Combined Characterization of Airborne Saharan Dust above Sofia, Bulgaria, during Blocking-Pattern Conditioned Dust Episode in February 2021
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Instrumentation and Methods
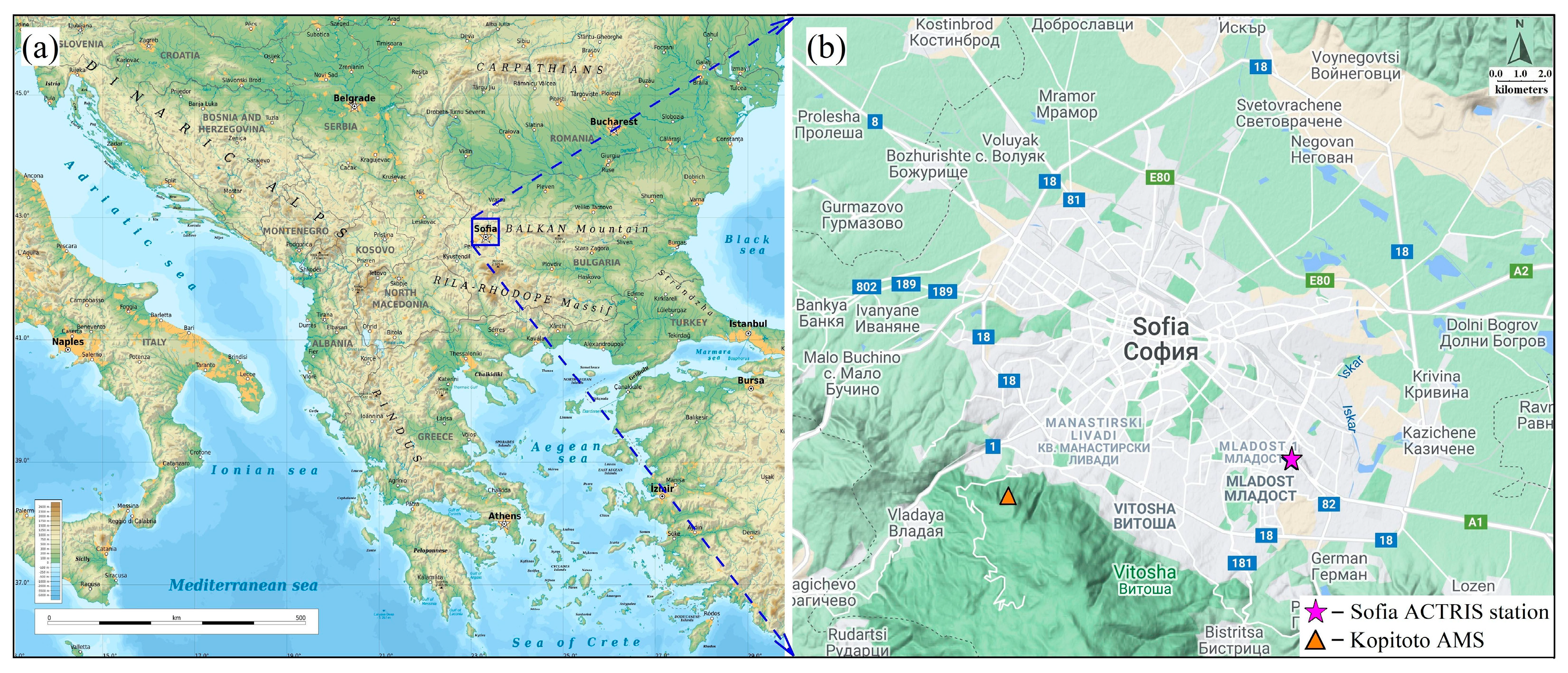
2.1. Measurement Site Description
2.2. Remote Sensing Observational Instruments and Methods
2.2.1. Lidar System and Methodology
2.2.2. Sun Photometer
2.2.3. MODIS-Terra Imaging of the Aerosol/Dust Plume Spread
2.3. In Situ PM10 Measurements
2.4. Modeling/Forecasting and Reanalysis Data Provision
2.5. LIRIC Inversion Code Analysis and Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synoptic Situation during the Dust Episode
3.1.1. Blocking Circulation Patterns
3.1.2. Air Temperature Composite Anomalies in the Dust-Affected Areas
3.2. Dust Episode Description
3.2.1. Dust Spread Mapping and Imaging
3.2.2. Dust Height Distribution and Dynamics
3.2.3. Dust Transport Tracking
3.3. Lidar Aerosol/Dust Retrievals and Radiosonde Data
3.4. Profiling Aerosol/Dust Mode Volume Concentration Using LIRIC-2 Inversion Code
3.5. AERONET Data and Retrievals
3.5.1. Basic Aerosol/Dust Properties
3.5.2. Aerosol/Dust Particle Size Distributions
3.6. In Situ PM10 Concentration Measurements

4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Middleton, N.J.; Goudie, A.S. Saharan Dust: Sources and Trajectories. Trans. Inst. Brit. Geogr. 2002, 26, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Ginoux, P.; Torres, O.; Nicholson, S.E.; Gill, T.E. Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the Nimbus 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol products. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, R.; Todd, M.C.; Middleton, N.J.; Goudie, A.S. Dust-storm source areas determined by the total ozone monitoring spectrometer and surface observations. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2003, 93, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.Y.; Chiba, M. A numerical study of the contributions of dust source regions to the global dust budget. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 52, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelstaedter, S.; Tegen, I.; Washington, R. North African dust emissions and transport. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2006, 79, 73–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Duce, R.A.; Jickells, T.D.; Kubilay, N.; Prospero, J.M.; Tegen, I. Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, GB4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.-H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in Earth system science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Adebiyi, A.A.; Albani, S.; Balkanski, Y.; Checa-Garcia, R.; Chin, M.; Colarco, P.R.; Hamilton, D.S.; Huang, Y.; Ito, A.; et al. Improved representation of the global dust cycle using observational constraints on dust properties and abundance. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 8127–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asutosh, A.; Vinoj, V.; Murukesh, N.; Ramisetty, R.; Mittal, N. Investigation of June 2020 giant Saharan dust storm using remote sensing observations and model reanalysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evan, A.; Flamant, C.; Gaetani, M.; Guichard, F. The past, present and future of African dust. Nature 2016, 531, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, S.; Gasteiger, J.; Freudenthaler, V.; Müller, T.; Sauer, D.; Toledano, C.; Ansmann, A. Saharan dust contribution to the Caribbean summertime boundary layer—A lidar study during SALTRACE. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11535–11546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubilay, N.; Nickovic, S.; Moulin, C.; Dulac, F. An illustration of the transport and deposition of mineral dust onto the eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannis, A.; Amiridis, V.; Mona, L.; Tsaknakis, G.; Balis, D.; Bösenberg, J.; Chaikovski, A.; De Tomasi, F.; Grigorov, I.; Mattis, I.; et al. Systematic lidar observations of Saharan dust over Europe in the frame of EARLINET (2000–2002). J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; Binietoglou, I.; Tsikerdekis, A.; Solomos, S.; Proestakis, E.; Konsta, D.; Papagiannopoulos, N.; Tsekeri, A.; Vlastou, G.; et al. Three-dimensional evolution of Saharan dust transport towards Europe based on a 9-year EARLINET-optimized CALIPSO dataset. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5893–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvador, P.; Pey, J.; Pérez, N.; Querol, X.; Artíñano, B. Increasing atmospheric dust transport towards the western Mediterranean over 1948–2020. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Bösenberg, J.; Chaikovsky, A.; Comerón, A.; Eckhardt, S.; Eixmann, R.; Freudenthaler, V.; Ginoux, P.; Komguem, L.; Linné, H.; et al. Long-range transport of Saharan dust to northern Europe: The 11–16 October 2001 outbreak observed with EARLINET. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkan, J.; Alpert, P. Synoptic analysis of a rare event of Saharan dust reaching the Arctic region. Weather 2010, 65, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippertz, P.; Stuut, J.-B.W. (Eds.) Mineral Dust: A Key Player in the Earth System; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Choobari, O.A.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. The global distribution of mineral dust and its impacts on the climate system: A review. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J. Desert dust hazards: A global review. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepanski, K. Transport of Mineral Dust and Its Impact on Climate. Geosciences 2018, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Kloster, S.; Engelstaedter, S.; Moore, J.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; McConnell, J.R.; Albani, S.; Doney, S.C.; Bhattacharya, A.; Curran, M.A.J.; et al. Observed 20th century desert dust variability: Impact on climate and biogeochemistry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10875–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helmert, J.; Heinold, B.; Tegen, I.; Hellmuth, O.; Wendisch, M. On the direct and semidirect effects of Saharan dust over Europe: A modeling study. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D13208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kok, J.F.; Storelvmo, T.; Karydis, V.A.; Adebiyi, A.A.; Mahowald, N.M.; Evan, A.T.; He, C.; Leung, D.M. Mineral dust aerosol impacts on global climate and climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Ward, D.S.; Mahowald, N.M.; Evan, A.T. Global and regional importance of the direct dust-climate feedback. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alizadeh-Choobari, O.; Sturman, A.; Zawar-Reza, P. A global satellite view of the seasonal distribution of mineral dust and its correlation with atmospheric circulation. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2014, 68, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelstaedter, S.; Washington, R. Atmospheric controls on the annual cycle of North African dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D03103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.; Di Sarra, A.; Biavati, G.; DeLuisi, J.J.; Monteleone, F.; Pace, G.; Piacentino, S.; Sferlazzo, D.M. Seasonal behavior of Saharan dust events at the Mediterranean island of Lampedusa in the period 1999–2005. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3041–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pey, J.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Forastiere, F.; Stafoggia, M. African dust outbreaks over the Mediterranean Basin during 2001–2011: PM10 concentrations, phenomenology and trends, and its relation with synoptic and mesoscale meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1395–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varga, G.; Kovács, J.; Újvári, G. Analysis of Saharan dust intrusions into the Carpathian Basin (Central Europe) over the period of 1979–2011. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 100, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, A.; Sousa, P.M.; Durão, R.M.; Ramos, A.M.; Salvador, P.; Linares, C.; Díaz, J.; Trigo, R.M. Saharan dust intrusions in the Iberian Peninsula: Predominant synoptic conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannis, A.; Mamouri, R.E.; Amiridis, V.; Kazadzis, S.; Pérez, C.; Tsaknakis, G.; Kokkalis, P.; Baldasano, J.M. Systematic lidar observations of Saharan dust layers over Athens, Greece in the frame of EARLINET project (2004–2006). Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 3611–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soupiona, O.; Papayannis, A.; Kokkalis, P.; Mylonaki, M.; Tsaknakis, G.; Argyrouli, A.; Vratolis, S. Long-term systematic profiling of dust aerosol optical properties using the EOLE NTUA lidar system over Athens, Greece (2000–2016). Atmos. Environ. 2018, 183, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, G. Changing nature of Saharan dust deposition in the Carpathian Basin (Central Europe): 40 years of identified North African dust events (1979–2018). Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajtai, N.; Stefanie, H.; Mereuta, A.; Radovici, A.; Botezan, C. Multi-sensor observation of a Saharan dust outbreak over Transylvania, Romania in April 2019. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peshev, Z.; Deleva, A.; Vulkova, L.; Dreischuh, T. Large-Scale Saharan Dust Episode in April 2019: Study of Desert Aerosol Loads over Sofia, Bulgaria, Using Remote Sensing, In Situ, and Modeling Resources. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastos, P.T. Meteorological patterns associated with intense Saharan dust outbreaks over Greece in winter. Adv. Meteorol. 2012, 2012, 828301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varga, G.; Cserháti, C.; Kovács, J.; Szeberényi, J.; Bradák, B. Unusual Saharan dust events in the Carpathian Basin (Central Europe) in 2013 and early 2014. Weather 2014, 69, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Titos, G.; Ealo, M.; Pandolfi, M.; Pérez, N.; Sola, Y.; Sicard, M.; Comerón, A.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Spatiotemporal evolution of a severe winter dust event in the western Mediterranean: Aerosol optical and physical properties. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4052–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, A.J.; Sicard, M.; Costa, M.J.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Gómez-Amo, J.L.; Molero, F.; Barragán, R.; Basart, S.; Bortoli, D.; Bedoya-Velásquez, A.E.; et al. Extreme, wintertime Saharan dust intrusion in the Iberian Peninsula: Lidar monitoring and evaluation of dust forecast models during the February 2017 event. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba-Jabonero, C.; Sicard, M.; del Águila, A.; Jiménez, M.; Zorzano, M.-P. Performance of a dust model to predict the vertical mass concentration of an extreme Saharan dust event in the Iberian Peninsula: Comparison with continuous, elastic, polarization-sensitive lidars. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleva, A.D.; Peshev, Z.Y.; Vulkova, L.A.; Dreischuh, T.N. Lidar study of unusual winter Saharan dust loads above Sofia, Bulgaria: Impacts on the local weather and troposphere. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 024517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriopedro, D.; García-Herrera, R.; Trigo, R.M. Application of blocking diagnosis methods to general circulation models. Part I: A novel detection scheme. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 35, 1373–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriopedro, D.; García-Herrera, R.; Lupo, A.R.; Hernández, E. A Climatology of Northern Hemisphere blocking. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 1042–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woollings, T.; Barriopedro, D.; Methven, J.; Son, S.-W.; Martius, O.; Harvey, B.; Sillmann, J.; Lupo, A.R.; Seneviratne, S. Blocking and its response to climate change. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2018, 4, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lupo, A.R. Atmospheric blocking events: A review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1504, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautz, L.A.; Martius, O.; Pfahl, S.; Pinto, J.G.; Ramos, A.M.; Sousa, P.M.; Woollings, T. Atmospheric blocking and weather extremes over the Euro-Atlantic sector–a review. Weather Clim. Dyn. 2022, 3, 305–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.; Nickovic, S.; Baldasano, J.M.; Sicard, M.; Rocadenbosch, F.; Cachorro, V.E. A long Saharan dust event over the western Mediterranean: Lidar, Sun photometer observations, and regional dust modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D15214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannis, A.; Balis, D.; Amiridis, V.; Chourdakis, G.; Tsaknakis, G.; Zerefos, C.; Castanho, A.D.A.; Nickovic, S.; Kazadzis, S.; Grabowski, J. Measurements of Saharan dust aerosols over the Eastern Mediterranean using elastic backscatter-Raman lidar, spectrophotometric and satellite observations in the frame of the EARLINET project. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Z.; Ansmann, A.; Baars, H.; Seifert, P.; Engelmann, R.; Radenz, M.; Jimenez, C.; Herzog, A.; Ohneiser, K.; Hanbuch, K.; et al. Aerosol measurements with a shipborne Sun–sky–lunar photometer and collocated multiwavelength Raman polarization lidar over the Atlantic Ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5685–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmid, B.; Redemann, J.; Russell, P.B.; Hobbs, P.V.; Hlavka, D.L.; McGill, M.J.; Holben, B.N.; Welton, E.J.; Campbell, J.R.; Torres, O.; et al. Coordinated airborne, spaceborne, and ground-based measurements of massive thick aerosol layers during the dry season in southern Africa. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mona, L.; Liu, Z.; Müller, D.; Omar, A.; Papayannis, A.; Pappalardo, G.; Sugimoto, N.; Vaughan, M. Lidar measurements for desert dust characterization: An overview. Adv. Meteorol. 2012, 2012, 356265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comerón, A.; Muñoz-Porcar, C.; Rocadenbosch, F.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A.; Sicard, M. Current Research in Lidar Technology Used for the Remote Sensing of Atmospheric Aerosols. Sensors 2017, 17, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soupiona, O.; Samaras, S.; Ortiz-Amezcua, P.; Böckmann, C.; Papayannis, A.; Moreira, G.A.; Benavent-Oltra, J.A.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Bedoya-Velásquez, A.E.; Olmo, F.J.; et al. Retrieval of optical and microphysical properties of transported Saharan dust over Athens and Granada based on multi-wavelength Raman lidar measurements: Study of the mixing processes. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleva, A.D.; Peshev, Z.Y.; Dreischuh, T.N.; Chaikovsky, A.P.; Slesar, A.S.; Fedarenka, A. Lidar observations of Saharan dust loads above Sofia, Bulgaria: Dust layers extending throughout the troposphere (a case study). J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 014504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreischuh, T.; Grigorov, I.; Peshev, Z.; Deleva, A.; Kolarov, G.; Stoyanov, D. Lidar Mapping of Near-Surface Aerosol Fields. In Aerosols—Science and Case Studies, 1st ed.; Volkov, K., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 85–107. [Google Scholar]
- Esselborn, M.; Wirth, M.; Fix, A.; Weinzierl, B.; Rasp, K.; Tesche, M.; Petzold, A. Spatial distribution and optical properties of Saharan dust observed by airborne high spectral resolution lidar during SAMUM 2006. Tellus B 2009, 61, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Omar, A.; Vaughan, M.; Hair, J.; Kittaka, C.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.; Trepte, C.; Winker, D.; Hostetler, C.; et al. CALIPSO lidar observations of the optical properties of Saharan dust: A case study of long-range transport. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarig, M.; Ansmann, A.; Engelmann, R.; Baars, H.; Toledano, C.; Torres, B.; Althausen, D.; Radenz, M.; Wandinger, U. First triple-wavelength lidar observations of depolarization and extinction-to-backscatter ratios of Saharan dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicka, L.; Stachlewska, I.S.; Veselovskii, I.; Baars, H. Temporal variations in optical and microphysical properties of mineral dust and biomass burning aerosol derived from daytime Raman lidar observations over Warsaw, Poland. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Mueller, D.; Althausen, D.; Mattis, I.; Heese, B.; Freudenthaler, V.; Wiegner, M.; Esselborn, M.; Pisani, G. Vertical profiling of Saharan dust with Raman lidars and airborne HSRL in southern Morocco during SAMUM. Tellus B 2009, 61, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groß, S.; Esselborn, M.; Weinzierl, B.; Wirth, M.; Fix, A.; Petzold, A. Aerosol classification by airborne high spectral resolution lidar observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2487–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karanasiou, A.; Moreno, N.; Moreno, T.; Viana, M.; de Leeuw, F.; Querol, X. Health effects from Sahara dust episodes in Europe: Literature review and research gaps. Environ. Intern. 2012, 47, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallone, S.; Stafoggia, M.; Faustini, A.; Gobbi, G.P.; Marconi, A.; Forastiere, F. Saharan dust and associations between particulate matter and daily mortality in Rome, Italy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Gu, J.; Wang, X. The impact of Sahara dust on air quality and public health in European countries. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 15, 117771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, G.; Amodeo, A.; Apituley, A.; Comeron, A.; Freudenthaler, V.; Linné, H.; Ansmann, A.; Bösenberg, J.; D’Amico, G.; Mattis, I.; et al. EARLINET: Towards an advanced sustainable European aerosol lidar network. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2389–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aerosol, Clouds and Trace Gases (ACTRIS) Research Infrastructure. Available online: https://www.actris.eu (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Barreto, Á.; Cuevas, E.; Granados-Muñoz, M.-J.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Romero, P.M.; Gröbner, J.; Kouremeti, N.; Almansa, A.F.; Stone, T.; Toledano, C.; et al. The new sun-sky-lunar Cimel CE318-T multiband photometer—A comprehensive performance evaluation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 631–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Rem. Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikovsky, A.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Bril, A.; Goloub, P.; Tanré, D.; Pappalardo, G.; Wandinger, U.; Chaikovskaya, L.; Denisov, S.; et al. Lidar-Radiometer Inversion Code (LIRIC) for the retrieval of vertical aerosol properties from combined lidar/radiometer data: Development and distribution in EARLINET. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1181–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsekeri, A.; Lopatin, A.; Amiridis, V.; Marinou, E.; Igloffstein, J.; Siomos, N.; Solomos, S.; Kokkalis, P.; Engelmann, R.; Baars, H. GARRLiC and LIRIC: Strengths and limitations for the characterization of dust and marine particles along with their mixtures. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 4995–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mamouri, R.E.; Ansmann, A. Fine and coarse dust separation with polarization lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3717–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovik, O.; Fuertes, D.; Litvinov, P.; Lopatin, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Doubovik, I.; Xu, F.; Ducos, F.; Chen, C.; Torres, B. A Comprehensive Description of Multi-Term LSM for Applying Multiple a Priori Constraints in Problems of Atmospheric Remote Sensing: GRASP Algorithm, Concept, and Applications. Front. Remote Sens. 2021, 2, 706851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Plana-Fattori, A.; N’doumé, C. Satellite detection of dust using the IR imagery of Meteosat: 1. Infrared difference dust index. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 18251–18274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Dubovik, O. Global aerosol optical properties and application to Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol retrieval over land. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D13210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer). Available online: https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Schladitz, A.; Müller, T.; Kaaden, N.; Massling, A.; Kandler, K.; Ebert, M.; Weinbruch, S.; Deutscher, C.; Wiedensohler, A. In situ measurements of optical properties at Tinfou (Morocco) during the Saharan Mineral Dust Experiment SAMUM 2006. Tellus B 2009, 61, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, S.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. A review of methods for long term in situ characterization of aerosol dust. Aeolian Res. 2012, 6, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Stunder, B. Real-time environmental applications and display system: READY. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallos, G.; Nickovic, S.; Papadopoulos, A.; Jovic, D.; Kakaliagou, O.; Misirlis, N.; Boukas, L.; Mimikou, N.; Sakellaridis, G.; Papageorgiou, J.; et al. The regional weather forecasting system SKIRON: An overview. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Regional Weather Prediction on Parallel Computer Environments, Athens, Greece, 15–17 October 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Nickovic, S.; Kallos, G.; Papadopoulos, A.; Kakaliagou, O. A model for prediction of desert dust cycle in the atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 18113–18129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez, C.; Haustein, K.; Janjic, Z.; Jorba, O.; Huneeus, N.; Baldasano, J.M.; Black, T.; Basart, S.; Nickovic, S.; Miller, R.L.; et al. An online mineral dust aerosol model for MESO to global scales: Model description, annual simulations and evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 13001–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basart, S.; Pérez, C.; Nickovic, S.; Cuevas, E.; Baldasano, J. Development and evaluation of the BSC-DREAM8b dust regional model over Northern Africa, the Mediterranean and the Middle East. Tellus B 2012, 64, 18539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nickovic, S.; Cvetkovic, B.; Madonna, F.; Rosoldi, M.; Pejanovic, G.; Petkovic, S.; Nikolic, J. Cloud ice caused by atmospheric mineral dust—Part 1: Parameterization of ice nuclei concentration in the NMME-DREAM model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11367–11378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klose, M.; Jorba, O.; Gonçalves Ageitos, M.; Escribano, J.; Dawson, M.L.; Obiso, V.; Di Tomaso, E.; Basart, S.; Montané Pinto, G.; Macchia, F. Mineral dust cycle in the Multiscale Online Nonhydrostatic AtmospheRe Chemistry model (MONARCH) version 2.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 6403–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF). Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/ (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, R.; Kalnay, E.; Collins, W.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; Chelliah, M.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kousky, V.; et al. The NCEP–NCAR 50-year reanalysis: Monthly means CD-ROM and documentation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA/ESRL Physical Sciences Laboratory, Boulder Colorado, Daily Mean Composites Website. Available online: https://psl.noaa.gov/data/composites/day (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- University of Wyoming. Upperair Air Data. Available online: http://weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Hoshyaripour, A. February 2021: A Dusty Month for Europe, Blog of the Atmospheric Sciences (AS) Division of the European Geosciences Union (EGU). Available online: https://blogs.egu.eu/divisions/as/2021/04/03/february-2021-a-dusty-month-for-europe (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Centers for Environmental Information, The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Climate Normals, World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Station Number: 15614. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/products/wmo-climate-normals (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Klett, D. Stable analytical inversion solution for processing lidar returns. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernald, G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenthaler, V.; Linné, H.; Chaikovski, A.; Rabus, D.; Groß, S. EARLINET LiDAR quality assurance tools. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2018. preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Berjón, A.; Barreto, A.; Hernández, Y.; Yela, M.; Toledano, C.; Cuevas, E. A 10-year characterization of the Saharan Air Layer lidar ratio in the subtropical North Atlantic. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6331–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peshev, Z.Y.; Dreischuh, T.N.; Evgenieva, T.T.; Deleva, A.D.; Tonev, D.; Stoyanov, D.V. Lidar observations of long-range transported Saharan dust over Sofia, Bulgaria: A case study of dust mixed with local aerosols. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 036009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, L.; Amodeo, A.; Pandolfi, M.; Pappalardo, G. Saharan dust intrusions in the Mediterranean area: Three years of Raman lidar measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D16203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Guasta, M. Daily cycles in urban aerosols observed in Florence (Italy) by means of an automatic 532–1064 nm LIDAR. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 2853–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimel. Multiband photometer CE318–T, User’s Manual (Revision V4.10 October 2021). Available online: https://www.cimel.fr/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/CE318_T_Photometer_UserManual_V4.10.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Evgenieva, T.; Gurdev, L.; Toncheva, E.; Dreischuh, T. Optical and Microphysical Properties of the Aerosol Field over Sofia, Bulgaria, Based on AERONET Sun-Photometer Measurements. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, N.T.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Thulasiraman, S. Spectral discrimination of coarse and fine mode optical depth. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4559–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, N.; Eck, T.; Holben, B.; Smirnov, A.; Dubovik, O.; Royer, A. Bimodal size distribution influences on the variation of Angstrom derivatives in spectral and optical depth space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 9787–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from AERONET sun and sky-radiometric measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Muñoz, O.; Veihelmann, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database—Automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sunphotometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinyuk, A.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.; Giles, D.; Slutsker, I.; Korkin, S.; Schafer, J.; Smirnov, A.; Sorokin, M.; Lyapustin, A. The AERONET Version 3 aerosol retrieval algorithm, associated uncertainties and comparisons to Version 2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 3375–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Koren, I.; Remer, L.A.; Tanré, D.; Ginoux, P.; Fan, S. Dust transport and deposition observed from the Terra-Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) spacecraft over the Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D10S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Executive Environment Agency (ExEA), Ministry of Environment and Water—Bulgaria, National System for Environmental Monitoring. Available online: http://www.eea.government.bg/kav/ (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Evgenieva, T.; Tatarov, B.; Kolev, N.; Iliev, I.; Savov, P.; Kaprielov, B.; Kolev, I. One year measurements of aerosol optical depth during development of the atmospheric boundary layer over urban area (Sofia, Bulgaria). In Proceedings of the 24th International Laser Radar Conference 2008 (ILRC 24), International Coordination Group on Laser Atmospheric Studies (ICLAS), Boulder, CO, USA, 23–27 June 2008; pp. 951–954. [Google Scholar]
- Evgenieva, T.; Kolev, N.; Iliev, T.; Savov, P.; Kaprielov, B.; Devara, P.; Kolev, I. Lidar and spectroradiometer measurements of atmospheric aerosol optical characteristics over an urban area in Sofia, Bulgaria. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 6381–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelona Dust Regional Center—The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Sand and Dust Storms Warning Advisory and Assessment System (SDS-WAS) Regional Center for Northern Africa, Middle East and Europe. Available online: https://dust.aemet.es (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Chaikovsky, A.; Chaikovskaya, L.; Denishchik-Nelubina, N.; Fedarenka, A.; Oshchepkov, S. Lidar&radiometer inversion code (LIRIC) for synergetic processing of Earlinet, Aeronet and Calipso lidar data. EDJ Web Conf. 2018, 176, 08007. [Google Scholar]
- Sun-Sky Radiometer Observation NETwork (SONET). Available online: http://www.sonet.ac.cn/en/index.php (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Su, X.; Yang, L.; Ye, S.; Xu, H. Aerosol Direct Radiative Effects over China Based on Long-Term Observations within the Sun–Sky Radiometer Observation Network (SONET). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Francisco State University, Analyses of Jet Stream Positions. Available online: https://squall.sfsu.edu/crws/archive/jet_arch.html (accessed on 26 June 2021).
- López-Caravaca, A.; Castañer, R.; Clemente, A.; Yubero, E.; Galindo, N.; Crespo, J.; Nicolás, J.F. The Impact of Intense Winter Saharan Dust Events on PM and Optical Properties at Urban Sites in the Southeast of the Iberian Peninsula. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.; Fonseca, R.; Nelli, N.; Bozkurt, D.; Picard, G.; Guan, B. Atmospheric rivers drive exceptional Saharan dust transport towards Europe. Atmos. Res. 2022, 266, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanik, D.M.; Ortiz-Amezcua, P.; Heese, B.; D’Amico, G.; Stachlewska, I.S. First Ever Observations of Mineral Dust in Wintertime over Warsaw, Poland. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.; Di Sarra, A.; Monteleone, F.; Pace, G.; Piacentino, S.; Sferlazzo, D.M. Seasonal transport patterns of intense Saharan dust events at the Mediterranean island of Lampedusa in the period 1999–2005. Atmos. Res. 2008, 88, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soupiona, O.; Papayannis, A.; Kokkalis, P.; Foskinis, R.; Sánchez, H.G.; Ortiz-Amezcua, P.; Mylonaki, M.; Papanikolaou, C.-A.; Papagiannopoulos, N.; Samaras, S.; et al. EARLINET observations of Saharan dust intrusions over the northern Mediterranean region (2014–2017): Properties and impact on radiative forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 15147–15166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirova, H.; Syrakov, D.; Prodanova, M.; Georgieva, E.; Atanassov, D. Background Concentration of Air Pollutants for Sofia City–Analysis For Summer and Winter Months. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConf. SGEM 2022, 22, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Current & Forecast Meteorology—Real-Time Environmental Applications and Display System (READY), National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Air Resources Laboratory (ARL). Available online: https://www.ready.noaa.gov/READYcmet.php (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- United States Committee on Extension to the Standard Atmosphere. U.S. Standard Atmosphere 1976; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Peshev, Z.; Deleva, A.; Chaikovsky, A.; Pescherenkov, V.; Vulkova, L.; Dreischuh, T. Vertical and near-horizontal scanning lidar observations of aerosol loads over Sofia, Bulgaria, in the presence of Saharan dust. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2240, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AERONET Technical and Quality Assurance Documents. Available online: https://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov/new_web/publications.html (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Sawamura, P.; Landulfo, E. AERONET sunphotometer products and backscatter lidar data: Systematic intercomparison over the city of São Paulo, Brazil. Opt. Pura Apl. 2008, 41, 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Nousiainen, T.; Muinonen, K.; Räisänen, P. Scattering of light by large Saharan dust particles in a modified ray optics approximation. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, O.; Volten, H.; Hovenier, J.W.; Nousiainen, T.; Muinonen, K.; Guirado, D.; Moreno, F.; Waters, L.B.F.M. Scattering matrix of large Saharan dust particles: Experiments and computations. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Date | Columnar Volume Concentration (μm3/μm2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Fine | Coarse | Coarse Spherical | Coarse Non-Spherical | |
| 22 Feb. | 0.034 | 0.019 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.000 |
| 23 Feb. | 0.126 | 0.020 | 0.106 | 0.001 | 0.105 |
| 24 Feb. | 0.138 | 0.054 | 0.084 | 0.006 | 0.077 |
| 25 Feb. | 0.068 | 0.016 | 0.052 | 0.002 | 0.050 |
| 26 Feb. | 0.063 | 0.015 | 0.048 | 0.012 | 0.036 |
| 27 Feb. | 0.114 | 0.040 | 0.074 | 0.010 | 0.063 |
| Parameter | λ (nm) | 22 Feb. | 23 Feb. | 24 Feb. | 25 Feb. | 26 Feb. | 27 Feb. | 28 Feb. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOD | 500 | 0.134 ± 0.0124 | 0.160 ± 0.038 | 0.438 ± 0.067 | 0.189 ± 0.045 | 0.135 ± 0.020 | 0.222 ± 0.054 | 0.116 ± 0.028 |
| AOD Fine Mode | 500 | 0.112 ± 0.025 | 0.072 ± 0.020 | 0.213 ± 0.025 | 0.085 ± 0.030 | 0.069 ± 0.014 | 0.103 ± 0.044 | 0.101 ± 0.029 |
| AOD Coarse Mode | 500 | 0.021 ± 0.002 | 0.088 ± 0.045 | 0.225 ± 0.056 | 0.104 ± 0.021 | 0.066 ± 0.006 | 0.119 ± 0.016 | 0.015 ± 0.003 |
| AE | 440/870 | 1.45 ± 0.06 | 0.79 ± 0.39 | 0.73 ± 0.15 | 0.65 ± 0.12 | 0.89 ± 0.08 | 0.68 ± 0.19 | 1.57 ± 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peshev, Z.; Chaikovsky, A.; Evgenieva, T.; Pescherenkov, V.; Vulkova, L.; Deleva, A.; Dreischuh, T. Combined Characterization of Airborne Saharan Dust above Sofia, Bulgaria, during Blocking-Pattern Conditioned Dust Episode in February 2021. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153833
Peshev Z, Chaikovsky A, Evgenieva T, Pescherenkov V, Vulkova L, Deleva A, Dreischuh T. Combined Characterization of Airborne Saharan Dust above Sofia, Bulgaria, during Blocking-Pattern Conditioned Dust Episode in February 2021. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(15):3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153833
Chicago/Turabian StylePeshev, Zahari, Anatoli Chaikovsky, Tsvetina Evgenieva, Vladislav Pescherenkov, Liliya Vulkova, Atanaska Deleva, and Tanja Dreischuh. 2023. "Combined Characterization of Airborne Saharan Dust above Sofia, Bulgaria, during Blocking-Pattern Conditioned Dust Episode in February 2021" Remote Sensing 15, no. 15: 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153833
APA StylePeshev, Z., Chaikovsky, A., Evgenieva, T., Pescherenkov, V., Vulkova, L., Deleva, A., & Dreischuh, T. (2023). Combined Characterization of Airborne Saharan Dust above Sofia, Bulgaria, during Blocking-Pattern Conditioned Dust Episode in February 2021. Remote Sensing, 15(15), 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153833






