Research on High Precision Positioning Method for Pedestrians in Indoor Complex Environments Based on UWB/IMU
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Analyze the difference of different NLOS effects on UWB ranging, classify NLOS into fixed spatial structure NLOS and human occlusion NLOS that changes with pedestrian movement for the first time.
- (2)
- Using the indoor spatial structure relationship, combined with the deployment location of base stations, the LOS/NLOS information mapping of anchors is quickly and conveniently established to accurately distinguish LOS/NLOS anchors and further optimize the range value of NLOS using the recursive position of IMU.
- (3)
- A UWB error correction model for human body occlusion is established to compensate for the error of NLOS for the dynamic human body occlusion.
- (4)
- A novel high-precision pedestrian positioning method is developed to handle UWB NLOS errors, and the system performance is verified.
2. Current Work
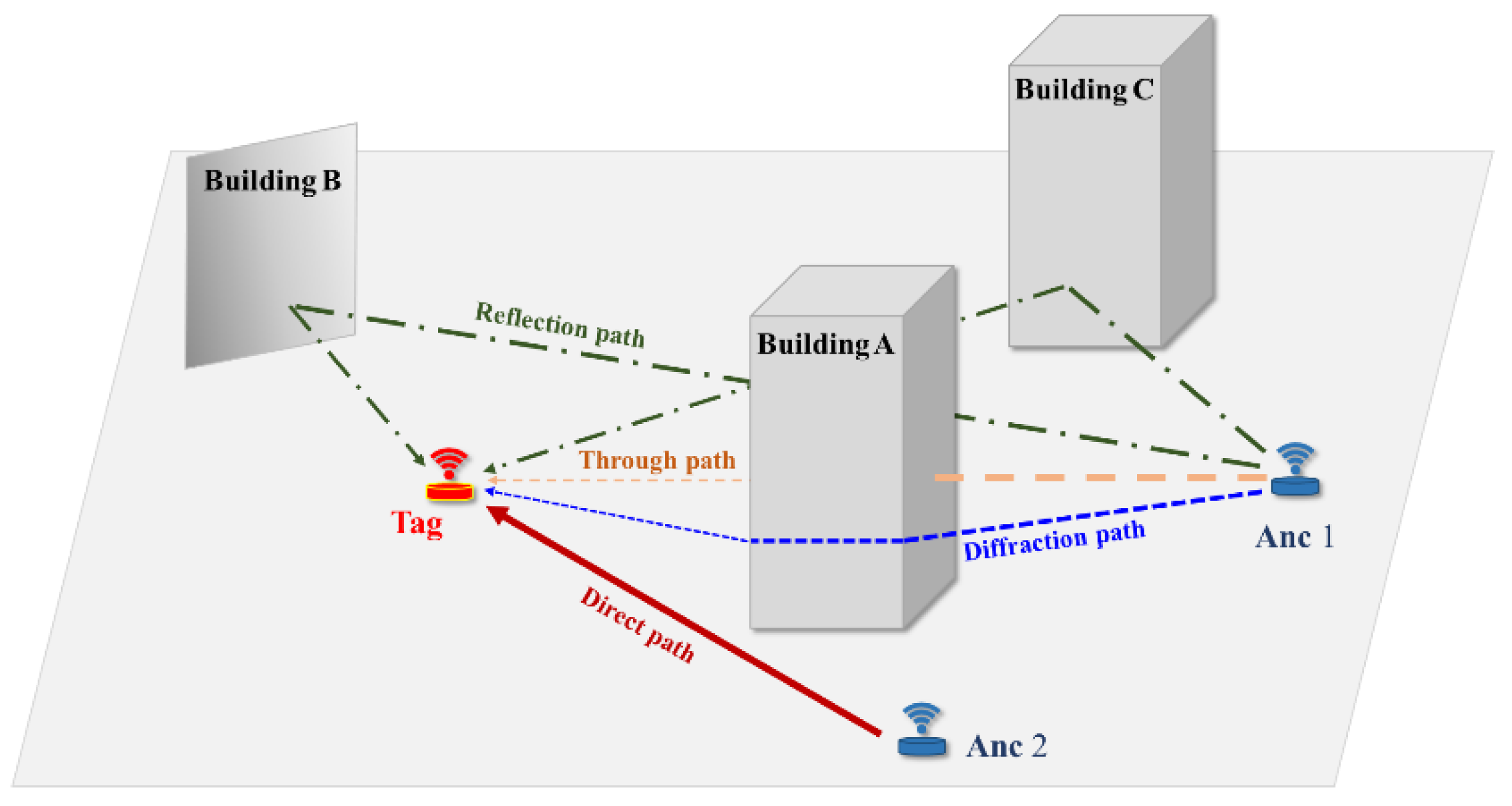
3. Spatial Structure NLOS Discrimination and Ranging Optimization Method
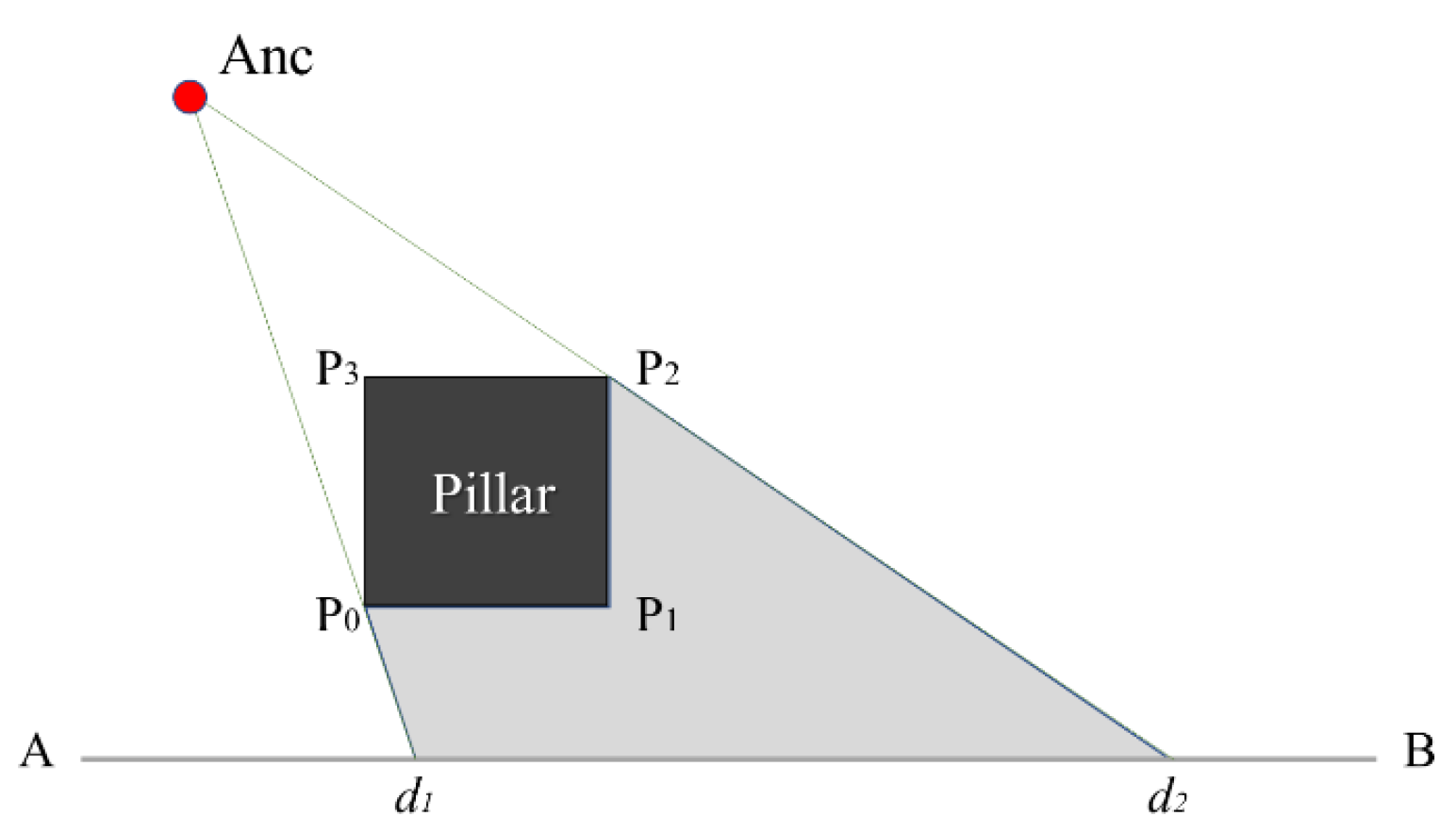
3.1. UWB LOS/NLOS Anchor Mapping Method
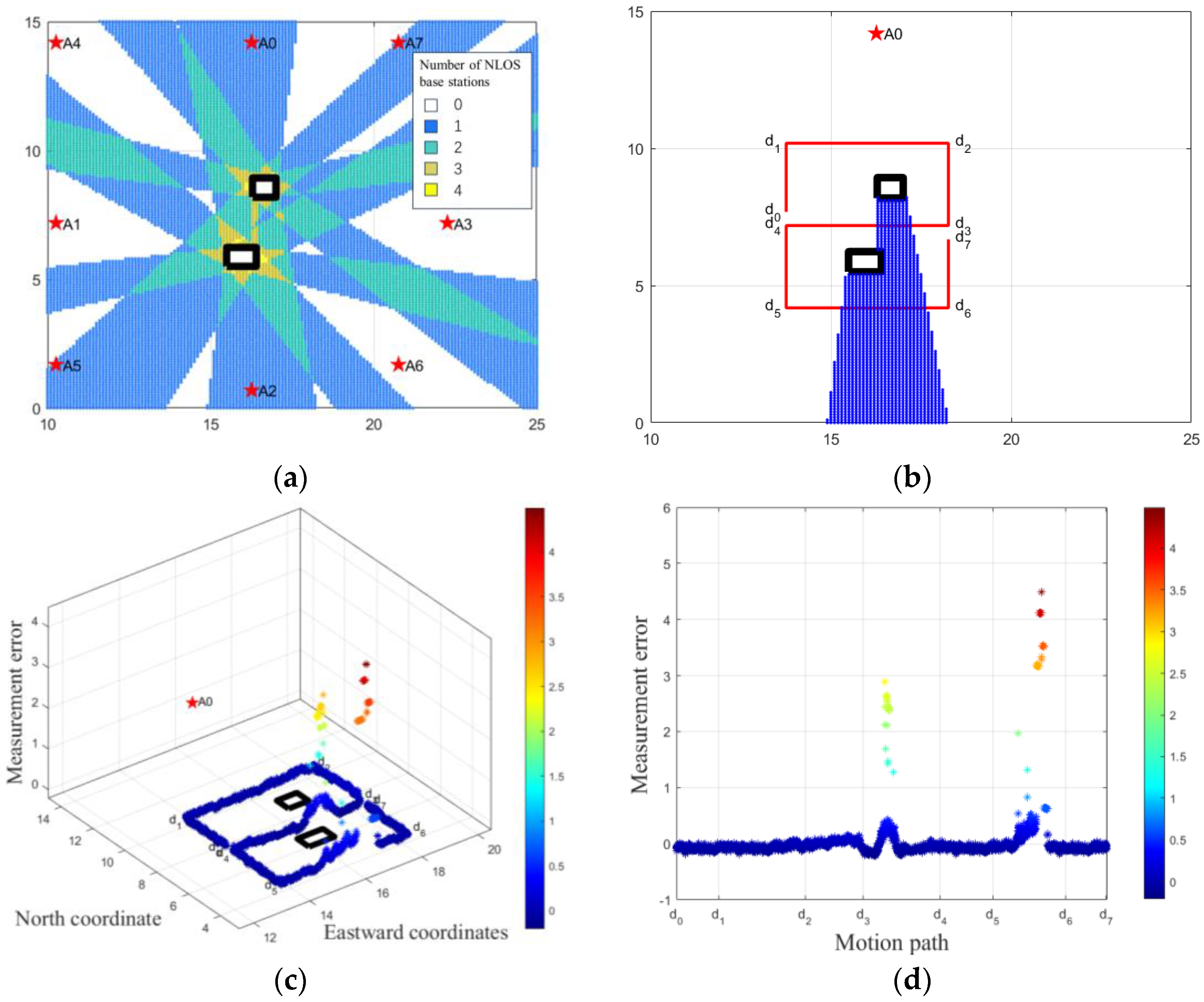
3.2. Algorithms LOS/NLOS Discrimination Effect Validation
3.3. Relationship between Positioning Solution and Ranging Error
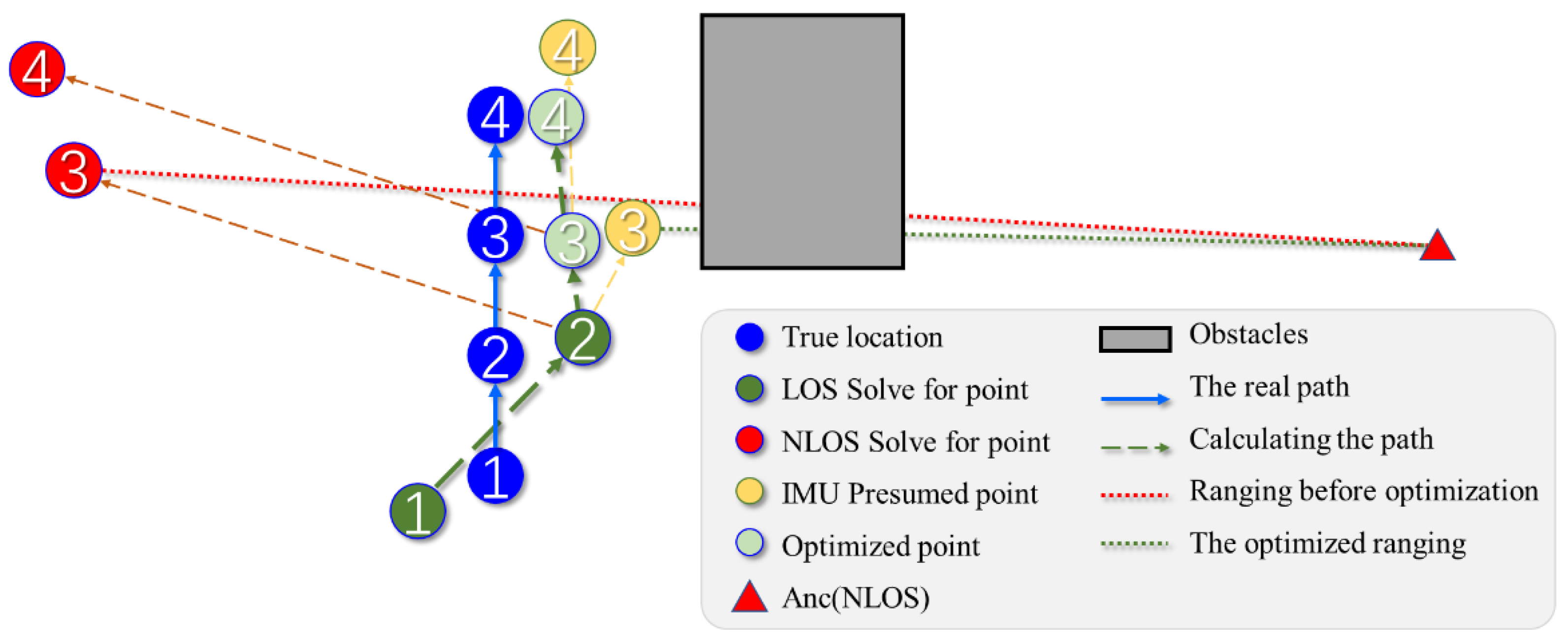
3.4. Spatial NLOS Error Optimization Method
4. Human Error Compensation Model
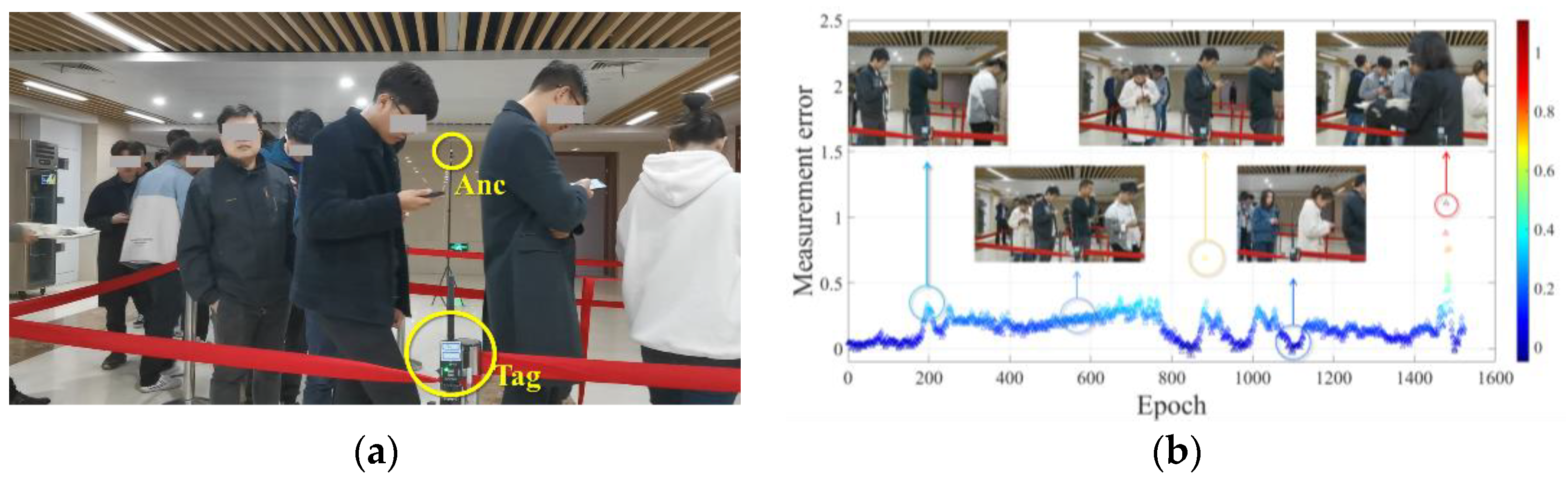
4.1. Analysis of Human Blocking Phenomenon
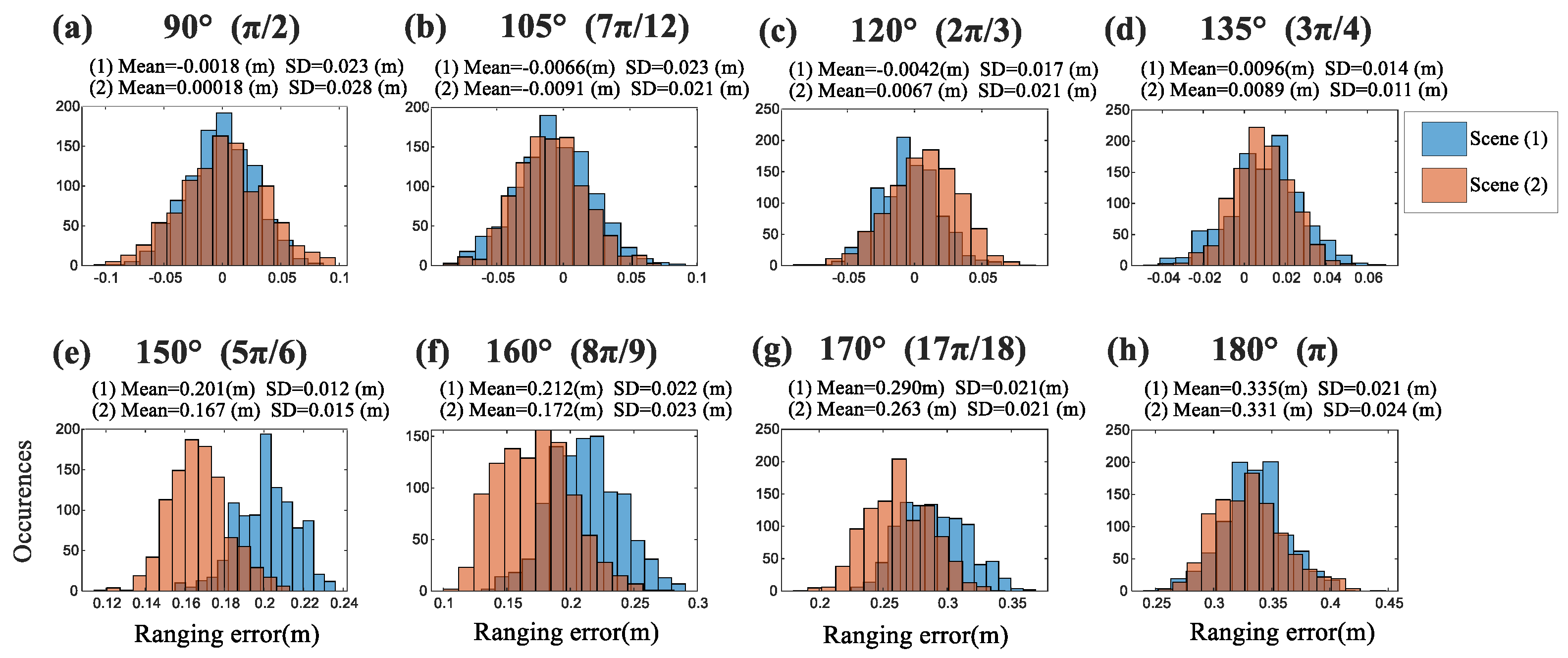
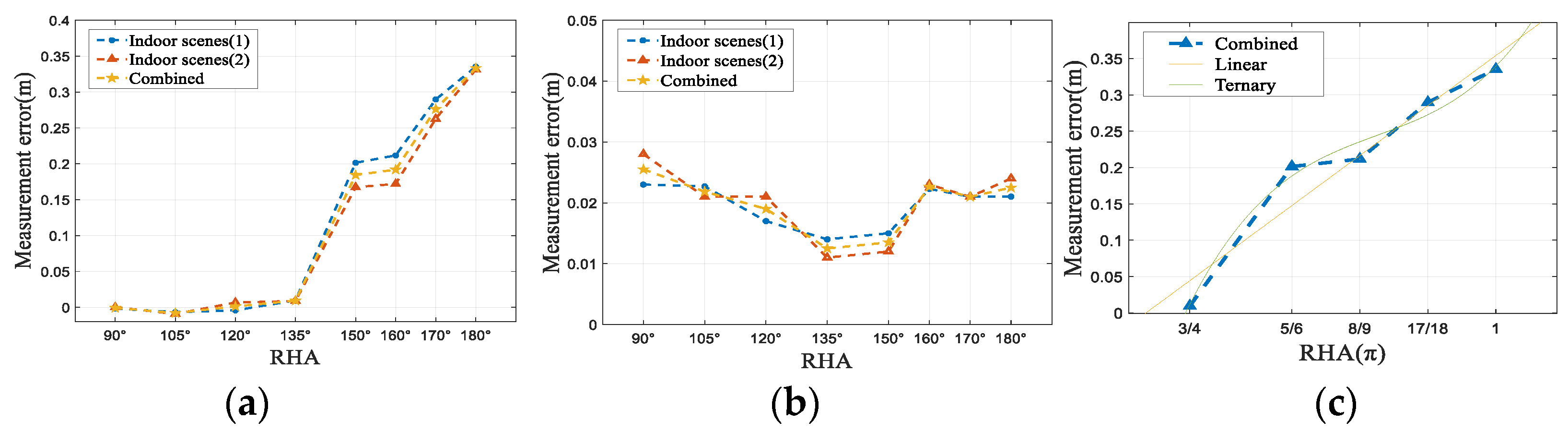
4.2. Vector Art Human Occlusion Error Modeling
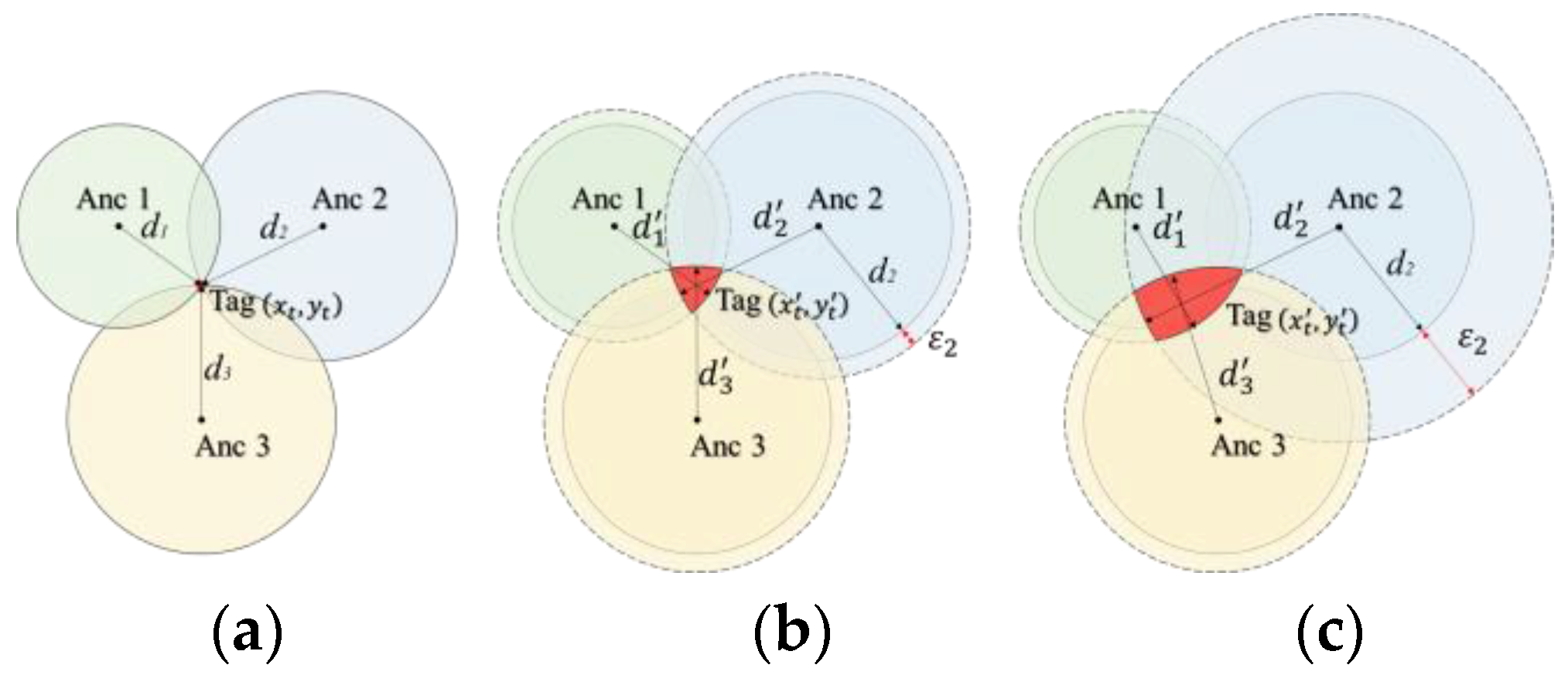
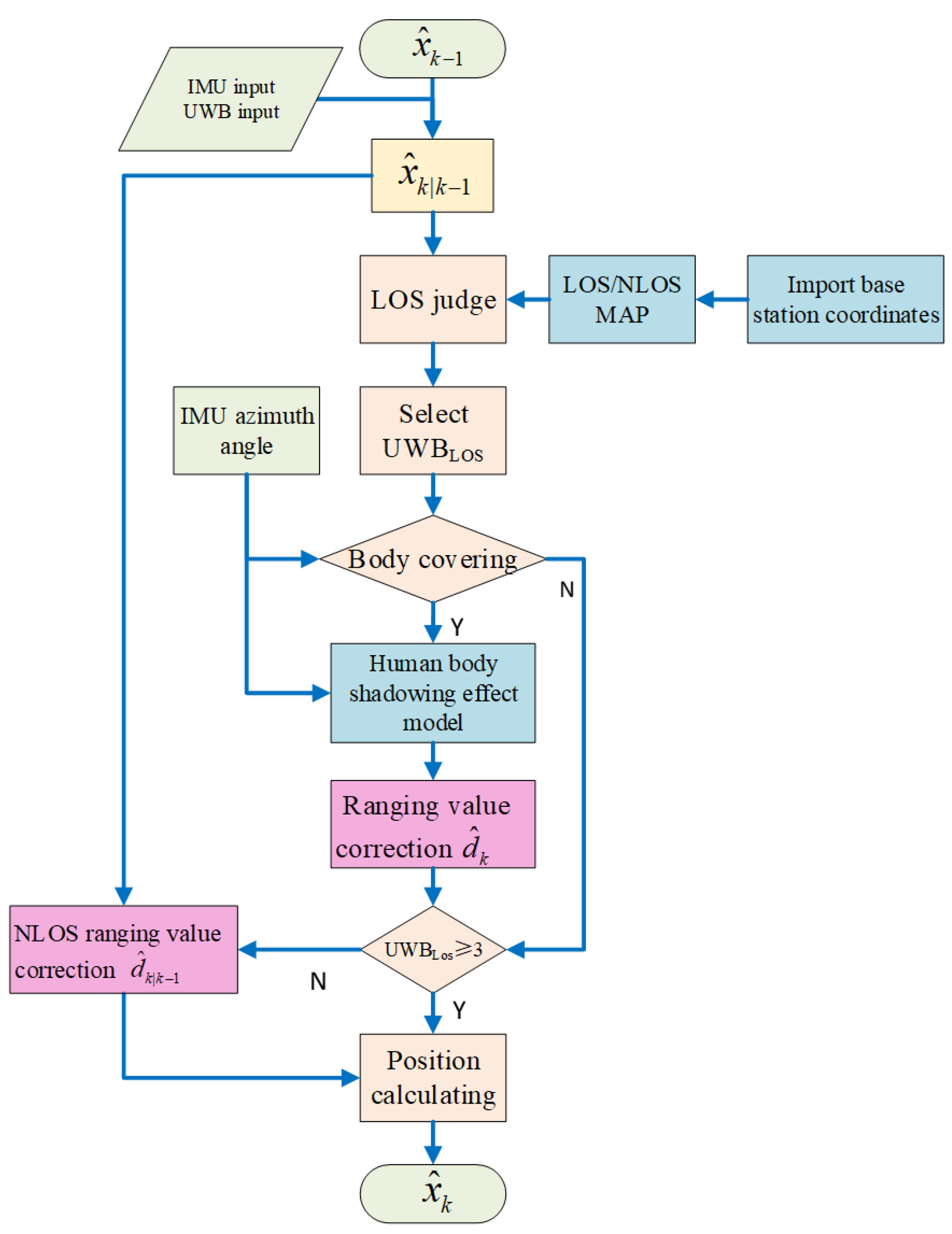
5. Positioning Algorithm
6. Experimental Verification and Analysis
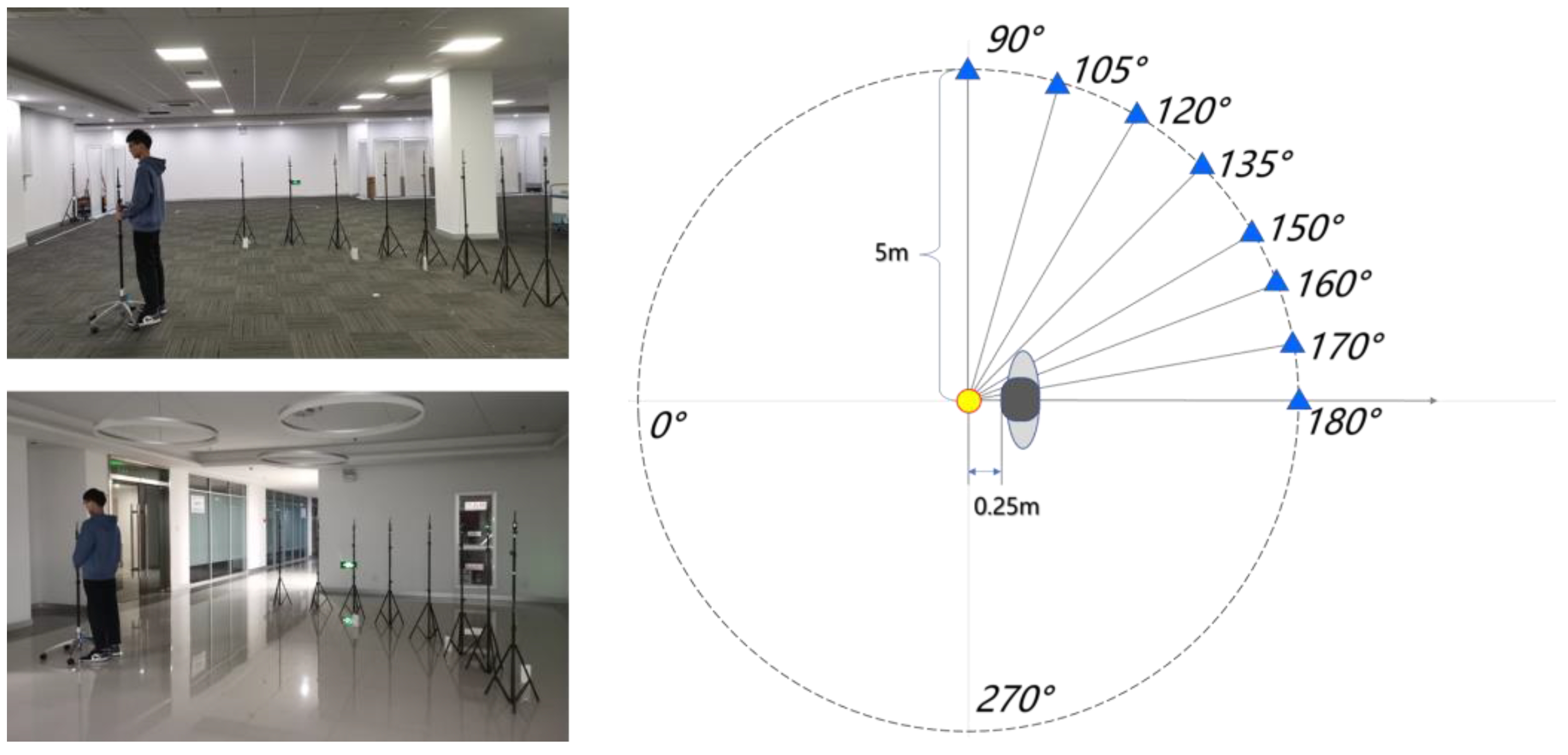
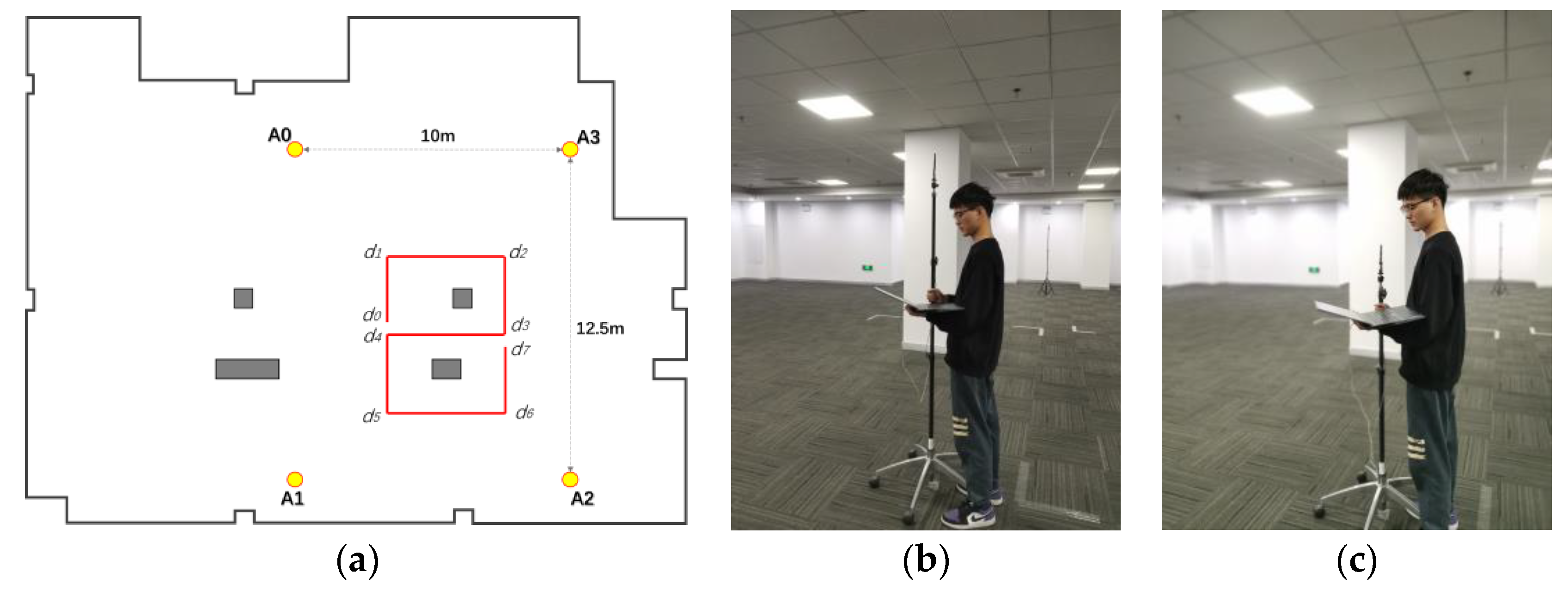
6.1. Experimental Scheme
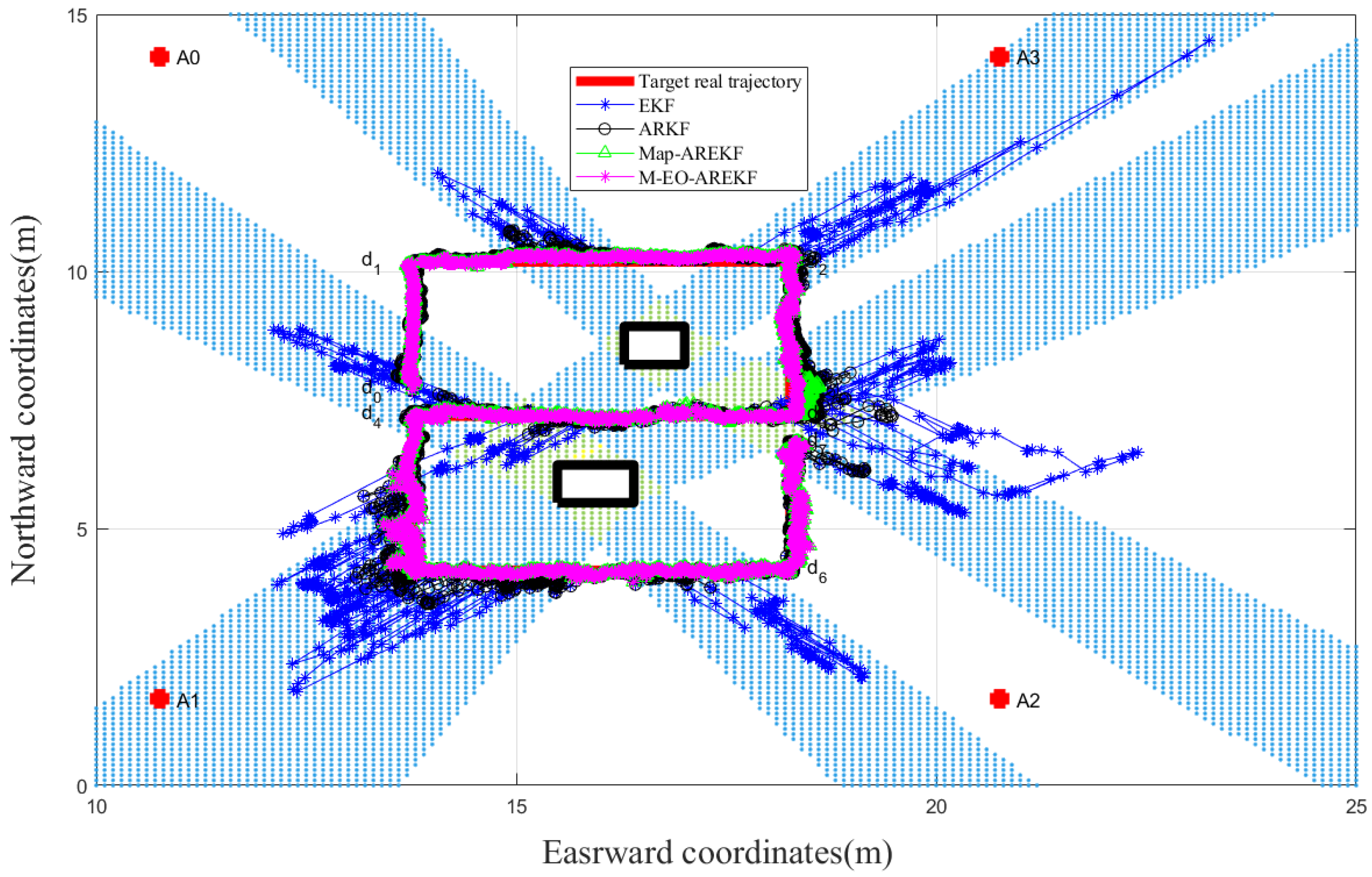
6.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
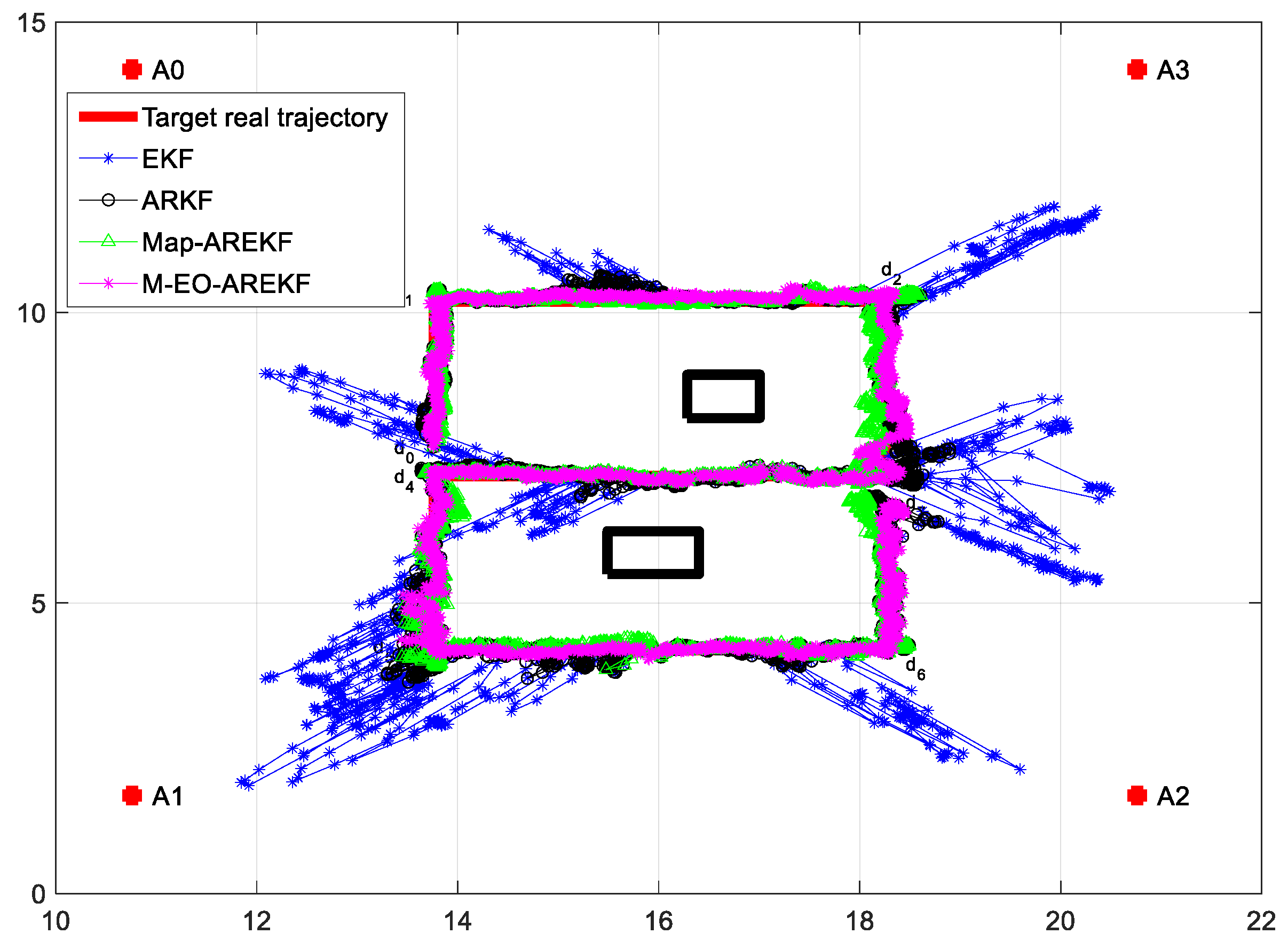
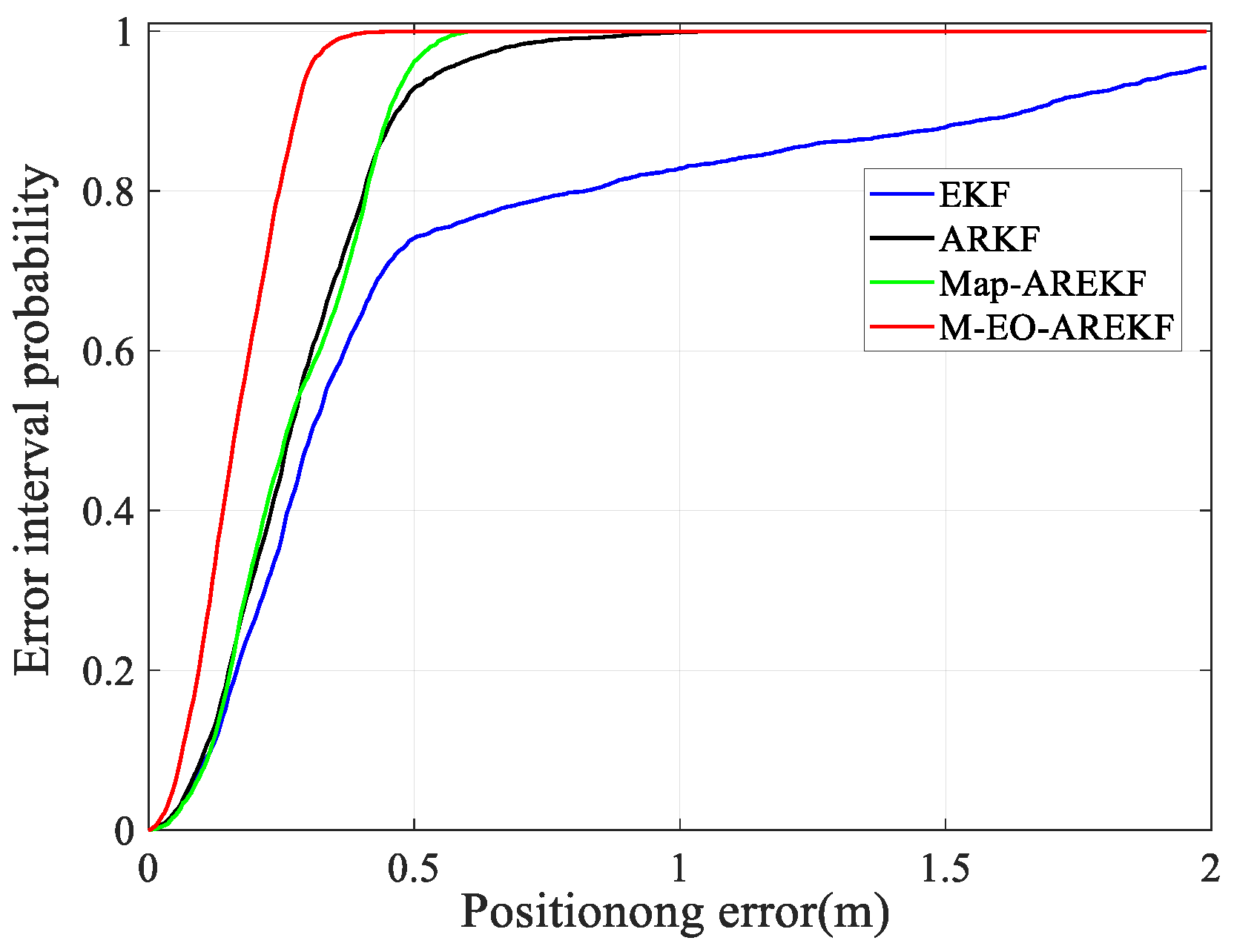
- The indoor spatial structure has a significant impact on the range, and if the NLOS error is not eliminated, serious positional deviations will occur when the ranging values with serious errors are brought into the algorithm for solving. The EKF algorithm directly uses the ranging values of the four UWB anchors for positioning without optimizing the NLOS ranging values. Due to the impact of NLOS, the positioning results have significant bias. This is also the reason why the EKF algorithm performs the worst in complex indoor scenarios.
- The ARKF algorithm can correct the short-term fluctuation of ranging errors to a certain extent and performs well in handling NLOS caused by random pedestrian occlusion. However, when facing large-scale NLOS caused by the indoor spatial structure and self-occlusion errors caused by the human body, the correction effect of the ARKF algorithm is moderate.
- Algorithms based on anchor LOS/NLOS map information can quickly and accurately identify the LOS/NLOS status of each anchor based on the indoor spatial structure. This method is a prerequisite for correcting the ranging values of NLOS anchors.
- The Map–AREKF algorithm uses a spatial NLOS error optimization method to effectively solve the NLOS error caused by indoor spatial structures. However, it cannot effectively correct ranging errors caused by pedestrian self-occlusion.
- In addition to the advantages of the Map–AREKF algorithm, the M–EO–AREKF algorithm proposed in this paper utilizes a human occlusion error correction model to effectively optimize the error caused by pedestrian self-occlusion. Experimental results demonstrate that this algorithm can achieve effective, reliable, and continuous high-precision pedestrian localization.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, X.; Ansari, N.; Hu, F.; Shao, Y.; Elikplim, N.R.; Li, L. A survey on fusion-based indoor positioning. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 22, 566–594. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, G. Intelligent positioning for a commercial mobile platform in seamless indoor/outdoor scenes based on multi-sensor fusion. Sensors 2019, 19, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wang, C.; He, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Xia, X.-G. Kalman-filter-based integration of IMU and UWB for high-accuracy indoor positioning and navigation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 3133–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein. Global Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN) Market Outlook, 2024. 2019. Available online: https://www.goldsteinresearch.com/report/global-indoor-positioning-and-indoor-navigation-ipin-market-outlook-2024-global-opportunity-and-demand-analysis-market-forecast-2016-2024 (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Chen, R.; Chen, L. Smartphone-based indoor positioning technologies. In Urban Informatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 467–490. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. An approach to improve the positioning performance of GPS/INS/UWB integrated system with two-step filter. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, H. An indoor localization method for pedestrians base on combined UWB/PDR/Floor map. Sensors 2019, 19, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. Orb-slam2: An open-source slam system for monocular, stereo, and rgb-d cameras. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Kevin, I.; Wang, K.; Salcic, Z. A low-cost INS and UWB fusion pedestrian tracking system. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 3733–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.R.J.; Granja, F.S. Comparing ubisense, bespoon, and decawave uwb location systems: Indoor performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 2106–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Huang, S.-P.; Wu, T.-W.; Tsai, W.-T.; Liou, C.-Y.; Mao, S.-G. UWB system for indoor positioning and tracking with arbitrary target orientation, optimal anchor location, and adaptive NLOS mitigation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 9304–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaja-Josko, V.; Kolakowski, M. A new map based method for NLOS mitigation in the UWB indoor localization system. In Proceedings of the 2017 25th Telecommunication Forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 21–22 November 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.G.; Fernandes, D.; Catarino, A.P.; Monteiro, J.L. Performance analysis of ToA-based positioning algorithms for static and dynamic targets with low ranging measurements. Sensors 2017, 17, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, E.; Poudereux, P.; Hernández, Á.; Ureña, J.; Gualda, D. Arobust uwb indoor positioning system for highly complex environments. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Seville, Spain, 17–19 March 2015; pp. 3386–3391. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. NLOS mitigation for UWB localization based on sparse pseudo-input Gaussian process. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 4311–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, S.; Kulon, J.; Partlow, A.; Rogers, P.; Gibson, C. A Robust Algorithm for Classification and Rejection of NLOS Signals in Narrowband Ultrasonic Localization Systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 68, 646–655. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, J.B.; Ginard, M.M.; Jensen, O.K.; Shen, M. Non-Line-of-Sight Identification for UWB Indoor Positioning Systems using Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium (IWS), Guangzhou, China, 19–22 May 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Alsindi, N.A.; Alavi, B.; Pahlavan, K. Measurement and Modeling of Ultrawideband TOA-Based Ranging in Indoor Multipath Environments. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 58, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Nam, S.; Choi, H.; Ko, Y.; Ko, Y.-B. Improving deep learning-based UWB LOS/NLOS identification with transfer learning: An empirical approach. Electronics 2020, 9, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Wang, S.; Ge, S.; Ma, X.; Liu, W. A Novel Mobile Target Localization Approach for Complicate Underground Environment in Mixed LOS/NLOS Scenarios. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 96347–96362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Khoshelham, K. A Robust and Adaptive Complementary Kalman Filter Based on Mahalanobis Distance for Ultra-Wideband/Inertial Measurement Unit Fusion Positioning. Sensors 2018, 18, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghani, S.K.; Asif, M.; Awin, F.; Tepe, K. Empirical based ranging error mitigation in IR-UWB: A fuzzy approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 33686–33697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Sun, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhuang, X. Performance Enhancement of MEMS-Based INS/UWB Integration for Indoor Navigation Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3116–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. An Adaptive UWB/MEMS-IMU Complementary Kalman Filter for Indoor Location in NLOS Environment. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, B. Ranging in the IEEE 802.15. 4a standard using energy detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE EUROCON 2009, St. Petersburg, Russia, 18–23 May 2009; pp. 1956–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Lan, H.; Liu, Z.; El-Sheimy, N.; Yu, F. Indoor map aiding/map matching smartphone navigation using auxiliary particle filter. In China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2016 Proceedings: Volume I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 321–331. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Yi, J.; Cheng, J.; He, L. Adapted error map based mobile robot UWB indoor positioning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 6336–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, A.; Kuang, J.; Sui, X.; Hao, Y.; Niu, X. A high-accuracy indoor localization system and applications based on tightly coupled UWB/INS/Floor map integration. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 18166–18177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, P.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Hu, J. Indoor Positioning System with UWB Based on a Digital Twin. Sensors 2022, 22, 5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kili, Y.; Ali, A.J.; Meijerink, A.; Bentum, M.J.; Scanlon, W.G. The effect of human-body shadowing on indoor UWB TOA-based ranging systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 9th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communication, Dresden, Germany, 15–16 March 2012; pp. 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.; Wan, Y.; He, J.; Pahlavan, K. An Empirical Channel Model for the Effect of Human Body on Ray Tracing. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 24th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), London, UK, 8–11 September 2013; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.; He, J.; Deng, H.; Pahlavan, K. Modeling the effect of human body on TOA ranging for indoor human tracking with wrist mounted sensor. In Proceedings of the 2013 16th International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC), Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 24–27 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Otim, T.; Bahillo, A.; Díez, L.E.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Falcone, F. FDTD and Empirical Exploration of Human Body and UWB Radiation Interaction on TOF Ranging. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otim, T.; Bahillo, A.; Díez, L.E.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Falcone, F. Impact of Body Wearable Sensor Positions on UWB Ranging. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 11449–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otim, T.; Bahillo, A.; Díez, L.E.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Falcone, F. Towards Sub-Meter Level UWB Indoor Localization Using Body Wearable Sensors. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 178886–178899. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Song, D.; Feng, B.; Ye, H. A Novel NLOS Error Compensation Method Based IMU for UWB Indoor Positioning System. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 11203–11212. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Kevin, I.; Wang, K.; Salcic, Z. Human body shadowing effect on UWB-based ranging system for pedestrian tracking. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 68, 4028–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Yan, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, B. Research on UWB Indoor Positioning Algorithm under the Influence of Human Occlusion and Spatial NLOS. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, D.; Li, B. An Emergency Seamless Positioning Technique Based on ad hoc UWB Networking Using Robust EKF. Sensors 2019, 19, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



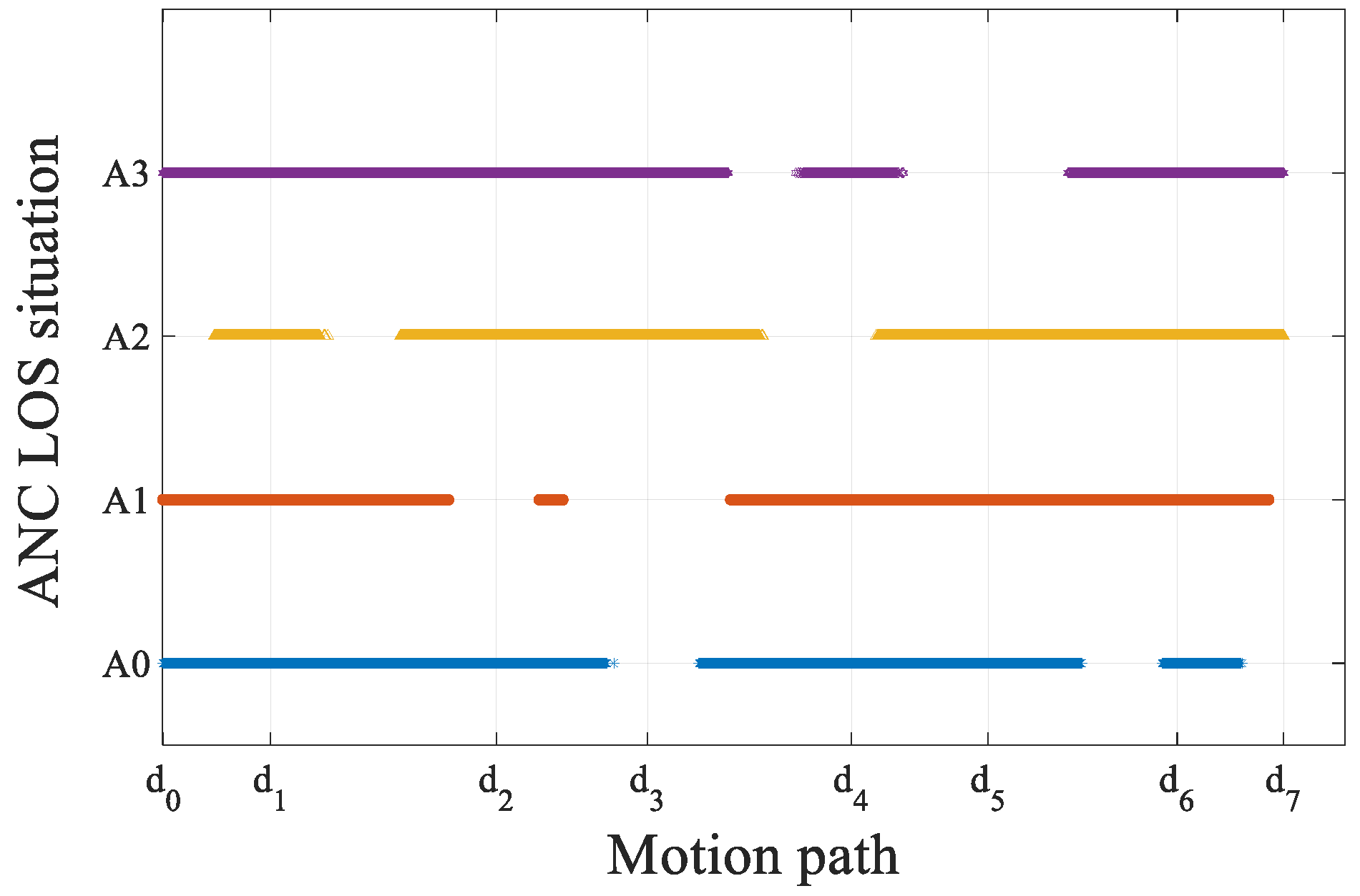
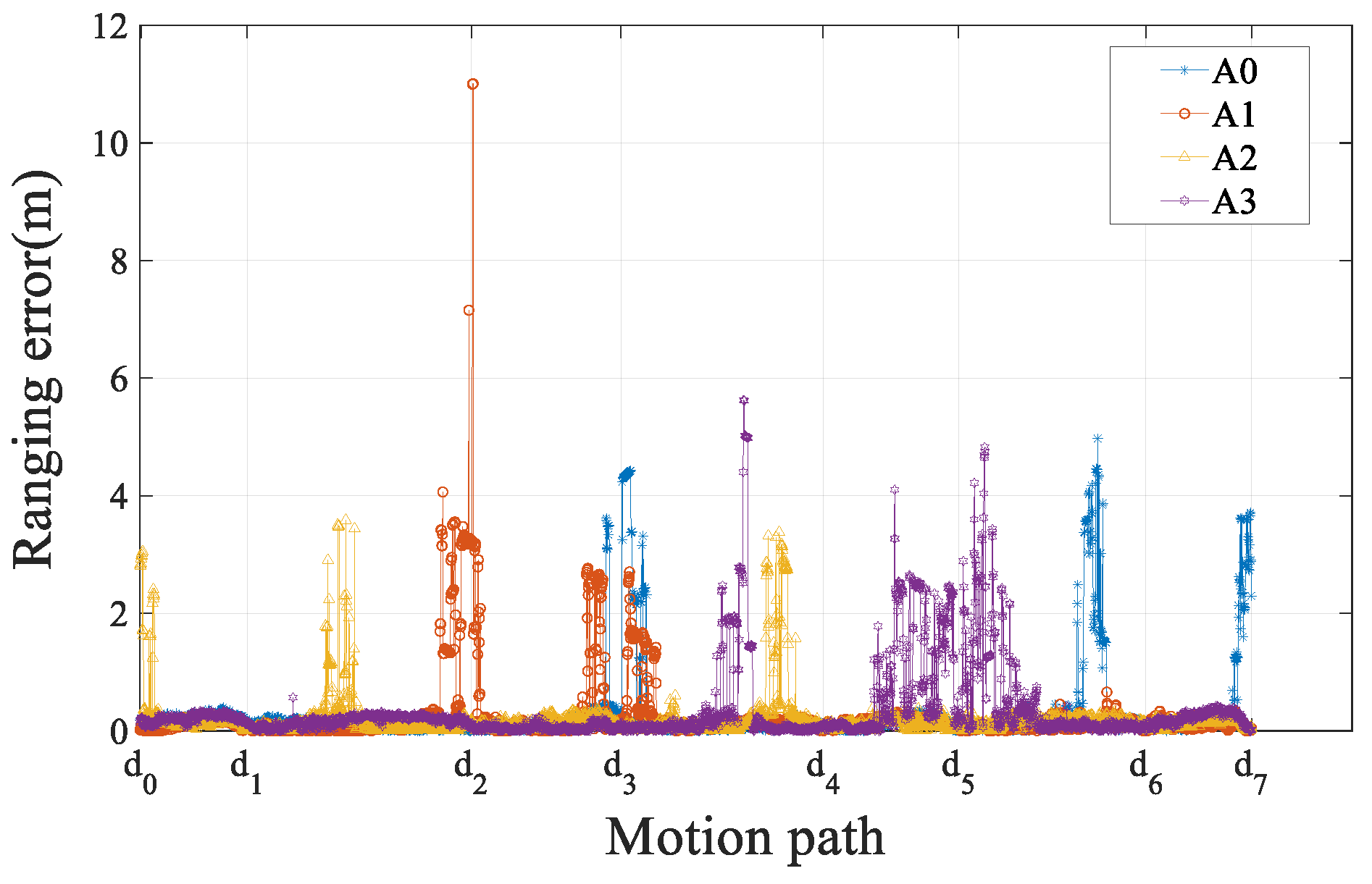

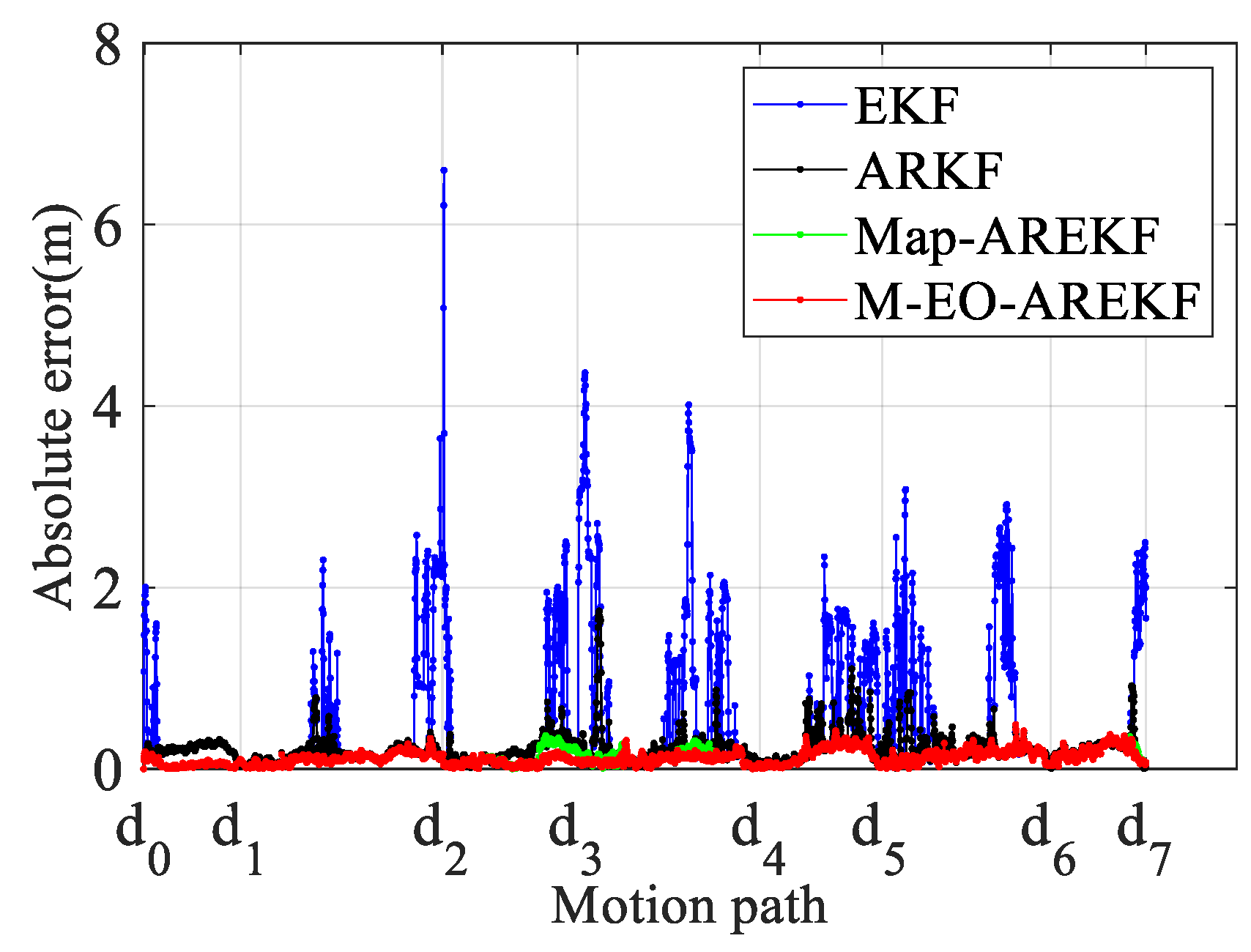


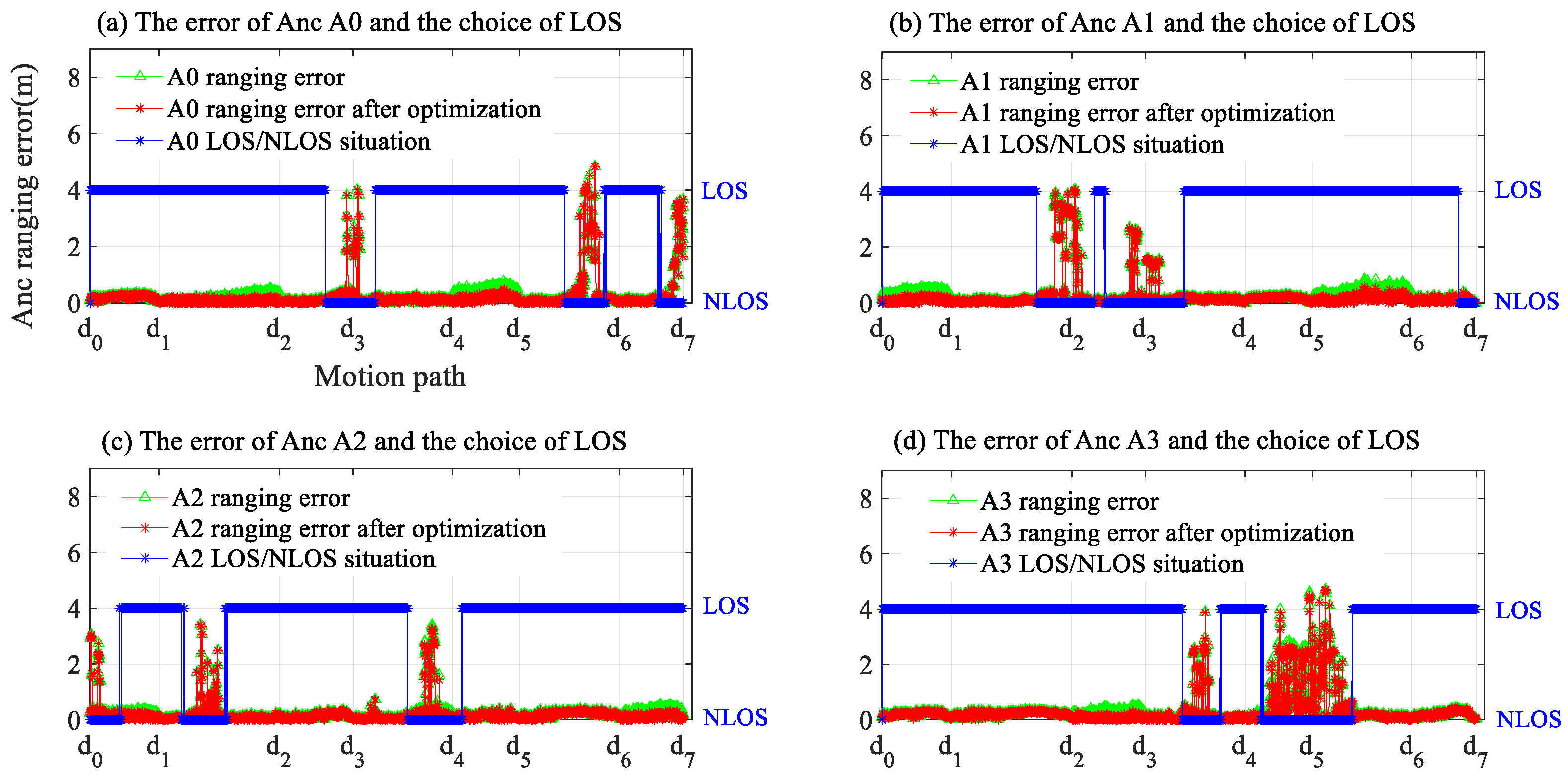


| Experimental Scenario | Number of Epochs Collected | Collection Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3407 | 68.14 |
| 2 | 3668 | 73.36 |
| Scene | EKF (m) | ARKF (m) | MAP–AREKF (m) | M–EO–AREKF (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.88 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.14 |
| 2 | 0.82 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.19 |
| Scenario | EKF | ARKF | Map–AREKF | M–EO–AREKF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.95 × 10−5 | 6.09 × 10−5 | 1.74 × 10−4 | 2.37 × 10−4 |
| 2 | 8.54 × 10−5 | 5.95 × 10−5 | 1.45 × 10−4 | 2.59 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Mi, J.; Zhang, K. Research on High Precision Positioning Method for Pedestrians in Indoor Complex Environments Based on UWB/IMU. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143555
Zhang H, Wang Q, Li Z, Mi J, Zhang K. Research on High Precision Positioning Method for Pedestrians in Indoor Complex Environments Based on UWB/IMU. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(14):3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143555
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hao, Qing Wang, Zehui Li, Jing Mi, and Kai Zhang. 2023. "Research on High Precision Positioning Method for Pedestrians in Indoor Complex Environments Based on UWB/IMU" Remote Sensing 15, no. 14: 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143555
APA StyleZhang, H., Wang, Q., Li, Z., Mi, J., & Zhang, K. (2023). Research on High Precision Positioning Method for Pedestrians in Indoor Complex Environments Based on UWB/IMU. Remote Sensing, 15(14), 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143555







