The Identification and Analysis of Long-Range Aerosol Transport Pathways with Layered Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization Datasets from 2006 to 2016
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CALIOP L3 Aerosol Observation Dataset
2.2. PBLH Reanalysis Data
2.3. Air Mass Forward Trajectories
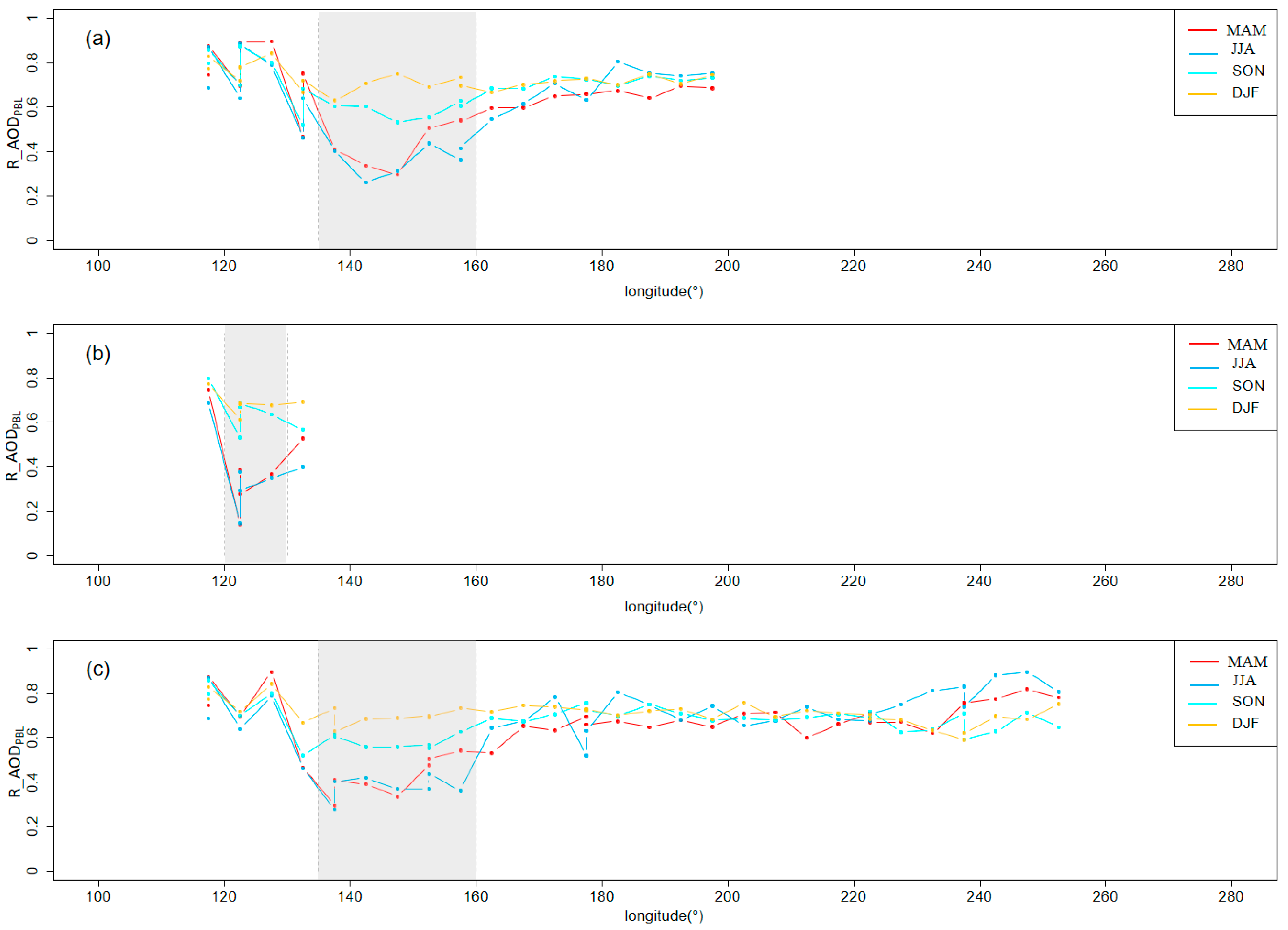
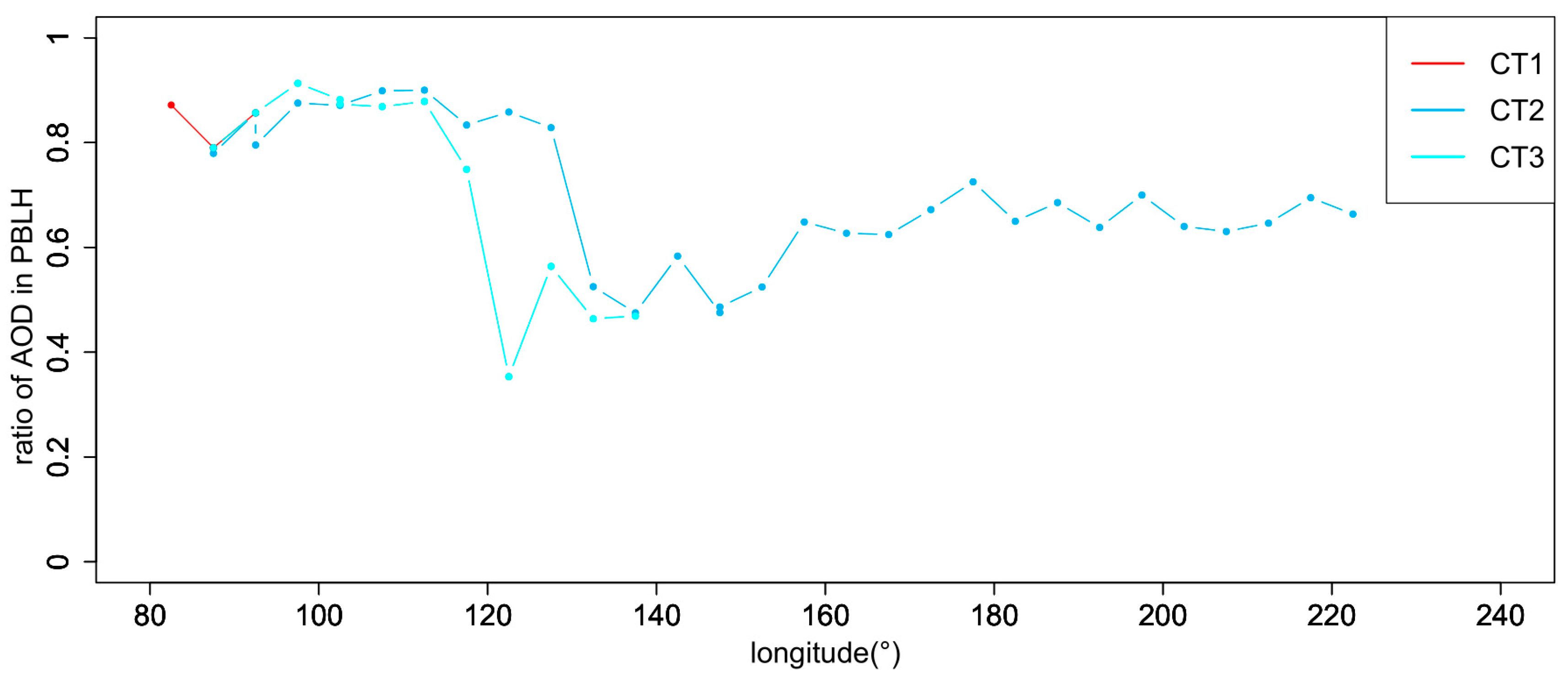
3. Results
3.1. Aerosol Transport Pathway Identification
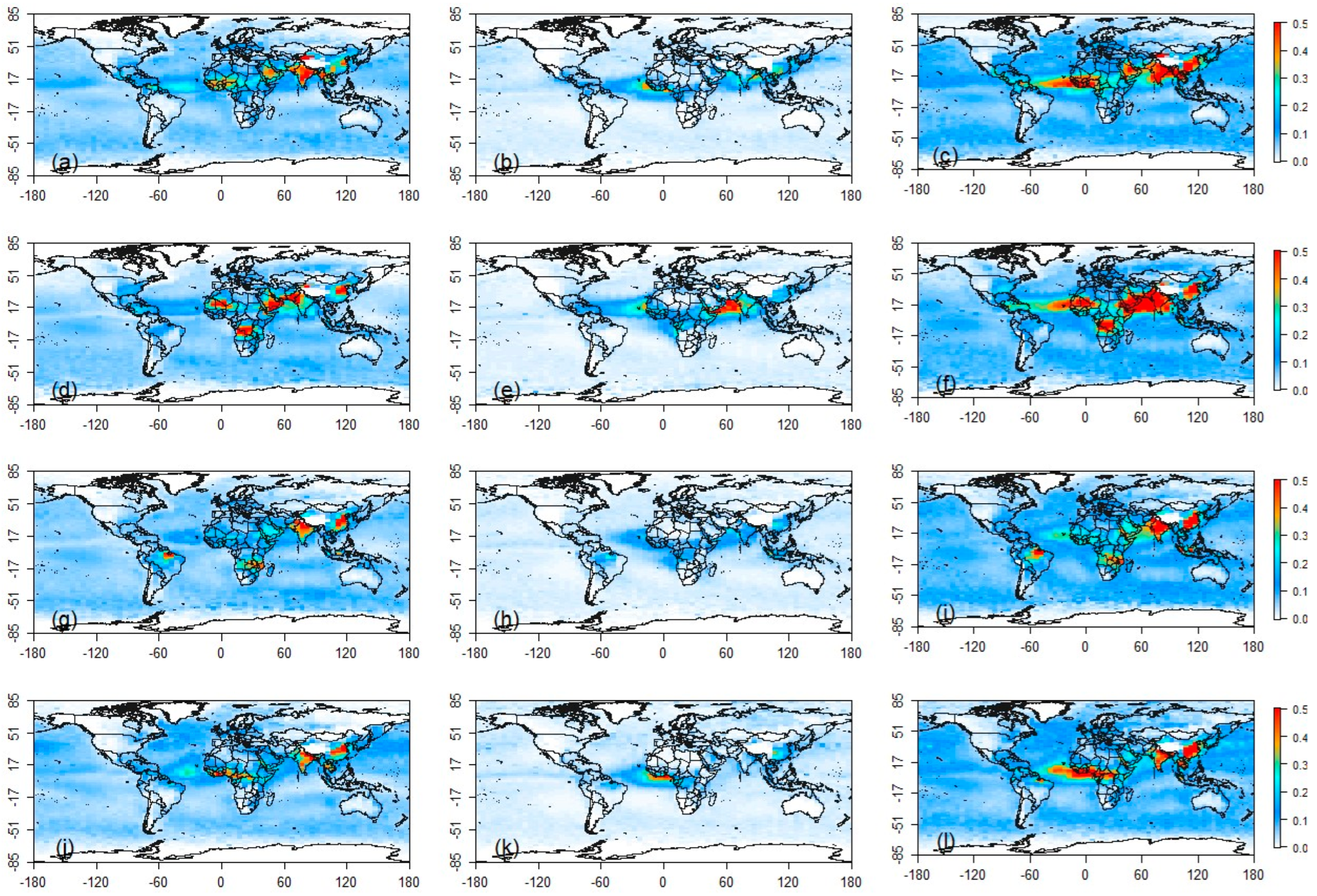
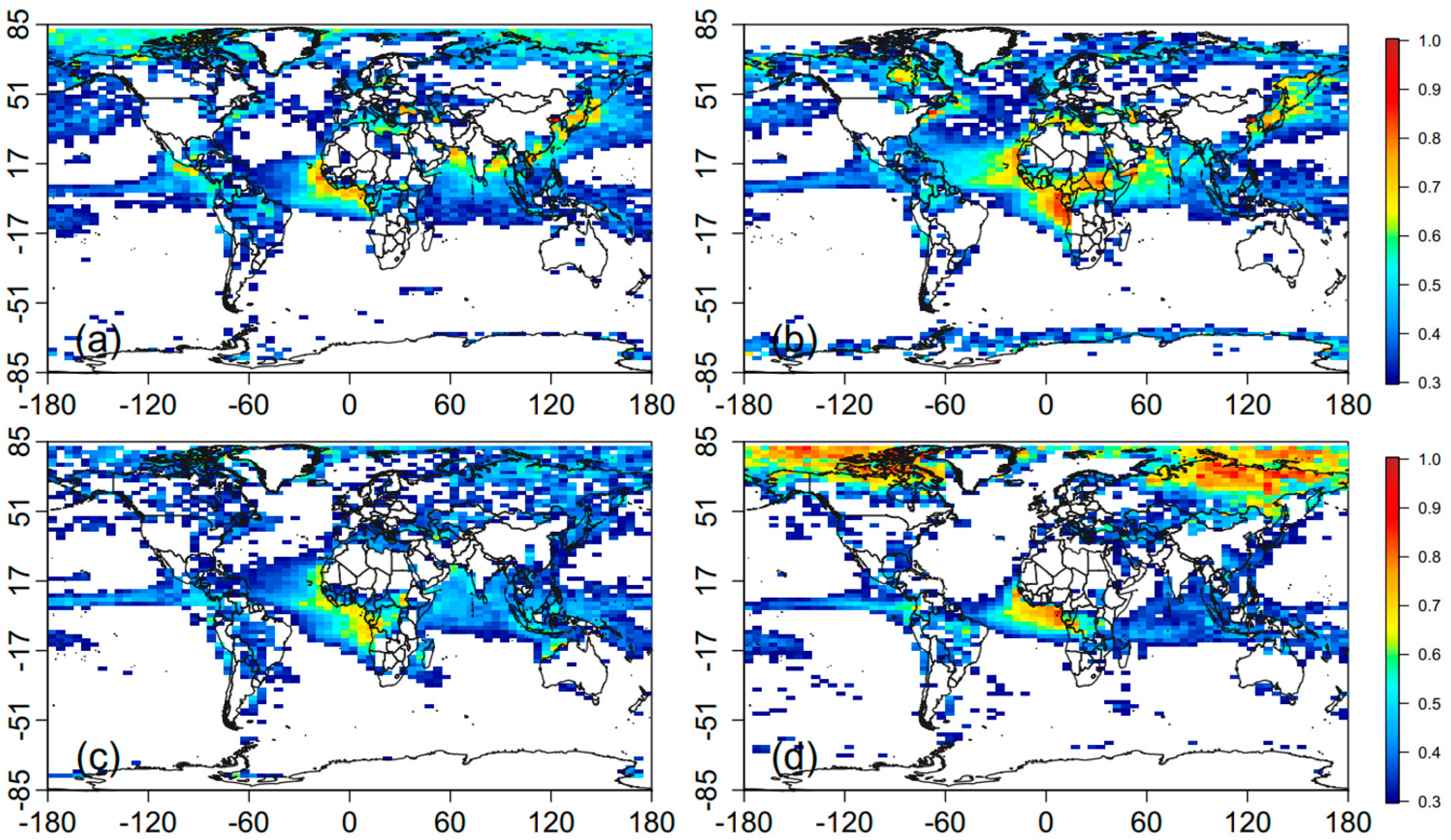
3.1.1. Generation of Global Distributions of High AOD Values
3.1.2. Identification of Global Aerosol Transport Pathways
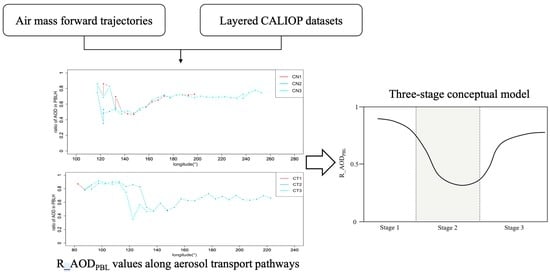
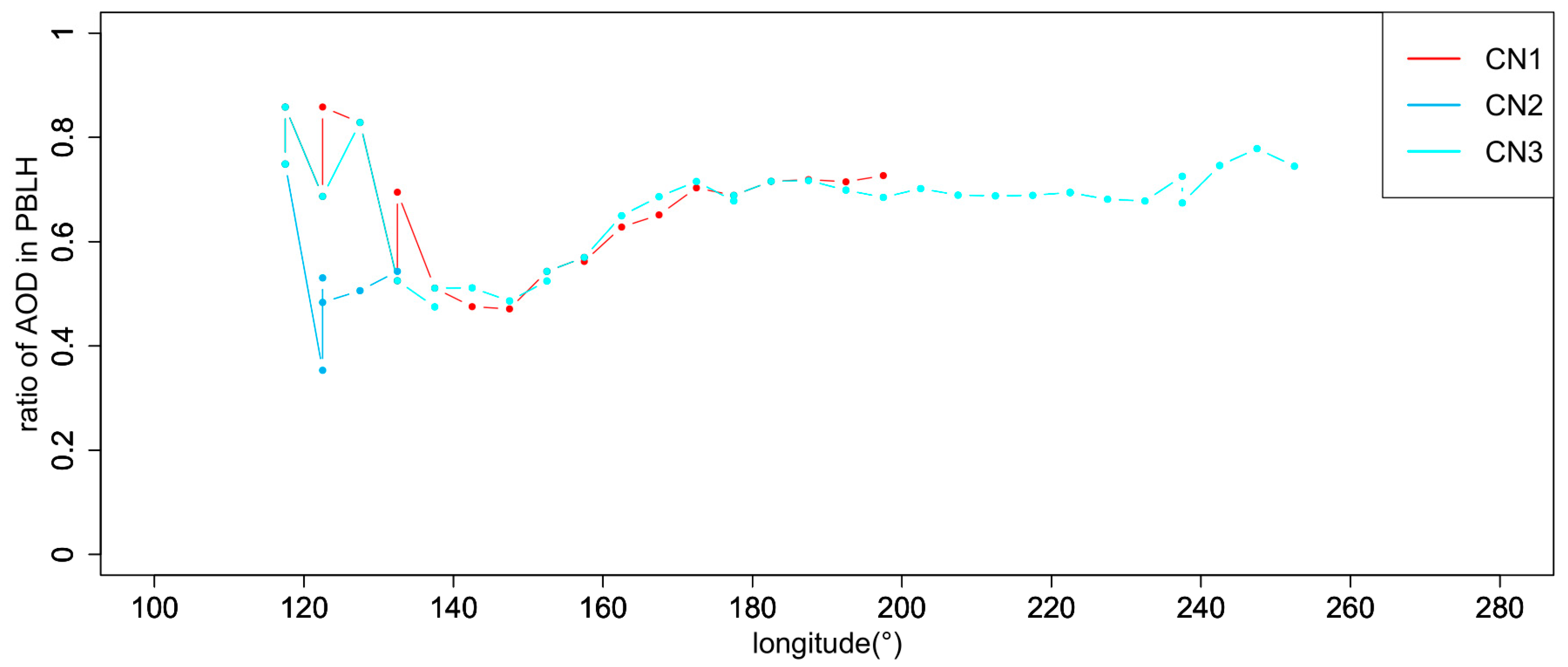
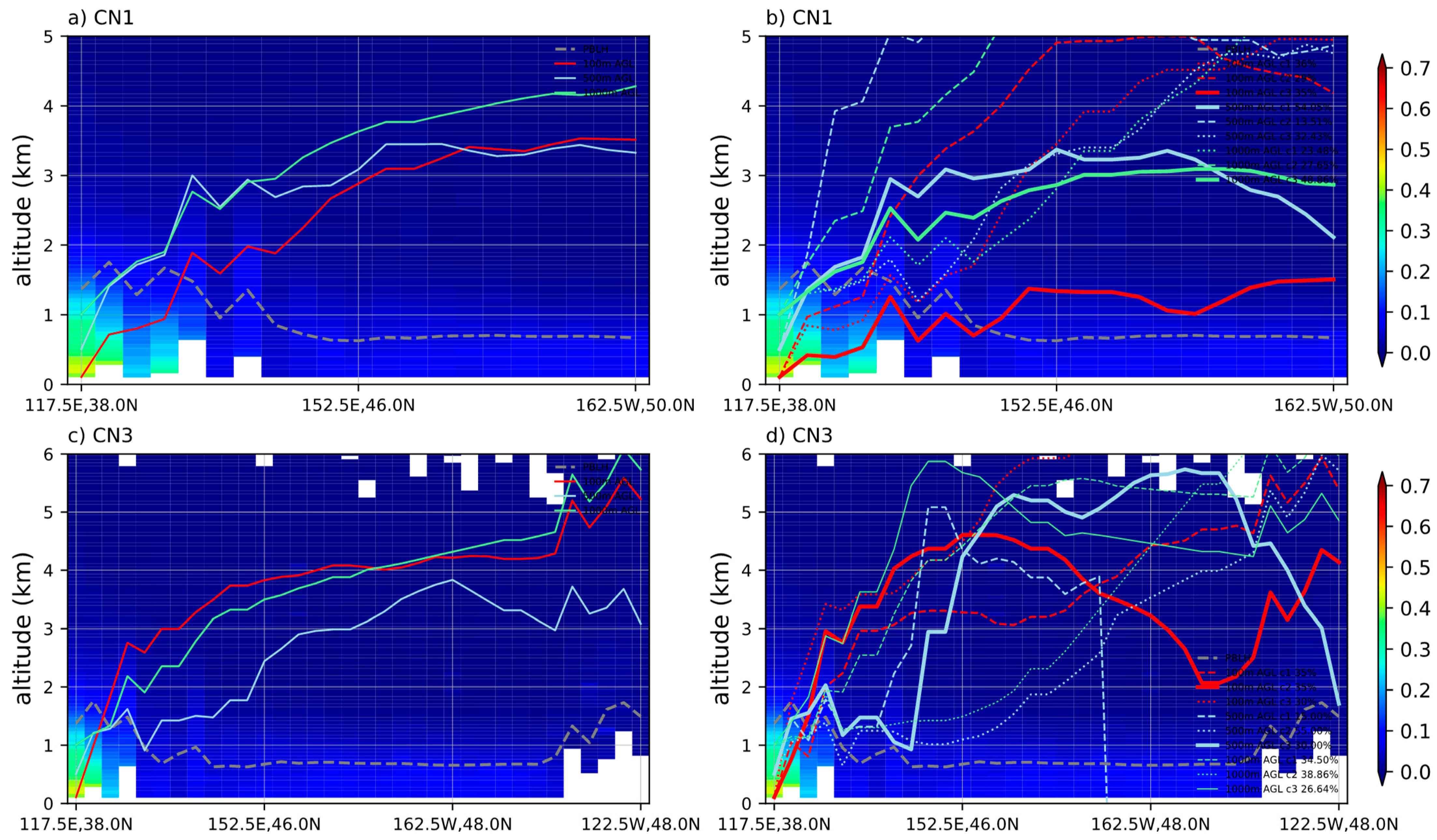
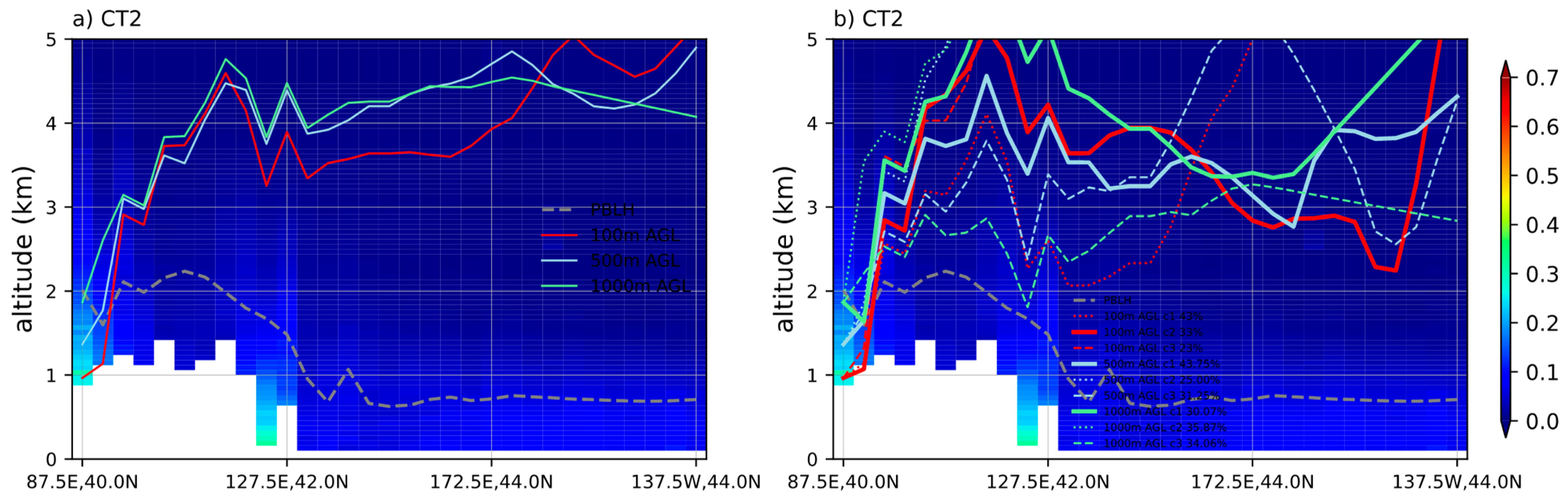
3.2. Three-Stage Conceptual Model
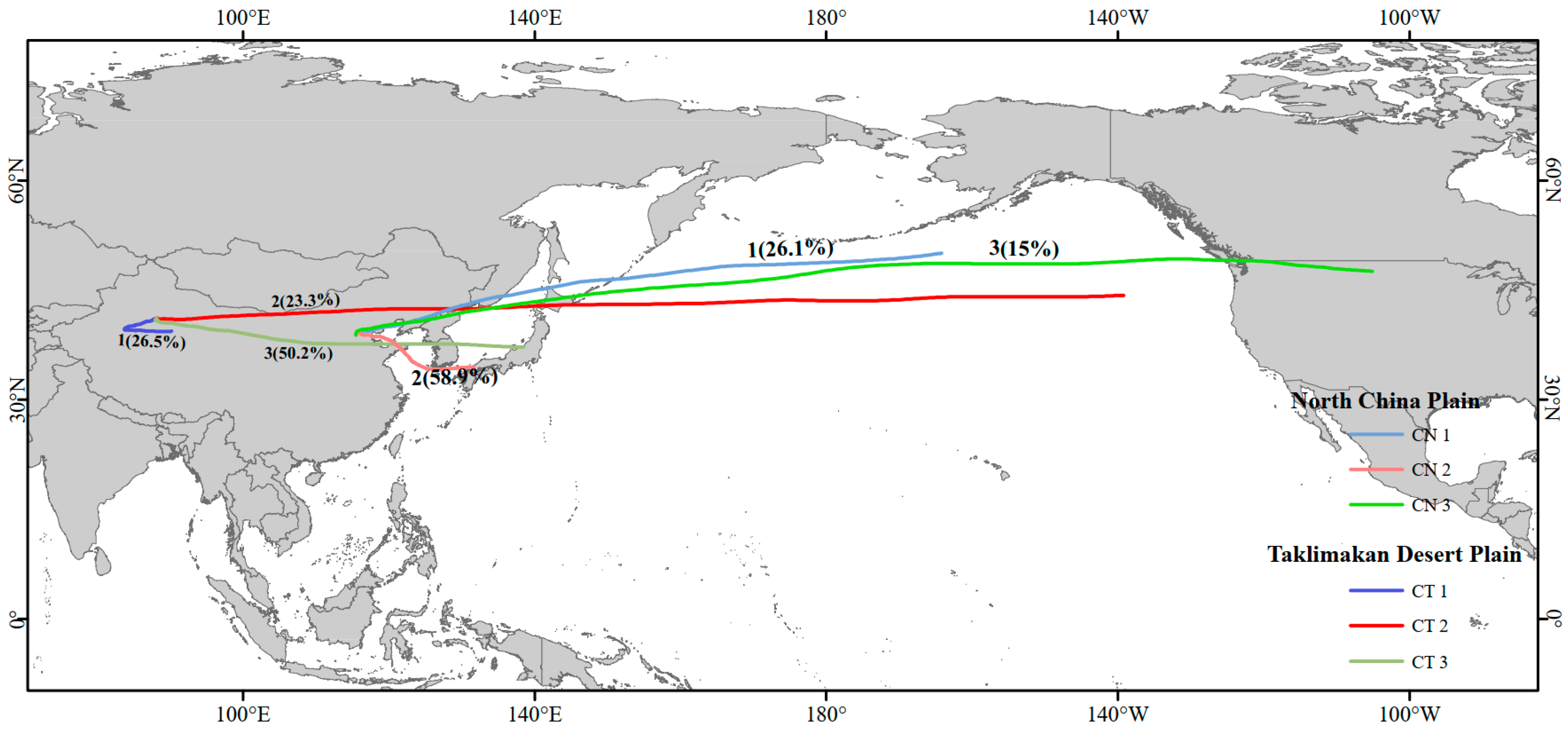
3.2.1. Polluted Dust Aerosol Transport Pathway
3.2.2. Dust Aerosol Transport Pathway
4. Conclusions and Discussions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, D.; Song, Y.; Liu, B. Visibility trends in six megacities in China 1973–2007. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Saide, P.E.; Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pagowski, M.; Guttikunda, S.K.; Carmichael, G.R. Estimates of health impacts and radiative forcing in winter haze in eastern China through constraints of surface PM2.5 predictions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Kong, L.; Du, C.; Zhanzakova, A.; Wang, L.; Fu, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Cheng, T. Long-range and regional transported size-resolved atmospheric aerosols during summertime in urban Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stier, P.; Feichter, J.; Kinne, S.; Kloster, S.; Vignati, E.; Wilson, J.; Ganzeveld, L.; Tegen, I.; Werner, M.; Balkanski, Y.; et al. The aerosol-climate model ECHAM5-HAM. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1125–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, K.S.; Boucher, O.; Spracklen, D.V.; Mann, G.W.; Rae, J.G.L.; Woodward, S.; Kulmala, M. A review of natural aerosol interactions and feedbacks within the Earth system. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 1701–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rap, A.; Scott, C.E.; Spracklen, D.V.; Bellouin, N.; Forster, P.M.; Carslaw, K.S.; Schmidt, A.; Mann, G. Natural aerosol direct and indirect radiative effects. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3297–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentener, F.; Kinne, S.; Bond, T.; Boucher, O.; Cofala, J.; Generoso, S.; Ginoux, P.; Gong, S.; Hoelzemann, J.J.; Ito, A.; et al. Emissions of primary aerosol and precursor gases in the years 2000 and 1750 prescribed data-sets for AeroCom. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 4321–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qian, X. Mortality effects assessment of ambient PM2.5 pollution in the 74 leading cities of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, D.Y.H.; Chen, S.-C.; Zuo, Z. PM2.5 in China: Measurements, sources, visibility and health effects, and mitigation. Particuology 2014, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chin, M.; Bian, H.; Yuan, T.; Prospero, J.M.; Omar, A.H.; Remer, L.A.; Winker, D.M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Quantification of trans-Atlantic dust transport from seven-year (2007–2013) record of CALIPSO lidar measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Garay, M.J.; Notaro, M. Climatology in Asian dust activation and transport based on MISR satellite observations and trajectory analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 1, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, O.L.; Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G.R.; Tang, Y.; Corrigan, C.E.; Roberts, G.C.; Mauger, G.S. Trans-Pacific transport of black carbon and fine aerosols (D < 2.5 μm) into North America. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D05309. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Huang, J.; Ruby, L.L.; Qian, Y.; Yu, H.; Huang, L.; Kalashnikova, O.V. Trans-Pacific transport and evolution of aerosols: Evaluation of quasi-global WRF-Chem simulation with multiple observations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1725–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Chin, M.; Yu, H.; Pan, X.; Bian, H.; Tan, Q.; Kahn, R.A.; Tsigaridis, K.; Bauer, S.E.; Takemura, T. Asian and trans-Pacific Dust: A Multimodel and Multiremote Sensing Observation Analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13534–13559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, P.; Joseph, P.; Arash, S. Geochemical Fingerprinting of Trans-Atlantic African Dust Based on Radiogenic Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopes and Rare Earth Element Anomalies. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2015, 17, EGU2015-1328. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Remer, L.A.; Chin, M.; Bian, H.; Kleidman, R.G.; Diehl, T. A satellite-based assessment of transpacific transport of pollution aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D14S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tan, Q.; Chin, M.; Bian, H.; Kim, D.; Winker, D.M.; Levy, R.C.; Zhang, Z.; Remer, L.A.; Kahn, R.A.; et al. Estimates of African Dust Deposition Along the Trans-Atlantic Transit Using the Decadelong Record ofAerosol Measurements from CALIOP, MODIS, MISR, and IASI. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7975–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.; Clemente-Colón, P.; Nalli, N.R.; Joseph, E.; Armstrong, R.A.; Detrés, Y.; Goldberg, M.D.; Minnett, P.J.; Lumpkin, R. Measuring Trans-Atlantic aerosol transport from Africa. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2011, 87, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-P.; Lu, C.-H.; McQueen, J.; Lee, P. Application of satellite observations in con-junction with aerosol reanalysis to characterize long-range transport of African and Asian dust on air quality in the contiguous U.S. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 174–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.; Rappenglueck, B.; Eltahir, E.A.B. The climatology of dust aerosol over the arabian peninsula. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1523–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Rahn, K.A.; Borys, R.D.; Shaw, G.E. The Asian source of Arctic haze bands. Nature 1977, 268, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Dey, S. Crop burning and forest fires: Long-term effect on adolescent height in India. Atmos. Res. 2021, 65, 101244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.T.; Ullah, S.; Majeed, M.T.; Usman, A.; Andlib, Z. The shadow economy in South Asia: Dynamic effects on clean energy consumption and environmental pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 29265–29275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Luo, B.; Sun, X.; Sun, Z.; Deng, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Fusion Method Combining Ground-Level Observations with Chemical Transport Model Predictions Using an Ensemble Deep Learning Framework: Application in China to Estimate Spatiotemporally-Resolved PM2.5 Exposure Fields in 2014–2017. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7306–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Singh, N. Global trends of columnar and vertically distributed properties of aerosols with emphasis on dust, polluted dust and smoke—Inferences from 10-year long CALIOP observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, I.; Eguchi, K.; Yumimoto, K.; Takemura, T.; Shimizu, A.; Uematsu, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hara, Y.; Sugimoto, N. Asian dust transported one full circuit around the globe. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Remer, L.A.; Chin, M.; Bian, H.; Tan, Q.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y. Aerosols from Overseas Rival Domestic Emissions over North America. Science 2012, 337, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Huang, R.-J.; Lin, C.; Xu, W.; Duan, J.; Gu, Y.; Huang, W.; Ni, H.; Zhu, C.; You, Y.; et al. Measurement report: On the contribution of long-distance transport to the secondary aerosol formation and aging. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 9513–9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.L.; Gong, S.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Blanchet, J.-P.; McKendry, I.G.; Zhou, Z.J. A Simulated Climatology of Asian Dust Aerosol and Its Trans-Pacific Transport. Part I: Mean Climate and Validation. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, Y.; Matsui, H.; Taketani, F.; Pan, X.; Komazaki, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chang, L.; Kang, D.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.-Y.; et al. Observed and Modeled Mass Concentrations of Organic Aerosols and PM2.5 at Three Remote Sites around the East China Sea: Roles of Chemical Aging. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 3091–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, Y.; Miyazaki, K.; Taketani, F.; Miyakawa, T.; Takashima, H.; Komazaki, Y.; Pan, X.; Kato, S.; Sudo, K.; Sekiya, T.; et al. Ozone and carbon monoxide observations over open oceans on R/V Mirai from 67°S to 75°N during 2012 to 2017: Testing global chemical reanalysis in terms of Arctic processes, low ozone levels at low latitudes, and pollution transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 7233–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, Y.; Yamaji, K.; Miyakawa, T.; Taketani, F.; Zhu, C.; Choi, Y.; Komazaki, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Kondo, Y.; Klimont, Z. Rapid reduction in black carbon emissions from China: Evidence from 2009–2019 observations on Fukue Island, Japan. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6339–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Uno, I.; Yumimoto, K.; Takemura, T.; Shimizu, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Liu, Z. Trans-pacific dust transport: Integrated analysis of NASA/CALIPSO and a global aerosol transport model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 3137–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Yang, X.; Zhao, T.; He, Q.; Mamtimin, A.; Wang, M.; Huo, W.; Yang, F.; Zhou, C.; Pan, H. Simulated regional transport structures and budgets of dust aerosols during a typical springtime dust storm in the Tarim Basin, Northwest China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 238, 104892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, Q.; Ekman, A.M.L.; Renard, J.-B.; Krejci, R.; Devasthale, A.; Bender, F.A.-M.; Riipinen, I.; Berthet, G.; Tackett, J.L. How much of the global aerosol optical depth is found in the boundary layer and free troposphere? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7709–7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lyu, B.; Bai, Y. Global aerosol vertical structure analysis by clustering gridded CALIOP aerosol profiles with fuzzy k-means. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukurov, K.A.; Simonenkov, D.V.; Nevzorov, A.V.; Rashki, A.; Hamzeh, N.H.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Shukurova, L.M.; Chkhetiani, O.G. CALIOP-Based Evaluation of Dust Emissions and Long-Range Transport of the Dust from the Aral−Caspian Arid Region by 3D-Source Potential Impact (3D-SPI) Method. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackett, J.L.; Winker, D.M.; Getzewich, B.J.; Vaughan, M.A.; Young, S.A.; Kar, J. CALIPSO lidar level 3 aerosol profile product: Version 3 algorithm design. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4129–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the HYSPLIT 4 modeling system for trajectories, dispersion, and deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.H.; Chen, K.; Adams, P.J. Development of a global model of mineral dust aerosol microphysics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2441–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; Tegen, I.; Perlwitz, J. Surface radiative forcing by soil dust aerosols and the hydrologic cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D04203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lyu, B.; Bai, Y. Aerosol vertical profile variations with seasons, air mass movements and local PM2.5 levels in three large China cities. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhao, T.; Kang, S. Long range trans-Pacific transport and deposition of Asian dust aerosols. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, P.P.; Tchakerian, V.P.; Tindale, N.W. Aerosols over the Arabian Sea: Geochemistry and source areas for aeolian desert dust. J. Arid. Environ. 1998, 39, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Merino, C.; Mateos, D.; Toledano, C.; Prospero, J.M.; Molinie, J.; Euphrasie-Clotilde, L.; González, R.; Cachorro, V.E.; Calle, A.; Frutos, A.M.d. Impact of long-range transport over the Atlantic Ocean on Saharan dust optical and microphysical properties based on AERONET data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9411–9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lou, M.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, H.; He, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Min, M.; et al. Trans-Pacific transport of dust aerosols from East Asia: Insights gained from multiple observations and modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelle, W.; Balkanski, Y.J.; Schulz, M.; Dulac, F.; Monfray, P. Wet deposition in a global size-dependent aerosol transport model: 1. Comparison of a 1-year 210Pb simulation with ground measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 11429–11445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Gong, S.L.; Zhou, C.H.; Hu, X.Q.; Liu, H.L.; Niu, T.; Yang, Y.Q. Surface observation of sand and dust storm in East Asia and its application in CUACE/Dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-X.; Sharratt, B.; Liu, L.-Y.; Wang, Z.-F.; Pan, X.-L.; Lei, J.-Q.; Wu, S.-X.; Huang, S.-Y.; Guo, Y.-H.; Li, J.; et al. East Asian dust storm in May 2017: Observations, modeling, and its influence on the Asia-Pacific region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 8353–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Lyu, B.; Zhang, J.; Han, Y.; Bai, Y.; Guo, Z. The Identification and Analysis of Long-Range Aerosol Transport Pathways with Layered Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization Datasets from 2006 to 2016. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184537
Wang L, Wang W, Lyu B, Zhang J, Han Y, Bai Y, Guo Z. The Identification and Analysis of Long-Range Aerosol Transport Pathways with Layered Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization Datasets from 2006 to 2016. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(18):4537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184537
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lingyu, Wensheng Wang, Baolei Lyu, Jinghua Zhang, Yilun Han, Yuqi Bai, and Zhi Guo. 2023. "The Identification and Analysis of Long-Range Aerosol Transport Pathways with Layered Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization Datasets from 2006 to 2016" Remote Sensing 15, no. 18: 4537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184537
APA StyleWang, L., Wang, W., Lyu, B., Zhang, J., Han, Y., Bai, Y., & Guo, Z. (2023). The Identification and Analysis of Long-Range Aerosol Transport Pathways with Layered Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization Datasets from 2006 to 2016. Remote Sensing, 15(18), 4537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184537