Abstract
Low-altitude slow-moving small (LSS) targets are defined as flying at altitudes less than 1000 m with speeds less than 55 m/s and a radar crossing-section (RCS) less than 2 . The detection performance of ground-based radar using the LSS target detection technique can be significantly deteriorated by the diversity of LSS targets, background clutter, and the occurrence of false alarms caused by multipath interference. To address the LSS target detection problem, we have devised a novel two-dimensional electronic scanning active phased array radar system that is implemented in the software-defined radar architecture and propose a transmit beam control algorithm based on the low peak-to-average ratio (PAPR). Meanwhile, we devised a flexible arbitrary radar waveform generator to adapt to complex environmental situations. Field experiment results effectively demonstrate that our radar can be used to detect LSS targets. Moreover, an ablation experiment was conducted to verify the role played by transmit beam control and adaptive waveform optimization and generation in improving the system performance.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, low-altitude slow-moving small (LSS) targets, which fly at altitudes less than 1000 m with speeds less than 55 m/s and a radar crossing-section (RCS) less than 2 [1], pose a severe threat to public safety and personal privacy [2]. In response to the potential threat of LSS targets, all kinds of sensors, including acoustic sensors [3,4], infrared cameras [5,6], and radars [7,8], have been comprehensively studied. Among those sensors, radar, especially ground-based radar, which can provide continuous all-day-long surveillance of a large area in all weather conditions, has become the major sensor of LSS target detection [9]. However, the LSS target detection technique via ground-based radar is still a demanding and challenging task. With the low altitude of the LSS targets, the candidate targets’ echoes are drowned in the strong ground-reflected clutter leading to either false alarms or false negatives. At the same time, due to the slow flight speed and the small RCS of the LSS targets, it is difficult to distinguish the targets from the slow-moving ground clutter even with the moving target indicator (MTI) and moving target detection (MTD) approaches resulting in large quantities of false negatives and false alarms. The characteristics of the LSS targets and the complexity of the background environment significantly deteriorate the detection of LSS targets.
Numerous studies have been carried out to improve the detection of LSS targets utilizing ground-based radar in complex environments. In summary, the LSS target detection strategies can be categorized into three types: methods based on sophisticated signal processing algorithms, methods based on transmit/receive beam optimization, and methods based on the optimization or innovation of radar systems [10].
Methods in the first category concentrate on algorithm design. Weak target signals can be detected with high confidence in complex environments with the help of specially designed signal processing algorithms. In [11], a new LSS target detection algorithm based on spatial-temporal features measure (STFM) was proposed, which enhanced targets and suppressed the background clutter. In [12], Huang proposed the improved complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise (ICEEMDAN) method and adaptive CFAR technology to suppress strong clutter, which realizes the effect of reducing the false alarm rate and improving the detection accuracy. Furthermore, Sun proposed an improved self-balanced sensitivity segment model to detect LSS targets, significantly improving the detection accuracy and computational efficiency [13]. In [14,15], a novel model of the echoes of LSS targets was proposed, considering multipath interference, atmospheric attenuation, and system loss. By comparing the performance of the Kalmus filter with that of the classic FIR filter, it was verified that Kalmus filters are indeed more suitable for low-speed target detection. Moreover, a novel long-time coherent integration (LTCI) method was established [16] to balance computational cost and integration gain. In [17], an LSS target detection system based on the multi living agent (MLA) was proposed [18]. Unlike the traditional methods based on clutter filtering, a new LSS target detection approach that integrated the whitening filter was used to extract the target information when the targets were mixed with the interfering signal, which provided a new way to solve the problem of slow target detection [19]. Compared with traditional detection methods, the LSS detection methods based on signal processing algorithms achieved a significant breakthrough [20]. However, these detection methods only consider the benefits of signal processing, without taking full advantage of beamforming, waveform generation, and other improvement aspects to fulfill a systematic optimization strategy. In addition, the proposed detection methods generally require certain assumptions about the observed targets and the environment. When the natural environment does not match the model hypothesis, the detection methods lack robustness for diverse targets and unexpected background clutter and interference, ultimately leading to the deterioration of the detection performance.
Due to the rapid development of classical array signal processing methods, LSS target detection methods based on transmit/receive beam optimization have been widely studied in recent years [21]. These methods have focused on interference suppression by beamforming, so that the clutter was counteracted. Abdulrazaq developed a small-scale digital array radar capable of detecting a slow-moving and small RCS UAV at a relatively long range, which produced the desired beam by summing the output [9]. Xu proposed a transmit beam control algorithm for phased array radar, which considered several practical requirements simultaneously, including robustness against the array error, main lobe loss minimization, and sidelobe suppression on the ground side [1]. Wan proposed an anti-jamming robust adaptive beamforming algorithm in FDA-MIMO radar. This algorithm utilizes covariance matrix reconstruction and spatial power spectrum estimation methods to improve the estimation accuracy of the signal covariance matrix and the desired target steering vector, thus calculating the optimal weights vector for the adaptive beamformer [22]. Liu proposed a transmit beamforming model for a dual-function multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) radar and a multiuser MIMO communication transmitter, which provided more degrees of freedom for MIMO radar and was, thus, able to obtain improved performance [23]. In [24], a new technique with two weight vectors was proposed, which can also achieve impressive results in LSS target detection by selecting waveforms for specific detection scenarios. McCormick proposed a two-stage iterative method of alternating projection to design multifunction waveforms [25,26]. This method can improve the power efficiency of the resulting set of multifunction waveforms. However, these methods only focus on the design of the transmit/receive beam and do not sufficiently consider adaptive waveform optimization to achieve optimal detection performance. Meanwhile, these methods are not explicitly designed to suppress ground clutter, and the echoes received by the radar will be swamped by clutter, which leads to the degradation of the radar’s detection performance.
Recently, methods based on the optimization or innovation of radar systems have become the rising approach for LSS target detection in complex environments, such as the methods used in environmental sensing radar, the methods adopted in the Doppler division multiple access (DDMA) MIMO radar system, and the methods utilized in the software-defined radar based on digital beamforming. In [27], a Fraunhofer Institute for High Frequency Physics and Radar Technology (FHR) cognitive radar architecture based on a three-layer model of human cognitive performance was presented, enabling the identification of air targets and target-matched waveform design. Yang proposed a novel DDMA MIMO radar system [28]. By designing DDMA waveforms, the orthogonality of the transmit signal is ensured. The optimization of array element positions using genetic algorithms improves angle estimation performance. The system has been experimentally verified to meet the detection and tracking performance of LSS targets. Software-defined radar, enabling adapting to complex environments and diverse targets, is an efficient radar system that has been widely applied for LSS target detection recently. It can flexibly alter the operating mode of the radar via control software [29], providing functions such as reconfiguring the transmit waveforms [9], selecting the orthogonal waveforms on transmit antennas adaptively [30], and applying different space modulations of the transmit signal [31]. Wu designed and implemented a software-defined phased array radar [32], effectively reducing the cost of a beam-pointing system, compared with traditional phased array radars. A minimum software-defined radar system proposed in [33] integrated various software-based functions such as waveform generation, beam control, and signal processing. With the arbitrary configuration of software parameters, the radar system could be applied in diverse LSS target detection environments. Although the software-defined radars provide a more flexible way for LSS target detection, the design of software-defined radar is mainly based on the characteristics of the signal, instead of focusing on the system architecture design.
Currently, the radars that detect LSS targets are designed for specific system components and lack a unified design. We have devised a novel two-dimensional electronic scanning active phased array radar system to tackle this challenge. This system systematically integrates a design for LSS target detection consisting of beamforming control, arbitrary waveform generation, signal processing, and environment sensing.
The main contributions of this study can be summarized as follows:
- 1.
- We developed a novel two-dimensional electronic scanning active phased array radar implemented in a software-defined radar architecture, providing an adaptive LSS target monitoring capability under various complex environments.
- 2.
- We proposed a transmit beam control algorithm based on the low peak-to-average ratio (PAPR) constraint that can significantly improve the LSS detection performance under strong ground clutter and inference.
- 3.
- We devised a flexible arbitrary radar waveform generator that can generate various complex waveforms depending on the feedback of the environmental sensing module.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. An overall overview of the radar system is given in Section 2. The first characteristic of the developed system, i.e., transmit beam control, is discussed in Section 3. Another feature of the developed system, i.e., arbitrary wave generation and signal processing, is introduced in Section 4. The system development is analyzed and concluded in Section 5. Finally, conclusions are drawn in Section 6.
2. System Overview
2.1. Specification
Due to the complex environment and the diversity of LSS targets, we devised this novel two-dimensional electronic scanning active phased array radar system. The devised radar can detect LSS targets ranging from 300 m to 6000 m under various complex detection environments and divergent targets with velocities smaller than 98 m/s. Furthermore, this radar works in the X-band, which has an instantaneous bandwidth of 40 MHz, providing sufficient range resolution for targets. Moreover, to tackle the complex clutter and various interferences, our system is implemented in the software-defined radar architecture with three characteristics: software-implemented real-time operations, working flow reconfiguration by adaptive waveform optimization, and transmit beam generation and optimization. The specifications of the entire system are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
System Specifications.
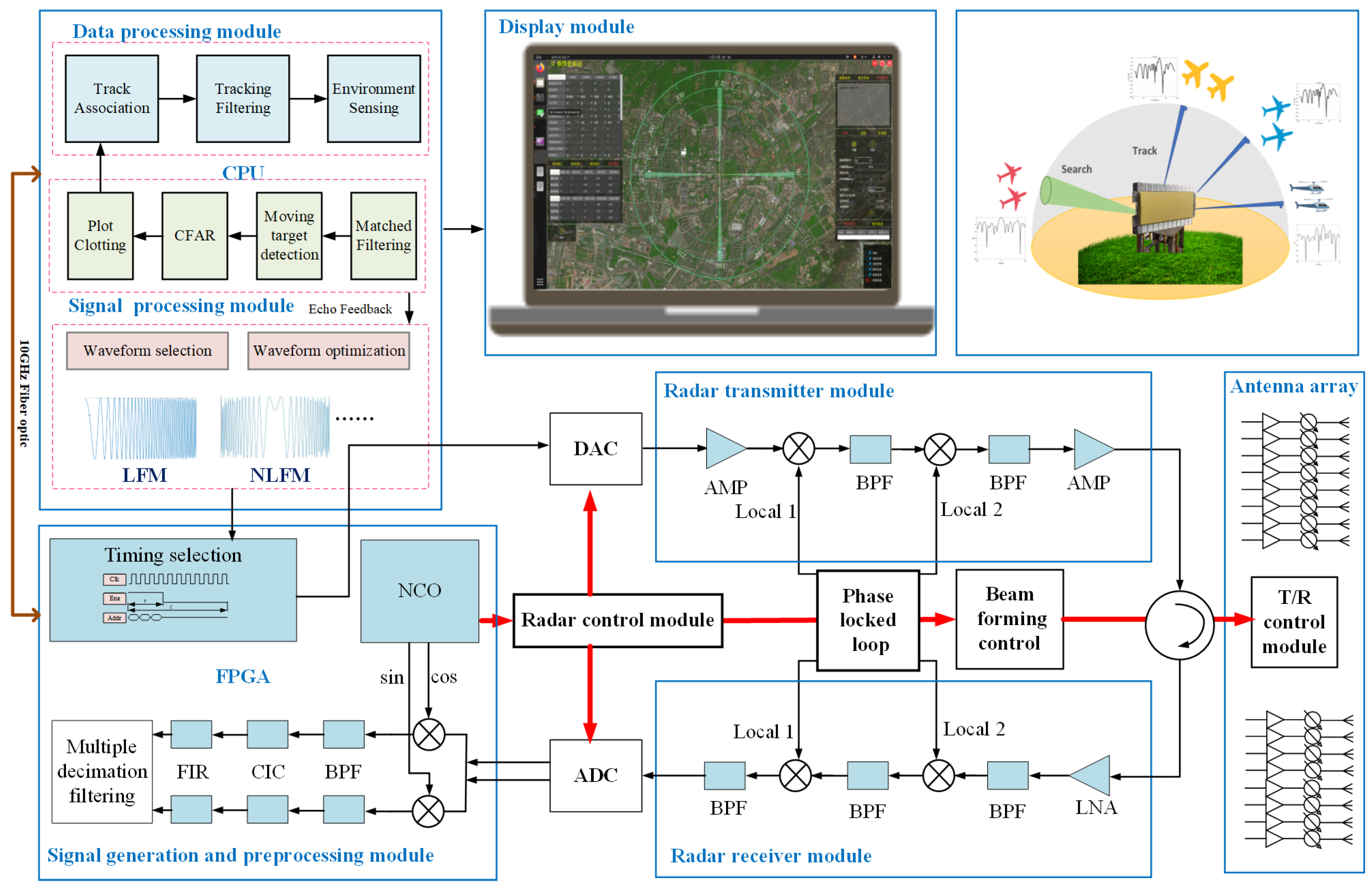
The devised radar, as shown in Figure 1, contains seven composition parts: the antenna array, the transmitter module, the receiver module, the radar control module, the signal generation and preprocessing module, the signal and data processing module, and the display module.
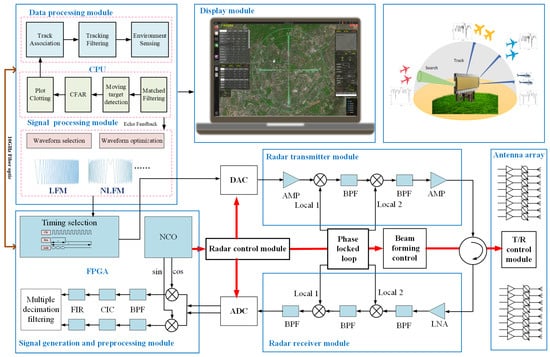
Figure 1.
Structure of the developed radar system (NCO: numerically controlled oscillator; FIR: finite impulse respond; CIC: cascaded integrator comb; BPF: band-pass filter; AMP: amplifier; LNA: low-noise amplifier).
The radar control module controls the digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to generate the transmit waveform, then sends it to the transmission module and the relevant phased array antenna module. The RF signal is transmitted into the free space and reflected backward once it reaches the candidate targets. The received echo passes through the RF front-end, the receiver, and the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) successively, and the IF signal is obtained. Subsequently, it is fed to the signal preprocessing module built on an FPGA, where digital orthogonal demodulation is applied to generate the baseband signal. The baseband signal is sent to the signal processing module for further processes, including matched filtering (MF), moving target detection (MTD), constant false alarm rate (CFAR) detection, and plot clotting. The plots are sent to the data processing module for track association, tracking filtering, and environment sensing. The environment sensing process will collect the required characteristics of the targets and the environment and send them to the arbitrary waveform generator. The arbitrary waveform generator will determine the optimal signal type and corresponding parameters of the waveform and generate them in the next dwell according to the data passed by the environment sensing process. It should be declared that the signal processing module, the data processing module, and the waveform optimization process are all implemented by software executed on the CPU of an industry computer.
2.2. Antenna Module
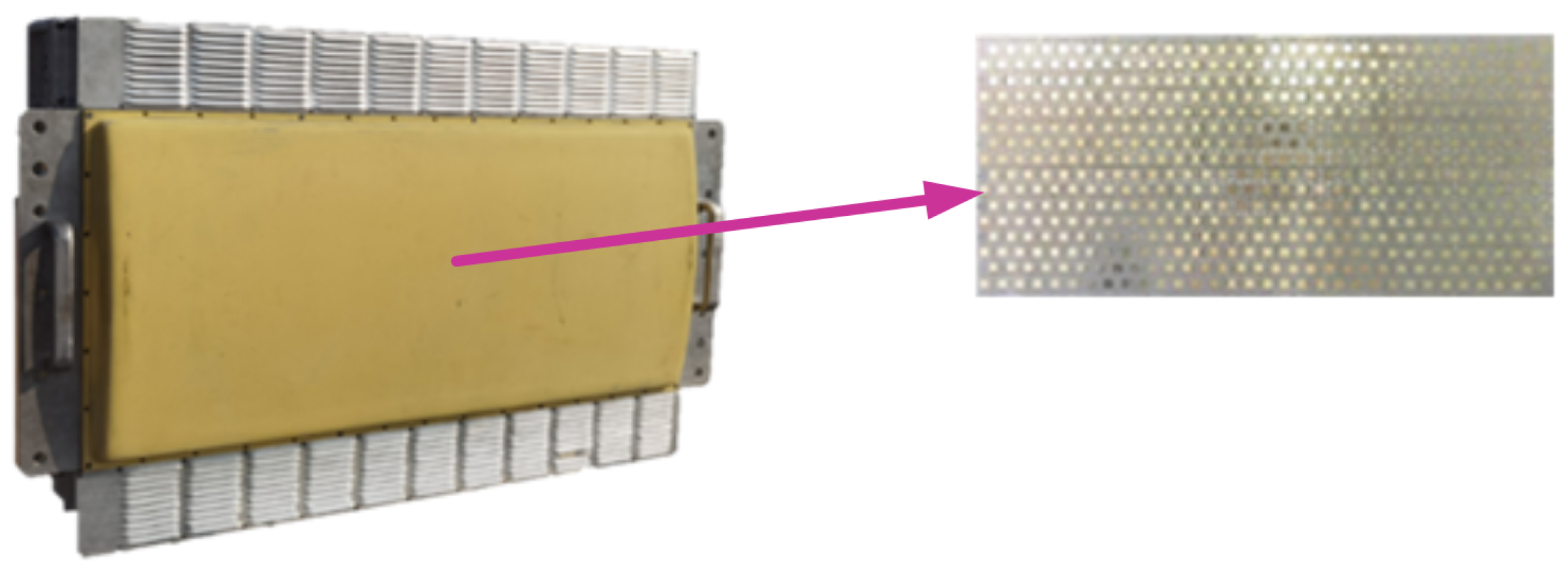
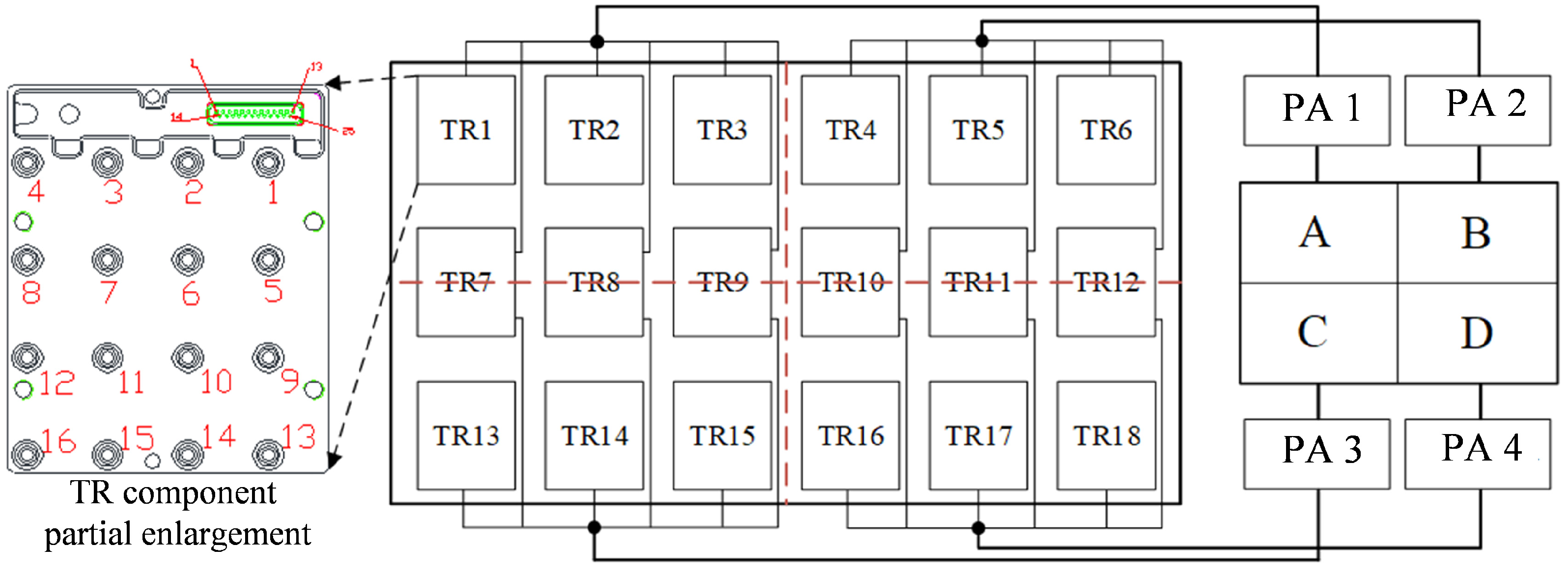
Each antenna array, whose structure is shown in Figure 2, can provide a coverage range of 90 degrees. Each array consists of 18 transmitter/receiver (TR) components that are organized in three rows and six columns without overlap between the arrays. As illustrated in Figure 3, each TR component contains 16 channels, arranged in 4 × 4 arrays. The 16 echoes of each TR component are synthesized into one signal via beamforming through the TR component. By configuring the phase shifter and attenuator in the TR components, the amplitude and the phase of the signal received by each antenna array element can be adjusted to achieve the function of analog beam control. Moreover, with the aid of transmit beam control, this system can enhance the capacity of interference suppression and improve the detection performance of LSS targets. Specifics on transmit beam control will be described in Section 3.
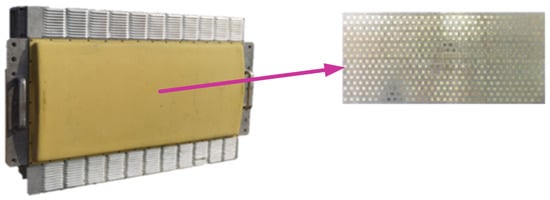
Figure 2.
Photograph of the antenna array.
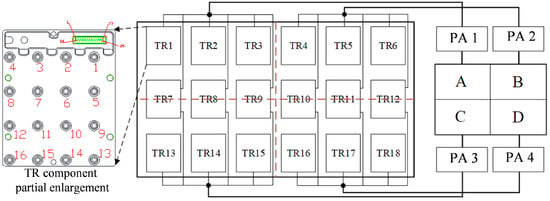
Figure 3.
Arrangement and structure of the TR component. Each TR component has a configuration interface for controlling channel switching and configuring the phase shift and attenuation values of each array element.
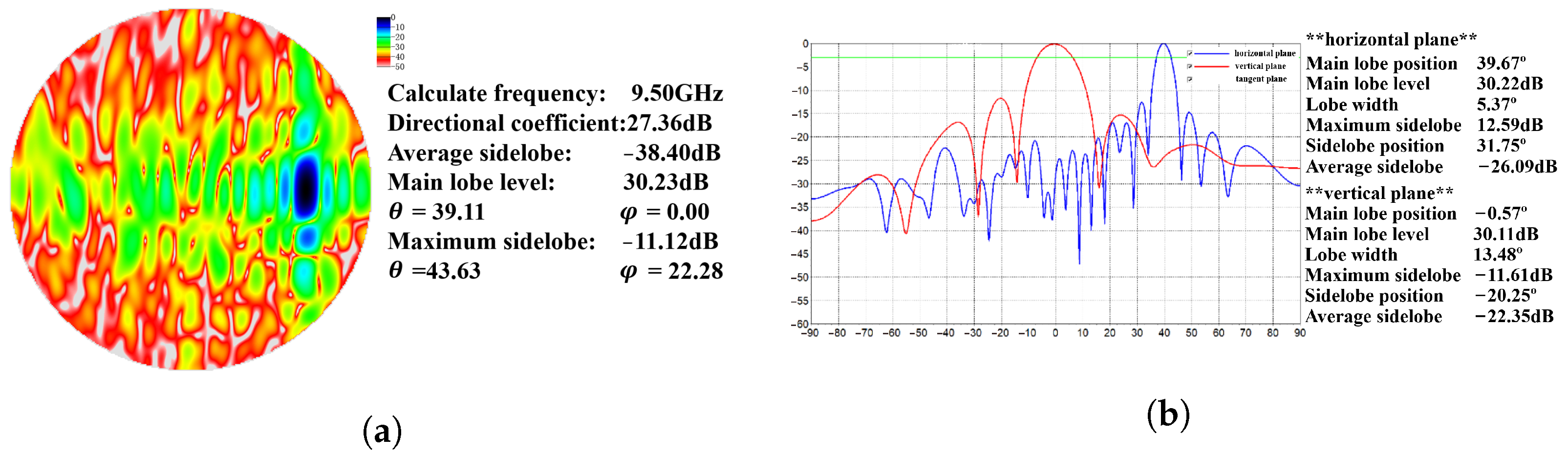
Figure 4 shows the antenna patterns of the measurement results. Measurements were performed using a near-field scanner (NFS) in an anechoic chamber which can avoid external interference on signal transmission and reception. Setting the beam direction towards for testing and plotting the two-dimensional transmitting pattern of the array is shown in Figure 4a, and the one-dimensional transmitting pattern of the UV cutting plane beam is shown in Figure 4a. Figure 4a shows that the beam gain near point is close to 0 dB, while the beam gain at all other angles is less than −13 dB. Figure 4b shows the azimuth beam width and elevation beam width of the UV cutting plane passing through point are and the highest sidelobe gain is −11.12 dB.
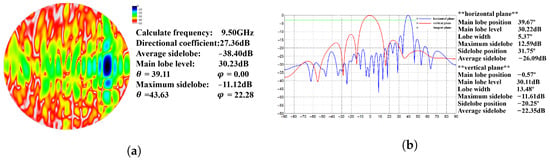
Figure 4.
The transmitting pattern when the beam is directed towards . (a) Two-dimensional array emission pattern; (b) one-dimensional emission pattern of over-beam UV section.
2.3. Transmitter and Receiver Module
For the transmitter module, we adopt the master oscillator power amplifier. It consists of a preamplifier, an intermediate RF power amplifier, and an output RF power amplifier capable of transmitting a phase-integrated signal with high-frequency stability through secondary up-conversion. A superheterodyne receiver is applied in the receiver module to filter out-of-band interference and noise through secondary down-conversion. The radar control module regulates the timing of the entire radar to ensure that it operates efficiently under the preset mode. Figure 5 shows the distribution of the modules.
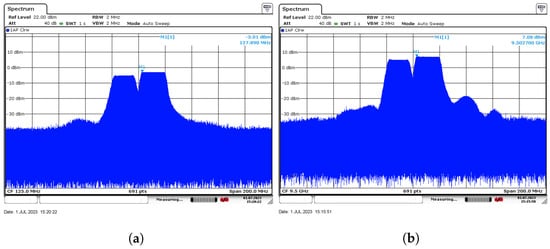
Figure 5.
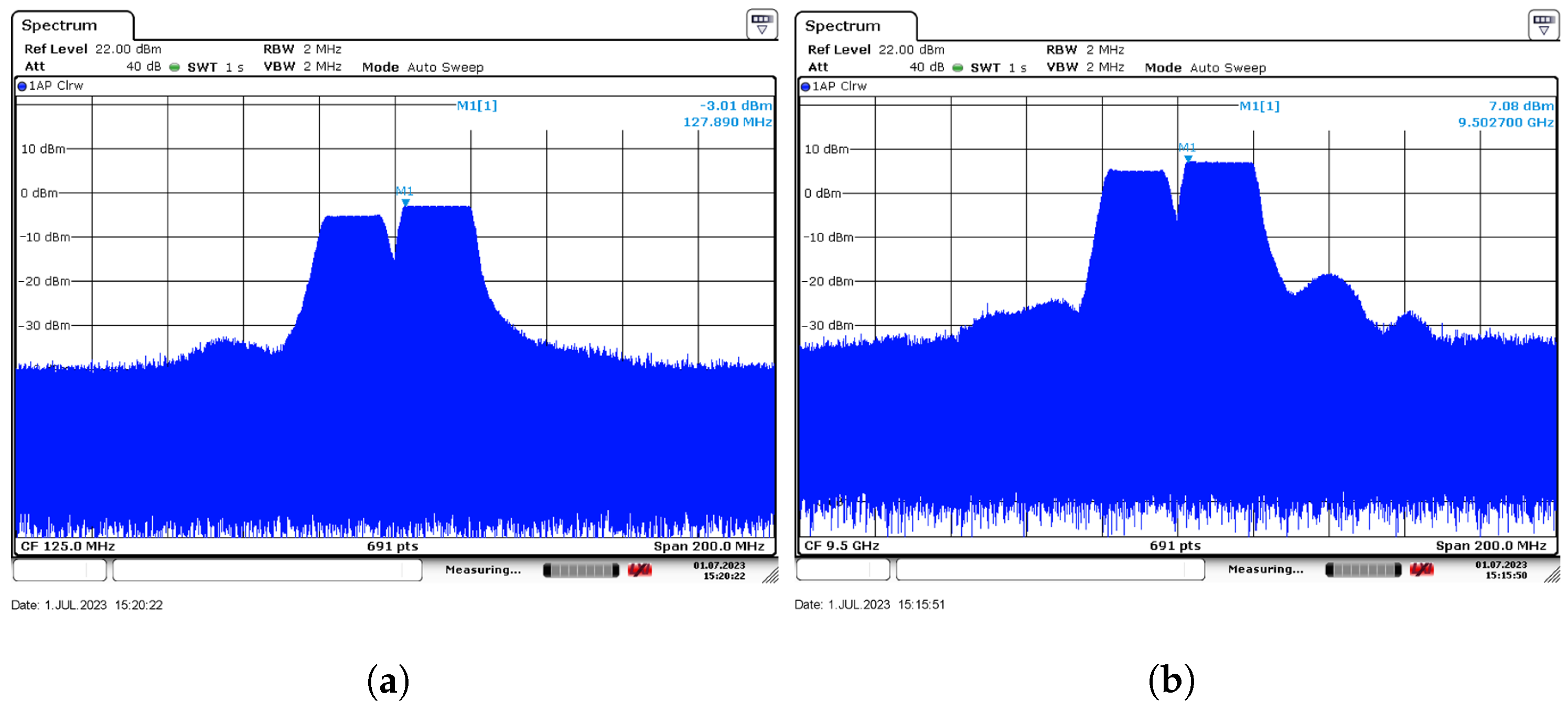
The frequency spectrum diagram of the IF input and the RF output. The spectrum graph (a) shows that the intermediate frequency (IF) signal has a center frequency of 125 MHz. The spectrum graph (b) shows that the radio frequency (RF) signal has a center frequency of 9.503 GHz.
We conducted tests on the transmitter module. The RF working frequency was set to 9.5 GHz, and a signal combining wide and narrow pulses was used for testing. The frequency ranges of the 20 s wide pulses and the 2 s narrow pulses varied from 127 MHz to 145 MHz and from 105 MHz to 123 MHz, respectively. Figure 5a shows the frequency spectrum, and it can be seen that the intermediate frequency (IF) signal has a central frequency of 125 MHz, and the amplitude of the wide pulse is larger than that of the narrow pulse. When this IF signal was connected to the IF end, the test results at the RF end are shown in Figure 5b, with an IF point of 128 MHz corresponding to an RF frequency point of 9.503 GHz, verifying the regular operation of the frequency conversion function on the transmitter module.
2.4. Signal Generation and Preprocessing Module
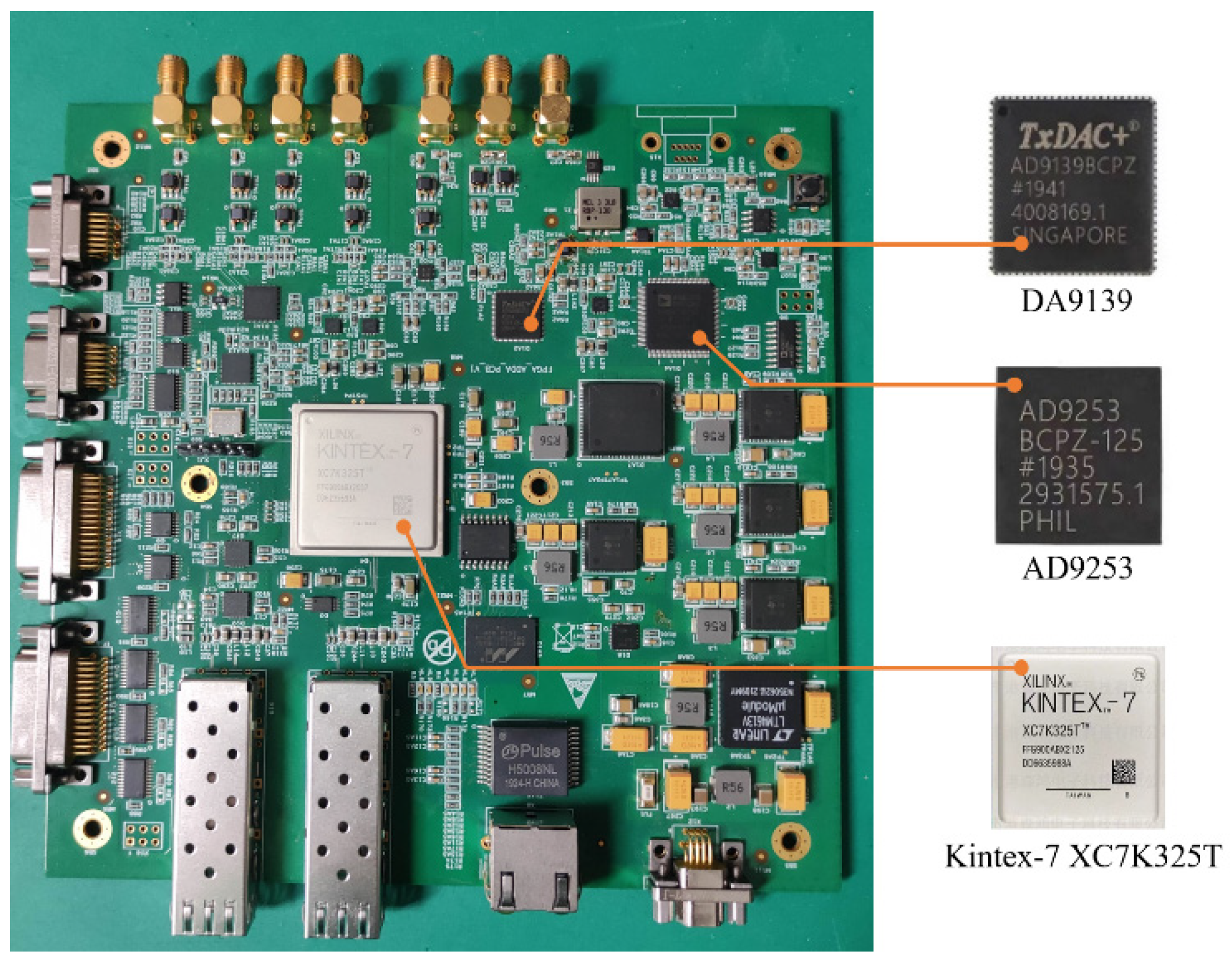
Figure 6 shows a photograph of the signal generation and preprocessing board, which was developed based on Xilinx’s Kintex 7 Series FPGA. The AD9253 chip is used for analog-to-digital conversion. The DA 9139 chip is configured to generate an analog IF transmission signal and the four intermediate frequency signals are sampled and digitally quadrature demodulated. The amplitude and phase of the baseband signal are then calibrated. Finally, the signal generation preprocessing module performs orthogonal demodulation on the raw data and sends it to the signal and data processing module through the optical fiber.
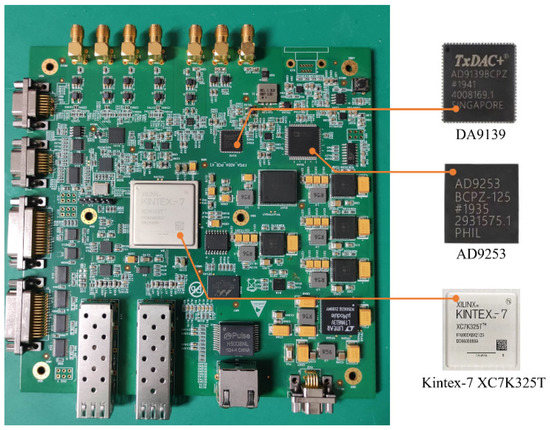
Figure 6.
Photograph of the signal generation and preprocessing board.
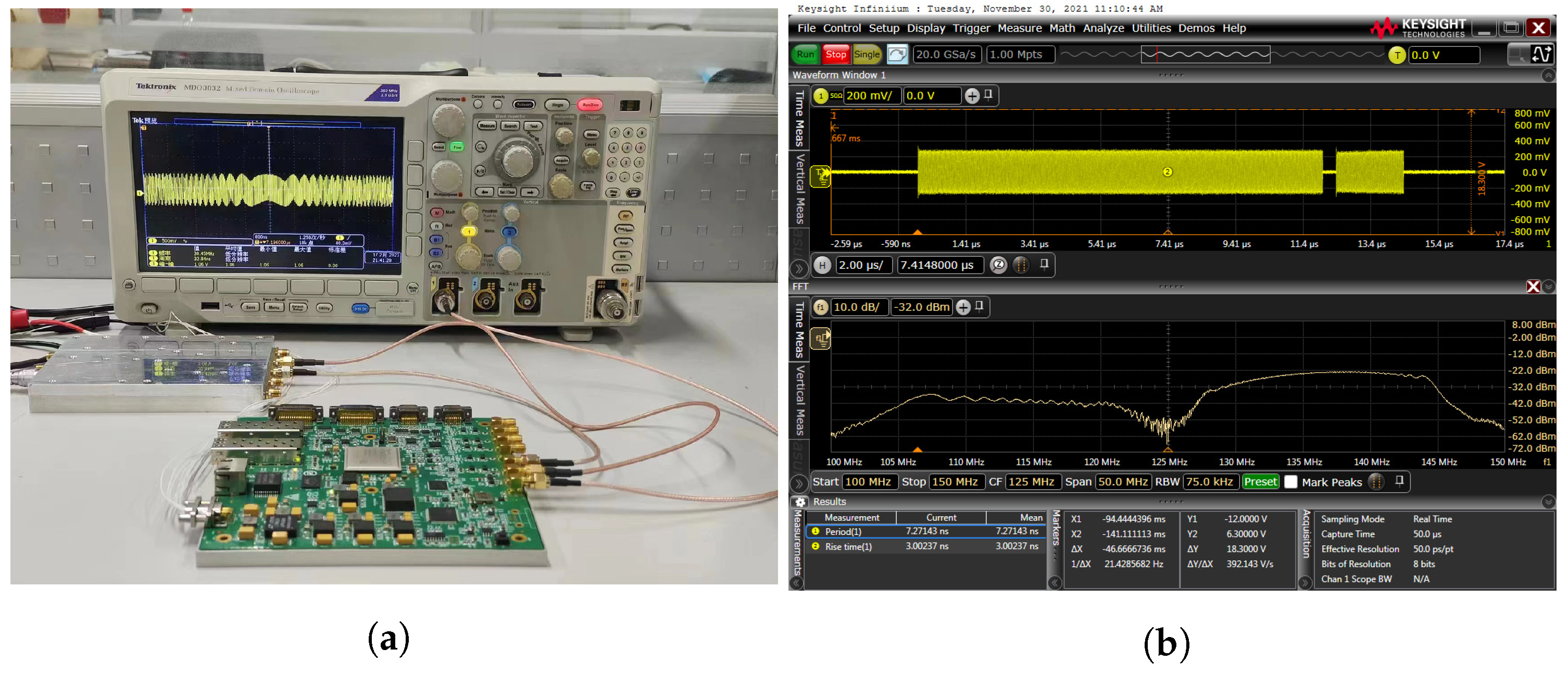
To simulate the actual working conditions of the system, we adopt a wide pulse frequency range of 127 MHz to 145 MHz and a duration of 20 μs, and a narrow pulse frequency range of 105 MHz to 123 MHz and a duration of 2 s. Figure 7a shows the corresponding frequency spectrum, where the intermediate frequency signal has a central frequency of 125 MHz, which demonstrates that the amplitude of the wide pulse is larger than that of the narrow pulse. The IF signal was then connected to the IF end and the corresponding channel of the RF end was connected to a spectrum analyzer. The RF test results are shown in Figure 7b, verifying that the frequency conversion function of the system works well.
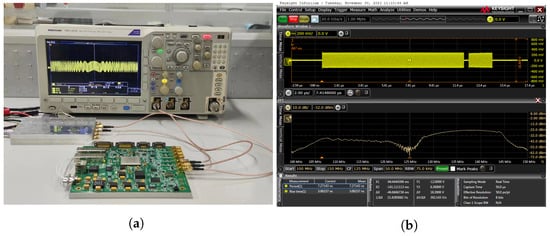
Figure 7.
The IF input and RF output of the transmitter module. (a) Waveform diagram connected to the sampling board; (b) Time-domain waveform and frequency-domain spectrum of the output waveform.
2.5. Signal and Data Processing Module
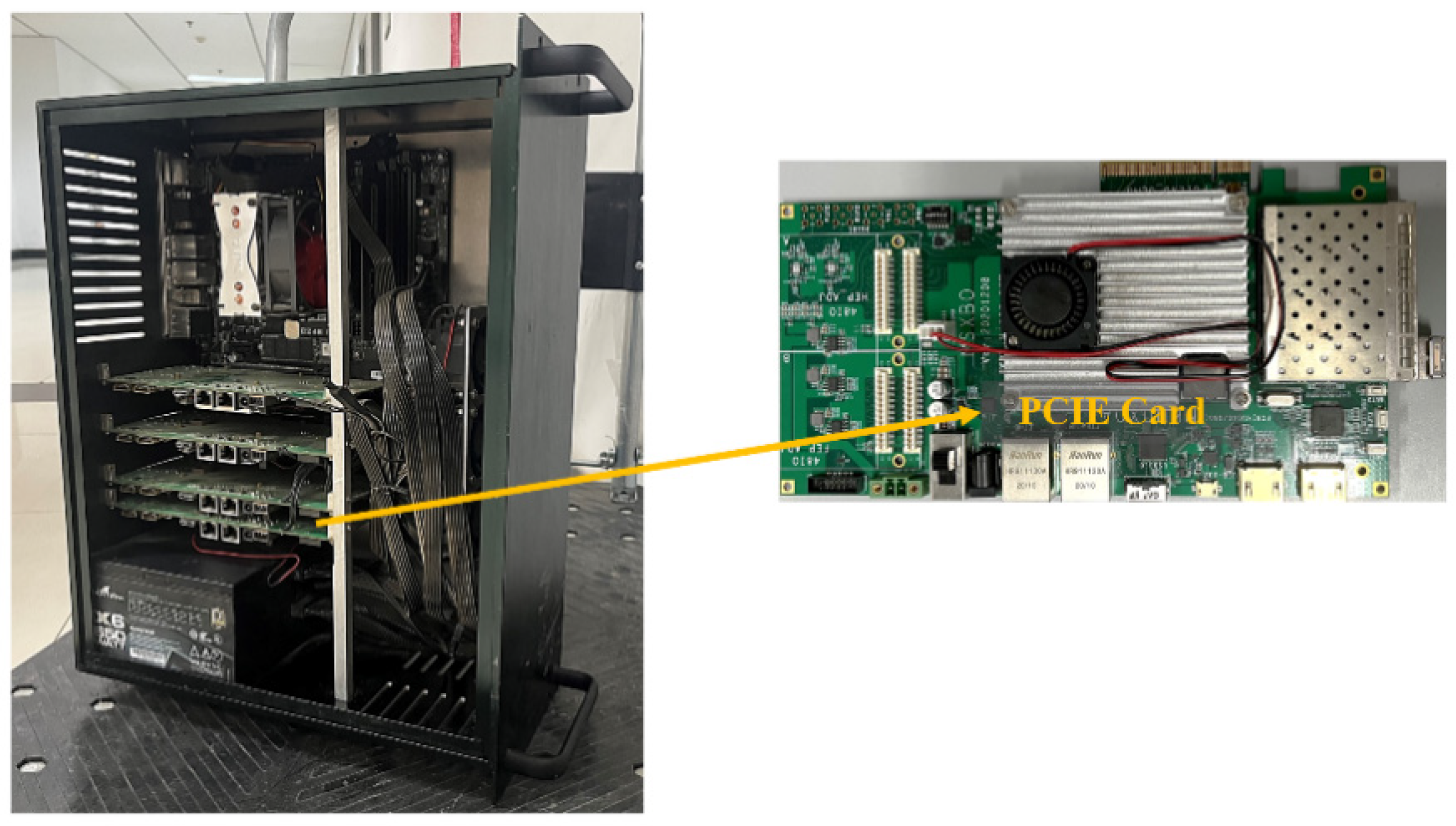
All the software used to realize the signal processing function works on a general-purpose industrial computer. Based on the current environment and target type, the system drafts the transmitted beam form and realizes the shape. Furthermore, it reduces the near-ground lobe and main beam form, and finally degrades the near-ground side reflection clutter. The echo signal goes through analog beamforming, RF front-end, and secondary up-conversion of the receiver to finally obtain the IF signal. It is sent into the FPGA for orthogonal demodulation processing to obtain the baseband sampling signal, which will be transmitted to the signal processing module in the CPU through an optical fiber. The module carries out PC, MTD, and CFAR detection on the baseband signal successively to obtain the target. The captured target’s basic information, category information, and environment information are sent to the environment sensing module. Waveform, beamform, and other indication system commands are adaptively created and communicated to the antenna subsystem and waveform generation subsystem to produce the corresponding beam and waveform. Figure 8 shows a photograph of the CPU chassis and PCIE card.
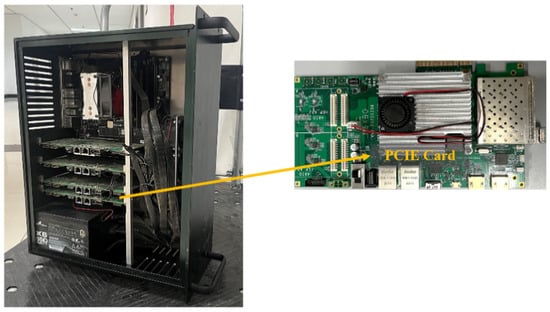
Figure 8.
The industry computer used for signal processing and data processing, including its CPU and PCIE card.
Traditional radar signal processing systems face challenges such as a low development efficiency and limited flexibility when implemented on platforms such as FPGA and DSP. To address these issues, a software-defined radar technology that is software-reconfigurable and customizable has been adopted to design and implement the radar signal processing system on a multi-core CPU server platform. The system employs a multi-process architecture and modular design for radar signal processing and data processing. It utilizes parallel real-time processing by leveraging multi-threading programming tools such as OpenMP and high-performance mathematical computation libraries such as FFTW for each functional module, enabling the transformation of raw echo signals into detected tracks. To adapt to different detection environments, a differentiated and reconfigurable configuration scheme is employed to achieve precise target search and tracking. The system has been validated to possess strong real-time capabilities and high flexibility, demonstrating its potential value in engineering applications.
Based on the requirements of real-time performance, compatibility, and scalability, we have chosen the Linux distribution operating system Ubuntu 20.04 [34] for the software-defined radar system. In the system, we have improved the efficiency of the operating system by optimizing task scheduling, using parallel programming, optimizing memory management, and reducing interrupts, thereby meeting the real-time requirements of the system.
3. Transmit Beam Control
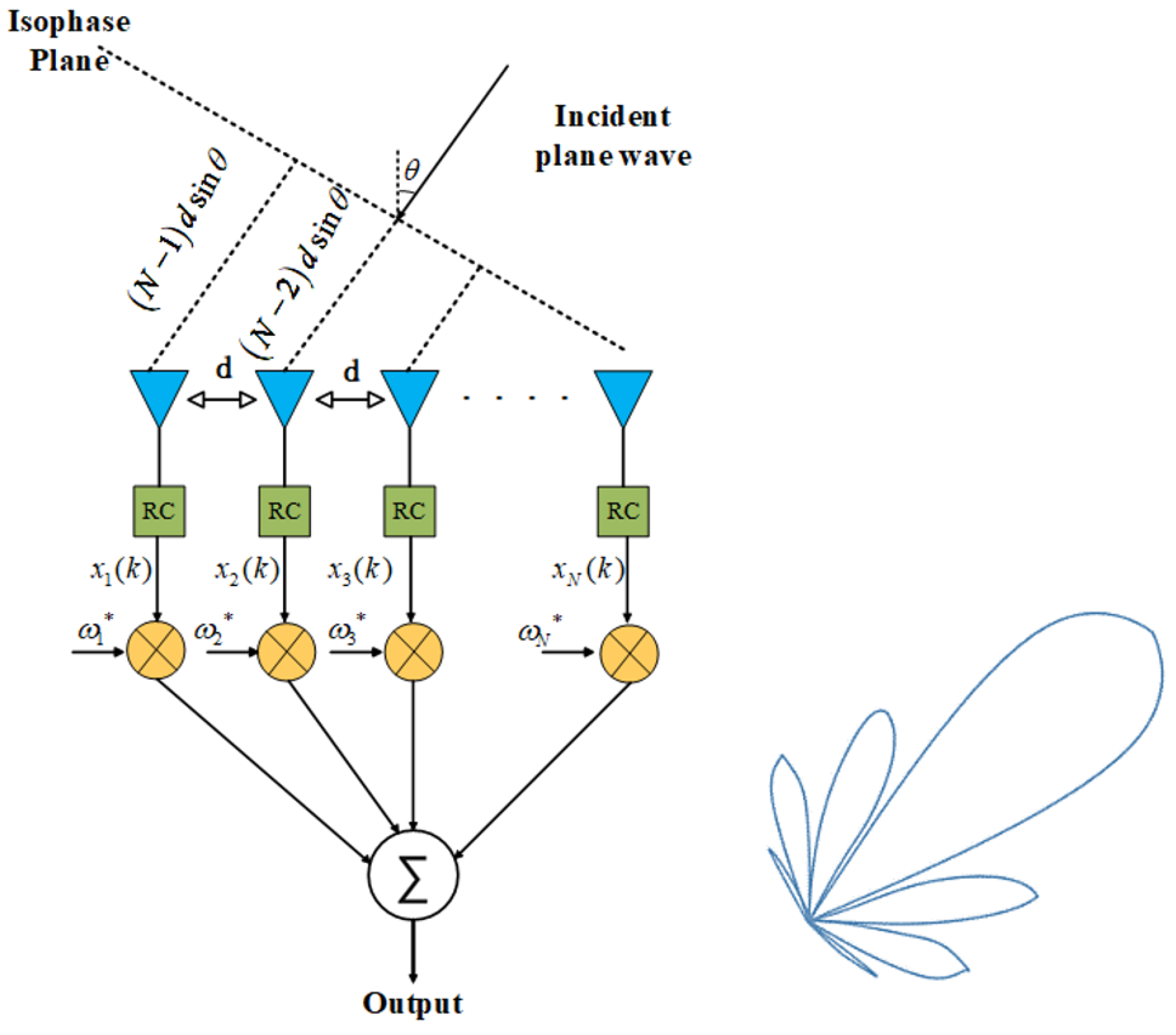
Consider a narrowband signal transmitted by an N-elements ULA with element spacing , as shown in Figure 9. In fact, if the gain and phase errors resulting from inaccurate element spacing and non-ideal RF chains are incorporated into the array element weight vector, when the error is small, the actual amplitude squared expectation of the beam response is a function of . In order to design a robust beamformer, should be small. Therefore, we set the following robust constraint
where b is the upper bound of the prescribed norm, and different values can be specified according to the specific requirements.
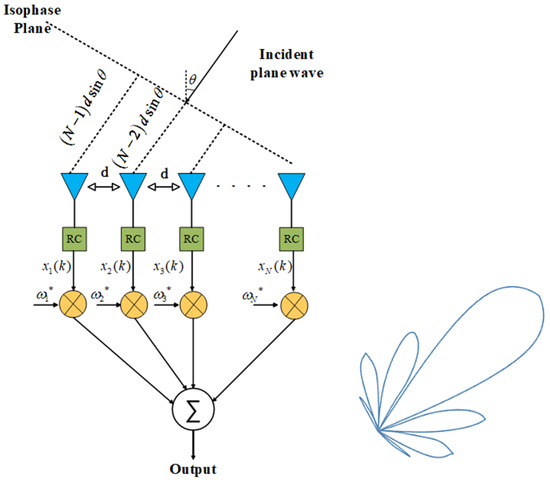
Figure 9.
Transmit array layout of a ULA.
In addition to improving the robustness, maximizing transmit power is important to improve the reliability of the sensing system. For TBF, the transmit signal needs to meet CM constraint or have low PAPR. According to the definition of PAPR, the constraint on transmit weights can be expressed as
During the LSS target detection, there is a large amount of clutter and interference existing on the ground, which increases the difficulty of LSS target detection. Therefore, we need to design the array weight vector to severely suppress the sidelobe levels of the transmit beampattern on the near-ground side so that the reflected ground clutter can be significantly reduced. Thus, we aim to minimize the PSL on the ground side while preserving the array response in the SOI direction. Then, the corresponding TBF problem can be formulated as the following min–max optimization problem [35],
where indicates the direction set corresponding to the ground side clutter region, is the array steering vector at the direction , and .
Based on the invariant characteristics of the constraint function under an arbitrary phase rotation of , the modulo operation () can be cleverly eliminated, further transforming the model into a simpler convex optimization problem. The global optimal solution is then obtained by solving using the CVX toolbox. In addition to CVX, there are multiple methods available for solving, and the results obtained by these methods are generally consistent.
In practical beamforming applications, the assumed signal steering vector often suffers from a certain error, i.e., a certain mismatch between the assumed signal steering vector and its actual value. In order to improve the robustness of beamforming against an arbitrary steering vector mismatch, the actual steering vector is introduced as follows
where is the steering vector error. The uncertainty region of can be modeled as a ball set , and is the radius of the ball.
Problem (5) can be finally transformed into the following convex optimization problem by the combination of the triangle inequality and Cauchy–Schwartz inequality
Note that the objective function and all the constraints in (6) are not influenced when an arbitrary phase rotation is introduced into . Therefore, we can replace the constraint with and then translate the problem (6) into a convex problem. Since convex problems always have a globally optimal solution, we can easily resolve the problem (6) by using an off-the-shelf toolbox, such as CVX [36].
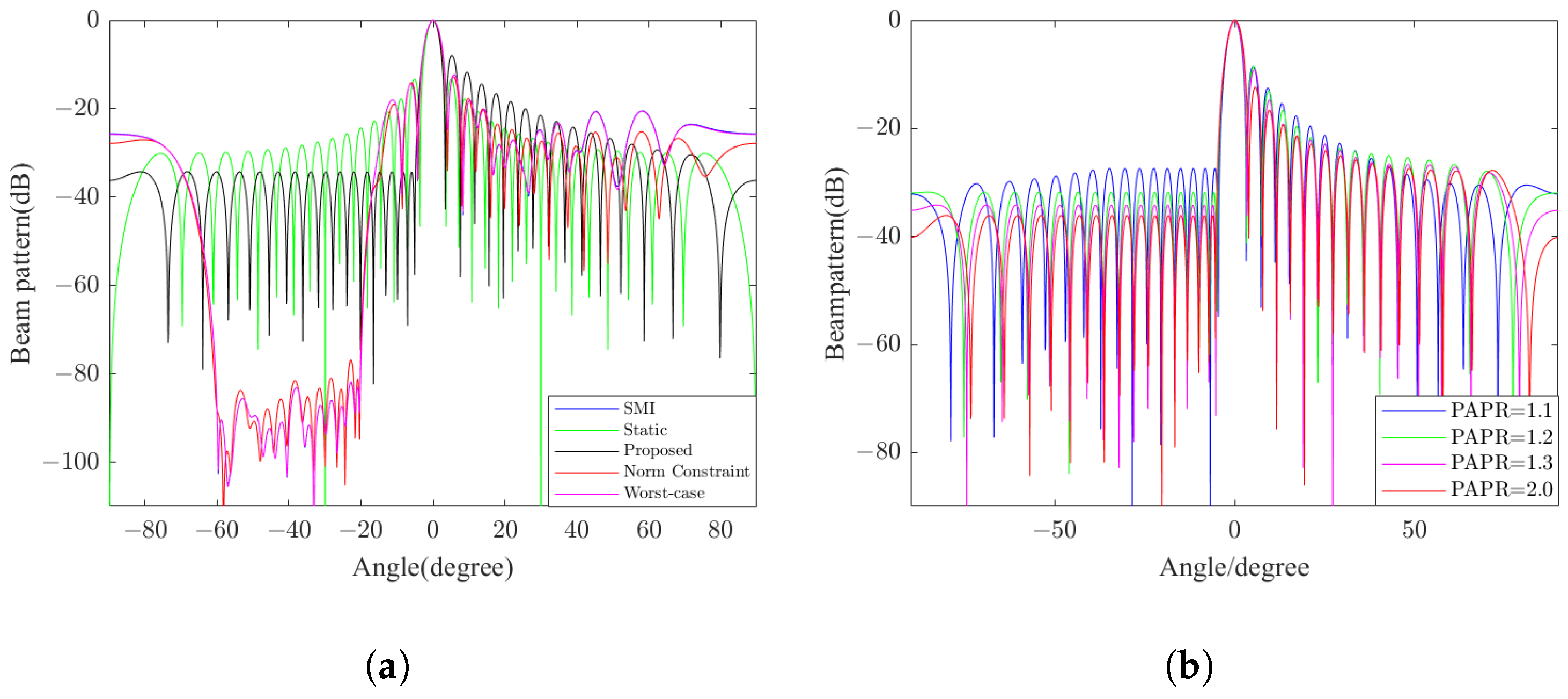
In the simulation part, we first compare the transmit beampatterns generated by the proposed method and other typical beamforming methods, including SMI beamforming, static beamforming, NCCB beamforming, and WCPO beamforming, to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed TBF method. Then, to quantize the influence of the PAPR and norm constraints on TBF, the performance under different parameter configurations is further studied. The simulation results are shown in Figure 10.
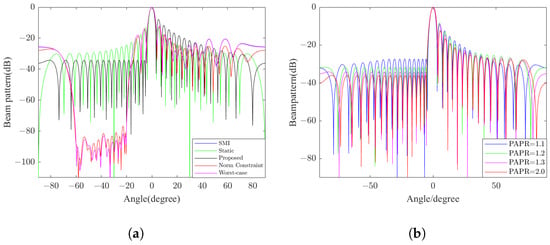
Figure 10.
The transmit beampatterns generated by the proposed TBF method. (a) Comparison of beampatterns generated by five different methods (snapshots = 32). (b) Beampatterns synthesized under varying PAPR tolerances with constant upper limits of norm = 0.035.
The numerical results prove that the proposed beamforming method can effectively suppress the interference on the ground side because of the very low sidelobe level and is robust to the steering vector mismatch. Obviously, the weights of the transmit beam control can be pre-calculated before the radar system runs.
4. Scalable Arbitrary Wave Generator and Signal Processing
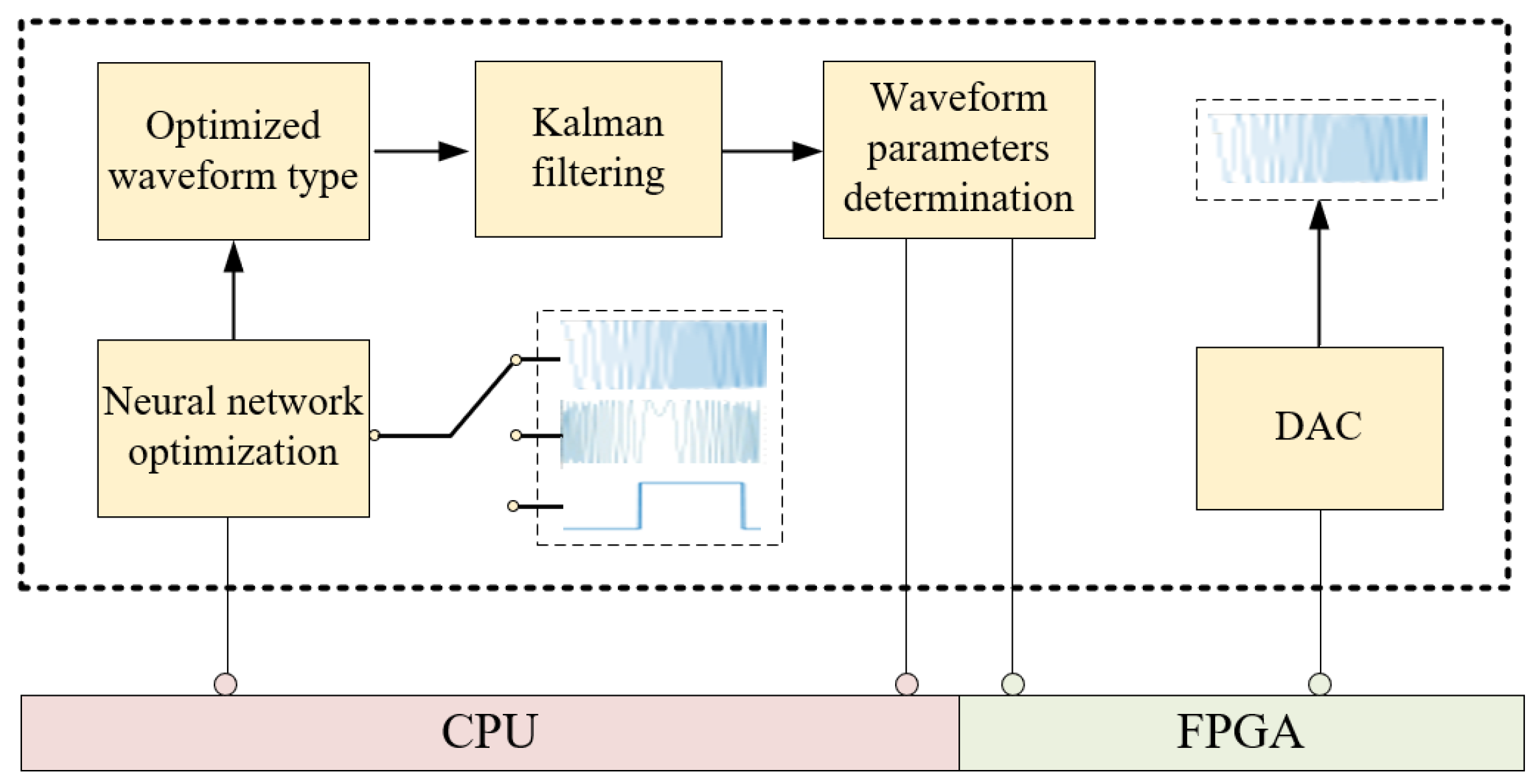
As shown in Figure 11, a scalable and adaptive waveform optimization framework is developed, improving the performance of LSS target tracking in complex environments. A hierarchical strategy based on a deep network and Kalman filtering is utilized to select the optimal type of transmit signal and optimize the corresponding parameters. The entire waveform optimization procedure is carried out by software implemented in a high-level programming language for convenience and scalability. Moreover, FPGA rather than the traditional DDS is utilized to generate the required analog waveforms, which are subsequently sent to the transmitter. Meanwhile, the optimal waveform generated by the waveform optimization software is also used to construct a matched filter for echo signal processing.
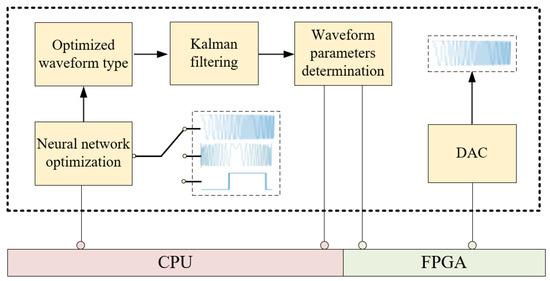
Figure 11.
Waveform generation and processing framework.
4.1. Adaptive Waveform Optimization Strategy for Target Tracking
To implement real-time waveform optimization for LSS target tracking, the system builds a waveform library composed of three types of signals, i.e., constant frequency (CF), linear frequency modulation (LFM), and non-linear frequency modulation (NLFM). The parameters of these signals are varied in a predefined range, as shown in Table 2. Then, based on the waveform library, a hierarchical decision scheme is established to select the waveform and the corresponding parameters.

Table 2.
The predefined waveform in the developed radar.
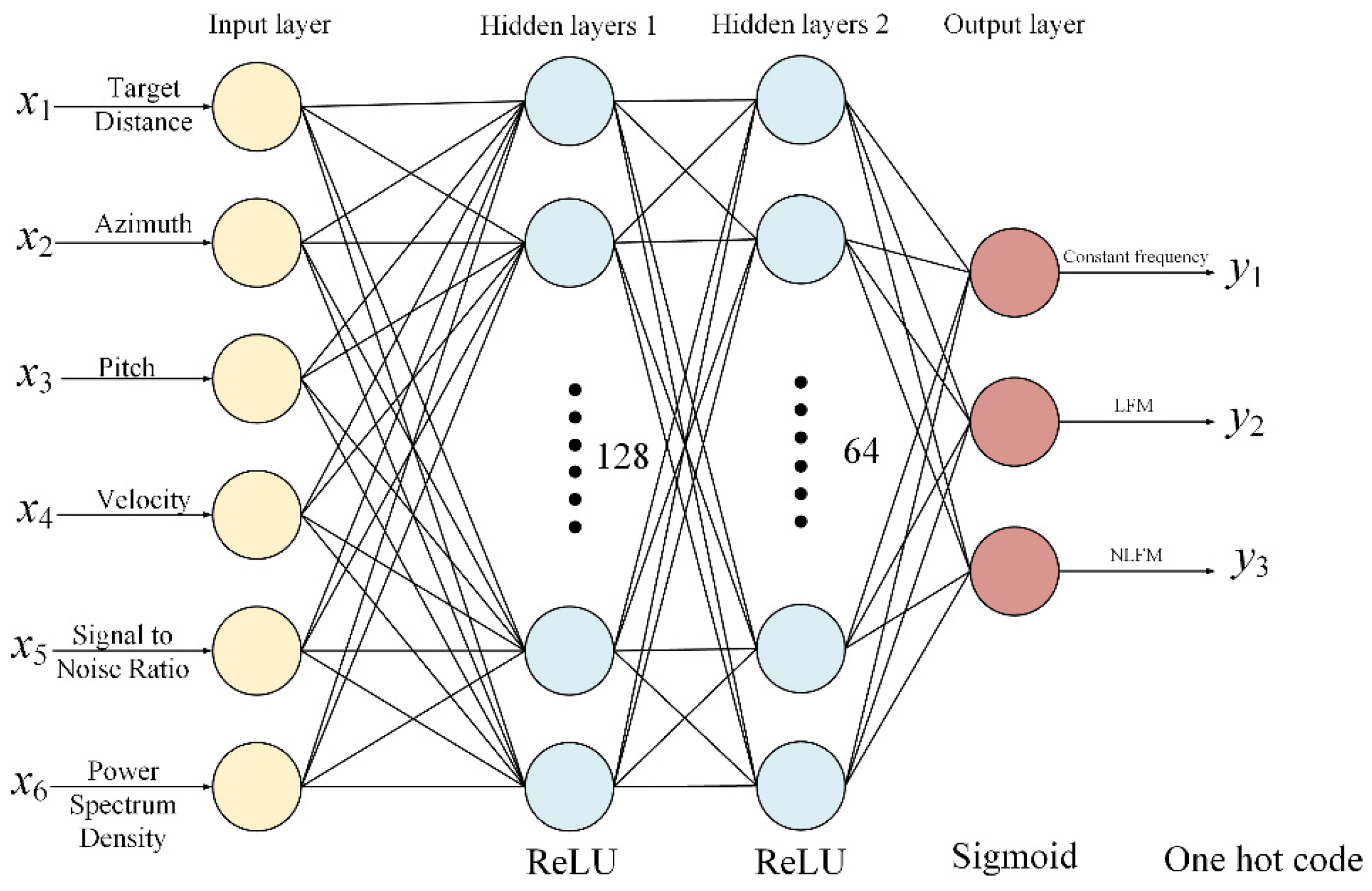
In the first stage, the type of transmitting signal is determined by modeling the waveform selection problem as a classification task. A waveform selector based on a four-layer multilayer perceptron is established to decide the optimal signal type, which is shown in Figure 12. The model’s input is a feature vector composed of the target information (i.e., distance, azimuth, elevation, and velocity), SNR, and a clutter power spectrum density obtained in the current dwell. The model’s output is the predicted signal type for the following dwell in the one-hot form. The model is trained offline with a training sample set constructed based on expert knowledge. The training data are obtained from field measurements. Prior to completing the network training, we fix the radar transmission parameters and transmission waveform. We conduct tracking tests on targets in different scenarios to obtain corresponding measurement accuracies. From these tests, we select the combination with the optimal measurement accuracy, which is then validated and evaluated by multiple domain experts. Based on this, we establish our neural network training database, which includes the optimal parameter combination, corresponding environmental factors, and waveform characteristics. We use the samples in this database to train the neural network. Using the backpropagation algorithm with gradient descent, we adjust and optimize the new network parameters. Once the training is finished, the model can select the optimal waveform online, according to the input feature vector.
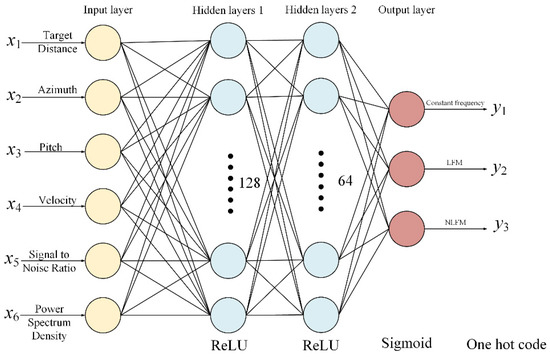
Figure 12.
Waveform selection neural network based on the multilayer perceptron.
In the second stage, the optimal parameters of the selected waveform will be searched in the corresponding parameter library utilizing the method proposed by Kershaw et al. [37]. The method integrates the parameter optimization procedure into the conventional Kalman filtering equations and solves it by minimizing the mean square tracking error. In this method, the Kalman filtering equations can be written as
where H is the state-to-measurement transformation matrix; is the measurement noise covariance matrix at time k that shows its explicit dependence on the transmitted waveform parameters; is the Kalman gain at time k; is the measurement at time k; F is the state-transition matrix; G is the state noise input matrix; is the covariance matrix of the process noise at time k; and are the prior state estimate and prior covariance matrix at time , respectively; and are the posterior state estimate and posterior covariance matrix at time k, respectively.
According to (12), it can be found that the covariance update equations in the Kalman filter are dependent on both (assumed known for all k) and . In [38], the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) of an unbiased estimator of is calculated by the inverse of the Fisher information matrix , i.e., . A is the transformation matrix between the receiver estimation parameters and the tracking system measurement vector, which is independent of the waveform parameters. If we use the CRLB as the estimation of , the measurement noise covariance matrix is dependent only on the background noise level and the transmitted waveform parameter vector. Hence, the measurement noise covariance matrix at time is known once the next waveform parameter vector is selected, thus allowing a prediction to be made of the smoothed tracking error covariance matrix at time . The matrix is given by
where the expressions for and have been included in full to show the dependence of the tracking error covariance on the measurement noise covariance matrix. The only unknown in (13) is the waveform parameter vector , thus providing us with a means of selecting the next transmitted waveform.
Taking the mean square tracking error minimization with a Kalman tracker as the criterion, the objective function of the optimal waveform parameters’ selection can be implemented by minimizing the trace of in terms of the transmitted waveform parameters, i.e.,
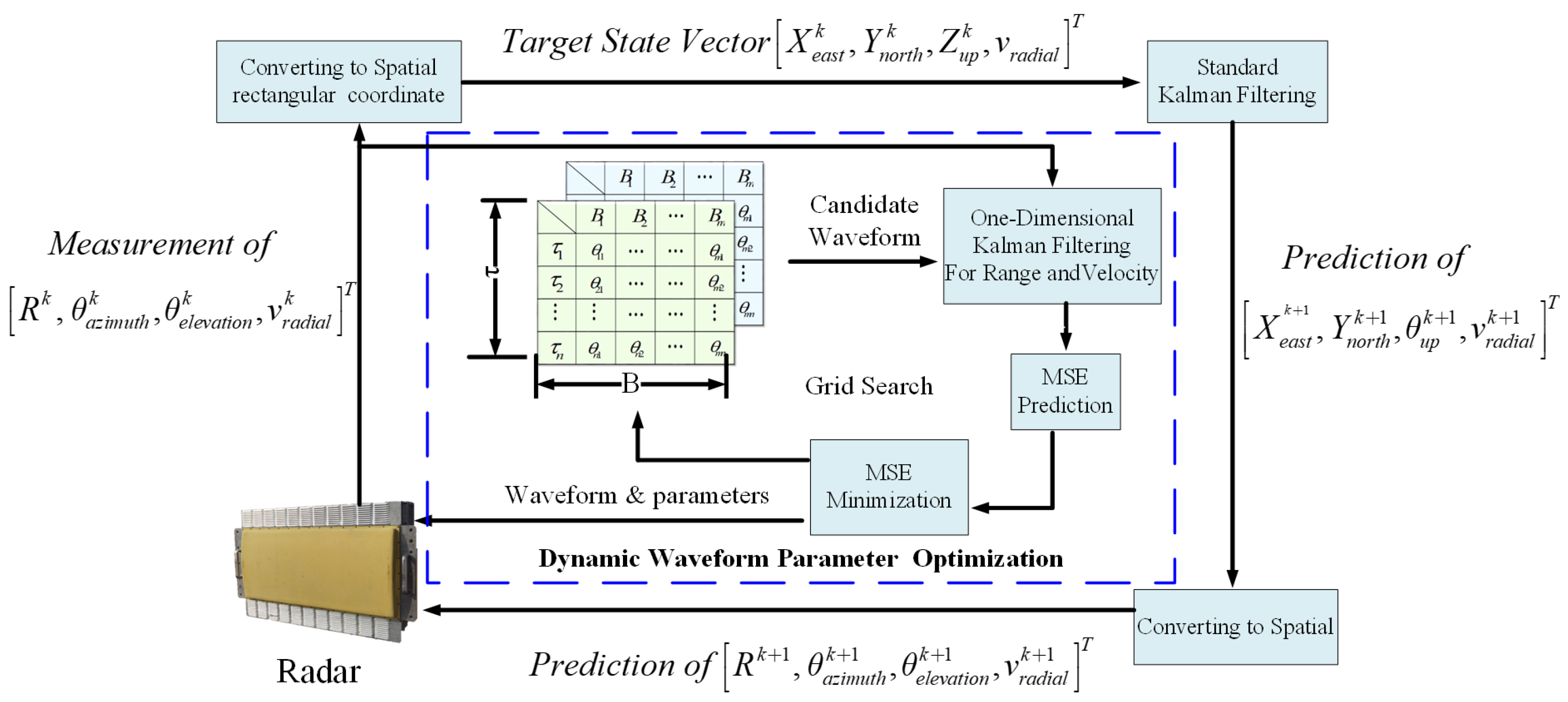
As presented in [37], the waveform parameters only influence the measurements of the range R and the radial velocity v. Hence, the Kalman tracker for searching for the optimal parameters of the waveform should work in a one-dimensional tracking scenario, concerning the range and the radial velocity. However, the standard Kalman tracker for a phase-array radar system usually works in four-dimensional space, including the three-dimensional position and the radial velocity. Accordingly, two Kalman trackers are adopted in the developed system to incorporate the waveform parameter optimization procedure into the standard target tracking process. One for conventional target tracking and the other for optimal parameter searching. The working flow of the waveform parameter optimization is illustrated in Figure 13, which determines the parameters of the selected waveform by a grid search over the space of allowable parameters in the predefined waveform library. Once the optimal parameters are determined, the selected waveform and the corresponding parameters will be sent to configure the radar system for the next dwell.
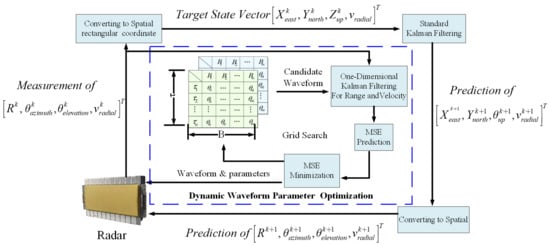
Figure 13.
Dynamic waveform parameter optimization algorithm based on Kalman filtering.
4.2. Software-Defined Arbitrary Waveform Generation and Processing
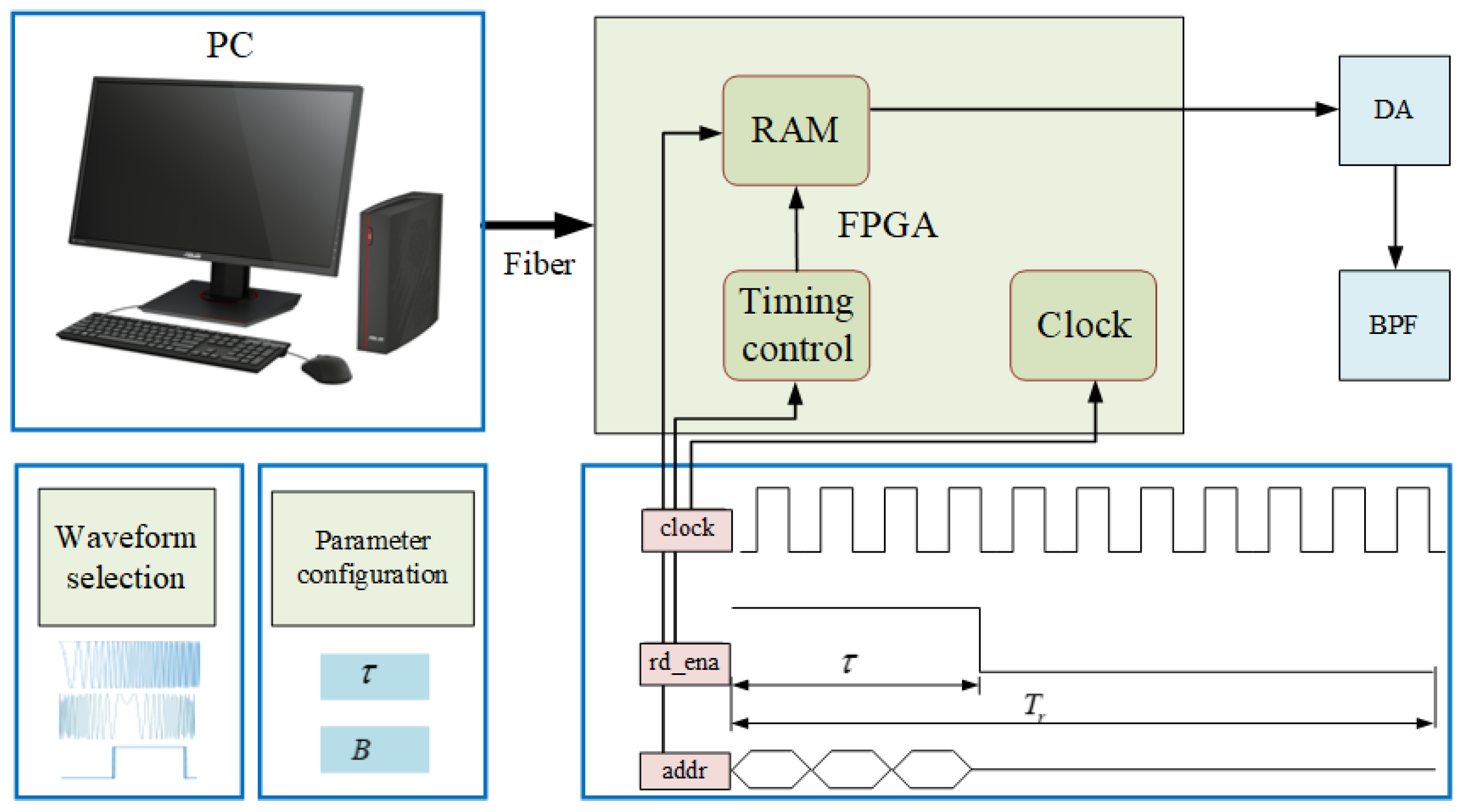
Although most of the current arbitrary waveform generators are implemented by combining a DSP and an FPGA, the developed arbitrary waveform generator with the software-defined architecture is built on a combination of a CPU and an FPGA. As shown in Figure 14, the arbitrary waveform generator comprises a digital signal optimizer, a digital signal generator, and a digital–analog converter (DAC). The digital signal optimizer is the software implemented in a high-level programming language and executed in a high-performance industry computer, determining the optimal waveform and the corresponding parameters. The digital signal generator is developed in the FPGA, which fetches the selected waveform and its parameters, analyzes the required parameter information, generates the corresponding parameters through timing control, and finally completes the waveform generation. The generated digital signal will be converted into an analog signal by the DAC and subsequently sent to the transmitter.
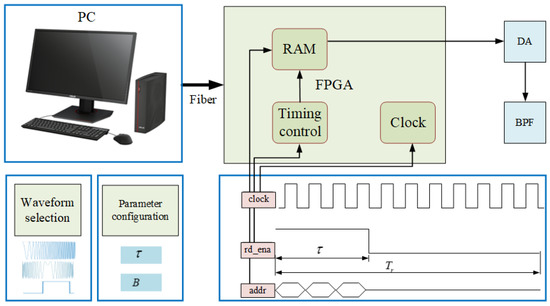
Figure 14.
Diagram of the arbitrary waveform generator with a software-defined architecture.
The signal type and the corresponding parameters are also used to construct the matched filter of the echoes in the signal and data processing subsystem on the CPU. In the upcoming dwell, pulse compression with the filter built with the optimal transmitted signal will be applied to the received baseband digital echoes, preparing range profiles for the following tasks, including MTD, CFAR, position measurement, and target tracking.
Compared with the mainstream arbitrary waveform generators based on the combination of an FPGA and a DSP, this system adopts a fully software-based structure, significantly alleviating the complexity of the FPGA timing design and the communication design between the DSP and FPGA, and guarantees the accuracy of the generated signal. Furthermore, such a structure is also a flexible and scalable framework into which advanced artificial intelligent approaches can easily be integrated to improve the waveform design and optimization performance, as well as to expand and update the candidate waveform library.
5. Experiments and Analysis
5.1. Experimental Setup
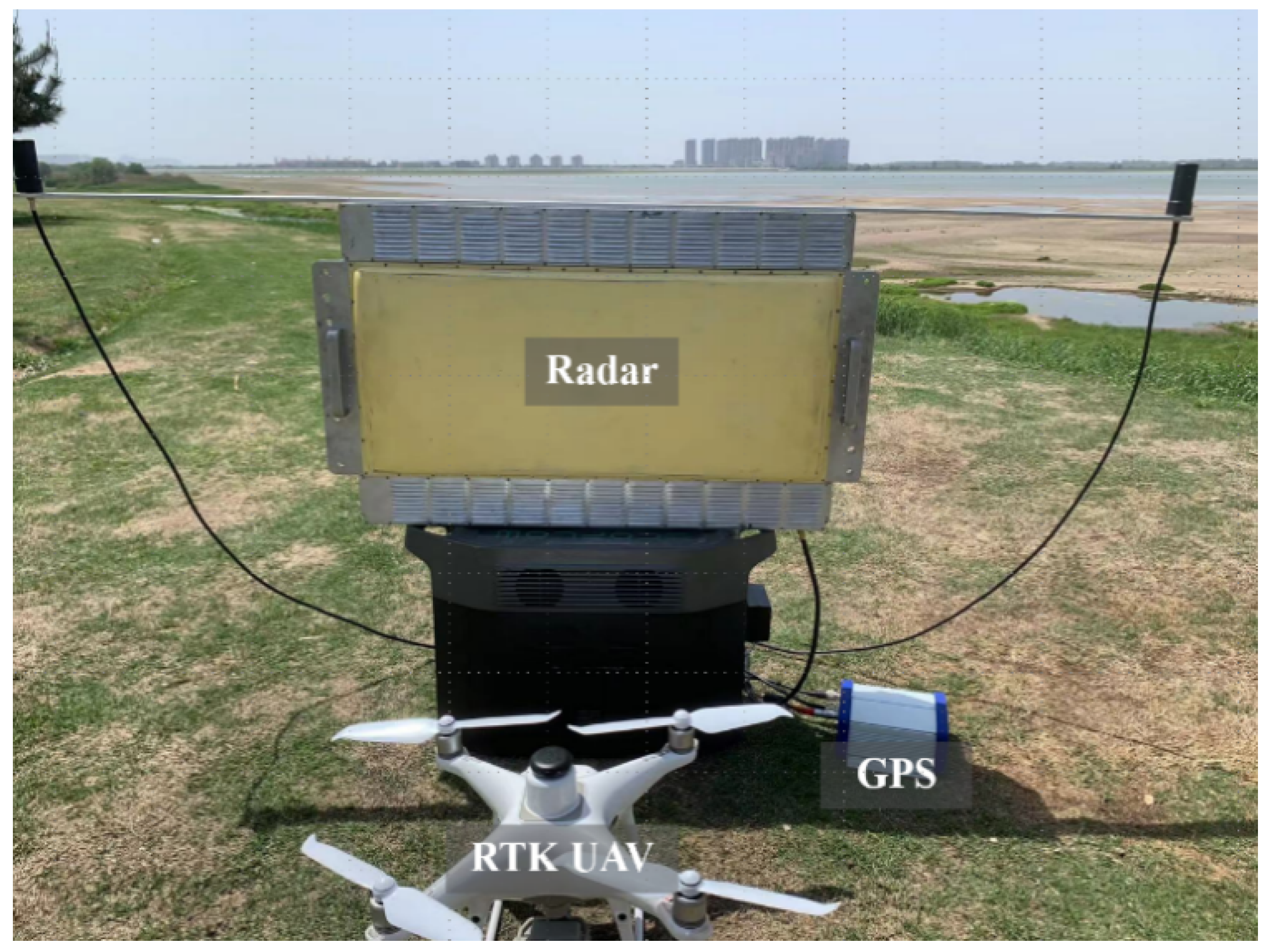
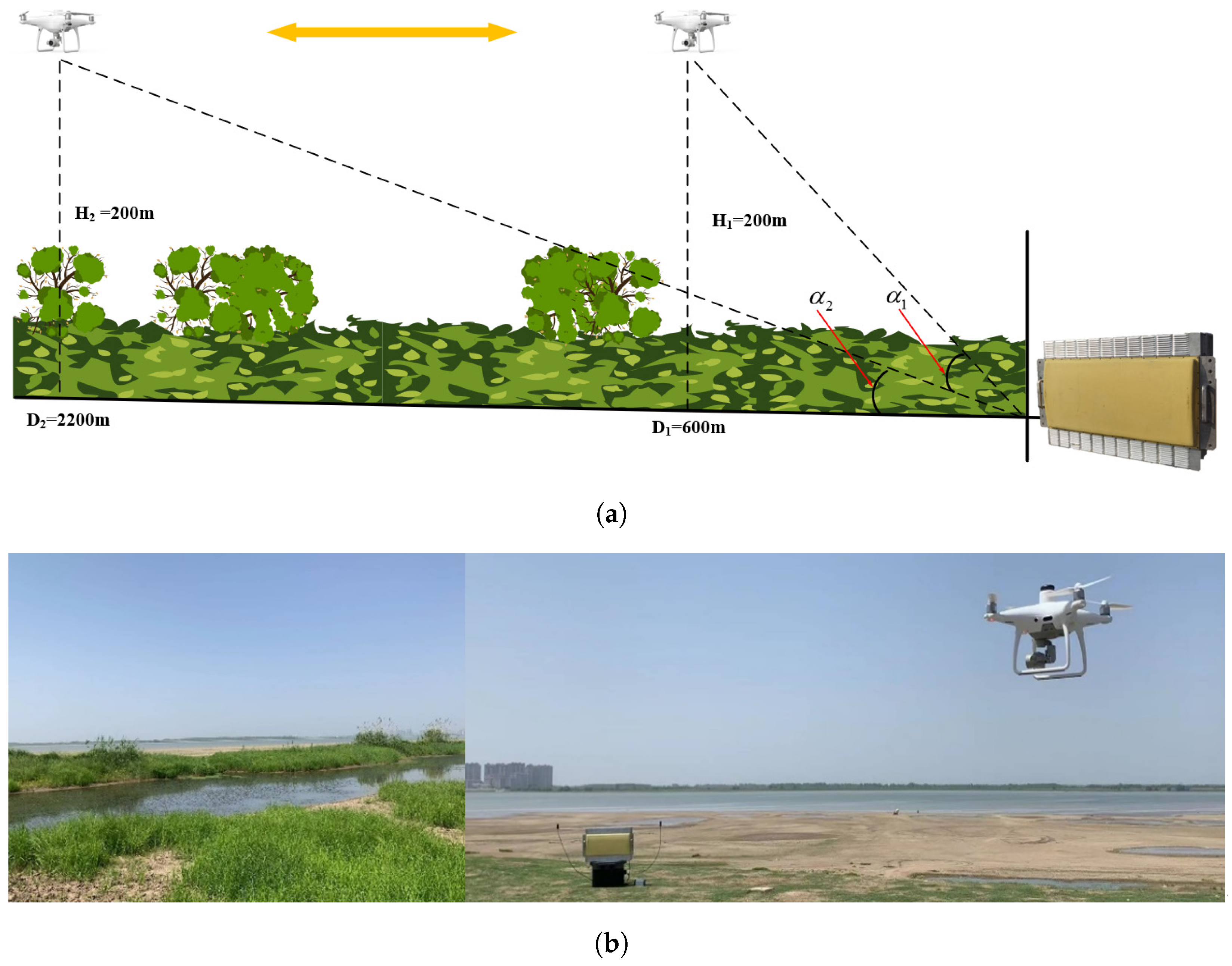
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of the developed radar system, a field experiment was conducted at Anhui East China Photoelectric Technology Research Institute. The diagram of the spatial relationship and the photography of the site view is presented in Figure 15. The radar system with only one array was placed at a flat beach against a small river, covered by grasses and brush. A 43 cm × 43 cm PHANTOM4 RTK unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) manufactured by Dajiang Innovation Technology Co., Ltd. (DJI), Shenzhen, China, was adopted as the candidate LSS target in the validation experiments. At the beginning of each experiment, the ground range between the UAV and the radar system is 600 m and the height of the UAV is 200 m. Due to the limited wireless transmission distance of the UAV flight control system, we set the maximum flight distance to 2200 m. In this experiment, the UAV flies horizontally at 10 m/s to 2200 m from the radar and then returns along the same route. A global positioning system (GPS) was installed on the UAV to provide ground truth for the accuracy evaluation.
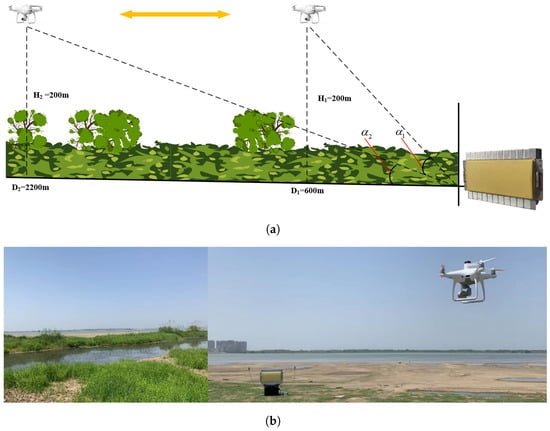
Figure 15.
The scenario of the validation experiment. (a) The spatial geometric relationship of the radar, the moving target, and the background clutter. (b) Photograph of the radar system, the UAV, and the environment.
The antenna transmits the raw data and all monitoring information of the antenna module to the server via 10G ethernet. The server stores the received data on the disk and then the processing software performs radar signal processing and data processing on the stored data.
The processing software synchronizes the received GPS timestamps to the target track information and stores them in the server disk. Meanwhile, real-time track and timestamp information of the UAV is stored in the UAV’s SD card. After the experiment, the position of the UAV and the measurements of the system are aligned according to the time stamp. The accuracy is measured by comparing the aligned measurements and the corresponding ground truth obtained by the UAV.
A series of evaluation experiments were conducted to comprehensively validate the developed system. First, the overall performance of the LSS target detection and tracking was evaluated by searching and tracking the UAV in the proposed scenarios with clutter caused by grasses and brush. Furthermore, ablation experiments were also carried out to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed transmit beam control approach and the adaptive waveform optimization and generation scheme. In the ablation experiments, the transmit beam control and the adaptive waveform optimization and generation were turned off by the system control code to demonstrate their contributions to the performance of the LSS target detection and measurement.
5.2. Performance Evaluation of the Developed Radar System
5.2.1. Detection and Tracking
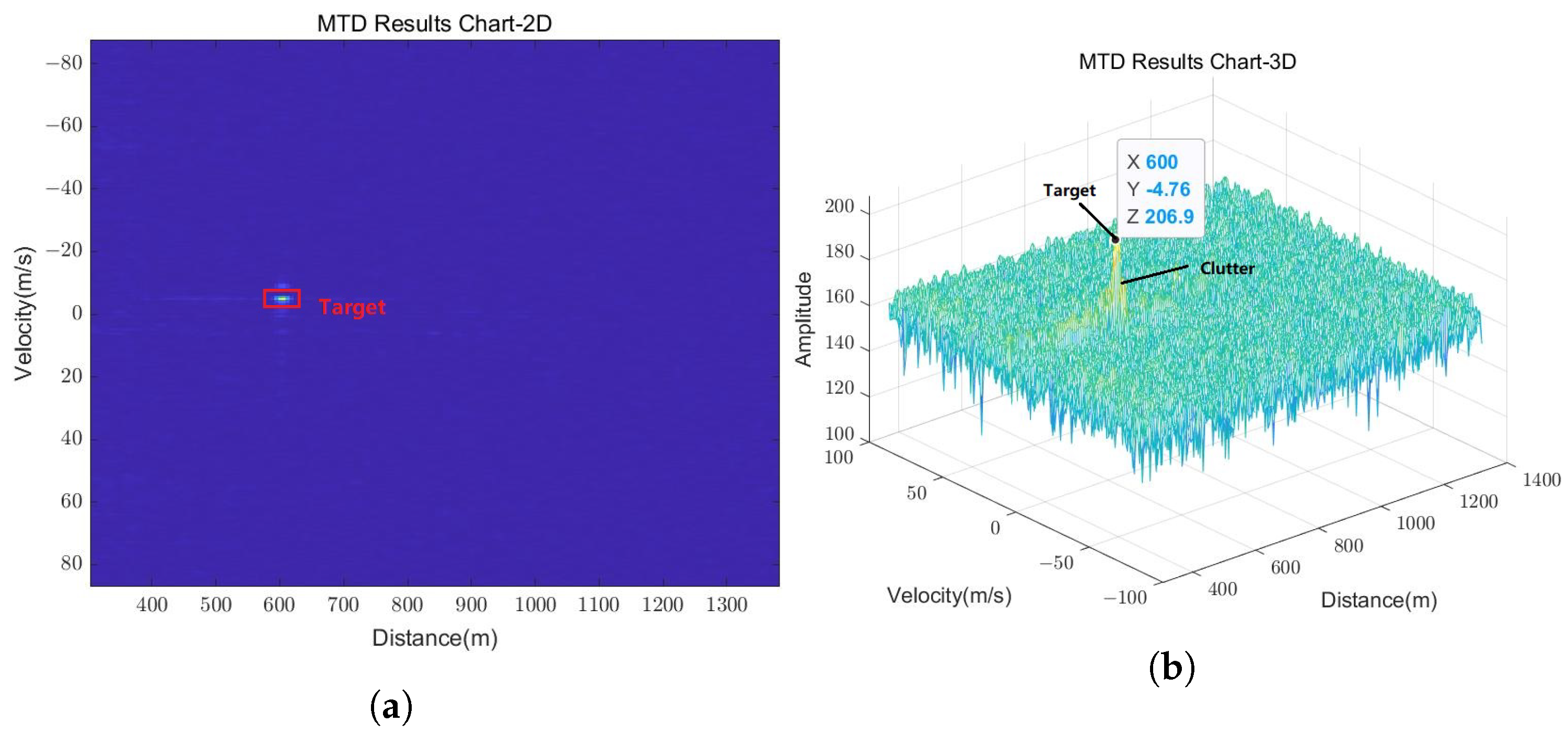
The detection and tracking performance of the developed radar were evaluated utilizing the UAV in the scenario presented in Figure 15. The 2D and 3D range-Doppler (RD) map of the UAV obtained by MTD with 256 pulses is shown in Figure 16, where the UAV appears in the range bin of 600 m and the velocity bin of 4.76 m/s. The target signal and the ground clutter can be easily distinguished due to the improved signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) brought about by coherent accumulation in MTD. Meanwhile, accurate target information can be obtained directly from the RD map, including the amplitude, the velocity, and the distance.
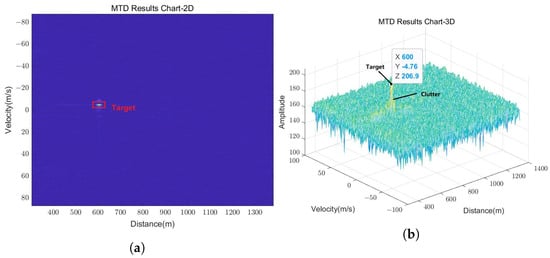
Figure 16.
Range-Doppler map of the UAV obtained by MTD with 256 pulses. (a) Two-dimensional MTD result chart. (b) Three-dimensional MTD result chart.
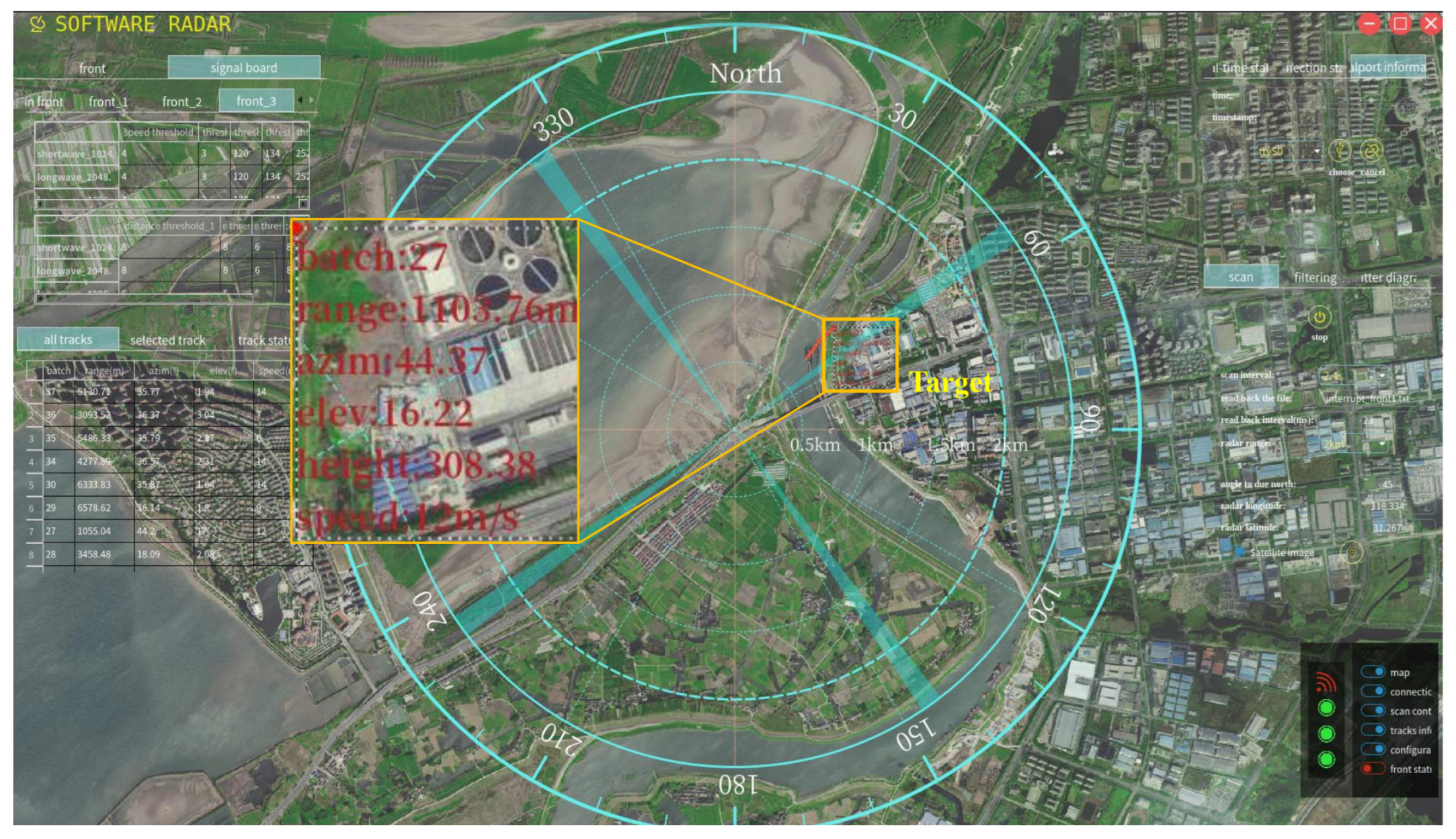
The candidate targets can subsequently be extracted from the RD map with a 2D CFAR detector, and the target detection results are sent to the P-type radar indicator presented in Figure 17. The satellite image of the experiment site is loaded with geocode and utilized as the base map in the radar indicator. The candidate target is plotted in the concentric circles of the indicator according to its range and azimuth angle. In addition, other information such as the elevation angle, the altitude, and the velocity is all listed in the target’s information table in the indicator, as shown in Figure 17.
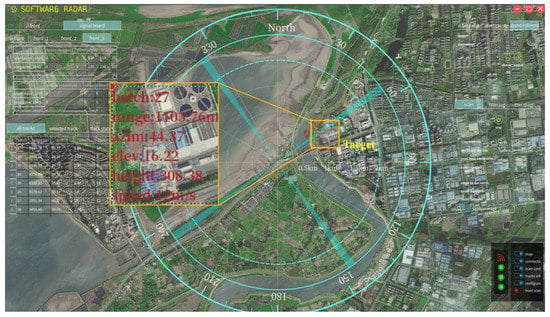
Figure 17.
The detection result shown in P Type Radar Indicator.
As shown in Figure 18, we installed a GPS module that can report the real-time position of the radar. Meanwhile, the RTK UAV can provide its real-time position information i.e., the latitude, the longitude, and the altitude. The GPS module and RTK UAV provide position information in the latitude and longitude coordinate system which will be converted according to the method described in “photogrammetric computer vision” to extract position information in the northeast celestial coordinate system [39]. By performing the GPS position and the RTK UAV information registration, the ground truth of the UAV’s relative distance, azimuth angle, and elevation angle to the radar can be obtained.
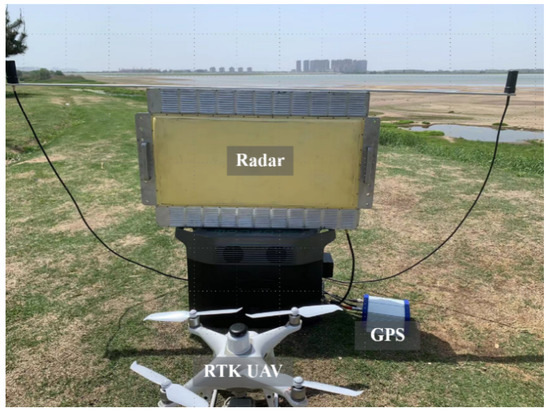

Figure 18.
The experimental equipment consists of a radar, UAV, and GPS.
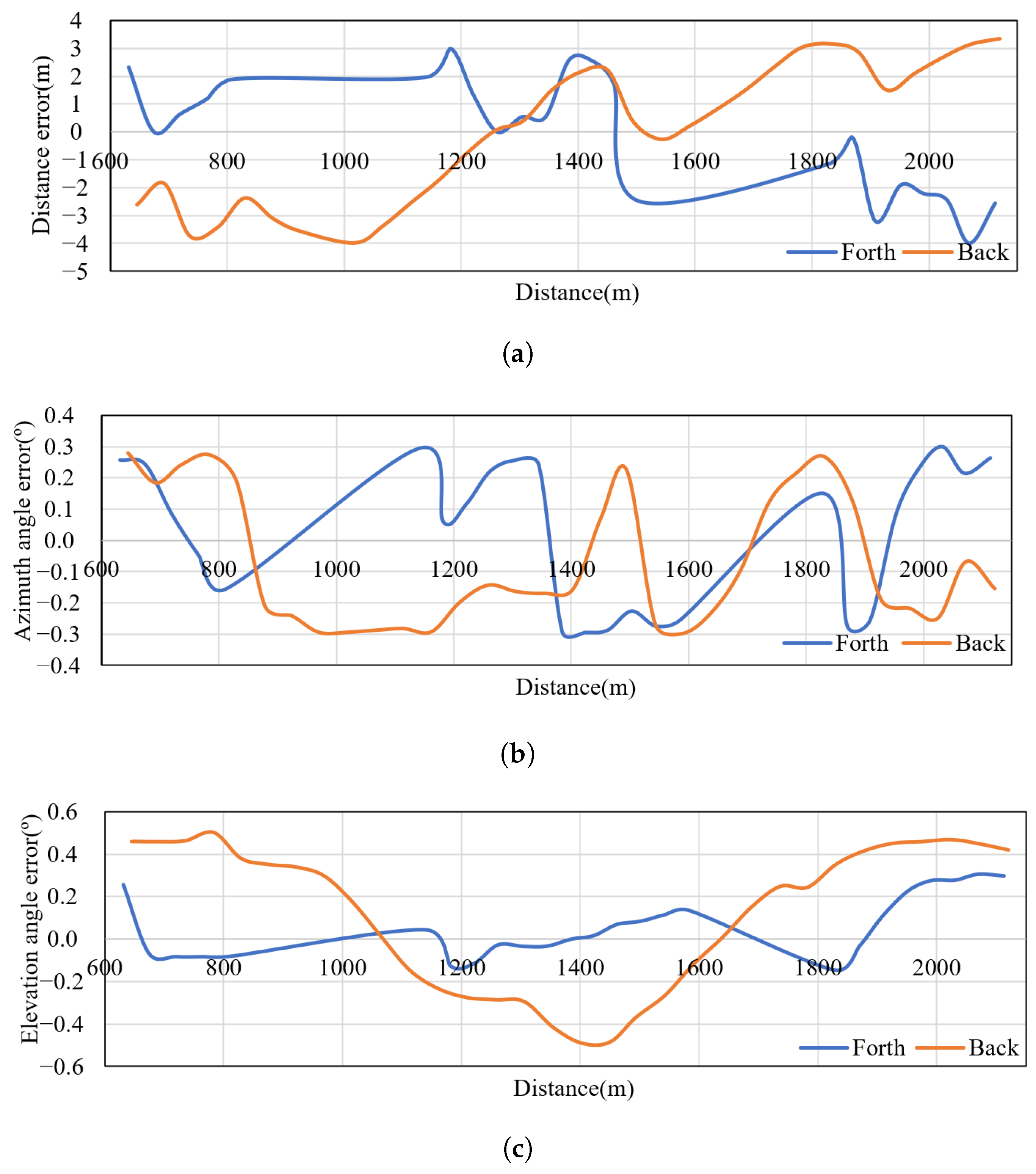
By comparing the measured data with the ground truth, the curve of the measurement errors of the distance, the azimuth angle, and the elevation angle can be depicted. The measurement experiments were carried out ten times to make a comprehensive evaluation, and the average errors of each parameter are plotted in Figure 19.
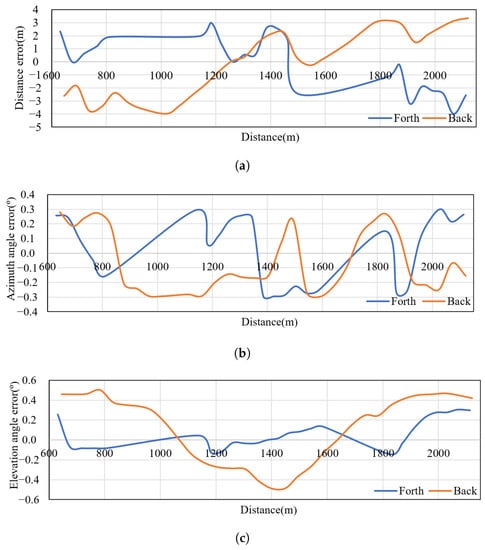
Figure 19.
Error curves according to the distance. (a) Distance curves’ variations with distance; (b) Azimuth angle curves’ variations with distance; (c) Elevation angle curves’ variations with distance.
The ideal error curve should oscillate around a zero value and gradually decrease in amplitude while the tracking process becomes stable. However, the actual error curves in Figure 19 do not meet expectations. Through analysis of the system, we attribute the results to two factors. First, the data rate of the RTK UAV and GPS is 20 Hz, while the radar data rate is 50 Hz, which causes registration errors due to inaccurate alignment during calculation. Secondly, the asynchronous clocks of the RTK UAV and the radar, as well as the absence of clock synchronization in the experiments, will lead to errors caused by clock jitter. Accordingly, the error curves stay within a certain range. As a result, we can derive the measurement accuracy of the system: range: ≤4 m, azimuth: ≤, and elevation: ≤0.5°, which meets the requirements of the system indices.
5.2.2. Real-Time Analysis
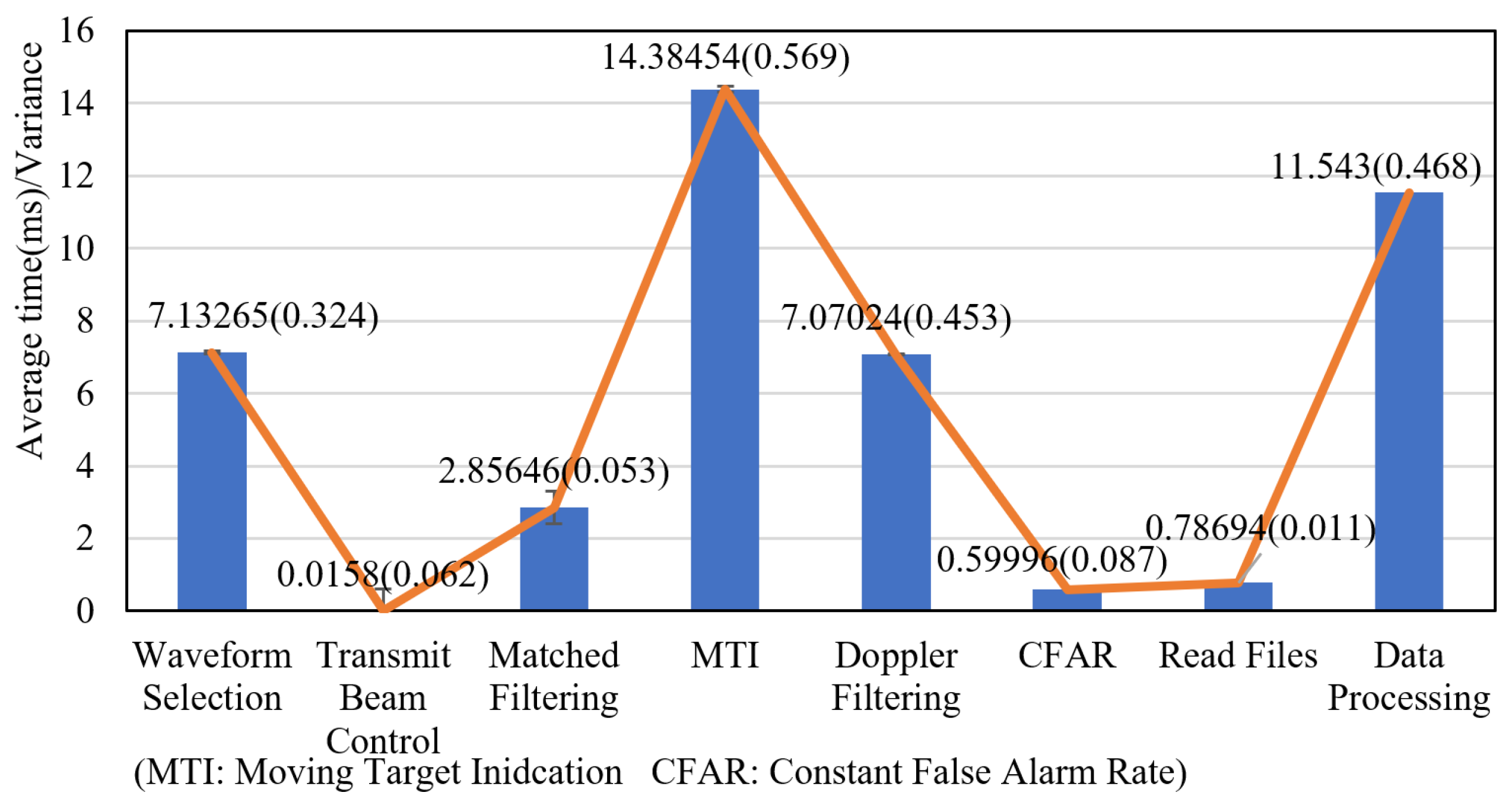
To verify the real-time performance of the entire system, we used the system’s internal clock to measure the time consumption of each processing step. The running time of each step was measured more than 10 times, and the average time and variance of each step are illustrated in Figure 20.
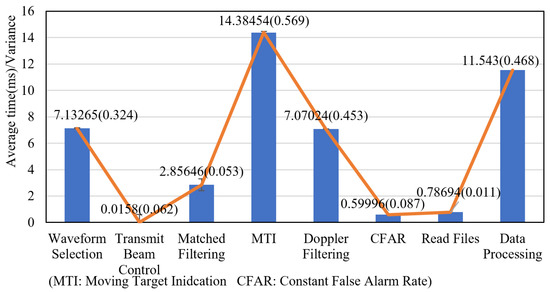
Figure 20.
Analysis of real-time performance.
As shown in Figure 20, the waveform selection, transmit beam control, signal processing, and data processing of the system is in a pipelined form, so although the total processing time is 45 ms, the processing time of each module is less than 20 ms, therefore, the system meets real-time requirements. The industry computer can guarantee the performance of the radar in real-time operation.
5.3. Ablation Experiments and Analysis
The main purpose of the ablation experiment is to verify the role played by transmit beam control and adaptive waveform optimization and generation in improving the system’s performance. Furthermore, in the same experimental environment, the corresponding target tracking and detection performance is tested with this feature turned on and off.
5.3.1. Validation of the Transmit Beam Control
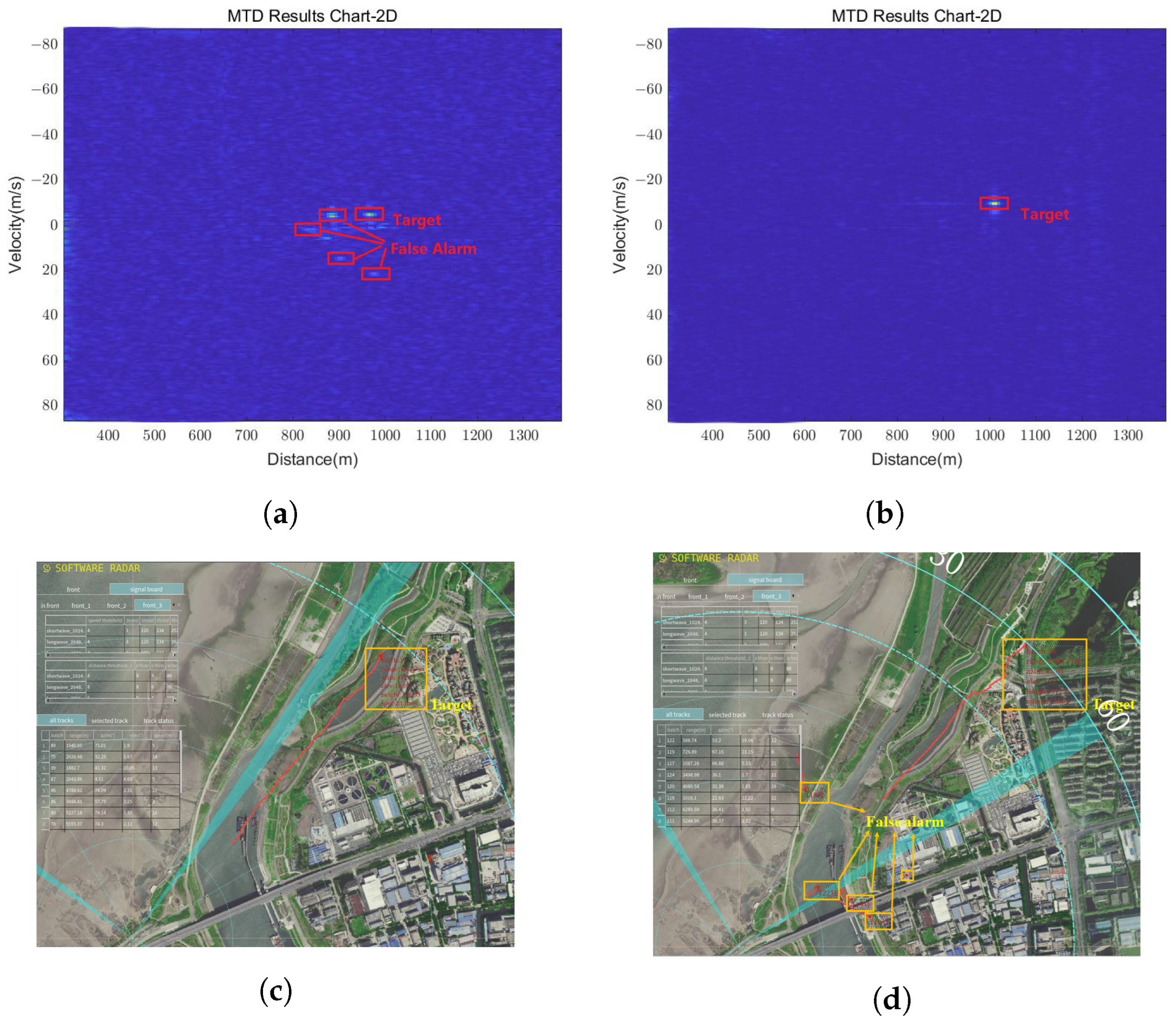
The contribution of the transmit beam control approach is validated by comparing the detection results obtained with and without this approach. Figure 21 depicts the comparison, where the first column represents the results obtained without the approach, and the second column shows the results obtained with the proposed method. In Figure 21a, there is heavy clutter around the candidate target in the range-Doppler map accumulated with 256 pulses thanks to ground echoes caused by the absence of the transmit beam control. In Figure 21b, most of the ground clutter is alleviated since the sidelobes of the transmit beam on the near-ground side are suppressed, and the reflected ground clutter is reduced. The detected targets in Figure 21c,d show the same results. Many false alarms, marked by red boxes, can be found in the detection result obtained without the transmit beam control, while few appear in the result obtained with the proposed method.
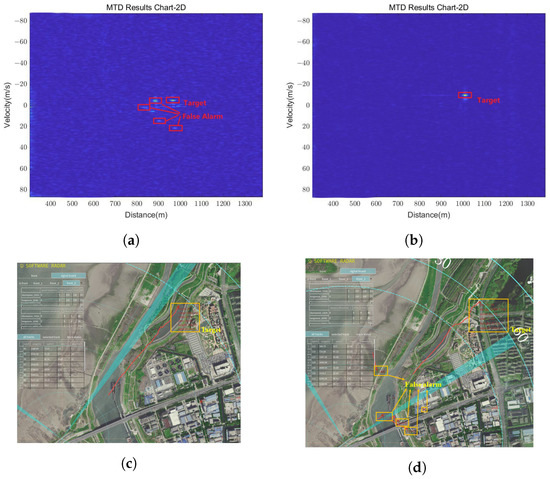
Figure 21.
The ablation experiment’s result of transmit beam control. (a) Two-dimensional MTD result chart, showing the target mixed with multiple false alarms. (b) Two-dimensional MTD result chart, showing an apparent target without any false alarms. (c) Detection result shown in P-type radar indicator, showing the target mixed with multiple false alarms. (d) Detection result shown in P-type radar indicator, showing an apparent target without any false alarms.
5.3.2. Validation of the Adaptive Waveform Optimization and Generation
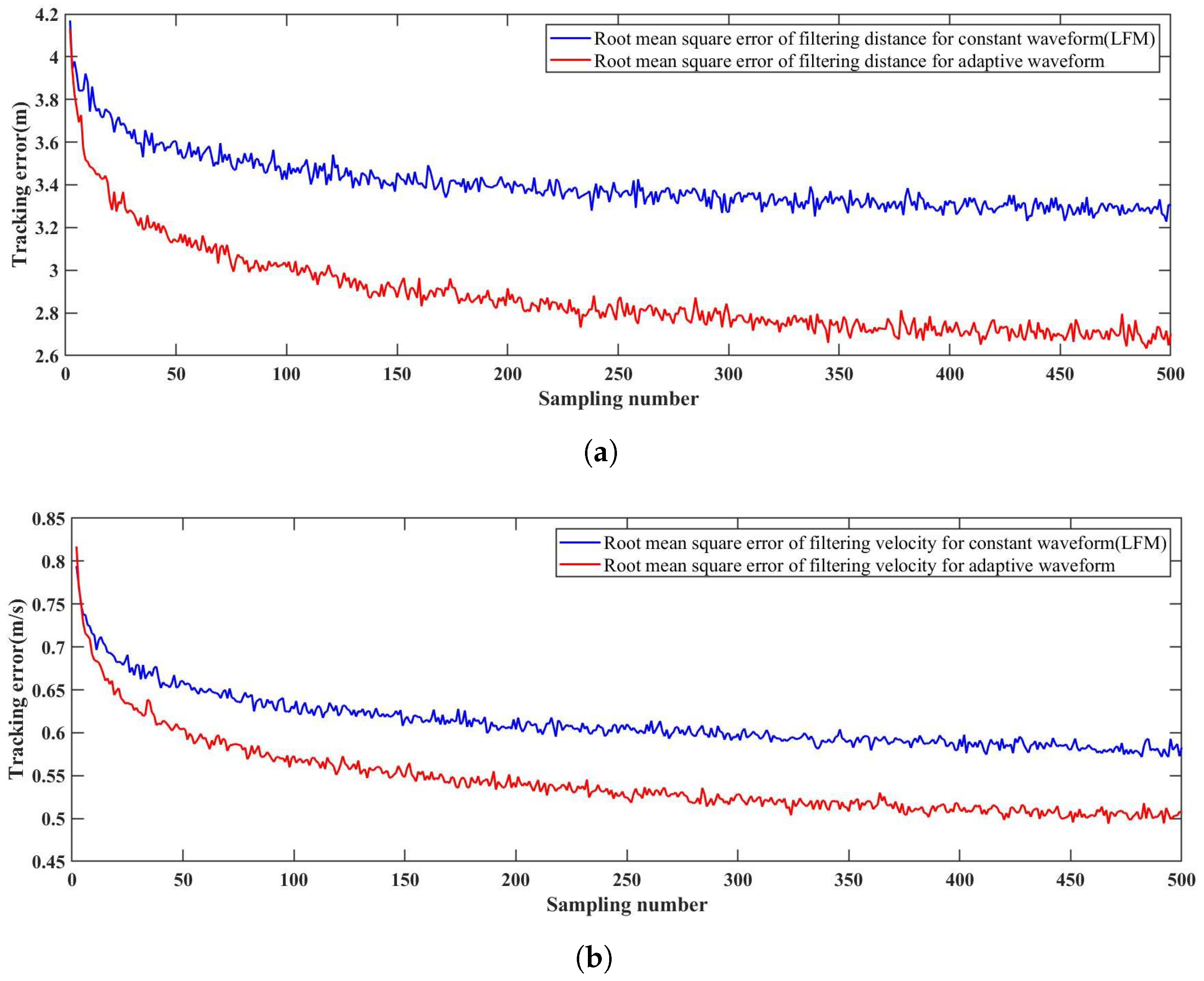
The contribution of the hierarchical adaptive waveform optimization and generation scheme is evaluated according to the target tracking accuracy. We conducted multiple ablation experiments and compared the results. The experimental results are shown in Table 3. In addition, we conducted comparative experiments using a constant waveform (LFM) and an adaptive waveform. The tracking error is calculated under two waveform selection methods for tracking targets in the same state. The root mean square error (RMSE) is utilized as an evaluation metric to analyze the effect of waveform parameter optimization. The calculation formula for the root mean square error in distance filtering using adaptive waveforms is as follows:
where is the measured distance using adaptive distance, is the ground truth of the UAV’s relative distance to the radar, and N is the sampling number of distance. The root mean square errors of the filtering distance and the filtering velocity are plotted in Figure 22. It can be seen that as the tracking loops are stably established, the root mean square errors of the measurements in the two conditions gradually decrease. However, the root mean square error in the measurement using the adaptive waveform scheme is smaller than that using the LFM.

Table 3.
Tracking errors of the adaptive waveform and the constant waveform.
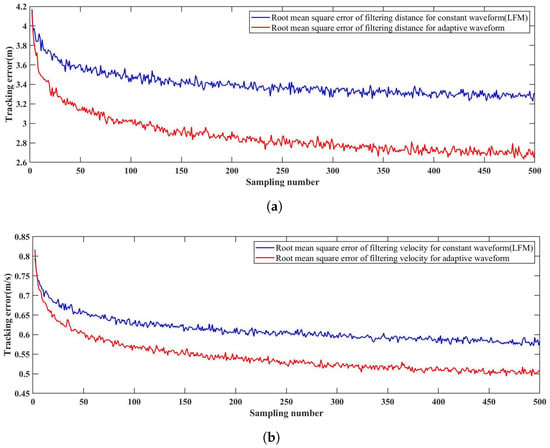
Figure 22.
Root mean square error curves for the constant waveform (LFM) and the adaptive waveform. (a) Range filtering results. (b) Velocity filtering results.
The above experiments proved that by using the adaptive waveform scheme, we could switch the type of waveform and update the corresponding parameters in real-time. Such an operation minimizes the mean square error in the target measurement by embedding mean square error in the Kalman filtering process and improving the measurement accuracy.
6. Conclusions
In this study, an X-band two-dimensional electronic scanning active phased array radar was developed in a software-defined radar architecture. It has numerous potential applications in LSS target detection under complex environments. To improve the detection performance and suppress the strong ground clutter, the authors proposed a transmit beam control algorithm based on the low peak-to-average ratio constraint. To further enhance the real-time target tracking accuracy, the authors devised a flexible radar waveform generator that adaptively generates various complex waveforms depending on the sensing of the current environment. Validation experiments in the UAV-simulated scenario demonstrate that the developed radar can obtain high detection and target tracking accuracy under complex backgrounds. Ablation experiments also proved the effectiveness of the proposed transmit beam control approach and the hierarchical waveform optimization and generation scheme.
With the increasing demand for LSS target detection, we anticipate that our radar can be applied to more fields due to its advantage of real-time performance and high accuracy under complex environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and validation, L.C. and H.Q.; methodology, L.C., Y.Z. and L.X.; writing—original draft preparation and editing, L.C., H.Q. and L.X.; Writing—review, L.Q., L.X., Y.Z. and Z.L.; project administration, H.Q., L.X. and Y.Z.; hardware, L.C., L.Q. and Z.L.; simulation testing, L.C., H.Q., Y.Z. and L.X.; field experiment, L.C., L.Q., H.Q., L.X. and Y.Z.; supervision, H.L. and S.T.; funding acquisition, H.L. and S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundations of China, grant number 41930110, and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, under Grant BK20221486.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xu, C.; Jin, S.; Ding, Z.; Kuang, Q.; Zhuang, S.; Li, H. Transmit beam control in low-altitude slow-moving small targets detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi’an, China, 15–17 April 2022; pp. 470–473. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, W.; Rao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Guan, J.; Dong, Y. Progress and prospects of radar target detection and recognition technology for flying birds and unmanned aerial vehicles. J. Radars 2020, 9, 803–827. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, J.; Li, Z. Application of acoustic detection technology in opening low altitude airspace. Electroacoust. Technol. 2015, 39, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Omologo, M.; Svaizer, P. Acoustic source location in noisy and reverberant environment using CSP analysis. In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Conference Proceedings, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9 May 1996; Volume 2, pp. 921–924. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, C.; Li, Z.; Hao, C.; Xiao, Q. Infrared small marine target detection based on spatiotemporal dynamics analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, R.; Ma, C.; Li, X. Fast and robust infrared small target detection using weighted local difference variance measure. Sensors 2023, 23, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Guo, J.; Zhu, R.; Le Kernec, J.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, T. Ground clutter mitigation for slow-time MIMO radar using independent component analysis. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y. A complete automatic target recognition system of low altitude, small rcs and slow speed (LSS) targets based on multi-dimensional feature fusion. Sensors 2019, 19, 5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldowesh, A.; Alnuaim, T.; Alzogaiby, A. Slow-moving micro-UAV detection with a small scale digital array radar. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, MA, USA, 22–26 April 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, J.; Rao, J.; Chen, R.; Li, F. Low-altitude infrared slow-moving small target detection via spatial-temporal features measure. Sensors 2022, 22, 5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C. Infrared detection of small-moving targets using spatial local vector difference and temporal sample consensus measures. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 113865–113874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Q.; Xu, H.; He, Z. LSS UAV target intelligent detection in urban complex environment. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Civil Aviation Safety and Information Technology (ICCASIT), Changsha, China, 20–22 October 2021; pp. 648–650. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, H. Fusion of infrared and visible images for remote detection of low-altitude slow-speed small targets. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 2971–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, H. Overview of radar LSS target detection technology. Mod. Def. Technol. 2018, 46, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, D.; Ma, J.; Ran, H. Radar detection method for low-altitude slow and small target based on radon transform. Mod. Def. Technol. 2018, 46, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Guan, J.; Huang, Y.; Yu, X.; Dong, Y.; Liu, N.; He, Y. Radar refinement of low-observable moving targets and applications. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2017, 35, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Analysis of detection system for “low, slow and small ” target based on multi living-agent. Guangxi Commun. Technol. 2012, 2, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tao, R.; Li, B. Research on complex information systems based on multi-active agents. Sci. China (Ser. E Inf. Sci.) 2008, 38, 2020–2037. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Qin, J.; Ma, X. Clutter-whitening-based low-speed weak target detection over the sea. Mod. Radar 2003, 25, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Hao, C.; Song, W.; Jiang, B.; Li, B. Adaptive slicing-aided hyper inference for small object detection in high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, Z.; Tian, S.; Jin, S. Transmit beam control in low-altitude slow-moving small targets detection based on peak to average power ratio constraint. Electronics 2022, 11, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, F.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z. Robust Beamforming Based on Covariance Matrix Reconstruction in FDA-MIMO Radar to Suppress Deceptive Jamming. Sensors 2022, 22, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, T.; Shlezinger, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Eldar, Y.C. Joint transmit beamforming for multiuser MIMO communications and MIMO radar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 3929–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, A.; Amin, M.G.; Zhang, Y.D.; Ahmad, F. Dual-function radar-communications: Information embedding using sidelobe control and waveform diversity. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 2168–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, P.M.; Blunt, S.D.; Metcalf, J.G. Simultaneous radar and communications emissions from a common aperture, Part I: Theory. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 1685–1690. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, P.M.; Ravenscroft, B.; Blunt, S.D.; Duly, A.J.; Metcalf, J.G. Simultaneous radar and communication emissions from a common aperture, Part II: Experimentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 1697–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Brüggenwirth, S.; Warnke, M.; Wagner, S.; Barth, K. Cognitive radar for classification. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2019, 34, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xu, F.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q. DDMA MIMO radar system for low, slow, and small target detection. J. Eng. 2019, 2019, 5932–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangbao, L. Research on antenna reconfigured software defined radar architecture. Mod. Navig. 2018, 9, 352–356. [Google Scholar]
- Baskar, S.; Ertin, E. A software defined radar platform for waveform adaptive MIMO radar research. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, USA, 10–15 May 2015; pp. 1590–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Hiari, O.; Mesleh, R. A reconfigurable SDR transmitter platform architecture for space modulation MIMO techniques. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 24214–24228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.M.; Chou, H.C.; Ke, C.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Li, C.T.; Chang, L.H.; Su, B.; Chu, T.S.; Wang, Y.J. An X-Band CMOS digital phased array radar from hardware to software. Sensors 2021, 21, 7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Luo, X.; Kong, F. A minimal software integrated processor design based on DBF radar system. J. China Acad. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2021, 16, 576–581. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B. Creating an ubuntu server virtual machine. In Introduction to Python Network Automation: The First Journey; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 169–222. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ding, Z.; Tian, S.; Jin, S. Robust adaptive transmit beamforming under the constraint of low peak-to-average ratio. Sensors 2022, 22, 7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassily, R.; Feldman, V.; Talwar, K.; Guha Thakurta, A. Private stochastic convex optimization with optimal rates. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kershaw, D.; Evans, R. Optimal waveform selection for tracking systems. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1994, 40, 1536–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trees, H.L.V. Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory, Part III; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Förstner, W.; Wrobel, B.P. Photogrammetric Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).