Abstract
In order to understand the mechanism of dust aerosol influence on regional climate change, it is crucial to quantify the radiative forcing effect of dust aerosols. However, studies on the direct radiative forcing of dust aerosols over long time series in China are still lacking. The direct radiative forcing effect of dust aerosols in China over the past 20 years was simulated and evaluated based on the WRF-Chem (Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled to Chemistry) model in conjunction with remote sensing satellites and ground-based observations. The results showed that dust aerosols exhibited an obvious inter-annual positive radiative forcing effect (about 0.38 W m−2) on net radiation at the top of the atmosphere, mainly in northwest China and the North China Plain, while at the atmosphere dust aerosols presented negative radiative forcing effects on shortwave radiation and positive effects on longwave radiation, with a value of 1.54 W m−2 of net radiative forcing, showing a warming effect. Dust aerosols have a net radiative forcing value of −1.16 W m−2 at the surface, indicating a cooling effect, with a positive forcing effect on longwave radiation and a negative forcing effect on shortwave radiation, both of which coincide with the geographical distribution of dust aerosol concentrations. In terms of inter-monthly variations, at both the atmosphere and top of the atmosphere, the dust aerosols net radiative forcing values showed an increasing trend, with March (−0.20 W m−2 and 0.68 W m−2) < April (0.48 W m−2 and 1.44 W m−2) < May (0.94 W m−2 and 2.42 W m−2). Meanwhile, at the surface, the dust aerosols net radiative forcing values displayed a decreasing trend, with March (−0.88 W m−2) > April (−0.96 W m−2) > May (−1.48 W m−2).
1. Introduction
Dust aerosol is an important component of tropospheric atmospheric aerosols, especially in arid and semi-arid regions, accounting for around half of the total mass of tropospheric atmospheric aerosols [1,2,3,4,5,6]. By scattering and absorbing solar radiation, dust aerosols can directly modify the radiative balance of the planet’s atmospheric system. They can also have indirect impacts on the climate by changing the processes of cloud formation [6]. In order to understand how dust aerosols affect regional climate change, it is crucial to quantitatively measure the radiative forcing effect of these particles.
The direct radiative forcing of dust aerosols has been well studied by scholars. Some scholars have used ground-based observations and remote sensing satellites to obtain dust aerosol data and to evaluate the influence of dust aerosols on the ground and on the atmospheric radiation balance [7,8,9,10,11,12]. Although ground-based monitoring and remote sensing satellites have also been more commonly used in dust monitoring, there is still a certain degree of uncertainty in the research. Because the study of dust aerosols involves meteorology, geology, physics, chemistry and other disciplines, and its impacts include climate, ecology, socio-economics and other aspects, these observatories alone cannot meet the needs of comprehensive research. Moreover, the sparse distribution of observation data stations, low resolution of satellite remote sensing and high influence of weather also restrict the research.
The application of numerical models to the simulation of dust aerosol processes can make up for the lack of data on vertical structural properties and spatiotemporal patterns of aerosols from ground-based observation networks and satellite inversions [13,14]. Francis et al. [15] studied a major dust event in the Sahara Desert in June 2020 using the WRF-Chem (weather research and forecasting model with chemistry) in combination with satellite and ground-based observations. The results showed that dust led to a net warming of up to 1.1 K at the tropical Atlantic ocean surface, a 1.8 K increase in air temperature, and a +14 W m−2 increase in net surface radiative flux at night. Hu et al. [16] simulated the dust transport characteristics and source contribution at various elevations of the Tibetan Plateau using the WRF-Chem in combination with a tracer labeling technique. The results showed that the direct radiative forcing value of dust aerosols were—1.68 W m−2 at the surface, 0.41 W m−2 in the atmosphere and −1.28 W m−2 at the top of the atmosphere. Péré et al. [17] modeled the radiative forcing effect of dust aerosols over West Africa in March–May 2015 using the WRF-Chem. The results showed a cooling effect in the radiative forcing of dust aerosols at the bottom of the atmosphere, with a reduction in net radiation of up to 44 W m−2. Alizadeh-Choobari et al. [18] modeled the global direct radiative forcing effects of dust aerosols by setting up two control scenarios based on the WRF-Chem. The results indicated that the global net direct radiative forcing reached its minimum under clear-sky conditions in summer, with a radiative forcing value of −2.85 W m−2 and −1.63 W m−2 on the surface and the top of the atmosphere, respectively. The surface cooling was due to the extinction of incident solar radiation by dust aerosols, while the top of the atmosphere is cooled primarily by an increase in outward shortwave radiation.
As it is one of the major sand and dust source areas in East Asia [19,20,21,22], the climate response to dust aerosols in China has attracted widespread attention in recent years, and some scholars have studied the dust aerosols radiative forcing effects by combining ground-based observations with models [10,23,24,25]. Chen et al. [26] used WRF-Chem to model a strong dust storm that occurred over the Taklamakan Desert in July 2006 and was transported to the Tibetan Plateau’s northern slope. The simulation results showed that the Taklamakan Desert had a cooling influence on the surface and a warming influence on the top of the atmosphere. On the top of the atmosphere, as well as in the atmosphere and on the surface, the mean net radiative forcing by the Taklamakan Desert dust event on the Tibetan Plateau was 3.97, 1.61 and −5.58 W m−2, respectively. Zhang et al. [27] used the WRF-Chem to simulate the direct radiative forcing effects of light-absorbing aerosols in various climatic zones of East Asia from 2007 to 2011. The results showed that the values of annual all-day direct radiative forcing black carbon and dust aerosols were 2.61 W m−2 and 0.39 W m−2 in the atmosphere, 1.06 W m−2 and −0.84 W m−2 at the top of the atmosphere, and −1.55 W m−2 and −1.23 W m−2 at the surface, respectively. Han et al. [28] simulated an intense dust event in the Gobi Desert along the Mongolia–China boundary in March 2010 based on a regional coupled climate–chemistry–aerosol model, and found that dust aerosols direct radiative forcing led to a significant drop in the surface wind speed and temperature in the dust source area, with the highest values of −7 °C and −4.0 m s−1, respectively. At night, the warming effect of longwave radiative forcing dominated, increasing air temperature and wind speed in the dust abatement area by 1 °C and 1 m s−1, while shortwave radiative forcing dominated during the daytime, reducing surface wind speed and temperature, respectively. Li et al. [29] used WRF-Chem to model a strong dust event at the Taklamakan Desert in June 2020 by setting up two controlled experiments. The results showed that dust aerosols shortwave radiative forcing had a cooling effect on the surface (−62.6 W m−2) and a net warming effect on the atmosphere (47.8 W m−2).
In summary, the current studies have certain limitations. Firstly, due to the different model parameterization schemes, there is uncertainty in simulating the radiative forcing effect of dust aerosols, and it is necessary to combine the characteristics of dust aerosols in China with the parameter localization settings of the model. Secondly, previous studies have mostly focused on the radiative forcing effect of individual dust events, mostly in northwest China, while the direct radiative forcing of dust aerosols over a long time series in China still needs further attention. Based on this, we used the WRF-Chem to model the spatiotemporal processes of spring dust aerosols in China over nearly 20 years and quantified dust aerosols radiative forcing effects based on parameter localization of the model. The purposes of this study are as follows: (1) To combine a local parameterization scheme for the model to realize the accurate simulation of the spatiotemporal evolution of spring dust aerosols in China from 2000 to 2020. (2) To realize the long-term simulation of the spatiotemporal change process of spring dust aerosol radiative forcing in China, and to elucidate spring dust aerosols radiative forcing effects on the surface, in the atmosphere and at the top of the atmosphere in China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. WRF-Chem Model
The simulation in this study was carried out using WRF-Chem v3.8.1, which introduced the chemical module on the basis of the WRF model. WRF is a next-generation numerical weather research and forecasting system created by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, and the Center for Atmospheric Research. The model can be applied to global- or regional-scale numerical simulation, physical parameterization scheme research, real-time weather forecast operation, regional climate simulation and coupled air quality models.
The advantage of the WRF-Chem model is that the chemical module is coupled with the meteorological module online in comparison with other models. In WRF-chem, the chemical and meteorological processes employ the same physical parameterization scheme, the same vertical and horizontal coordinate system, complete temporal synchronization, and take into consideration the feedback of chemical processes on meteorological operations. Specifically, WRF-Chem can model the diffusion and transport of aerosols and trace gases, dry and wet sedimentation, meteorological chemical reaction, etc., and reproduce a more real atmospheric environment, which has unique advantages for simulating the dust process.
2.2. Model Setup
The direct radiative forcing is calculated based on the variations in the radiative forcing in scenario experiments with or without dust emission [30]. For this reason, two experiments were carried out. In the first experiment (Exp. 1), the dust option was turned off, and the WRF-Chem model was used to calculate the net radiation forcing at the surface and the top of the atmosphere when there was no dust. In the second experiment (Exp. 2), the dust option was turned on, and the WRF-Chem model was used to calculate the net radiation forcing at the surface and the top of the atmosphere when there was dust. Notably, we only considered the climate impacts of dust aerosols in the second experiment, while the climate impacts of other aerosols, such as sea salt, sulfate, organic carbon and black carbon, were not accounted for at this time. Moreover, the simulations of the dust radiative forcing effect were performed under clear-sky conditions.
In this study, the simulation region covers the whole of China (Figure 1). Lambert projection is adopted in the model. The simulation region’s center is located at 105°E and 37.5°N latitude, with 193 grid points from east to west and 163 from north to south. The longitude and latitude of the central point of the simulation region are 105°E, 37.5°N, the number of grid points from east to west is 193, the number of grid points from north to south is 163, the horizontal resolution is 27 km, the time integration step is 60 s, the model is vertically stratified at 28, and the atmospheric top pressure is 100 hPa.
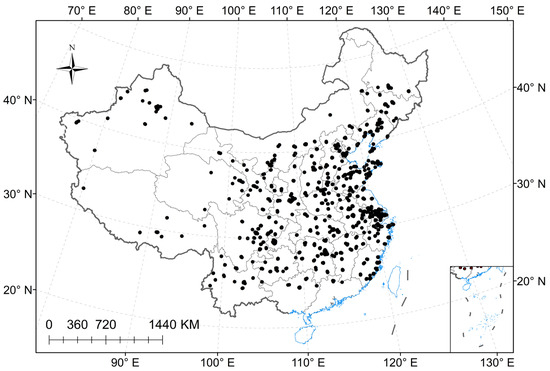
Figure 1.
Mode region setting and distribution of meteorological stations.
We applied a New Goddard long and shortwave radiation scheme [31], the Noah land surface process model [32] and the Lin microphysical scheme [33]. A MYJ boundary layer scheme with small calculation amount and high accuracy [34] was used. The BMJ cumulus parameterization scheme is one of the most suitable schemes for this study [35]. To simulate the emission, transmission and deposition of chemical aerosol component parts, as well as the specifics of interactions between aerosol radiation, we employed the GOCART (Goddard Chemistry Aerosol Radiation and Transport) aerosol scheme [36]. The particle size classification intervals of this scheme are 0.2~2, 2~3.6, 3.6~6, 6~12, and 12~20 μm. It is one of the most frequently utilized aerosol modules in WRF-Chem and only needs a small amount of supplementary data.
2.3. Methods
The direct radiation forcing brought on by dust aerosols is what distinguishes Exp. 2 from Exp. 1 at the surface and at the top of the atmosphere. By subtracting the radiative force at the surface from that at the top of the atmosphere, we can compute the radiative forcing of the atmosphere. See below for the calculation formula of dust aerosols direct radiative forcing:
where SUR (surface), TOA (top of the atmosphere) and ATM (atmosphere) denote the top of the atmosphere, the surface and the atmosphere, respectively; R is the dust aerosols radiative forcing. Note that “dust” denotes that dust aerosols are added to the model, while “nodust” means that dust aerosols are not considered. ΔF is the net flux in shortwave or longwave radiation. The longwave (LW) and shortwave (SW) radiative forcing are obtained according to the formulas above. The total of the longwave and shortwave radiative force is the net radiative forcing.
2.4. Datasets
This paper used MODIS-based land use data as the subsurface data; these data were provided by WRF official website. The data include land use type, vegetation type, leaf area index, water cover, surface albedo and other elements, with a resolution of 2 km.
The FNL (Final Run Global Analysis) global reanalysis data were provided by the United States National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) with a temporal resolution of 6 h and a spatial resolution of 1° × 1°. They include a 500 hPa height field, temperature field and wind field. This dataset is mainly used to assimilate and reanalyze various observational data using the global assimilation system, supplying the preliminary climatic field conditions and boundary conditions desired for WRF-Chem.
The United States Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA, https://www.noaa.gov/, accessed on 10 September 2022) provide hourly meteorological station detection data. There are 416 meteorological stations distributed in the simulation study area. The station monitoring elements mainly include hourly observation values of wind direction (°), wind speed (m s−1), air temperature (°C) and air pressure (hPa).
The air quality data come from the Ministry of Ecology and Environment in China and include more than 300 cities with over 1400 national pollutant monitoring stations (http://106.37.208.233:20035/, accessed on 10 September 2022). Pollutant types include NO2, PM10, PM2.5, SO2, CO and O3. The time resolution is 1 h. This paper mainly selects the coarse particle pollutant PM10 from 206 stations in the north to verify the dust aerosol concentration.
The spatial distribution of the model-simulated AOD is validated in this paper using MODIS data (Modern Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer), which has a spatial resolution of 1° × 1° and a monthly temporal resolution, and MERRA2 data (Modern era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications), which is supplied by NASA’s Goddard Center for Earth Science Data and Information Services (GCESDIS). The selected data time periods are spring 2015 and spring 2019.
3. Results
3.1. Model Performance Evaluation
In this paper, data from 413 meteorological stations nationwide in spring 2000–2020 and 219 pollution monitoring stations in the northern region in spring 2015–2020 were used. The simulation of AOD was evaluated in a previous study [37]. The accuracy of the WRF-Chem model for each climatic conditions simulation was evaluated based on the root mean square error (RMSE), normalized mean deviation (NMB), mean deviation (MB), correlation coefficient (R) and normalized mean error (NME) [38]. The calculation method is presented below:
in which Co is the observed value, Cm is the simulated value and n is the number of valid samples involved in the calculation.
As shown in Table 1, the correlation ratio between the observed value and simulated value of spring temperatures is 0.96, which is the best simulation, and both MB and MFB show negative deviation, which is consistent with the previous results. The correlation coefficient of spring wind speed is 0.36, and MB, NMB and NME are smaller. The simulation results of wind direction have large deviations. The correlation coefficient, MB, NMB and NME of the simulated and observed values are 0.24, −23.45, −0.11 and 0.19, respectively. There are also some deviations in the simulations for precipitation, with MB, NMB and NME of 5.84 mm, 26.78% and 27.41%, respectively, between the simulated and observed values. The simulated values of PM10 are close to the observed values, with a mean deviation of 5.68, NMB and NME of 0.05 and 0.76, respectively, and the model can be used to replicate the variation in the dust concentration to some extent. Therefore, the “reasonable” range of model forecasts for NME ≤ 0.75 and −0.6 ≤ NMB ≤ 0.6, and the “ideal” range is NME ≤ 0.5 and −0.3 ≤ NMB ≤ 0.3. The simulation values of meteorological conditions are suitable for further study of the occurrence and transport processes of dust days.

Table 1.
Evaluation of wind speed, wind direction, temperature, precipitation and PM10 (meteorological stations: 2000–2020, China; pollution monitoring stations: 2015–2020, northern region).
To evaluate the performance of the WRF-Chem model with regard to simulating dust aerosol particle size variations, we compared the remotely sensed AOD and the WRF-Chem model-simulated AOD in 2015, 2018 and 2019 (Figure 2). It can be seen that the WRF-Chem model-simulated AOD has similar spatial patterns to MODIS and MERRA2 in the dust source region of northwest China. The AOD of MODIS is higher than that of MERRA2 and WRF-Chem model simulations, especially in east China, which is mainly due to the fact that MODIS extracts all types of aerosols, such as black carbon, sulfate, and anthropogenic organic carbon, which are not included in the current WRF-Chem model or MERRA2. Comparison of the WRF-Chem simulated AOD with the AOD from MERRA2 shows that both have similar distribution patterns, indicating that the WRF-Chem model is able to capture the spatial variability of dust AOD.
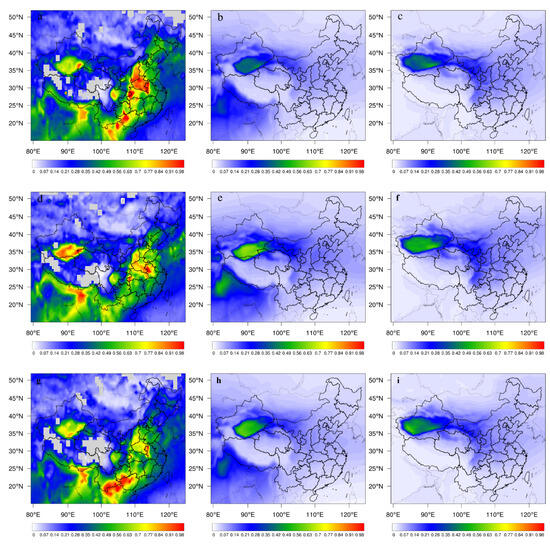
Figure 2.
AOD maps of MODIS (a) 2015, MERRA2 (b), and WRF-Chem simulation (c) in 2015 [37], and of MODIS (d), MERRA2 (e), and WRF-Chem (f) simulation in 2018, and of MODIS (g), MERRA2 (h), and WRF-Chem (i) simulation in 2019 [37].
3.2. Temporal Trends in the Radiative Forcing of Dust Aerosols
3.2.1. Temporal Trends in Longwave Radiative Forcing Effect
Due to the significant variations in the results of the simulation of aerosol radiative forcing in 2018, in order to ensure the objectivity of the analysis, the data from 2018 were not taken into account in the analysis of the average trend from 2000 to 2020. Figure 3 shows the inter-season and inter-month variation of the longwave radiative forcing effect of spring dust aerosols at TOA, surface and in the atmosphere in China during the past 20 years. Figure 3a indicates that the overall trend of the radiative forcing effect is almost zero at the top of the atmosphere in March over the last 20 years. The radiative forcing value basically remained unchanged at 0.05 W m−2 during 2000–2016, while a large fluctuation was observed during 2016–2019, showing a decreasing and then increasing trend, with the maximum value occurring in 2018 (0.36 W m−2). Inter-month variation in atmospheric longwave radiative forcing (Figure 3c) in the atmosphere showed an increasing trend of about 0.0012 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.002, p = 0.843) and reached the extreme value (3.3 W m−2) in March 2018. From 2017 to 2019, this variation was characterized by a significant increase and a significant decrease. The surface longwave radiative forcing effect (Figure 3e) shows an overall downward trend of 0.005 W m−2 (R2 = 0.069, p = 0.261) in March. A strong trend of decreasing and then increasing was observed during 2017–2019, reaching a minimum value (−3.2 W m−2) in 2018.
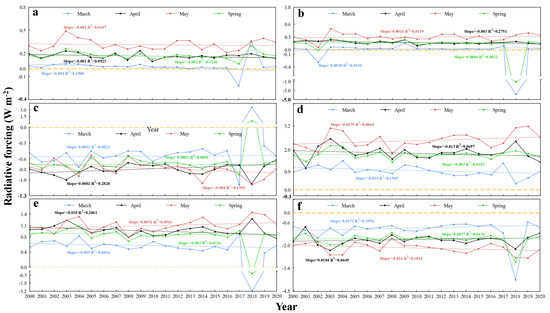
Figure 3.
Inter−season and inter-month variation of long− (left)/short− (right) wave radiative forcing effect in spring and March, April and May at TOA, surface and in the atmosphere from 2000 to 2020 ((a): TOA; (b): TOA; (c): ATM; (d): ATM; (e): SUR; (f): SUR).
At the top of the atmosphere, inter-month trends of the longwave radiative forcing effect of dust aerosols in April during 2000–2016 are all more similar to those in March, but in April, the radiative forcing value increase compared to March and is all positive. In contrast, during 2016–2019, there is almost no change in April relative to March, when drastic changes occur. The atmospheric radiative forcing effect showed a statistically significant increase trend of 0.0081 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.283, p = 0.016) in April, a decrease compared to March. During 2017–2019, April showed a downward and then upward trend compared to March, which showed an upward and then downward trend. The decreasing trend of the inter-annual variation of the ground-level radiative forcing effect in April was slower than that in March, showing a statistically significant downward trend: about 0.010 W m−2 (R2 = 0.286, p = 0.015) per year. It is worth noting that the March minimum (−3.2 W m−2) of the terrestrial radiation forcing effect occurred in 2018, while the April maximum (1.3 W m−2) occurred in 2018.
Inter-month fluctuations in longwave radiative forcing on the top of atmosphere increased in May compared to March and April, but the overall inter-month trend remained at zero. In terms of radiative forcing values, there was another increase in May compared to April. The inter-month trend of the radiative forcing effect of the atmosphere and surface in May was more consistent compared to April, but the inter-month trend of the radiative forcing effect of the atmosphere in May was −0.008 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.159, p = 0.081), while the ground showed a fluctuating upward pattern of 0.0076 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.091, p = 0.195). Numerically, the radiative forcing of the atmosphere fluctuated roughly around −1.0 W m−2, while the radiative forcing of the ground was just the opposite, basically fluctuating around 1.0 W m−2.
In general, although at the top of the atmosphere the longwave radiative forcing of spring dust aerosols fluctuated in China over the past 20 years, the overall trend was stable, with the value of radiative forcing fluctuating around 0.2 W m−2. In the atmosphere, the radiative forcing effect of spring dust aerosols tended to increase by about 0.0001 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.0001, p = 0.954). Between 2017 and 2019, there was a sharp rise followed by a significant decline. In contrast to the atmosphere, the surface radiative forcing effect showed an overall decreasing trend with a slope of 0.002 (R2 = 0.032, p = 0.446). It showed a strong fluctuation of increasing and then decreasing during 2017–2019.
3.2.2. Temporal Trends in Shortwave Radiative Forcing Effect
The shortwave radiation forcing effect at the top of the atmosphere in March remained largely unchanged at 0.03 W m−2 between 2003 and 2017, but there was a significant decline and rise between 2017 and 2019, with the lowest value in 2018 (−3.9 W m−2) (Figure 3b). The overall trend of dust aerosols radiative forcing effect in April was basically zero, with only slight fluctuations, and the radiative forcing value was stable at about 0.2 W m−2. The radiation forcing effect in May varied in the same way as in April, but the variation of the inter-month fluctuation of the radiative forcing effect in May intensified compared with that in April. The shortwave radiation forcing at the top of the atmosphere in spring remained largely unchanged between 2000 and 2017, with values fluctuating around 0.2 W m−2, but showing a downward trend followed by an upward trend between 2017 and 2019, with the lowest value occurring in 2018 (−1.2 W m−2).
In March, the shortwave radiative forcing effect in the atmosphere typically exhibited a fluctuating downward trend of roughly −0.014 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.155, p = 0.086), with maximum values in 2004 (1.5 W m−2) and lowest values in 2018 (0.3 W m−2) (Figure 3d). In the atmosphere, the dust aerosols’ radiative forcing effect in April showed a fluctuating decreasing trend of about 0.013 W m−2 (R2 = 0.070, p = 0.26) per year, with the minimum (1.0 W m−2) and maximum (2.3 W m−2) values occurring in 2001 and 2003, respectively. The atmospheric radiative forcing effect fluctuated incrementally with a trend of about 0.0179 W m−2 (R2 = 0.086, p = 0.208) per year in May, with the minimum (1.5 W m−2) and maximum (3.1 W m−2) values occurring in 2002 and 2019, respectively. Although the spring atmospheric radiative forcing effect fluctuated widely from year to year, the overall interannual trend was basically zero, reaching the minimum (1.3 W m−2) value in 2001 and the maximum (2.3 W m−2) value in 2003.
The surface radiative forcing effect in March (Figure 3f) showed a similar trend compared to the top of the atmosphere, and it also reached its minimum value (−4.2 W m−2) in 2018. The intermonth fluctuations during 2000–2017 slowed down compared to the top of the atmosphere, but the minimum value of the surface radiative forcing effect (−4.2 W m−2) increased compared to the top of the atmosphere (−3.9 W m−2). In April, the surface radiation forcing showed a trend of change contrary to the atmosphere, with a maximum (−0.8 W m−2) in 2001 and a minimum (−2.5 W m−2) in 2003, but the increase in annual fluctuations of the radiation forcing was slower than in the atmosphere, with a value of 0.0104 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.045, p = 0.369). The surface radiative forcing effect in May showed an opposite trend to that of the atmosphere, with a maximum value in 2002 (−1.8 W m−2) and a minimum value in 2019 (−2.8 W m−2). The surface shortwave radiative forcing in spring showed fluctuating changes in contrast to the atmosphere, with the maximum value occurring in 2001 (−1.2 W m−2) and the minimum value in 2018 (−3 W m−2). Compared to the atmosphere, the variation of the terrestrial shortwave radiative forcing effect fluctuated more sharply during 2017–2019.
3.2.3. Temporal Trends in Net Radiative Forcing Effect
Figure 4 shows the inter-season and inter-month variation of the net radiative forcing effect of dust aerosols in spring and March, April and May at different altitude layers in China over the past 20 years. At the top of the atmosphere, the radiative forcing effect in March (Figure 4a) basically fluctuated around 0.1 W m−2 up and down during 2000–2017, but showed a sharp decrease and increase during 2017–2019, with the minimum value occurring in 2018 (−3.5 W m−2), and the overall inter-month variation trend was −0.001 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.008, p = 0.694). The inter-annual variation of the net radiative forcing effect in the atmosphere (Figure 4b) and surface (Figure 4c) had a more similar trend to the top of the atmosphere in March during 2000–2017, with the surface radiative forcing values fluctuating around −0.5 W m−2. Between 2017 and 2019, net radiative forcing showed a similar trend of decreasing first and then increasing at the surface and the top of the atmosphere, with the minimum occurring in March 2018 (−7.5 W m−2), while net radiative forcing at the atmosphere showed the opposite trend of first increasing and then decreasing, reaching its maximum in 2018 (4.1 W m−2).
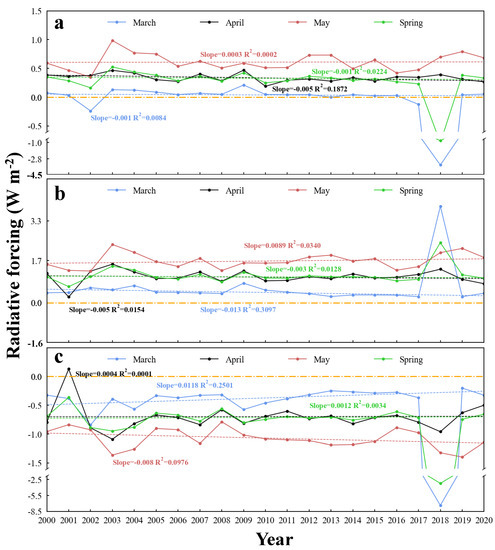
Figure 4.
Inter−season and inter−month variation in net radiative forcing effect in spring and March, April and May at TOA, surface and in the atmosphere from 2000 to 2020 ((a): TOA; (b): ATM; (c): SUR).
The inter-month trends of net radiative forcing in April were basically 0 W m−2 yr−1 at the top of the atmosphere, in the atmosphere and at the surface. In terms of radiative forcing values, the top atmosphere basically stayed around 0.4 W m−2, the atmosphere basically stayed around 1.1 W m−2, and surface radiative forcing fluctuated around −0.7 W m−2. Although the overall inter-month trends were almost the same for the last two decades, the inter-month fluctuations of the net radiative forcing effect in April varied among the three altitude layers, with the most drastic inter-month fluctuations in the atmosphere, followed by the ground, and the most moderate fluctuations at the top of the atmosphere.
The overall net radiative forcing effect in May at the top of the atmosphere showed a fluctuating increasing trend of about 0.0003 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.0002, p = 0.949), and the radiative forcing value fluctuated up and down around 0.6 W m−2. The inter-month variation in atmospheric radiative forcing in May showed a fluctuating increasing trend of about 0.0089 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.034, p = 0.436), with the maximum value occurring in 2003 (2.3 W m−2) and the minimum value in 2002 (1.3 W m−2). The net radiative forcing effect on the ground showed a downward trend of −0.008 W m−2 yr−1 (R2 = 0.098, p = 0.18) fluctuations, with the maximum radiative forcing occurring in 2008 (−0.8 W m−2) and the minimum in 2019 (−1.4 W m−2).
Generally speaking, the trends of net radiative forcing of atmospheric top, atmosphere, and surface dust aerosols in spring in China over the past 20 years were more consistent with the trends of shortwave radiative forcing corresponding to the height layer. The atmosphere remained largely unchanged between 2000 and 2017, with radiation forcing values fluctuating around 0.4 W m−2, but showed a downward trend followed by an upward trend between 2017 and 2019, with the lowest values occurring in 2018 (−0.8 W m−2). While the atmospheric radiation forcing effect in the spring was highly variable from year to year, the overall annual variation tended to be about −0.003 W m−2 (R2 = 0.013, p = 0.634) per year, reaching its maximum in 2018 (2.3 W m−2). The terrestrial net radiative forcing showed a trend very similar to that of the shortwave radiative forcing, with slight inter-annual fluctuations between 2000 and 2017, while it showed a dramatic change, decreasing and then increasing, between 2017 and 2019. The difference is that the surface net radiation forcing was higher than the surface shortwave radiation.
3.3. Spatial Variations in Effects of Dust Aerosol on Radiative Forcing
3.3.1. Inter-Season Average Longwave Radiative Forcing Effect
The simulated spatial distribution of the annual longwave, shortwave and net radiative forcing of spring dust aerosols in atmosphere, surface and at the top of the atmosphere of China from 2000 to 2020 is shown in Figure 4. Due to the different concentrations of dust aerosols at different vertical heights, the radiative forcing on various height layers is different, and there are obvious differences between longwave and shortwave radiation.
The dust aerosols radiative forcing at the top of the atmosphere (Figure 5a) is almost always a positive radiative forcing effect leading to a temperature rise, and has a relatively obvious spatial distribution pattern, showing a double-peaked structure with the Taklamakan Desert region and North China as the core, and the radiative forcing values gradually decrease around the peak. The high values are concentrated in central Xinjiang, northern China and the southern Liaoning province, where the longwave radiative forcing at the top of the atmosphere is above 0.55 W m−2, with a maximum value close to 1.6 W m−2.
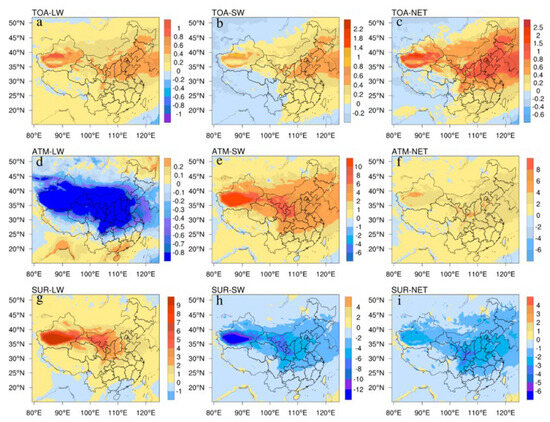
Figure 5.
Average long/shortwave (longwave, LW; shortwave, SW) and net radiative forcing effect (W m−2) of each height layer of spring dust aerosol in China from 2000 to 2020 ((a): TOA−LW; (b): TOA−SW; (c): TOA−NET; (d): ATM−LW; (e): ATM−SW; (f): ATM−NET; (g): SUR−LW; (h): SUR−SW; (i): SUR−NET).
The dust aerosols longwave radiative forcing at the atmosphere (Figure 5d) is almost always negative and shows a weak spatially based circle pattern. The spatial distribution of atmospheric radiative forcing is in good agreement with the spatial pattern of dust concentration. The high values of positive radiative forcing are located in areas such as the southeastern coast of China and the northeastern Heilongjiang Province. Longwave radiative forcing values in western Inner Mongolia and central Xinjiang are around −4 W m−2 with a minimum of −12.57 W m−2. The dust aerosols longwave radiative forcing in a small part of the southern coastal areas, such as Hainan Province, are close to zero.
The dust aerosols longwave radiative forcing at the surface (Figure 5g) is almost all positive in the whole of China, and the comparison reveals a good correspondence between the radiative forcing caused by dust aerosols at ground level and the spatial distribution of dust aerosol concentrations. On the whole, only a few areas such as the Guangdong Province and southeastern Guangxi Province are cooled by negative radiative forcing. The high radiative forcing in spring in China is situated in southwestern Inner Mongolia and central Xinjiang, with a maximum value of 13 W m−2, and the dust aerosols radiative forcing shows a circular structure with positive radiative forcing centers in Xinjiang and Inner Mongolia that decrease outwards until they are close to zero.
3.3.2. Inter-Season Average Short Wave Radiative Forcing Effect
Based on the distribution of radiative forcing effects estimated from data simulations, the dust aerosols radiative forcing at the top of the atmosphere (Figure 5b) is a warming radiative forcing effect in some areas and a cooling radiative forcing effect in other areas. The radiative forcing west of the line from Hotan, Xinjiang to Markang County, Sichuan Province to Wenshan County, Yunnan Province is negative for temperature decline, and east of the line is positive for temperature increase. In Hami, Hotan, Korla, Aksu, and Turpan in the Chinese provinces of Xinjiang, Hebei, Shandong, and northern Henan, the radiative forcing effect is positive and typically exceeds 0.5 W m−2, while the radiative forcing is negative with a minimum value of −0.4 W m−2 in the southwest regions of Tibet, Sichuan, and Yunnan provinces.
The shortwave radiative forcing at the atmosphere (Figure 5e) in spring is almost always positive in the Chinese region, leading to an increase in temperature, and the spatial distribution of the radiative forcing shows a decreasing trend with the Taklamakan and Tengger Deserts as the core of high values. A few areas in western Hulunbeier City in Inner Mongolia, southwestern Rikaze in Tibet and southwestern Kashgar in Xinjiang show negative radiative forcing, leading to a decrease in temperature. Shortwave radiative forcing is above 7 W m−2 in eastern Kashgar, northern Hotan, Aksu, central Bayingoleng Mongol Autonomous Prefecture in Xinjiang and southwestern Alashan and Tengger Desert in Inner Mongolia, with a maximum value of 17 W m−2 in the western Taklamakan Desert.
On the whole, it is observed that the ground-level shortwave radiative forcing (Figure 5h) is a negative radiative forcing effect leading to a decrease in temperature, except for the western part of the Ali region in Tibet, the southern part of the Shigatse region, the western part of the Hohhot city in Inner Mongolia and a few areas in the Hainan Province. The high absolute values of dust aerosol shortwave radiative forcing are found in the ring formed by the cities of Hami, Hotan, Korla, Aksu, Turpan and Atushi in Xinjiang, as well as in the western part of Jiuquan, the northern part of Wuwei, central and western part of Baiyin, Lanzhou and the southwestern part of Alashan League in Inner Mongolia, with a maximum value of 15 W m−2.
3.3.3. Inter-Season Average Net Radiative Forcing Effect
As observed in Figure 5c, the net radiative forcing effect of dust aerosols on the top of the atmosphere shows positive radiative forcing to enhance climate warming east of the Kashgar region in Xinjiang, west of Hotan region, west of Bayingoleng Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, west of Hami region and Turpan region, and in the south-central Hebei province, northern Henan province, western Liaoning province and Shandong province. The extreme value is nearly 3 W m−2. As a whole, the net radiation intensity at the top of the atmosphere is bounded by Xinjiang Hotan City, Markang County, in the Sichuan Province, and Luxi City in the Yunnan Province, with a cooling effect in the west and a positive radiation forcing effect in the east.
As shown in Figure 5f, the dust aerosols net radiative forcing at the atmosphere in the Chinese region is almost always positive in spring. The radiative forcing values exceeded 3 W m−2 in the oval area surrounded by Hotan, Atushi, Aksu and Kullu in Xinjiang and the rectangular region composed of Weifang in Shandong, Chengdu in Sichuan, Linxia in Gansu, and Tianjin, with the maximum value occurring in Aksu in Xinjiang (9 W m−2). The negative radiative forcing effect of cooling was observed in a few areas such as Aketao County, the southwestern Kashgar region, the western Hotan region in Xinjiang, the southwestern Shigatse region in Tibet, and the western Hohhot city in Inner Mongolia. The dust aerosols net radiative forcing at the atmosphere has obvious spatial distribution characteristics, which manifest as a double-core structure centered in the high-value areas of southwestern Xinjiang, Shaanxi Province, and in the Gansu Province, and gradually decreases in all directions with the double core as the center.
The dust aerosols net radiative forcing effect at the surface in spring in China is below 0 W m−2 in almost the entire area (Figure 5i). A few areas in the western Hotan region of Xinjiang, southwestern Shigatse region of Tibet, western Hulunbeier city of Inner Mongolia and southern Hainan province show positive radiative forcing effects of warming. The eastern part of Kashgar region in Xinjiang, the northern part of the Hotan region, the western part of the Bayingoleng Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, Aksu region, southern Gansu province, eastern Sichuan province, southern Hebei province, western Henan province, and the Shaanxi province are the low-value areas of dust aerosol radiative forcing, with the lowest value reaching −5.5 W m−2. The dust aerosols’ net radiative forcing shows a double-peak structure in spatial distribution. It is centered in low-value areas such as Taklamakan Desert and the Loess Plateau, and it increases in all directions.
3.3.4. Inter-Month Average Net Radiation Forcing Effect
The spatial patterns of inter-month average direct radiative forcing of dust aerosols at the atmosphere, the top of the atmosphere and the surface was calculated (Figure 6). The net radiative forcing shows the upward patterns at the top of the atmosphere, with March (−0.20 W m−2) < April (0.48 W m−2) < May (0.94 W m−2) (Figure 6a–c). The net radiative forcing in March shows a rough distribution pattern with negative values in the west and positive values in the east side, with the line from Tahe County in the Heilongjiang Province to Wenshan City in the Yunnan Province as the boundary. The positive radiative forcing in the east shows a decreasing trend from east to west, while the high value of negative radiative forcing is mainly distributed in the central Taklamakan Desert in Xinjiang, the Badain Jaran and Tengger Deserts in western Inner Mongolia, and most areas in Gansu and Qinghai. The spatial distribution of net radiative forcing in April and May is relatively similar, with the Taklamakan Desert and northern China as the core of high values, but the coverage of positive radiative forcing of dust aerosols in May is expanded in the northeastern part of China. The net radiative forcing at the top of the dust aerosol atmosphere was almost positive throughout the country, with the maximum value of positive radiative forcing occurring in the Taklamakan Desert in Xinjiang, but negative radiative forcing occurred in a small part of the northern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau bordering the Taklamakan Desert region.
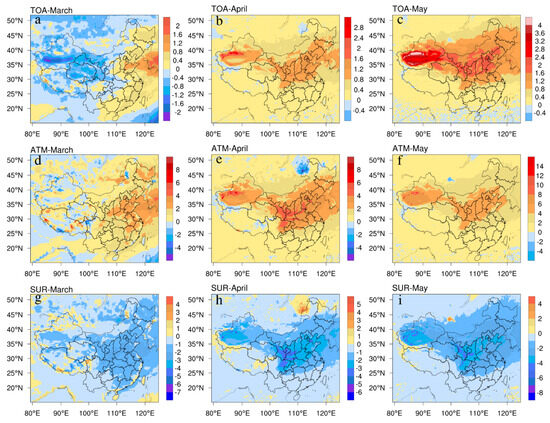
Figure 6.
Mean net radiative forcing effect (W m−2) of dust aerosols at TOA, surface and in the atmosphere for March, April and May 2000–2020 ((a): TOA−March; (b): TOA−April; (c): TOA−May; (d): ATM−March; (e): ATM−April; (f): ATM−May; (g): SUR−March; (h): SUR−April; (i): SUR−May).
The inter-month mean net surface radiative forcing values of dust aerosols (Figure 6g–i) show a downward variation of March (−0.88 W m−2) > April (−0.96 W m−2) > May (−1.48 W m−2). The dust aerosols’ negative radiative forcing decreases from east to west in March, and shows positive radiative forcing in the Gurbantunggut Desert region of northern Xinjiang and the northern part of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. The spatial distribution of negative radiative forcing from dust aerosols in both April and May showed a decreasing trend from northeast to southwest. It is noteworthy that a clear break in the variation of net radiative forcing values was observed at the boundary of the line connecting three locations in Hotan County, Xinjiang Province; Zhaotong City, Yunnan Province; and Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province. The dust aerosols’ net surface radiative forcing in May showed relatively similar variations to that in April, but its negative radiative forcing expanded in the northeastern part of China compared to April. In April and May, the dust aerosols’ net radiative forcing at the surface is mostly negative in all regions of China, except for the northern of the Tibetan Plateau and the junction with the Taklamakan Desert, which show significant positive values.
The direct radiative forcing (Figure 6d–f) was largely positive in March, April and May, indicating a warming effect of dust aerosols in the atmosphere. Inter-month mean net atmospheric radiative forcing is shown on a regional scale as May (2.42 W m−2) > April (1.44 W m−2) > March (0.68 W m−2). In March, the positive radiative forcing gradually decreases from east to west, showing a more pronounced negative forcing effect in northern and southern Xinjiang, northern Gansu, western Qinghai and the central Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. The atmospheric radiative forcing in April and May has a similar spatial pattern. By comparing Figure 6e and Figure S2, it can be found that the area of high values of radiative forcing of dust aerosols in the atmosphere is consistent with the spatial distribution of dust concentrations. The higher the dust aerosol concentration, the more pronounced the radiative forcing effect. Therefore, it can be found that the radiative forcing effect of dust aerosols has a significant warming effect on the atmosphere.
3.4. Spatial and Temporal Trends in Effects of Dust Aerosol on Radiative Forcing
3.4.1. Trends in Longwave Radiative Forcing Effects
Figure 6 shows the rising and falling trend of the direct radiative forcing value of spring dust aerosol in China on the pixel scale in the past 20 years.
Figure 7a shows the variations in spring dust aerosols longwave radiative forcing at the top of the atmosphere in China during 2000–2020. The dust aerosols radiative forcing in the area east of the line from Wenshan County, Yunnan Province, to Nantong City, Jiangsu Province, mainly shows an increasing trend. The regions showing a downward trend are mainly clustered in the central and western parts of China, such as the Qinghai Province, Gansu Province, Shaanxi Province, northeastern Hubei Province, southwestern Henan Province, and southern Ningxia, but the central–eastern part of the Heilongjiang Province, the northern part of Shandong Province, the Aksu, Hotan, and Turpan regions in Xinjiang, and the Ali region in Tibet show a clear upward trend.
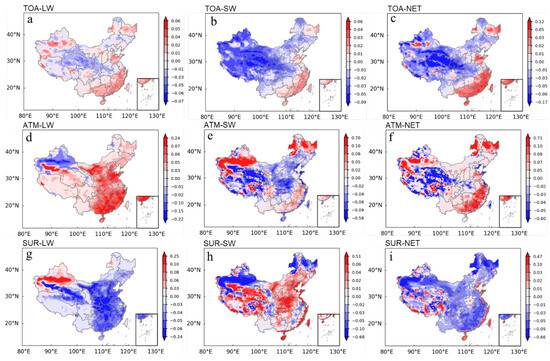
Figure 7.
Spatiotemporal variations (W m−2) of spring dust aerosols longwave/shortwave (longwave, LW; shortwave, SW) and net radiative forcing at each height layer in China during 2000–2020 ((a): TOA−LW; (b): TOA−SW; (c): TOA−NET; (d): ATM−LW; (e): ATM−SW; (f): ATM−NET; (g): SUR−LW; (h): SUR−SW; (i): SUR−NET).
During the spring of 2000–2020, the atmospheric longwave radiative forcing (Figure 7d) showed an increase in most of China except for a small part of northwestern Xinjiang. The overall spatial distribution shows a trend of faster inter-annual growth in the east than in the west, with Nanning–Yinchuan City as the boundary. The growth trend is most significant in the southeastern coast of China, northwestern Shandong Province, northeastern Xinjiang Hotan Region, southwestern Bayingoleng Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, southern Alashan League of Inner Mongolia, and southern Bayannur, while the decreasing trend is most obvious in the central and western Hulunbeier City of Inner Mongolia, Kashgar of Tibet, and Aksu Region.
The net radiative forcing of dust aerosol (Figure 7g) has a double-peak structure in spatial distribution. It is centered in low-value areas such as Taklamakan Desert and the Loess Plateau, and increases in all directions. The remaining areas other than Xinjiang showed an overall decreasing trend. Specifically, with Baise City–Pingliang City as the boundary, the inter-annual decline in the western region occurs more slowly than the inter-annual decline in the eastern region. The most significant decreasing trend was observed in the northeastern of the Hotan region of Xinjiang, the southwestern of Bayingguoleng Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, the Haixi Mongolian–Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture of Qinghai Province, and the eastern of the boundary line in the Henan Province, Hubei Province and Shaanxi Province.
3.4.2. Trends in Shortwave Radiative Forcing Effects
During 2000–2020, shortwave radiative forcing of spring dust aerosols showed a downward pattern in the central and western parts and an upward pattern in eastern China (Figure 7b). The most significant downward pattern was in the desert of Qaidam Basin located in Qinghai Province, and the most obvious upward pattern was in the southeastern coastal region as well as the northern part of Shandong Province and the eastern part of the Heilongjiang Province.
There is an obvious spatial heterogeneity in shortwave radiative forcing of dust aerosols at the atmosphere in China (Figure 7e). Specifically, Nanyang City, Henan Province, Suizhou City, Hubei Province, the northeastern part of Xinjiang Hotan Region, the southern part of Bayingoleng Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, the area north of Golmud City-Dulan County and the area around Qumalai County in Qinghai Province and the area along the eastern coastline of China showed significant decreasing trends, while the areas around Hotan City, Atushi City, Aksu City, Kulle City, Turpan City, and Hami City in Xinjiang and the northeastern part of the Heilongjiang Province, and the western part of Hulunbeier City in Inner Mongolia showed a significant increasing trend.
The shortwave radiative forcing of dust aerosols at the surface has strong geographical heterogeneity in spatial patterns (Figure 7h). The high-value areas of the downward trend are concentrated in a few areas such as northwestern Xinjiang and northeastern Inner Mongolia. The central and western Henan Province, Hainan Province, and the eastern coastal line areas showed a significant upward trend.
3.4.3. Trends in the Net Radiative Forcing Effect
From 2000 to 2020, the net radiative forcing of dust aerosols at the top of the atmosphere (Figure 7c) was spatially bounded by Xidu City, Yunnan Province and Nantong City, Jiangsu Province, showing a distribution trend of decreasing in the west and increasing significantly in the east. The declining trend was most obvious in the desert of the Qaidam Basin and the rising trend was most obvious in the coastal areas.
The trends of the net radiative forcing of dust aerosol in the atmosphere (Figure 7f) showed obvious spatial heterogeneity from 2000 to 2020. In general, there was a decreasing trend in the western region and an increasing trend in the eastern region. The net radiative forcing of dust aerosols at the surface (Figure 7i) only showed a year-to-year increase in the eastern of the Ali region of Tibet, the southwestern Shigatse region, the central Nagqu region, the western Sichuan province, and the eastern coastal region of China in general, while the rest of the regions showed a year-to-year decrease. The decreasing trend was most significant in western Xinjiang and northeastern of Inner Mongolia.
4. Discussion
In this paper, we simulated the spring dust process in China during 2000–2020 based on the WRF-Chem and quantified the radiative forcing effect of dust aerosols on at different altitude layers. Compared with previous studies, this study has two novelties. One is that we established a localization scheme for dust aerosol simulation suitable for the Chinese region. In addition, we carried out a long time series of direct radiative forcing simulations of dust aerosols in China and further analyzed the variability of the radiative forcing effect based on different temporal and spatial scales. This study has significant implications for understanding how dust particles in China contribute to regional climate change.
The dust emission flux and dust aerosol concentration in 2018 were greater than those in adjacent years, and net radiative forcing of the atmosphere reached its maximum absolute value (2.5 W m−2), and the thick dust aerosols increased the absorption of solar radiation. The surface net radiative forcing experienced a significant decline in 2018, and then the radiative forcing value began to rise more significantly, because the thick dust aerosols reduced the solar radiation reaching the ground by refracting and scattering solar radiation. As the net radiative forcing at the top of the atmosphere was greatly affected by the cold air flow and the prevailing westerly wind in March, the dust aerosols in the northwest were easily transported to the southeast with the movement of the wind direction. This reduced the dust aerosol concentration in the region, reducing the radiative forcing at the top of the atmosphere in spring.
Both longwave and shortwave radiation showed significant positive radiative forcing at the top of the atmosphere, with high radiative forcing values mainly in northwest China and northern China, while longwave radiation in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau region produced positive radiative forcing effects and shortwave radiation had negative radiative forcing effects. The positive radiative forcing effect at the top of the atmosphere is significantly higher in these regions than in other regions because of the widespread deserts in northwest China and the large surface albedo [39], which exacerbates the reflection of solar radiation (Figure S1). The Himalayas, the Kunlun Mountains and the Pamir Plateau around the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau have a high surface albedo due to glaciers and snow [40], while the dust aerosol concentration in this region is low (Figure S2), resulting in a slight positive radiative forcing effect at the top of the atmosphere. The high longwave positive radiative forcing in northern China may be due to the low dust concentrations in the region, which reduce the planetary albedo [41] in the region and thus increase the absorption of solar radiation caused by dust aerosols [42].
Compared to the radiative forcing at the top of the atmosphere, the shortwave and net radiative forcing at the surface shows a significant negative effect because of the scattering and absorption effects of dust aerosols as well as factors such as surface albedo, which result in a reduction in solar radiation reaching the surface, and negative radiative forcing at the surface [43,44]. The spatial patterns of surface radiative forcing correspond well to the dust aerosols concentration, and the surface radiative forcing is stronger in areas with a higher concentration of dust aerosols. In the vicinity of the dust source area, not only is the dust particle size larger, but also the dust aerosol concentration is higher, and therefore larger particles interact more with longwave radiation, compared to smaller particles [45]. Moreover, there is a large difference in surface longwave radiative forcing between the dust source region and the downstream region due to the shorter lifetime of larger dust particles in the atmosphere and the shorter transport distance [41]. In contrast, smaller dust particle sizes are more easily transported over long distances due to their longer lifetime in the atmosphere, so the surface shortwave radiative forcing remains more significant in downstream areas, and the dust source area has less surface shortwave radiative forcing compared to downstream areas.
In May and April, at the top of the atmosphere, the net radiative forcing of dust aerosols is high and positive. This is mainly due to the transport of coarse-grained dust aerosols from the north-western desert region with the movement of prevailing winds [46], resulting in higher aerosol optical thickness, which exacerbates the absorption of reflected solar radiation at the surface and produces higher positive radiative forcing [47]. At the top of the atmosphere, the spatial patterns of net radiative forcing in March are significantly different from those in April and May. This may be due to the greater influence of cold air currents and prevailing westerly winds in March [48], which tend to transport dust aerosols from the northwest to the southeast with the movement of the winds, thus reducing the dust aerosol concentration in the region, which in turn results in less absorption of solar radiation by dust aerosols, making a larger area of net radiative forcing show a negative effect.
The net radiative forcing of dust aerosols at the surface in May has a similar spatial pattern to that of April, but its negative radiative forcing coverage has expanded. This is due to the increased flux and concentration of dust emissions in May compared to March and April [48], which promotes the absorption and scattering of solar radiation, thereby increasing the amount of radiative energy that reaches the surface. The net radiative forcing at the surface of the northern Tibetan Plateau at the junction with the Taklamakan Desert shows positive radiative forcing effects in March, April and May, probably because the accumulation of dust aerosols from the Taklamakan Desert forms a deep dust aerosol atmosphere in the Kunlun Mountains [41], which can have a heating effect on the Tibetan Plateau by absorbing solar radiation [49]. Unlike the surface radiative forcing, the net radiative forcing at the atmosphere and at the top of the atmosphere in the junction of the northern Tibetan Plateau and the Taklamakan Desert is negative in April and May, probably because the Kunlun Mountains in the northern Tibetan Plateau block the uplift of dust aerosols [26], making dust aerosols concentration at the atmosphere smaller and reducing its ability to absorb solar radiation.
Compared to previous studies, we have carried out a long time series simulation of the spring dust emissions process and quantified the direct radiative forcing effect of spring dust aerosols at different altitude layers in China over the last 20 years. However, there is still a need to further improve our study. First, this study used PM10 from the atmospheric monitoring stations and AOD from remote sensing products to validate the simulation results of dust aerosol concentrations, and there is some uncertainty in the assessment of the simulation results, which need to be evaluated with other observational data. Secondly, the simulation results of different sand parameterization schemes need to be compared and evaluated because of the large differences in the simulation of dust processes. Thirdly, we did not discuss the influence of dust single scatter albedo on aerosol radiative effects, which needs to be considered in the next study. Finally, given the strong seasonal variation of dust emission, the radiative forcing effect and climate impact of dust emission in different seasons need to be analyzed intensively in the future. Our study can support an ecological sustainability assessment [50,51,52,53,54].
5. Conclusions
The analysis indicted significant spatiotemporal differences in the dust aerosols’ radiative forcing effect on different altitude layers in China during 2000–2020. Dust aerosols show an obvious inter-annual positive radiative forcing effect (about 0.38 W m−2) on both shortwave and longwave radiation at the top of the atmosphere, mainly in northwest China and the North China Plain, while in the atmosphere they show negative and positive effects on longwave and shortwave radiation, respectively, with a net radiative forcing of 1.54 W m−2, showing a warming effect. Longwave radiation forcing of dust aerosols have a positive effect at the surface, but show a negative forcing effect on shortwave radiation, and both correspond well to the spatial distribution of dust aerosol concentrations with a net radiative forcing of −1.16 W m−2, showing a cooling effect.
From the month-to-month variation, at the top of the atmosphere, the dust aerosols’ net radiative forcing shows a trend of May (0.94 W m−2) > April (0.48 W m−2) > March (−0.20 W m−2). The spatial distribution of net radiative forcing in March is positive in the east and negative in the west, while net radiative forcing in April and May has similar spatial patterns, exibiting a positive effect over the whole of China. The dust aerosols net radiative forcing at the atmosphere shows a trend of May (2.42 W m−2) > April (1.44 W m−2) > March (0.68 W m−2), and the atmospheric radiative forcing decreases from east to west in March, and the radiative forcing in April and May show a significant positive correlation with dust aerosols concentrations. However, the dust aerosols’ net surface radiative forcing shows a trend of March (−0.88 W m−2) > April (−0.96 W m−2) > May (−1.48 W m−2). The dust aerosols’ radiative forcing at the surface in March showed a decreasing distribution from east to west in China, whereas the radiative forcing in April and May showed a decreasing trend from northeast to southwest.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs15184564/s1, Figure S1: Spatial distributions of surface albedo of China during 2000−2020; Figure S2: Spatial distributions of annual mean dust concentrations (µg kg−1-dry air) of China during 2000−2020.
Author Contributions
F.W.: Conceptualization, Writing—original draft, Investigation; M.Q.: Writing—original draft; M.Z.: Software; S.R.: Software; Q.X.: Visualization; M.W.: Validation; H.S.: Resources, Funding acquisition, Supervision; Q.W.: Software; Visualization; P.L.: writing—review and editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41871316; 42101424) and by the Training Plan for Young Backbone Teachers in Colleges and Universities in Henan Province of China (2021GGJS024) and by the Natural Science Foundation of Henan (202300410076; 232300421244).
Data Availability Statement
The authors do not have permission to share data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huang, J.; Guan, X.; Ji, F. Enhanced Cold-Season Warming in Semi-Arid Regions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 5391–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-P.; Huang, Z.-W.; Bi, J.-R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Micro-Pulse Lidar Measurements of Aerosol Vertical Structure over the Loess Plateau. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2008, 1, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Radiative Forcing by Mineral Dust Aerosols: Sensitivity to Key Variables. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 31637–31645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.-H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust Cycle: An Emerging Core Theme in Earth System Science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Meng, H.; Song, H.; Zheng, H. Progress in dust modelling, global dust budgets, and soil organic carbon dynamics. Land 2022, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Arimoto, R.; An, Z.S. Dust Emission from Chinese Desert Sources Linked to Variations in Atmospheric Circulation. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 28041–28047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Minnis, P.; Yi, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ayers, K.; Trepte, C.; Winker, D. Summer Dust Aerosols Detected from CALIPSO over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L18805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswini, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Das, S.K. Quantification of Long-Range Transported Aeolian Dust towards the Indian Peninsular Region Using Satellite and Ground-Based Data—A Case Study during a Dust Storm over the Arabian Sea. Atmos. Res. 2020, 239, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Gharai, B.; Rao, P.V.N.; Dutt, C.B.S. Satellite-Based Shortwave Aerosol Radiative Forcing of Dust Storm over the Arabian Sea: A Relationship Is Developed between SWARF and MODIS AOD. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2016, 17, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupakheti, D.; Rupakheti, M.; Yin, X.; Hofer, J.; Rai, M.; Hu, Y.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Kang, S. Modifications in Aerosol Physical, Optical and Radiative Properties during Heavy Aerosol Events over Dushanbe, Central Asia. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zong, X. Shortwave versus Longwave Direct Radiative Forcing by Taklimakan Dust Aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L07803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Christopher, S.A. Longwave Radiative Forcing of Saharan Dust Aerosols Estimated from MODIS, MISR, and CERES Observations on Terra. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Du, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, M. Aerosol Optical Properties Affected by a Strong Dust Storm over Central and Northern China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 27, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Kang, L.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, T.; Wang, T.; et al. An Overview of Mineral Dust Modeling over East Asia. J. Meteorol. Res. 2017, 31, 633–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.; Nelli, N.; Fonseca, R.; Weston, M.; Flamant, C.; Cherif, C. The Dust Load and Radiative Impact Associated with the June 2020 Historical Saharan Dust Storm. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 268, 118808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Jin, Q.; Ma, Y.; Yang, B. Modeling Dust Sources, Transport, and Radiative Effects at Different Altitudes over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1507–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péré, J.-C.; Rivellini, L.; Crumeyrolle, S.; Chiapello, I.; Minvielle, F.; Thieuleux, F.; Choël, M.; Popovici, I. Simulation of African Dust Properties and Radiative Effects during the 2015 SHADOW Campaign in Senegal. Atmos. Res. 2018, 199, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Choobari, O.; Sturman, A.; Zawar-Reza, P. Global Distribution of Mineral Dust and Its Impact on Radiative Fluxes as Simulated by WRF-Chem. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2015, 127, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, H.; Lei, T.; Liu, P.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Yang, Z.; Xia, H.; Wang, T.; Zhao, H. Effects of natural and anthropogenic factors and their interactions on dust events in Northern China. Catena 2021, 196, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, K.; Piao, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.-P.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wan, S. Soil organic carbon and nutrient losses resulted from spring dust emissions in Northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xia, J.; Piao, S.; Hui, D.; Zhong, M.; Ru, J.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Plant feedback aggravates soil organic carbon loss associated with wind erosion in Northwest China. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2019, 124, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, K.; Piao, S.; Wan, S. Spatial and temporal variations of spring dust emissions in northern China over the last 30 years. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 126, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Kang, L.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; He, Y.; Yuan, T.; Yang, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, G. Emission, Transport, and Radiative Effects of Mineral Dust from the Taklimakan and Gobi Deserts: Comparison of Measurements and Model Results. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2401–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.-T.; Wang, H.-J.; Zhang, Z.-B. Radiative Forcing and Temperature Response of Dust Aerosols over East Asia in the Latest Decade. Sci. Cold Arid. Reg. 2012, 4, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tan, S.-C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Shi, G.-Y.; Zhang, M.-X.; Che, H.-Z. A Multisource Observation Study of the Severe Prolonged Regional Haze Episode over Eastern China in January 2013. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Leung, L.R.; Yang, B. Modeling the Transport and Radiative Forcing of Taklimakan Dust over the Tibetan Plateau: A Case Study in the Summer of 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Kang, L.; Yuan, T.; Luo, Y.; Alam, K.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Bi, H.; Zhao, D. Direct Radiative Forcing Induced by Light-Absorbing Aerosols in Different Climate Regions Over East Asia. JGR Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD032228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, W.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, W. A Study of Dust Radiative Feedback on Dust Cycle and Meteorology over East Asia by a Coupled Regional Climate-Chemistry-Aerosol Model. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C. Impact of Dust Radiation Effect on Simulations of Temperature and Wind—A Case Study in Taklimakan Desert. Atmos. Res. 2022, 273, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liao, H.; Chang, W.; Liu, R. Direct Radiative Forcing by Dust in China Based on Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Model Intercomparison Project(ACCMIP) Datasets. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 40, 1242–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Ruiz-Arias, J.A.; Kleissl, J. Dissecting Surface Clear Sky Irradiance Bias in Numerical Weather Prediction: Application and Corrections to the New Goddard Shortwave Scheme. Sol. Energy 2016, 132, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, M.B.; Mitchell, K.E.; Lin, Y.; Rogers, E.; Grunmann, P.; Koren, V.; Gayno, G.; Tarpley, J.D. Implementation of Noah Land Surface Model Advances in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction Operational Mesoscale Eta Model. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 2002JD003296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-H.; Sun, W.-Y. A One-Dimensional Time Dependent Cloud Model. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 80, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjić, Z.I. The Step-Mountain Coordinate: Physical Package. Mon. Weather Rev. 1990, 118, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjić, Z.I. The Step-Mountain Eta Coordinate Model: Further Developments of the Convection, Viscous Sublayer, and Turbulence Closure Schemes. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122, 927–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Chin, M.; Tegen, I.; Prospero, J.M.; Holben, B.; Dubovik, O.; Lin, S.-J. Sources and Distributions of Dust Aerosols Simulated with the GOCART Model. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 20255–20273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, M.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ru, X.; Song, H. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Spring Dust Concentrations from 2000 to 2020 in China: Simulations with WRF-Chem. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, C.; Zhou, S. Simulation and Evaluation of Dust Emissions with WRF-Chem (v3.7.1) and Its Relationship to the Changing Climate over East Asia from 1980 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Feng, T.; Zhao, D.; Zang, Z.; Liao, S.; Ma, X.; Jiang, N.; et al. Dust Modeling over East Asia during the Summer of 2010 Using the WRF-Chem Model. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 213, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Fu, J.S.; Huang, K.; Zhu, Q.; Tipton, M. Regional Climate Effects of Biomass Burning and Dust in East Asia: Evidence From Modeling and Observation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 11490–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.T.; Li, K.; Wei, Q.; Wen, W. The Optical Properties of East Asian Dust Aerosol and Its Impact on Radiative Forcing and Temperature. J. Desert Res. 2016, 36, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Ma, J. Numerical Simulation of Aerosol Direct Radiation Forcing over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Environ. Res. 2021, 26, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L. Estimation of the Dust Aerosol Shortwave Direct Forcing Over Land Based on an Equi-albedo Method From Satellite Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 8793–8807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.; Fonseca, R.; Nelli, N.; Bozkurt, D.; Cuesta, J.; Bosc, E. On the Middle East’s severe dust storms in spring 2022: Triggers and impacts. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 296, 119539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, M.; Mahowald, N.M.; Conley, A.J.; Collins, W.D.; Fillmore, D.W.; Zender, C.S.; Coleman, D.B. Impact of Desert Dust Radiative Forcing on Sahel Precipitation: Relative Importance of Dust Compared to Sea Surface Temperature Variations, Vegetation Changes, and Greenhouse Gas Warming. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 1445–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Zheng, Y. A modeling study of global radiative forcing due to dust aerosol. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2009, 67, 510–521. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y. The optical depth global distribution of dust aerosol and its possible reason analysis. Clim. Environ. Res. 2007, 12, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Kang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, G.; Liu, T.; Chen, C.; et al. The Influence of Dusts on Radiation and Temperature over the Eastern Asia with a Regional Climate Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, K.M. Asian Summer Monsoon Anomalies Induced by Aerosol Direct Forcing: The Role of the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2006, 26, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Liang, J.; Li, J.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shui, W.; Wang, Q. Ecological sustainability assessment of the carbon footprint in Fujian Province, southeast China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 15, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, R.; Bento, V.A.; Leng, S.; Qi, J.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Q. The effect of drought on vegetation gross primary productivity under different vegetation types across China from 2001 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.; Huete, A.; Cleverly, J.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Q. Spatiotemporal variations of dryland vegetation phenology revealed by satellite-observed fluorescence and greenness across the North Australian Tropical Transect. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.; Huete, A.; Cleverly, J.; Gao, S.; Yu, Q.; Meng, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Q. Assessing the impact of extreme droughts on dryland vegetation by multi-satellite solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Qi, J.; Leng, S.; Wang, Q. Long-term vegetation phenology changes and responses to preseason temperature and precipitation in Northern China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).