A Generic, Multimodal Geospatial Data Alignment System for Aerial Navigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
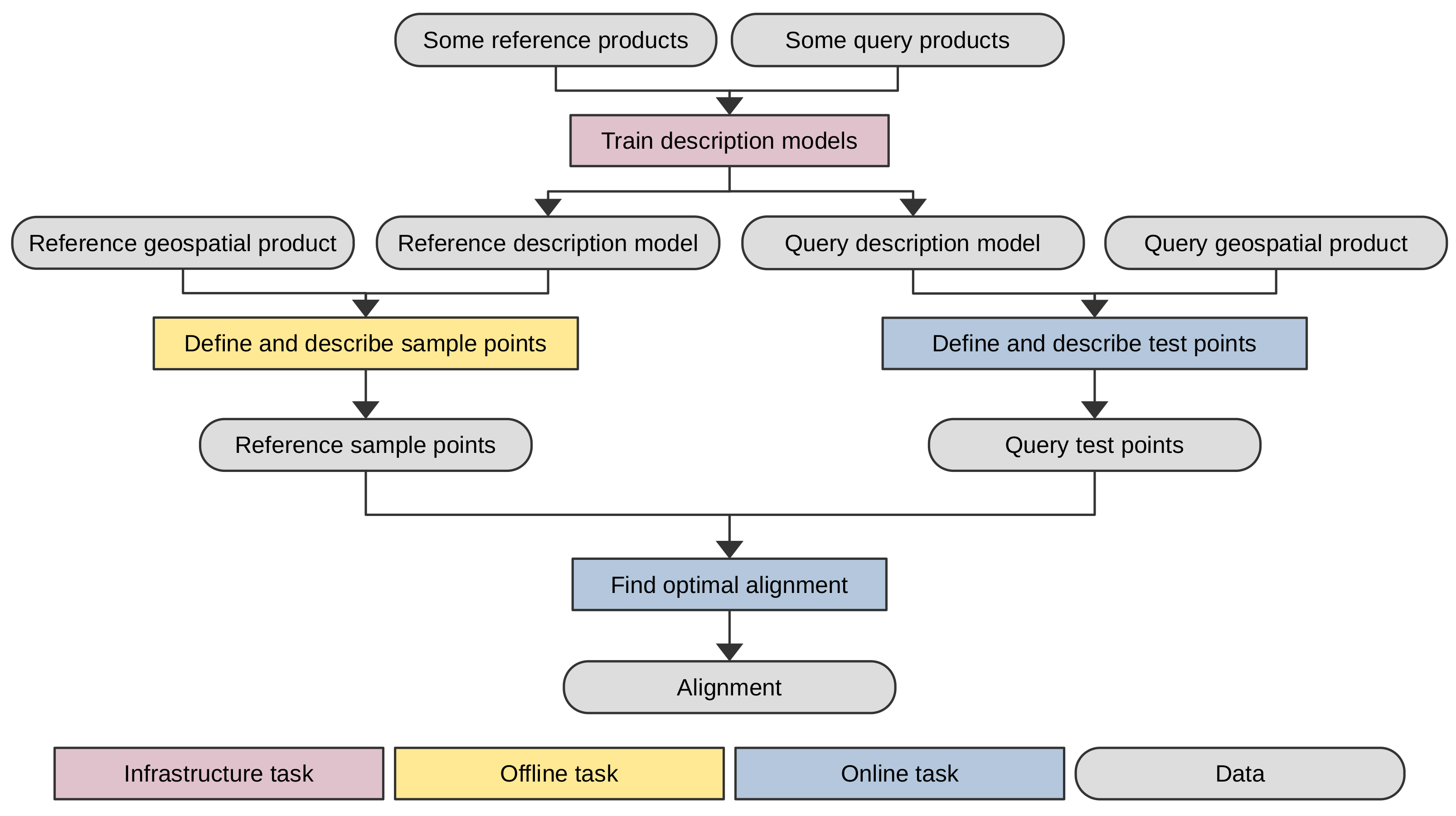
2.1. Overview
2.2. Sampling Local Descriptors
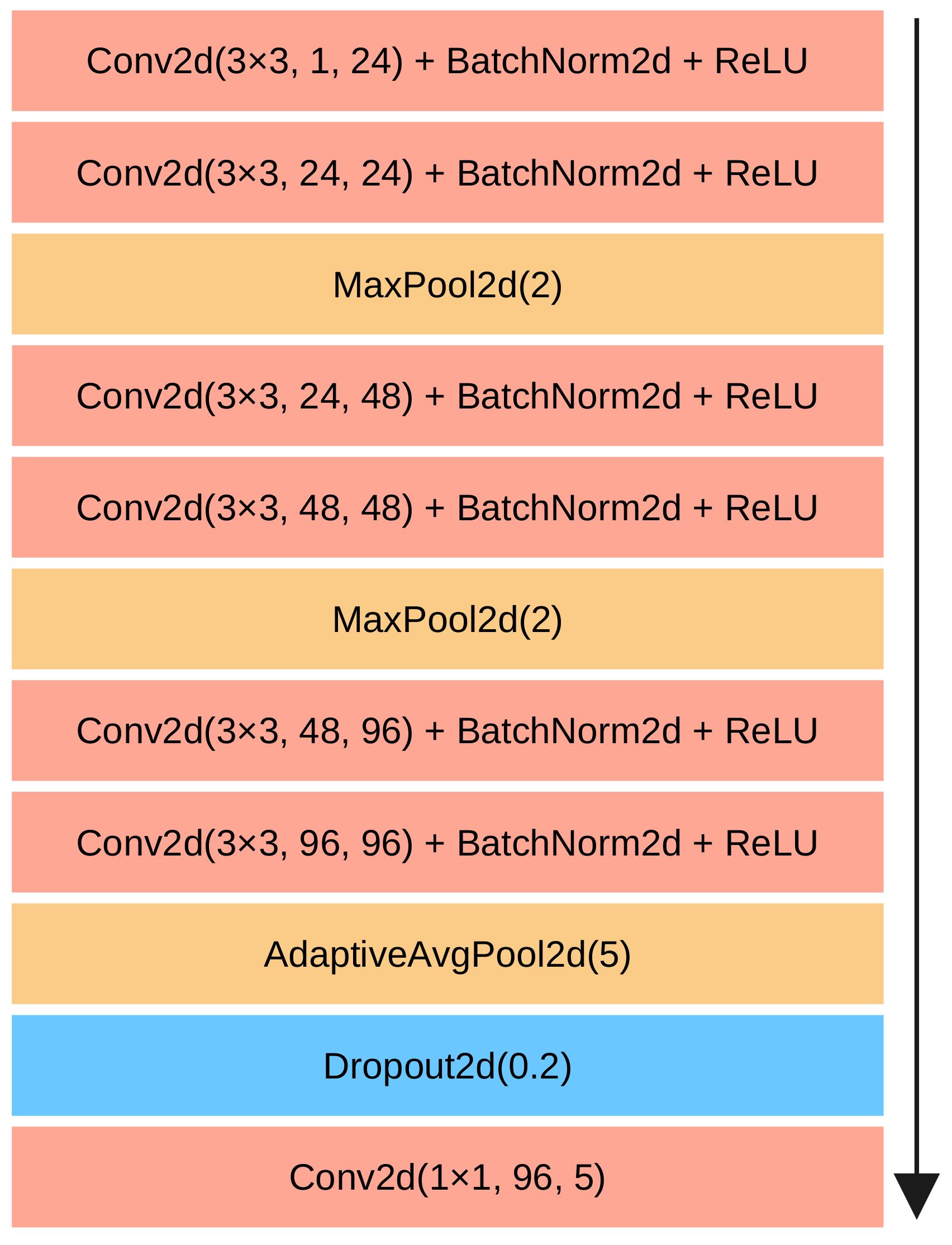
2.3. Computing Local Descriptors
2.4. Optimization
2.5. Usage
3. Experiments
3.1. Implementation
3.2. Data
3.2.1. Pléiades
3.2.2. Miranda
3.2.3. OpenStreetMap
3.2.4. DOP
3.2.5. KOMPSAT-5
3.3. Protocol
3.4. Results
3.4.1. Local Description Models
3.4.2. Alignment
- Pléiades + DOP < Miranda + DOP < Miranda + KOMPSAT-5
- Pléiades + DOP < Pléiades + KOMPSAT-5 < Miranda + KOMPSAT-5.
4. Discussion
4.1. Relation to Image Retrieval
4.2. Class of Transformations
4.3. Real-Time Use
4.4. Similarity Metric
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFOG | Channel features of oriented gradient |
| DOP | Digitale OrthoPhotos |
| DSMAC | Digital Scene Matching Area Correlator |
| EU | European Union |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transform |
| FMCW | Frequency-modulated continuous wave |
| GSD | Ground sampling distance |
| ICP | Iterative closest point |
| KOMPSAT | KOrean MultiPurpose SATellite |
| MI | Mutual information |
| NCC | Normalized cross-correlation |
| RADAR | Radio detection and ranging |
| SAR | Synthetic aperture radar |
References
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5967–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott Shaham, T.; Gharbi, M.; Zhang, R.; Shechtman, E.; Michaeli, T. Spatially-Adaptive Pixelwise Networks for Fast Image Translation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Irani, G.; Christ, H. Image Processing for Tomahawk Scene Matching. Johns Hopkins APL Tech. Dig. 1994, 15, 250–264. [Google Scholar]
- Costea, D.; Leordeanu, M. Aerial image geolocalization from recognition and matching of roads and intersections. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.08323. [Google Scholar]
- Kovesi, P. Image Features From Phase Congruency. Videre J. Comput. Vis. Res. 1995, 1, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Zhao, S. A New Feature Descriptor for Multimodal Image Registration Using Phase Congruency. Sensors 2020, 20, 5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Shan, J.; Bruzzone, L.; Shen, L. Robust Registration of Multimodal Remote Sensing Images Based on Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2941–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Tao, R.; Wang, F.; You, H.; Han, B. Automatic Registration of Optical and SAR Images Via Improved Phase Congruency Model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5847–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wan, L.; You, H. SAR-PC: Edge Detection in SAR Images via an Advanced Phase Congruency Model. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, M.; Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Ma, G. A Robust Algorithm Based on Phase Congruency for Optical and SAR Image Registration in Suburban Areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragb, H.K.; Asari, V.K. Histogram of oriented phase (HOP): A new descriptor based on phase congruency. In Mobile Multimedia/Image Processing, Security, and Applications 2016; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9869, pp. 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, F.; Delon, J.; Gousseau, Y.; Michel, J.; Tupin, F. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-Like Algorithm for SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Shan, J.; Bovolo, F.; Zhu, Q. Fast and Robust Matching for Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Registration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9059–9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Xu, Q.; Jin, G.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X. Rank-Based Local Self-Similarity Descriptor for Optical-to-SAR Image Matching. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1742–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shechtman, E.; Irani, M. Matching Local Self-Similarities across Images and Videos. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 18–23 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, E.; Ailon, N. Deep metric learning using Triplet network. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1412.6622. [Google Scholar]
- Simo-Serra, E.; Trulls, E.; Ferraz, L.; Kokkinos, I.; Fua, P.; Moreno-Noguer, F. Discriminative Learning of Deep Convolutional Feature Point Descriptors. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Washington, DC, USA, 7–13 December 2015; IEEE: Santiago, Chile, 2015; pp. 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchuk, A.; Mishkin, D.; Radenovic, F.; Matas, J. Working hard to know your neighbor’s margins: Local descriptor learning loss. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zagoruyko, S.; Komodakis, N. Learning to Compare Image Patches via Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.03641. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Leung, T.; Jia, Y.; Sukthankar, R.; Berg, A.C. MatchNet: Unifying feature and metric learning for patch-based matching. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; IEEE: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 3279–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Fan, B.; Wu, F. L2-Net: Deep Learning of Discriminative Patch Descriptor in Euclidean Space. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6128–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balntas, V.; Johns, E.; Tang, L.; Mikolajczyk, K. PN-Net: Conjoined Triple Deep Network for Learning Local Image Descriptors. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1601.05030. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, L.H.; Schmitt, M.; Mou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.X. Identifying Corresponding Patches in SAR and Optical Images With a Pseudo-Siamese CNN. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X. Mining Hard Negative Samples for SAR-Optical Image Matching Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.H.; Merkle, N.; Bürgmann, T.; Auer, S.; Schmitt, M. Deep Learning for SAR-Optical Image Matching. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 4877–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.H.; Marcos, D.; Lobry, S.; Tuia, D.; Schmitt, M. A deep learning framework for matching of SAR and optical imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 169, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Di, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, A.; Liu, J.; Lu, M.; Duan, Q. Feature Matching and Position Matching Between Optical and SAR With Local Deep Feature Descriptor. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgmann, T.; Koppe, W.; Schmitt, M. Matching of TerraSAR-X derived ground control points to optical image patches using deep learning | Elsevier Enhanced Reader. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 158, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Tao, R.; Wang, S. Transfer Learning for Optical and SAR Data Correspondence Identification with Limited Training Labels. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frioud, M.; Wahlen, A.; Wellig, P.; Meier, E. Processing of MIRANDA35 FMCW-SAR Data using a Time-Domain Algorithm. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2014, 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 2–6 June 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Stanko, S.; Johannes, W.; Sommer, R.; Wahlen, A.; Wilcke, J.; Essen, H.; Tessmann, A.; Kallfass, I. SAR with MIRANDA—Millimeterwave radar using analog and new digital approach. In Proceedings of the 2011 8th European Radar Conference, Manchester, UK, 12–14 October 2011; pp. 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Henke, D.; Frioud, M.; Fagir, J.; Guillaume, S.; Meindl, M.; Geiger, A.; Sieger, S.; Janssen, D.; Klöppel, F.; Caris, M.; et al. Miranda35 Experiments in Preparation for Small Uav-Based Sar. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 8542–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, K.; Schmid, C. A Performance Evaluation of Local Descriptors. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjanic, Z.; Gustafsson, F. Navigation and SAR focusing with map aiding. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, J.; Abratkiewicz, K.; Gromek, A.; Ostrowski, W.; Samczyński, P.; Gromek, D. Geometrical Matching of SAR and Optical Images Utilizing ASIFT Features for SAR-based Navigation Aided Systems. Sensors 2019, 19, 5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivic, Z. Video Google: A text retrieval approach to object matching in videos. In Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sardinia, Italy, 13–16 October 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Newsam, S. Geographic Image Retrieval Using Local Invariant Features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jégou, H.; Douze, M.; Schmid, C.; Pérez, P. Aggregating local descriptors into a compact image representation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 3304–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbriaco, R.; Sebastian, C.; Bondarev, E.; de With, P.H.N. Aggregated Deep Local Features for Remote Sensing Image Retrieval. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Guan, H.; Li, Z.; Shao, Z.; Delavar, M.R. Remote Sensing Image Retrieval in the Past Decade: Achievements, Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 1447–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Gu, X. A Deep Cross-Modality Hashing Network for SAR and Optical Remote Sensing Images Retrieval. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5284–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
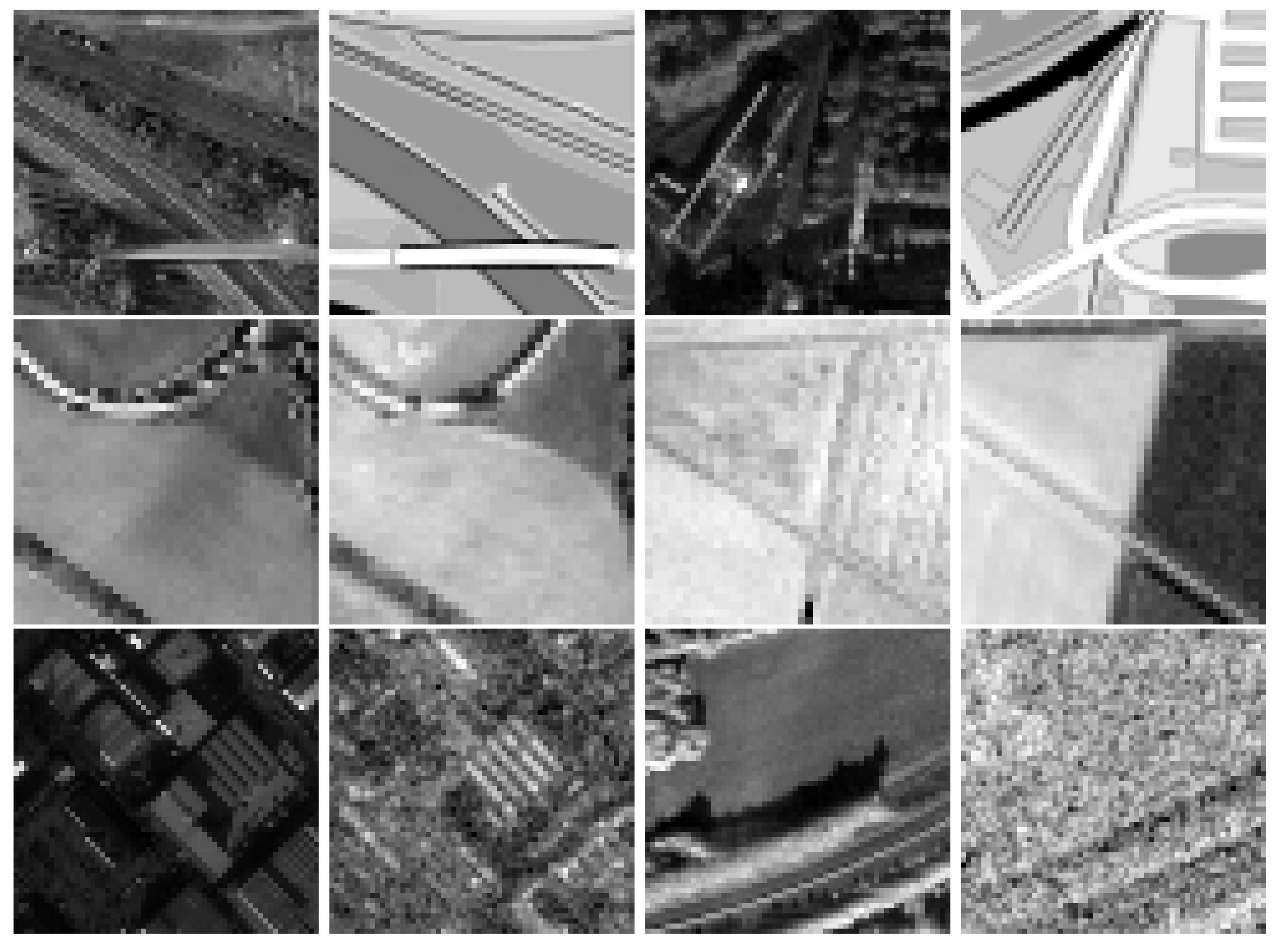




| Query Modality | Reference Modality | Patch Footprint | Patch Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pléiades | OpenStreetMap | (150 m)2 | (60 px)2 |
| Pléiades | DOP | (150 m)2 | (40 px)2 |
| Pléiades | KOMPSAT-5 | (200 m)2 | (60 px)2 |
| Miranda | OpenStreetMap | (150 m)2 | (60 px)2 |
| Miranda | DOP | (150 m)2 | (40 px)2 |
| Miranda | KOMPSAT-5 | (200 m)2 | (60 px)2 |
| Query Image | False Positive Rate (OpenStreetMap) | False Positive Rate (DOP) | False Positive Rate (KOMPSAT-5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Miranda A | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| Miranda B | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Miranda C | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.31 |
| Miranda D | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.20 |
| Miranda E | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.47 |
| Miranda (mean) | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.27 |
| Pléiades A | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.33 |
| Pléiades B | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.24 |
| Pléiades C | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.22 |
| Pléiades D | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.25 |
| Pléiades E | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.22 |
| Pléiades (mean) | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.25 |
| Query Modality | Reference Modality | Number of Experiments | Success Rate (Our Method) | Success Rate (MI) | Success Rate (NCC) | Success Rate (CFOG) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pléiades | OpenStreetMap | 74 | 100% | 33.0% | 1.1% | 0.0% |
| Pléiades | DOP | 74 | 100% | 63.5% | 45.9% | 16.2% |
| Pléiades | KOMPSAT5 | 94 | 94% | 3.2% | 1.1% | 0.0% |
| Miranda | OpenStreetMap | 46 | 98% | 11.1% | 1.9% | 0.0% |
| Miranda | DOP | 45 | 100% | 4.4% | 6.7% | 0.0% |
| Miranda | KOMPSAT5 | 48 | 78% | 14.6% | 14.6% | 8.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin-Lac, V.; Petit-Frere, J.; Le Caillec, J.-M. A Generic, Multimodal Geospatial Data Alignment System for Aerial Navigation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184510
Martin-Lac V, Petit-Frere J, Le Caillec J-M. A Generic, Multimodal Geospatial Data Alignment System for Aerial Navigation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(18):4510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184510
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin-Lac, Victor, Jacques Petit-Frere, and Jean-Marc Le Caillec. 2023. "A Generic, Multimodal Geospatial Data Alignment System for Aerial Navigation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 18: 4510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184510
APA StyleMartin-Lac, V., Petit-Frere, J., & Le Caillec, J.-M. (2023). A Generic, Multimodal Geospatial Data Alignment System for Aerial Navigation. Remote Sensing, 15(18), 4510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15184510







