Exploring the Best-Matching Precipitation Traits in Four Long-Term Mainstream Products over China from 1981 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets and Preprocessing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
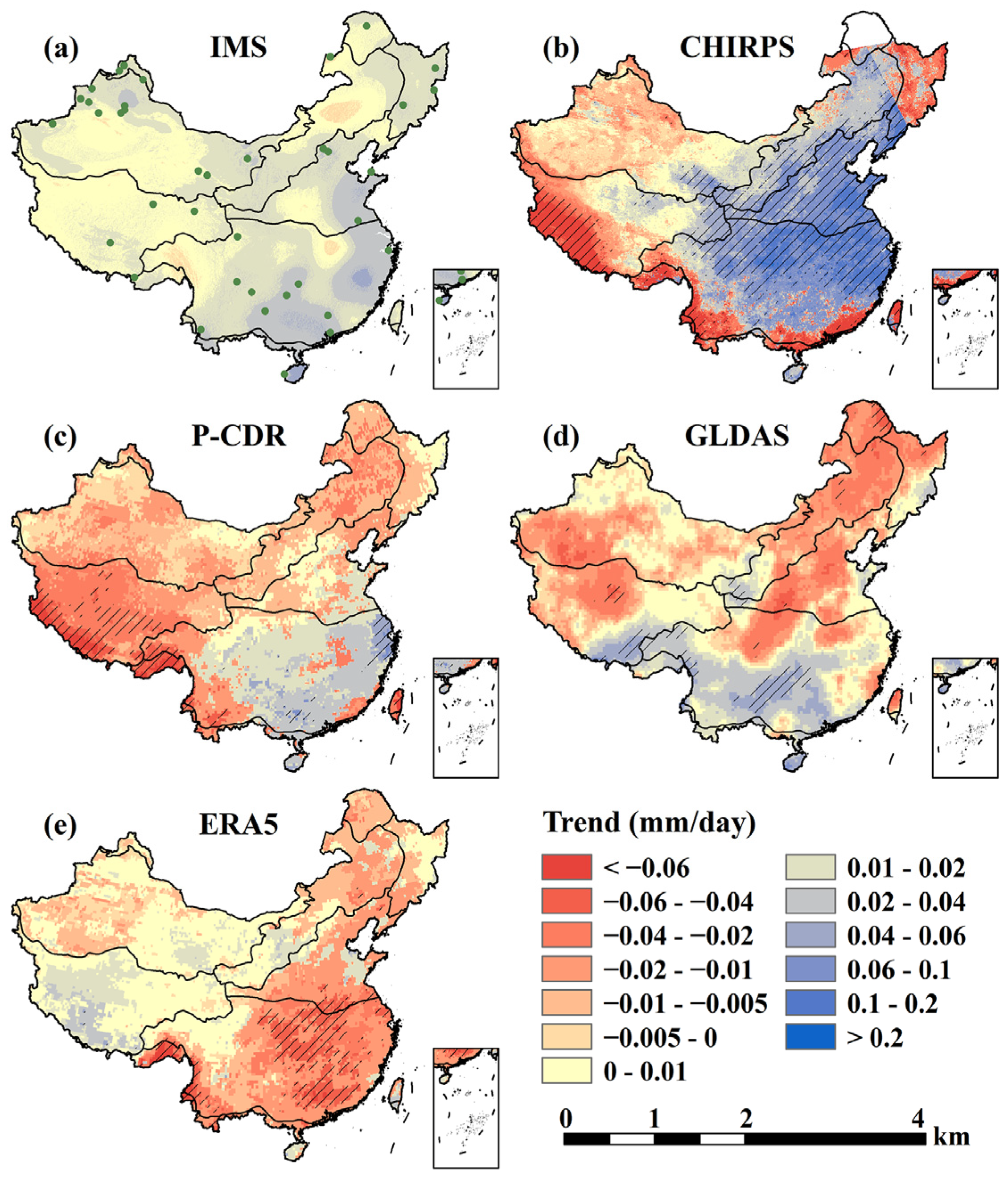
3. Results
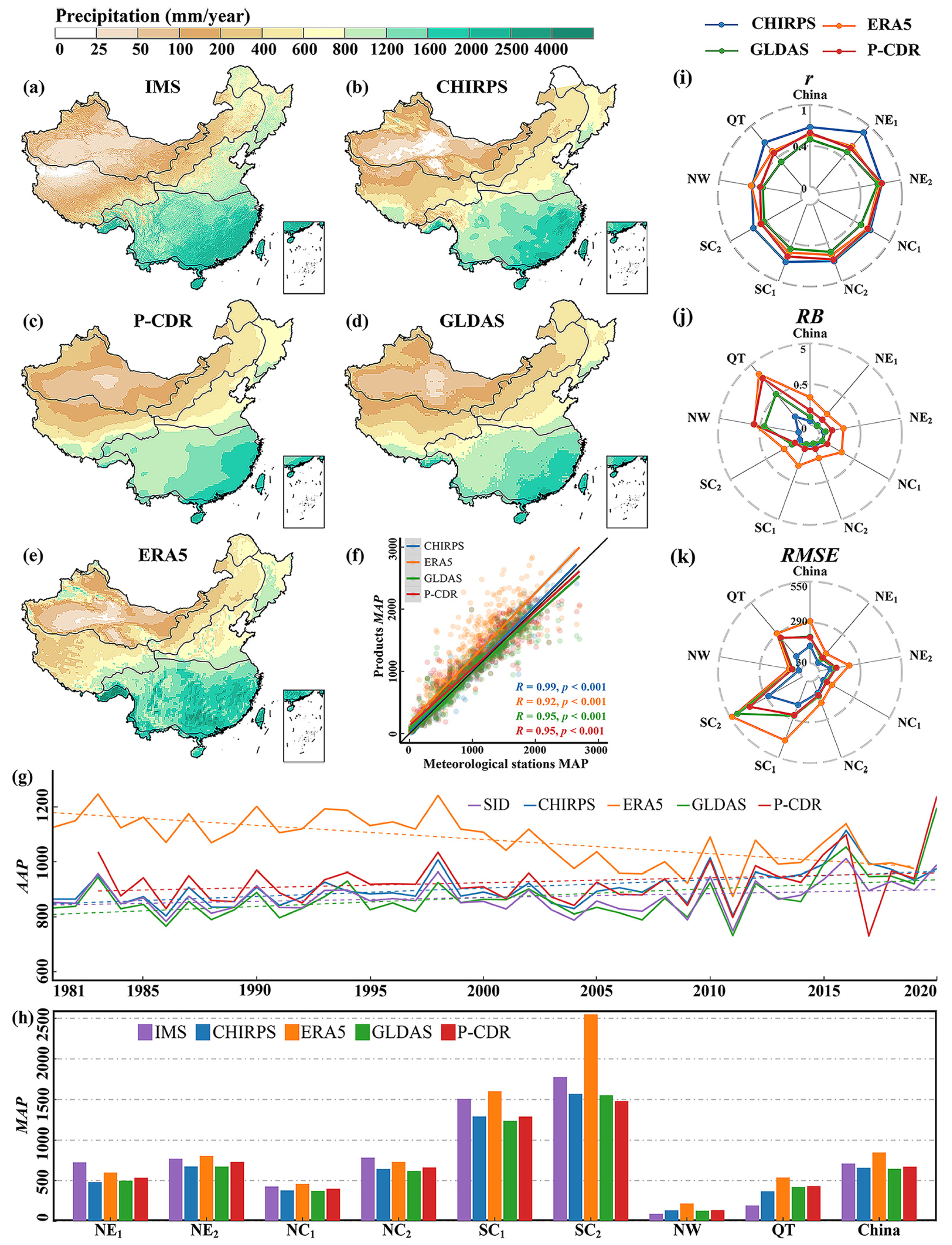
3.1. Spatial Patterns of Multi-Year Average Precipitation
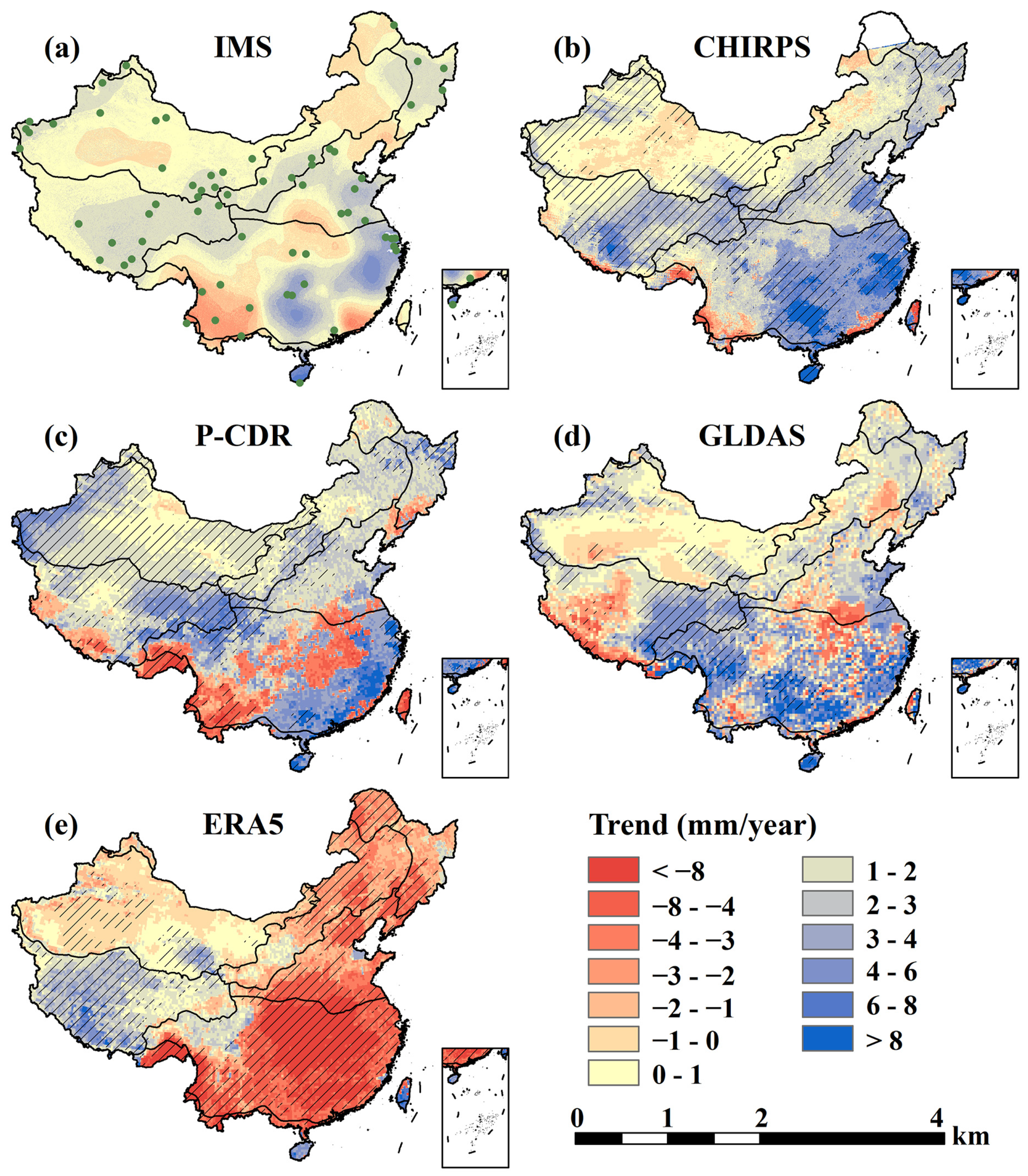
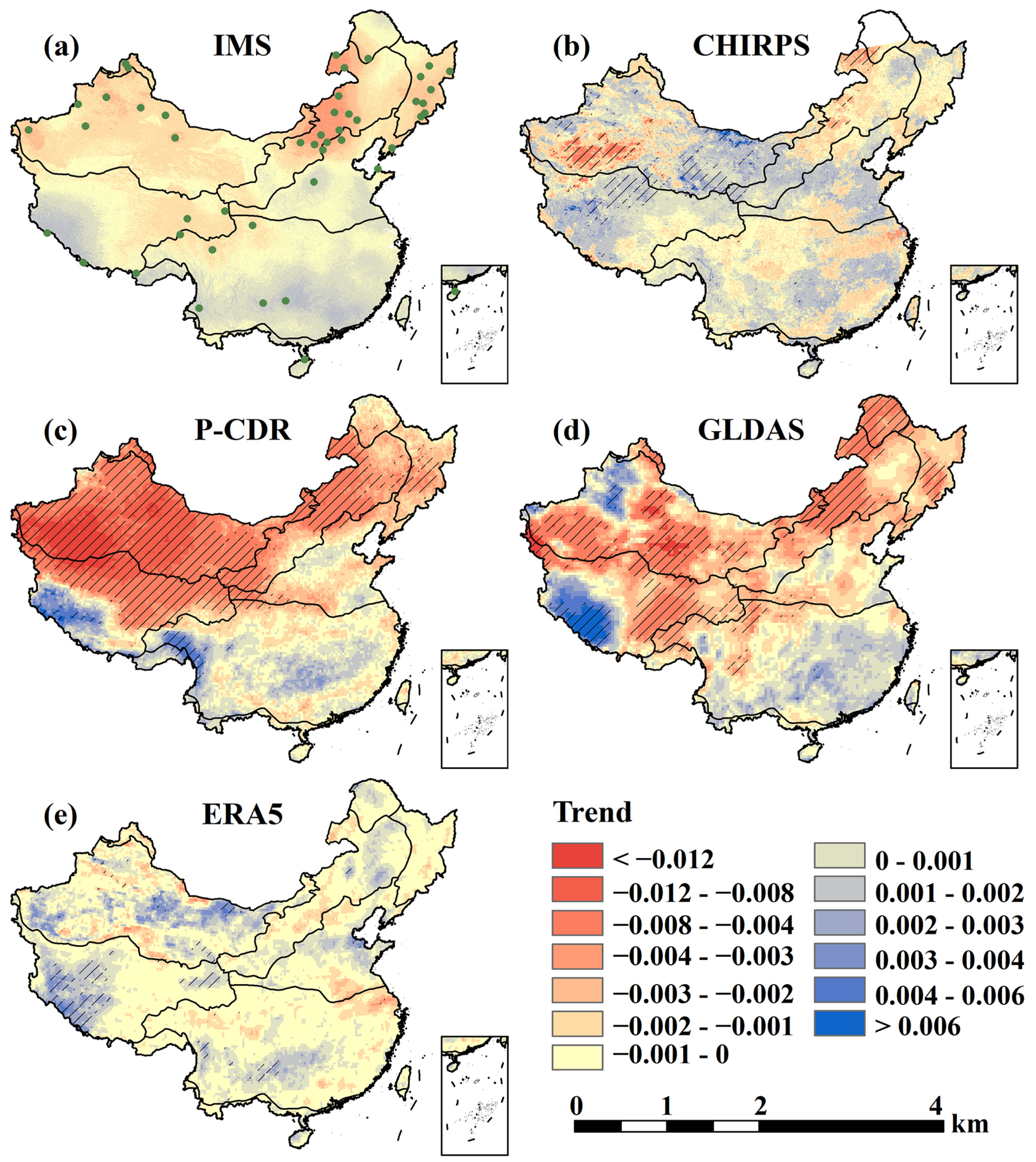
3.2. Trends of Annual Precipitation
3.3. Seasonality of Monthly Precipitation
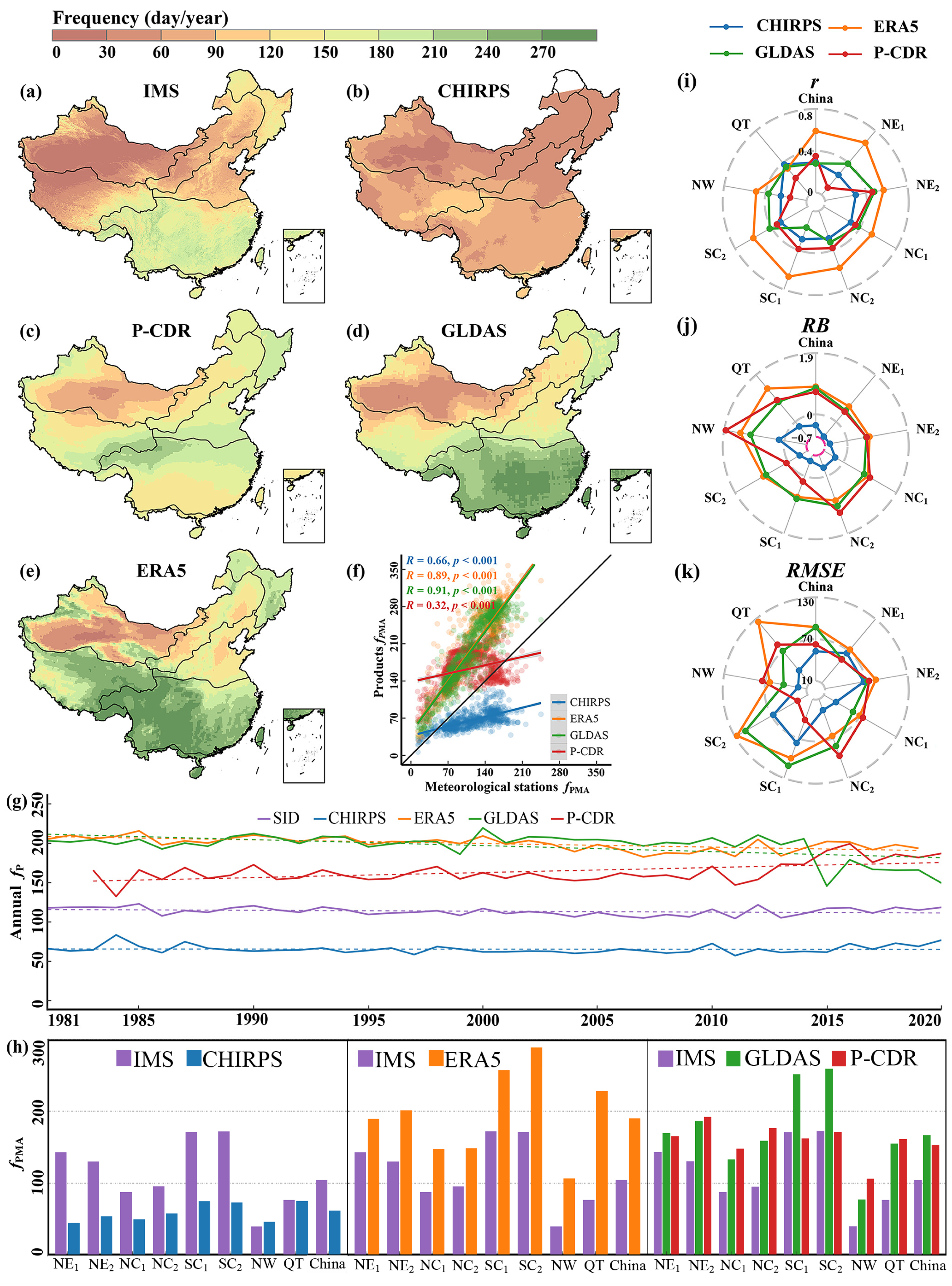
3.4. Frequency of Daily Precipitation
3.5. Intensity of Daily Precipitation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burls, N.J.; Fedorov, A.V. Wetter subtropics in a warmer world: Contrasting past and future hydrological cycles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12888–12893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, S.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Reconciling disagreement on global river flood changes in a warming climate. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Furtado, K.; Wu, P.; Zhou, T.; Chadwick, R.; Marzin, C.; Rostron, J.; Sexton, D. Increasing precipitation variability on daily-to-multi-year time scales in a warmer world. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.W.; Tissue, D.T.; Loik, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Erickson, R.A.; Zak, J.C. Soil microbial and nutrient responses to 7 years of seasonally altered precipitation in a Chihuahuan Desert grassland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1657–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Yu, G.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Mu, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Contrasting responses of gross primary productivity to precipitation events in a water-limited and a temperature-limited grassland ecosystem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 214–215, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Lv, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhuang, L. Future N deposition and precipitation changes will be beneficial for the growth of Haloxylon ammodendron in Gurbantunggut Desert, northwest China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B. Potentials of meteorological characteristics and synoptic conditions to mitigate urban heat island effects. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londe, D.W.; Dvorett, D.; Davis, C.A.; Loss, S.R.; Robertson, E.P. Inundation of depressional wetlands declines under a changing climate. Clim. Chang. 2022, 172, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Liu, S. Drought Affected Ecosystem Water Use Efficiency of a Natural Oak Forest in Central China. Forests 2021, 12, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, X.; Li, J. Impacts of Precipitation and Temperature on Changes in the Terrestrial Ecosystem Pattern in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palagi, E.; Coronese, M.; Lamperti, F.; Roventini, A. Climate change and the nonlinear impact of precipitation anomalies on income inequality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2203595119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, X.; Qian, C.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Variations and changes of annual precipitation in Central Asia over the last century. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, S.P.; Guan, K.; Caylor, K.K. Global Patterns of the Contributions of Storm Frequency, Intensity, and Seasonality to Interannual Variability of Precipitation. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, X.; Duan, Z.; Jiang, J.; Reichstein, M.; Jung, M. Impact of temporal precipitation variability on ecosystem productivity. WIREs Water 2020, 7, e1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, K. Quantifying the Sensitivity of Precipitation to the Long-Term Warming Trend and Interannual–Decadal Variation of Surface Air Temperature over China. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3687–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Balling, J.; Sy, V.D.; Herold, M.; Keersmaecker, W.D.; Slagter, B.; Mullissa, A.; Shang, X.; Reiche, J. Intra-annual relationship between precipitation and forest disturbance in the African rainforest. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.A.; White, C.T.; Silver, W.L.; Suding, K.N.; Hallett, L.M. Intra-annual precipitation effects on annual grassland productivity and phenology are moderated by community responses. J. Ecol. 2021, 110, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, S. Inconsistent changes in global precipitation seasonality in seven precipitation datasets. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 3091–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Novak, L.; Schneider, T. Predicting the Interannual Variability of California’s Total Annual Precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, C.W.; Hall, A.; Norris, J.; Chen, D. Constraining the increased frequency of global precipitation extremes under warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Min, S.-K.; Hu, T. Human influence on historical heaviest precipitation events in the Yangtze River Valley. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 024044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, P.Y.; Knight, R.W.; Karl, T.R.; Easterling, D.R.; Sun, B.; Lawrimore, J.H. Contemporary Changes of the Hydrological Cycle over the Contiguous United States: Trends Derived from In Situ Observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 64–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, H. Interannual Variation of the Spring and Summer Precipitation over the Three River Source Region in China and the Associated Regimes. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 7441–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, L.A.; Sala, O.E. Effect of interannual precipitation variability on dryland productivity: A global synthesis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 25, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, X. The role of land use change in affecting ecosystem services and the ecological security pattern of the Hexi Regions, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, L.; Biederman, J.A.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Kang, X.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, Z.; et al. Repackaging precipitation into fewer, larger storms reduces ecosystem exchanges of CO2 and H2O in a semiarid steppe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 247, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Ashouri, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-L. A Review of Global Precipitation Data Sets: Data Sources, Estimation, and Intercomparisons. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrawan, V.S.A.; Kim, W.; Touge, Y.; Ke, S.; Komori, D. A global-scale relationship between crop yield anomaly and multiscalar drought index based on multiple precipitation data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 014037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoleni, M.; Brandimarte, L.; Amaranto, A. Evaluating precipitation datasets for large-scale distributed hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Brissette, F.; Arsenault, R. Uncertainty of gridded precipitation and temperature reference datasets in climate change impact studies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 3331–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Lai, R.; Zhu, Z. Performance of satellite-based and reanalysis precipitation products under multi-temporal scales and extreme weather in mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, Y.; Anagnostou, E.; Berne, A.; Borga, M.; Boudevillain, B.; Buytaert, W.; Chang, C.-H.; Chen, H.; Delrieu, G.; Hsu, Y.; et al. Evaluation of GPM-era Global Satellite Precipitation Products over Multiple Complex Terrain Regions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Hu, D.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Di, Y. Spatio-temporal accuracy evaluation of three high-resolution satellite precipitation products in China area. Atmos. Res. 2020, 241, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, H.; Piao, S. Vegetation-Climate Relationship and Its Application in the Division of Vegetation Zone in China. Acta Bot. Sin. 2002, 44, 1105–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Z.; Xie, S.; Pan, C. Probability and Statistics, 4th ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 112–114. [Google Scholar]
- Eischeid, J.K.; Pasteris, P.A.; Diaz, H.F.; Plantico, M.S.; Lott, N.J. Creating a Serially Complete, National Daily Time Series of Temperature and Precipitation for the Western United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1580–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations-a new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.K.; Knapp, K.R.; Cecil, L.D.; Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P. PERSIANN-CDR: Daily Precipitation Climate Data Record from Multisatellite Observations for Hydrological and Climate Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Günther, G.; Li, D.; Stein, O.; Wu, X.; Griessbach, S.; Heng, Y.; Konopka, P.; Müller, R.; Vogel, B.; et al. From ERA-Interim to ERA5: The considerable impact of ECMWF’s next-generation reanalysis on Lagrangian transport simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3097–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Xu, N.; Yang, F.; Xu, K. Evaluation of spatial-temporal variation performance of ERA5 precipitation data in China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.-J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.P.D.; Lawler, D.M. Rainfall Seasonality Description Spatial Patterns and Change Through Time. Weather Clim. Extrem. 1981, 36, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, S.P.; Caylor, K.K. Climatological determinants of woody cover in Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4902–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A. Analysis and prediction of soil properties using local regression-kriging. Geoderma 2012, 171–172, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric test against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Baig, F.; Wrzesiński, D.; Naz, F. Identification and inter-comparison of appropriate long-term precipitation datasets using decision tree model and statistical matrix over China. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 5003–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, W.; Fan, Z.; He, X.; Sun, W.; Chen, S.; Wen, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. Evaluation of the ERA5 reanalysis precipitation dataset over Chinese Mainland. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, N. Evaluation of Eight High-Resolution Gridded Precipitation Products in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.E. Observed and simulated changes in precipitation seasonality in Argentina. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 40, 1716–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wu, G.; Xu, G.; Wang, K. Reduction in Precipitation Seasonality in China from 1960 to 2018. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Feng, Q.; Wen, X.; Barzegar, R.; Adamowski, J.F.; Zhu, M.; Yin, Z. Contributions of climate, elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration and land surface changes to variation in water use efficiency in Northwest China. Catena 2022, 213, 106220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Pandey, A.; Dayal, D. Spatiotemporal assessment of precipitation variability, seasonality, and extreme characteristics over a Himalayan catchment. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 147, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroulis, A.G.; Tsanis, I.K.; Daliakopoulos, I.N. Seasonality of floods and their hydrometeorologic characteristics in the island of Crete. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, A.A.; Yasuda, H.; Shimizu, K.; Haregeweyn, N.; Kawai, T.; Sultan, D.; Ebabu, K.; Belay, A.S. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of rainfall and erosivity in the Eastern Africa region. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4555–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Shi, C.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J. Accuracy of CHIRPS Satellite-Rainfall Products over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shangguan, D.; Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Evaluation and comparison of CHIRPS and MSWEP daily-precipitation products in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during the period of 1981–2015. Atmos. Res. 2019, 230, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmocker, J.; Liniger, H.P.; Ngeru, J.N.; Brugnara, Y.; Auchmann, R.; Brönnimann, S. Trends in mean and extreme precipitation in the Mount Kenya region from observations and reanalyses. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 1500–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelle, L.; Myhre, G.; Steensen, B.M.; Hodnebrog, Ø.; Alterskjær, K.; Sillmann, J. Urbanization in megacities increases the frequency of extreme precipitation events far more than their intensity. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 124072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Xu, M.; Zhao, F.; Tijjani, S.B. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Precipitation Amount, Frequency, Intensity, and Persistence in China, 1973–2016. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Sorí, R.; Vázquez, M.; Stojanovic, M.; Algarra, I.; Eiras-Barca, J.; Gimeno-Sotelo, L.; Nieto, R. Extreme precipitation events. WIREs Water 2022, 9, e1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Pan, M.; Roy, T.; Weedon, G.P.; Pappenberger, F.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Wood, E.F. Daily evaluation of 26 precipitation datasets using Stage-IV gauge-radar data for the CONUS. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D. Effects of climate change and human activities on vegetation coverage change in northern China considering extreme climate and time-lag and -accumulation effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Dataset | Category | Period | Resolution | Frequency | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHIRPS V2.0 | Remote Sensing | 1981–present | 0.05 × 0.05 | Daily | 50°S–50°N, land |
| PERSIANN-CDR | Remote Sensing | 1983–present | 0.25 × 0.25 | Daily | 60°S–60°N |
| ERA5-LAND Hourly | Reanalysis | 1950–present | 0.1 × 0.1 | Hourly | Global |
| GLDAS_NOAH025_3H 2.0 | Reanalysis | 1948–2014 | 0.25 × 0.25 | 3Hour | Global, land |
| GLDAS_NOAH025_3H 2.1 | Reanalysis | 2000–present | 0.25 × 0.25 | 3Hour | Global, land |
| Class Range | Rainfall Regime |
|---|---|
| [0–0.19) | Very equable |
| [0.20–0.39) | Equable but with a definite wetter season |
| [0.40–0.59) | Rather seasonal with a short drier season |
| [0.60–0.79) | Seasonal |
| [0.80–0.99) | Markedly seasonal with a long drier season |
| [1.00–1.19) | Most rain in 3 months or less |
| [1.20–1.83) | Extreme, almost all rain in 1–2 months |
| Statistic Metrics | Formula | Values Range | Perfect Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias | [−∞,+∞] | 0 | % | |
| r | [−1,1] | 1 | N/A | |
| RE | [−∞,+∞] | 0 | N/A | |
| RMSE | [0,+∞] | 0 | mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Q.; Liu, W.; Ao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Yang, L.; Yin, X.; Li, Y.; Han, T. Exploring the Best-Matching Precipitation Traits in Four Long-Term Mainstream Products over China from 1981 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133355
Li X, Zhang J, Feng Q, Liu W, Ao Y, Zhu M, Yang L, Yin X, Li Y, Han T. Exploring the Best-Matching Precipitation Traits in Four Long-Term Mainstream Products over China from 1981 to 2020. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(13):3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133355
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuejiao, Jutao Zhang, Qi Feng, Wei Liu, Yong Ao, Meng Zhu, Linshan Yang, Xinwei Yin, Yongge Li, and Tuo Han. 2023. "Exploring the Best-Matching Precipitation Traits in Four Long-Term Mainstream Products over China from 1981 to 2020" Remote Sensing 15, no. 13: 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133355
APA StyleLi, X., Zhang, J., Feng, Q., Liu, W., Ao, Y., Zhu, M., Yang, L., Yin, X., Li, Y., & Han, T. (2023). Exploring the Best-Matching Precipitation Traits in Four Long-Term Mainstream Products over China from 1981 to 2020. Remote Sensing, 15(13), 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15133355









