Influence of the Coriolis Force on Spreading of River Plumes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
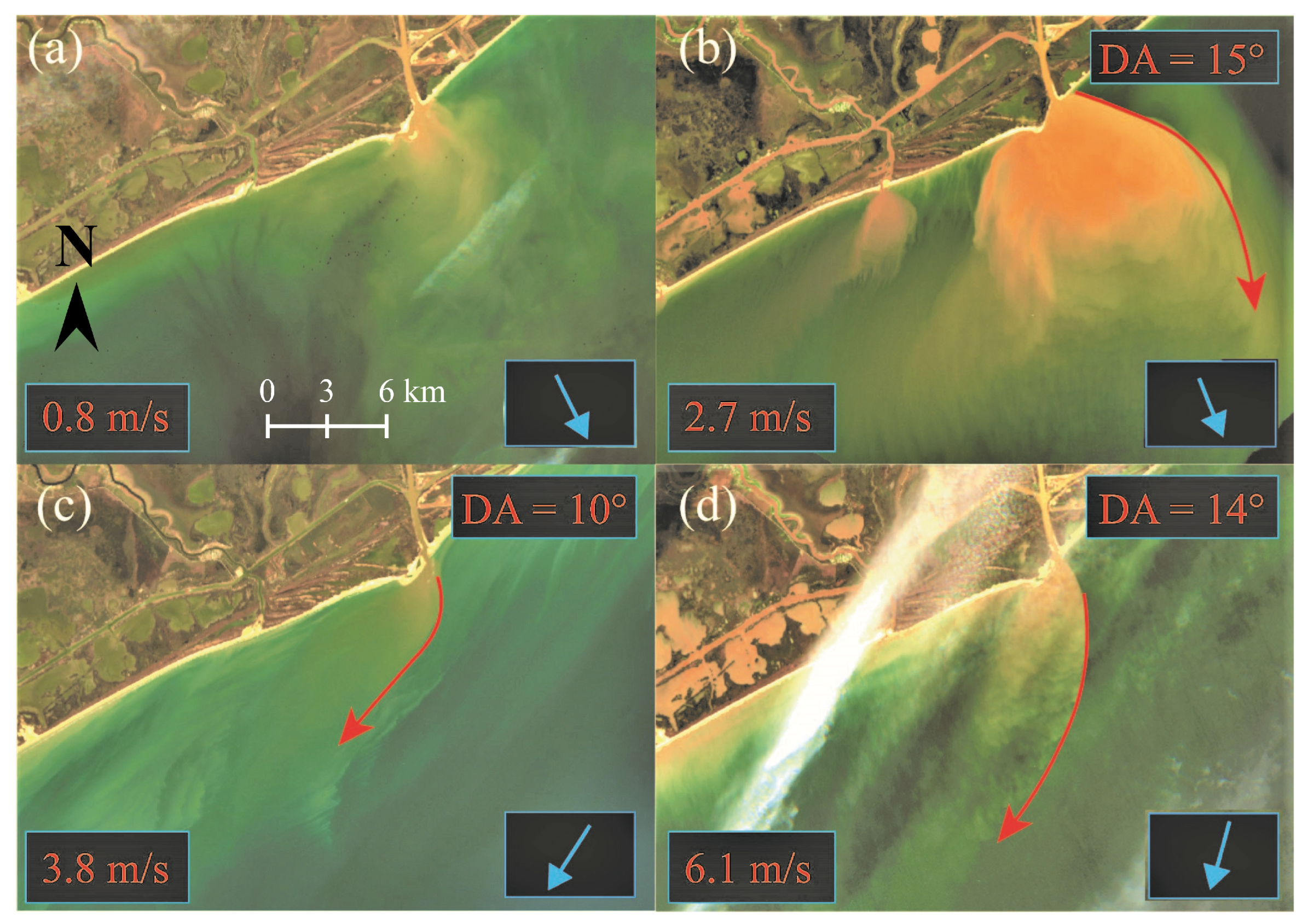
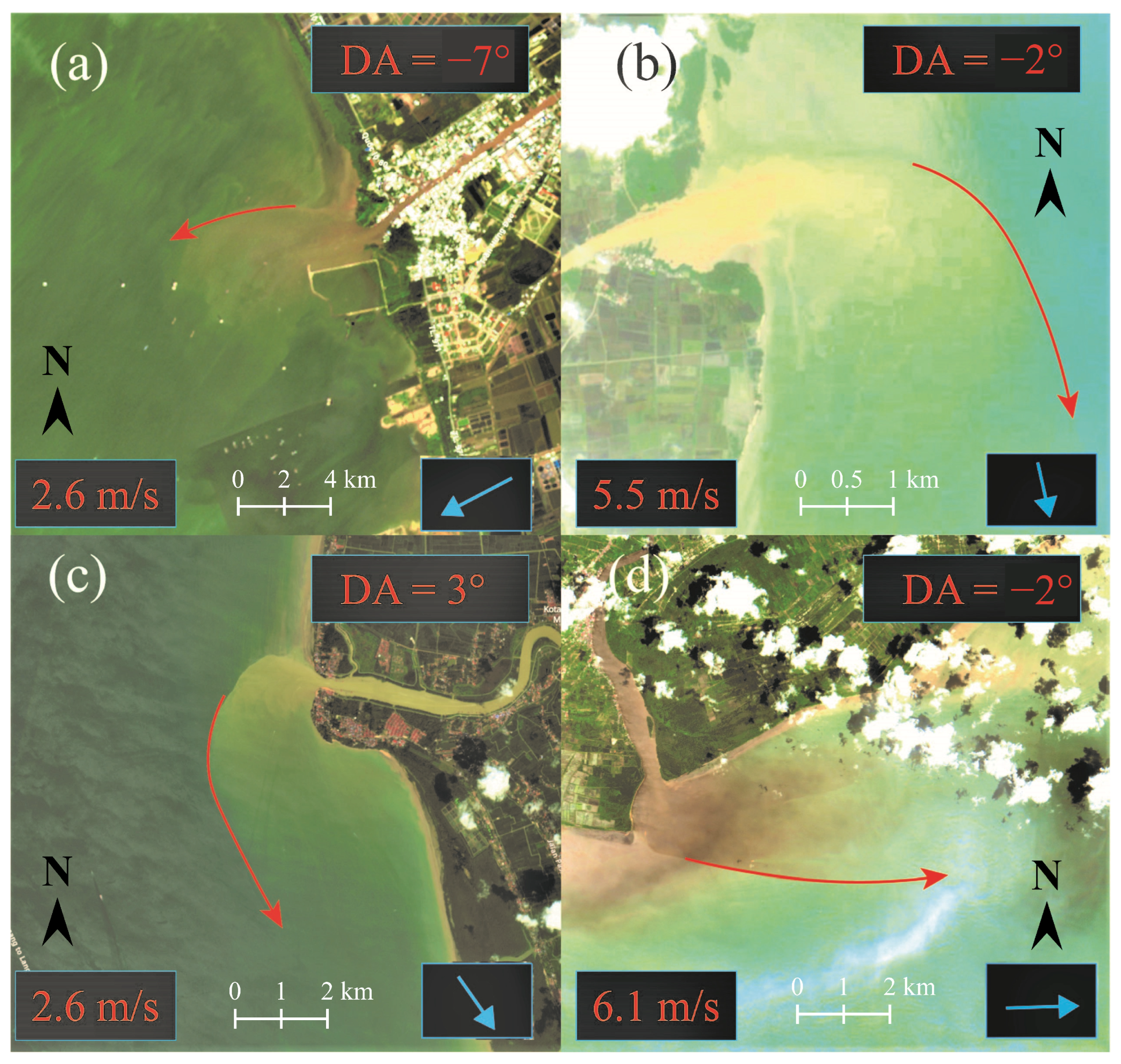
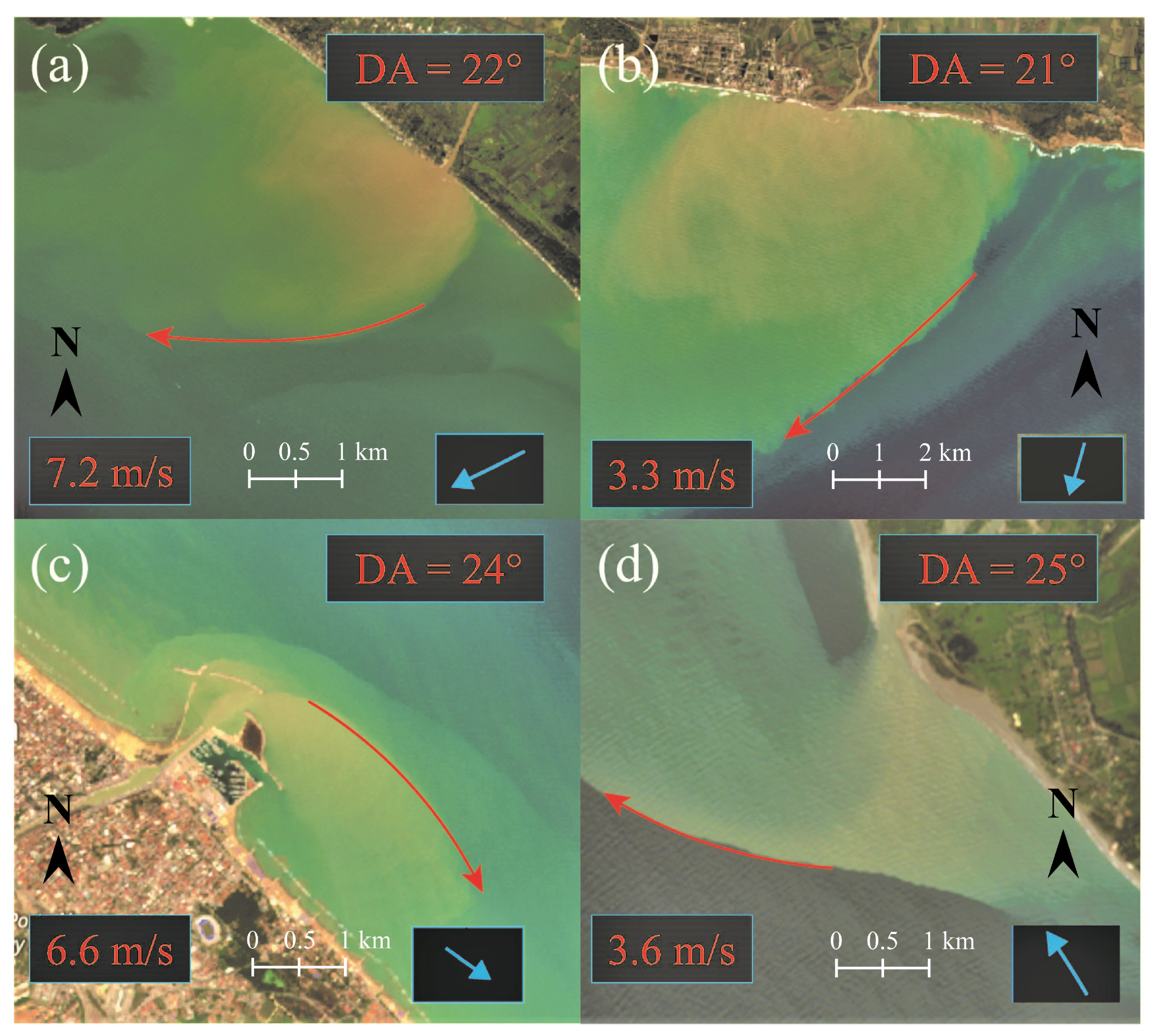
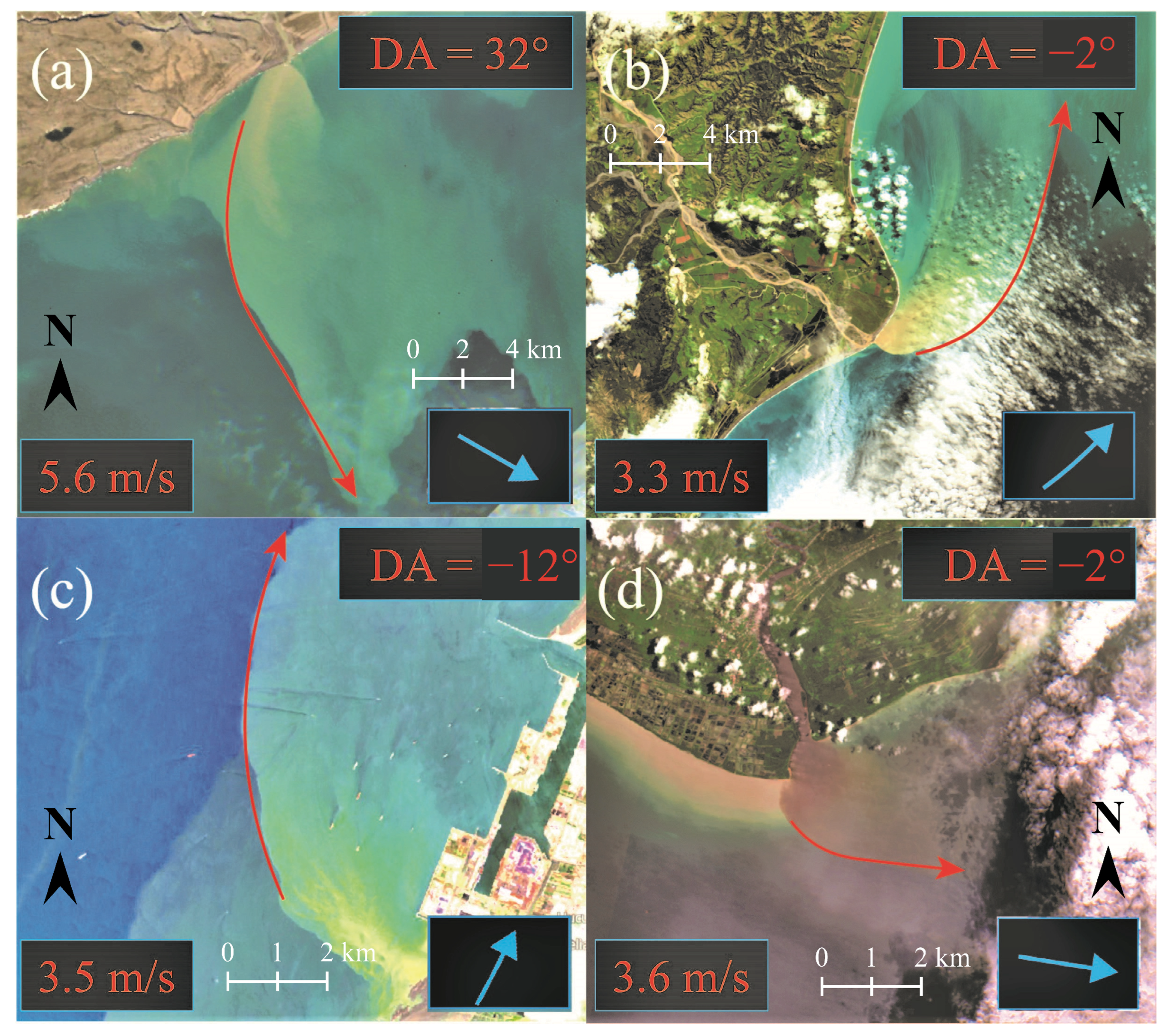
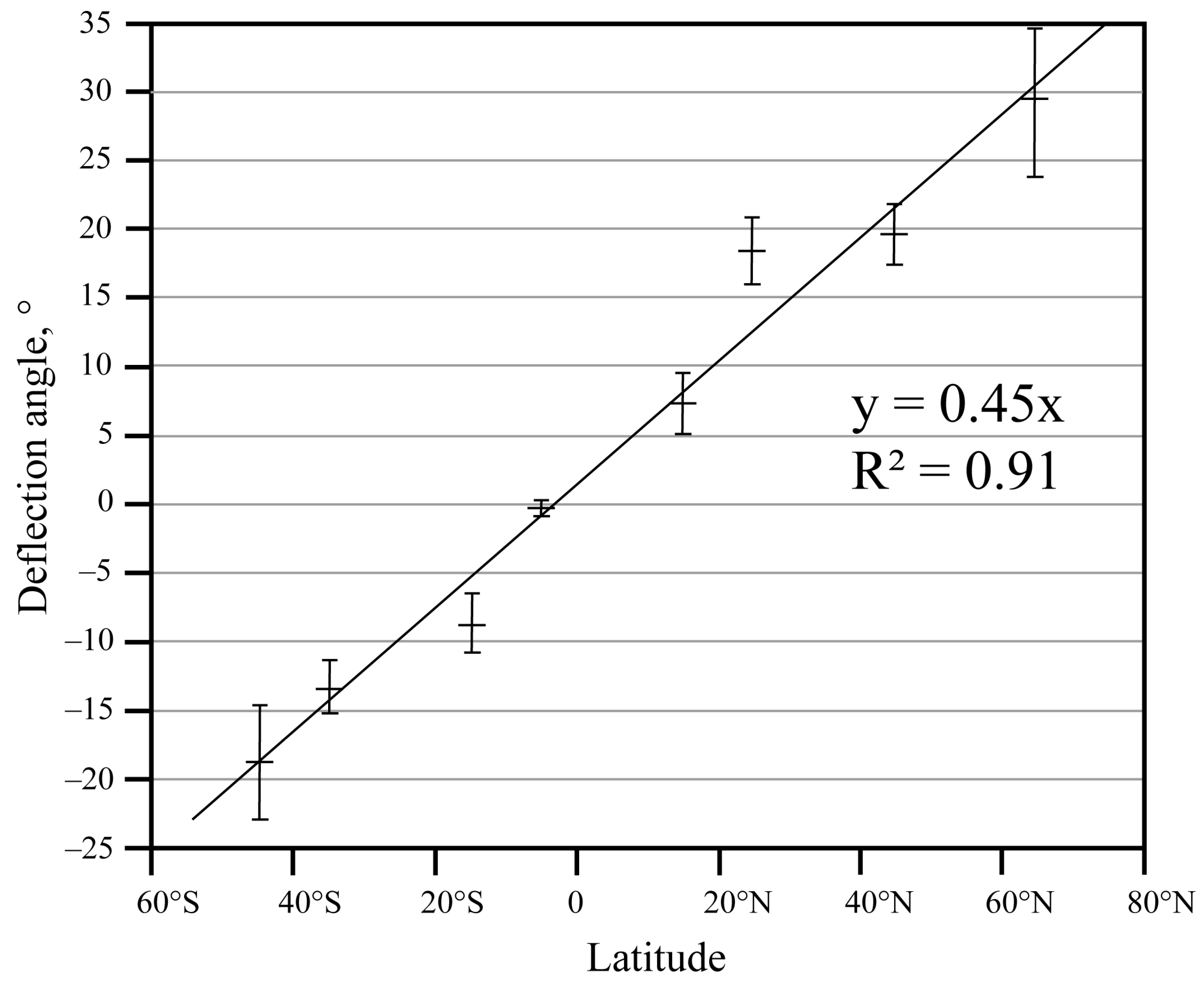
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simpson, J.H.; Sharples, J.; Rippeth, T.P. A prescriptive model of stratification induced by freshwater runoff. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1991, 33, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Pan, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.T.A.; Wang, D. Areas of the global major river plumes. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2013, 32, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kester, D.R.; Ni, I.H.; Qi, Y.; Kawamura, H. In situ and satellite observations of a harmful algal bloom and water condition at the Pearl River estuary in late autumn 1998. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, E.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Galloway, J.N.; Dentener, F.J.; Green, P.A.; Vörösmarty, C.J. Riverine nitrogen export from the continents to the coasts. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, GB1S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Farnsworth, K.L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean: A Global Synthesis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; 393p. [Google Scholar]
- Osadchiev, A.A. Spreading of the Amur river plume in the Amur Liman, the Sakhalin Gulf, and the Strait of Tartary. Oceanology 2017, 57, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetland, R.D. Relating river plume structure to vertical mixing. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 35, 1667–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner-Devine, A.R.; Hetland, R.D.; MacDonald, D.G. Mixing and transport in coastal river plumes. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 47, 569–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, P.; Cole, K.L.; Huguenard, K.; MacDonald, D.G.; Whitney, M.M. The effect of bottom-generated tidal mixing on tidally pulsed river plumes. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2021, 51, 2223–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.; Gordey, A.; Barymova, A.; Sedakov, R.; Rogozhin, V.; Zhiba, R.; Dbar, R. Lateral border of a small river plume: Salinity structure, instabilities and mass transport. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, T.; Wang, D.; Gan, J.; Guan, W. On the role of wind and tide in generating variability of Pearl River plume during summer in a coupled wide estuary and shelf system. J. Mar. Sys. 2014, 136, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Ruiz-Villarreal, M.; Peliz, A. Variability of river plumes off Northwest Iberia in response to wind events. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 72, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.A.; Barymova, A.A.; Sedakov, R.O.; Zhiba, R.Y.; Dbar, R.Y. Spatial structure, short-temporal variability, and dynamical features of small river plumes as observed by aerial drones: Case study of the Kodor and Bzyp river plumes. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.A.; Sedakov, R.O.; Barymova, A.A. Response of a small river plume on wind forcing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basdurak, N.B.; Largier, J.L. Wind effects on small-scale river and creek plumes. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2022, 127, e2021JC018381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J. The formation and fate of a river plume: A numerical model. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1990, 20, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, V.W. On the influence of the earth’s rotation on ocean currents. Ark. Mat. Astron. Fys. 1905, 2, 1874–1954. [Google Scholar]
- Yankovsky, A.E.; Chapman, D.C. A simple theory for the fate of buoyant coastal discharges. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1997, 27, 1386–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.A.; Zavialov, P.O. Structure and dynamics of plumes generated by small rivers. In Estuaries and Coastal Zones—Dynamics and Response to Environmental Changes; Pan, J., Devlin, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhurbas, N.V. The wind-induced drift velocity of the freshwater layer on the sea’s surface. Oceanology 2013, 53, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.; Sedakov, R. Spreading dynamics of small river plumes off the northeastern coast of the Black Sea observed by Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, O.S. A realistic model of the wind-induced Ekman boundary layer. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1977, 7, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, A.D., Jr.; McNally, G.; Pazan, S.; Wert, R. Analysis of surface current response to wind. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1979, 9, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Geomorphic/tectonic control of sediment discharge to the ocean: The importance of small mountainous rivers. J. Geol. 1992, 100, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatcroft, R.A.; Goni, M.A.; Hatten, J.A.; Pasternack, G.B.; Warrick, J.A. The role of effective discharge in the ocean delivery of particulate organic carbon by small, mountainous river systems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotkina, O.A.; Zavialov, P.O.; Osadchiev, A.A. Submesoscale variability of the current and wind fields in the coastal region of Sochi. Oceanology 2011, 51, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotkina, O.A.; Zavialov, P.O.; Osadchiev, A.A. Synoptic variability of currents in the coastal waters of Sochi. Oceanology 2014, 54, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavialov, I.B.; Osadchiev, A.A.; Sedakov, R.O.; Barnier, B.; Molines, J.-M.; Belokopytov, V.N. Water exchange between the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea through the Kerch Strait. Ocean Sci. 2020, 16, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiema, O.; Devenon, J.-L.; Baklouti, M. Numerical modeling of the Amazon River plume. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 873–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.D.; Kilcher, L.F.; Moum, J.N. Structure and composition of a strongly stratified, tidally pulsed river plume. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2009, 114, C00B12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.A.; Medvedev, I.P.; Shchuka, S.A.; Kulikov, M.E.; Spivak, E.A.; Pisareva, M.A.; Semiletov, I.P. Influence of estuarine tidal mixing on structure and spatial scales of large river plumes. Ocean Sci. 2020, 16, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.Y. The oil spill from a shipwreck in Kerch Strait: Radar monitoring and numerical modelling. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4853–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemirovskaya, I.A.; Zavialov, P.O.; Khramtsova, A.V. Hydrocarbon pollution in the waters and sediments of the Kerch Strait. Mar. Pol. Bull. 2022, 180, 113760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotenko, K.A.; Mamedov, R.M.; Kontar, A.E.; Korotenko, L.A. Particle tracking method in the approach for prediction of oil slick transport in the sea: Modelling oil pollution resulting from river input. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 48, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotenko, K.A. Effects of mesoscale eddies on behavior of an oil spill resulting from an accidental deepwater blowout in the Black Sea: An assessment of the environmental impacts. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshenko, E.A.; Zhurbas, V.M.; Osadchiev, A.A.; Belyakova, P.A. Fate of river-borne floating litter during the flooding event in the northeastern part of the Black Sea in October 2018. Mar. Pol. Bull. 2020, 160, 111678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogojeva, M.; Zhdanov, I.; Berezina, A.; Lapenkov, A.; Kosmach, D.; Osadchiev, A.; Hanke, G.; Semiletov, I.; Yakushev, E. Distribution of floating marine macro-litter in relation to oceanographic characteristics in the Russian Arctic Seas. Mar. Pol. Bull. 2021, 166, 112201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Kester, D.R.; Wang, Z.; Lian, J.; Kawamura, H. AVHRR satellite remote sensing and shipboard measurements of the thermal plume from the Daya Bay, nuclear power station, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Colmenares, A.; Barrios-Pina, H.; Ramirez-Leon, H. Numerical modeling of water thermal plumes emitted by thermal power plants. Water 2016, 8, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
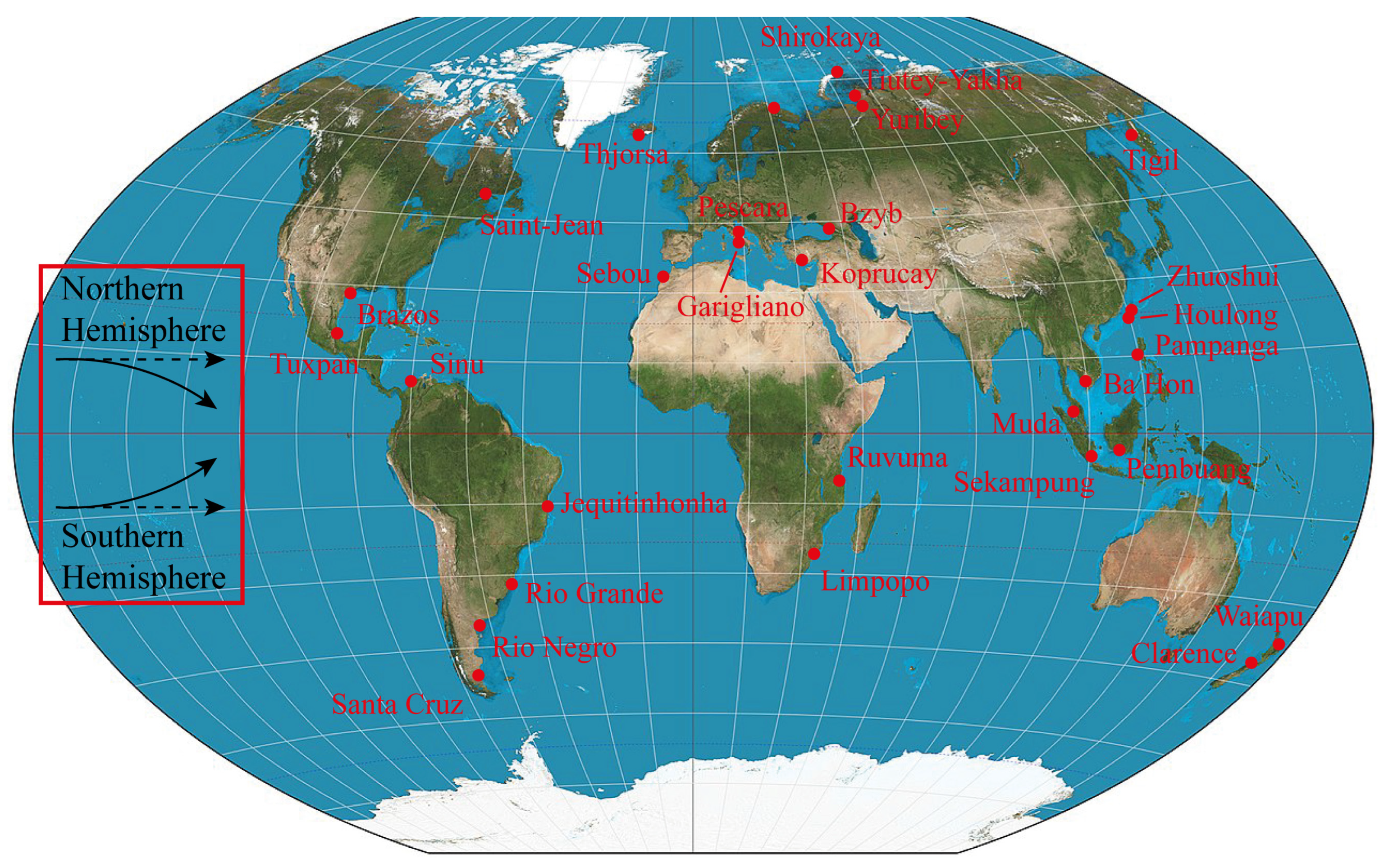

| River (Region) | Location of River Mouth | Watershed Basin Area, km2 | Average Discharge Rate, m3/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shirokaya (Novaya Zemlya) | 76.085°N, 67.181°E | - * | - * |
| Tiutey-Yakha (Yamal) | 71.421°N, 67.580°E | 3200 | 50 |
| Yuribey (Yamal) | 68.891°N, 68.852°E | 9700 | 80 |
| Thjorsa (Iceland) | 63.773°N, 20.797°W | 7500 | 390 |
| Tigil (Kamchatka) | 58.024°N, 158.2017°E | 17,800 | 200 |
| Saint-Jean (Labrador) | 50.279°N, 64.334°W | 5600 | 130 |
| Bzyb (Abkhazia) | 43.186°N, 40.281°E | 1500 | 100 |
| Pescara (Italy) | 42.469°N, 14.231°E | 3200 | 60 |
| Garigliano (Italy) | 41.222°N, 13.762°E | 5000 | 120 |
| Koprucay (Turkey) | 36.828°N, 31.170°E | 2400 | 100 |
| Sebou (Morocco) | 34.266°N, 6.687°W | 14,600 | 140 |
| Brazos (Texas) | 28.876°N, 95.378°W | 116,000 | 240 |
| Houlong (Taiwan) | 24.625°N, 120.742°E | 540 | 50 |
| Zhuoshui (Taiwan) | 23.841°N, 120.239°E | 3200 | 170 |
| Tuxpan (Mexico) | 20.972°N, 97.300°W | 5900 | 2100 |
| Pampanga (Luzon) | 14.768°N, 120.656°E | 9800 | |
| Ba Hon (Vietnam) | 10.243°N, 104.583°W | - ** | - ** |
| Sinu (Colombia) | 9.444°N, 75.952°W | 13,700 | 450 |
| Muda (Malaysia) | 5.567°N, 100.323°E | 4300 | 110 |
| Pembuang (Borneo) | 3.434°S, 112.567°E | 12,900 | 1200 |
| Sekampung (Sumatra) | 5.577°S, 105.814°E | 5700 | 240 |
| Ruvuma (Tanzania) | 10.474°S, 40.437°E | 155,500 | 475 |
| Jequitinhonha (Brazil) | 15.850°S, 38.857°W | 78,500 | 410 |
| Doce (Brazil) | 19.656°S, 39.815°W | 86,200 | 900 |
| Limpopo (Mozambique) | 25.221°S, 33.517°E | 415,000 | 170 |
| Rio Grande (Brazil) | 32.199°S, 52.071°W | 200,000 | 1200 |
| Waiapu (New Zealand) | 37.814°S, 178.386°E | 1700 | 80 |
| Rio Negro (Patagonia) | 41.044°S, 62.782°W | 95,000 | 860 |
| Clarence (New Zealand) | 42.174°S, 173.931°E | 3300 | 50 |
| Santa Cruz (Patagonia) | 50.133°S, 68.343°W | 29,700 | 800 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osadchiev, A.; Alfimenkov, I.; Rogozhin, V. Influence of the Coriolis Force on Spreading of River Plumes. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133397
Osadchiev A, Alfimenkov I, Rogozhin V. Influence of the Coriolis Force on Spreading of River Plumes. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(13):3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133397
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsadchiev, Alexander, Ivan Alfimenkov, and Vladimir Rogozhin. 2023. "Influence of the Coriolis Force on Spreading of River Plumes" Remote Sensing 15, no. 13: 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133397
APA StyleOsadchiev, A., Alfimenkov, I., & Rogozhin, V. (2023). Influence of the Coriolis Force on Spreading of River Plumes. Remote Sensing, 15(13), 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133397








