 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, L.; Yang, X.; Feng, P.; Liu, L.; Wu, N. TBC-Net: A real-time detector for infrared small target detection using semantic constraint. arXiv 2019, arXiv:2001.05852. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, M.; An, W.; Guo, Y. Dense nested attention network for infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 32, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Wang, T.; Bai, H.; Yue, K.; Li, Y. CHFNet: Curvature Half-Level Fusion Network for Single-Frame Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wu, X.; Bu, W. Deeply-supervised recurrent convolutional neural network for saliency detection. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 15–19 October 2016; pp. 397–401. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.M.; Ward, R.D.; Ingleby, M. Classifying pretended and evoked facial expressions of positive and negative affective states using infrared measurement of skin temperature. ACM Trans. Appl. Percept. (TAP) 2009, 6, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Niu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L. Context-aware feature generation for zero-shot semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 1921–1929. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Lang, C.; Liew, J.H.; Li, Y.; Hou, Q.; Feng, J. Cross-layer feature pyramid network for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4587–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Han, L.; Tong, Y.; Tan, S.; Yang, K. Gated fully fusion for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11418–11425. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Ponce, J.; Ham, B. Sfnet: Learning object-aware semantic correspondence. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2278–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Ocnet: Object context network for scene parsing. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.00916. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhong, Z.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, H. Expectation-maximization attention networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9167–9176. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Lin, Z.Q.; Bidart, R.; Hu, X.; Daya, I.B.; Li, Z.; Zheng, W.S.; Li, J.; Wong, A. Squeeze-and-attention networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13065–13074. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.S.; Huang, J.B.; Ahuja, N.; Yang, M.H. Fast and accurate image super-resolution with deep laplacian pyramid networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 2599–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R.; Rueckert, D.; Wang, Z. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part II 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 391–407. [Google Scholar]
- Haris, M.; Shakhnarovich, G.; Ukita, N. Deep back-projection networks for super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1664–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Perazzi, F.; McWilliams, B.; Sorkine-Hornung, A.; Sorkine-Hornung, O.; Schroers, C. A fully progressive approach to single-image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 864–873. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, D.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, L.; Shan, Y. Dual super-resolution learning for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3774–3783. [Google Scholar]
- Weinan, E. A proposal on machine learning via dynamical systems. Commun. Math. Stat. 2017, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hamming, R.W. Stable predictor-corrector methods for ordinary differential equations. J. ACM 1959, 6, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Huang, Z. Hamming method for solving uncertain differential equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 313, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, M.; Vuorinen, A. Basics of Thermal Field Theory; Lecture Notes in Physics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 925. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, G.; Diaco, M.; Barretta, R. Variational formulation of the first principle of continuum thermodynamics. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 2010, 22, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, Y. Reweighted infrared patch-tensor model with both nonlocal and local priors for single-frame small target detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3752–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; An, W. Infrared dim and small target detection via multiple subspace learning and spatial-temporal patch-tensor model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 3737–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Pixel-Level | Object-Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU↑ | nIoU↑ | Pd↑ | Fa↓ | |
| Top-Hat [17] | 7.14 | 5.20 | 79.8 | 1012 |
| Max-Median [12] | 4.17 | 2.15 | 69.2 | 53.3 |
| IPI [36] | 25.7 | 24.6 | 85.6 | 11.5 |
| NRAM [7] | 12.2 | 10.2 | 74.5 | 13.9 |
| WSLCM [15] | 1.16 | 0.85 | 77.9 | 5446 |
| TLLCM [16] | 1.03 | 0.91 | 79.1 | 5899 |
| PSTNN [6] | 22.4 | 22.4 | 77.9 | 29.1 |
| RIPT [68] | 11.1 | 10.2 | 79.1 | 22.6 |
| MSLSTIPT [69] | 10.3 | 9.58 | 82.1 | 1131 |
| MDvsFA [18] | 60.3 | 58.3 | 89.4 | 56.4 |
| ACMNet [21] | 72.3 | 71.4 | 96.9 | 9.33 |
| ALCNet [22] | 74.3 | 73.1 | 97.4 | 19.2 |
| FC3-Net [28] | 74.8 | 74.3 | 98.1 | 7.34 |
| APAFNet [33] | 76.8 | 74.9 | 98.1 | 6.97 |
| TMNet (ours) | 77.1 | 75.3 | 98.3 | 5.73 |
| Model | Pixel-Level | Object-Level | FLOPs | Params | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU↑ | nIoU↑ | Pd↑ | Fa↓ | |||
| TMNet | 77.1 | 75.3 | 98.3 | 5.73 | 3.95 | 0.74 |
| w/o AFCE | 75.6 | 73.2 | 96.6 | 21.6 | 3.66 | 0.71 |
| w/o TSB | 76.2 | 72.8 | 96.3 | 16.3 | 2.13 | 0.54 |
| w/o AFCE&TSB | 73.3 | 70.9 | 96.1 | 39.8 | 1.92 | 0.50 |
| Number of Blocks | Pixel-Level | Object-Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU↑ | nIoU↑ | Pd↑ | Fa↓ | |
| 0 | 75.6 | 74.1 | 96.9 | 13.4 |
| 1 | 76.1 | 74.8 | 97.1 | 9.43 |
| 2 | 77.1 | 75.3 | 98.3 | 5.73 |
| Method | Pixel-Level | Object-Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU↑ | nIoU↑ | Pd↑ | Fa↓ | |
| CFF | 77.1 | 75.3 | 98.3 | 5.73 |
| SCFF | 74.3 | 72.4 | 95.4 | 11.2 |
| DCFF | 74.7 | 72.7 | 97.3 | 9.87 |
| Method | Pixel-Level | Object-Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU↑ | nIoU↑ | Pd↑ | Fa↓ | |
| TSB | 77.1 | 75.3 | 98.3 | 5.73 |
| NCSB | 73.9 | 70.9 | 96.1 | 26.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Yue, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y. Thermodynamics-Inspired Multi-Feature Network for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4716. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194716
Zhang M, Yang H, Yue K, Zhang X, Zhu Y, Li Y. Thermodynamics-Inspired Multi-Feature Network for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4716. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194716
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mingjin, Handi Yang, Ke Yue, Xiaoyu Zhang, Yuqi Zhu, and Yunsong Li. 2023. "Thermodynamics-Inspired Multi-Feature Network for Infrared Small Target Detection" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4716. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194716
APA StyleZhang, M., Yang, H., Yue, K., Zhang, X., Zhu, Y., & Li, Y. (2023). Thermodynamics-Inspired Multi-Feature Network for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4716. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194716









