Remote Sensing Estimates of Particulate Organic Carbon Sources in the Zhanjiang Bay Using Sentinel-2 Data and Carbon Isotopes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. In Situ Sampling and Analysis of Chemical Parameters
2.3. Calculation of POC Sources Based on δ13C
2.4. Acquisition and Processing of Satellite Data
2.5. Algorithm Evaluation
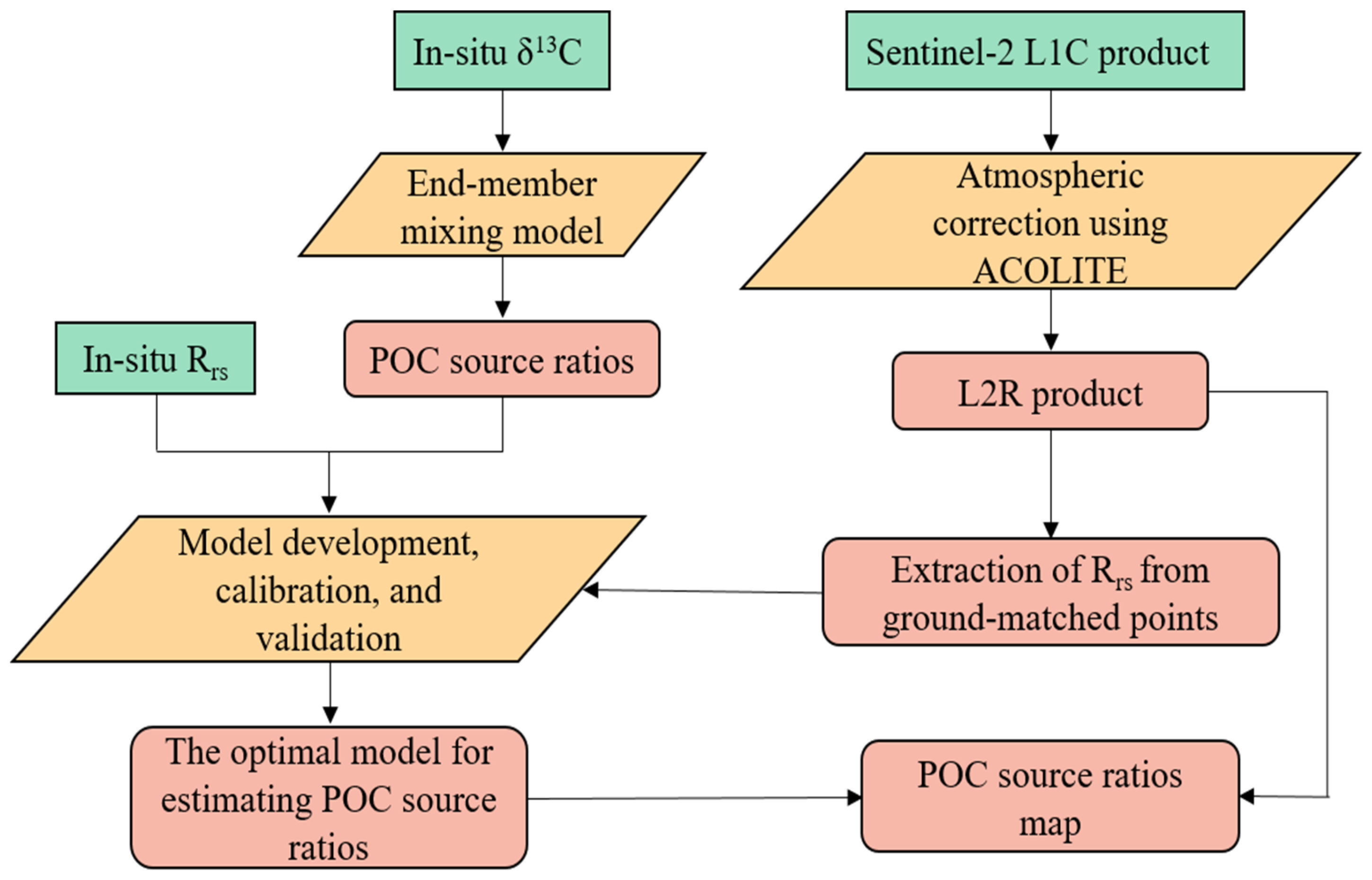
2.6. Method Framework
3. Results
3.1. δ¹³ CPOC and POC Sources
3.2. Model Development, Calibration and Validation
3.3. Model Application Example for Sentinel-2 Image
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Influencing the Source of POC Inside and Outside Zhanjiang Bay
4.2. Evaluation of the POC Source Algorithm
4.3. Biogeochemical Implications of the POC Source Algorithm
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The outer regions of Zhanjiang Bay were characterized by high δ13CPOC values and high chlorophyll-a concentrations, indicating the occurrence of phytoplankton blooms. In contrast, the inner bay was characterized by low δ13CPOC and low salinity values, reflecting the influence of organic matter input from terrestrial sources;
- (2)
- A combination of stable isotope and remote sensing data can better estimate POC sources in eutrophic bays; the four-band algorithm showed good performance and was suitable for analyzing Sentinel-2 data;
- (3)
- The algorithm stability may be insufficient due to the limited scope of the datasets. More coastal water datasets are required to further enhance the robustness of the algorithm and to improve and validate our approach.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bauer, J.E.; Cai, W.J.; Raymond, P.A.; Bianchi, T.S.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Regnier, P.A. The changing carbon cycle of the coastal ocean. Nature 2013, 504, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnier, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ciais, P.; Mackenzie, F.T.; Gruber, N.; Janssens, I.A.; Laruelle, G.G.; Lauerwald, R.; Luyssaert, S.; Andersson, A.J.; et al. Anthropogenic perturbation of the carbon fluxes from land to ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Cai, W.J.; He, X.; Zhai, W.; Pan, D.; Dai, M.; Yu, P. A mechanistic semi-analytical method for remotely sensing sea surface pCO2 in river-dominated coastal oceans: A case study from the East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 2331–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Tao, B.; Pan, D.; Chen, C.T.A.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Gong, C. Satellite estimation of particulate organic carbon flux from Changjiang River to the estuary. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lu, X.; Song, Z.; Huang, C.; Jin, G.; Chen, C.; Zhou, X.; Lao, Q.; Zhu, Q. Coastal currents regulate the distribution of the particulate organic matter in western Guangdong offshore waters as evidenced by carbon and nitrogen isotopes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Huang, C.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Lao, Q.; Chen, C.; Wu, J.; Jin, G.; Zhu, Q. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of particulate organic matter in the upwelling zone off the east coast of Hainan Island, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Prairie, Y.T.; Caraco, N.F.; McDowell, W.H.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; Duarte, C.M.; Kortelainen, P.; Downing, J.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; et al. Plumbing the global carbon cycle: Integrating inland waters into the terrestrial carbon budge. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Middelburg, J.J.; Herman, P.M.J. Organic matter processing in tidal estuaries. Mar. Chem. 2007, 106, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, G.V.; Martinelli, L.A.; Novais, T.M.O.; Ometto, J.P.H.; Zuppi, G.M. Stable isotopes of bulk organic matter to trace carbon and nitrogen dynamics in an estuarine ecosystem in Babitonga Bay (Santa Catarina, Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.K.; Kao, S.J.; Wen, L.S.; Chen, K.L. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of particulate organic matter and biogeochemical processes in the eutrophic Danshuei Estuary in northern Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 382, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, W.M.; Bowler, B.C.; Drapeau, D.T.; Lubelczyk, L.C.; Lyczkowski, E. Vertical distributions of coccolithophores, PIC, POC, biogenic Silica, and chlorophyll a throughout the global ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2018, 32, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, B.P.; Kattner, G.; Witt, M.; Passow, U. Molecular insights into the microbial formation of marine dissolved organic matter: Recalcitrant or labile? Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 4173–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daesslé, L.W.; Orozco, A.; Struck, U.; Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; van Geldern, R.; Santamaría-del-Angel, E.; Barth, J.A.C. Sources and sinks of nutrients and organic carbon during the 2014 pulse flow of the Colorado River into Mexico. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I.; Keil, R.G.; Benner, R. What happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean? Org. Geochem. 1997, 27, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y. Priming effects: Interactions between living and dead organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lei, S.; Bi, S.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Mu, M.; Miao, S.; Zeng, S.; et al. Tracking spatio-temporal dynamics of POC sources in eutrophic lakes by remote sensing. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lao, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Bian, P.; Zhu, Q. Distribution and sources of particulate organic matter in the Northern South China Sea: Implications of human activity. J. Ocean Univ. China 2021, 20, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Meng, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Song, Z. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic composition of particulate organic matter in the Pearl River Estuary and the adjacent shelf. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 246, 107003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.N.; Epstein, S. Two categories of 13C/12C ratios for higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1971, 47, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyers, P.A. Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanographic, paleolimnologic, and paleoclimatic processes. Org. Geochem. 1997, 27, 213–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipale, S.J.; Vuorio, K.; Brett, M.T.; Peltomaa, E.; Hiltunen, M.; Kankaala, P. Lake zooplankton δ13C values are strongly correlated with the δ13C values of distinct phytoplankton taxa. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thornton, S.F.; McManus, J. Application of organic carbon and nitrogen stable isotope and C/N ratios as source indicators of organic matter provenance in estuarine systems: Evidence from the Tay Estuary, Scotland. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1994, 38, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Huang, C.; Meng, L.; Lu, L.; Wu, Y.; Fan, R.; Li, S.; Sui, Z.; Huang, T.; Huang, C.; et al. Eutrophication and lakes dynamic conditions control the endogenous and terrestrial POC observed by remote sensing: Modeling and application. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramski, D.; Reynolds, R.A.; Babin, M.; Kaczmarek, S.; Lewis, M.R.; Röttgers, R.; Sciandra, A.; Stramska, M.; Twardowski, M.S.; Franz, B.A.; et al. Relationships between the surface concentration of particulate organic carbon and optical properties in the eastern South Pacific and eastern Atlantic Oceans. Biogeosciences 2008, 5, 171–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cetinić, I.; Perry, M.J.; Briggs, N.T.; Kallin, E.; D’Asaro, E.A.; Lee, C.M. Particulate organic carbon and inherent optical properties during 2008 North Atlantic Bloom Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117, C06028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, E.; Guidi, L.; Richardson, M.J.; Stemmann, L.; Gardner, W.; Bishop, J.K.; Anderson, R.F.; Sherrell, R.M. Optical techniques for remote and in-situ characterization of particles pertinent to GEOTRACES. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 133, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.; He, M.; He, S.; He, S.; Pan, Y.; Yin, W.; Li, P. An improved cloud masking method for GOCI data over turbid coastal waters. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.B.; Gardner, W.D.; Mishonov, A.V.; Richardson, M.J. Multispectral remote-sensing algorithms for particulate organic carbon (POC): The Gulf of Mexico. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, W.; Cao, W.; Yin, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. Variation of particulate organic carbon and its relationship with bio-optical properties during a phytoplankton bloom in the Pearl River estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Pan, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Wang, D.; Wei, J.A.; Zhang, L. Remote sensing observation of particulate organic carbon in the Pearl River Estuary. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8683–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stramski, D.; Reynolds, R.A.; Kahru, M.; Mitchell, B.G. Estimation of particulate organic carbon in the ocean from satellite remote sensing. Science 1999, 285, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishonov, A.V.; Gardner, W.D.; Richardson, M.J. Remote sensing and surface POC concentration in the South Atlantic. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2003, 50, 2997–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Loiselle, S.A.; Yang, D.; Gao, C.; Ma, R.; Su, W.; Duan, H. An absorption-specific approach to examining dynamics of particulate organic carbon from VIIRS observations in inland and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, L.A.; Sharp, J.H.; Fogel, M.L. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope biogeochemistry in the Delaware estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, K.; Zeng, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, M.; Qiu, Y. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes as tracers of sources of suspended particulate organic matter in the Daya Bay in summer. Haiyang Xuebao 2017, 39, 39–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, F.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, F. Spatial distribution and correlation characteristics of heavy metals in the seawater, suspended particulate matter and sediments in Zhanjiang Bay, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Lao, Q.; Jia, G.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, X. Seasonal variations of nitrate dual isotopes in wet deposition in a tropical city in China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 196, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, R.; Lao, Q.; Chen, F.; Chen, C.; Zhou, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhu, Q. Assessing seasonal nitrate contamination by nitrate dual isotopes in a monsoon-controlled bay with intensive human activities in South China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.X.; Zhang, Y.C.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.Q. Spatiotemporal dissolved silicate variation, sources, and behavior in the eutrophic Zhanjiang Bay, China. Water 2020, 12, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 7442–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Fang, C.; Gao, D.; Zhang, H.; Gao, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. Optical models for remote sensing of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) absorption in Poyang Lake. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 142, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Liu, G.; Wen, Z.; Jacinthe, P.A.; Song, K.; Zhang, B.; Lyu, L.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, X. Remote estimates of CDOM using Sentinel-2 remote sensing data in reservoirs with different trophic states across China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, F.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X. Analysis of dissolved oxygen and nutrients in Zhanjiang Bay and the adjacent sea area in spring. Sustainability 2020, 12, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lao, Q.; Liu, G.; Shen, Y.; Su, Q.; Lei, X. Biogeochemical processes and eutrophication status of nutrients in the northern Beibu Gulf, South China. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 130, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jin, G.; Li, J.; Song, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Huang, C.; Chen, F.; Zhu, Q.; Meng, Y. Effects of typhoon Mujigae on the biogeochemistry and ecology of a semi-enclosed bay in the northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2020JG006031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Huang, C.; Chen, C.; Zhou, F.; Wu, J.; Jin, G.; Zhu, Q. Origin of the particulate organic matter in a monsoon-controlled bay in southern China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kang, Q.; Liu, Z. Carbon and nitrogen composition and stable isotope as potential indicators of source and fate of organic matter in the salt marsh of the Changjiang Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramska, M.; Stramski, D. Variability of particulate organic carbon concentration in the north polar Atlantic based on ocean color observations with Sea-viewing Wide Field-of-view Sensor (SeaWiFS). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2005, 110, C10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, F.; Guo, W.; Shi, Z.; Jia, G.; Wei, G. Seasonal dynamics of particulate organic matter and its response to flooding in the Pearl River Estuary, China, revealed by stable isotope (δ13C and δ15N) analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 6835–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Bauer, J.E. Use of 14C and 13C natural abundances for evaluating riverine, estuarine, and coastal DOC and POC sources and cycling: A review and synthesis. Org. Geochem. 2001, 32, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Tan, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, X. Spatial distributions of δ13C, δ15N and C/N ratios in suspended particulate organic matter of a bay under serious anthropogenic influences: Daya Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Tan, Y. The effects of anthropogenic nutrient inputs on stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes in suspended particulate organic matter in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 208, 104244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Cao, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Evaluation of chlorophyll-a retrieval algorithms based on MERIS bands for optically varying eutrophic inland lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Shi, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Developing a semi-analytical algorithm to estimate particulate organic carbon (POC) levels in inland eutrophic turbid water based on MERIS images: A case study of Lake Taihu. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 62, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of constituent retrieval in optically deep and complex waters from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yacobi, Y.Z.; Moses, W.J.; Kaganovsky, S.; Sulimani, B.; Leavitt, B.C.; Gitelson, A.A. NIR-red reflectance-based algorithms for chlorophyll-a estimation in mesotrophic inland and coastal waters: Lake Kinneret case study. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2428–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. A novel remote sensing algorithm to quantify phycocyanin in cyanobacterial algal blooms. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 114003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A. The peak near 700 nm on radiance spectra of algae and water: Relationships of its magnitude and position with chlorophyll concentration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



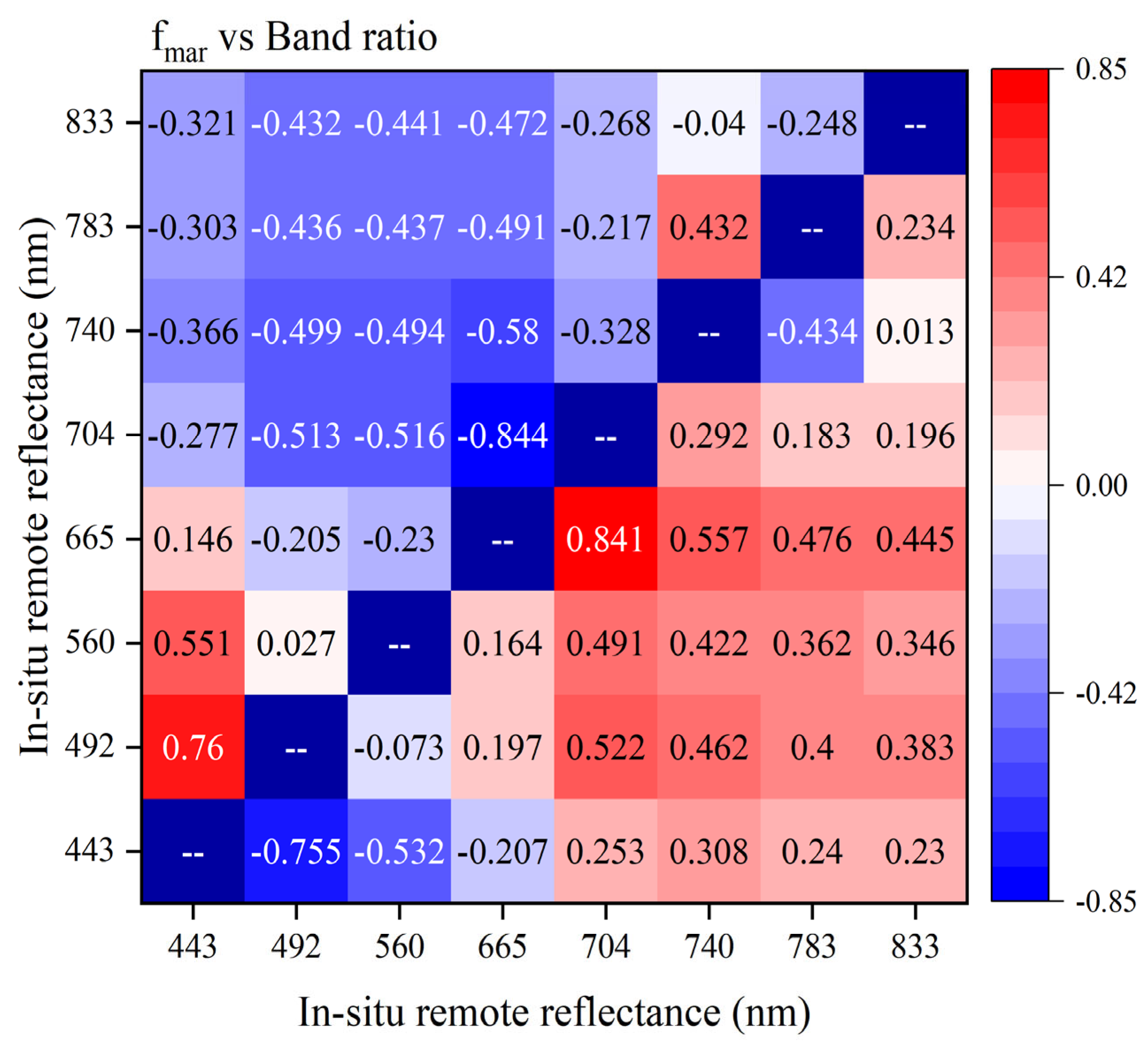





| Sl. No. | Variable | R |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rrs(443)/Rrs(492) + Rrs(492)/Rrs(443) | −0.698 ** |
| 2 | Rrs(443)/Rrs(492) − Rrs(492)/Rrs(443) | 0.759 ** |
| 3 | (Rrs(443)/Rrs(492))/(Rrs(492)/Rrs(443)) | 0.746 ** |
| 4 | Rrs(443)/Rrs(492) + Rrs(665)/Rrs(704) | −0.524 ** |
| 5 | Rrs(443)/Rrs(492) − Rrs(665)/Rrs(704) | 0.879 ** |
| 6 | (Rrs(443)/Rrs(492)) × (Rrs(665)/Rrs(704)) | −0.279 |
| 7 | (Rrs(443)/Rrs(492))/(Rrs(665)/Rrs(704)) | 0.884 ** |
| 8 | Rrs(443)/Rrs(492) + Rrs(704)/Rrs(665) | 0.882 ** |
| 9 | Rrs(443)/Rrs(492) − Rrs(704)/Rrs(665) | −0.244 |
| 10 | Rrs(492)/Rrs(443) + Rrs(665)/Rrs(704) | −0.876 ** |
| 11 | Rrs(492)/Rrs(443) − Rrs(665)/Rrs(704) | 0.341 * |
| 12 | (Rrs(492)/Rrs(443)) × (Rrs(665)/Rrs(704)) | −0.865 ** |
| 13 | (Rrs(492)/Rrs(443))/(Rrs(665)/Rrs(704)) | 0.307 |
| 14 | Rrs(492)/Rrs(443) + Rrs(704)/Rrs(665) | −0.012 |
| 15 | Rrs(492)/Rrs(443) − Rrs(704)/Rrs(665) | −0.876 ** |
| 16 | Rrs(665)/Rrs(704) + Rrs(704)/Rrs(665) | −0.788 ** |
| 17 | Rrs(665)/Rrs(704) − Rrs(704)/Rrs(665) | −0.844 ** |
| 18 | (Rrs(665)/Rrs(704))/(Rrs(704)/Rrs(665)) | −0.833 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, G.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, S.; Lao, Q.; Chen, C.; Fu, D.; Chen, F. Remote Sensing Estimates of Particulate Organic Carbon Sources in the Zhanjiang Bay Using Sentinel-2 Data and Carbon Isotopes. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153768
Yu G, Zhong Y, Liu S, Lao Q, Chen C, Fu D, Chen F. Remote Sensing Estimates of Particulate Organic Carbon Sources in the Zhanjiang Bay Using Sentinel-2 Data and Carbon Isotopes. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(15):3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153768
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Guo, Yafeng Zhong, Sihai Liu, Qibin Lao, Chunqing Chen, Dongyang Fu, and Fajin Chen. 2023. "Remote Sensing Estimates of Particulate Organic Carbon Sources in the Zhanjiang Bay Using Sentinel-2 Data and Carbon Isotopes" Remote Sensing 15, no. 15: 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153768
APA StyleYu, G., Zhong, Y., Liu, S., Lao, Q., Chen, C., Fu, D., & Chen, F. (2023). Remote Sensing Estimates of Particulate Organic Carbon Sources in the Zhanjiang Bay Using Sentinel-2 Data and Carbon Isotopes. Remote Sensing, 15(15), 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15153768





