Calibrating Nighttime Satellite Imagery with Red Photometer Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
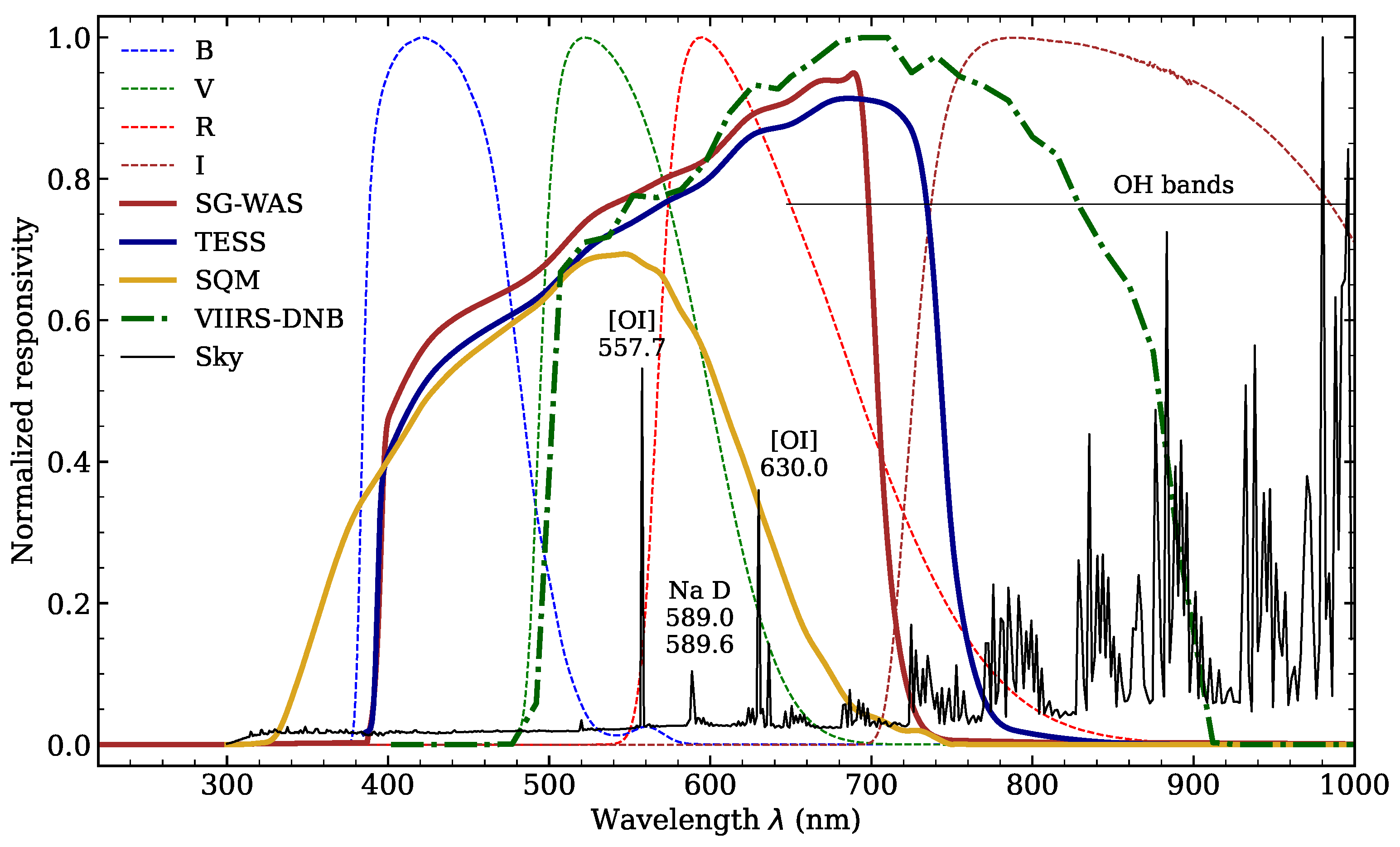
2. Materials
2.1. Photometer Network and VIIRS DNB Data
2.2. Natural Effects That Contribute to the Night Sky Brightness
3. Methods
3.1. Photometer Data Analysis
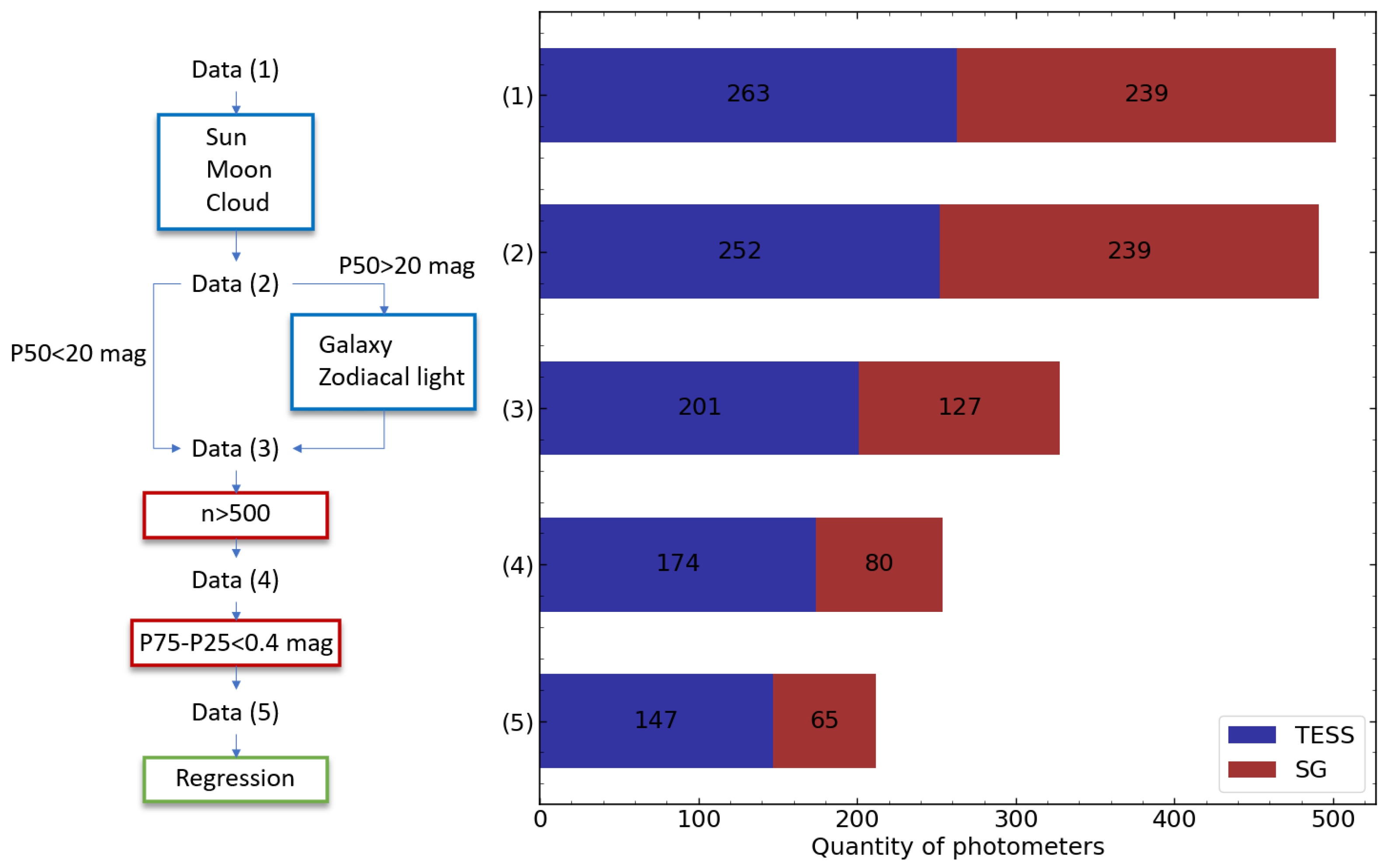
3.1.1. Optimal Minimum Sample Size
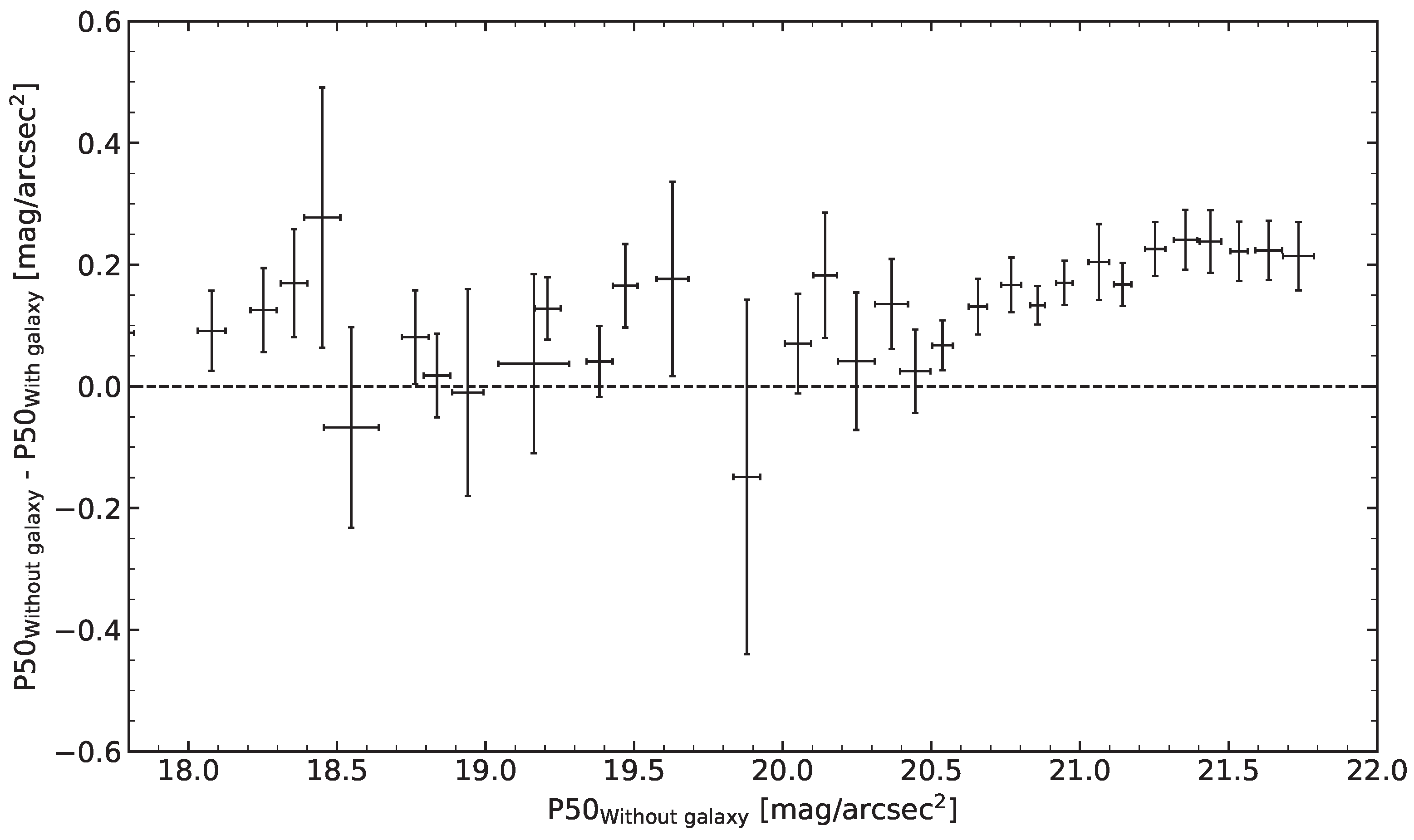
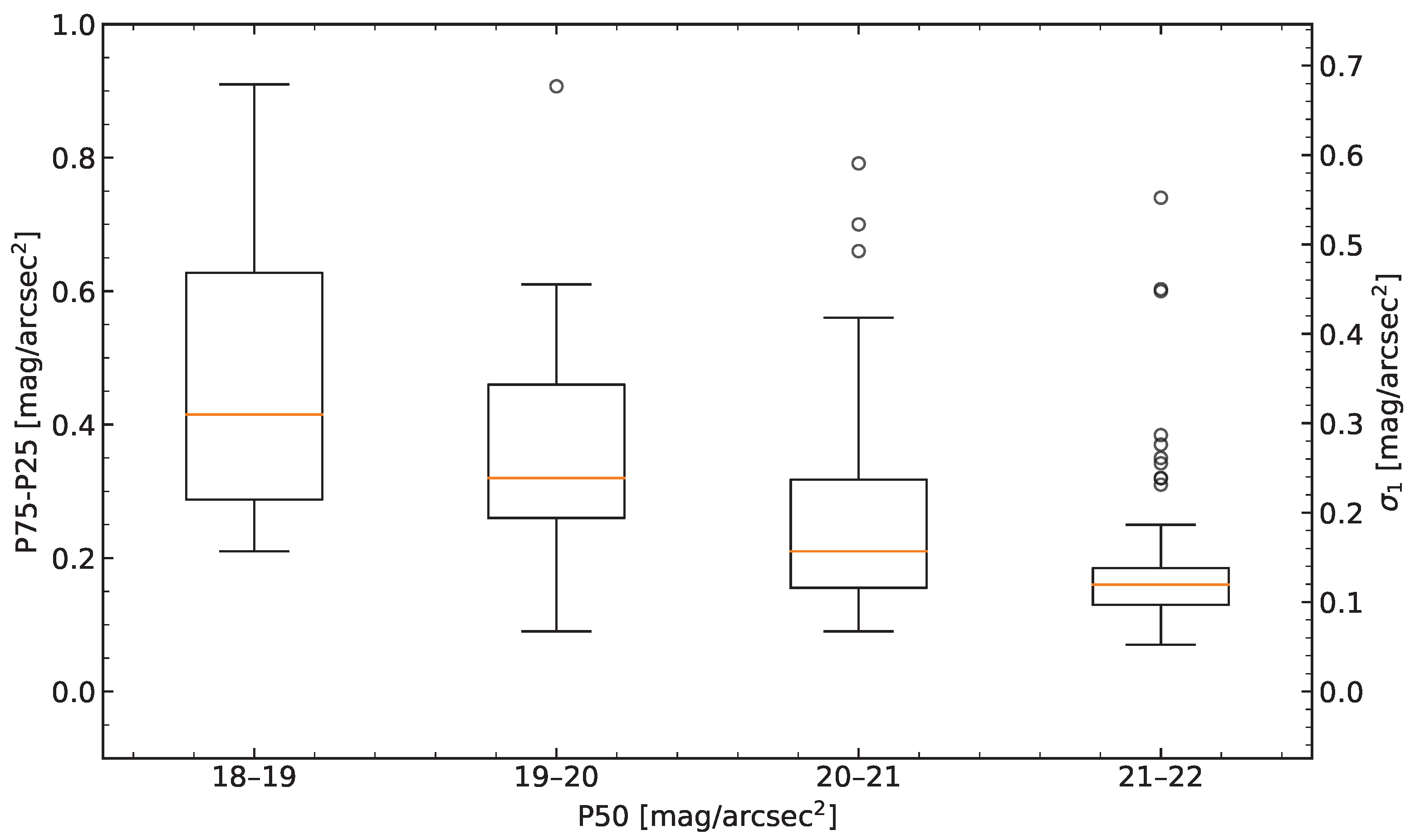
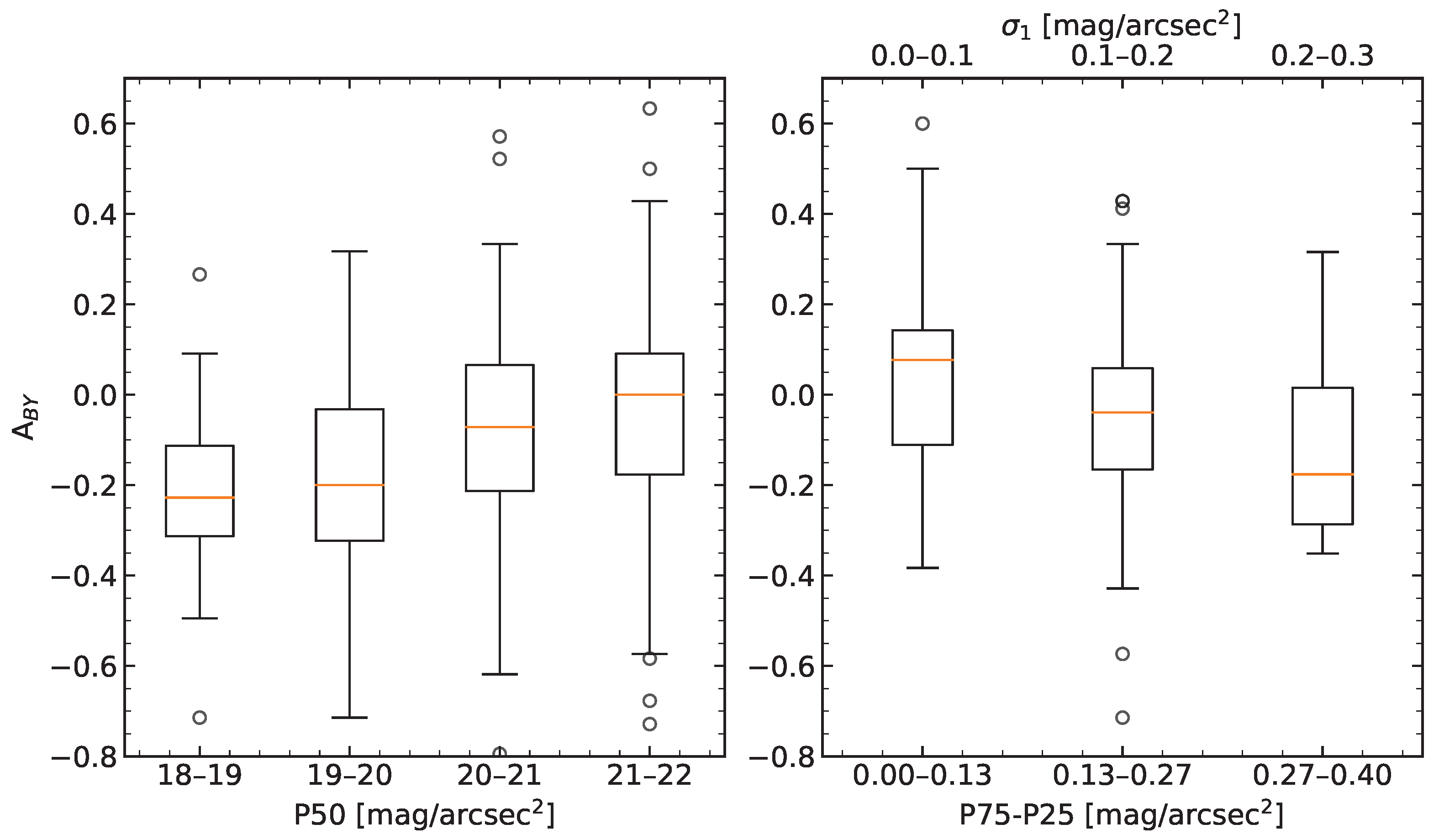
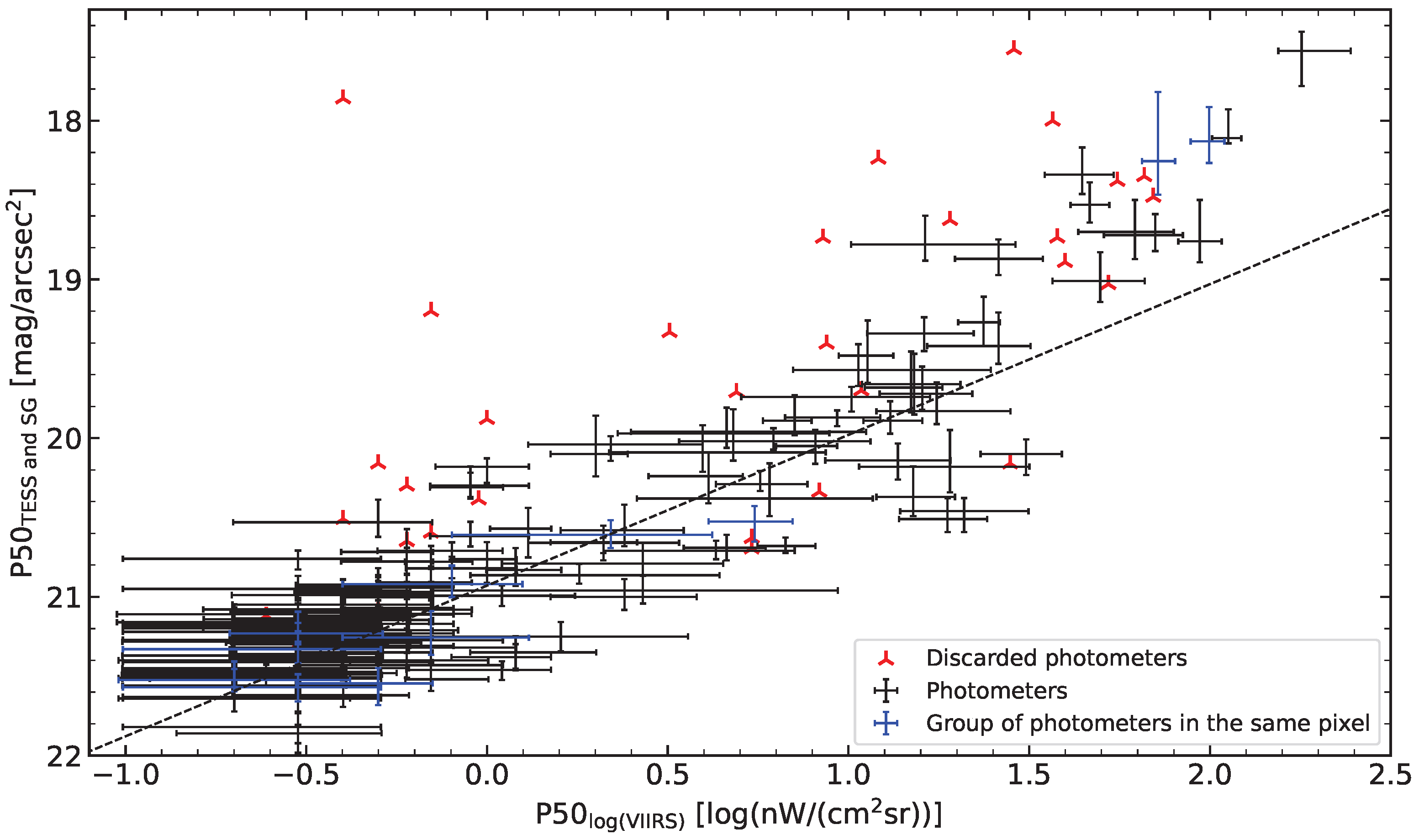
3.1.2. The Milky Way Effect as a Function of Location Brightness and Re-Evaluation of the Galaxy Filter
3.1.3. Photometer Data Distribution
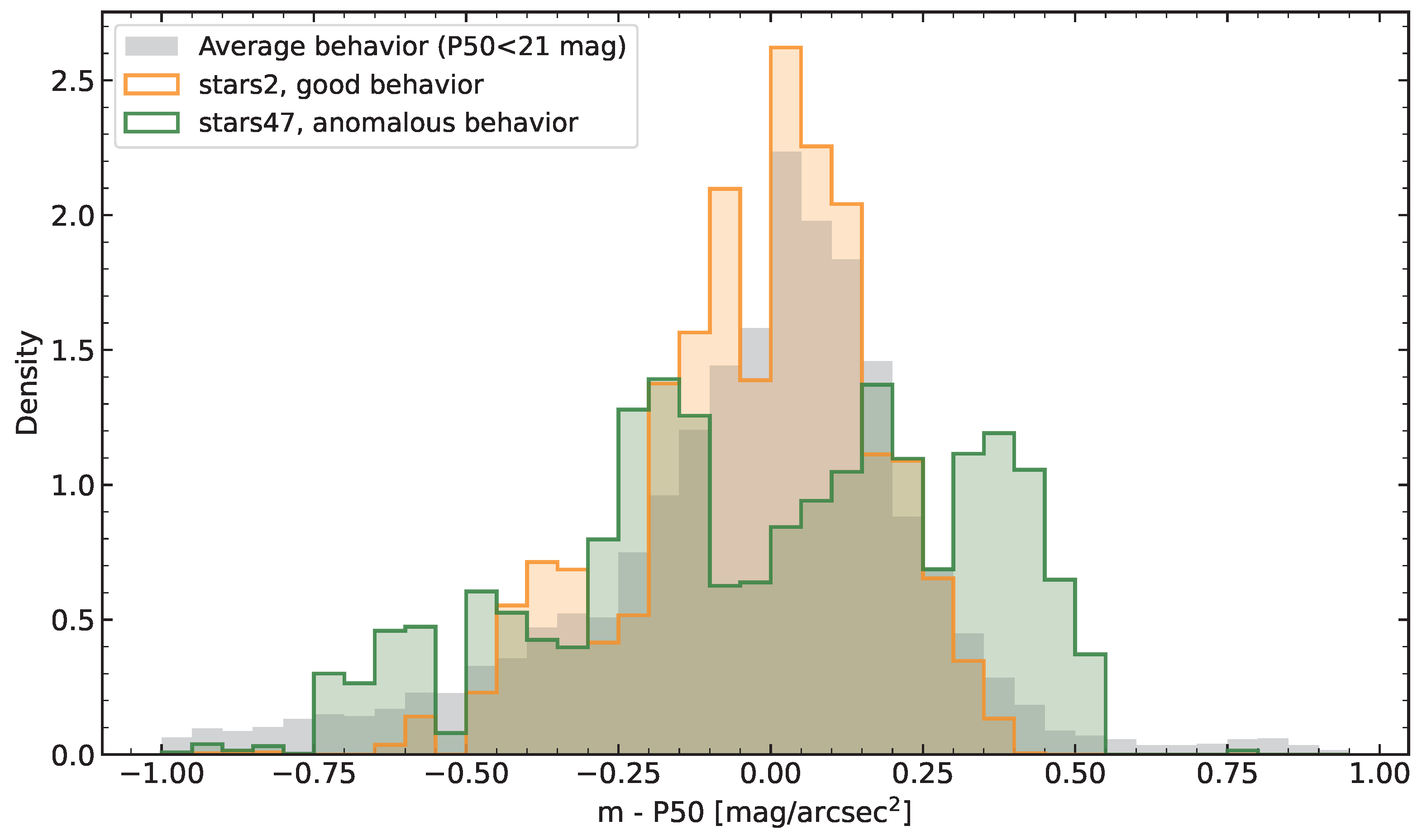
3.1.4. Optimal Behavior
3.2. Photometer Data Cleaning and Wrangling
3.3. Regression
4. Results
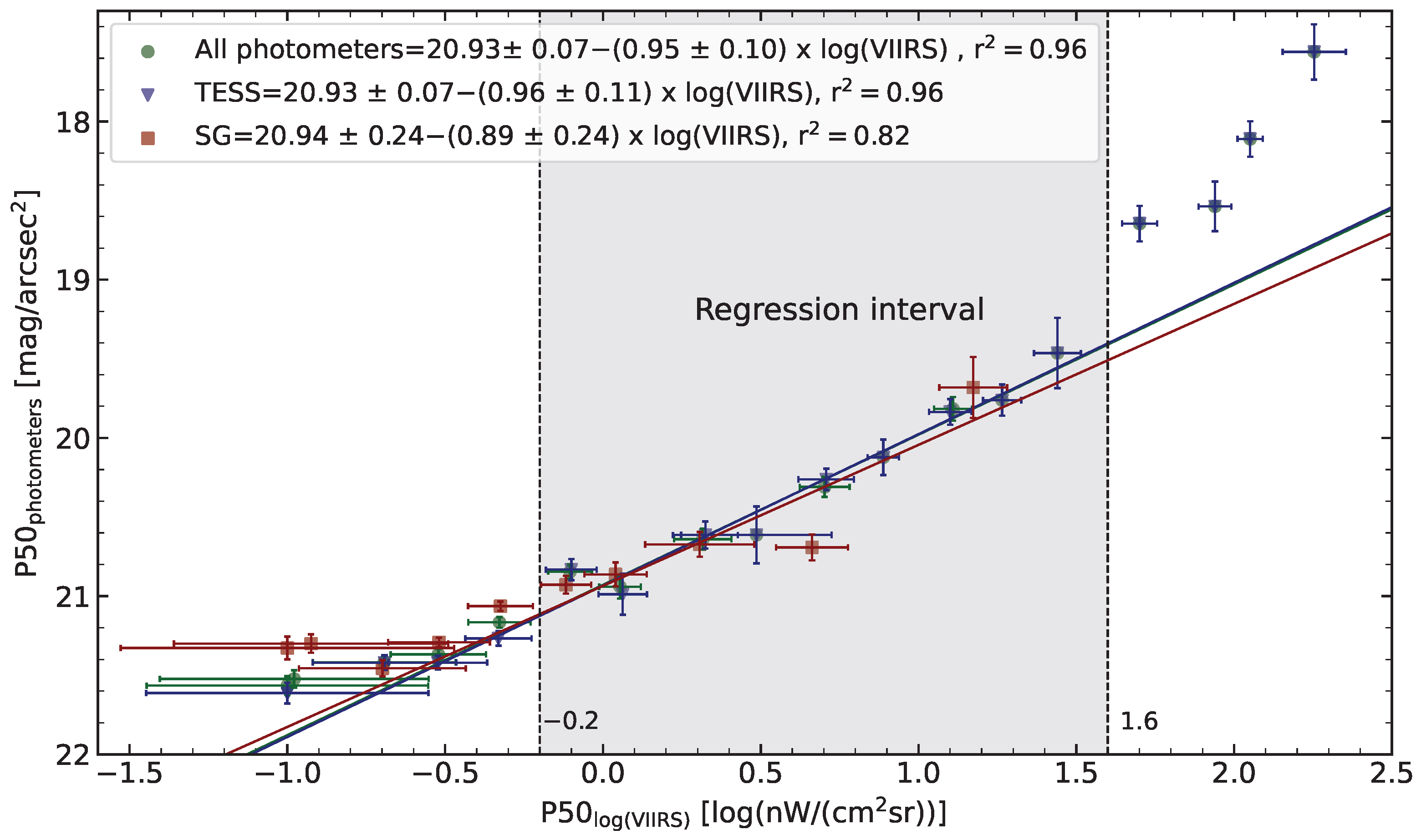
4.1. VIIRS and Photometer Data Correlation
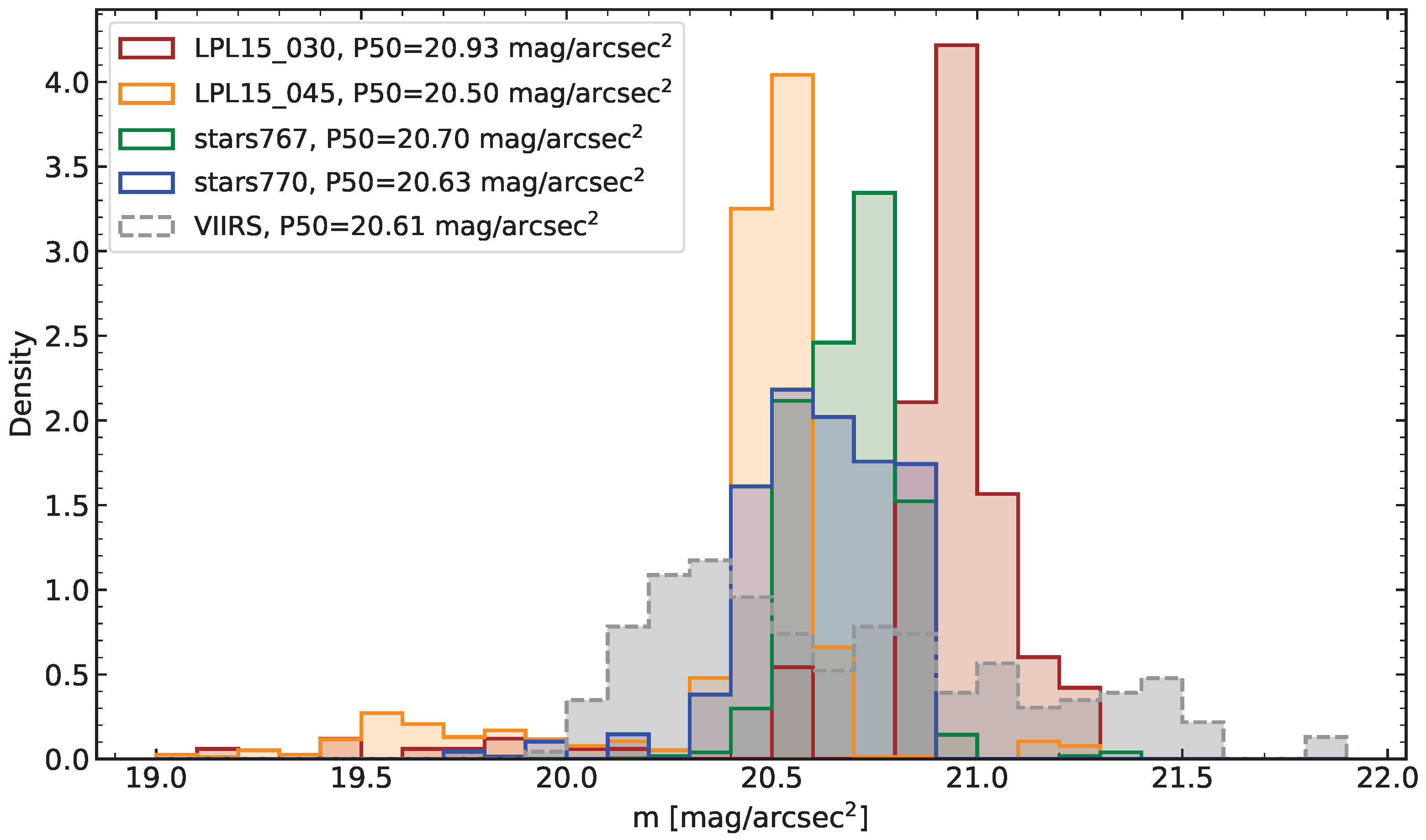
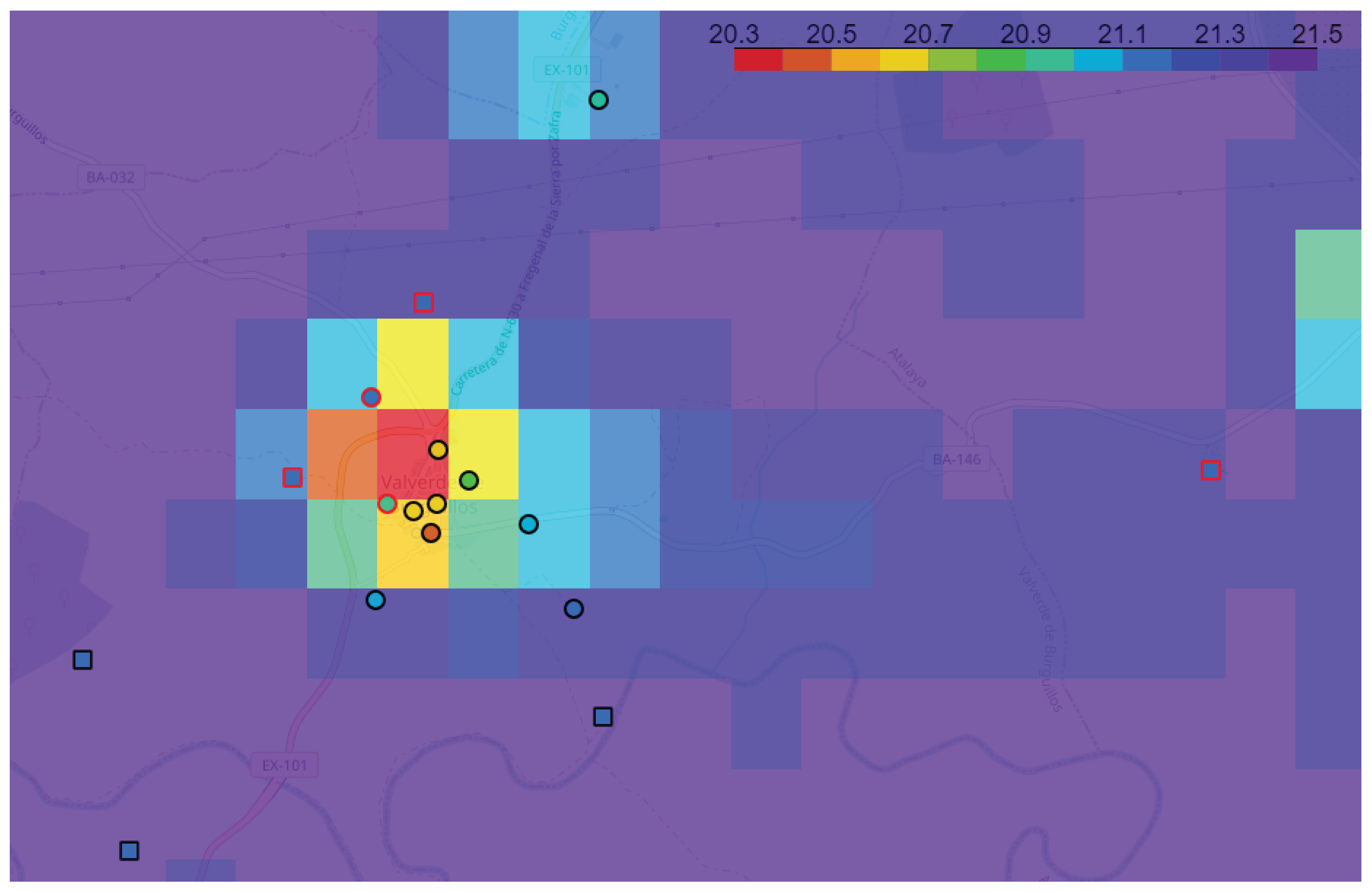
4.2. Application to Valverde de Burguillos
5. Discussion
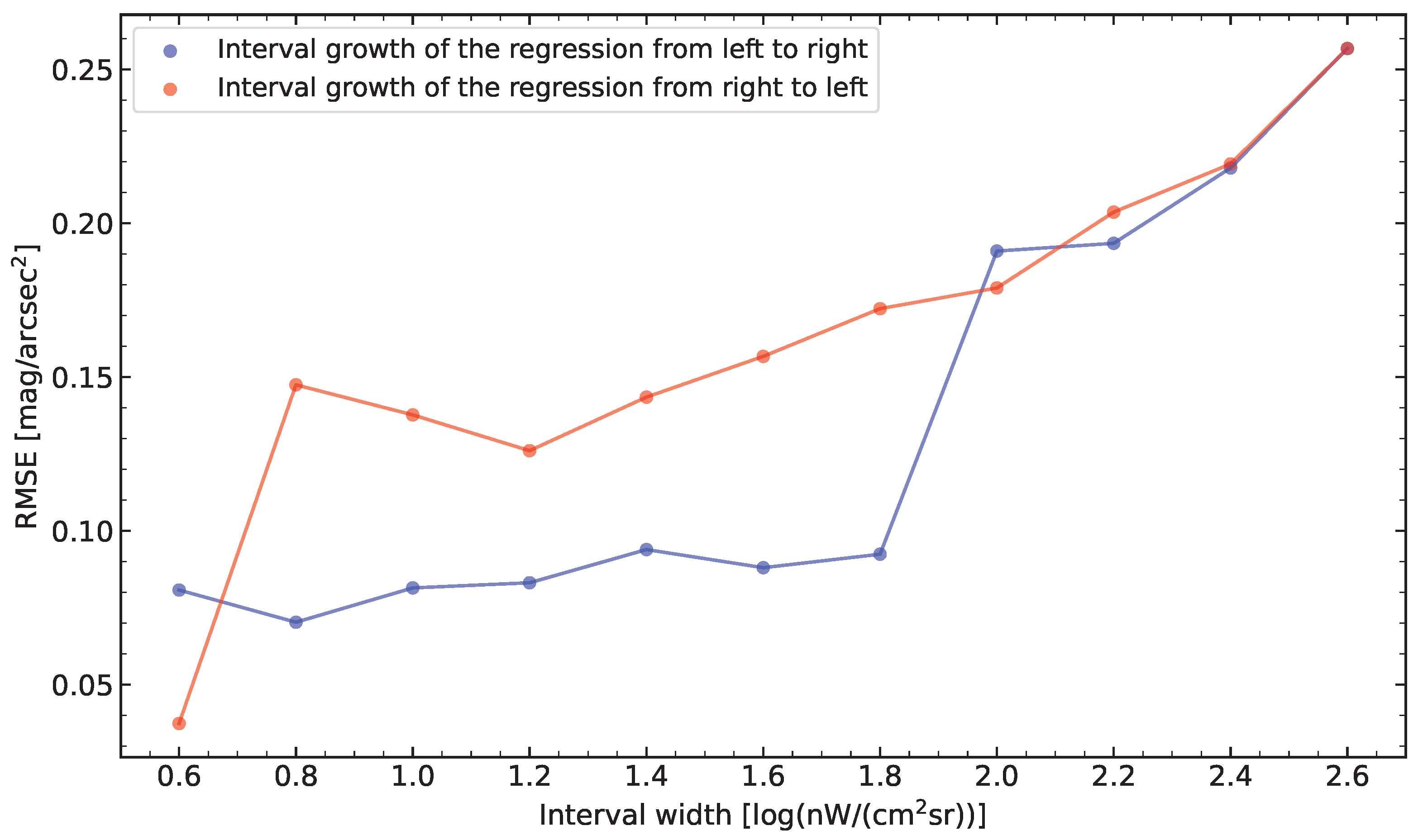
5.1. Comparison of Regression and Range of Applicability
5.2. Error and VIIRS Spatial Resolution
5.3. Potential Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Uncertainty Calculation for Galaxy Filter Re-Evaluation
Appendix B. Uncertainty Calculation for the Data Points of the Regression
Appendix C. Uncertainty Calculation for Transforming VIIRS Data to SG and TESS Units
References
- Falchi, F.; Cinzano, P.; Duriscoe, D.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Portnov, B.A.; Rybnikova, N.A.; Furgoni, R. The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölker, F.; Wolter, C.; Perkin, E.K.; Tockner, K. Light pollution as a biodiversity threat. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 681–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J.; Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Hopkins, J. The ecological impacts of nighttime light pollution: A mechanistic appraisal. Biol. Rev. 2013, 88, 912–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Cruse, D.; Gaston, K.J. Ecological effects of artificial light at night on wild plants. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, A.C.; Lewis, S.M. The impact of artificial light at night on nocturnal insects: A review and synthesis. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 11337–11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.H.; Walton, J.C.; DeVries, A.C.; Nelson, R.J. Circadian rhythm disruption and mental health. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.H.; Bumgarner, J.R.; Walton, J.C.; Liu, J.A.; Meléndez-Fernández, O.H.; Nelson, R.J.; DeVries, A.C. Light Pollution and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, C.; Pattison, P.M.; Houser, K.; Herf, M.; Phillips, A.J.K.; Wright, K.P.; Skene, D.J.; Brainard, G.C.; Boivin, D.B.; Glickman, G. A Review of Human Physiological Responses to Light: Implications for the Development of Integrative Lighting Solutions. LEUKOS 2022, 18, 387–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Langevelde, F.; van Grunsven, R.H.A.; Veenendaal, E.M.; Fijen, T.P.M. Artificial night lighting inhibits feeding in moths. Biol. Lett. 2017, 13, 20160874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shier, D.M.; Bird, A.K.; Wang, T.B. Effects of artificial light at night on the foraging behavior of an endangered nocturnal mammal. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, C.; Fournari–Konstantinidou, I.; Sourbès, L.; Koutsoubas, D.; Mazaris, A.D. Reduction of sea turtle population recruitment caused by nightlight: Evidence from the Mediterranean region. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 153, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doren, B.M.V.; Willard, D.E.; Hennen, M.; Horton, K.G.; Stuber, E.F.; Sheldon, D.; Sivakumar, A.H.; Wang, J.; Farnsworth, A.; Winger, B.M. Drivers of fatal bird collisions in an urban center. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101666118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubisic, M.; Haim, A.; Bhusal, P.; Dominoni, D.M.; Gabriel, K.M.A.; Jechow, A.; Kupprat, F.; Lerner, A.; Marchant, P.; Riley, W.; et al. Light Pollution, Circadian Photoreception, and Melatonin in Vertebrates. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, J.D.; Buler, J.J.; Schreckengost, T.; Smolinsky, J.A.; Boone, M.; Emiel van Loon, E.; Dawson, D.K.; Walters, E.L. Artificial light at night confounds broad-scale habitat use by migrating birds. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doren, B.M.V.; Horton, K.G.; Dokter, A.M.; Klinck, H.; Elbin, S.B.; Farnsworth, A. High-intensity urban light installation dramatically alters nocturnal bird migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11175–11180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.F. The California Site Survey. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1970, 82, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, A.S.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Zamorano, J.; Gallego, J.; Gaston, K.J. The nature of the diffuse light near cities detected in nighttime satellite imagery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T.; Guo, H.; Yin, R.; Leng, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, G. Potentiality of Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Imagery to Investigate Artificial Light Pollution. Sensors 2018, 18, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinzano, P. Report on Sky Quality Meter, Version L. 2007. Available online: https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.35630.51526 (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Zamorano, J.; García, C.; Tapia, C.; de Miguel, A.S.; Pascual, S.; Gallego, J. STARS4ALL Night Sky Brightness Photometer. Int. J. Sustain. Light. 2017, 18, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, M.R.; Puig-Subirà, M.; Serra-Ricart, M.; Lemes-Perera, S.; Mallorquín, M.; López, C. SG-WAS: A New Wireless Autonomous Night Sky Brightness Sensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyatikanto, R.; Admiranto, A.G.; Putri, G.P.; Elyyani; Siti; Maryam; Suryana, N. Map of Sky Brightness over Greater Bandung and the Prospect of Astro-Tourism. Indones. J. Geogr. 2019, 51, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, M.R.; Serra-Ricart, M.; Lemes-Perera, S.; Mallorquín, M. Natural Night Sky Brightness during Solar Minimum. Astron. J. 2021, 162, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.L. Astronomical Measurements in the Infrared. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1966, 4, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessell, M.S. UBVRI passbands. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1990, 102, 1181–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, S.; Kausch, W.; Barden, M.; Jones, A.M.; Szyszka, C.; Kimeswenger, S.; Vinther, J. An atmospheric radiation model for Cerro Paranal. I. The optical spectral range. A&A 2012, 543, A92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Kalb, V.; Miller, S.D.; Molthan, A.; Schultz, L.; Bell, J.; Stokes, E.C.; Pandey, B.; et al. NASA’s Black Marble nighttime lights product suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Bootstrap Methods: Another Look at the Jackknife. Ann. Stat. 1979, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
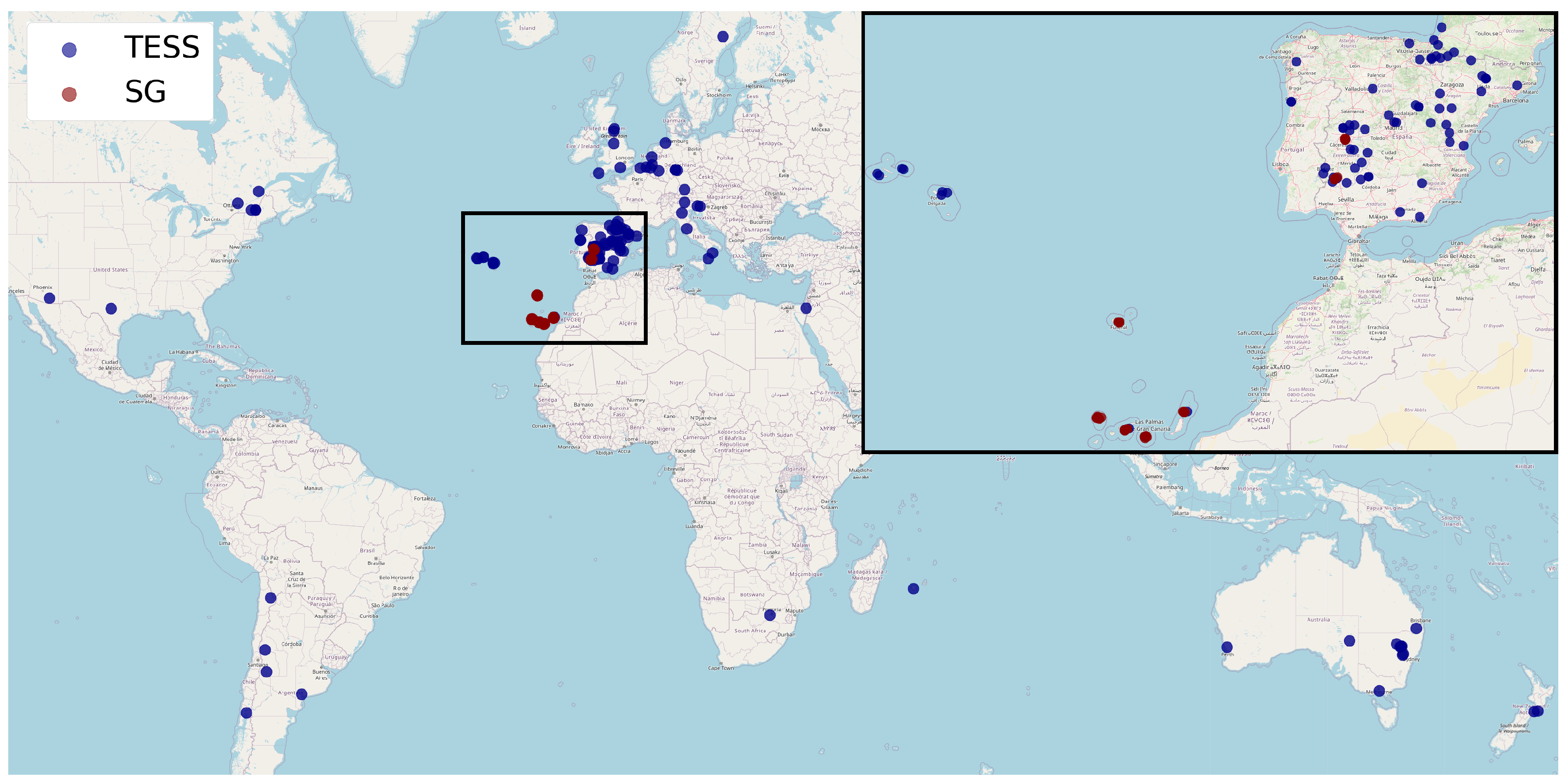
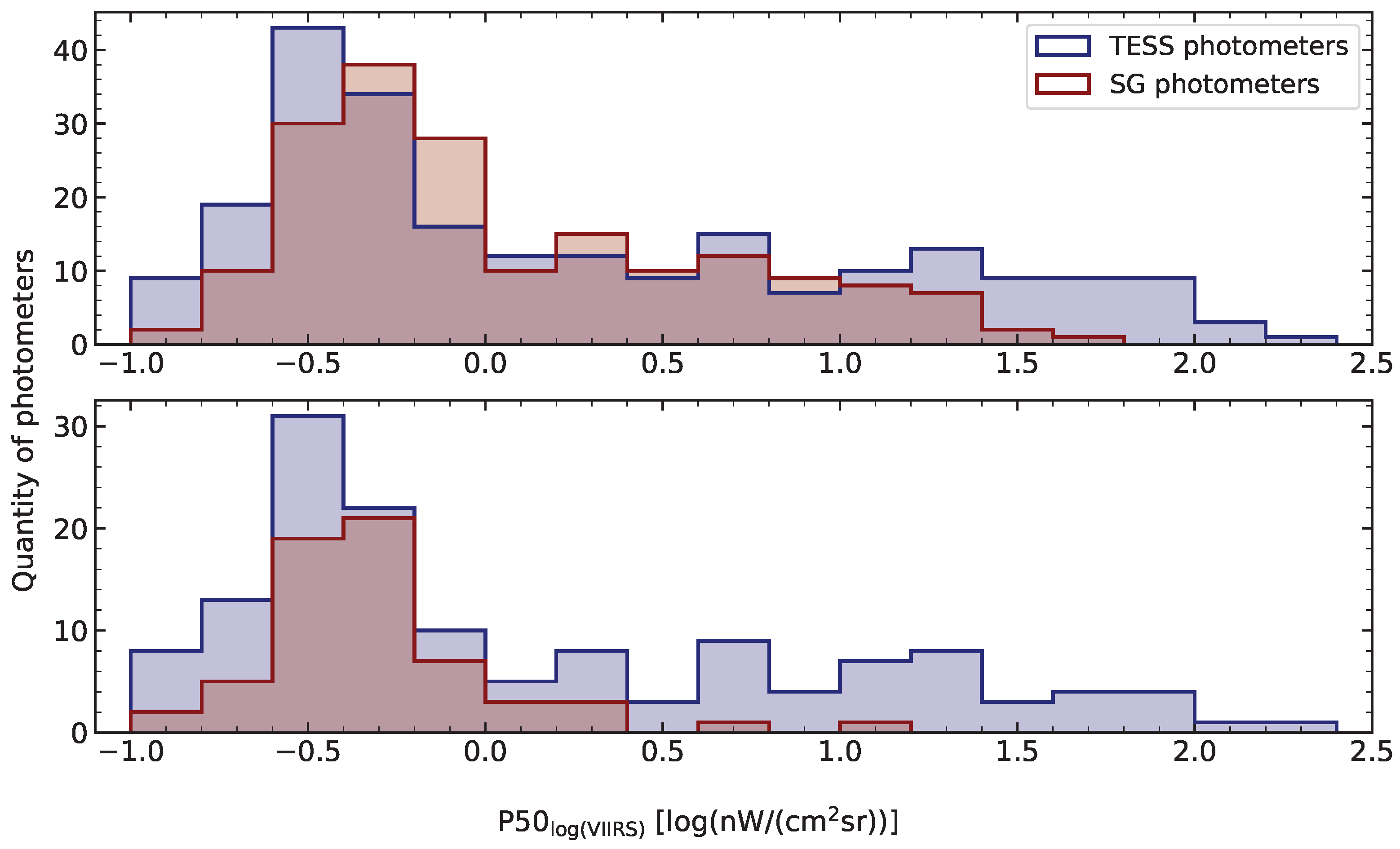
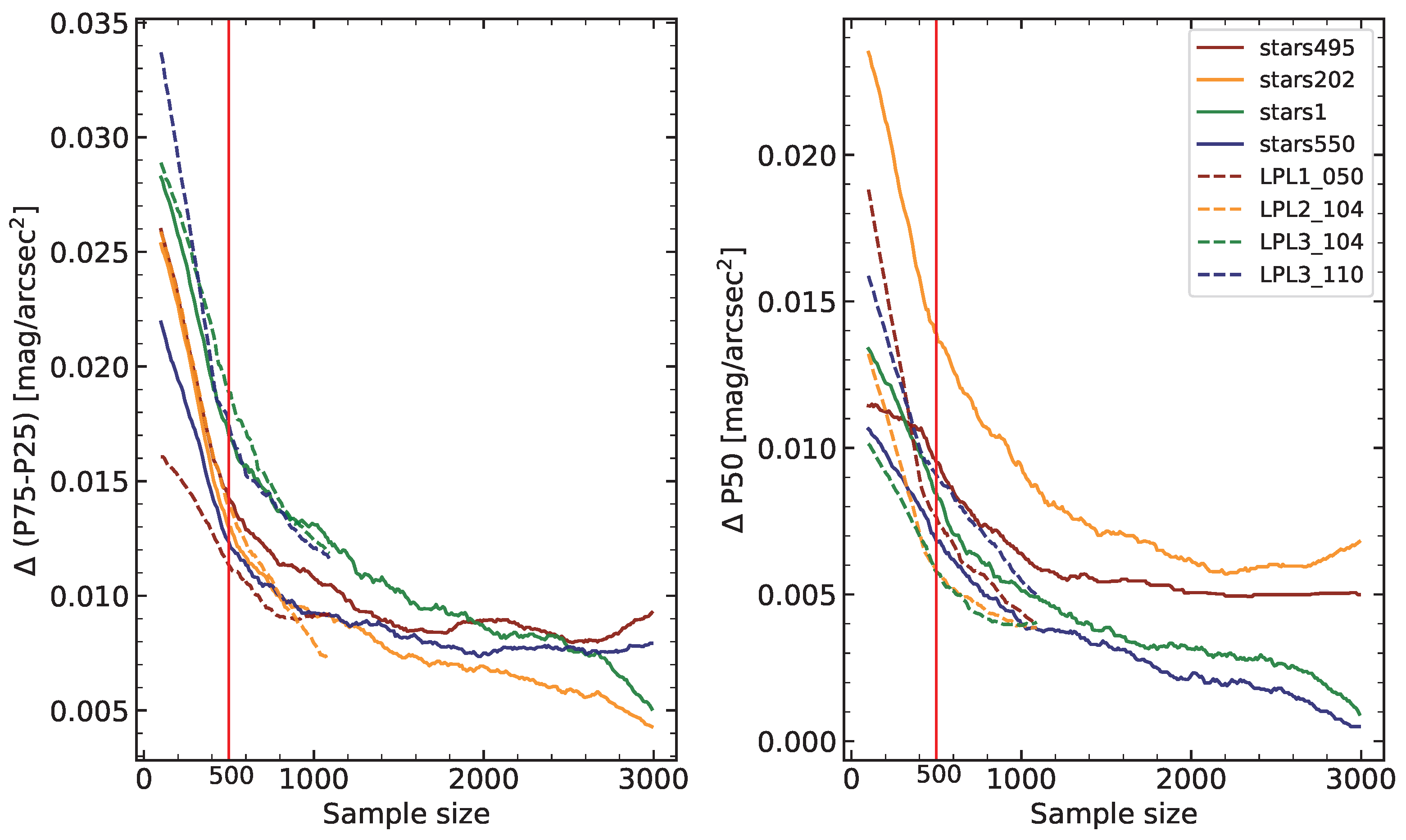


| TESS | SG | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor | TSL37 | TSL37 |
| Field of view | 17 | 18 vertical and 20 horizontal |
| Communication unit | WIFI | WIFI, LoRA and LTE-M |
| Autonomous | No | Yes |
| Other uncertainty | 0.04 mag/arcsec | 0.02 mag/arcsec |
| Time interval between | 1 min | 5 min |
| measurements | (One measurement) | (Average of 10 measurements) |
| Time Interval between Measurements | Photometers |
|---|---|
| 30 s | stars33, stars52, stars4, stars1 |
| 10 s | stars36, stars550 |
| Photometer | Type | Location | Number of | P50 | P75−P25 | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Points | (mag/arcsec) | |||||
| LPL1_050 | SG | Tenerife | 1608 | 21.28 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
| LPL2_104 | SG | La Palma | 1506 | 21.51 | 0.14 | 0.02 |
| LPL3_104 | SG | Madeira | 1365 | 20.62 | 0.15 | −0.17 |
| LPL3_110 | SG | Madeira | 1562 | 20.78 | 0.16 | −0.07 |
| stars1 | TESS | Madrid | 7557 | 18.37 | 0.16 | −0.25 |
| stars202 | TESS | Extremadura | 5663 | 21.46 | 0.18 | 0.00 |
| stars495 | TESS | Extremadura | 5948 | 21.17 | 0.18 | 0.00 |
| stars550 | TESS | Utrecht | 20,468 | 18.86 | 0.11 | −0.09 |
| VIIRS | VIIRS | VIIRS | VIIRS | VIIRS | VIIRS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (nW/(cmsr)) | (log(nW/(cmsr))) | (mag/arcsec) | |||
| 1.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 20.93 | 0.08 |
| 0.90 | 0.10 | −0.05 | 0.05 | 20.97 | 0.08 |
| 0.80 | 0.10 | −0.10 | 0.05 | 21.02 | 0.09 |
| 0.70 | 0.10 | −0.15 | 0.06 | 21.08 | 0.09 |
| 0.60 | 0.10 | −0.22 | 0.07 | 21.14 | 0.10 |
| 0.50 | 0.10 | −0.30 | 0.09 | 21.22 | 0.11 |
| 0.40 | 0.10 | −0.40 | 0.11 | 21.31 | 0.13 |
| 0.30 | 0.10 | −0.52 | 0.14 | 21.43 | 0.16 |
| 0.20 | 0.10 | −0.70 | 0.22 | 21.59 | 0.23 |
| 0.10 | 0.10 | −1.00 | 0.43 | 21.88 | 0.43 |
| Name | P50 | P25 | P75 | VIIRS | VIIRS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mag/arcsec) | (mag/arcsec) | ||||
| LPL15_043 | 20.69 | 20.61 | 20.77 | 20.30 | 0.10 |
| LPL15_045 | 20.50 | 20.43 | 20.54 | 20.57 | 0.08 |
| stars770 | 20.63 | 20.52 | 20.77 | 20.57 | 0.08 |
| stars767 | 20.70 | 20.60 | 20.76 | 20.57 | 0.08 |
| LPL15_030 | 20.93 | 20.89 | 21.00 | 20.57 | 0.08 |
| LPL15_057 | 20.86 | 20.79 | 20.92 | 20.64 | 0.08 |
| LPL15_027 | 21.12 | 21.04 | 21.17 | 21.02 | 0.09 |
| LPL15_046 | 21.08 | 21.01 | 21.14 | 21.08 | 0.09 |
| LPL15_006 | 20.94 | 20.86 | 20.99 | 21.14 | 0.10 |
| LPL15_011 | 21.17 | 21.10 | 21.21 | 21.14 | 0.10 |
| LPL15_005 | 21.09 | 21.02 | 21.13 | 21.31 | 0.13 |
| LPL15_007 | 21.10 | 21.03 | 21.14 | 21.31 | 0.13 |
| LPL15_022 | 21.13 | 21.09 | 21.17 | 21.31 | 0.13 |
| LPL15_029 | 21.20 | 21.19 | 21.21 | 21.31 | 0.13 |
| LPL15_008 | 21.16 | 21.09 | 21.21 | 21.43 | 0.16 |
| LPL15_055 | 21.18 | 21.11 | 21.23 | 21.43 | 0.16 |
| LPL15_002 | 21.20 | 21.12 | 21.25 | 21.43 | 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandez-Ruiz, B.; Serra-Ricart, M.; Alarcon, M.R.; Lemes-Perera, S.; Santana-Perez, I.; Ruiz-Alzola, J. Calibrating Nighttime Satellite Imagery with Red Photometer Networks. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174189
Fernandez-Ruiz B, Serra-Ricart M, Alarcon MR, Lemes-Perera S, Santana-Perez I, Ruiz-Alzola J. Calibrating Nighttime Satellite Imagery with Red Photometer Networks. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(17):4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174189
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandez-Ruiz, Borja, Miquel Serra-Ricart, Miguel R. Alarcon, Samuel Lemes-Perera, Idafen Santana-Perez, and Juan Ruiz-Alzola. 2023. "Calibrating Nighttime Satellite Imagery with Red Photometer Networks" Remote Sensing 15, no. 17: 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174189
APA StyleFernandez-Ruiz, B., Serra-Ricart, M., Alarcon, M. R., Lemes-Perera, S., Santana-Perez, I., & Ruiz-Alzola, J. (2023). Calibrating Nighttime Satellite Imagery with Red Photometer Networks. Remote Sensing, 15(17), 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174189








