Abstract
Seagrasses are habitat-forming species that support biodiversity and a wide range of associated ecosystem services, from blue carbon capture to providing nursery areas for a variety of organisms. Their decline has been documented worldwide and is attributed to human impacts ranging from habitat loss and eutrophication to the effects of climate change. However, recent recovery trends have also been documented due to reductions in stressors, passive and active restoration, and even changes in environmental conditions owing to local management. In this study, we document for the first time the occurrence of Zostera noltei in the downstream area of the River Minho Estuary. This occurrence was unexpected given the hydrological conditions of the estuary, characterised by dredging and siltation. We reconstructed the occurrence and historical distribution of seagrass beds, and showed that they have existed in the region for more than a decade. The current distribution area was mapped using high-resolution multispectral remote sensing techniques, and in situ photoquadrats to complement the remote sensing information with an evaluation of the seagrass cover. A current seagrass area of 0.81 ha was found with an average cover of 70%. However, the Minho Estuary continues to be strongly affected by sediment deposition, which may affect the seagrass population in the long term. Continued surveys are recommended to confirm the long-term trend of colonisation of this important habitat, which ultimately provides so many benefits to coastal ecosystems and humankind.
1. Introduction
Seagrasses are aquatic plants with a three-dimensional structure that provide habitat for a variety of other species, thus providing the basis for high faunal productivity [1,2,3]. In addition to this fundamental role in coastal ecosystems, they also provide other ecosystem services that translate into various benefits for social communities, such as coastal protection through sediment stabilisation, fisheries as nursery grounds for a variety of commercial species or by mediating a rich food-web, mediation of water quality through nutrient cycling, climate regulation, and various related cultural services [2,3,4]. Recently, their potential for climate regulation has received a significant amount of attention [5,6]. As one of the most important primary producers in coastal ecosystems, seagrasses can sequester carbon more efficiently than their terrestrial relatives, and the carbon then sinks into the sediment where it can be stored for millennia, forming blue carbon [5,7]. This blue carbon may help improve the ability of marine ecosystems to adapt to and mitigate future undesirable climate-related changes [5,6,8]. In addition, the conservation and restoration of seagrass species would also help increase the biodiversity of local communities [9], including endangered or threatened species [10], their productivity (e.g., [1]), functional redundancy, and potential ecosystem resilience to other threats [11,12]. As a result, their importance is now recognized globally [3,13], and various initiatives have been developed to promote their conservation [7,14] and even active restoration as nature-based solutions to address a variety of environmental challenges, ranging from mitigating climate change and biodiversity loss to delivering other societal benefits [15,16].
Despite their momentous importance, seagrasses have remained largely unnoticed and unprotected, and are extremely vulnerable to human action [3]. They have declined over time due to intense human activity, including pollution and eutrophication (e.g., [1,12]), dredging [17], hydrological changes that also affect sedimentation dynamics [18], habitat reclamation, and climate change itself (e.g., [19,20]). However, despite these decadal downward trends, recovery trends have also been observed and demonstrated recently [13,14]. For example, in Portuguese transitional ecosystems, Zostera noltei Hornemann, 1832 meadows in the Mondego estuary recovered from 0.2 ha in 1997 [1,19] to nearly 19 ha in 2019 (Verdelhos, personal communication) after the implementation of mitigation measures. In Ria de Aveiro, the extent of Z. noltei has also been increasing after a historical minimum extent in the 2000s [8], while a Zostera marina Linnaeus, 1753 population in Ria that had been nearly extinct since 2010 is now recovering (FITA, https://bio-eco.wixsite.com/fita, accessed on 1 May 2023). Finally, in the downstream Mira estuary, Z. noltei meadows completely collapsed from a stable population in 2008 [18] and recovered back to a healthy population by 2015 [11]. Reasons for their recovery include eutrophication amelioration [1], the implementation of environmental measures to avoid physical disturbance [1,8], increased awareness and social programs for their conservation (e.g., OceanAlive, www.ocean-alive.org, accessed on 15 May 2023), and active restoration initiatives [4,21].
In Portugal, seagrass beds on the northern coast have not been described before, with the northernmost description being for the Ria de Aveiro [22]. However, we recently discovered Z. noltei in the Minho Estuary. This occurrence is somewhat unexpected due to the hydrological conditions of the Minho Estuary in its downstream area, which is characterized by dredging and siltation [23]. Thus, in this study, we aim to map its distribution, reconstruct its occurrence and dynamics, and derive hypotheses for its existence in this location.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The study was carried out in a mudflat of the Minho River estuary, hereafter referred to as the Minho Estuary, in an area downstream from the city of Caminha, next to the estuarine spit, where a Z. noltei bed was found (Figure 1). The Minho Estuary is located on the border between northern Portugal and Galicia-Spain, and is 40 km long, with a maximum width of 2 km [24,25]. The estuary is mesotidal with a tidal range between 2 m and 4 m (during neap and spring tides, respectively) and partially mixed [23]. Nevertheless, it tends to develop into a salt-wedge estuary during high tide periods [24]. The estuary is shallow, and about 9% of the intertidal zone is composed of sand and mudflats. In downstream Caminha, a narrow and shallow navigation channel is artificially maintained by dredging to preserve the navigability of the lower Minho Estuary [26]. The outlet is narrow and shallow, reaching depths as low as 2 m during spring low tides. One of the main problems of the estuary is siltation, due to an imbalance in the sediment budget and sedimentation caused by tidal currents and their asymmetry due to bathymetric constraints or river flows, especially during flood events [23] and dredging. Regarding anthropogenic pressures, the estuary is considered a low-impacted system [23,27].
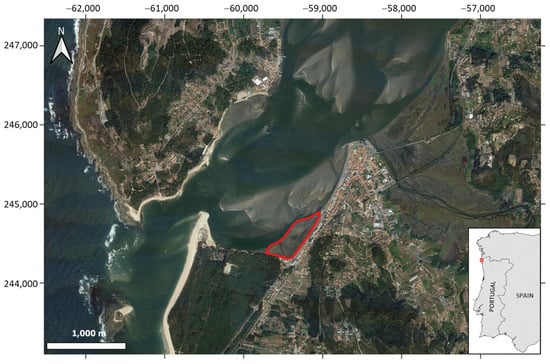
Figure 1.
Lower estuary of the Rio Minho with the location of the study area (red polygon). The inset map shows the location of the lower estuary in NW Portugal (Coordinate system: ETRS89/Portugal TM06; Image: Google, SIO, NOAA, U.S. Navy NGA).
2.2. Data Acquisition and Analyses
The seagrass monitoring campaign was conducted in June 2022. In the field, 16 PVC squares of 50 × 50 cm2 were randomly placed on Zostera patches and photographed, and additional 10 squares were placed at the edges of the meadows, from which the coordinates were assessed. The photographs were analysed with the online photo editor (www.photopea.com, accessed on 23 January 2023) to assess seagrass density in the study area, measured as the percentage of cover, following [28], to determine the percent cover.
In addition, the study area was surveyed using a DJI M200 drone equipped with a MicaSense RedEdge-MX multispectral camera providing imagery with five spectral bands: blue (Central Wavelength (CW) 475 nm and Bandwidth (BW) 32 nm), green (CW 560 nm, BW 27 nm), red (CW 668 nm, BW 16 nm), red edge (CW 717 nm, BW 12 nm) and near infrared (CW 842 nm, BW 57 nm). The flight was made at an altitude of 80 m, resulting in 1332 images with 70% lateral and 80% longitudinal overlap and a Ground Sample Distance (GSD), i.e., image pixel size on the ground, of 5.6 cm.
Before the flight, 9 additional ground control points (GCP) were marked, with crosses visible in the aerial photographs, and georeferenced using a Trimble R6 GNSS receiver in RTK mode with fixed-station corrections from the Portuguese Network of Permanent Stations (RENEP). The quadrats marking the Z. noltei cover were also georeferenced in the field, recording the position of two opposing corners of the square frames to be identified in the aerial photos. The GCP and the quadrats were later used to generate and georeference an orthomosaic of the images. Additionally, about 40 points with specific cover (Z. noltei and/or Ulva or Laminaria, or bare ground) were also identified and georeferenced. These points and the quadrats were used to identify the cover classes in the aerial image and train the image classification algorithm.
The images were processed with Agisoft Metashape Professional (Version 1.8.0) [29] to create a point cloud and a digital elevation model (DEM), referred to as the mean sea level (MSL), with an estimated vertical accuracy of 5 cm (RMS). The DEM was used to create a multispectral orthomosaic. Reflectance was calibrated with measurements from the camera sun sensor and from a set of images of the camera calibration panel, taken before and after the flight. The orthomosaic was subsequently classified to quantify the area covered with Z. noltei. A supervised classification procedure was carried out using QGIS (Version 3.28.3; [30]), the dezetsaka classification tool (Version 3.70; [31]), and the Random Forest classification algorithm [32,33]. The classification considered the five bands from the multispectral images plus a sixth band consisting of the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI; [34]). The number of classes used for the classification was defined to represent the main cover types found in the field, based on the in situ georeferenced samples, as well as on cover types that were visually distinctive in the orthomosaic.
Depending on the cover class, two different methodologies were used for selecting Region of Interest (ROI) training areas: (i) for vegetation covers, training areas were selected based on the georeferenced in situ information (quadrats and sample points); (ii) for the other classes, training areas were delimited based on visual identification in the orthomosaic. In addition, the separability of the spectral signatures was evaluated, and training areas with a significant signature overlap were redimensioned or reselected prior to the classification [33].
Classification accuracy was estimated using randomly selected pixels for which the ground truth class was identified based on visual identification and proximity to georeferenced known ground truth points. The number of pixels for the accuracy test was defined based on the following equation:
where:
= number of pixels for accuracy assessment;
= mapped area proportion of class i;
= standard deviation of stratum i;
= expected standard deviation of overall accuracy.
The distribution of randomly generated pixels for each class was determined based on good practices of land cover classification accuracy assessment. For this study, two methodologies presented by [35] were merged, focusing on improving the accuracy and reducing standard error for the Z. noltei cover class. As a result, some of the defined number of random pixels were equally distributed through all classes, and the remaining pixels were distributed according to the class cover percentage.
The resulting random forest classification was evaluated by its F1 score (Equation (2)) of the Z. noltei cover class, which indicates how well the classification performed as it evaluates User Accuracy (UA) and Production Accuracy (PA) [36]. In addition, overall accuracy (OA) was also considered but not as the primary evaluation criterion since the classification focus was to identify the Z. noltei cover.
The DEM of the study area created from the drone images was used in order to assess whether Zostera occurs within a certain range of elevation, as elevation determines whether and how long the area becomes submerged by the tide.
Recent developments of the Z. noltei cover in the study area were assessed using existing imagery of the region (from Google Earth and from an aerial survey carried out during the MarRisk project). Notice that seagrass is only visible in images taken at low tide and that the quality and resolution of images available in GoogleEarth™ (https://earth.google.com/web/, accessed on 15 March 2023) may provide some qualitative information about the (more visible) central seagrass patch of the mudflat but does not allow inferences about the overall cover nor about the seagrass species.
3. Results
3.1. Seagrass Density and Cover Classification
Analysis of the in situ photos from the quadrats showed a percent of Zostera cover ranging from 29% to 98% (Figure 2a), with an average seagrass cover of 69.3 ± 19.7% in the 26 quadrats. Some plants had green algal epiphytes (Figure 2b), while others had visible sediment deposits in the leaves (Figure 2c).
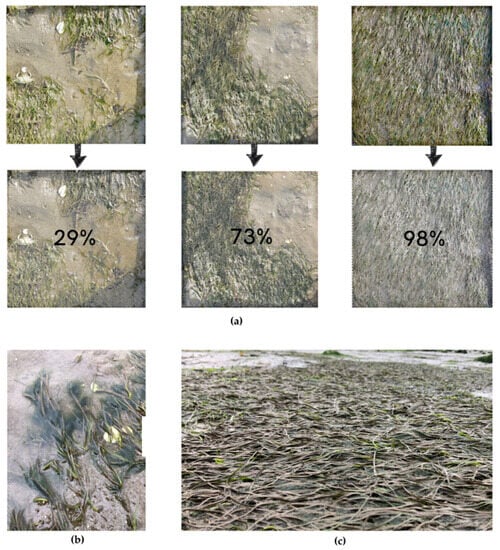

Figure 2.
Examples of (a) density of Zostera noltei Hornemann, 1832 determined from in situ photos (upper photos) using the online editor Photopea (lower photos), with percent cover indicated; and the detail of (b) green algal epiphytes of Z. noltei; and (c) leaves with sedimentation.
Six distinct cover classes were identified in the aerial image cover classification procedure: Zostera noltei, Ulva sp., water, bare sediment, submerged sediment, and rock/sand. The number of training pixels used per class was 426, 2560, 6661, 8010, 6732, and 649, respectively. For the Zostera target cover class, the training pixels/areas were limited to the specific georeferenced points/quadrats of known, pure Zostera cover identified in the field. For the other classes, training pixels were easily identified in the orthomosaic.
To evaluate class separability, a mean spectral signature was generated for every class, based on the individual spectral signature and NDVI of each training pixel (Figure 3).
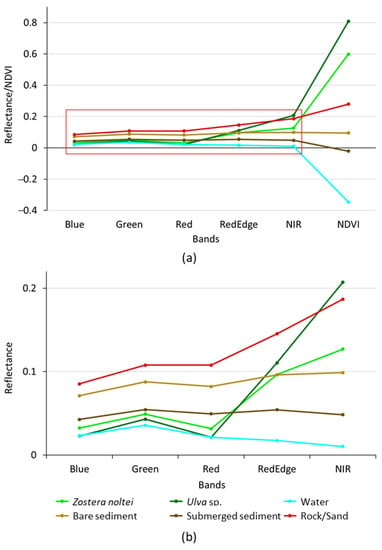
Figure 3.
Mean spectral signatures (for the 5 multispectral image bands + NDVI) of the training pixels for each cover class (a) and a zoom in on the red rectangle in the upper figure (b) to show the separability of the spectral signatures for the 5 image bands.
Based on Equation (1), the accuracy assessment used 798 randomly generated pixels, of which 600 were equally distributed through the classes, and the remaining 198 were allocated proportionally to the cover percentages. From the initial 798 generated pixels, 733 could be securely identified in the orthomosaic.
The random forest classification achieved high performance, accurately identifying the vegetation cover class, with accuracy ranging from 80% to 95% and F1 scores of 0.87 and 0.89 (Table 1). Although the identification of the rock/sand cover class presented poorer results, it had a minimal effect on the final results since it had the smallest cover area, and the misclassifications were mostly of sediment classes, not affecting the vegetation cover estimation. The classification overall accuracy was 0.91, and Kappa hat 0.85.

Table 1.
Area-based classification error matrix, for the vegetation and non-vegetation classification classes, with the indication of the respective classified area and its percentage.
According to the classification (Figure 4, Table 1), 8336 m2, i.e., about 5%, of the study area was coveres with Zostera. The estimated Zostera cover area on the reference raster was 8137 ± 492 m2. Z. noltei occurred predominantly in a large central patch (Figure 4c,d) and along the north-eastern border of the area, sometimes mixed with Ulva sp. The class Ulva sp. only covered about 3% of the total area.
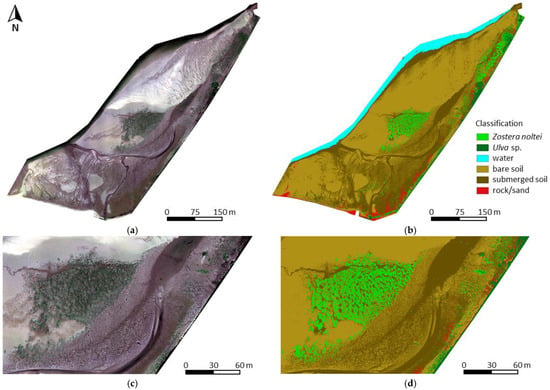
Figure 4.
Orthomosaic (a) and classification of the study area (b) and a zoom-in on the central Zostera patch of the orthomosaic (c) and classification (d).
3.2. Cover-Elevation Relationship
Regarding the DEM, Z. noltei occurred predominantly at surface heights between −1 cm and 14 cm (related to MSL), which were the height values for the 25% and 75% quartiles (Figure 5a). Only 5% of the pixels classified as Zostera occurred below −15 cm and only 5% above 40 cm height. All Zostera pixels above 40 cm in height were located next to the margin, between rocks covered in Ulva sp., suggesting that they are either misclassified or that the rocks and Ulva sp. provide some form of protection, like a shadow and additional humidity, allowing Zostera to survive. Looking at the validation data set, we see that the confirmed Z. noltei pixels did not occur at heights above 50 cm (Figure 5b). The Ulva sp. pixels that were wrongly classified as Z. noltei tended to be on slightly higher elevations than the correctly classified pixels (Figure 5b), and all lay close to the study site margin. This means that height could be an additional criterion to filter results.
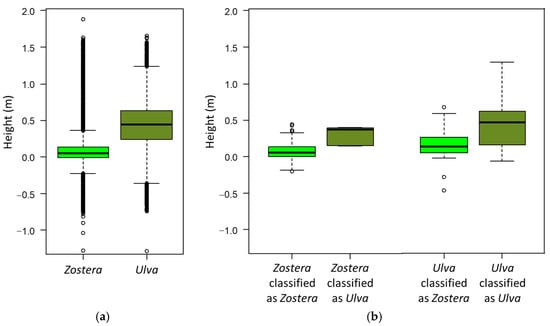
Figure 5.
Surface heights for Zostera noltei and Ulva sp. in the classification (a) and surface heights for the validation data pixels correctly and wrongly classified as Z. noltei and for Ulva sp. classified as Z. noltei (b).
Ulva sp. was more tolerant to exposure/drought, occurring predominantly between 24 cm and 64 cm (height values for the 25% and 75% quartiles), with 5% at heights below −1 cm and 5% at heights above 86 cm.
3.3. Recent Trends
Previous remote sensing images show that the central patch (the only vegetated area clearly distinguishable in most of the existing images) started to develop at least two decades ago (Figure 6). In most of the images found for the period 2001–2021, vegetation appears to be sparse or partially covered with sediment. Looking at the 2019 images, we see that the vegetation (visible in 2017), which appears to have almost vanished in February, reappears in July. The most recent survey shows the most developed seagrass patch, possibly indicating a positive trend in local seagrass growth. Notice that the historical images are from remote sensing at unknown but no doubt lower resolutions than the 2019 and 2022 images. They do not allow inferences about the seagrass species or density.
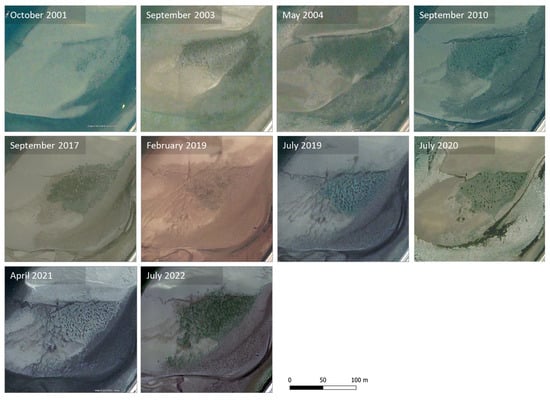
Figure 6.
Recent development of the central Zostera patch; images obtained from GoogleEarth™ (Maxar Technologies, CNES, Airbus), except for February 2019 (high-resolution orthomosaic from the MarRisk project) and July 2022 (high-resolution orthomosaic from the present study).
4. Discussion
Seagrass beds are among the most productive habitats, with a wide range of ecosystem services, and could serve as nature-based solutions for mitigating climate change and other human-induced stressors [3,15,16]. The paradox is that seagrasses themselves are highly vulnerable to a variety of pressures that could be exacerbated by climate change impacts [37,38,39], such as sea level rise [40,41], ocean warming [42], and extreme weather events in the form of heat waves and floods [12,20]. Adding to the human-induced stressors, natural causes such as wasting disease can also affect the distribution and density of seagrass meadows [8,43]. Thus, it becomes fundamental to understand the drivers of their existence in coastal ecosystems and the reasons for their successful colonisation, which naturally entails a variety of ecosystem services that ultimately translate into benefits for humankind.
Surveys to assess seagrass distribution patterns along the Portuguese coast from 2007 to 2010 did not detect Z. noltei or any other seagrass in the Minho Estuary [22]. This work also included interviews with local fishermen for a historical distribution assessment, which did not mention their occurrence before 2010 [22]. Like other seagrasses, Z. noltei growth appears to depend on the interaction between the condition of the plant itself, associated biological communities [2], including opportunistic [1] and invasive species [44], and the physical environment (e.g., light, salinity, nutrients, temperature, depth, currents, and sedimentation [39,43,44,45,46,47), which in turn may be affected by anthropogenic pressures [8,17,47]. The complexity of such interactions and the lack of historical data on the physical environment of the Minho Estuary make it difficult to draw conclusions about the mechanisms influencing seagrass growth dynamics, which can be highly variable [46]. However, the physical environment, due to the hydrodynamics of Minho River promoting sedimentation and low salinity [23,48], could be one of the possible reasons for the absence of Zostera patches in the past. In fact, the Minho Estuary is highly affected by sediment deposition caused, on the one hand, by the tides that transport material upstream and, on the other hand, by the Frieira Dam, located 80 km upstream, which controls fluvial discharges during flood events [23,48]. A decline in seagrass beds in the Ria de Aveiro in the 1990s has also been attributed to changes in hydrodynamics due to port activities and channel navigation works that increased current velocity and tidal circulation, preventing the establishment of seagrass meadows [8,17]. Other studies have also specifically addressed sedimentary dynamics as stressors for Z. noltei establishment since the species is highly sensitive to burial and erosion disturbance due to shoot mortality combined with its small size and lack of vertical rhizomes, to the latter of which allow survival under low-light conditions [49].
Nevertheless, this study confirms that Zostera patches have been present in downstream areas of the Minho Estuary for more than a decade, despite being sparse and occasionally completely disappearing, possibly due to the sediment siltation and seasonality. The origin of these patches and potential connectivity with the donor populations remains unknown. Seagrass species can reproduce sexually, producing seeds, or asexually, by clonal growth. A dispersal of seeds from a donor population seems the most probable origin for the Minho population, and this could be mediated by the river/estuarine plume or oceanic transport of flowering shoots containing seeds that drift [50], through grazers’ transport [51], or even ducks and birds feeding on intertidal beds [45] transporting seeds. The closest locations along the coastline with abundant seagrass meadows are the Galician Rias Baixas in NW Spain [43,47], about 30 km distant, and the Ria de Aveiro and Mondego estuary, 135 km and 190 km distant to the south, respectively. For a drifting-dispersal hypothesis, river/estuarine plumes could be a possible vector for donor populations. For instance, the Western Iberian Buoyant plume (WIBP) combines the influence of terrestrial freshwater and estuarine sources from the Douro, Minho, Mondego, and even the Galician Rias [52], thus including potential sources of Z. noltei. On the other hand, the Minho’s River buoyant plume alone seems to promote the northward spread into the Rias Baixas [53] and not the other way around, but in less than 9% of the cases [54], and presumably only during high flood periods [23,24]. Also, water exchanges from the Ria de Aveiro’s coastal lagoon to the ocean seem too limited to induce ocean transport upwards [55]. This reinforces the idea of WIBP as the most likely possibility of drift dispersal.
Another important issue potentially related to the permanence of the Zostera patches in the Minho Estuary downstream region in recent years is the occurrence of several precipitation anomalies, with the number of dry periods surpassing the flooding ones [56]. Similarly, higher salinity intrusion has been documented for the Minho Estuary [57], meaning the average salinity in the downstream region could be more compatible with the preferences of Z. noltei.
Our inspection of the Zostera beds at Minho Estuary also showed that they were partially covered or mixed with sediment, which corroborates the sedimentation dynamics described for the system. This aspect could make it difficult to determine the percentage of cover from aerial photographs for the present situation as well as regarding their historical occurrence and dynamics. Nonetheless, the classification procedure used here identified Zostera cover with very good accuracy (F1 Score = 0.89). The NDVI and the five bands of the multispectral image, calibrated with the in situ ground truth observations, allowed excellent discrimination between vegetated and non-vegetated areas.
The use of unoccupied aircraft systems (UAS) equipped with multispectral cameras for coastal cover mapping is novel [34,58], but has shown great potential, although, particularly for intertidal monitoring, when high resolution is required, the area that can be covered within a low-tide window is relatively small (1 to 2 km2). For regional surveys of seagrass populations, an approach combining UAS and plane-based aerial imagery, or even satellite imagery may be a solution [59].
Zostera was present predominantly at elevations close to or up to 40 cm above mean sea level (MSL) and was sometimes slightly intermixed with Ulva sp. in a region with pronounced sedimentation dynamics that appears to influence seagrass distribution as well as detection. Plants covered due to siltation sediment may become invisible and/or disappear.
The present study’s results suggest that currently the presence and development of seagrass beds in Minho’s downstream mudflats are controlled by the following factors: (i) the accentuated sedimentary dynamics in the estuary [23,48], with suspended and deposited sediments causing a reduction in light availability, thus affecting the plants’ ability to photosynthesise [60], and causing eventual shoot mortality [49]; and/or (ii) seasonality of the species in terms of growth and shoot density [46,61].
Our records also showed that Zostera cover was on average 70% in the main meadows for the summer conditions and for a total area of 0.81 ha. Although this seems a small population compared to other seagrass meadows, even in Portuguese coastal areas, it is a positive sign of a new habitat establishment in the region. Naturally, this emerging seagrass habitat deserves to be monitored and preserved, as it contributes all of the aforementioned benefits. Nevertheless, without effective integrated management, the long-term viability of the seagrass could be further disrupted. The intricate interplay between sediment siltation, hydrodynamics, and human activities requires a comprehensive approach that considers both local and transboundary cooperation [62]. First, it is fundamental to acknowledge the presence and expansion of the habitat in the system, as reinforced by this study. Then, collaboration between different stakeholders (including research) is essential to develop and implement strategies that not only mitigate the impacts of siltation, but also consider climate change [63]. By carefully balancing the trade-offs between dam activities and dredging, and using innovative techniques to control and mitigate siltation, we could protect seagrass habitat and promote ecological resilience in the face of ongoing challenges.
Overall, this study reported the occurrence of Z. noltei populations in the Minho Estuary and mapped its distribution for the first time. We conclude that there is a positive trend in local Z. noltei distribution in the Minho Estuary over the past 10 years. Nevertheless, the Minho Estuary has been identified as one of the European estuaries most affected by sediment accumulation [48], and these dynamics together with sea level rise [63] may impair a stable colonisation of the seagrass in the area. Continued high-resolution multispectral surveys are recommended to confirm whether the long-term trend of colonisation is consistent in the years to come.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, M.D., D.d.A.C. and A.B.; methodology, M.D., A.B. and J.A.G.; formal analysis, M.D., J.A.G., M.M. and A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D.; writing—review and editing, M.D., D.d.A.C., M.M., J.A.G. and A.B.; funding acquisition, M.D. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the ATLANTIDA project (ref. NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000040), supported by the Norte Portugal Regional Operational Programme (NORTE 2020), under the PORTUGAL 2020 Partnership Agreement and through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), and supported by national funds through FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology within the scope of UIDB/04423/2020 and UIDP/04423/2020. M.D. was supported by the FCT-Scientific Employment Stimulus Institutional Call (CEECINST/00027/2021/CP2789/CT0001).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analysed will be made available (upon request) through the institution’s geographic data server (gis.ciimar.up.pt, accessed on 30 June 2023).
Acknowledgments
We thank the MarRISK project (0262_MarRISK_1_E) for providing remote sensing imagery.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dolbeth, M.; Cardoso, P.P.G.; Grilo, T.F.; Bordalo, M.D.; Raffaelli, D.; Pardal, M.Â. Long-term changes in the production by estuarine macrobenthos affected by multiple stressors. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, P.S.; Eklöf, J.S.; van Katwijk, M.M.; O’Brien, K.R.; de la Torre-Castro, M.; Boström, C.; Bouma, T.J.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Unsworth, R.K.F.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; et al. The fundamental role of ecological feedback mechanisms for the adaptive management of seagrass ecosystems—A review. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Out of the Blue: The Value of Seagrasses to the Environment and to People>; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020; Available online: www.unep.org/resources/report/out-blue-value-seagrasses-environment-and-people (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Orth, R.J.; Lefcheck, J.S.; McGlathery, K.S.; Aoki, L.; Luckenbach, M.W.; Moore, K.A.; Oreska, M.P.J.; Snyder, R.; Wilcox, D.J.; Lusk, B. Restoration of seagrass habitat leads to rapid recovery of coastal ecosystem services. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Anton, A.; Raven, J.A.; Beaumont, N.; Connolly, R.M.; Friess, D.A.; Kelleway, J.J.; Kennedy, H.; Kuwae, T.; Lavery, P.S.; et al. The future of Blue Carbon science. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, O.; Lovelock, C.E.; Atwood, T.B.; Macreadie, P.I.; Canto, R.; Phinn, S.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; Bai, L.; Baldock, J.; Bedulli, C.; et al. Australian vegetated coastal ecosystems as global hotspots for climate change mitigation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, J.E.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Trinanes, J.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Ambo-Rappe, R.; Boström, C.; Buschmann, A.H.; Byrnes, J.; Coles, R.G.; Creed, J.; et al. Toward a coordinated global observing system for seagrasses and marine macroalgae. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.I.; da Silva, J.F.; Azevedo, A.; Lillebø, A.I. Blue Carbon stock in Zostera noltei meadows at Ria de Aveiro coastal lagoon (Portugal) over a decade. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHenry, J.; Rassweiler, A.; Hernan, G.; Uejio, C.K.; Pau, S.; Dubel, A.K.; Lester, S.E. Modelling the biodiversity enhancement value of seagrass beds. Divers. Distrib. 2021, 27, 2036–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, M. Monitoring of Seahorse Populations, in the Ria Formosa Lagoon (Portugal), Reveals Steep Fluctuations: Potential Causes and Future Mitigations. Proc. Zool. Soc. 2022, 75, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, N.; Penedos, C.; Félix, P.; Chainho, P.; Pereira, T.; Costa, M.J.; Almeida, A.J.; Adão, H.; Costa, J.L. Structural and functional composition of fish communities associated to Zostera noltii meadows as a response to natural habitat recovery. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolbeth, M.; Cardoso, P.P.G.; Grilo, T.F.; Raffaelli, D.; Pardal, M.Â. Drivers of estuarine benthic species distribution patterns following a restoration of a seagrass bed: A functional trait analyses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 72, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause-Jensen, D.; Duarte, C.M.; Sand-Jensen, K.; Carstensen, J. Century-long records reveal shifting challenges to seagrass recovery. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de los Santos, C.B.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Alcoverro, T.; Marbà, N.; Duarte, C.M.; van Katwijk, M.M.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Roca, G.; et al. Recent trend reversal for declining European seagrass meadows. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rifai, H.; Quevedo, J.M.D.; Lukman, K.M.; Sondak, C.F.A.; Risandi, J.; Hernawan, U.E.; Uchiyama, Y.; Ambo-Rappe, R.; Kohsaka, R. Potential of seagrass habitat restorations as nature-based solutions: Practical and scientific implications in Indonesia. Ambio 2023, 52, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddon, N.; Smith, A.; Smith, P.; Key, I.; Chausson, A.; Girardin, C.; House, J.; Srivastava, S.; Turner, B. Getting the message right on nature-based solutions to climate change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 1518–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.; Sousa, A.I.; Lencart e Silva, J.D.; Dias, J.M.; Lillebø, A.I. Application of the generic DPSIR framework to seagrass communities of Ria de Aveiro: A better understanding of this coastal lagoon. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materatski, P.; Vafeiadou, A.M.; Ribeiro, R.; Moens, T.; Adão, H. A comparative analysis of benthic nematode assemblages from Zostera noltii beds before and after a major vegetation collapse. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 167, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilo, T.F.; Cardoso, P.G.; Dolbeth, M.; Bordalo, M.D.; Pardal, M.Â. Effects of extreme climate events on the macrobenthic communities’ structure and functioning of a temperate estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Ortiz, A.; Serrano, O.; Masqué, P.; Lavery, P.S.; Mueller, U.; Kendrick, G.A.; Rozaimi, M.; Esteban, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Marbà, N.; et al. A marine heatwave drives massive losses from the world’s largest seagrass carbon stocks. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, D.; Cunha, A.H.; Boavida, J.; Serrão, E.A.; Gonçalves, E.J.; Fonseca, M. Open coast seagrass restoration. Can we do it? Large scale seagrass transplants. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.H.; Assis, J.F.; Serrão, E.A. Seagrasses in Portugal: A most endangered marine habitat. Aquat. Bot. 2013, 104, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, I.; Avilez-Valente, P.; Bio, A.; Bastos, L. Modelling the main hydrodynamic patterns in shallow water estuaries: The Minho case study. Water 2019, 11, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, R.G.; Dias, S.; Freitas, V.; Antunes, C. Subtidal macrozoobenthic assemblages along the River Minho estuarine gradient (north-west Iberian Peninsula). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2008, 18, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolbeth, M.; Martinho, F.; Freitas, V.; Costa-Dias, S.; Campos, J.; Pardal, M.Â. Multi-year comparisons of fish recruitment, growth and production in two drought-affected Iberian estuaries. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2010, 61, 1399–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.I.; Oliveira, A.; Carinhas, D.; Pinto, J.P.; Freitas, M.C. Hydrodynamic and Sediment Transport Patterns in the Minho and Douro Estuaries (NW Portugal) Based on ADCP Monitoring Data: Part 2—Statistical Interpretation of Bottom Moored Datasets. Coasts 2021, 1, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, R.P.; Reis-Santos, P.; Fonseca, V.; Maia, A.; Ruano, M.; França, S.; Vinagre, C.; Costa, M.J.; Cabral, H.N. Assessing anthropogenic pressures on estuarine fish nurseries along the Portuguese coast: A multi-metric index and conceptual approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 374, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khaled, Y.C.; Lago, A.K.; Mezger, S.D.; Wild, C. Comparative Evaluation of Free Web Tools ImageJ and Photopea for the Surface Area Quantification of Planar Substrates and Organisms. Diversity 2022, 14, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AgiSoft. AgiSoft PhotoScan Professional, Version 1.80 Software; Agisoft LLC: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2021. Available online: http://www.agisoft.com/downloads/installer/(accessed on 15 October 2022).
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System; Open Source Geospatial Foundation: Beaverton, OR, USA, 2022; Available online: http://qgis.osgeo.org (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Karasiak, N. Dzetsaka Qgis Classification Plugin. 2006. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2552284 (accessed on 15 October 2022). [CrossRef]
- Tin Kam, H. Random decision forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; Volume 1, pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.d.F.; Gonçalves, J.A.; Cunha, J.F.R.; Ramos, S.C.d.C.e.S.; Bio, A.M.F. Application of a Multispectral UAS to Assess the Cover and Biomass of the Invasive Dune Species Carpobrotus edulis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W.; Harlan, J.C. Monitoring the Vernal Advancements and Retrogradation of Natural Vegetation. NASA/GSFC, Final Report, Greenbelt, MD, USA, September 1972, pp. 1–137. Available online: http://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=related:kfZY0xukQScJ:scholar.google.com/&hl=en&num=20&as_sdt=0,5%5Cnpapers2://publication/uuid/FB22B85B-B2F9-442E-AF63-58F3517012FC (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurqani, H.A.; Post, C.J.; Mikhailova, E.A.; Cope, M.P.; Allen, J.S.; Lytle, B.A. Evaluating the integrity of forested riparian buffers over a large area using LiDAR data and Google Earth Engine. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefaoui, R.M.; Duarte, C.M.; Serrão, E.A. Dramatic loss of seagrass habitat under projected climate change in the Mediterranean Sea. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 4919–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Frazier, M.; Afflerbach, J.; Lowndes, J.S.; Micheli, F.; O’Hara, C.; Scarborough, C.; Selkoe, K.A. Recent pace of change in human impact on the world’s ocean. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, F.T.; Neckles, H.A. The effects of global climate change on seagrasses. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 63, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondiviela, B.; Galván, C.; Recio, M.; Jiménez, M.; Juanes, J.A.; Puente, A.; Losada, I.J. Vulnerability of Zostera noltei to Sea Level Rise: The Use of Clustering Techniques in Climate Change Studies. Estuaries Coasts 2020, 43, 2063–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, M.; Chust, G.; del Campo, A.; Wisz, M.S.; Olsen, S.M.; Garmendia, J.M.; Borja, Á. Projecting future distribution of the seagrass Zostera noltii under global warming and sea level rise. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 170, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Martins, I.; Rosa, R.; Matos, A.R.; Roleda, M.Y.; Reusch, T.B.H.; Engelen, A.H.; Serrão, E.A.; Pearson, G.A.; Marques, J.C.; et al. Climate change impacts on seagrass meadows and macroalgal forests: An integrative perspective on acclimation and adaptation potential. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochón, G.; Sánchez, J.M. Variations of Seagrass Beds in Pontevedra (North-Western Spain): 1947–2001. Thalassas 2005, 21, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, V.; Flindt, M.R.; Lopes, M.; Coelho, J.P.; Costa, A.F.; Lillebø, A.I.; Sousa, A.I. Enhancing the resilience of Zostera noltei seagrass meadows against Arenicola spp. bio-invasion: A decision-making approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borum, J.; Duarte, C.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Greve, T.M. European Seagrasses: An Introduction to Monitoring and Management. In Management 2004. Available online: http://www.seagrasses.org (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Cognat, M.; Ganthy, F.; Auby, I.; Barraquand, F.; Rigouin, L.; Sottolichio, A. Environmental Factors Controlling Biomass Development of Seagrass Meadows of Zostera Noltei after a Drastic Decline (Arcachon Bay, France). J. Sea Res. 2018, 140, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.; Fernández, E.; Zamborain-Mason, J.; Méndez, G. Anthropogenic Impact on Zostera noltei Seagrass Meadows (NW Iberian Peninsula) Assessed by Carbon and Nitrogen Stable Isotopic Signatures. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, A.; Ballinger, R.; Ibáñez, C.; Parker, P.; Dominguez, M.D.; Simon, X.; Lewandowski, A.; Hochfeld, B.; Tudor, M.; Vernaeve, L. Sediment imbalances and flooding risk in European deltas and estuaries. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1493–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaço, S.; Santos, R. Effects of burial and erosion on the seagrass Zostera noltii. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 340, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Harwell, M.C.; Inglis, G.J. Ecology of seagrass seeds and seagrass dispersal processes. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 111–133. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/227177291_Ecology_of_Seagrass_Seeds_and_Seagrass_Dispersal_Processes (accessed on 30 June 2023). [CrossRef]
- Tavares, A.I.; Assis, J.; Patrício, A.R.; Ferreira, R.; Cheikh, M.A.S.; Bandeira, S.; Regalla, A.; Santos, I.; Potouroglou, M.; Nicolau, S.; et al. Seagrass Connectivity on the West Coast of Africa Supports the Hypothesis of Grazer-Mediated Seed Dispersal. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 809721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peliz, Á.; Rosa, T.L.; Santos, A.M.P.; Pissarra, J.L. Fronts, jets, and counter-flows in the Western Iberian upwelling system. J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 35, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.C.; Vaz, N.; Alvarez, I.; Dias, J.M. Effect of Minho estuarine plume on Rias Baixas: Numerical modeling approach. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 165, 2059–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des, M.; deCastro, M.; Sousa, M.C.; Dias, J.M.; Gómez-Gesteira, M. Hydrodynamics of river plume intrusion into an adjacent estuary: The Minho River and Ria de Vigo. J. Mar. Syst. 2019, 189, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; Ramos, M. Water Exchange Mechanisms between Ria de Aveiro and the Atlantic Ocean. J. Coast. Res. SI 2006, 2004, 1622–1626. Available online: http://siaiacad09.univali.br/ics2004/arquivos/341_silva.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Ilarri, M.; Souza, A.T.; Dias, E.; Antunes, C. Influence of climate change and extreme weather events on an estuarine fish community. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menten, G.; Melo, W.; Pinho, J.; Iglesias, I.; Antunes do Carmo, J. Simulation of Saltwater Intrusion in the Minho River Estuary under Sea Level Rise Scenarios. Water 2023, 15, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, D.; Duarte, L.; Costa, I.; Bio, A.; Silva, J.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Gonçalves, J.A. New Methodology for Intertidal Seaweed Biomass Estimation Using Multispectral Data Obtained with Unoccupied Aerial Vehicles. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; Byfield, V.; Felgate, S.L.; Price, D.M.; Andrade, V.; Cobb, E.; Strong, J.; Lichtschlag, A.; Brittain, H.; Barry, C.; et al. Using Unoccupied Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to Map Seagrass Cover from Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.C.; Griffiths, G.; Vercaemer, B. Seasonal Response and Recovery of Eelgrass (Zostera marina) to Short-Term Reductions in Light Availability. Estuaries Coasts 2020, 43, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaat, J.; Hootsmans, M.; Nienhuis, P. Seasonal dynamics and leaf growth of Zostera noltii Hornem., a perennial intertidal seagrass. Aquat. Bot. 1987, 28, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolbeth, M.; Stålnacke, P.; Alves, F.A.; Sousa, L.P.; Gooch, G.D.; Khokhlov, V.; Tuchkovenko, Y.; Lloret, J.; Bielecka, M.; Grzegorz Różyński, G.; et al. An Integrated Pan-European Perspective on Coastal Lagoons Management through a Mosaic-DPSIR Approach. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, W.; Pinho, J.; Iglesias, I.; Bio, A.; Avilez-Valente, P.; Vieira, J.; Bastos, L.; Veloso-Gomes, F. Hydro-and morphodynamic impacts of sea level rise: The Minho estuary case study. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).