Accounting for Non-Stationary Relationships between Precipitation and Environmental Variables for Downscaling Monthly TRMM Precipitation in the Upper Indus Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.2.1. TRMM Precipitation Dataset
2.2.2. Precipitation Gauge Data
2.2.3. Environmental Variables
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. The Stepwise Regression Analysis (SRA)
2.3.2. Geographically Weighted Regression Model (GWR)
2.3.3. Disaggregation of Annual Precipitation
2.3.4. Performance of Variables Filtration and Data Downscaling
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Variables Filtration
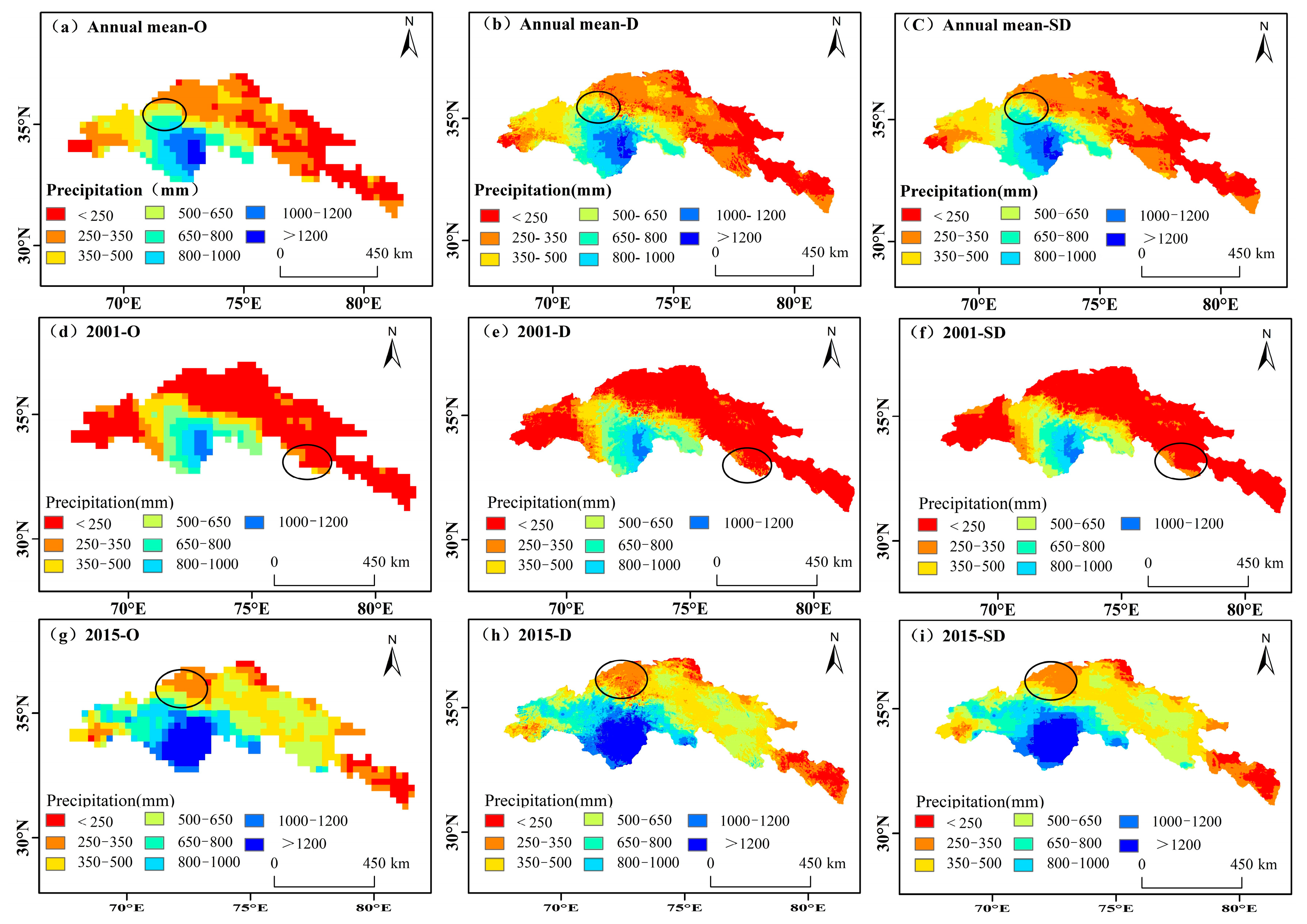
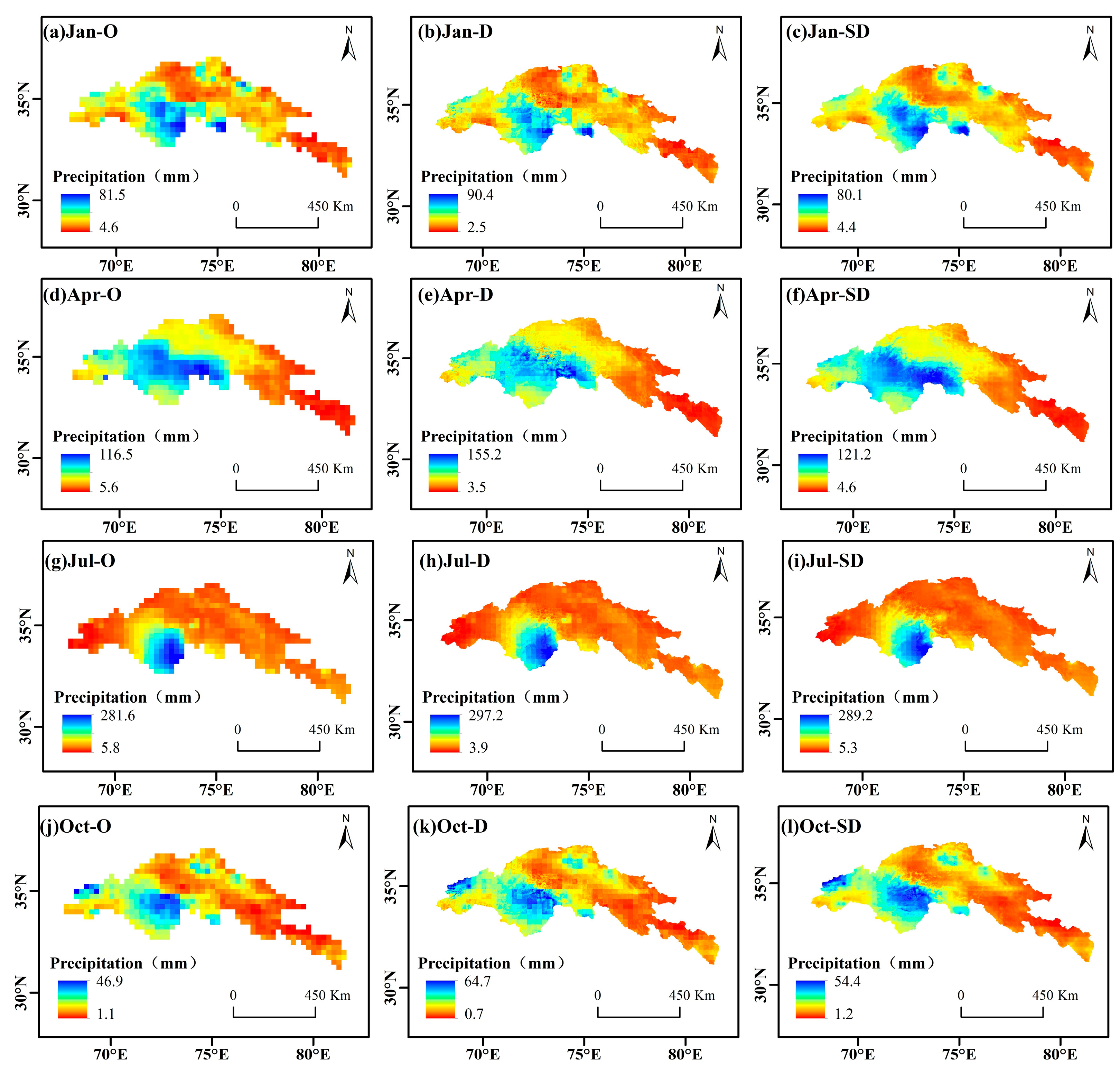
3.2. Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy of Downscaled TRMM Data with GWR and S-GWR Models
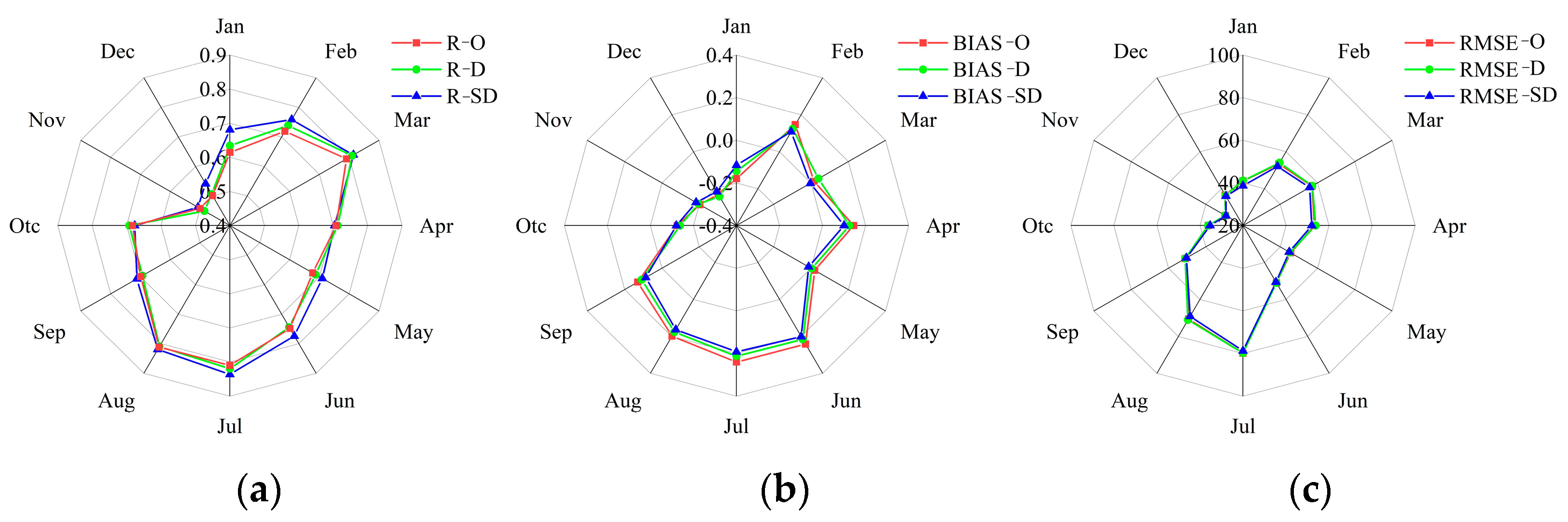
3.2.1. Temporal Scale Evaluation
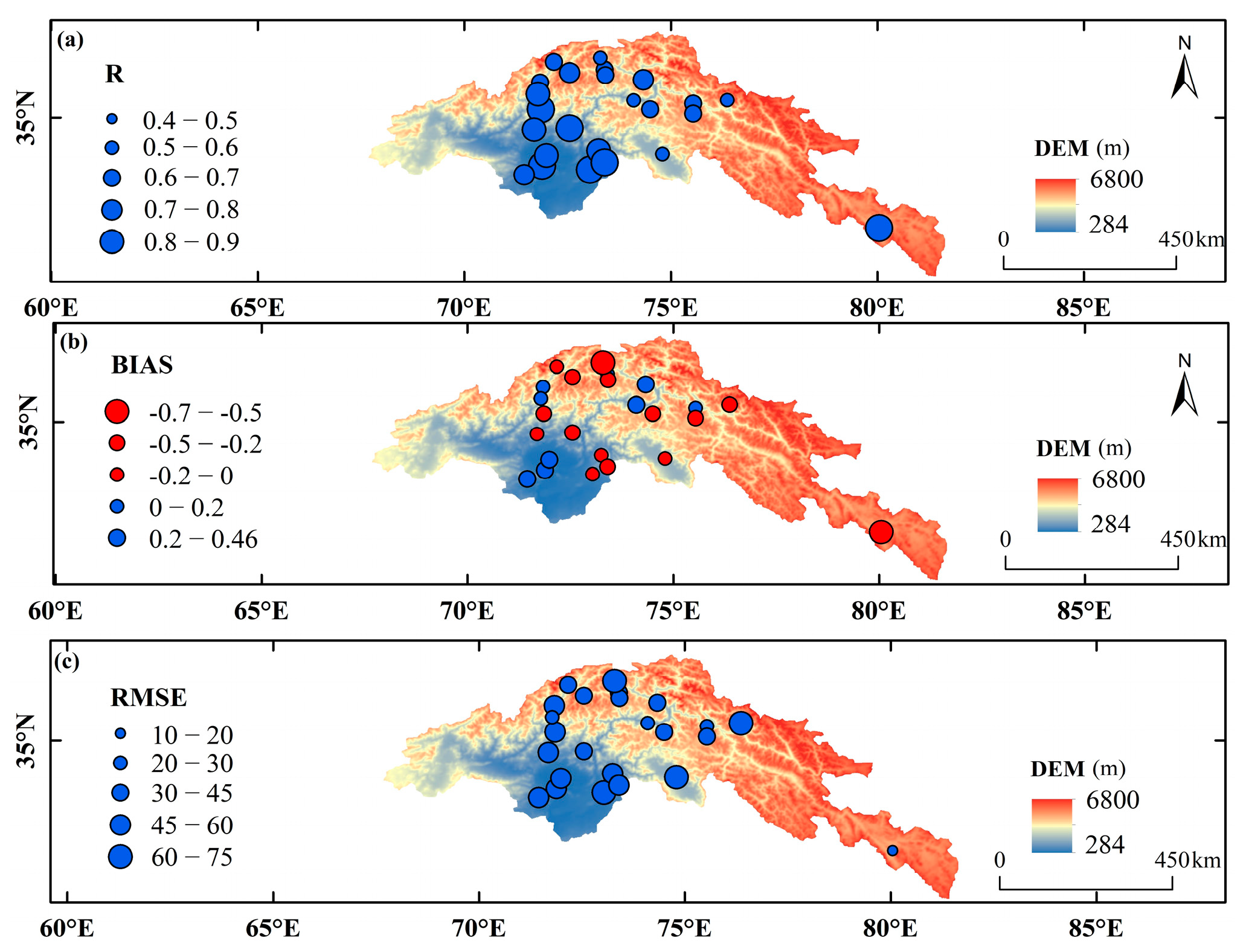
3.2.2. Spatial Scale Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental Variables Filtration
4.2. TRMM Data Downscaling in the UIB
4.3. Uncertainty Analysis and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, Y.-J.; Shen, Y.J.; Fink, M.; Kralisch, S.; Brenning, A. Unraveling the hydrology of the glacierized Kaidu Basin by integrating multisource data in the Tianshan Mountains, Northwestern China. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Regionalization of hydrological modeling for predicting streamflow in ungauged catchments: A comprehensive review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistical approaches for incorporating elevation into the spatial interpolation of rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Z.; Liang, X.; Leung, L.R. Impacts of different precipitation data sources on water budgets. J. Hydrol. 2004, 298, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langella, G.; Basile, A.; Bonfante, A.; Terribile, F. High-resolution space–time rainfall analysis using integrated ANN inference systems. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.H.; Ren, L.L.; Hong, Y.; Yong, B.; Yang, X.; Yuan, F.Y.; Ma, M.W. Comprehensive evaluation of multi-satellite precipitation products with a dense rain gauge network and optimally merging their simulated hydrological flows using the Bayesian model averaging method. J. Hydrol. 2012, 452–453, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-J.; Shen, Y.J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Pei, H.W.; Brenning, A. Review of historical and projected future climatic and hydrological changes in mountainous semiarid Xinjiang (northwestern China), central Asia. Catena 2019, 187, 104343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collischonn, B.; Collischonn, W.; Tucci, C.E.M. Daily hydrological modeling in the Amazon basin using TRMM rainfall estimates. J. Hydrol. 2008, 360, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.Z.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Xu, J.; Ye, J.S.; Li, F.M.; Zhang, F. HRLT: A high-resolution (1 d, 1 km) and long-term (1961–2019) gridded dataset for surface temperature and precipitation across China, Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4793–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Arkin, P.; Arkin, P.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Gruber, A.; Janowiak, J.; McNab, A.; Rudolf, B.; et al. The Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) combined precipitation dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.; Hulme, M.; Jones, P. Representing twentieth century space–time climate variability. Part 2: Development of 1901–96 monthly grids of terrestrial surface climate. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 2217–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatagai, A.; Kamiguchi, K.; Arakawa, O.; Hamada, A.; Yasutomi, N.; Kitoh, A. APHRODITE: Constructing a Long-Term Daily Gridded Precipitation Dataset for Asia Based on a Dense Network of Rain Gauges. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.; Barnes, W.; Kozu, T.; Shiue, J.; Simpson, J. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) Sensor Package. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, K.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Q.H.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xue, X.W.; Chen, S. Evaluation of the TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis and its applicability in supporting reservoir operation and water resources management in Hanjiang basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.C.; Liu, M.F. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation products using rain gauge observations over the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastos, P.T.; Kapsomenakis, J.; Philandras, K.M. Evaluation of the TRMM 3B43 gridded precipitation estimates over Greece. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Barros, A.P. Using Fractal Downscaling of Satellite Precipitation Products for Hydrometeorological Applications. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahipour, A.; Ahmadi, H.; Aminnejad, B. A review of downscaling methods of satellite-based precipitation estimates. Earth Sci. Inform. 2021, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J. Predictions of climate change over Europe using statistical and dynamical downscaling techniques. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.G.; Ji, X.; Luo, X.; Li, X. Fine-Resolution Precipitation Mapping in a Mountainous Watershed: Geostatistical Downscaling of TRMM Products Based on Environmental Variables. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Rutten, M.M.; Droogers, P. Spatial downscaling of TRMM precipitation using vegetative response on the Iberian Peninsula. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, R.; Kliegrová, S.; Metelka, L. Non-linearity in statistical downscaling: Does it bring an improvement for daily temperature in Europe? Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.L.; Song, L. Spatial downscaling of monthly TRMM precipitation based on EVI and other geospatial variables over the Tibetan Plateau from 2001 to 2012. Mt. Res. Dev. 2015, 35, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.L.; Yang, Y.P.; Yue, X.F.; Zhao, X.D. A comparison of different regression algorithms for downscaling monthly satellite-based precipitation over north China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.H.; Duan, Z.; Qin, Z.H. An Improved Spatial Downscaling Procedure for TRMM 3B43 Precipitation Product Using Geographically Weighted Regression. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4592–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, X. Spatial downscaling of TRMM 3B43 precipitation considering spatial heterogeneity. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 3074–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Xiong, L.H.; Ma, Q.M.; Kim, J.S.; Chen, J.; Xu, C.Y. Improving daily spatial precipitation estimates by merging gauge observation with multiple satellite-based precipitation products based on the geographically weighted ridge regression method. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.N.; Wang, J.C.; Zhang, L.W.; Ji, C.J.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.K. Spatial Downscaling Model Combined with the Geographically Weighted Regression and Multifractal Models for Monthly GPM/IMERG Precipitation in Hubei Province, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Gao, J.B.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, J.G.; Li, S.C. Exploring spatially variable relationships between NDVI and climatic factors in a transition zone using geographically weighted regression. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 120, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, A.F.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Kraaijenbrink, P.D.A.; Shrestha, A.B.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate Change Impacts on the Upper Indus Hydrology: Sources, Shifts and Extremes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafeeque, M.E.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Sun, L. Revealing vertical distribution of precipitation in the glacierized Upper Indus Basin based on multiple datasets. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 2291–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Lakhankar, T.; Dars, G.H. Precipitation Trends over the Indus Basin. Climate 2019, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.; Zhang, W.C.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, B.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Shalamzari, M.J. Reconstructing high-resolution gridded precipitation data using an improved downscaling approach over the high altitude mountain regions of Upper Indus Basin (UIB). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. First results from Version 7 TRMM 3B43 precipitation product in combination with a new downscaling–calibration procedure. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanpour, A.K.; Hessels, T.; Moghim, S.; Afshar, A. Comparison and assessment of spatial downscaling methods for enhancing the accuracy of satellite-based precipitation over Lake Urmia Basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Q.; Zhou, L.Q.; Yu, W.; Yang, Y.; Teng, H.F.; Shi, Z. Improving TMPA 3B43 V7 Data Sets Using Land-Surface Characteristics and Ground Observations on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafeeque, M.; Luo, Y. A multi-perspective approach for selecting CMIP6 scenarios to project climate change impacts on glacio-hydrology with a case study in Upper Indus river basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 599, 126466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Droogers, P.; Jong, S.M.D.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Large-scale monitoring of snow cover and runoff simulation in Himalayan river basins using remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Zhang, F.; Tayyab, M.; Anjum, M.N.; Zaman, M.; Liu, J.G.; Farid, H.U.; Saddique, Q. Spatiotemporal analysis of precipitation variability in annual, seasonal and extreme values over upper Indus River basin. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, A.F.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Shrestha, A.B.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Consistent increase in High Asia’s runoff due to increasing glacier melt and precipitation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viviroli, D.; Weingartner, R. The hydrological significance of mountains: From regional to global scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.J.; Chen, Y.N. Global perspective on hydrology, water balance, and water resources management in arid basins. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbhandari, R.; Shrestha, A.B.; Kulkarni, A.; Patwardhan, S.K.; Bajracharya, S.R. Projected changes in climate over the Indus river basin using a high resolution regional climate model (PRECIS). Clim. Dynam. 2014, 44, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y. Suitability of the TRMM satellite rainfalls in driving a distributed hydrological model for water balance computations in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426–427, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Wang, N.L.; Wang, S.J.; Zhou, L. Performance comparison of three predictor selection methods for statistical downscaling of daily precipitation. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 131, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, A.; Pourreza-Bilondi, M.; Khashei Siuki, A.K.; Moghadam, J.R. Examination of Various Feature Selection Approaches for Daily Precipitation Downscaling in Different Climates. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.; Brunsdon, C.F.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2003, 86, 554–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Geographical weighting as a further refinement to regression modelling: An example focused on the NDVI–rainfall relationship. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.G.; Wu, C.Y.; Wang, L.; Gonsamo, A.; Shen, Y.; Niu, Z. A new satellite-based monthly precipitation downscaling algorithm with non-stationary relationship between precipitation and land surface characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, D.; Lee, T.S.; Ouarda, T.B.M.J.; Lee, J. Predictor selection for downscaling GCM data with LASSO. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D17116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teegavarapu, R.S.V.; Goly, A. Optimal selection of predictor variables in statistical downscaling models of precipitation. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 1969–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zang, F.; Zhao, C.; Liu, C. A GWR downscaling method to reconstruct high-resolution precipitation dataset based on GSMaP-Gauge data: A case study in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunsell, N.A. Characterization of land-surface precipitation feedback regimes with remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahri, Z.H.; Ludwig, F.; Moors, E.; Ahmad, B.; Khan, A.; Kabat, P. An appraisal of precipitation distribution in the high-altitude catchments of the Indus basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.R.; Fowler, H.J. Spatial and temporal variations in precipitation in the Upper Indus Basin, global teleconnections and hydrological implications. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.P.; Kim, G.; Williams, E.; Nesbitt, S. Probing orographic controls in the Himalayas during the monsoon using satellite imagery. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 4, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, J.P.; Herzog, M.; Cameron, A.P. Contribution of Cross-Barrier Moisture Transport to Precipitation in the Upper Indus River Basin. Mon. Weather Rev. 2020, 148, 2801–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.G.; Hong, Y.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) and its utility in hydrologic prediction in the La Plata Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Q.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.F.; Yu, W.; Yang, Y.Y. A spatial data mining algorithm for downscaling TMPA 3B43 V7 data over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau with the effects of systematic anomalies removed. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 20, 378–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.E.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Barella-Ortiz, A. A nonparametric statistical technique for combining global precipitation datasets: Development and hydrological evaluation over the Iberian Peninsula. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1371–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.W.; Maggioni, V.; Houser, P.; Xue, Y.; Rouf, T. A Nonparametric Statistical Technique for Spatial Downscaling of Precipitation over High Mountain Asia. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
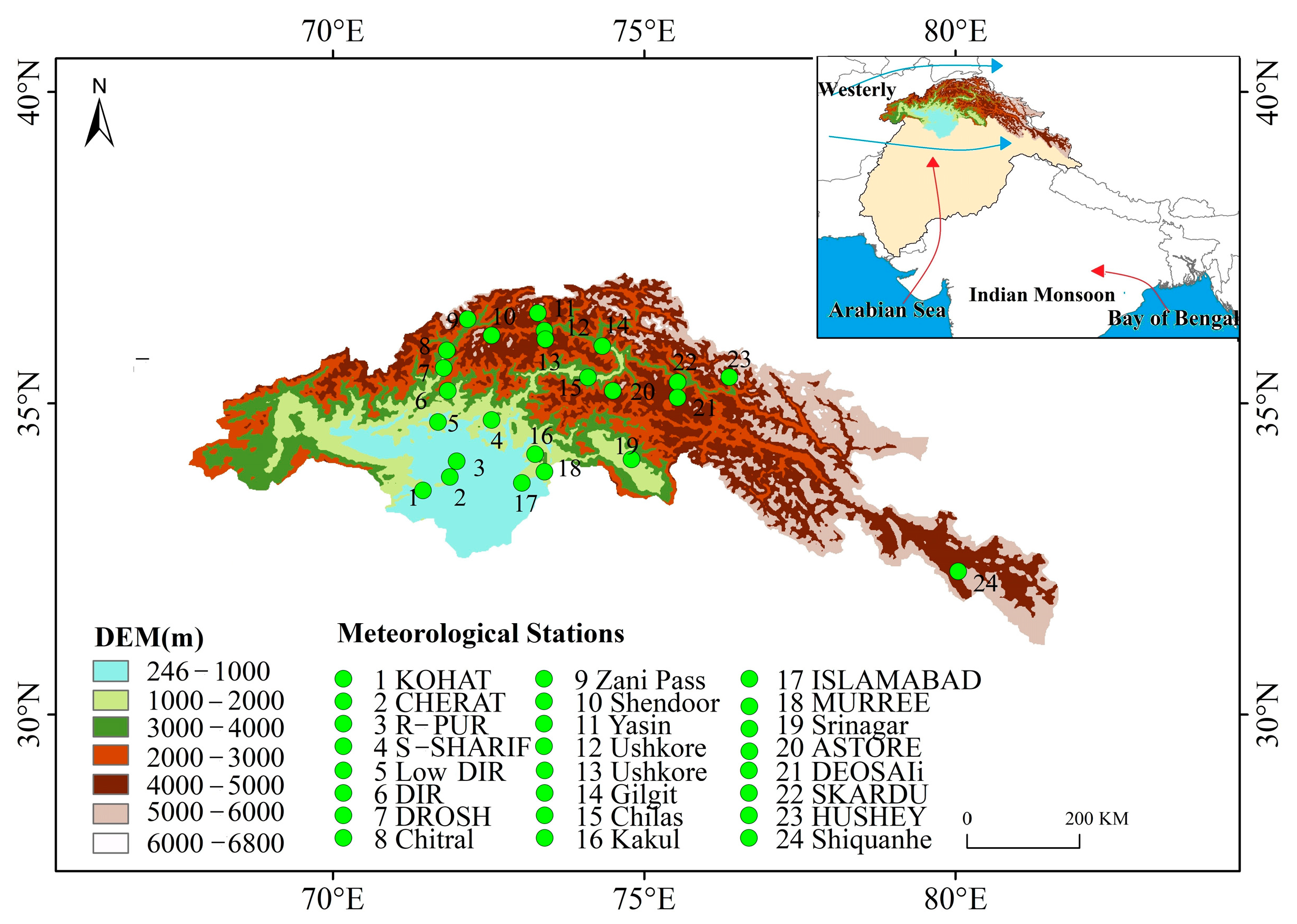
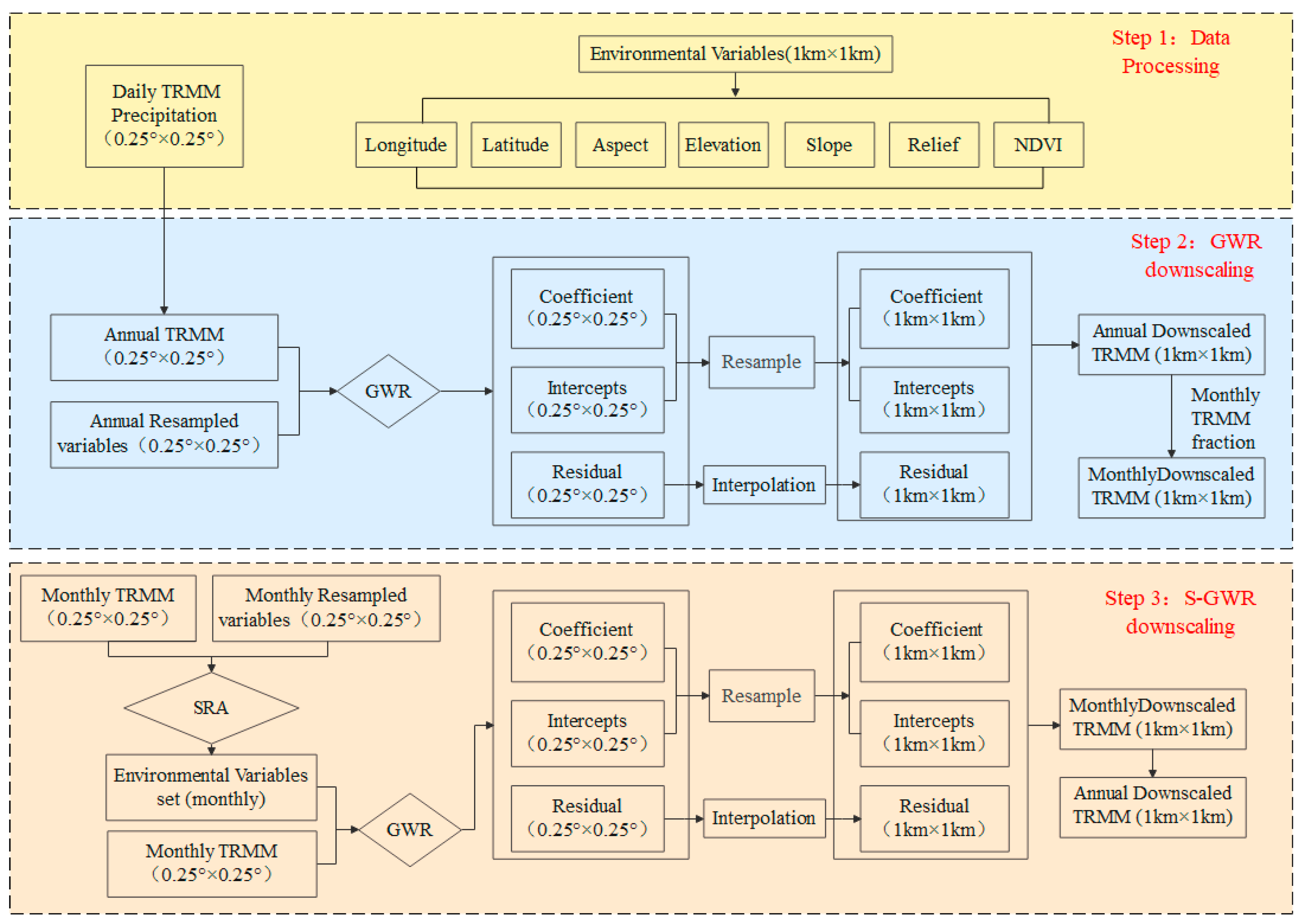
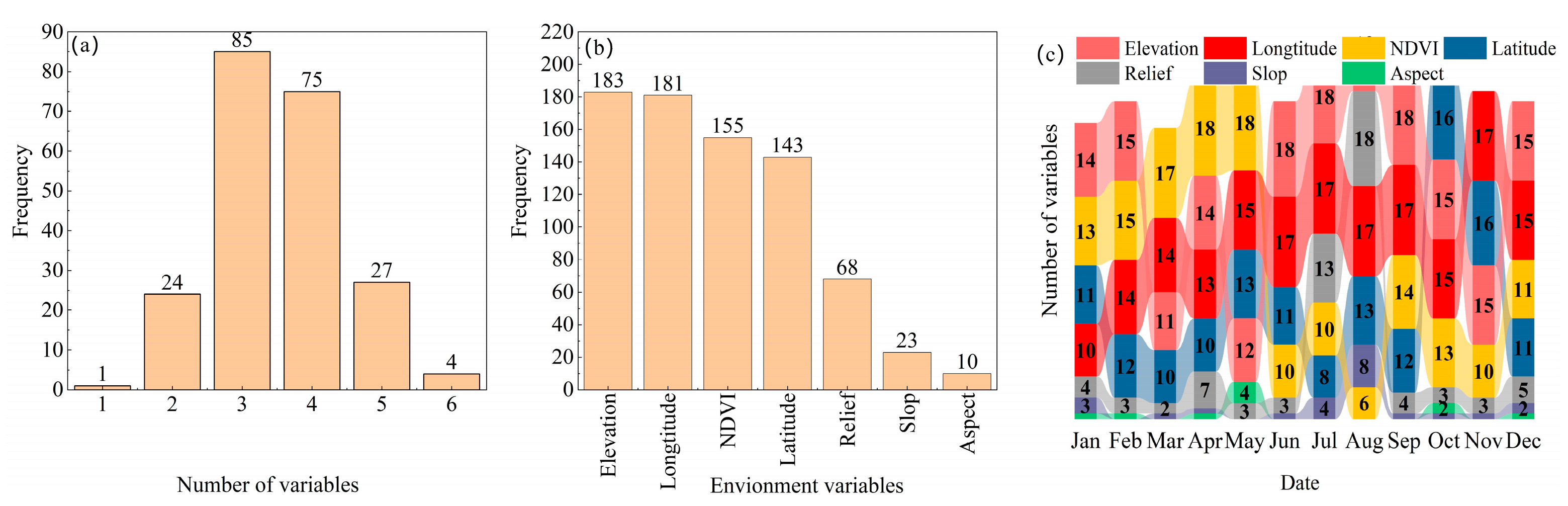
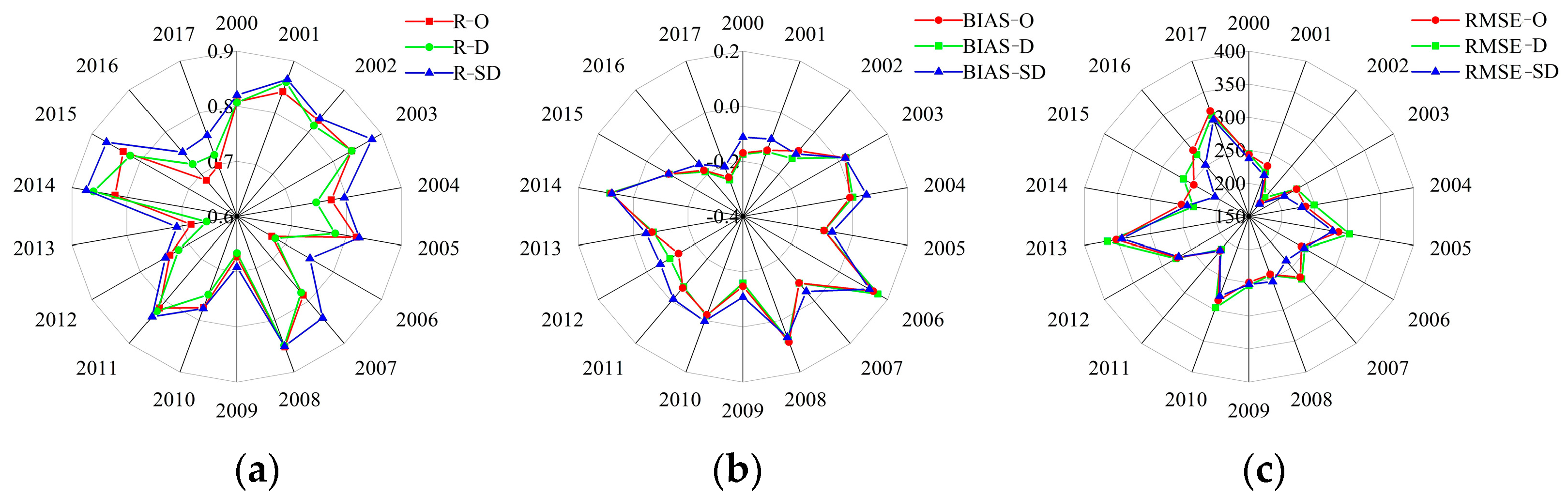
| Name | Agency | Longitude | Latitude | Elevation (m) | Annual Mean Precipitation (mm) | Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTORE | PMD | 74.9 | 35.37 | 2168 | 408.79 | 2000–2017 |
| CHERAT | PMD | 71.88 | 33.82 | 1372 | 635.51 | 2000–2017 |
| CHILAS | PMD | 74.1 | 35.42 | 1250 | 179.51 | 2000–2017 |
| DIR | PMD | 71.85 | 35.2 | 1375 | 1198.93 | 2000–2013 |
| DROSH | PMD | 71.783 | 35.57 | 1464 | 529.51 | 2000–2013 |
| Chitral | PMD | 71.83 | 35.85 | 1498 | 452.08 | 2000–2017 |
| Gilgit | PMD | 74.33 | 35.92 | 1460 | 148.79 | 2000–2017 |
| Gupis | PMD | 73.4 | 36.17 | 2156 | 234.23 | 2000–2017 |
| ISLAMABAD | PMD | 73.04 | 33.72 | 831 | 1215.75 | 2000–2017 |
| Lower Dir | PMD | 71.69 | 34.7 | 1375 | 835.57 | 2000–2017 |
| KAKUL | PMD | 73.3 | 34.18 | 1308 | 1159.29 | 2000–2013 |
| KOHAT | PMD | 71.43 | 33.55 | 513 | 564.38 | 2000–2013 |
| MURREE | PMD | 73.4 | 33.9 | 2291 | 1539.37 | 2000–2017 |
| R-PUR | PMD | 71.97 | 34.08 | 320 | 762.57 | 2000–2013 |
| SKARDU | PMD | 75.54 | 35.34 | 2267 | 233.86 | 2000–2013 |
| S-SHARIF | PMD | 72.35 | 34.82 | 970 | 988.24 | 2000–2013 |
| Srinagar | PMD | 74.8 | 34.1 | 1604 | 565.22 | 2000–2017 |
| Shiquanhe | CIMISS | 80.05 | 32.3 | 4280 | 67.53 | 2000–2013 |
| Ushkore | WAPDA | 73.42 | 36.03 | 3051 | 454.31 | 2000–2017 |
| Yasin | WAPDA | 73.29 | 36.45 | 3280 | 673.11 | 2000–2017 |
| Zani Pass | WAPDA | 72.17 | 36.35 | 3839 | 315.06 | 2000–2017 |
| Deosai | WAPDA | 75.54 | 35.09 | 4149 | 435.98 | 2000–2017 |
| Hushey | WAPDA | 76.37 | 35.42 | 3076 | 666.58 | 2000–2017 |
| Shendoor | WAPDA | 72.55 | 36.09 | 3712 | 408.18 | 2000–2017 |
| Stations | R | BIAS | RMSE(mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | GWR | S-GWR | O | GWR | S-GWR | O | GWR | S-GWR | |
| ASTORE | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.56 | −0.27 | −0.23 | −0.28 | 31.11 | 31.44 | 31.59 |
| CHERAT | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.83 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.34 | 56.00 | 49.06 | 45.62 |
| Chitral | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.52 | 0.26 | 0.34 | 0.16 | 57.35 | 59.35 | 57.90 |
| CHILAS | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.46 | 27.15 | 27.50 | 26.41 |
| DIR | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.83 | −0.38 | −0.30 | −0.28 | 55.68 | 50.79 | 48.63 |
| DROSH | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 28.92 | 27.06 | 26.78 |
| Gilgit | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.62 | 0.85 | 0.46 | 0.36 | 33.64 | 27.76 | 30.52 |
| Gupis | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.59 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 32.90 | 33.55 | 31.96 |
| M-ABAD | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.01 | −0.03 | −0.07 | 73.28 | 73.25 | 73.63 |
| KOHAT | 0.53 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.41 | 0.54 | 0.37 | 52.91 | 58.26 | 51.90 |
| KAKUL | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.78 | −0.03 | −0.09 | −0.07 | 49.55 | 50.12 | 48.50 |
| Lower dir | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.75 | 0.04 | −0.02 | 0.02 | 89.13 | 86.88 | 48.05 |
| MURREE | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.89 | −0.24 | −0.40 | −0.40 | 71.40 | 87.81 | 55.58 |
| R-PUR | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 52.73 | 50.09 | 51.83 |
| S-SHARIF | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.83 | 0.25 | −0.22 | −0.20 | 57.06 | 40.25 | 40.47 |
| Srinagar | 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.42 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 66.27 | 66.31 | 66.25 |
| SKARDU | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.54 | −0.32 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 20.17 | 21.10 | 20.17 |
| Shiquanhe | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.82 | −0.72 | −0.73 | −0.71 | 10.36 | 9.51 | 9.09 |
| Ushkore | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.51 | −0.44 | −0.46 | −0.43 | 44.46 | 43.27 | 44.90 |
| Yasin | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.47 | −0.58 | −0.56 | −0.56 | 74.50 | 75.36 | 74.81 |
| Zani Pass | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.55 | −0.15 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 36.43 | 42.10 | 37.34 |
| Deosai | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.59 | −0.44 | −0.44 | −0.41 | 39.48 | 39.32 | 38.36 |
| Hushey | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.49 | −0.47 | −0.43 | −0.43 | 60.07 | 59.84 | 60.30 |
| Shendoor | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.60 | −0.31 | −0.24 | −0.25 | 43.41 | 43.68 | 42.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.-J.; Zaman, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X. Accounting for Non-Stationary Relationships between Precipitation and Environmental Variables for Downscaling Monthly TRMM Precipitation in the Upper Indus Basin. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4356. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174356
Wang Y, Shen Y-J, Zaman M, Guo Y, Zhang X. Accounting for Non-Stationary Relationships between Precipitation and Environmental Variables for Downscaling Monthly TRMM Precipitation in the Upper Indus Basin. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(17):4356. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174356
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yixuan, Yan-Jun Shen, Muhammad Zaman, Ying Guo, and Xiaolong Zhang. 2023. "Accounting for Non-Stationary Relationships between Precipitation and Environmental Variables for Downscaling Monthly TRMM Precipitation in the Upper Indus Basin" Remote Sensing 15, no. 17: 4356. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174356
APA StyleWang, Y., Shen, Y.-J., Zaman, M., Guo, Y., & Zhang, X. (2023). Accounting for Non-Stationary Relationships between Precipitation and Environmental Variables for Downscaling Monthly TRMM Precipitation in the Upper Indus Basin. Remote Sensing, 15(17), 4356. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174356








