Review Analysis of Irrigation and Application of Remote Sensing in the Lower Mekong River Basin
Abstract
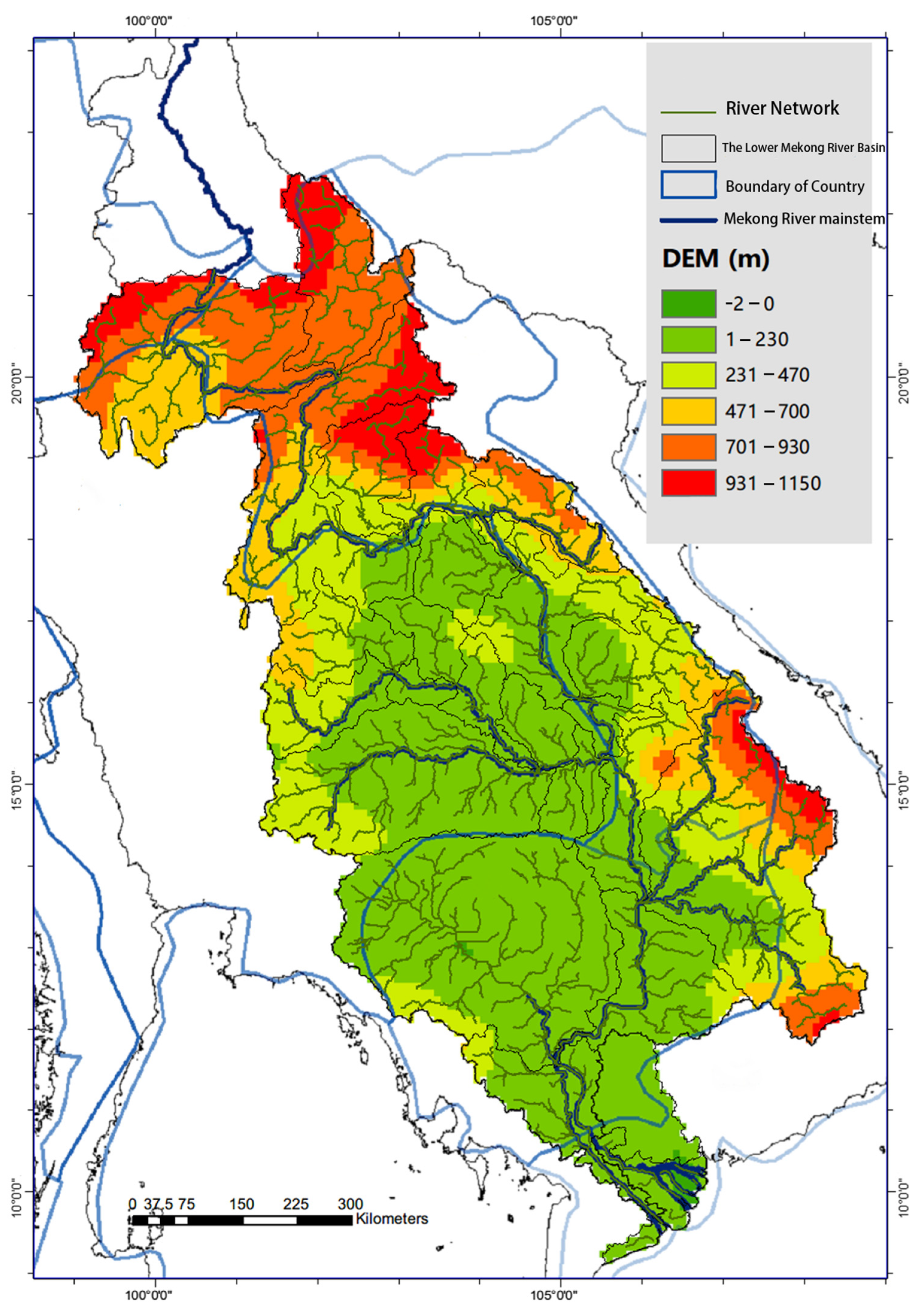
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Bibliometric Analysis
2.4. Thematic Analysis
3. Bibliometric Analysis Results
3.1. Literature Statistics
3.2. Collaboration Analysis
4. Thematic Analysis and Application of Remote Sensing
4.1. Irrigation and Crop Production
4.2. Water Availability and Land Use
4.3. Climate Change Impacts
4.4. Environment Impacts
4.5. Comprehensive Water Resource Management
4.5.1. Rational Water Allocation
4.5.2. Transboundary Water Management
4.5.3. Reconciling Hydropower and Irrigation
4.5.4. WEF Nexus in the Mekong
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Bank Group. World Bank Mekong Vision 3.0, Supporting Riparian Countries of the Mekong River Basin and Related Stakeholders to Align Their Development Goals and Natural Resources Management Activities More Closely towards Long-Term Sustainability in the Context of Emerging Chall; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, K. Climate Change Impacts on Agriculture and Irrigation in the Lower Mekong Basin. Paddy Water Environ. 2014, 12, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economic Dimension—State of the Basin Report 2018 Findings. Available online: https://www.mrcmekong.org/interactive-publications/state-of-the-basin-report-2018/economic-dimension.html (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Molle, F.; Foran, T.; Käkönen, M. Irrigation in the Lower Mekong Basin Countries: The Beginning of a New Era? In Contested Waterscapes in the Mekong Region: Hydropower, Livelihoods and Governance; Routledge: London, UK, 2012; pp. 165–194. ISBN 9781849770. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Water for Sustainable Food and Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sagara, J. Surface Water Resources Improving Climate Resilience, Mekong Delta River Basin Groups: Assessment of the Tonle Sap and Productivity, and Sustainability; ADB Briefs: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2021; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Boretti, A. Implications on Food Production of the Changing Water Cycle in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, Y.; Burbano, M.; Roush, J.; Kang, H.; Sridhar, V.; Hyndman, D.W. A Review of the Integrated Effects of Changing Climate, Land Use, and Dams on Mekong River Hydrology. Water 2018, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smajgl, A.; Ward, J. The Water-Food-Energy Nexus in the Mekong Region; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 971–978. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, X. Calculation of Carbon Footprints for Water Diversion and Desalination Projects. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 2483–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vora, N.; Shah, A.; Bilec, M.M.; Khanna, V. Food–Energy–Water Nexus: Quantifying Embodied Energy and GHG Emissions from Irrigation through Virtual Water Transfers in Food Trade. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holger, H. Clean Energy Solutions Center Understanding the Nexus. Background Paper for the Bonn 2011 Conference: The Water, Energy and Food Security Nexus. In Proceedings of the Bonn 2011 Conference, Bonn, Germany, 5 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Tang, Q.; Liu, X. Understanding the Water-Food-Energy Nexus for Supporting Sustainable Food Production and Conserving Hydropower Potential in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shen, L. A Collaborative Framework for Hydropower Development and Sustainable Livelihood of Farmers in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin: A Review with the Perspective of Energy-Water-Food Nexus. Water 2022, 14, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piman, T.; Lennaerts, T.; Southalack, P. Assessment of Hydrological Changes in the Lower Mekong Basin from Basin-Wide Development Scenarios. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowsky, I.; Hensengerth, O. Governing the Water-Energy-Food Nexus Related to Hydropower on Shared Rivers—The Role of Regional Organizations. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.-Y.; Deng, Z.D.; Ringler, C.; Gao, Y.; Hejazi, M.I.; Leung, L.R. Impacts of Climate Change, Policy and Water-Energy-Food Nexus on Hydropower Development. Renew. Energy 2018, 116, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabo, J.L.; Ruhi, A.; Holtgrieve, G.W.; Elliott, V.; Arias, M.E.; Ngor, P.B.; Räsänen, T.A.; Nam, S. Designing River Flows to Improve Food Security Futures in the Lower Mekong Basin. Science 2017, 358, 6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamidov, A.; Helming, K. Sustainability Considerations in Water-Energy-Food Nexus Research in Irrigated Agriculture. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Guo, H.-C. Nitrogen Research at Watershed Scale: A Bibliometric Analysis during 1959–2011. Scientometrics 2014, 99, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Predictive Effects of Structural Variation on Citation Counts. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opejin, A.K.; Aggarwal, R.M.; White, D.D.; Jones, J.L.; Maciejewski, R.; Mascaro, G.; Sarjoughian, H.S. A Bibliometric Analysis of Food-Energy-Water Nexus Literature. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Zou, D.; Xie, H. A Decade of Learning Analytics: Structural Topic Modeling Based Bibliometric Analysis. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2022, 27, 10517–10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to Conduct a Bibliometric Analysis: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Science Mapping: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and Visualizing Emerging Trends and Transient Patterns in Scientific Literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace: A Practical Guide for Mapping Scientific Literature; Nova Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-5361-0280-2. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Mao, G.; Irannezhad, M.; Pokhrel, Y. Past and Future Changes in Climate and Water Resources in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin: Current Understanding and Future Research Directions. Engineering 2022, 13, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Tuan, L.M.; Minamikawa, K.; Yokoyama, S. Assessment of the Relationship between Adoption of a Knowledge-Intensive Water-Saving Technique and Irrigation Conditions in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.; Tian, F.; Zhu, T.; Zohidov, B.; Ni, G.; Lu, H.; Liu, H. Exploring Synergies in the Water-Food-Energy Nexus by Using an Integrated Hydro-Economic Optimization Model for the Lancang-Mekong River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 137996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, L.P.; van Vliet, M.T.H.H.; Kummu, M.; Lauri, H.; Koponen, J.; Supit, I.; Leemans, R.; Kabat, P.; Ludwig, F. The Mekong’s Future Flows under Multiple Drivers: How Climate Change, Hydropower Developments and Irrigation Expansions Drive Hydrological Changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z.; Meng, Y.; Chen, H.; Mao, G.; Ye, B. Understanding the Impacts of Climate Change and Socio-Economic Development through Food-Energy-Water Nexus: A Case Study of Mekong River Delta. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polizzotto, M.L.; Kocar, B.D.; Benner, S.G.; Sampson, M.; Fendorf, S. Near-Surface Wetland Sediments as a Source of Arsenic Release to Ground Water in Asia. Nature 2008, 454, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlet, L.; Polya, D.A. Arsenic in Shallow, Reducing Groundwaters in Southern Asia: An Environmental Health Disaster. Elements 2006, 2, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Van Nguyen, N.; Ohno, H.; Ishitsuka, N.; Yokozawa, M. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Rice Phenology and Cropping Systems in the Mekong Delta with Special Reference to the Seasonal Water Flow of the Mekong and Bassac Rivers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddeland, I.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Skaugen, T. Effects of Irrigation on the Water and Energy Balances of the Colorado and Mekong River Basins. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.T.; Chen, C.F.; Chen, C.R.; Chang, L.Y.; Minh, V.Q. Monitoring Agricultural Drought in the Lower Mekong Basin Using MODIS NDVI and Land Surface Temperature Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 18, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Wardlow, B.D.; Gitelson, A.A.; Verma, S.B.; Suyker, A.E.; Arkebauer, T.J. A Two-Step Filtering Approach for Detecting Maize and Soybean Phenology with Time-Series MODIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polya, D.A.; Gault, A.G.; Diebe, N.; Feldman, P.; Rosenboom, J.W.; Gilligan, E.; Fredericks, D.; Milton, A.H.; Sampson, M.; Rowland, H.a.L.; et al. Arsenic Hazard in Shallow Cambodian Groundwaters. Mineral. Mag. 2005, 69, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Sarkkula, J. Impact of the Mekong River Flow Alteration on the Tonle Sap Flood Pulse. Ambio 2008, 37, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocar, B.D.; Polizzotto, M.L.; Benner, S.G.; Ying, S.C.; Ung, M.; Ouch, K.; Samreth, S.; Suy, B.; Phan, K.; Sampson, M.; et al. Integrated Biogeochemical and Hydrologic Processes Driving Arsenic Release from Shallow Sediments to Groundwaters of the Mekong Delta. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3059–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Zhang, L.; Ou, T.; Chen, D.; Yao, T.; Tong, K.; Qi, Y. Hydrological Response to Future Climate Changes for the Major Upstream River Basins in the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 136, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.E.; Cochrane, T.A.; Kummu, M.; Lauri, H.; Holtgrieve, G.W.; Koponen, J.; Piman, T. Impacts of Hydropower and Climate Change on Drivers of Ecological Productivity of Southeast Asia’s Most Important Wetland. Ecol. Model. 2014, 272, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J.S.; Lacombe, G.; Arias, M.E.; Dang, T.D.; Piman, T. Hydropower Dams of the Mekong River Basin: A Review of Their Hydrological Impacts. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.M.; Brandt, K.K.; Sørensen, J.; Hung, N.N.; Hach, C.V.; Tan, P.S.; Dalsgaard, T. Effects of Alternating Wetting and Drying versus Continuous Flooding on Fertilizer Nitrogen Fate in Rice Fields in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.E.; Cochrane, T.A.; Piman, T.; Kummu, M.; Caruso, B.S.; Killeen, T.J. Quantifying Changes in Flooding and Habitats in the Tonle Sap Lake (Cambodia) Caused by Water Infrastructure Development and Climate Change in the Mekong Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.-T.; Chen, C.-F.; Chen, C.-R.; Duc, H.-N.; Chang, L.-Y. A Phenology-Based Classification of Time-Series MODIS Data for Rice Crop Monitoring in Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biradar, C.M.; Xiao, X. Quantifying the Area and Spatial Distribution of Double- and Triple-Cropping Croplands in India with Multi-Temporal MODIS Imagery in 2005. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; De Bie, C.A.J.M.; Ali, A.; Smaling, E.M.A.; Chu, T.H. Mapping the Irrigated Rice Cropping Patterns of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam, through Hyper-Temporal SPOT NDVI Image Analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benner, S.G.; Polizzotto, M.L.; Kocar, B.D.; Ganguly, S.; Phan, K.; Ouch, K.; Sampson, M.; Fendorf, S. Groundwater Flow in an Arsenic-Contaminated Aquifer, Mekong Delta, Cambodia. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3072–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbers, G.-J.; Becker, M.; Nga, L.T.; Sebesvari, Z.; Renaud, F.G. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Surface Water Pollution in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Van Phung, C.; Kotera, A.; Nguyen, K.D.; Yokozawa, M. Analysis of Rapid Expansion of Inland Aquaculture and Triple Rice-Cropping Areas in a Coastal Area of the Vietnamese Mekong Delta Using MODIS Time-Series Imagery. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2009, 92, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, M. Extended Co-Citation Search: Graph-Based Document Retrieval on a Co-Citation Network Containing Citation Context Information. Inf. Process. Manag. 2019, 56, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surwase, G.; Sagar, A.; Kademani, B.S.; Bhanumurthy, K. Co-Citation Analysis: An Overview. In Beyond Librarianship: Creativity, Innovation and Discovery; BOSLA: Mumbai, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J. Generalization of Bibliographic Coupling and Co-Citation Using the Node Split Network. J. Informetr. 2022, 16, 101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J. Optimal Allocation of Regional Water Resources Based on Multi-Objective Dynamic Equilibrium Strategy. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 90, 1183–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döll, P.; Siebert, S. Global Modeling of Irrigation Water Requirements. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.; Tang, Q. Modeling the Impacts of Future Climate Change on Irrigation over China: Sensitivity to Adjusted Projections. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 2085–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashiki, Y. Effect of Irrigation Water Withdrawals on Water and Energy Balance in the Mekong River Basin Using an Improved VIC Land Surface Model with Fewer Calibration Parameters. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.T. Water Balance for Agriculture Production in the Dry Seasons of the Mekong River Delta in Vietnam. Vietnam. J. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 62, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.R.; Park, E.; Loc, H.H.; Tien, P.D. Long-Term Hydrological Alterations and the Agricultural Landscapes in the Mekong Delta: Insights from Remote Sensing and National Statistics. Environ. Chall. 2022, 7, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.T.D.; Tran, D.D.; Schenk, A.; Nguyen, C.P.; Vu, H.L.; Oberle, P.; Trinh, V.C.; Nestmann, F. Land Use Change in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta: New Evidence from Remote Sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 151918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, I.N.; Bolten, J.D.; Srinivasan, R.; Lakshmi, V. Satellite Observations and Modeling to Understand the Lower Mekong River Basin Streamflow Variability. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonji, S.F.; Taff, G.N. Using Satellite Data to Monitor Land-Use Land-Cover Change in North-Eastern Latvia. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.; Sridhar, V.; Mainuddin, M.; Trung, L.D. Future Rice Farming Threatened by Drought in the Lower Mekong Basin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, W.; Song, W. Assessment of Agricultural Drought Risk in the Lancang-Mekong Region, South East Asia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Guo, H.; Leinenkugel, P.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Shen, Q. Drought Impact on Vegetation Productivity in the Lower Mekong Basin. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 2835–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Baiyinbaoligao; Mu, X. Summary of Flood and Drought in Mekong River Basin. In Flood Prevention and Drought Relief in Mekong River Basin; Liu, H., Ed.; Springer Tracts in Civil Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 27–54. ISBN 9789811520068. [Google Scholar]
- Tilleard, S.; Turral, H.; Ketelsen, T.; Whiting, L. Climate Change, Water Scarcity and Agriculture: Lessons from the Countries of the Lower Mekong. In Climate Risks to Water Security: Framing Effective Response in Asia and the Pacific; Ojha, H., Schofield, N., Camkin, J., Eds.; Palgrave Studies in Climate Resilient Societies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 215–238. ISBN 978-3-031-16648-8. [Google Scholar]
- Adeola, O.M.; Ramoelo, A.; Mantlana, B.; Mokotedi, O.; Silwana, W.; Tsele, P. Review of Publications on the Water-Energy-Food Nexus and Climate Change Adaptation Using Bibliometric Analysis: A Case Study of Africa. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhẫn, P.P.; Hòa, L.V.; Quí, C.N.; Huy, N.X.; Hữu, T.P.; Macdonald, B.C.T.; Tường, T.P. Increasing Profitability and Water Use Efficiency of Triple Rice Crop Production in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 154, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Remote Sensing Applications to Climate Change. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gong, P.; Fu, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Liang, S.; Xu, B.; Shi, J.; Dickinson, R. The Role of Satellite Remote Sensing in Climate Change Studies. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Erkens, G.; Kuniansky, E.L.; Rowland, J.C. Preface: Land Subsidence Processes. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toan, T.Q. 9-Climate Change and Sea Level Rise in the Mekong Delta: Flood, Tidal Inundation, Salinity Intrusion, and Irrigation Adaptation Methods. In Coastal Disasters and Climate Change in Vietnam; Thao, N.D., Takagi, H., Esteban, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 199–218. ISBN 978-0-12-800007-6. [Google Scholar]
- Khang, N.D.; Kotera, A.; Sakamoto, T.; Yokozawa, M. Sensitivity of Salinity Intrusion to Sea Level Rise and River Flow Change in Vietnamese Mekong Delta-Impacts on Availability of Irrigation Water for Rice Cropping. J. Agric. Meteorol. 2008, 64, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, C.; Reidy, C.A.; Dynesius, M.; Revenga, C. Fragmentation and Flow Regulation of the World’s Large River Systems. Science 2005, 308, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, D.; Moggridge, H.; Warren, P.; Shucksmith, J. The Impacts of ‘Run-of-River’ Hydropower on the Physical and Ecological Condition of Rivers. Water Environ. J. 2015, 29, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benejam, L.; Saura-Mas, S.; Bardina, M.; Solà, C.; Munné, A.; García-Berthou, E. Ecological Impacts of Small Hydropower Plants on Headwater Stream Fish: From Individual to Community Effects. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2016, 25, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaka, J.G.; Wanjiru Mwaniki, M. A Global Review of the Downstream Effects of Small Impoundments on Stream Habitat Conditions and Macroinvertebrates. Environ. Rev. 2015, 23, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Pander, J.; Geist, J. The Effects of Weirs on Structural Stream Habitat and Biological Communities. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.E.; Cochrane, T.A. Impacts of Hydrological Alterations to the Tonle Sap Ecosystem of the Mekong River Basin; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane, T.A.; Arias, M.E.; Piman, T. Historical Impact of Water Infrastructure on Water Levels of the Mekong River and the Tonle Sap System. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4529–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frappart, F.; Biancamaria, S.; Normandin, C.; Blarel, F.; Bourrel, L.; Aumont, M.; Azemar, P.; Vu, P.-L.; Le Toan, T.; Lubac, B.; et al. Influence of Recent Climatic Events on the Surface Water Storage of the Tonle Sap Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1520–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, L.; Liu, J.; Hou, X.; Chen, D. Changes of Inundation Area and Water Turbidity of Tonle Sap Lake: Responses to Climate Changes or Upstream Dam Construction? Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 0940a1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, L.; Han, F.; Zhang, C. Balancing Competing Interests in the Mekong River Basin via the Operation of Cascade Hydropower Reservoirs in China: Insights from System Modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 119967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Tran, T.; Kervyn, M. Dynamics of Land Cover/Land Use Changes in the Mekong Delta, 1973–2011: A Remote Sensing Analysis of the Tran Van Thoi District, Ca Mau Province, Vietnam. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2899–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosegrant, M.W.; Ringler, C.; Zhu, T. Water for Agriculture: Maintaining Food Security under Growing Scarcity. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, J.; Pathirana, A. Adaptation to Climate Change in the Mekong River Basin: Introduction to the Special Issue. Clim. Change 2018, 149, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhong, B.; Yang, A.; Jue, K.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Wu, S.; Zhang, N.; et al. Ecological Environment Assessment for Greater Mekong Subregion Based on Pressure-State-Response Framework by Remote Sensing. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; He, W.; Liao, Z.; Degefu, D.M.; An, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X. Allocating Water in the Mekong River Basin during the Dry Season. Water 2019, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degefu, D.M.; He, W. Allocating Water under Bankruptcy Scenario. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 3949–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurford, A.P.; Harou, J.J. Balancing Ecosystem Services with Energy and Food Security—Assessing Trade-Offs from Reservoir Operation and Irrigation Investments in Kenya’s Tana Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3259–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tingsanchali, T.; Singh, P.R. Optimum Water Resources Allocation for Mekong-Chi-Mun Transbasin Irrigation Project, Northeast Thailand. Water Int. 1996, 21, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R.; Kummu, M. Water Resource Models in the Mekong Basin: A Review. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringler, C. ZEF Discussion Papers on Development Policy. In Optimal Water Allocation in the Mekong River Basin; ZEF Center for Development Research: Bonn, Germany, 2016; p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Z.; Fang, L.; Hipel, K.W. Water Resources Allocation: A Cooperative Game Theoretic Approach. J. Environ. Inform. 2003, 2, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, G.; Baran, E.; Nam, S.; Rodríguez-Iturbe, I.; Levin, S.A. Trading-off Fish Biodiversity, Food Security, and Hydropower in the Mekong River Basin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5609–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruida, Z.; Tongtiegang, Z.; Xiaohong, C. Evaluating the Tradeoff between Hydropower Benefit and Ecological Interest under Climate Change: How Will the Water-Energy-Ecosystem Nexus Evolve in the Upper Mekong Basin? Energy 2021, 237, 121518. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, R. Dam-Building Threatens Mekong Fisheries. Science 2016, 354, 1084–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.; Pittock, J.; Chapagain, A.; Dumaresq, D. Dams on the Mekong River: Lost Fish Protein and the Implications for Land and Water Resources. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Wang, Z. Effects of Hydrologic Conditions and Reservoir Operation on Transboundary Cooperation in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2019, 145, 04019020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskinen, M.; Salminen, E.; Haapala, J. Water Diplomacy Paths—An Approach to Recognise Water Diplomacy Actions in Shared Waters. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, C.; Devlaeminck, D.J. Reciprocity in Practice: The Hydropolitics of Equitable and Reasonable Utilization in the Lancang-Mekong Basin. Int. Environ. Agreem. Politics Law. Econ. 2021, 21, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Qi, J. A New Remote Sensing Approach to Enrich Hydropower Dams’ Information and Assess Their Impact Distances: A Case Study in the Mekong River Basin. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Tang, H. Automatic Damage Detection and Diagnosis for Hydraulic Structures Using Drones and Artificial Intelligence Techniques. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covarrubias, M. The Nexus between Water, Energy and Food in Cities: Towards Conceptualizing Socio-Material Interconnections. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 14, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leck, H.; Conway, D.; Bradshaw, M.; Rees, J. Tracing the Water–Energy–Food Nexus: Description, Theory and Practice. Geogr. Compass 2015, 9, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smajgl, A.; Ward, J.; Pluschke, L. The Water–Food–Energy Nexus–Realising a New Paradigm. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, N.; Strambo, C.; Kemp-Benedict, E.; Nilsson, M. Closing the Governance Gaps in the Water-Energy-Food Nexus: Insights from Integrative Governance. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 45, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskinen, M.; Varis, O. Water-Energy-Food Nexus in Large Asian River Basins. Water 2016, 8, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, Z.; Xiaoxian, C.; Yu, L.; Wei, D.; Guangtao, F. Water-Energy-Food Nexus: Concepts, Questions and Methodologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 2018, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, E.M.; Bruce, E.; Boruff, B.; Duncan, J.M.A.; Horsley, J.; Pauli, N.; McNeill, K.; Neef, A.; Van Ogtrop, F.; Curnow, J.; et al. Sustainable Development and the Water–Energy–Food Nexus: A Perspective on Livelihoods. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, X.; Wallington, K.; Shafiee-Jood, M.; Marston, L. Understanding and Managing the Food-Energy-Water Nexus—Opportunities for Water Resources Research. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 111, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grenade, R.; House-Peters, L.; Scott, C.A.; Thapa, B.; Mills-Novoa, M.; Gerlak, A.; Verbist, K. The Nexus: Reconsidering Environmental Security and Adaptive Capacity. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2016, 21, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wichelns, D. The Water-Energy-Food Nexus: Is the Increasing Attention Warranted, from Either a Research or Policy Perspective? Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 69, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wu, S.; Han, G.; Weinberg, J.; Xie, X.; Wu, X.; Song, X.; Jia, B.; Xue, W.; Yang, Q. Water-Energy Nexus: A Review of Methods and Tools for Macro-Assessment. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddoura, S.; El Khatib, S. Review of Water-Energy-Food Nexus Tools to Improve the Nexus Modelling Approach for Integrated Policy Making. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 77, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakilifard, N.; Anda, M.; Bahri, P.A.; Ho, G. The Role of Water-Energy Nexus in Optimising Water Supply Systems—Review of Techniques and Approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, J.; Lebel, L.; Molle, F. A Framework for Analysing Transboundary Water Governance Complexes, Illustrated in the Mekong Region. J. Hydrol. 2012, 466–467, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, N.; Motta, S. Chinese State-Owned Enterprise Investment in Mekong Hydropower: Political and Economic Drivers and Their Implications across the Water, Energy, Food Nexus. Water 2015, 7, 6269–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zambrano-Prado, P.; Muñoz-Liesa, J.; Josa, A.; Rieradevall, J.; Alamús, R.; Gasso-Domingo, S.; Gabarrell, X. Assessment of the food-water-energy nexus suitability of rooftops. A methodological remote sensing approach in an urban Mediterranean area. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, A.; Samy, G.; Hagras, M.A.; ElKholy, R. Geographic Information Systems-Based Framework for Water–Energy–Food Nexus Assessments. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 102224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cambodia | Lao PDR | Thailand | Vietnam | Myanmar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP (106 USD) | 26,961 | 18,827 | 505,947 | 366,137 | 65,091 |
| Agriculture, forestry, and fishing, value added (% of GDP) | 22.8 | 16.1 | 8.5 | 12.6 | 23.4 |
| Population (103) | 16,589 | 7425 | 71,601 | 97,468 | 53,798 |
| GDP Growth (%) | 3.0 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 2.6 | −17.9 |
| GDP per capita (USD) | 1625 | 2535 | 7066 | 3756 | 1209 |
| Urban population growth rate (%) | 2.9 | 3.2 | 1.6 | 2.7 | 1.7 |
| Poverty (%) | 16.7 | 27.6 | 9.8 | 2.8 | 25.6 |
| Research Areas | Record Count | % of 270 |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Sciences Ecology | 189 | 70.0% |
| Agriculture | 167 | 61.9% |
| Water Resources | 162 | 60.0% |
| Plant Sciences | 100 | 37.0% |
| Meteorology Atmospheric Sciences | 78 | 28.9% |
| Marine Freshwater Biology | 76 | 28.2% |
| Biodiversity Conservation | 68 | 25.2% |
| Geography | 65 | 24.1% |
| Business Economics | 61 | 22.6% |
| Science Technology Other Topics | 61 | 22.6% |
| Engineering | 59 | 21.9% |
| Mathematics | 50 | 18.5% |
| Energy Fuels | 41 | 15.2% |
| Geochemistry Geophysics | 40 | 14.8% |
| Oceanography | 40 | 14.8% |
| Physical Sciences Other Topics | 37 | 13.7% |
| Geology | 36 | 13.3% |
| Public Environmental Occupational Health | 36 | 13.3% |
| Fisheries | 30 | 11.1% |
| Food Science Technology | 25 | 9.3% |
| Journal | Impact Factor (2021) | H-Index (2021) | Average Number of Citations per Paper (2021) | Record Count | Share in Total Number of Selected Publications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 3.530 | 69 | 7.91 | 9 | 3.3% |
| Agricultural Water Management | 6.611 | 139 | 13.67 | 7 | 2.6% |
| Field Crops Research | 6.145 | 161 | 19.56 | 7 | 2.6% |
| Advances in Climate Change Research | 4.746 | 30 | 5.93 | 6 | 2.2% |
| Paddy and Water Environment | 1.554 | 38 | 9.24 | 6 | 2.2% |
| Science of The Total Environment | 7.963 | 221 | 6.29 | 6 | 2.2% |
| Hydrological Processes | 4.015 | 128 | 27.12 | 5 | 1.9% |
| International Journal of Remote Sensing | 2.581 | 106 | 10.47 | 5 | 1.9% |
| Remote Sensing | 5.076 | 161 | 25.19 | 5 | 1.9% |
| Water International | 2.22 | 57 | 9.48 | 5 | 1.9% |
| Ambio | 4.022 | 97 | 23.87 | 4 | 1.5% |
| Food Security | 4.603 | 62 | 16.42 | 4 | 1.5% |
| Frontiers in Environmental Science | 5.646 | 48 | 8.22 | 4 | 1.5% |
| Journal of Health and Pollution | 2.249 | 10 | 4.82 | 4 | 1.5% |
| Journal of Hydrology | 4.646 | 203 | 36.90 | 4 | 1.5% |
| Applied Geochemistry | 3.621 | 121 | 24.86 | 3 | 1.1% |
| Country | Paper Record Count | % of 270 |
|---|---|---|
| Vietnam | 75 | 27.8% |
| United States of America | 59 | 21.9% |
| Japan | 51 | 18.9% |
| Australia | 46 | 17.0% |
| P.R. China | 37 | 13.7% |
| Cambodia | 29 | 10.7% |
| Laos | 24 | 8.9% |
| Thailand | 23 | 8.5% |
| Germany | 18 | 6.7% |
| Netherlands | 15 | 5.6% |
| England | 10 | 3.7% |
| Publication | Average per Year | Total |
|---|---|---|
| Matthew L. Polizzotto [33] | 30.6 | 429 |
| Laurent Charlet [34] | 13.4 | 214 |
| Toshihiro Sakamoto [35] | 12.4 | 198 |
| Ingjerd Haddeland [36] | 11.3 | 181 |
| N.T. Sona [37] | 16.8 | 168 |
| Toshihiro Sakamoto [38] | 14.0 | 168 |
| Polya, DA [39] | 9.8 | 167 |
| Matti Kummu [40] | 10.8 | 151 |
| Benjamin D. Kocar [41] | 9.6 | 135 |
| F. Su [42] | 18.3 | 110 |
| Mauricio E. Arias [43] | 13.1 | 105 |
| Jory S. Hecht [44] | 34.3 | 103 |
| Nguyen Minh Dong [45] | 9.9 | 99 |
| Mauricio E. Arias [46] | 9.3 | 93 |
| Nguyen-Thanh Son [47] | 10.8 | 86 |
| Chandrashekhar M. Biradar [48] | 7.3 | 80 |
| Thi Thu Ha Nguyen [49] | 7.9 | 79 |
| Shawn G.Benner [50] | 5.4 | 76 |
| Gert-Jan Wilbers [51] | 9.4 | 75 |
| Toshihiro Sakamoto [52] | 5.6 | 73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Bibi, S.; Zhu, T.; Tian, F.; Olivares, M.A. Review Analysis of Irrigation and Application of Remote Sensing in the Lower Mekong River Basin. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3856. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153856
Wang G, Bibi S, Zhu T, Tian F, Olivares MA. Review Analysis of Irrigation and Application of Remote Sensing in the Lower Mekong River Basin. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(15):3856. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153856
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guanghui, Sadia Bibi, Tingju Zhu, Fuqiang Tian, and Marcelo A. Olivares. 2023. "Review Analysis of Irrigation and Application of Remote Sensing in the Lower Mekong River Basin" Remote Sensing 15, no. 15: 3856. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153856
APA StyleWang, G., Bibi, S., Zhu, T., Tian, F., & Olivares, M. A. (2023). Review Analysis of Irrigation and Application of Remote Sensing in the Lower Mekong River Basin. Remote Sensing, 15(15), 3856. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153856







