Long-Time Coherent Integration for Marine Targets Based on Segmented Compensation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Aiming at the problem of mismatch between the complex motion and the single motion model, this paper presents a new modeling method that decomposes the complex motion of the target into the combination of multiple uniformly accelerated motions to achieve a simplified description.
- For each segment, the parameters under low SCR are estimated under the model constraints, and then the compensation factor is constructed according to the parameter estimation to compensate the secondary order phase to eliminate the Doppler frequency modulation caused by the complex motion.
- To eliminate the false alarms that may exist in the detection results, a target discrimination method based on the 3 dB spectrum width of the symmetric instantaneous autocorrelation function is proposed, which can effectively distinguish the false alarm caused by the sea clutter.
2. Signal Processing Models
2.1. Marine Target Echo Model
2.2. Coherent Integration
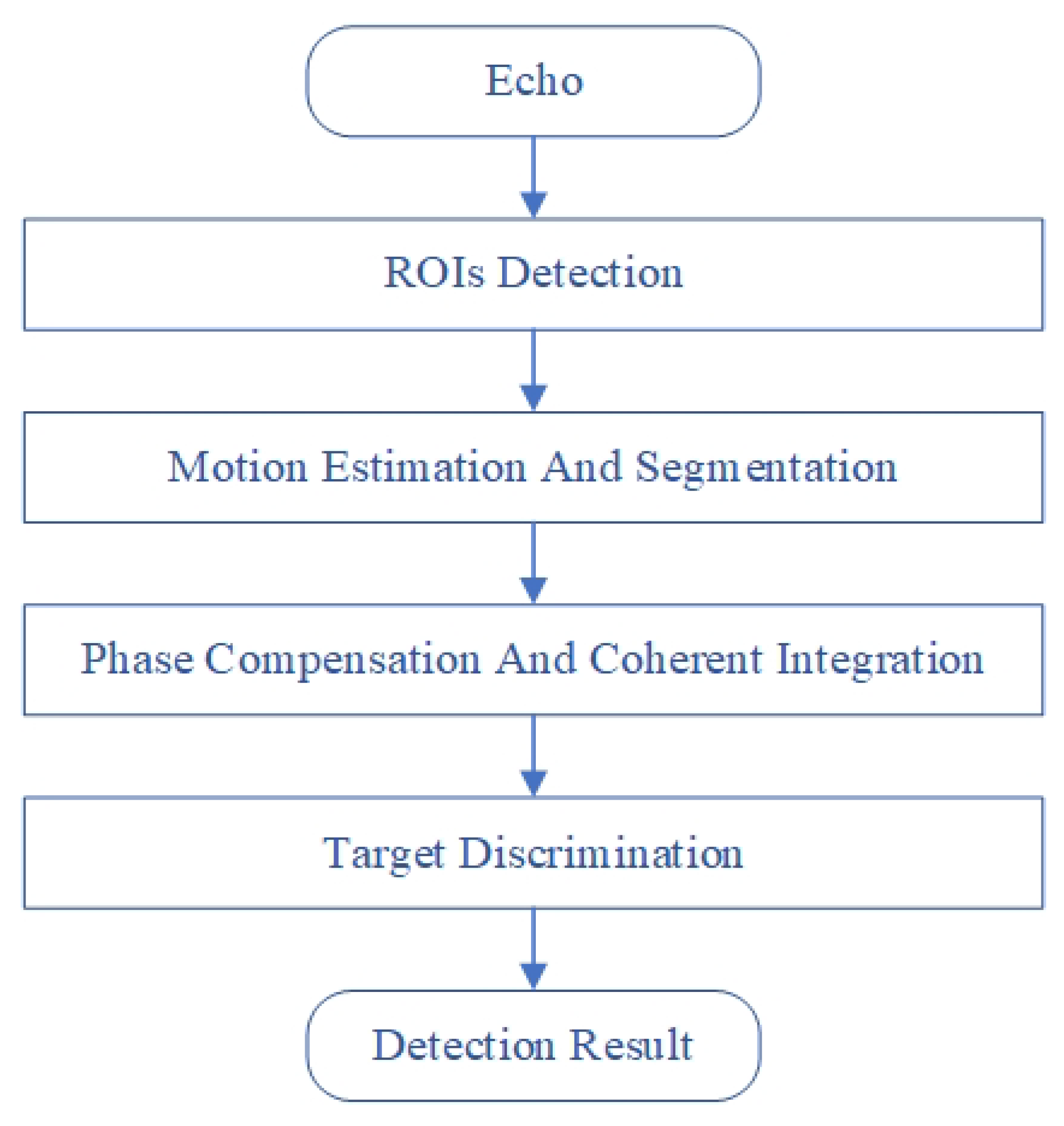
3. Long-Time Coherent Integration Based on Segmented Compensation
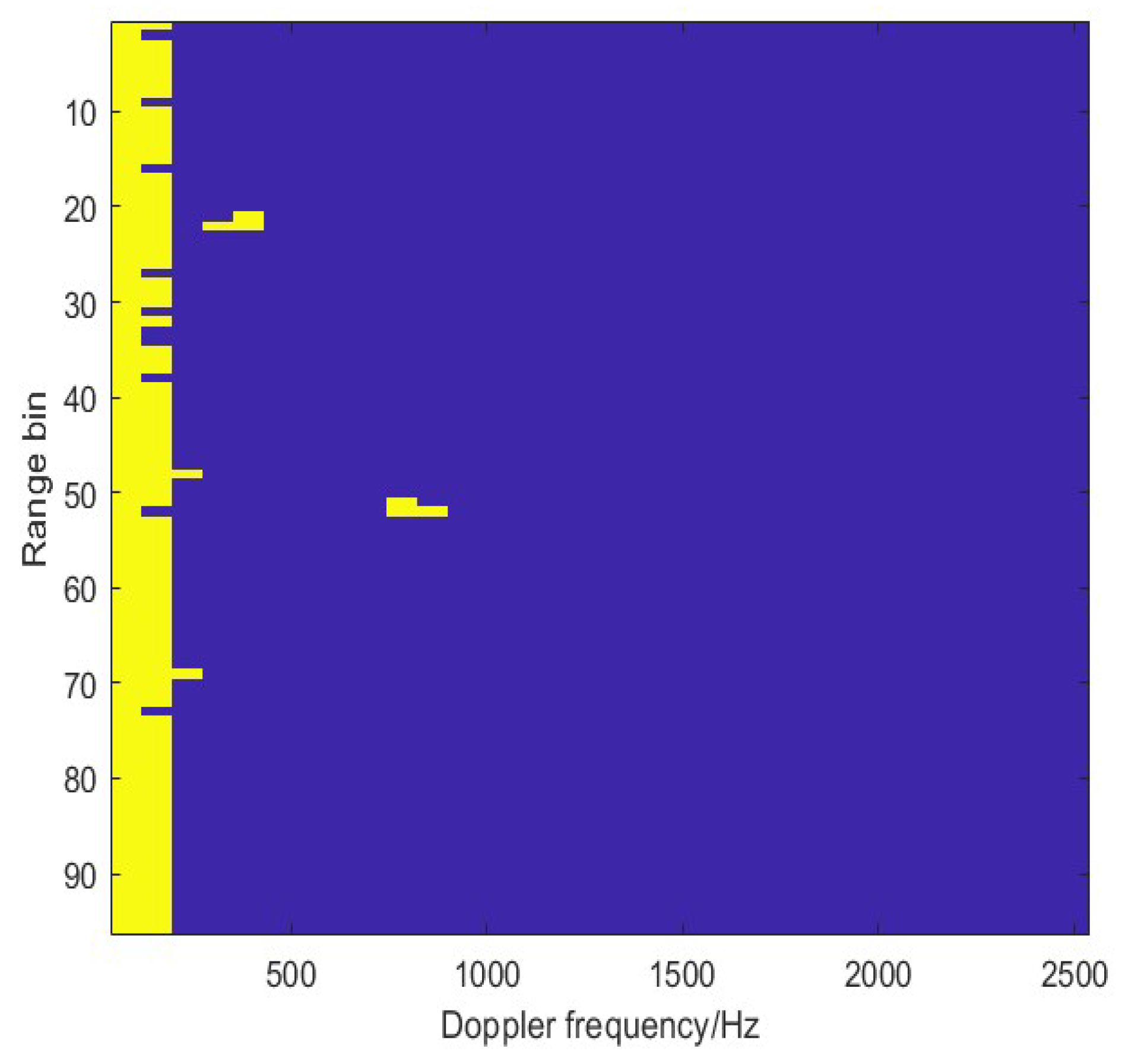
3.1. ROI Detection
3.2. Motion Estimation and Segmentation
3.3. Phase Compensation and Long-Time Coherent Integration
3.4. Target Discrimination
4. Experimental Verification
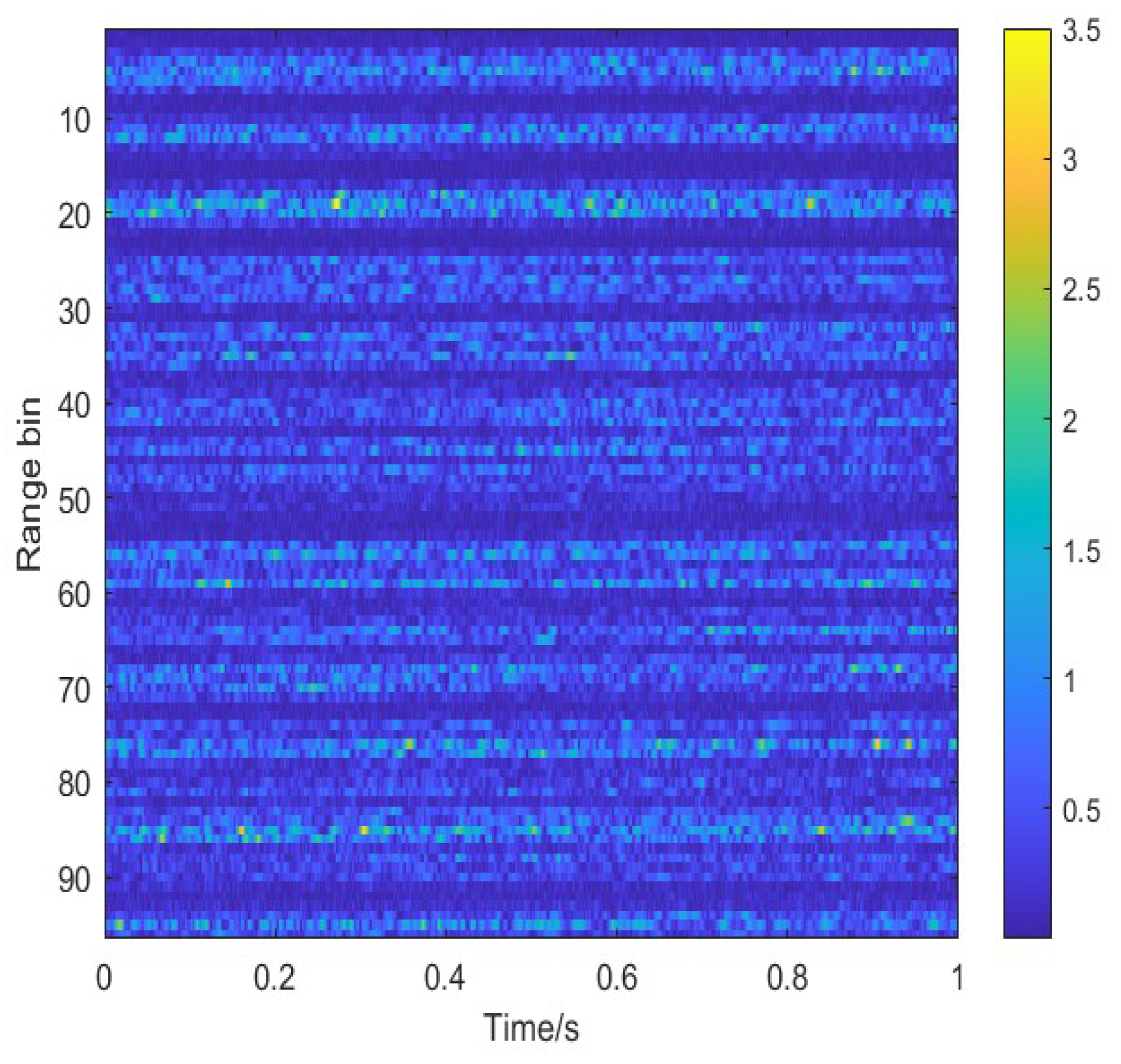
4.1. Dim Targets Detection
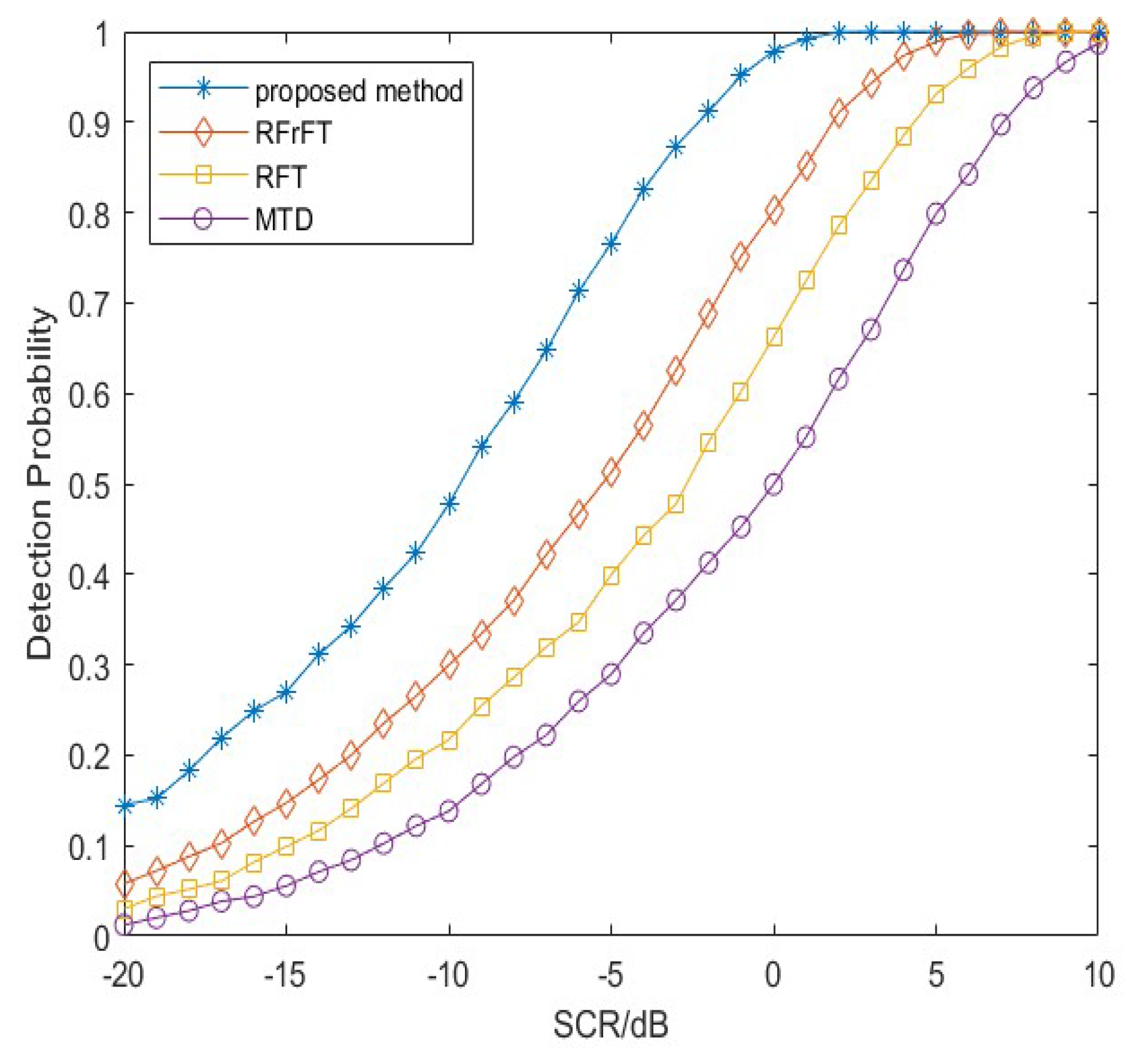
4.2. Detection Performance Simulation
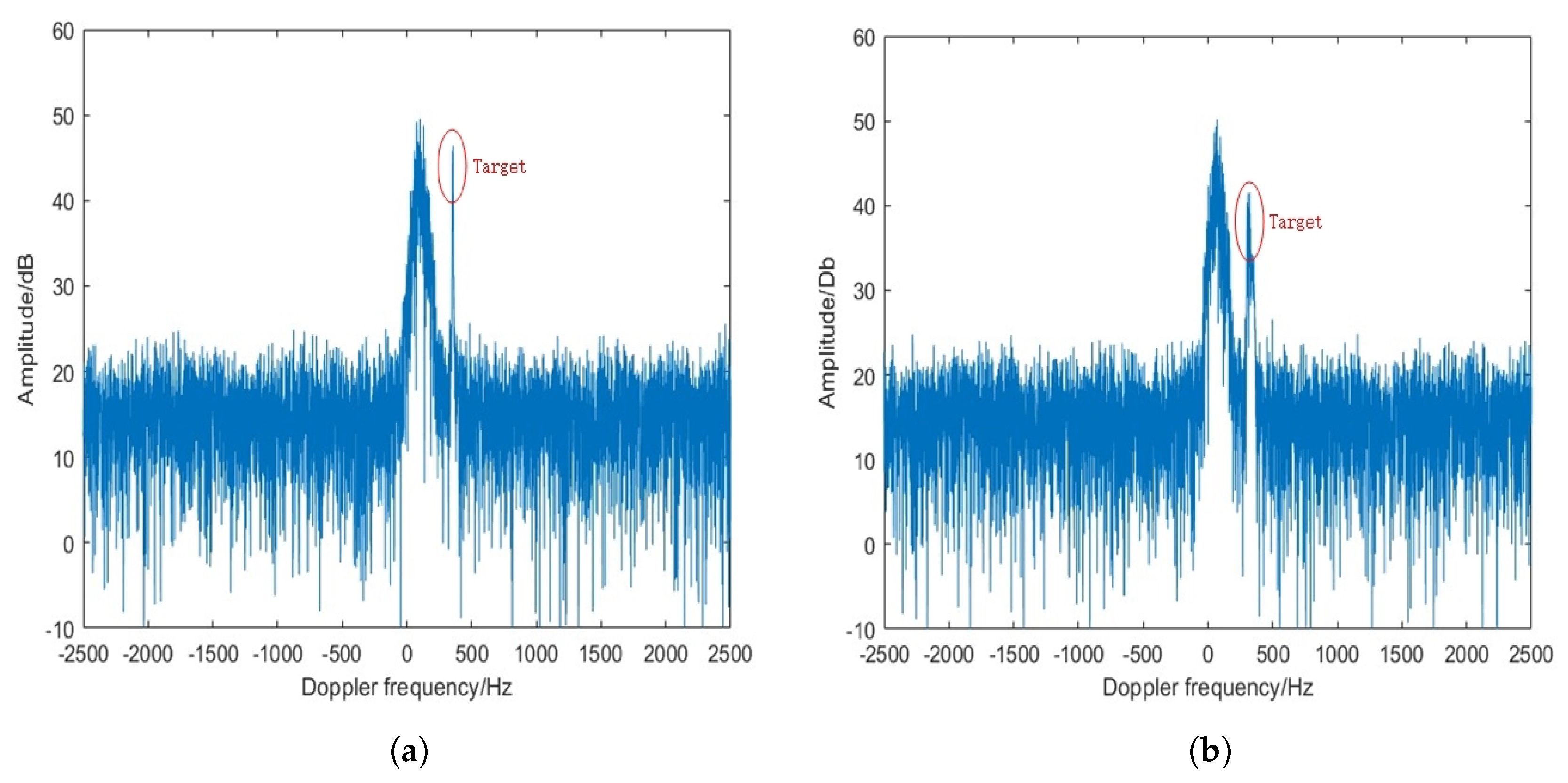
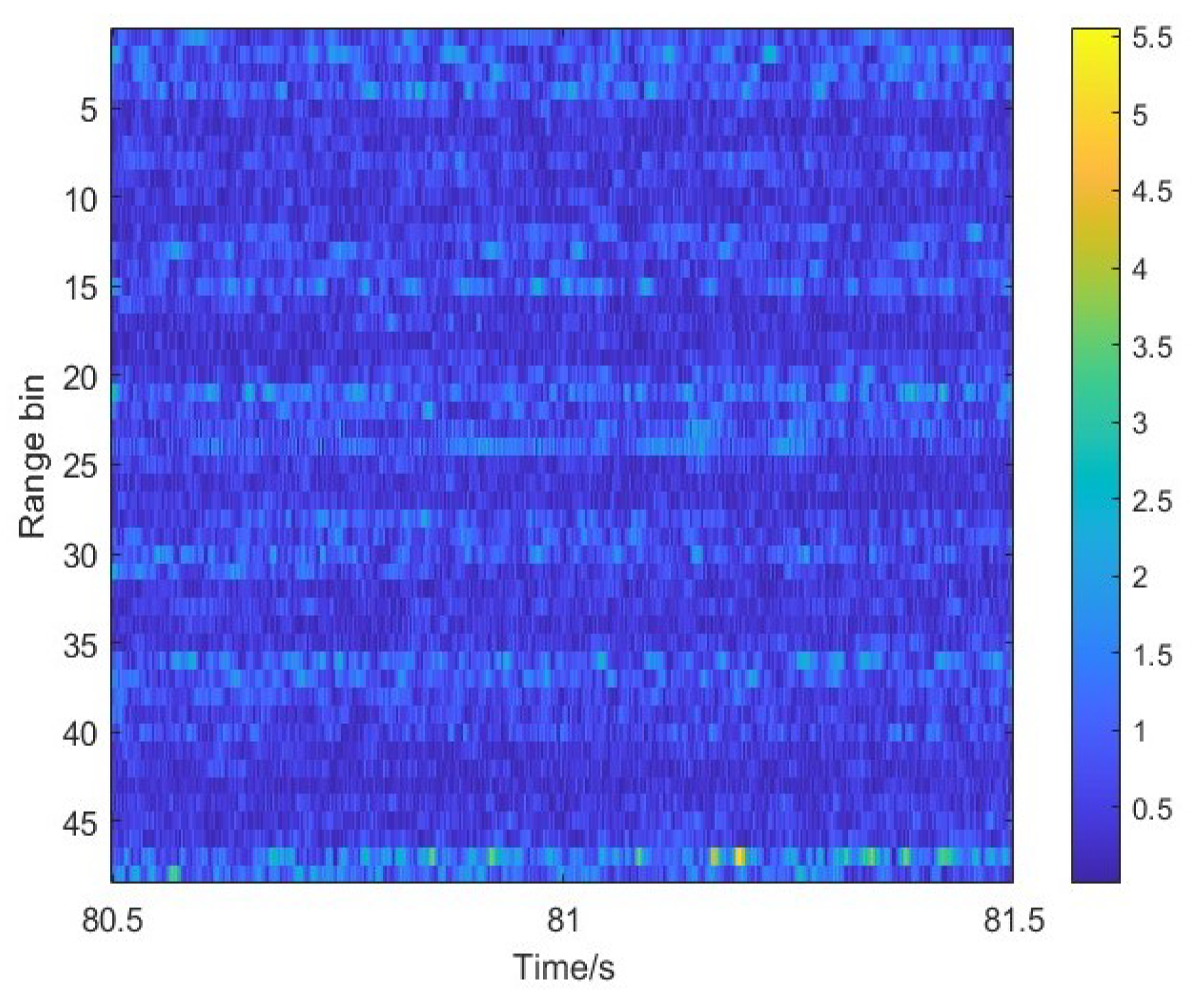
4.3. Target Detection Based on Measured Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richards, M. Coherent integration loss due to white Gaussian phase noise. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2003, 10, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.; Evans, E.; Wilson, S. Search radar detection and track with the Hough transform. I. system concept. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Liao, G.; Yang, Z.; Xia, X.G.; Ma, J.; Zheng, J. Ground Maneuvering Target Imaging and High-Order Motion Parameter Estimation Based on Second-Order Keystone and Generalized Hough-HAF Transform. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.K.; Cho, B.L.; Kim, Y.S. Ambiguity-free Doppler centroid estimation technique for airborne SAR using the Radon transform. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenezer, S.P.; Papandreou-Suppappola, A. Generalized Recursive Track-Before-Detect with Proposal Partitioning for Tracking Varying Number of Multiple Targets in Low SNR. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 2819–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Ristic, B.; Guan, R.; Rosenberg, L. A Bernoulli Track-Before-Detect Filter for Interacting Targets in Maritime Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, G.; Yeo, T.S. Coherent Integration and Parameter Estimation for High-Speed Target Detection with Bistatic MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5107915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.P.; DiPietro, R.C.; Fante, R.L. Coherent Integration with Range Migration Using Keystone Formatting. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Waltham, MA, USA, 17–20 April 2007; pp. 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z. A Keystone Transform without Interpolation for SAR Ground Moving-Target Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Liao, G.; Yang, Z.; Xia, X.G.; Ma, J.T.; Ma, J. Long-Time Coherent Integration for Weak Maneuvering Target Detection and High-Order Motion Parameter Estimation Based on Keystone Transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 4013–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. An Airborne SAR Moving Target Imaging and Motion Parameters Estimation Algorithm with Azimuth-Dechirping and the Second-Order Keystone Transform Applied. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3967–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, J.; Peng, Y.N.; Xia, X.G. Radon-Fourier Transform for Radar Target Detection, I: Generalized Doppler Filter Bank. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 1186–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Dong, X.; Zeng, T.; Ke, M. A Ship ISAR Imaging Algorithm Based on Generalized Radon-Fourier Transform with Low SNR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6385–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.; Fu, X.; Dong, J.; Yang, J. An Efficient Radon Fourier Transform-Based Coherent Integration Method for Target Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 3501905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.Q. Phase Compensation and Time-Reversal Transform for High-Order Maneuvering Target Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4025905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Sun, G.; Cheng, Z.; He, Z. Long-Time Coherent Integration for Maneuvering Target Detection Based on ITRT-MRFT. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 3718–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, B.; Lu, J.; Liao, G. Detection and Speed Estimation of Moving Target Based on Phase Compensation and Coherent Accumulation Using Fractional Fourier Transform. Sensors 2020, 20, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Guan, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, J. Detection of low observable moving target in sea clutter via fractal characteristics in fractional Fourier transform domain. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2013, 7, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Bi, G.; Wan, C.; Xing, M. Lv’s Distribution: Principle, Implementation, Properties, and Performance. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 3576–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Guan, J. Fast Detection Method for Low-Observable Maneuvering Target via Robust Sparse Fractional Fourier Transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Bi, G.; Lv, X.; Hu, F. Performance analysis on Lv distribution and its applications. Digit. Signal Process. 2013, 23, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, G.; Kong, L.; Yi, W. Fast Non-Searching Method for Maneuvering Target Detection and Motion Parameters Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 2232–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Cui, W.; Tian, J. Coherent Integration Algorithm for a Maneuvering Target Based on Frequency Spectrum Segment Processing. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 115646–115654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Tao, R.; Kang, X. Weak Target Detection in the Presence of Sea Clutter Using Radon-Fractional Fourier Transform Canceller. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5818–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guan, J.; Liu, N.; He, Y. Maneuvering Target Detection via Radon-Fractional Fourier Transform-Based Long-Time Coherent Integration. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Qu, G.; Zuo, Y.; Zeng, G. Low-observable target detection using two-stage RFRFT. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2019, 13, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, D.K.; Leonov, S.A. Radar Technology Encyclopedia; Artech House Inc.: Norwood, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Levanon, N.; Mozeson, E.; Signals, R.; Levanon, C. Radar Signals. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2013, 20, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Ahmed, R.; Cheema, H.M. Segmented Radon Fourier Transform for Long-Time Coherent Radars. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 9582–9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.B.; Liu, G.S.; Gu, H.; Su, W.M. Application of the fractional Fourier transform to moving target detection in airborne SAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2002, 38, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Huang, Y.; Guan, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, X. Long-time coherent integration method combining pulse compression and Radon fractional Fourier transform. In Proceedings of the 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 15–19 December 2021; pp. 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claasen, T.A.C.M.; Mecklenbrauker, W.F.G. The Wigner Distribution—A Tool for Time-Frequency Signal Analysis Part Ill: Relations with Other Time-Frequency Signal Transformations. Philips J. Res. 1980, 35, 372–389. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing (Richards, M.A.; 2005) [Book review]. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2009, 26, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]


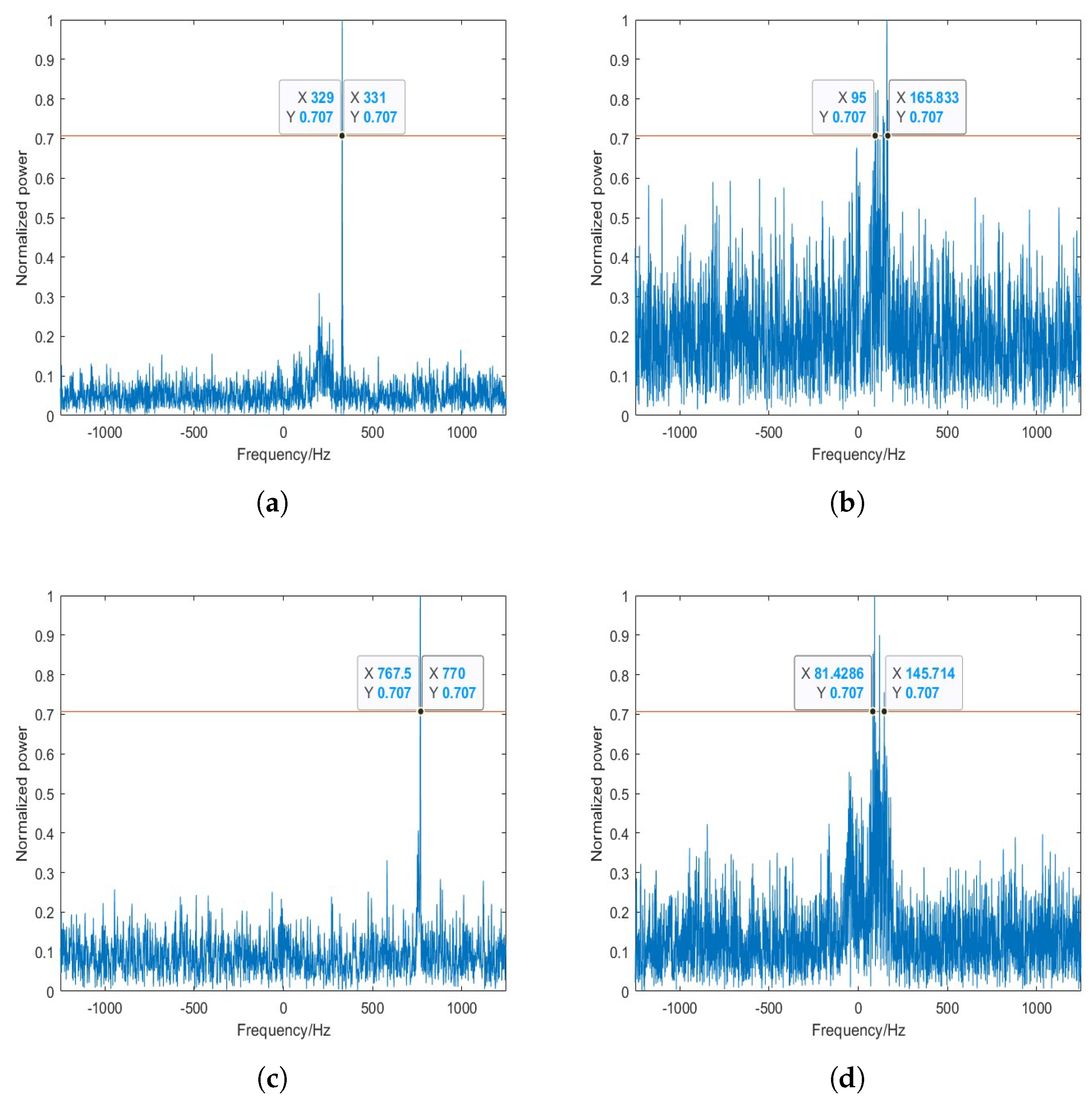


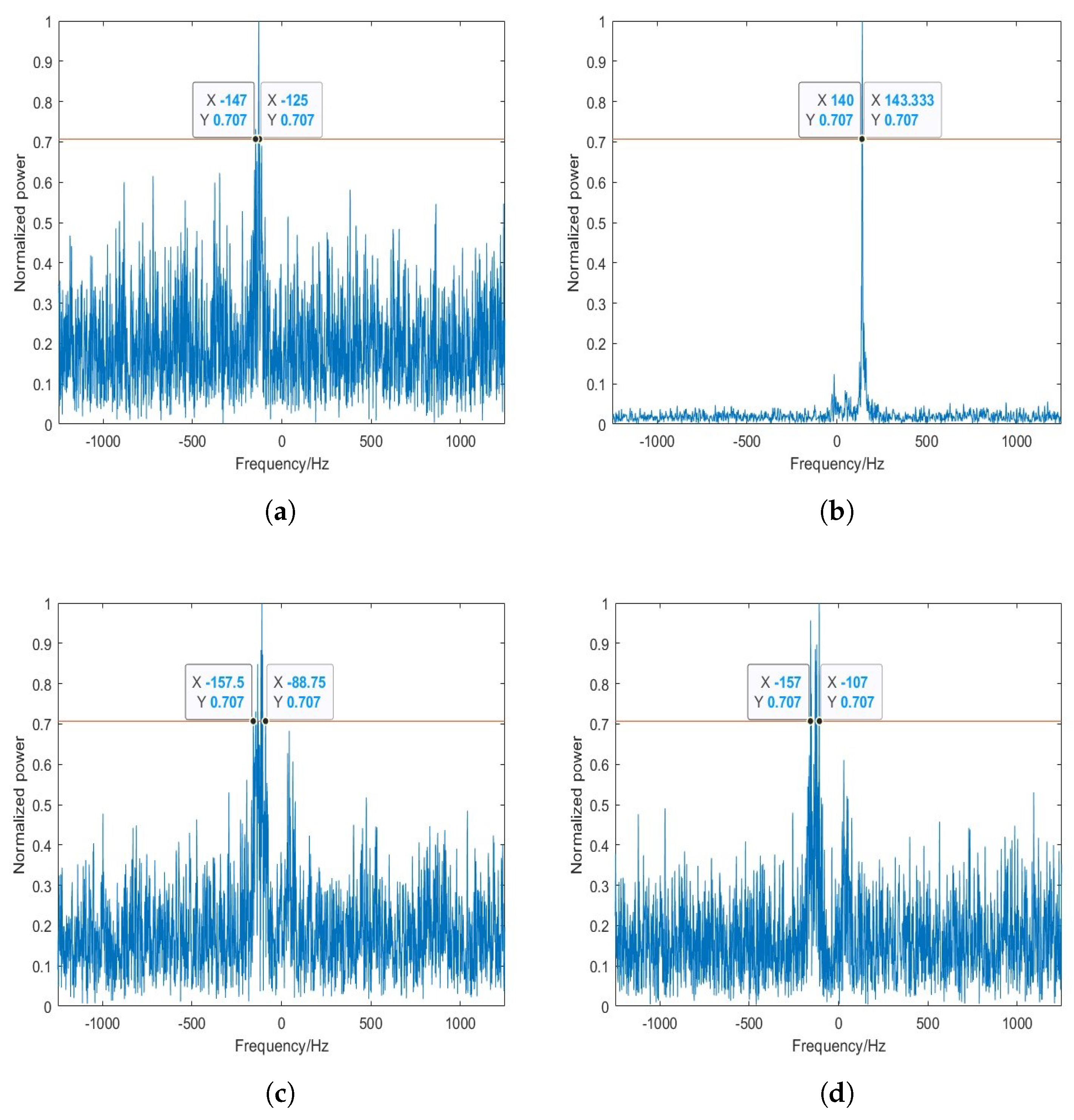
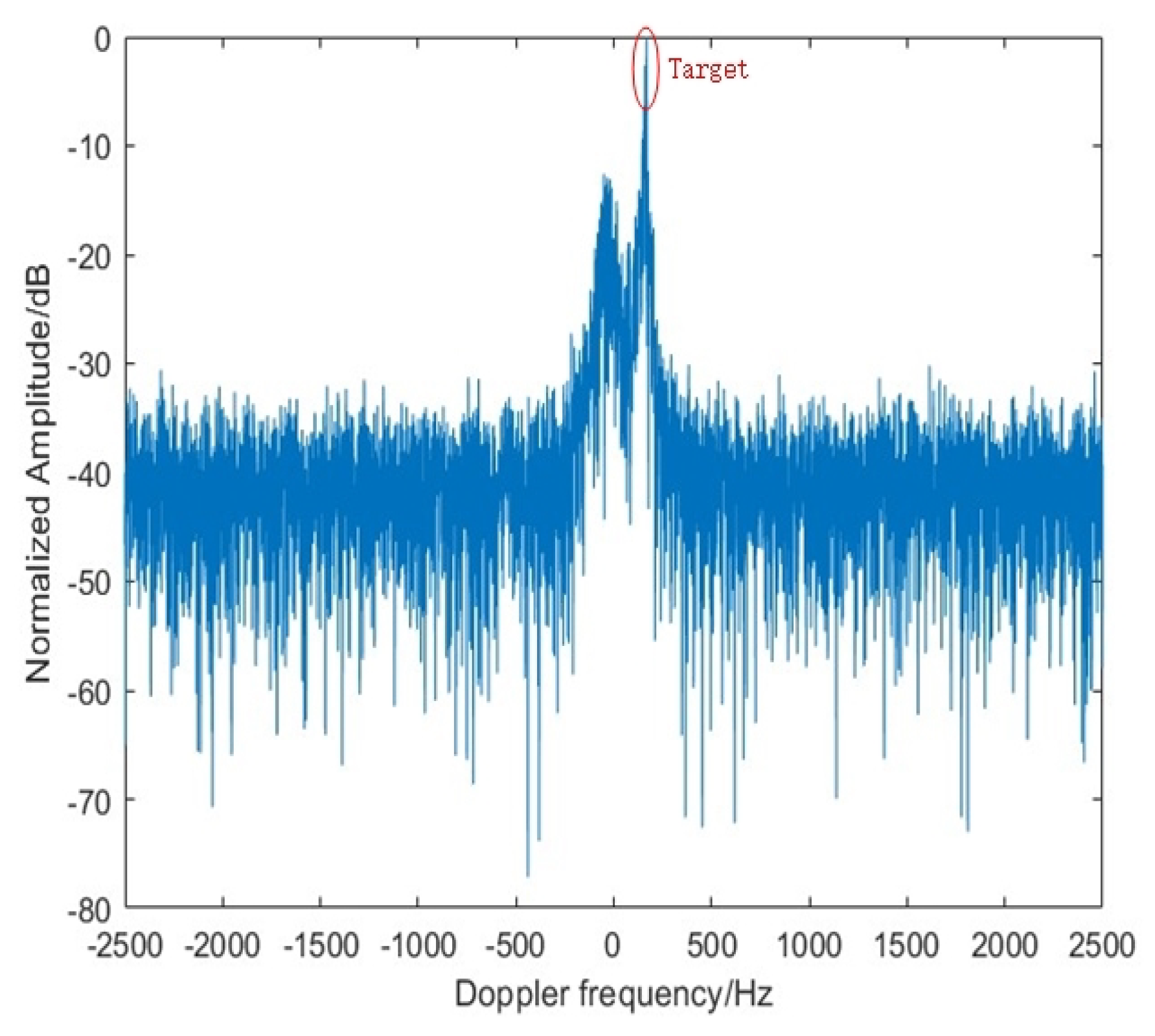
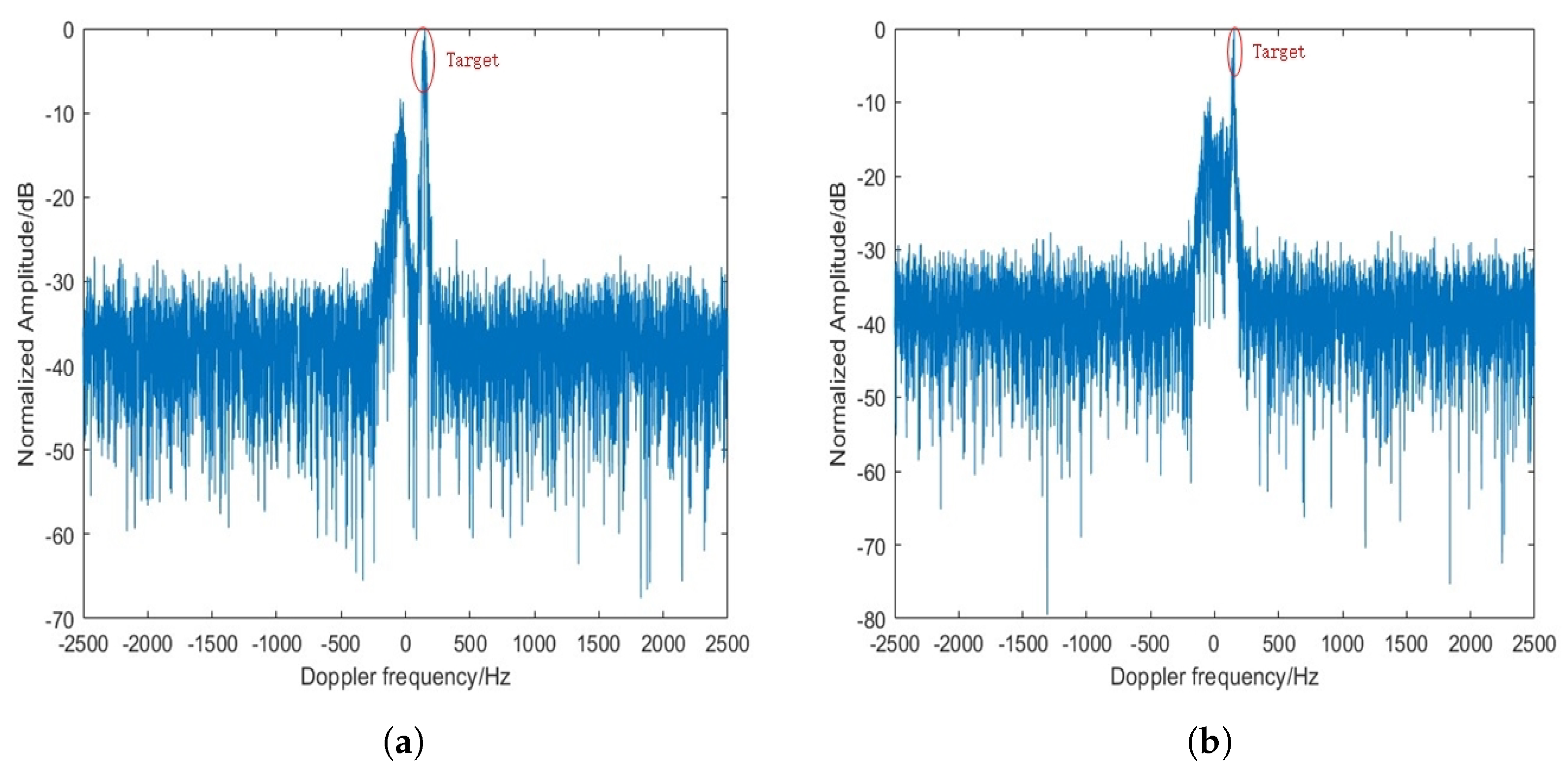
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Frequency (GHz) | 9 |
| PRF (KHz) | 5 |
| Initial distance (m) | 3000.63 |
| Range resolution (m) | 15 |
| Grazing angle (deg) | 0.853–1.27 |
| Wind speed (m/s) | 7.97 |
| Parameters | Target 1 | Target 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Initial distance (m) | 310 | 755 |
| Initial velocity (m/s) | 6 | 12 |
| Accelerations (m/s2) | −2, 1 | 4, −3, 2 |
| Duration (s) | 0.5, 0.5 | 0.3, 0.3, 0.4 |
| SCR (dB) | −15 | −17 |
| ROI | Range Bin | Doppler Frequency/Hz |
|---|---|---|
| ROI 1 | 21, 22 | 312.5∼390.6 |
| ROI 2 | 48 | 156.3∼234.4 |
| ROI 3 | 51, 52 | 781.3∼859.4 |
| ROI 4 | 69 | 156.3∼234.4 |
| ROI | 3 dB Band Width/Hz | Threshold/Hz | Discrimination |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROI 1 | 2 | 2.67 | T |
| ROI 2 | 70.8 | 2.23 | F |
| ROI 3 | 2.5 | 3.34 | T |
| ROI 4 | 64.3 | 2.23 | F |
| Methods | SCR/dB |
|---|---|
| MTD of 23rd range bin | 25.9 |
| MTD of 24th range bin | 26.3 |
| RFrFT | 28.5 |
| Proposed method | 33.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Wu, W. Long-Time Coherent Integration for Marine Targets Based on Segmented Compensation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184530
Zhao Z, Zhang Y, Wang W, Liu B, Wu W. Long-Time Coherent Integration for Marine Targets Based on Segmented Compensation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(18):4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184530
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhenfang, Yisong Zhang, Wenguang Wang, Ben Liu, and Wei Wu. 2023. "Long-Time Coherent Integration for Marine Targets Based on Segmented Compensation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 18: 4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184530
APA StyleZhao, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, W., Liu, B., & Wu, W. (2023). Long-Time Coherent Integration for Marine Targets Based on Segmented Compensation. Remote Sensing, 15(18), 4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184530









