Using Wavelet Coherence to Aid the Retrieval of Volcanic SO2 from UV Spectra
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- An efficient way to identify spectra which contain the signature of the volcanic plume.
- An objective means to validate results obtained using traditional fitting routines that typically necessitate a visual inspection of the fit results.
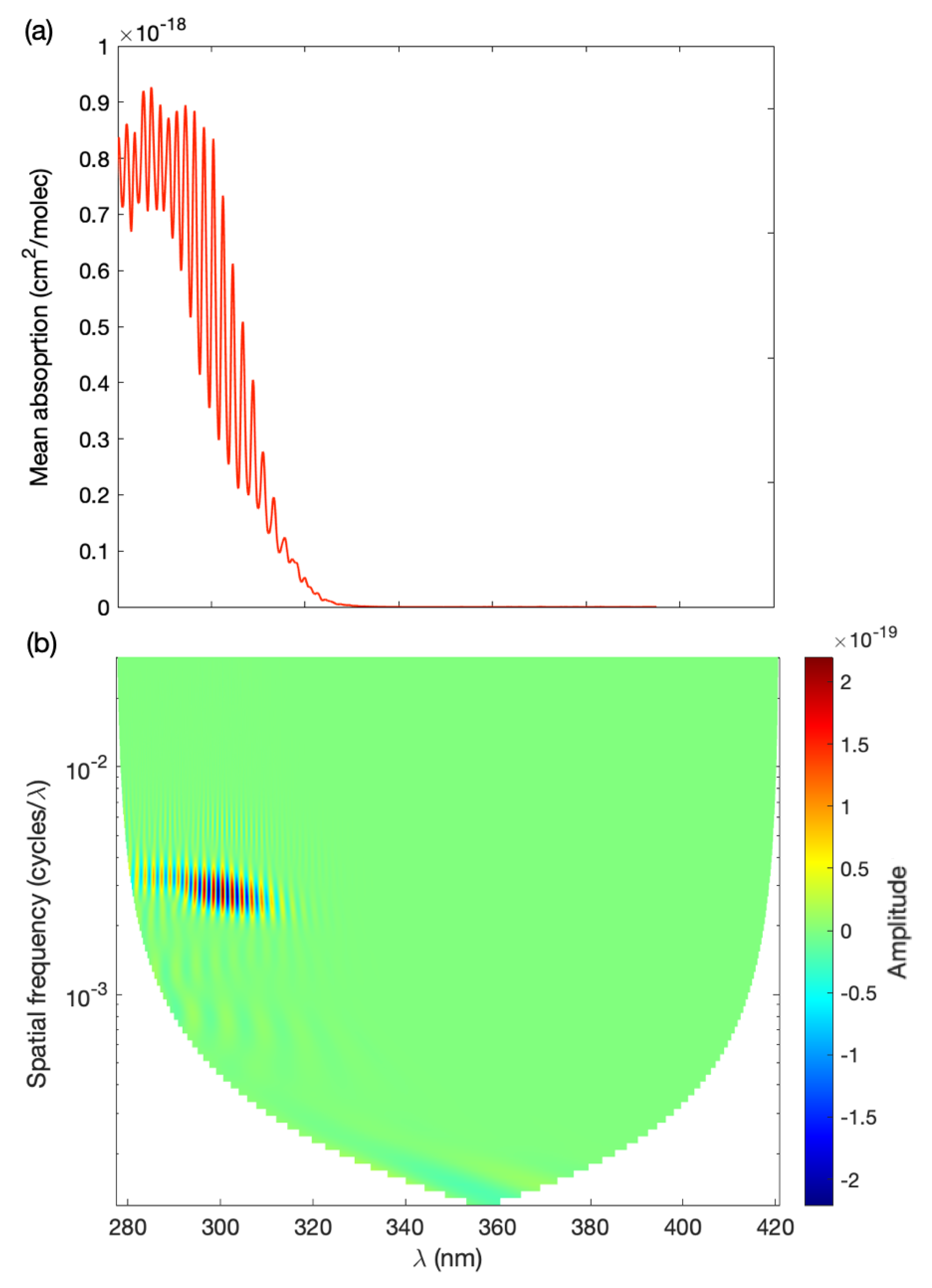
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Magnitude-Squared Wavelet Coherence (MSWC)
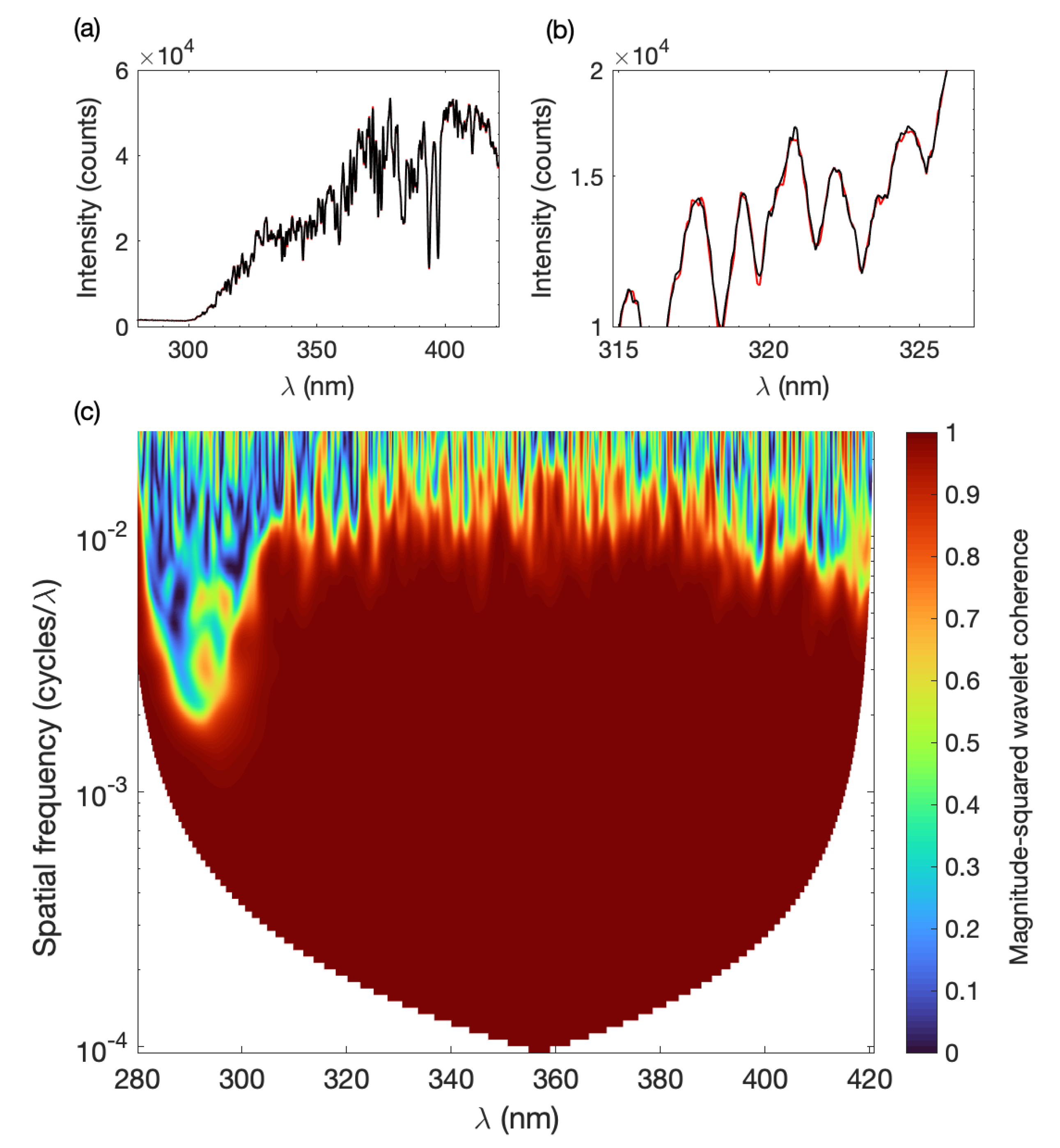
2.2. Spectral Analysis
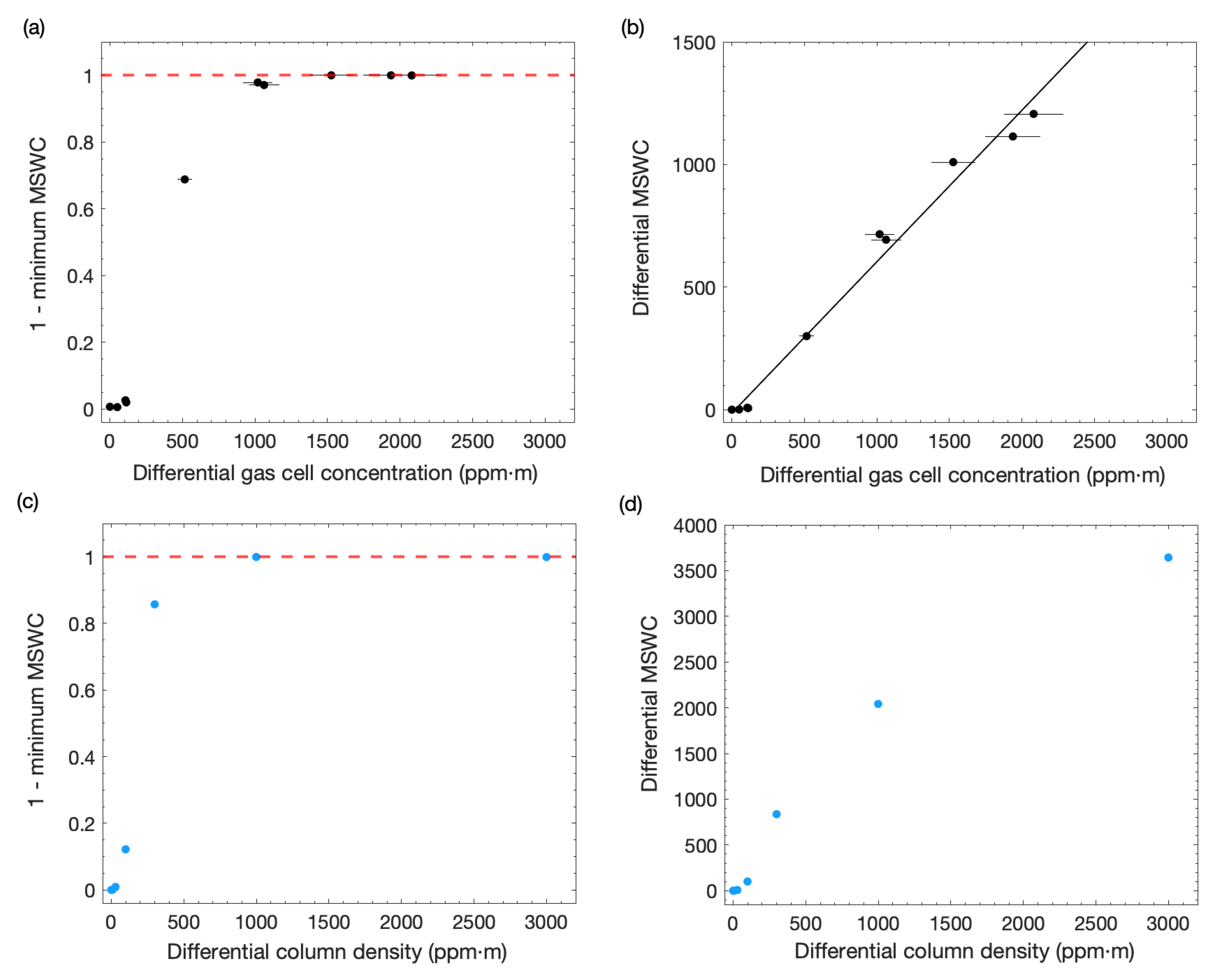
2.3. Application to Spectra of Volcanic Plumes
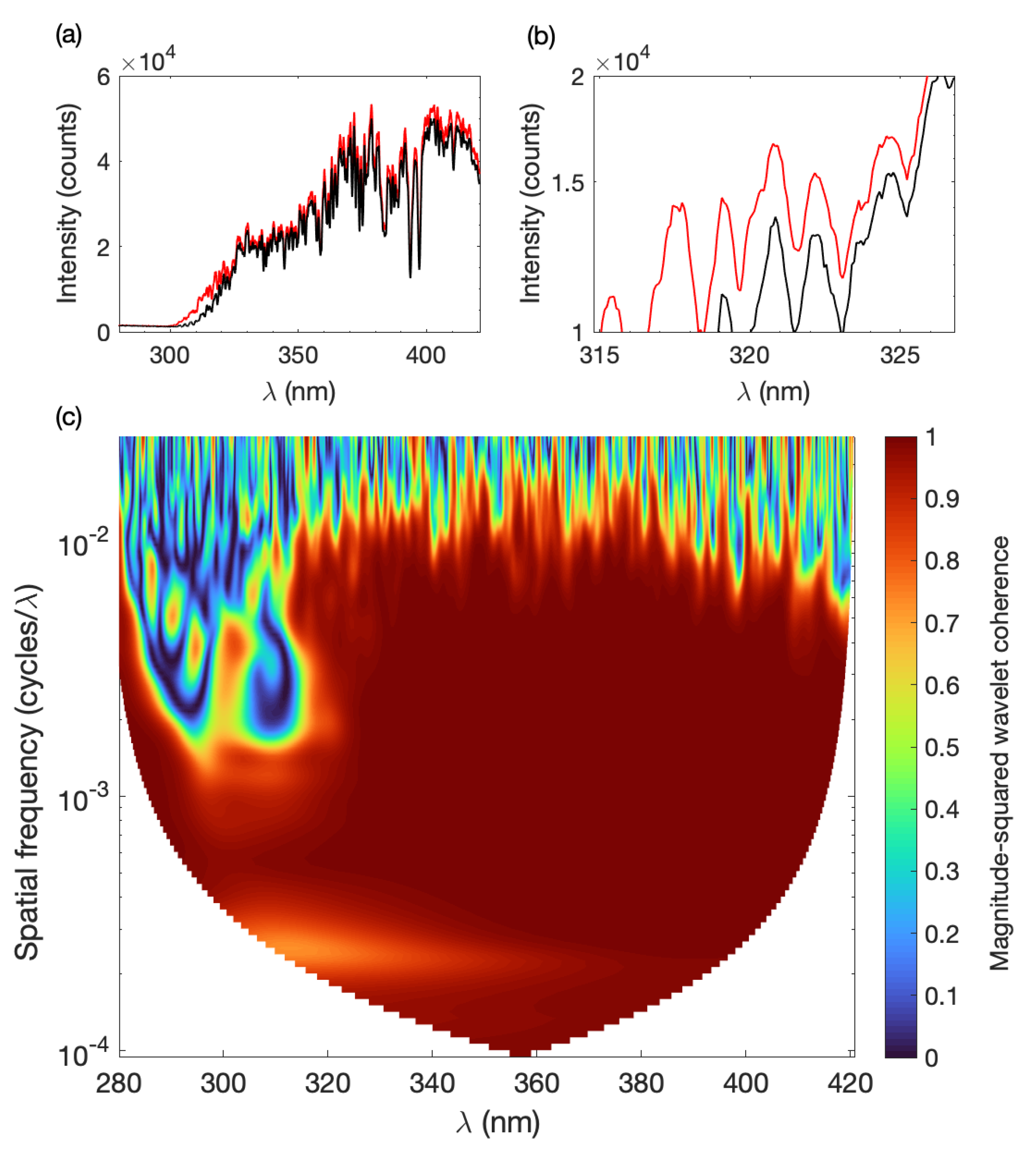
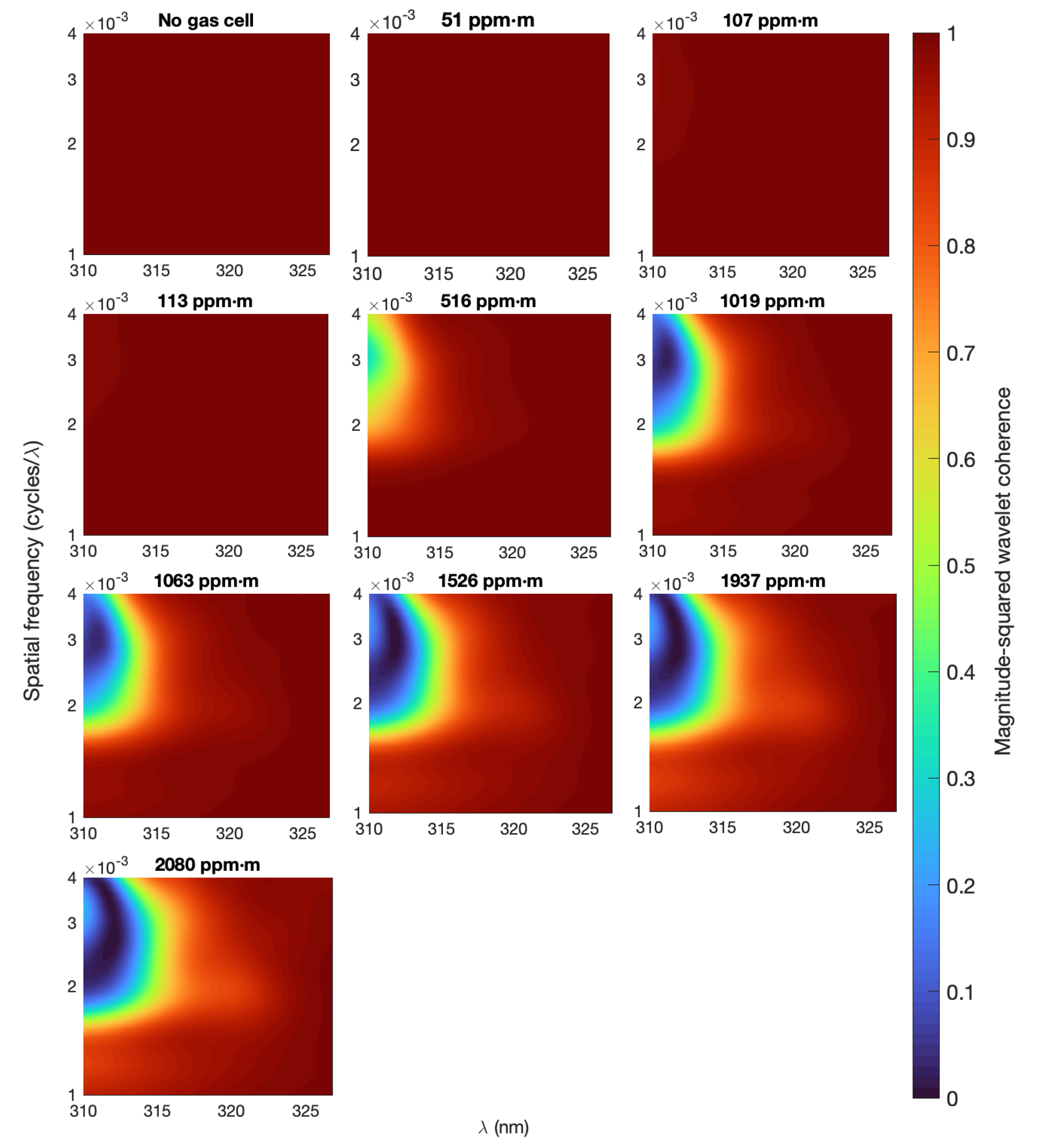
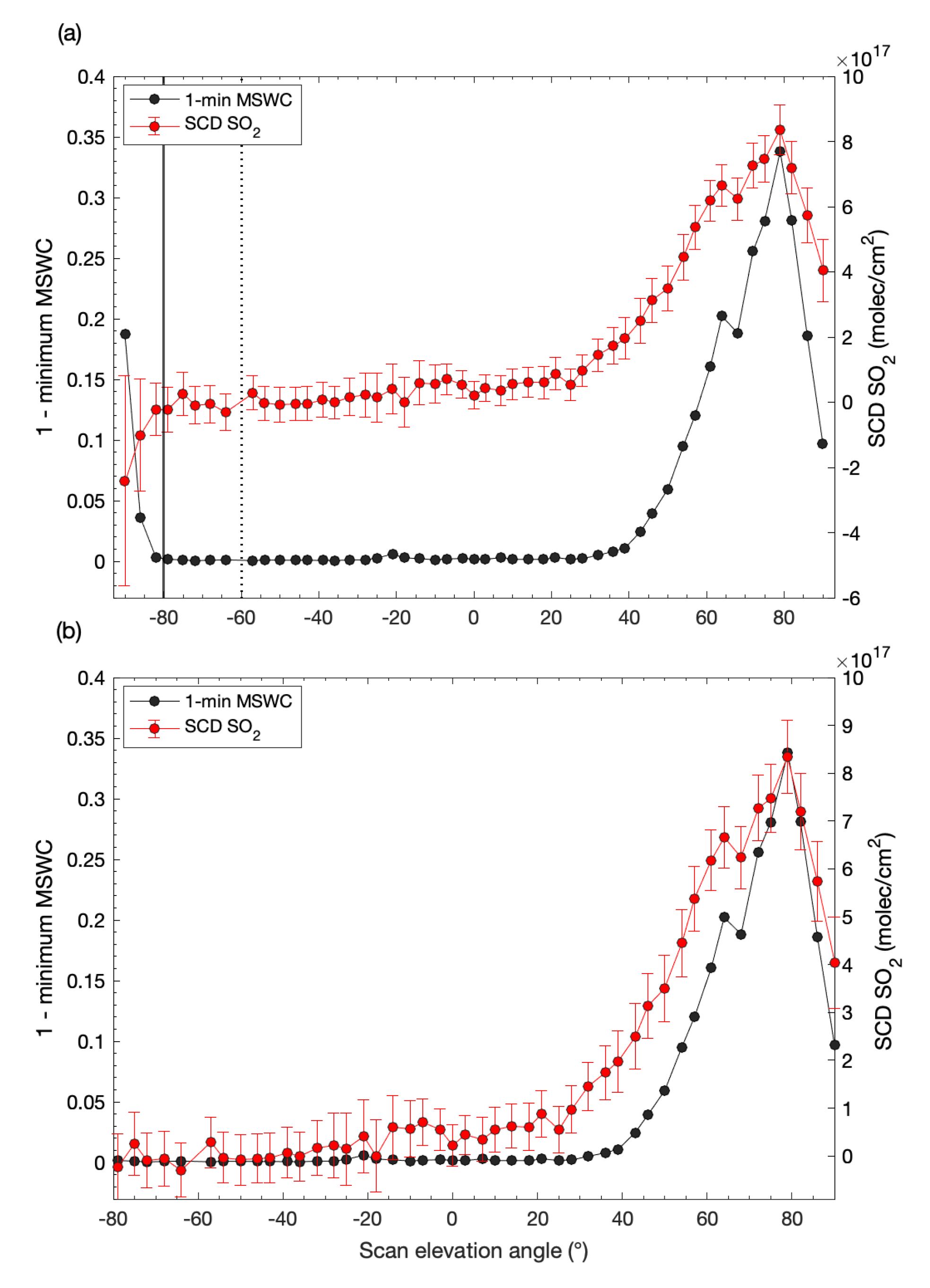
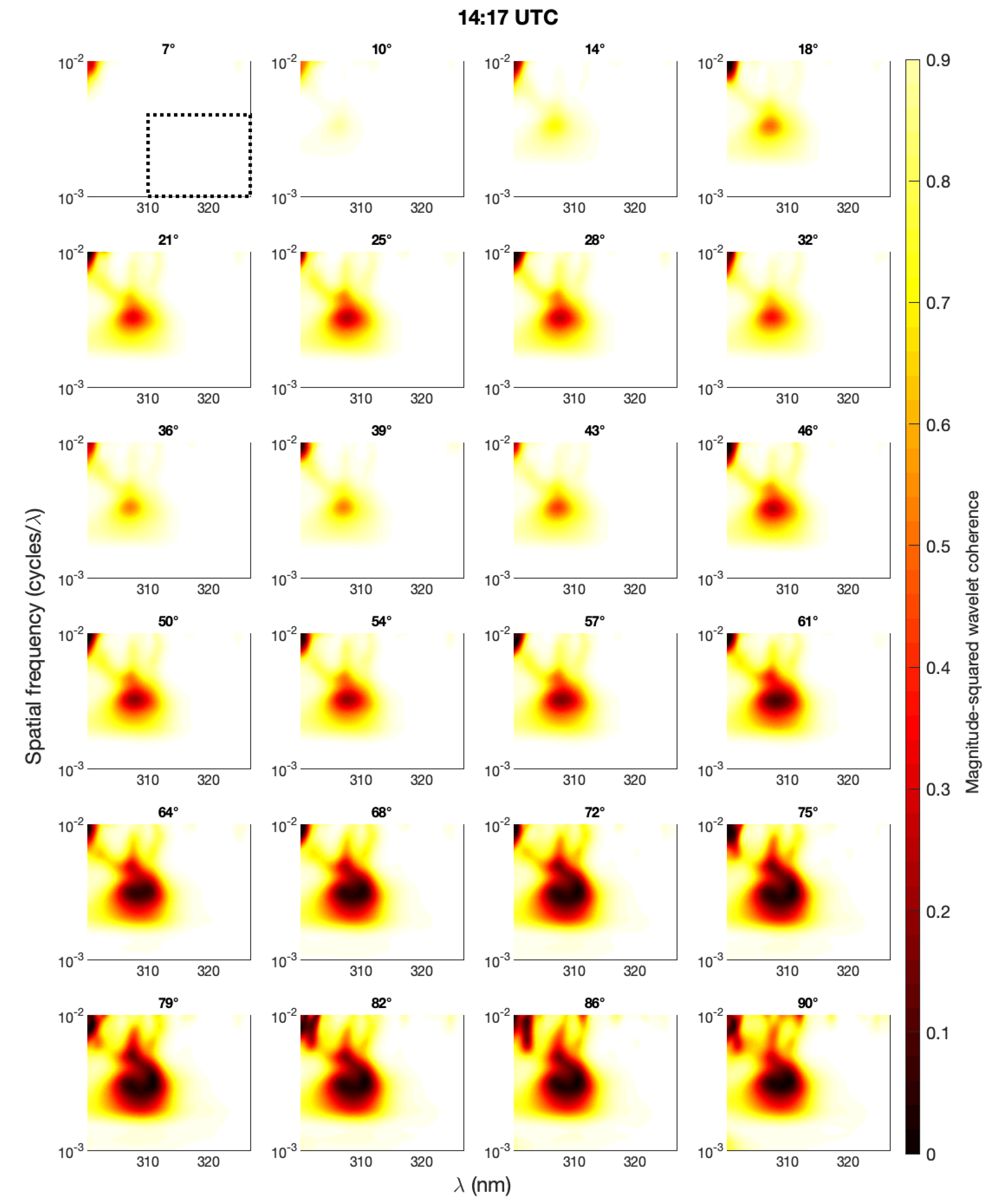
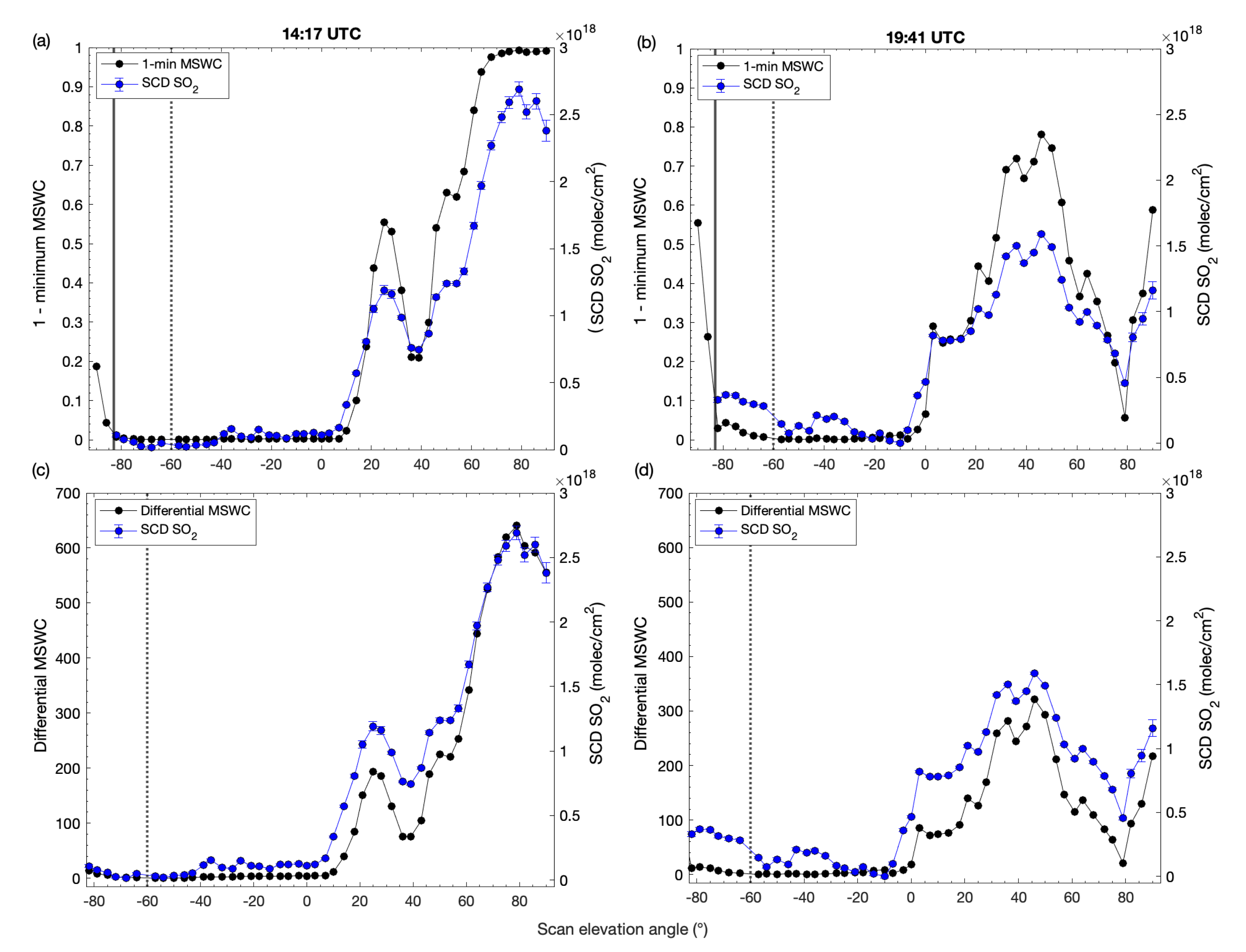
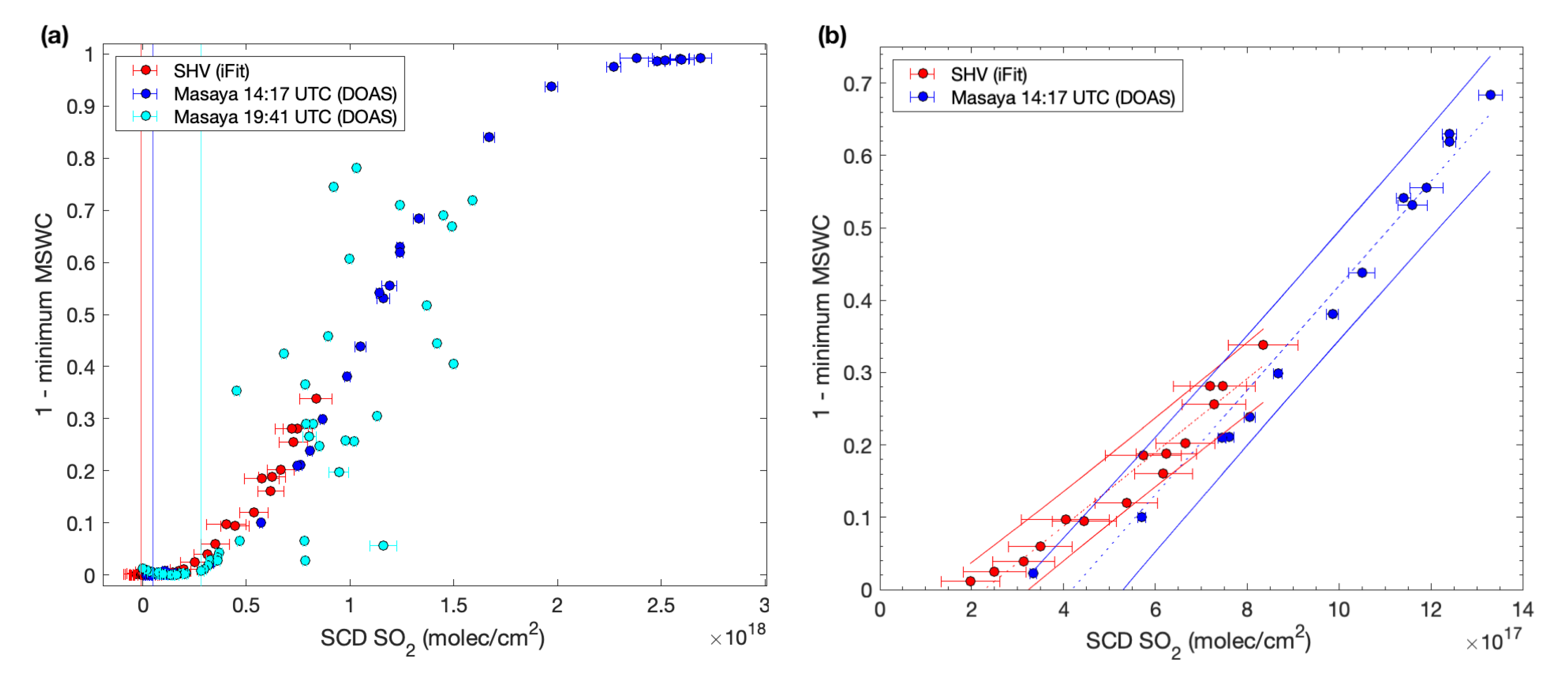
3. Results
3.1. Soufriere Hills Volcano
3.2. Masaya Volcano
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edmonds, M.; Oppenheimer, C.; Pyle, D.; Herd, R.; Thompson, G. SO2 emissions from Soufrière Hills Volcano and their relationship to conduit permeability, hydrothermal interaction and degassing regime. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2003, 124, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuppa, A.; Giudice, G.; Gurrieri, S.; Liuzzo, M.; Burton, M.; Caltabiano, T. Total volatile flux from Mount Etna. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L24302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilliaert, N.; Allard, P.; Métrich, N.; Sobolev, A. Melt inclusion record of the conditions of ascent, degassing, and extrusion of volatile-rich alkali basalt during the powerful 2002 flank eruption of Mount Etna (Italy). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2006, 111, B04203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, A.; Elias, T.; Gerlach, T.; Stokes, J. Implications for eruptive processes as indicated by sulfur dioxide emissions from Kılauea Volcano, Hawaii, 1979–1997. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2001, 108, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazahaya, K.; Shinohara, H.; Uto, K.; Odai, M.; Nakahori, Y.; Mori, H. Gigantic SO2 emission from Miyakejima volcano, Japan, caused by caldera collapse. Geology 2004, 32, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M.; Caltabiano, T.; Murè, F.; Salerno, G.; Randazzo, D. SO2 flux from Stromboli during the 2007 eruption: Results from the FLAME network and traverse measurements. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2009, 182, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, S.; Battaglia, J.; Arellano, S.; Sierra, D.; Bernard, B.; Parra, R.; Kelly, P.; Dinger, F.; Barrington, C.; Samaniego, P. Evolution of the 2015 Cotopaxi eruption revealed by combined geochemical and seismic observations. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2018, 19, 2087–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, J.; Hidalgo, S.; Bernard, B.; Steele, A.; Arellano, S.; Acuña, K. Autopsy of an eruptive phase of Tungurahua volcano (Ecuador) through coupling of seismo-acoustic and SO2 recordings with ash characteristics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 511, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, M.; Herd, R.; Galle, B.; Oppenheimer, C. Automated, high time-resolution measurements of SO2 flux at Soufri re Hills Volcano, Montserrat. Bull. Volcanol. 2003, 65, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonigle, A.; Oppenheimer, C.; Hayes, A.; Galle, B.; Edmonds, M.; Caltabiano, T. Sulphur dioxide fluxes from Mount Etna, Vulcano, and Stromboli measured with an automated scanning ultraviolet spectrometer. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, B.; Johansson, M.; Rivera, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kihlman, M.; Kern, C.; Lehmann, T.; Platt, U.; Arellano, S.; Hidalgo, S. Network for Observation of Volcanic and Atmospheric Change (NOVAC)—A global network for volcanic gas monitoring: Network layout and instrument description. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, 05304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, T.; Pering, T.; McGonigle, A.; Willmott, J.; Bryant, R.; Smalley, A. The PiSpec: A Low-Cost, 3D-Printed Spectrometer for Measuring Volcanic SO2 Emission Rates. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonigle, A. Measurement of volcanic SO2 fluxes with differential optical absorption spectroscopy. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2007, 162, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, S.; Galle, B.; Apaza, F.; Avard, G.; Barrington, C.; Bobrowski, N.; Bucarey, C.; Burbano, V.; Burton, M.; Chacón, Z.; et al. Synoptic analysis of a decade of daily measurements of SO2; emission in the troposphere from volcanoes of the global ground-based Network for Observation of Volcanic and Atmospheric Change. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 1167–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, C.; Deutschmann, T.; Vogel, L.; Wöhrbach, M.; Wagner, T.; Platt, U. Radiative transfer corrections for accurate spectroscopic measurements of volcanic gas emissions. Bull. Volcanol. 2010, 72, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Mori, T.; Kazahaya, K.; Ohwada, M.; Hirabayashi, J.; Yoshikawa, S. Effect of UV scattering on SO2 emission rate measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 17315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnam, M.; Burton, M.; Esse, B.; Kazahaya, R.; Salerno, G.; Caltabiano, T.; Ibarra, M. Quantifying Light Dilution in Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Measurements of Volcanic SO2 Using Dual-Band Modeling. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 528753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer. Bestimmung der Absorption des Rothen Lichts in Farbigen Flüssigkeiten. Ann. Der Phys. 1852, 162, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguer, P. Essai d’Optique, sur la Gradation de la Lumière; Claude Jombert: Paris, France, 1729. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, I. Photometria Sive de Mensura et Gradibus Luminis, Colorum et Umbrae; Eberhard Klett: Augsberg, Germany, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bogumil, K.; Orphal, J.; Homann, T.; Voigt, S.; Spietz, P.; Fleischmann, O.C.; Vogel, A.; Hartmann, M.; Kromminga, H.; Bovensmann, H.; et al. Measurements of molecular absorption spectra with the SCIAMACHY pre-flight model: Instrument characterization and reference data for atmospheric remote-sensing in the 230–2380 nm region. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 157, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, C.; Deutschmann, T.; Werner, C.; Sutton, A.; Elias, T.; Kelly, P. Improving the accuracy of SO2 column densities and emission rates obtained from upward-looking UV-spectroscopic measurements of volcanic plumes by taking realistic radiative transfer into account. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D20302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, Z.Y.W.; McLaren, R. Recommendations for spectral fitting of SO2 from miniature multi-axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 3993–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esse, B.; Burton, M.; Varnam, M.; Kazahaya, R.; Salerno, G. iFit: A simple method for measuring volcanic SO2 without a measured Fraunhofer reference spectrum. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2020, 402, 107000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübcke, P.; Bobrowski, N.; Arellano, S.; Galle, B.; Garzón, G.; Vogel, L. BrO/SO2 molar ratios from scanning DOAS measurements in the NOVAC network. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, L.; Sihler, H.; Lampel, J.; Wagner, T.; Platt, U. Retrieval interval mapping: A tool to visualize the impact of the spectral retrieval range on differential optical absorption spectroscopy evaluations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, A.; Tsanev, V.; Oppenheimer, C.; Edmonds, M. Reactive halogens (BrO and OClO) detected in the plume of Soufrière Hills Volcano during an eruption hiatus. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 3346–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliß, J.; Bobrowski, N.; Vogel, L.; Pöhler, D.; Platt, U. OClO and BrO observations in the volcanic plume of Mt. Etna—Implications on the chemistry of chlorine and bromine species in volcanic plumes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5659–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrington, C.; Costa Rodriguez, F.; Taisne, B. Exploiting the Frequency Signature of Trace Gas Absorption: A New Model to Quantify SO2 from UV Spectra of Volcanic Plumes. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; AGU Fall Meeting: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2021; Volume 2021, p. V41A-03. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiki, A.T.; Kyambikwa, A.M.; Namogo, D.B.; Diomi, L.N.; Munguiko, O.M.; Balezi, G.M.; Sifa, L.L.; Nzamu, S.M.; Mashagiro, N.; Balagizi, C.M.; et al. Analysis of the Seismicity Recorded before the May 22, 2021 Eruption of Nyiragongo Volcano, Democratic Republic of the Congo. J. Volcanol. Seismol. 2023, 17, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, E.; Mazzanti, P.; Mugnozza, G.S.; Bozzano, F. Coherency and phase delay analyses between land cover and climate across Italy via the least-squares wavelet software. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 118, 103241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cai, H.; Shi, H. Assessing the responses of vegetation to meteorological drought and its influencing factors with partial wavelet coherence analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Naseem, S.; Mohsin, M.; Bhutta, M.S. Recent analytical tools to mitigate carbon-based pollution: New insights by using wavelet coherence for a sustainable environment. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, H. Investigating the spatiotemporal variations of extreme rainfall and its potential driving factors with improved partial wavelet coherence. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 951468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah, M.A.; Morshed, S.R.; Kafy, A.A.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Rahman, M.T. Wavelet coherence analysis of PM2. 5 variability in response to meteorological changes in South Asian cities. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Song, C.; Chen, X. Clarifying the relationship between annual maximum daily precipitation and climate variables by wavelet analysis. Atmos. Res. 2023, 2023, 106981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, S. DOASIS: A Framework Design for DOAS; Shaker: Duren, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- MathWorks. MATLAB; The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gorshelev, V.; Serdyuchenko, A.; Weber, M.; Chehade, W.; Burrows, J.P. High spectral resolution ozone absorption cross-sections – Part 1: Measurements, data analysis and comparison with previous measurements around 293 K. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocean Insight. OceanView; Ocean Insight: Orlando, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vandaele, A.; Hermans, C.; Fally, S. Fourier transform measurements of SO2 absorption cross sections: II. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer. 2009, 110, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, K.; Kurucz, R. An improved high-resolution solar reference spectrum for earth’s atmosphere measurements in the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer. 2010, 111, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinger, F.; Bobrowski, N.; Warnach, S.; Bredemeyer, S.; Hidalgo, S.; Arellano, S.; Galle, B.; Platt, U.; Wagner, T. Periodicity in the BrO/SO2 molar ratios in the volcanic gas plume of Cotopaxi and its correlation with the Earth tides during the eruption in 2015. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 9, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnach, S.; Bobrowski, N.; Hidalgo, S.; Arellano, S.; Sihler, H.; Dinger, F.; Lübcke, P.; Battaglia, J.; Steele, A.; Galle, B.; et al. Variation of the BrO/SO2 molar ratio in the plume of Tungurahua Volcano between 2007 and 2017 and its relationship to volcanic activity. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOVAC Project. NOVAC Database. 2020. Available online: https://novac.chalmers.se/ (accessed on 24 April 2023).
- Lübcke, P.; Lampel, J.; Arellano, S.; Bobrowski, N.; Dinger, F.; Galle, B.; Garzón, G.; Hidalgo, S.; Chacón Ortiz, Z.; Vogel, L.; et al. Retrieval of absolute SO2 column amounts from scattered-light spectra: Implications for the evaluation of data from automated DOAS networks. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5677–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinger, F.; Kleinbek, T.; Dörner, S.; Bobrowski, N.; Platt, U.; Wagner, T.; Ibarra, M.; Espinoza, E. SO2 and BrO emissions of Masaya Volcano from 2014–2020. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9367–9404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan Chair, W.M. Remote Sensing Terminology. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1991, 41, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, C. Spectroscopic Measurements of Volcanic Gas Emissions in the Ultra-Violet Wavelength Region. Doctoral Dissertation, Heidelberg University, Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, U.; Marquard, L.; Wagner, T.; Perner, D. Corrections for zenith scattered light DOAS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 1759–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirle, S.; Sihler, H.; Wagner, T. Linearisation of the effects of spectral shift and stretch in DOAS analysis. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcher, B.; Guttorp, P.; Percival, D.B. Wavelet analysis of covariance with application to atmospheric time series. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 14941–14962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, R.G.; Lowe, R.P.; Mansinha, L. Localized cross-spectral analysis with phase-corrected wavelets. In Wavelet Applications III; Szu, H.H., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1996; Volume 2762, pp. 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrowski, N.; Kern, C.; Platt, U.; Hörmann, C.; Wagner, T. Novel SO2 spectral evaluation scheme using the 360–390 nm wavelength range. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fickel, M.; Delgado Granados, H. On the use of different spectral windows in DOAS evaluations: Effects on the estimation of SO2 emission rate and mixing ratios during strong emission of Popocatépetl volcano. Chem. Geol. 2017, 462, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theys, N.; De Smedt, I.; van Gent, J.; Danckaert, T.; Wang, T.; Hendrick, F.; Stavrakou, T.; Bauduin, S.; Clarisse, L.; Li, C.; et al. Sulfur dioxide vertical column DOAS retrievals from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument: Global observations and comparison to ground-based and satellite data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2470–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barrington, C.; Taisne, B.; Costa, F. Using Wavelet Coherence to Aid the Retrieval of Volcanic SO2 from UV Spectra. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184532
Barrington C, Taisne B, Costa F. Using Wavelet Coherence to Aid the Retrieval of Volcanic SO2 from UV Spectra. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(18):4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184532
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarrington, Charlotte, Benoit Taisne, and Fidel Costa. 2023. "Using Wavelet Coherence to Aid the Retrieval of Volcanic SO2 from UV Spectra" Remote Sensing 15, no. 18: 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184532
APA StyleBarrington, C., Taisne, B., & Costa, F. (2023). Using Wavelet Coherence to Aid the Retrieval of Volcanic SO2 from UV Spectra. Remote Sensing, 15(18), 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184532





