Abstract
The analysis and evaluation of landslide susceptibility are of great significance in preventing and managing geological hazards. Aiming at the problems of insufficient information caused by the limited number of landslide datasets, complex information of landslide evaluation factors, and low prediction accuracy of landslide susceptibility, a landslide susceptibility evaluation method based on the deep attention dilated residual convolutional neural network (DADRCNN) is proposed. First, the dilated convolution unit (DCU) is used to increase the network receptive field, aggregate multi-scale information, and enhance the model ability to capture the characteristics of landslide evaluation factors. Second, the deep residual module (DRM) is used to solve the issue of gradient disappearance and better extract data features by overlaying the residual function mapping layer and increasing the network depth. Finally, the channel attention residual module (CARM) is introduced to learn the varying importance of different landslide evaluation factors, and assign different weights to improve the susceptibility prediction accuracy. The experimental results show that the DADRCNN method can extract features around the sample points, expand the receptive field, and deeply mine the information. It mitigates the lack of sample information in training, focuses on important feature information, and significantly improves the prediction accuracy.
1. Introduction
Landslides are natural phenomena in which rock or soil masses on slopes slide downward along a certain weak surface due to external factors, such as river erosion, rainwater immersion, earthquakes, and artificial slope cutting. China has a vast territory, complex geographical environments, and variable geological conditions. As one of the most common types of geological disasters in China, landslides have the characteristics of wide distribution, large destructiveness, and high frequency, causing significant damage to human life and the ecological environment. Therefore, the study of regional landslide susceptibility is of great significance and practical application value for the prevention and treatment [1].
Traditional machine learning models take into account the nonlinear and uncertain effects of evaluation factors on landslide occurrence, and excavate landslide information hidden within the data, which has important significance for improving the evaluation effect of landslide susceptibility. At present, the mainstream traditional machine learning models used in landslide susceptibility mapping mainly include logical regression [2,3], random forest [4,5,6,7], decision tree [8,9], support vector machine [10,11,12], etc. With the continuous in-depth study of machine learning, it is found that the deep learning algorithms have more layers of nonlinear operation compared to “shallow learning” methods such as support vector machine. Deep learning algorithms gradually transform the initial low-level feature representation into more abstract high-level feature representation through multi-level processing [13].
Convolutional neural networks (CNN) are a common deep learning model utilized for landslide susceptibility mapping. These networks have the advantages of local connection, weight sharing, and pooling operations, reducing the number of training parameters and network complexity [13]. Liu et al. [14] introduced a model based on CNN, systematically compared its overall performance with three methods that consists of random forest (RF), logical regression (LR), and support vector machine (SVM), and drew maps of landslide susceptible areas, indicating that CNN has the advantage of learning more spatial information and reducing salt and pepper effects. Yi et al. [15], based on a multi-scale sampling strategy and CNN, attempted to compare three traditional machine learning algorithms including LR, multi-layer perception (MLP), and radical basis functions (RBF) neural network, drew landslide susceptibility maps, and highlighted the advantages of CNN’s great fitting. Jiang et al. [16] compared the effectiveness of CNN and traditional methods including adaboost, MLP, RF, naive bayesian (NB), decision tree (DT), and gradient elevation decision tree (GBDT) and highlighted the good results of CNN models in identifying landslide cluster regions.
Aiming at the problems of insufficient feature information obtained from model samples, the disappearance of learning gradients and the varying importance of different features for landslide susceptibility assessment, this study proposes a DADRCNN, which effectively increases the receptive field of the model, solves the problem of gradient disappearance, and focuses on the important information in the evaluation factors. The prediction accuracy of landslide susceptibility has been improved. The main contributions of this study are as follows:
(1) The DCU is integrated into CNN to obtain the characteristics of landslide evaluation factors. The DCU can enlarge the receptive field of the convolution layer which extracts disaster-causing factor features without increasing the network parameters, ensure that the size of the output feature map remains unchanged, and effectively improve the ability of the model to capture the characteristics of landslide evaluation factors;
(2) The DRM is utilized to extract deeper features from sample data. By superimposing the residual function mapping layer and increasing the network depth, the problem of model performance degradation caused by gradient vanishing can be avoided, which can better mine the data characteristics, and analyze the influence of landslide evaluation factors on the landslide susceptibility;
(3) The CARM is proposed to highlight the impact of main characteristic factors on landslides. According to the different hazard degrees of landslides caused by various landslide evaluation factors, it learns the importance of different features, assigns different weights, highlights important features, and ignores secondary features to achieve effective improvement in prediction accuracy of landslide susceptibility;
(4) In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed DADRCNN method, the study conducted an experiment on landslide susceptibility using 10 landslide evaluation factors in Hanzhong City, Shaanxi Province. The results show that the DADRCNN method can effectively predict the landslide susceptibility with high accuracy and reliability.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
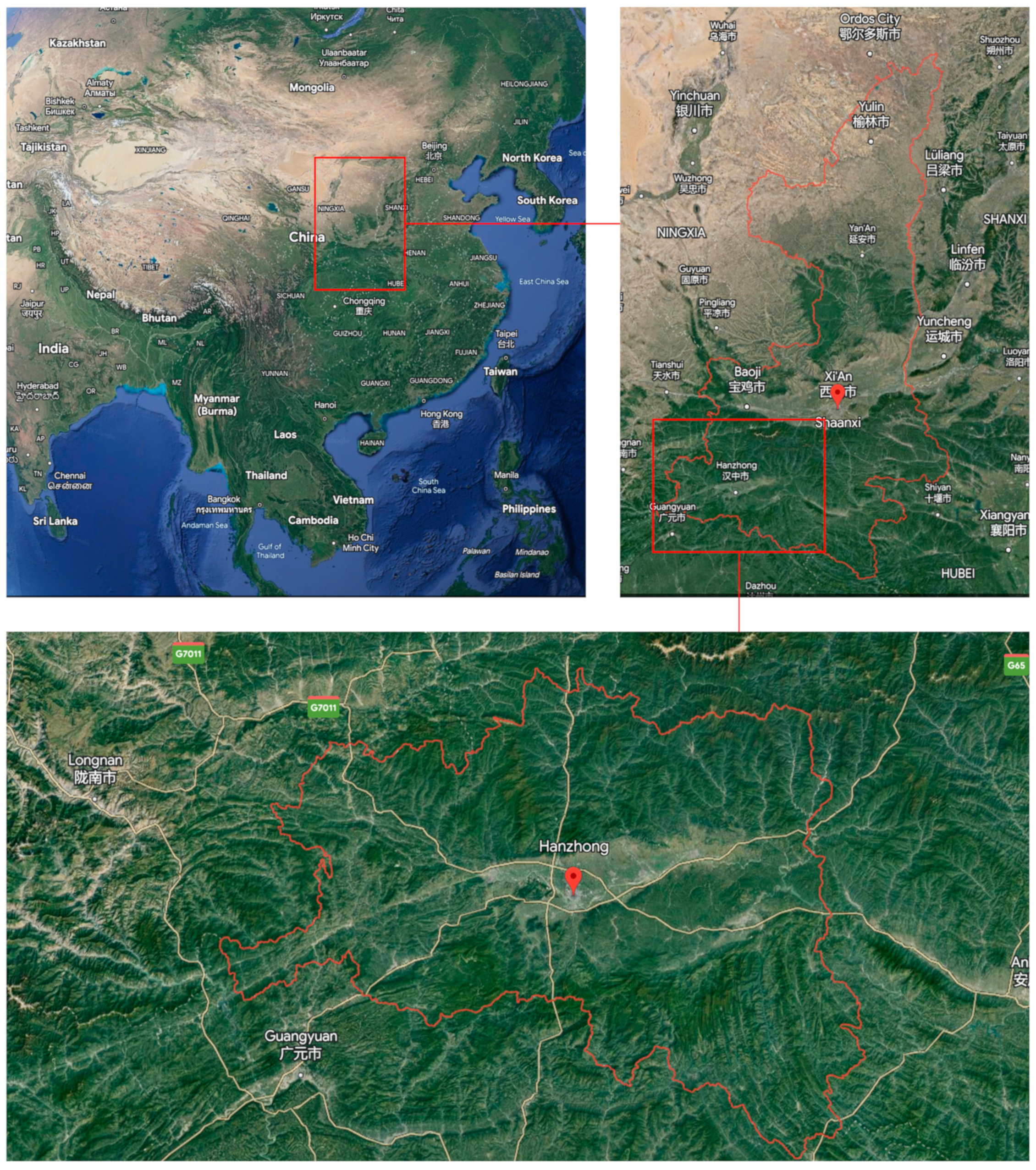
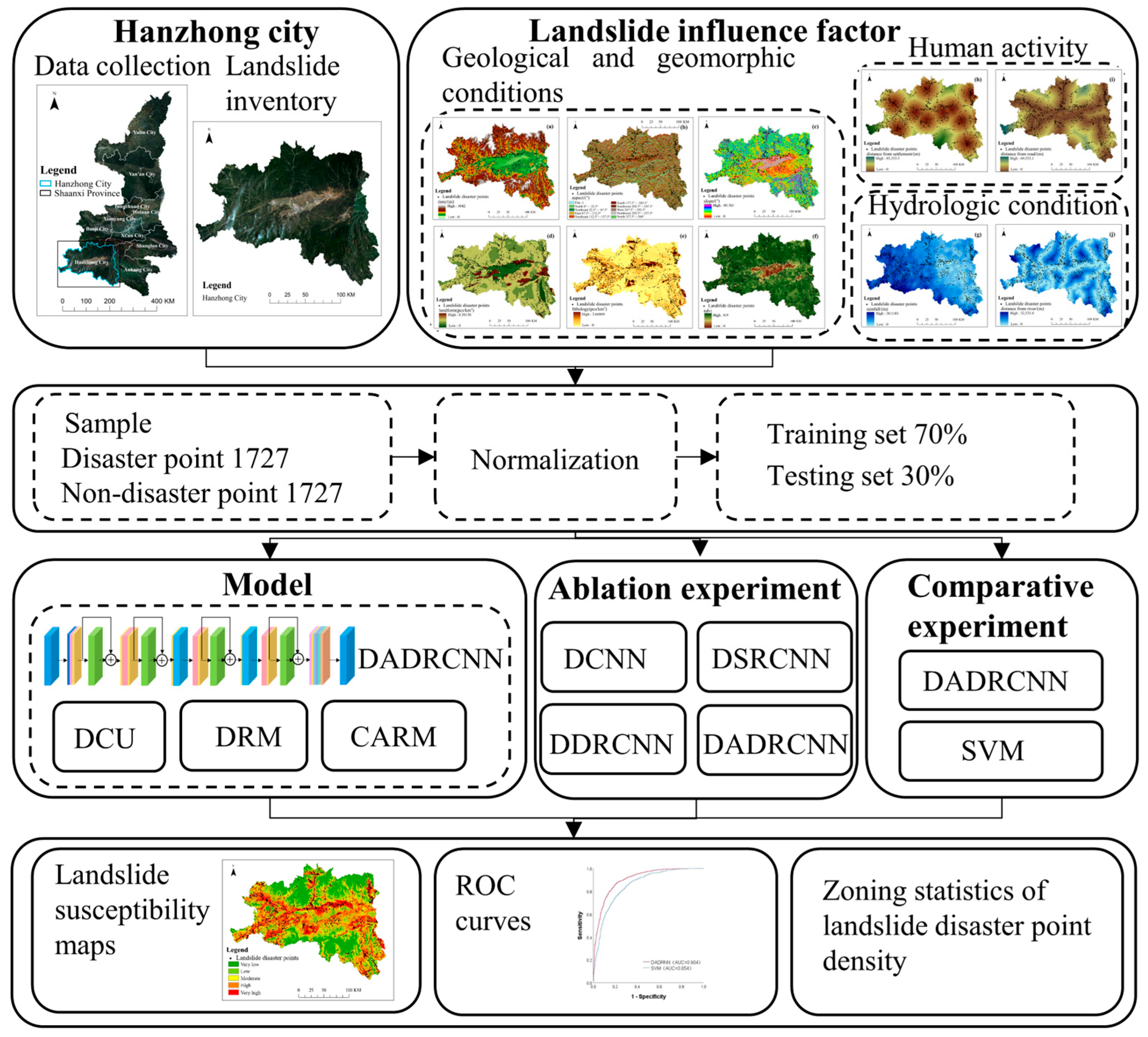
Hanzhong City is located between 105°29′14″E and 108°16′49″E, and 32°08′52″N and 33°52′46″N in the southwest of Shaanxi Province, with a total area of 27,246 square kilometers, a length of 261.5 km from east to west, and a width of 192.6 km from north to south. The terrain is high in the north and low in the south, and the landform types are diverse. Among them, the mountain areas are the shallow and middle mountain areas which are formed by the southern slope of the Qinling Mountains, with altitudes ranging from 701 to 2038 m; the hills are broad valleys and shallow hills formed by the piedmont alluvial fan, with altitudes between 601 and 800 m; the flat dam is the first and second steps of the alluvial plain of the Han River, with altitudes ranging from 500 to 600 m. The geotectonic areas in Hanzhong City are located between the Qinling fold system and the Yangtze paraplatform that they are called first-order geotectonic areas. The geological structures are complex, with strong magma and volcanic activities. The mineral resources are widely distributed, with superior metallogenic conditions and relatively complete types, mainly consisting of shallow marine metallic minerals with geosyncline sedimentary characteristics and non-metallic minerals. Hanzhong City has an obvious vertical difference in climate, with an annual average temperature of about 14.5 °C and annual precipitation of about 890.6 mm. The water system is mainly composed of the Hanjiang River system and the Jialing River system. The Hanjiang River system runs from west to east, with a mainstream length of 277.8 km and a drainage area of 19,692 square kilometers, and it is the backbone of the Hanzhong City water system network; the Jialing River system runs from north to south, with a main stream length of 141.7 km and a drainage area of 7554 square kilometers, and it is a major transit river in the city.
Hanzhong City has complex geological conditions and diverse geomorphic types. With the needs of social and economic development, human demand for various natural resources is also increasing and the scale of human life and engineering activities is gradually expanding which poses a serious threat to environmental and engineering safety, and geological hazards are significantly increasing. Therefore, Hanzhong City is selected as the research area of this study. The geographical location of Hanzhong City is shown in Figure 1.
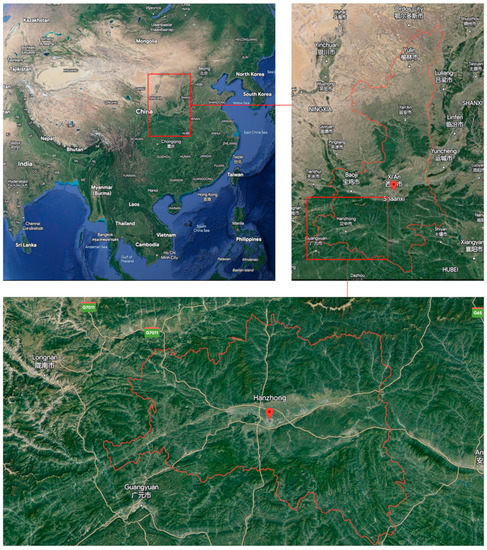
Figure 1.
The geographical location of the study area.
2.2. Data Source
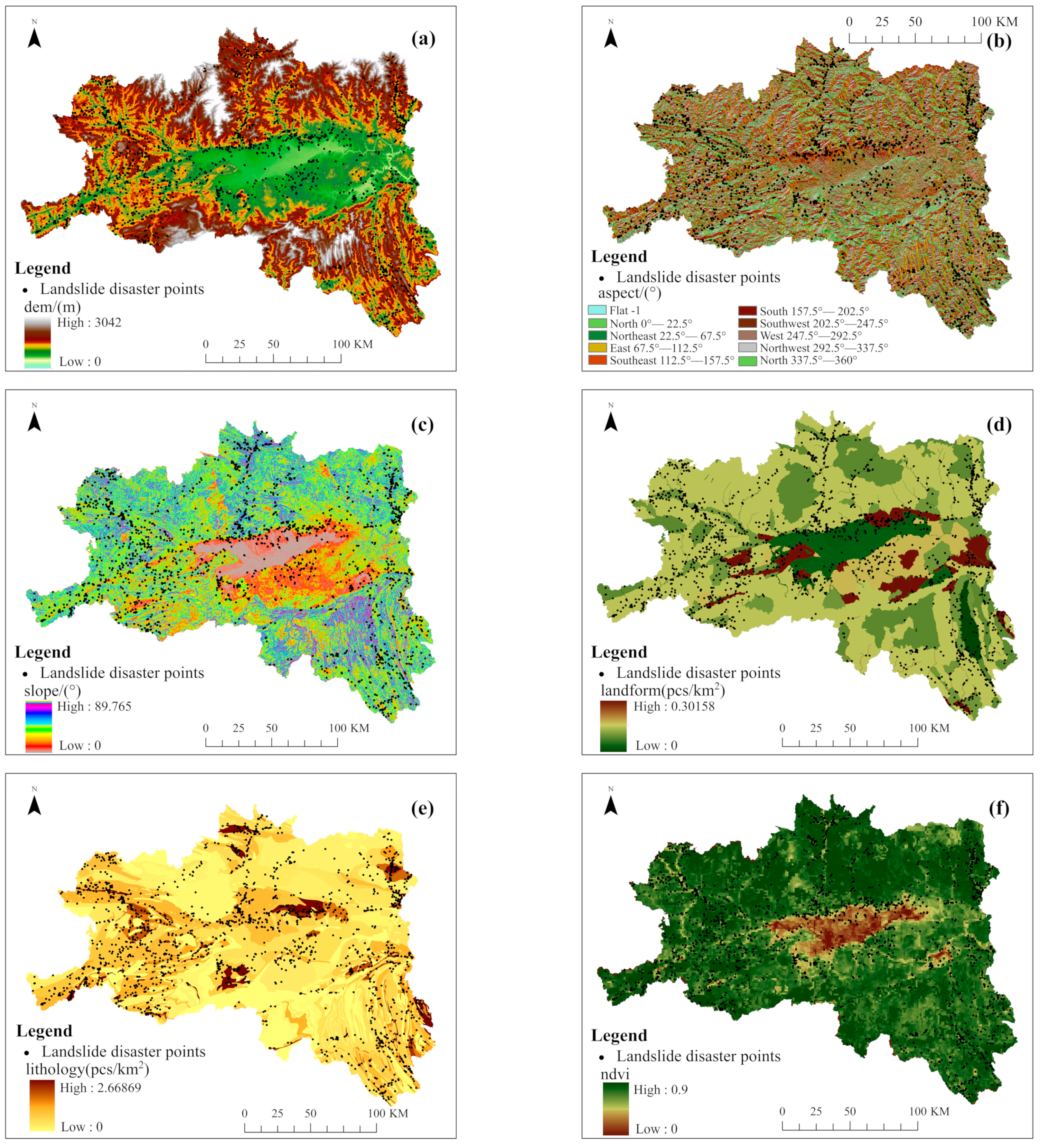
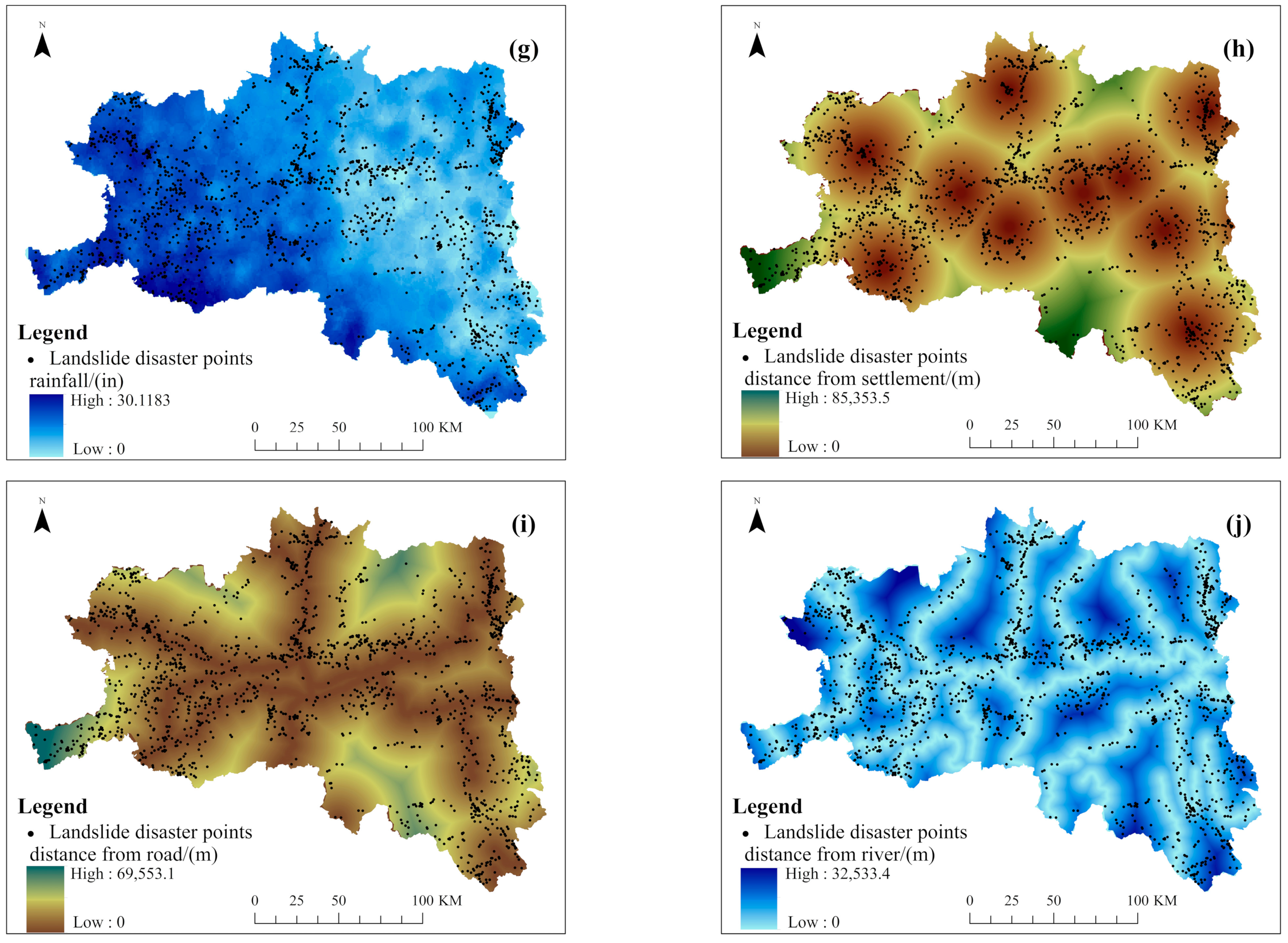
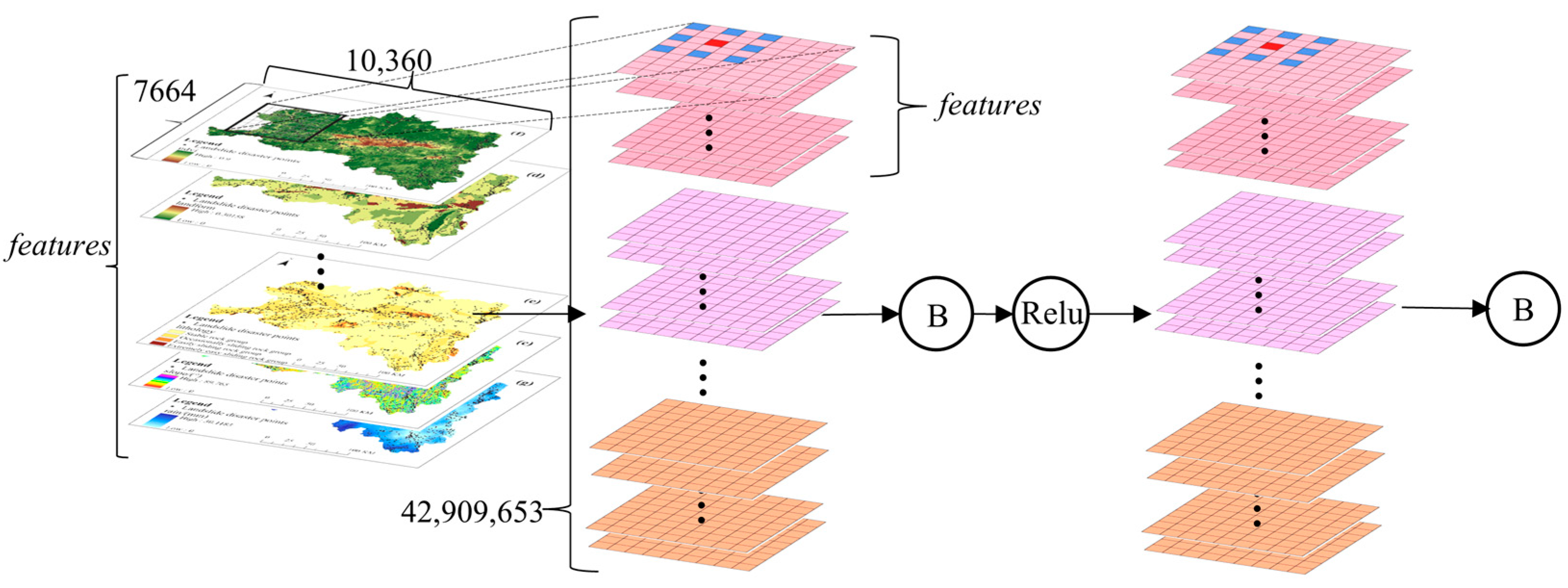
In terms of the selection of evaluation factors, considering geological and geomorphic conditions, the slopes which are formed by the rock and soil can only slide downward if they are cut and separated into discontinuous states by various structural planes. The digital elevation model (DEM), slope, aspect, landform, lithology, and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) were selected as the evaluation factors. Considering the hydrological conditions, which soften the landslide surface and reduce the strength, the annual rainfall and the distance from the river were selected as the evaluation factors. Considering the frequent engineering activities of human beings, which alter the basic conditions of the slopes and induce landslides, the distance from the road and the distance from the settlement were selected as the evaluation factors [17]. In view of the integrity and complexity of landform and lithology, combined with the distribution of landslide disaster points in the region, the regional disaster point densities were used to quantify the landform and lithology [18,19]. The data sources of evaluation factors are shown in Table 1. In order to facilitate statistics and analysis, the regular grid units were selected as the landslide susceptibility assessment units in the study area. According to 30 × 30 grid cells [18], the study area was divided into 10,360 columns and 7664 rows, totaling 42,909,653 grid cells. The evaluation factors are shown in Figure 2.

Table 1.
Data Source.
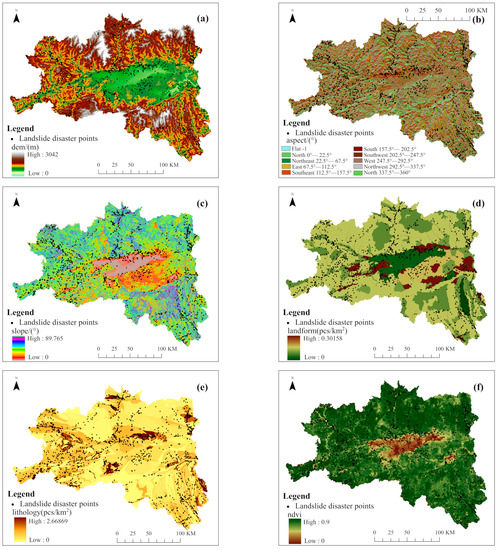
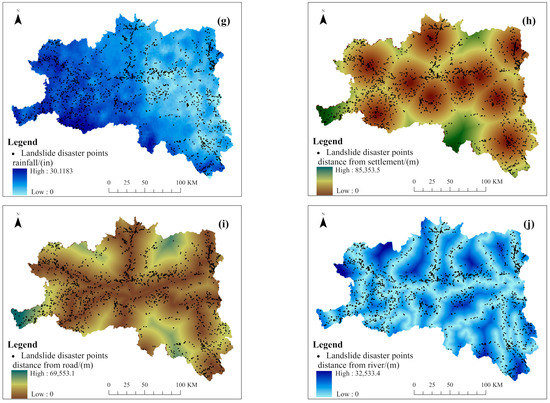
Figure 2.
Evaluation factors: (a) DEM; (b) aspect; (c) slope; (d) landform; (e) lithology; (f) NDVI; (g) rainfall; (h) distance from the settlement; (i) distance from the road; (j) distance from the river.
To enhance the accuracy of the training and prediction of the landslide susceptibility network model, the sample dataset was divided into 30 m × 30 m grid units, and 1727 landslide hazard units were extracted out of a total of 42,909,653 landslide units. In order to obtain accurate negative sample training data, the non-landslide hazard units with the same number of landslide hazard units were randomly selected based on the distance constraints that the distances between landslide points and non-landslide points are not less than 1 km, and the distances between non-landslide points are not less than 1 km. The dataset was divided into 70% for the training set and 30% for the test set. Each dataset contains landslide attributes and 10 evaluation factor values [7]. In view of the problem that the evaluation factors have different dimensions and dimensional units, this study normalized the data, limited the data range to [0, 1], and then conducted subsequent model training and prediction. The normalization formula is as follows [20]:
where and are the input value and normalized value of the evaluation factors and and are the maximum and minimum values of the original evaluation factors, respectively.
3. Methods
The section introduces the DADRCNN network structure and the principles and advantages of its various sub-modules, including DCU, DRM, and CARM. Furthermore, it provides a detailed explanation of the entire landslide susceptibility research process.
3.1. DADRCNN
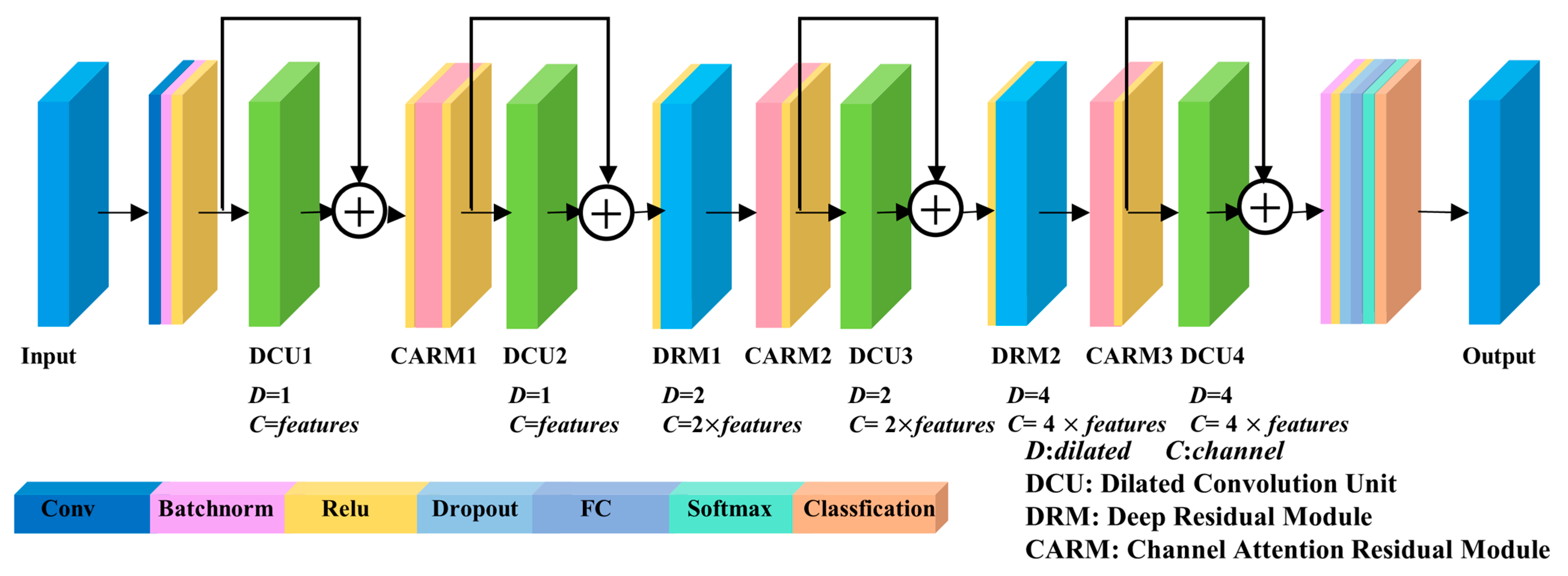
The DCU can effectively increase the range of the receptive field of the model, DRM can extract deeper features from sample data, and CARM can focus on important information among many complex and diverse landslide evaluation factors. Consequently, this study constructs the DADRCNN structure based on the DCU, DRM, and CARM, providing an effective network learning model for landslide susceptibility analysis. The network structure of DADRCNN is shown in Figure 3.
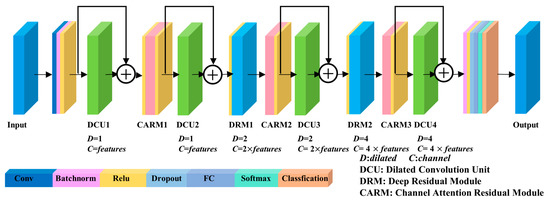
Figure 3.
The network structure of DADRCNN.
3.1.1. DCU
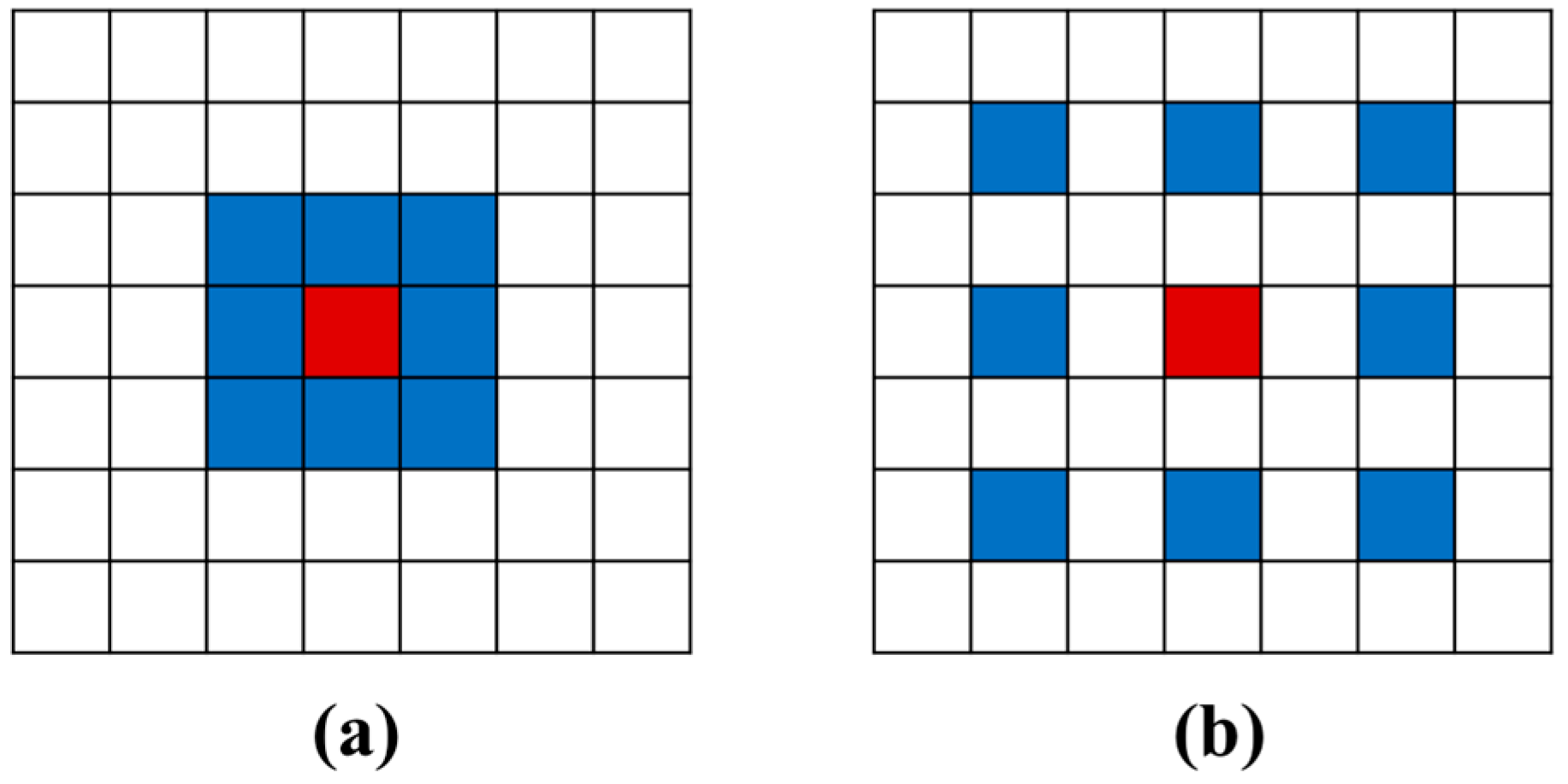
Dilated convolution [21] introduces the concept of expansion on the basis of ordinary convolution. As shown in Figure 4, the dilated convolution has the same convolution kernel and the same number of parameters in the neural network compared with the ordinary convolution. Without increasing the parameters or the amount of calculation, the dilated factor is used to increase the receptive field of the layer, and ensure that the size of the output feature mapping remains unchanged, which effectively improves the ability of the model to capture sample features, systematically aggregates multi-scale information without reducing the resolution, and enhances the prediction accuracy of the deep neural network model [22].
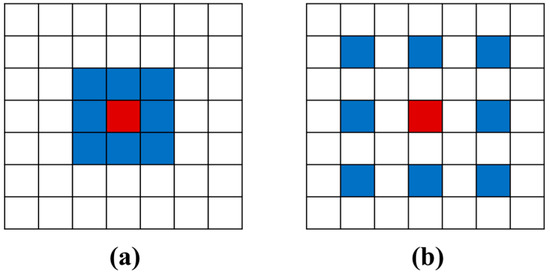
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of standard convolution and dilated convolution: (a) standard convolution; (b) dilated convolution ( = 1).
The dilated convolution receptive field is a progressive process, that is, the receptive field of the latter layer is directly related to that of the previous layer. The formula is as follows:
In the formula, and represent the receptive field of the convolution kernel in the , convolution layer, respectively; is the size of the convolution kernel; is the dilated factor; and is the convolution step size.
The acquired receptive field increases with the increase in the convolution kernel filter. However, according to the covariance analysis theory, 3 × 3 has been proved to be the most effective size for image processing, so a 3 × 3 convolution filter is selected. At the same time, the dilated convolution used in this study can effectively increase the receptive field through the dilated factor, allowing for the extraction of more feature information [23].
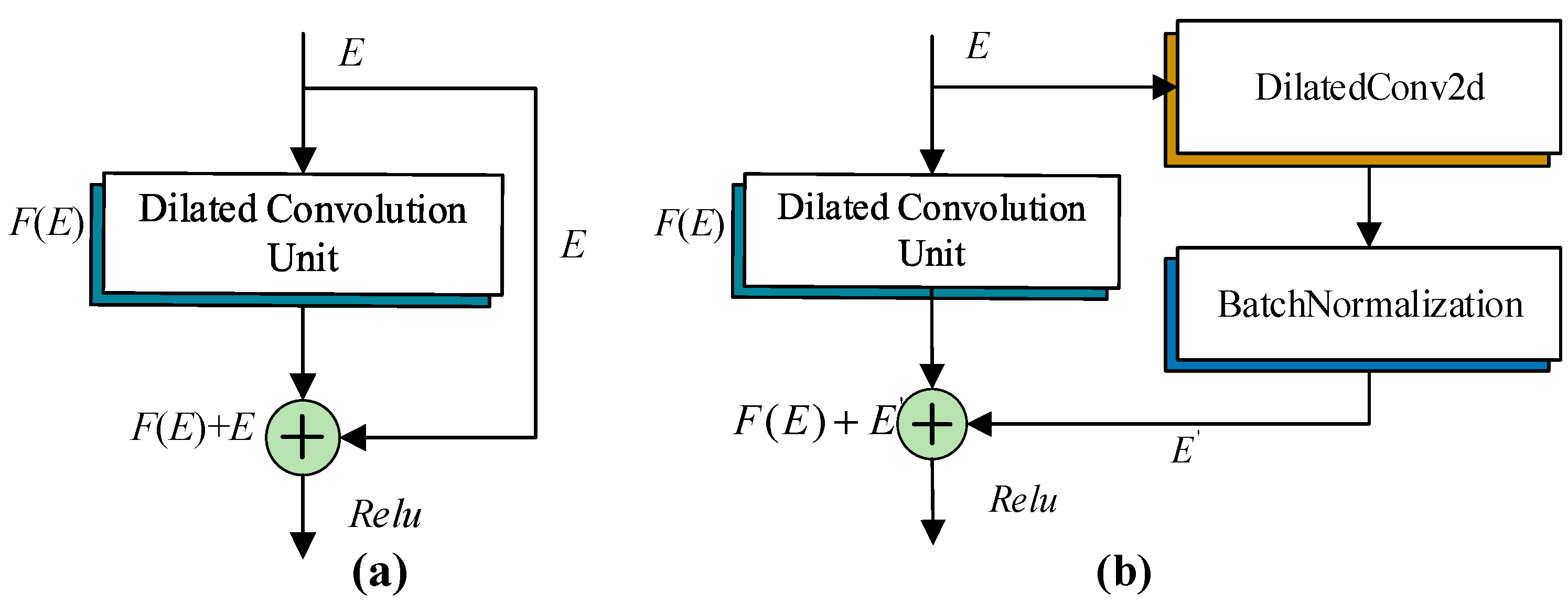
In order to clearly construct and express the network structure, this study constructs a DCU, as shown in Figure 5. This unit is an important basis for the DADRCNN structure, including two dilated convolution layers, two batch normalization layers, and a nonlinear activation function Relu layer. The size of dilated convolution is 3 × 3, the dilated factors are, respectively, 1, 2, and 4 in different DRUs, and the corresponding channel numbers are, respectively, , , and (where are the number of evaluation factors). The dilated convolution can be independent of the pooling operation, and more features in the sample can be obtained by expanding the range of the receptive field to reduce the computational load. The batch normalization layer normalizes each mini-batch of data by introducing some normalization restrictions to reduce the sensitivity to hyperparameter, speed up convergence, and improve the training stability of the model. The nonlinear activation function Relu layer can avoid the problem of vanishing gradients and non-convergence [24,25,26].
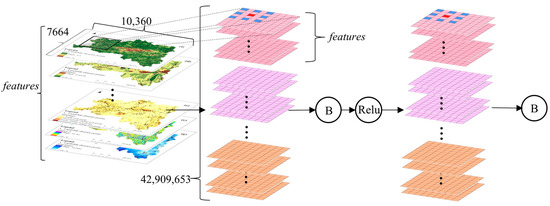
Figure 5.
Structure of DRU (example with dilated factors = 1).
3.1.2. DRM
Increasing network depth can better extract the data features and analyze the impact of landslide evaluation factors on landslide susceptibility, but it is easy to cause the model learning gradient to vanish [27]. To address this issue, the ResNet structure [28,29] is introduced. The core of this structure is to overlay the residual function mapping layer on the basis of the shallow network, transfer the feature information from the front layer to the back layer, and form a skip connection for residual learning to solve the gradient vanishing problem.
This study proposes two types of residual modules, as shown in Figure 6. Figure 6a is the standard residual module (SRM) constructed using formula , where is the input of the model and is the output after the DRU. Figure 6b is the improved DRM in this study. When the residual skip connection is made, the deep feature of the sample data feature is extracted using the dilated convolution and batch normalization to obtain , and the residual connection is obtained. The formulas for residual and are shown in (3) and (4).
where, , , are the weights of each dilated convolution layer; , , are offsets; is the normalization of the batch processing layer; and is the nonlinear activation function.
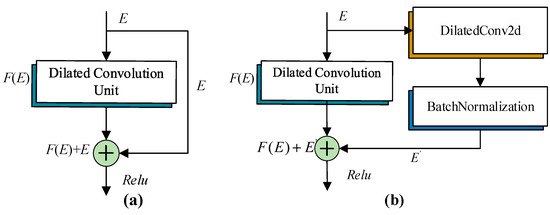
Figure 6.
Residual module: (a) SRM; (b) DRM.
3.1.3. CARM
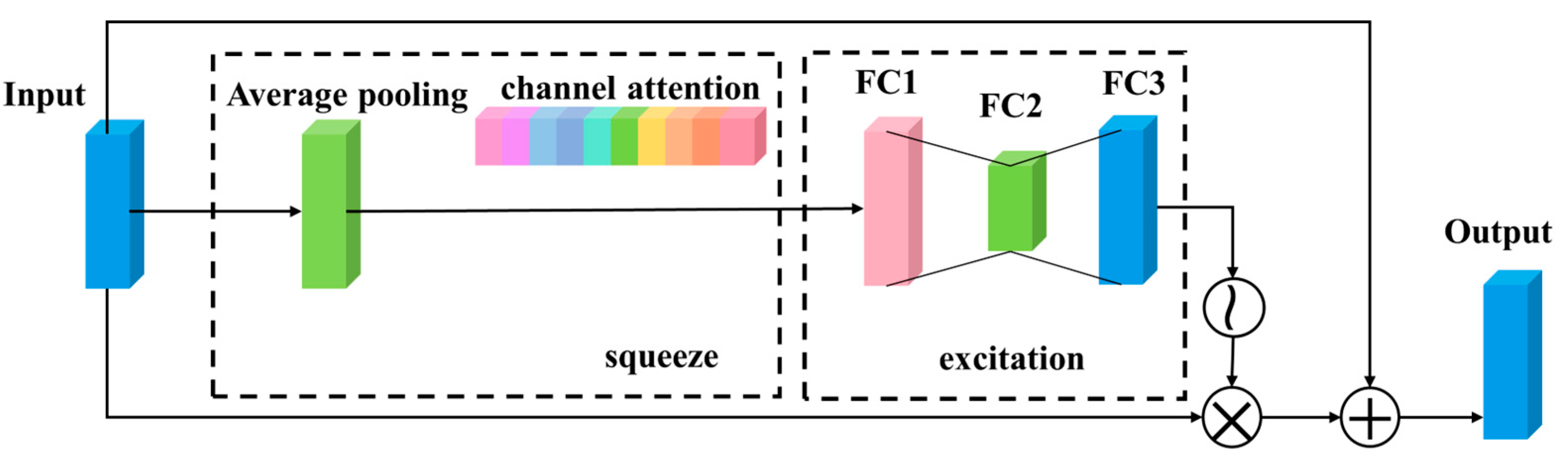
The attention mechanism enables the network to focus on important information from many complex and diverse sources, and ignore unimportant information according to current task requirements [30]. Considering the varying importance of different evaluation factors for landslide, the CARM is introduced [31]. Among them, the squeeze and exclusion module (SEM) is a common channel attention module [32]. SEM focuses on the feature relationship between different channels, and automatically learns the importance of various feature channels by learning a set of weight coefficients, then dynamically applying weights to each feature channel, and assigning different weights to each channel, to highlight important features and suppress unimportant features [32].
The combination of SEM and residual structure is shown in Figure 7. First, the average pooling is used to squeeze the input feature graph, and the feature graph with the shape of (, , ) is compressed to (1, 1, ) to obtain the global features on each channel (where is the size of the input image, the corresponding value is different in different DRMs, and is the number of feature factors). Then the excitation operation is carried out to obtain the correlation between different channels. This step is mainly completed by three fully connected layers. The first fully connected layer has channels, and the second fully connected layer compresses channels into channels, reducing the number of parameters. The third fully connected layer recovers to channels. The activation function sigmoid is used to learn the correlation of each channel and generate different weights for each characteristic channel, thus improving the network’s ability to identify the characteristics of each channel. The final input is added to the output of SEM through the skip connection as the input of the next layer. The formula for CARM is as follows:
where, represents average pooling, represents fully connected layer, represents a sigmoid function, represents matrix multiplication, and represents matrix addition.
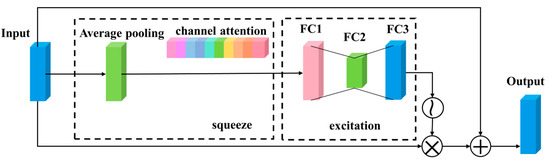
Figure 7.
Structure of CARM.
3.2. Research Flow of Landslide Susceptibility
In this study, Hanzhong City in Shaanxi Province was selected as the research area. Ten landslide-causing factors, including DEM, aspect, slope, landform, lithology, NDVI, annual rainfall, distance from settlement, distance from road, and distance from river, were normalized as the evaluation factors of landslide susceptibility. The spatial dimension of the input cubic data block was discussed. To address the problem of insufficient information due to the small number of landslide datasets, the complexity of landslide evaluation factors, and low prediction accuracy of landslide susceptibility, the DADRCNN method was proposed based on DCU, DRM, and CARM. Ablation experiments and comparison experiments with SVM were conducted in terms of the landslide susceptibility map, landslide disaster point density zoning statistics, and the evaluation of model accuracy. The research flow chart of landslide susceptibility prediction in Hanzhong City based on DADRCNN is shown in Figure 8.
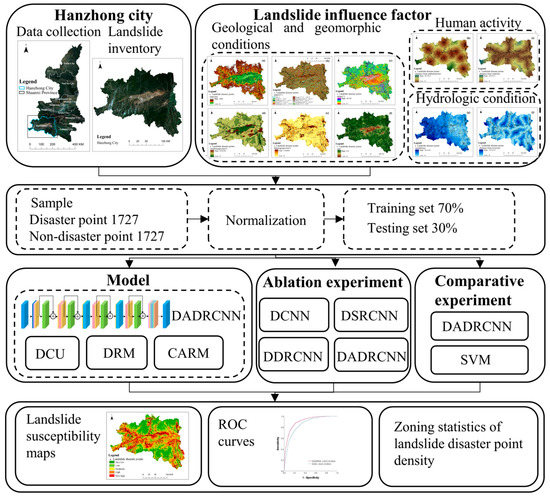
Figure 8.
Research flow chart of landslide susceptibility.
4. Results
This section introduces the experimental environment, parameter settings, and evaluation metrics. The effects of different spatial neighborhood sizes on landslide susceptibility prediction are discussed using the overall accuracy (), , , and . The ablation experiments of sub-models and the comparison experiment between the DADRCNN model and the SVM model were analyzed and discussed from three aspects: landslide susceptibility map, landslide disaster point density zoning statistics, and evaluation of model accuracy.
4.1. Parameter Settings
In the process of data training and testing, the experimental environment of the proposed model is based on the Windows 11 system, an Intel (R) Core (TM) i7-9750H CPU, and 64 GB memory. The network was trained using the Adam optimizer, with an initial learning rate of 0.001. Additionally, a discard parameter retention rate of 0.5 was used for the fully connected layer [33].
4.2. Evaluation Indicators
In order to evaluate the performance of different spatial neighborhood sizes on landslide susceptibility prediction, this study used the , , , and to evaluate the test results [34,35], as shown in Formulas (6)–(9):
represents the ratio of the number of correctly predicted landslide and non-landslide samples to the total number of samples.
represents the ratio of the number of correctly predicted landslide samples to the number of landslide samples before prediction.
represents the ratio of the number of correctly predicted landslide samples to the number of landslide samples after prediction.
The is the harmonic mean of (7) and (8).
Among them, true positive () represents the number of landslide samples classified as landslide samples; true negative () represents the number of non-landslide samples classified as non-landslide samples; false positive () represents the number of landslide samples incorrectly predicted as non-landslide samples; false negative () represents the number of non-landslide samples incorrectly predicted as landslide samples.
In the ablation experiment and contrast experiment, the landslide susceptibility map, landslide disaster point density zoning statistics, and evaluation model accuracy were analyzed. In terms of the division of landslide susceptibility areas, the geometric interval method takes the minimum sum of squares of the number of elements in each category as the division standard, which has the advantage of ensuring the relative consistency of various intervals. Therefore, the geometric interval method was used to divide the landslide susceptibility map into very low, low, moderate, high, and very high areas. In terms of landslide disaster point density zoning statistics, the number of landslide disaster points in different areas was counted, and the areas of the susceptibility zones were calculated to obtain the landslide disaster point densities. In terms of model accuracy evaluation, the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve is simple, intuitive, and has the advantage of not being constrained by critical conditions. The ROC curve, which can accurately reflect the relationship between the specificity and sensitivity of the model, was used for landslide susceptibility assessment [11].
4.3. Results of Different Spatial Neighborhood Sizes
The input of the network structure in this study is a three-dimensional data block composed of the labeled pixels in the hyperspectral image of the landslide evaluation factor and all the pixels in the spatial neighborhood. The size of the spatial neighborhood determines the amount of information accepted by the network, thus affecting the final landslide prediction accuracy. To select the appropriate spatial neighborhood size, five different sizes were chosen to train and test the network, and the results are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from the table that within a certain range, the accuracy will improve as the size of the spatial neighborhood increases. This is because a smaller spatial neighborhood contains fewer pixels, resulting in an insufficient receptive field. The network can only learn a limited range of local information and ignore the impact of surrounding disaster factors on the landslide, leading to lower accuracy. However, if the spatial neighborhood is too large, it will affect the spatial feature extraction of small targets and the accuracy will decrease. At the same time, there will be an issue of longer training time. Through the above experiments and analysis, a 9 × 9 space size was selected as the input data block.

Table 2.
Comparison of different spatial neighborhood sizes.
4.4. Ablation Experiment
To verify the effectiveness of each module in the DADRCNN method, the CNN with DCU designed in this study was selected as the benchmark to conduct module ablation experiments, and the following modules were defined:
(1) The benchmark model (DCU + CNN, DCNN) designed in this study: refer to Figure 3, only DCU was included;
(2) The dilated residual network model (DCU + SRM + CNN, DSRCNN) formed by adding SRM to the benchmark model: refer to Figure 3 and Figure 6, the network structure included DCU and SRM, and SRM did not extract the depth feature of the sample data during the residual skip connection;
(3) The deep dilated residual network model (DCU + DRM + CNN, DDRCNN) formed by adding DRM to the benchmark model: refer to Figure 3 and Figure 6, the network structure included DCU and DRM;
(4) The deep attention dilated residual network model (DCU + DRM + CARM + CNN, DADRCNN) was formed by adding CARM on DDRCNN.
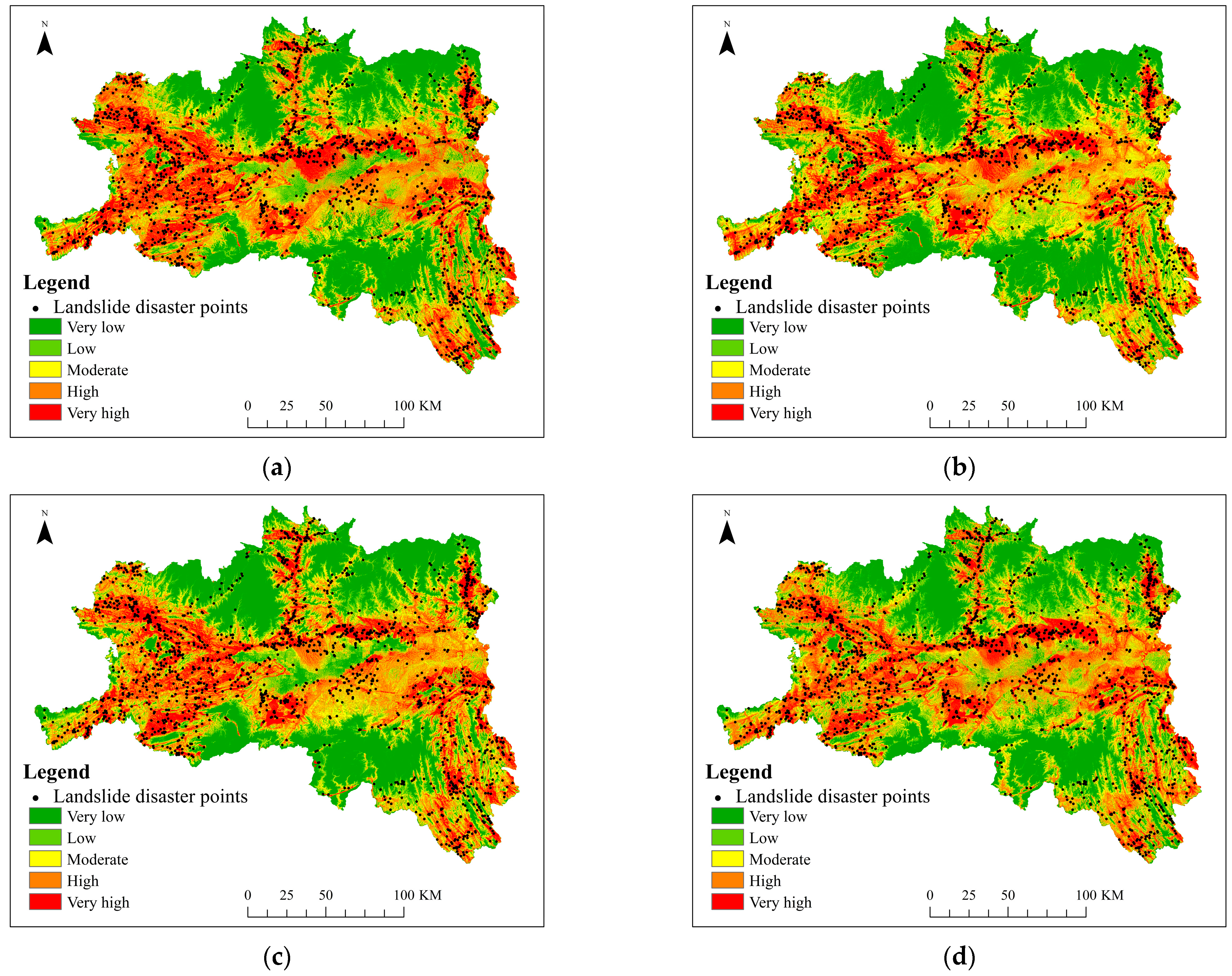
The landslide susceptibility maps corresponding to this method and other sub-models are shown in Figure 9. Overall, the trends of landslide susceptibility zoning in different sub-models are roughly similar to that in this method, and are consistent with the actual situation of the study area. The very high susceptibility and high susceptibility areas for landslides are mainly distributed along rivers and roads; the moderate susceptibility and low susceptibility areas for landslides are distributed around the high areas, mainly in the central Hanzhong Basin; very low susceptibility areas for landslides are mainly distributed in mountainous areas with stable rock formations and gentle slopes
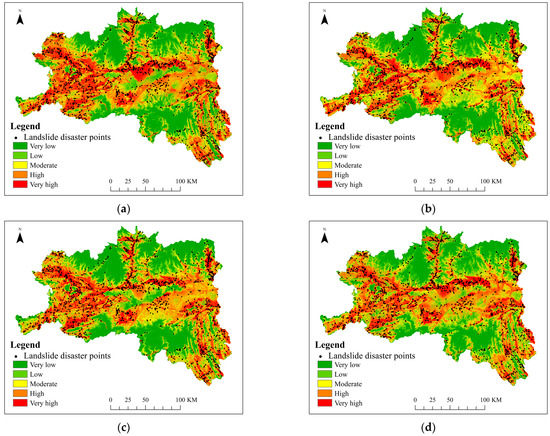
Figure 9.
Landslide susceptibility maps of different sub-models: (a) DCNN; (b) DSRCNN; (c) DDRCNN; (d) DADRCNN.
Taking the west of Hanzhong City as an example, the DCNN model divides some areas into high susceptibility and low susceptibility areas, ignoring the impact of moderate susceptibility areas. This is because although the DCNN model can extract features favorable for susceptibility assessment, too many network layers may cause the model to suffer from gradient disappearance during learning, resulting in inaccurate prediction of susceptibility areas. Taking the central part of Hanzhong City as an example, the DSRCNN model mistakenly divides some low susceptibility areas into moderate susceptibility areas, and there are many areas of moderate susceptibility areas in the zoning. This is because the problem of gradient disappearance is solved by adding residual learning modules, but the feature mining of landslide disaster factors is not enough, resulting in incorrect zoning. Taking the southwest and east of Hanzhong City as examples, some areas are distributed in a scattered manner. This is because the DDRCNN model ignores the different degrees of impact on landslides when deeply mining the characteristics of disaster factors. Compared with the DDRCNN model, the DADRCNN model can pay attention to the characteristic relationship between different channels, and automatically learn the importance of different characteristic channels. The landslide susceptibility areas are distributed along rivers and roads in strips, and the zoning spreads from very high to very low, effectively improving the accuracy of landslide susceptibility assessment.
The landslide susceptibility zoning statistics of this method and other sub-models are shown in Table 3. The number and density of landslide disaster points falling into five susceptibility zones in the training samples were analyzed and counted. The density of landslide disaster points in each susceptibility area has gradually increased with the increase in the degree of disaster susceptibility, achieving a minimum in a region of very low susceptibility and a maximum in a region of very high susceptibility, which is congruent with the actual scenario. The DCNN model only uses the basic convolutional network structure incorporating DCU, resulting in relatively low classification performance. However, the DCNN model lays a foundation for subsequent sub-modules. In the very low susceptibility area, the point densities of DCNN, DSRCNN, DDRCNN, and DADRCNN were 0.003, 0.002, 0.002, and 0.001, respectively. In the very high susceptibility area, the point densities were 0.146, 0.156, 0.168, and 0.171, respectively. These results demonstrate that the method proposed in this study and other sub-models can effectively predict landslide susceptibility, and the point densities gradually increase, which shows the effectiveness of each module, and highlights the relatively high prediction ability of the method in this study.

Table 3.
Landslide susceptibility zoning statistics of different sub-models.
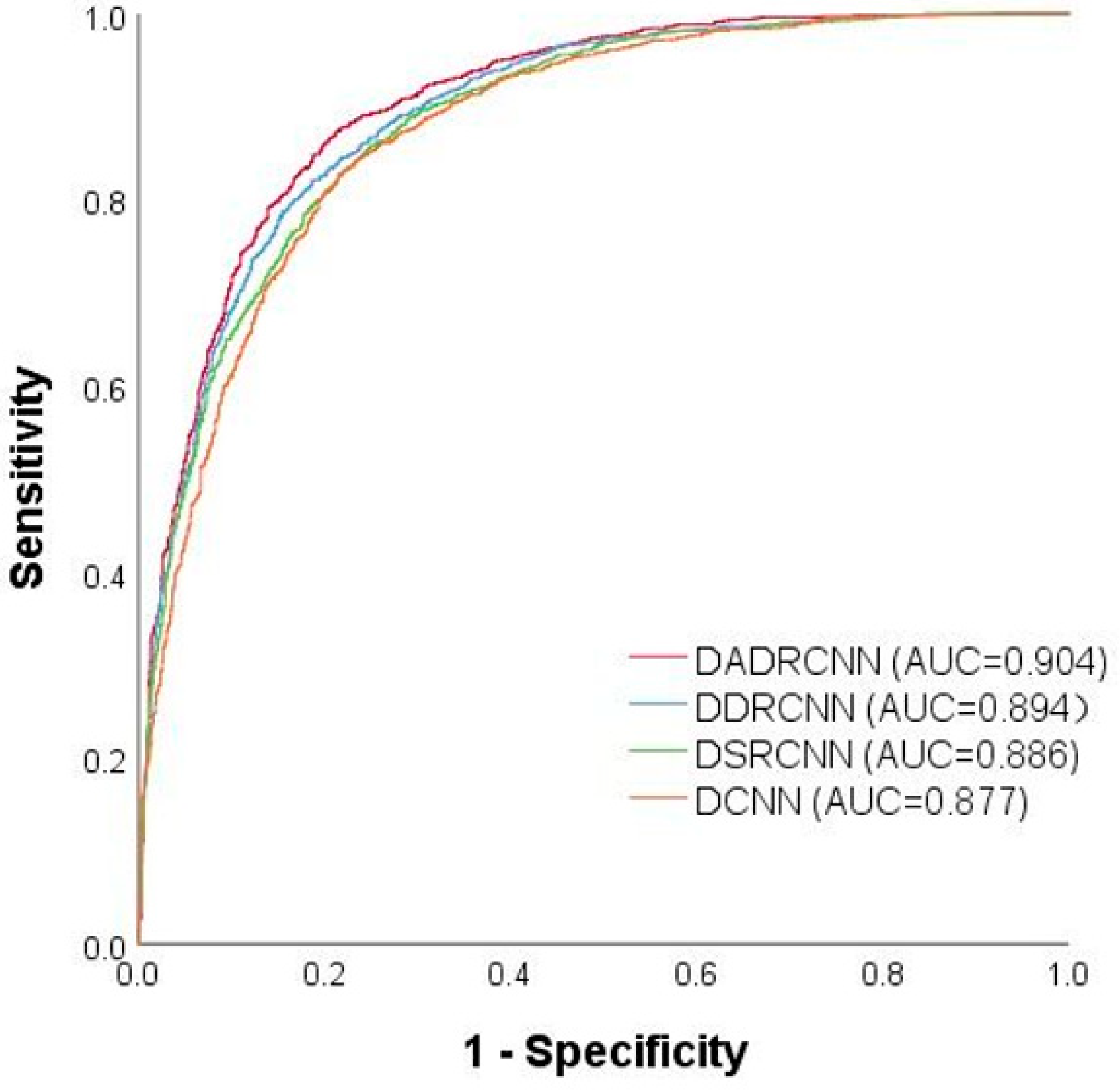
The ROC curves of different sub-models are shown in Figure 10. The values of the area under the curve (AUC) for DCNN, DSRCNN, DDRCNN, and DADRCNN were 0.877, 0.886, 0.894, and 0.904, respectively. It can be seen that the DADRCNN model has a higher prediction accuracy than the other three evaluation sub-models, and it is more accurate and reliable for the analysis and evaluation of landslide susceptibility in Hanzhong City, providing a reference basis for the landslide treatment and decision-making.
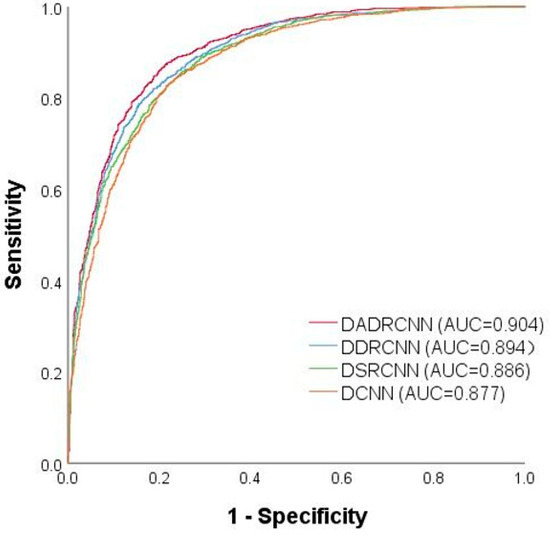
Figure 10.
ROC curves of different sub-models.
4.5. Comparison with SVM
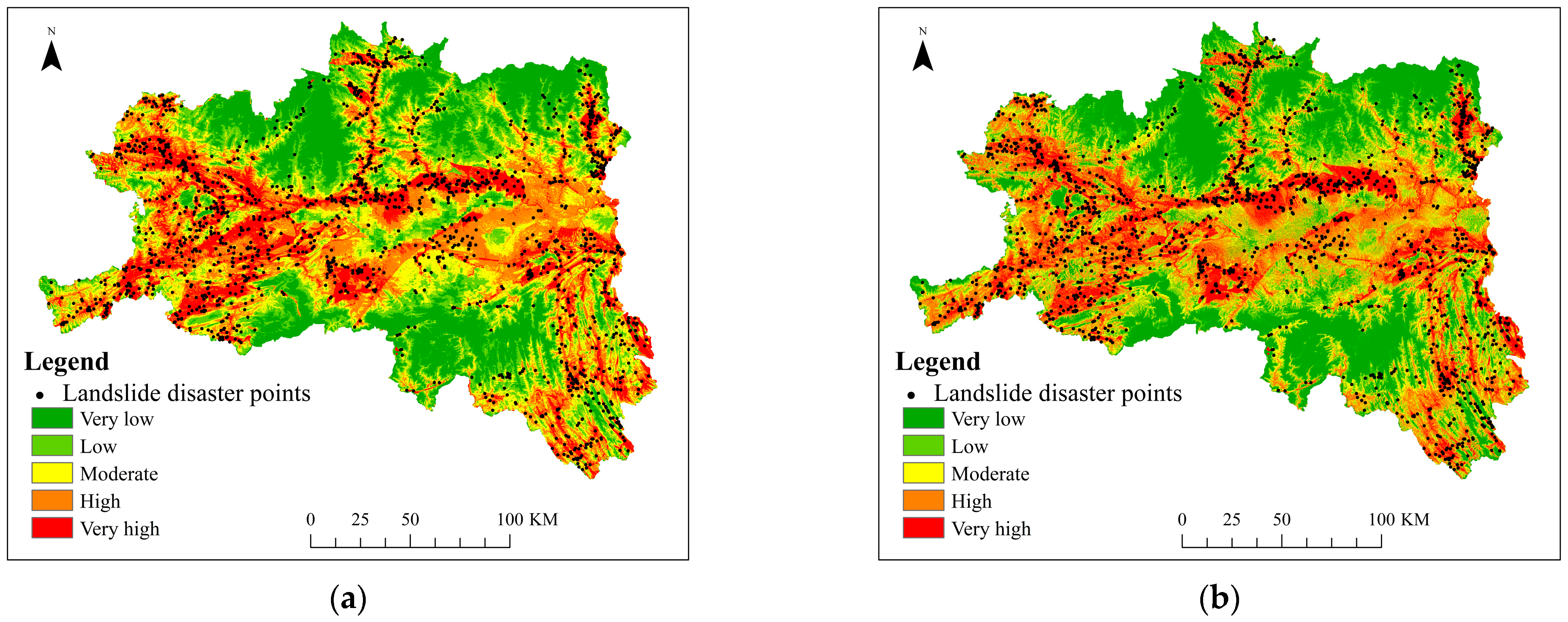
The SVM method, which utilizes training error as the constraint condition of the optimization problem, sets minimizing the confidence interval as the optimization target, and offers a variety of special benefits for tackling nonlinear, high-dimensional pattern recognition issues, was chosen as the comparison method in order to further confirm the accuracy and dependability of the proposed method [35]. Figure 11 shows the landslide susceptibility maps of the SVM method and the method in this study. Combined with the remote sensing image in Figure 1, it can be seen that the landslide susceptibility prediction trends of the two methods are roughly the same, which are roughly in line with the actual situation of the study area. However, compared with the DADRCNN method, the classification of the SVM method is not clear enough, and the different areas are isolated, which does not highlight the interaction between the various areas, and lacks pertinence in practical application. It demonstrates that the landslide susceptibility zoning divided by DADRCNN method is more reasonable and trustworthy.
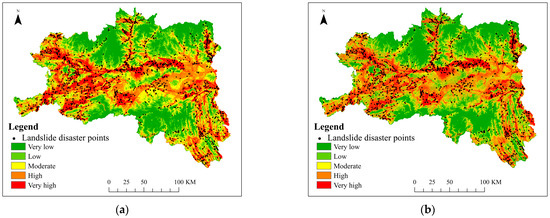
Figure 11.
Landslide susceptibility maps of different models: (a) SVM; (b) DADRCNN.
The statistics of landslide susceptibility zoning for the two methods are shown in Table 4. The disaster point densities of the two methods were 0.001 and 0.001 in the very low susceptibility area, 0.009 and 0.008 in the low susceptibility area, 0.022 and 0.019 in the moderate susceptibility area, 0.054 and 0.055 in the high susceptibility area, and 0.161 and 0.171 in the very high susceptibility area.

Table 4.
Landslide susceptibility zoning statistics of different models.
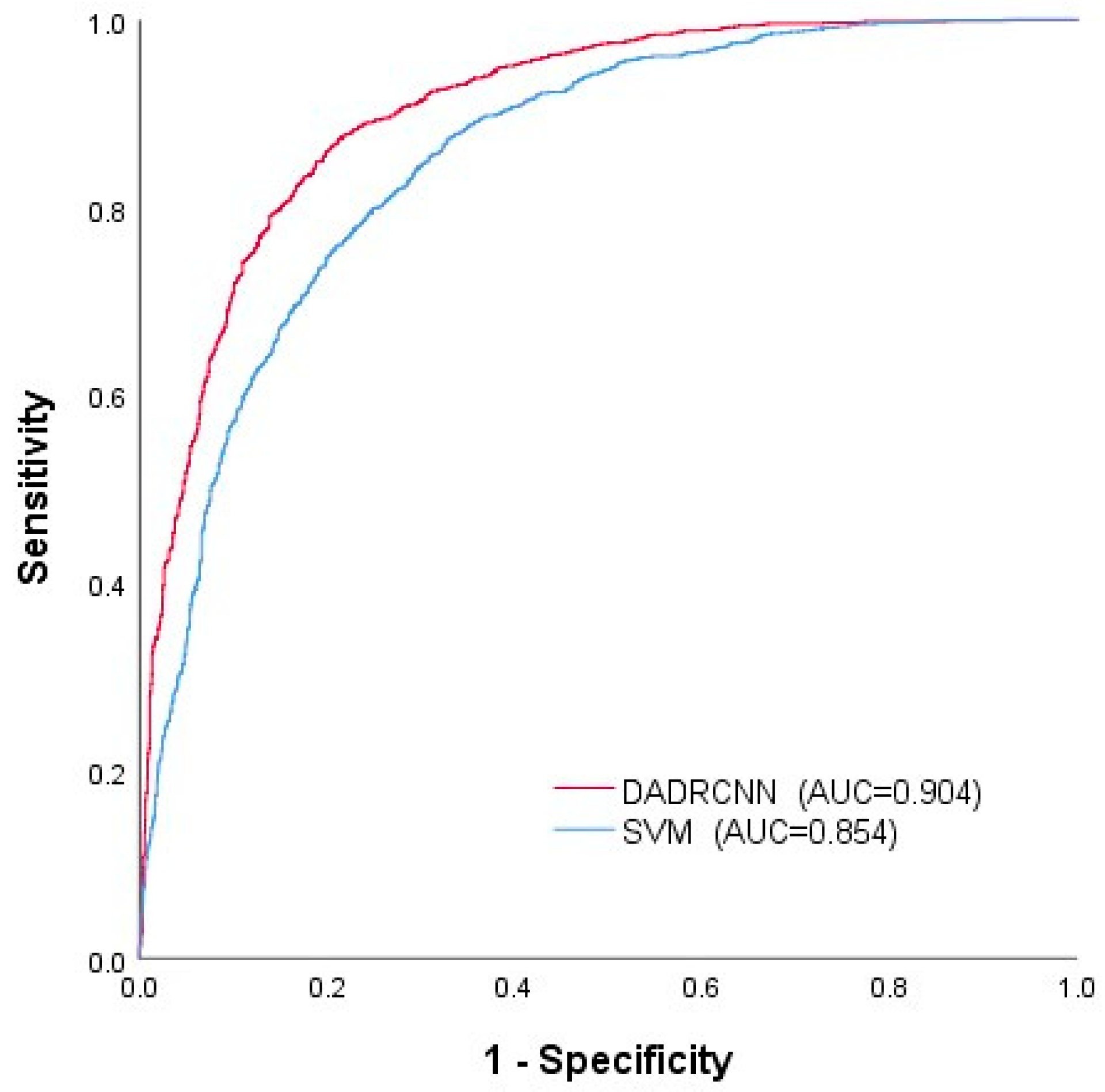
The ROC curves of the two methods are shown in Figure 12. The AUC values of the SVM method and the DADRCNN method were 0.854 and 0.904, respectively. It shows that the accuracy of the DADRCNN method is higher than that of SVM method, and the prediction effect is better.
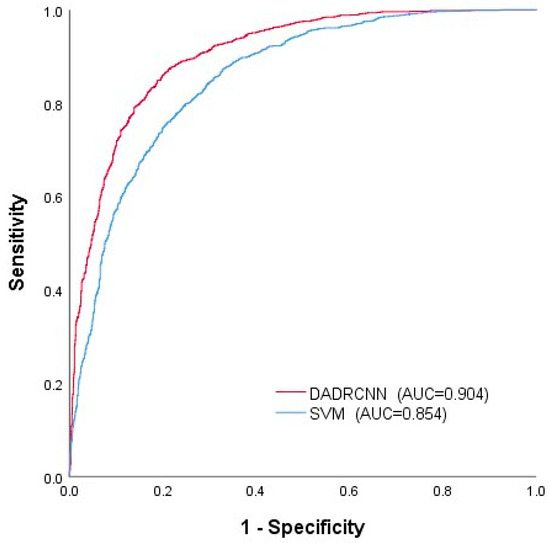
Figure 12.
ROC curves of different models.
5. Discussion
A DADRCNN model in Hanzhong City was proposed. The landslide susceptibility maps were significant, the disaster point density zone statistics were in line with the actual situation and the statistics were optimal, and the AUC value was high, indicating that the model has high accuracy and reliability. The experimental results are discussed as follows.
5.1. Influence of Different Spatial Neighborhood Sizes
The input of the network structure in this study is a three-dimensional data block composed of the labeled pixels in the 10 evaluation factor images and all pixels in the spatial neighborhood. To address the issue of how different spatial neighborhood sizes affect the prediction performance of landslide susceptibility, the study selected various sizes (3 × 3, 5 × 5, 7 × 7, 9 × 9, and 11 × 11) to train and test the network. When the spatial neighborhood size is too small, the receptive field is insufficient, neglecting the impact of surrounding disaster factors on landslides and resulting in lower accuracy. When the spatial neighborhood size is too large, information redundancy occurs, leading to longer training time. The spatial neighborhood size of 9 × 9 achieved the best performance in , , , and , with values of 0.7524, 0.7235, 0.8170, and 0.7674, respectively. Therefore, 9 × 9 was chosen as the spatial size for input cubic data blocks.
5.2. Characteristics of the DADRCNN Compared to DCNN, DSRCNN, and DDRCNN
The DADRCNN method was proposed based on DCU, DRM, and CARM. To demonstrate the effectiveness of each module, we conducted ablation experiments. The point densities of DCNN, DSRCNN, DDRCNN, and DADRCNN in the very low susceptibility areas were 0.003, 0.002, 0.002, and 0.001, respectively. In the very high susceptibility areas, the point densities were 0.146, 0.156, 0.168, and 0.171, respectively. With the increase in each module, the nearest point of the ROC curve from the upper left corner was gradually farther away from the reference line, which indicates the advantages of each module to a certain extent. In order to quantitatively analyze this point, the AUC was used to evaluate the model, and the AUC values were 0.877, 0.886, 0.894, and 0.904, respectively. The effectiveness of each module was analyzed as follows: (1) The network structure with the DCU can achieve relatively accurate landslide partitioning. This is because the DCU can expand the receptive field of the convolution layers without increasing network parameters, and effectively enhance the ability of the model to capture landslide evaluation factor features. (2) The DRM refines the landslide partitioning, subdividing some high susceptibility and low susceptibility areas into moderate susceptibility areas, and reducing misclassified areas. This is because the DRM increases the network depth and overlays the residual function mapping layers, which can address the gradient vanishing issue and better extract data features. (3) The CARM emphasizes the distribution of landslide susceptibility areas along rivers, roads, and slopes, which corresponds to the characteristics of landslide disasters. This is because CARM examines the importance of various characteristics and assigns different weights based on the varying hazard degrees of landslides caused by different evaluation factors, which improves the prediction accuracy of landslide susceptibility.
5.3. Advantages of the DADRCNN Compared to SVM
To further verify the correctness and dependability of the proposed method, we conducted a comparative experiment with the traditional machine learning method SVM, which has several unique benefits in addressing nonlinear high-dimensional pattern recognition issues. The disaster point densities in the very high susceptibility areas for DADRCNN and SVM methods were 0.171 and 0.161. The disaster point densities in the high susceptibility areas were 0.055 and 0.054. The disaster point densities in the very low susceptibility areas were both 0.001. The disaster point densities in the low susceptibility areas were 0.008 and 0.009. The distribution densities of landslide disaster points in the high and very high susceptibility areas obtained by the DADRCNN method are higher than those of the SVM method, while the distribution densities of disaster points in the low and very low susceptibility areas are also lower than those of the SVM method. The study indicates that the susceptibility areas divided by the DADRCNN method are more consistent with the actual distribution, and the partition effect is better. The points closest to the upper left corner on the ROC curve of both methods were far from the reference line, but the point closest to the upper left corner in this study was farther away from the reference line than the point in the SVM method, and the AUC values were 0.904 and 0.854, respectively. This demonstrates that the accuracy of the DADRCNN method proposed in this study is higher than that of the SVM method, with better prediction performance.
At the same time, the AUC value of the study in the prediction of landslide susceptibility of the Hanzhong City, Shaanxi Province was higher than that of the DAE-MRCNN method. Meanwhile, due to the introduction of the concept of data blocks, the zoning effect of this study was better than that of the DAE-MRCNN method [29]. Therefore, the DADRCNN method can improve predictive performance and provide a reference for landslide susceptibility research. Although the DADRCNN method has high accuracy and reliability, there is still a need to optimize the selection of negative samples and continue to optimize the network structure.
6. Conclusions
The DADRCNN method presented in this study exhibits high accuracy and reliability. It has significant theoretical value and practical application potential for minimizing losses caused by landslides and enhances the efficiency of landslide prevention and management. This method also provides a reference basis for landslide treatment and decision-making in Hanzhong City. However, the strategy of negative sample selection in existing methods is somewhat random, and the deep learning based on CNN involves numerous parameters. Future study will focus on optimizing negative sample selection and further refining the network structure to improve the prediction accuracy of landslide susceptibility.
Author Contributions
Data processing, methodology, programming, validation, draft writing, Y.M., T.J. and Z.W.; methodology, programming, revision, funding acquisition, S.X.; funding acquisition, project administration, Y.W.; data processing, revision, M.L., X.L. and X.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFC1511704) and the Basic Research Fund of CASM (Grant No. AR2310).
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yan, J. Uncertainty in Landslide Susceptibility Prediction Modeling: The Influence of Landslide Boundaries and Environmental Factor Errors. Master’s Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wen, H.; Sun, D. Study on the zoning of landslide susceptibility in Wushan County based on logistic regression. J. Chongqing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 38, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Bao, A.; Li, J.; Yan, X. Chinese High-Resolution Satellite Data and GIS-Based Assessment of Landslide Susceptibility along Highway G30 in Guozigou Valley Using Logistic Regression and MaxEnt Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Shi, X.; Sun, D.; Xu, J. Landslide susceptibility zoning in Wushan County based on GIS and random forest. J. Chongqing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 37, 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Hu, X.; Mei, H.; He, J.; Yang, J. Spatial susceptibility assessment of landslides based on random forest: A case study of the Hubei section of the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Kavzoglu, T.; Teke, A. Predictive Performances of ensemble machine learning algorithms in landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest, extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) and natural gradient boosting (NGBoost). Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 7367–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wen, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, R. Essential insights into decision mechanism of landslide susceptibility mapping based on different machine learning models. Geocarto Int. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhice, F.; Yi, W.; Gonghao, D.; Ling, P. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Rotation Forest Ensemble Technique with Different Decision Trees in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 238–259. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, W.; Peng, C.; Wang, D.; Xue, W.; Bian, H. Modeling landslide susceptibility using an evidential belief function-based multiclass alternating decision tree and logistic model tree. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, M.; Ghasemian, B.; Shirzadi, A.; Bui, D.T. A comparative study of support vector machine and logistic model tree classifiers for shallow landslide susceptibility modeling. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, R.; Zhang, M.; Liu, M.; Jiang, T. Support vector machine combined with entropy index for landslide hazard susceptibility assessment: A case study of Shaanxi Province. J. Wuhan Univ. (Inf. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 45, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Duan, H.; Niu, R.; Peng, L. Comparison of general kernel, multiple kernel, infinite ensemble and semi-supervised support vector machines for landslide susceptibility prediction. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 3535–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhuang, J.; Zheng, J.; Mou, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y. Assessment of landslide susceptibility along the Kangding-Litang section of CZ railway based on deep learning. J. Eng. Geol. 2022, 30, 908–919. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Yang, X.; Xu, C.; Wei, L.; Zeng, X. Comparative Study of Convolutional Neural Network and Conventional Machine Learning Methods for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jia, H.; Zhang, J. Landslide susceptibility mapping using multiscale sampling strategy and convolutional neural network: A case study in Jiuzhaigou region. Catena 2020, 195, 104851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, K. Comparisons of Convolutional Neural Network and Other Machine Learning Methods in Landslide Susceptibility Assessment: A Case Study in Pingwu. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chen, G.; Zhao, J.; Lin, Y.; Qin, B.; Yao, W.; Cao, Q. Landslide susceptibility evaluation of machine learning based on information volume and frequency ratio: A case study of Weixin County, China. Sensors 2023, 23, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhu, V.-H.; Mohammadi, A.; Shahabi, H.; Ahmad, B.B.; Al-Ansari, N.; Shirzadi, A.; Clague, J.J.; Jaafari, A.; Chen, W.; Nguyen, H. Landslide susceptibility mapping using machine learning algorithms and remote sensing data in a tropical environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Liu, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, M.; Zhang, M.; Liang, E. Evaluation method of landslide susceptibility based on random forest weighted information. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2020, 45, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, D.; Tang, H.; Sun, S.; Tang, C.; Zhang, B. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on the germinal center optimization algorithm and support vector classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, S.; Jiang, T.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Luo, A.; Ma, Y. Integrating Normal Vector Features into an Atrous Convolution Residual Network for LiDAR Point Cloud Classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, D.; Akram, M.U.; Hassan, T.; Anwar, T.; Salam, A.A. Dilated Convolution and Residual Network based Convolutional Neural Network for Recognition of Disastrous Events. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Robotic and Sensors Environments (ROSE), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 14–15 November 2022; pp. 01–08. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, F.; Fern, X.; Raich, R. Filter Shaping for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Gan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, L. EAGNet: A method for automatic extraction of agricultural greenhouses from high spatial resolution remote sensing images based on hybrid multi-attention. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 202, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Chen, B.; Niu, B.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Remote sensing recognition of urban villages based on multiscale dilated convolutional neural networks. J. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Chen, T.; Niu, R.; Plaza, A. Landslide Detection Mapping Employing CNN, ResNet, and DenseNet in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 11417–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Jiang, T.; He, X.; Han, Z. A Combination of Deep Autoencoder and Multi-Scale Residual Network for Landslide Susceptibility Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Yu, D.; Shen, C.; Li, W.; Xu, Q. Landslide detection from an open satellite imagery and digital elevation model dataset using attention boosted convolutional neural networks. Landslides 2020, 17, 1337–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; An, S.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, D. L-Unet: A Landslide Extraction Model Using Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; He, J.; Liu, G. Hyperspectral Image Classification Based on Convolutional Neural Network with Attention Mechanism. Adv. Laser Optoelectron. 2022, 59, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Skourt, B.A.; El Hassani, A.; Majda, A. Mixed-pooling-dropout for convolutional neural network regularization. J. King Saud Univ-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 4756–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, S.; Çan, T. Slide type landslide susceptibility assessment of the Büyük Menderes watershed using artificial neural network method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 47174–47188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, T.; Yin, H.; Zhou, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Dai, R. Evaluation of linear, nonlinear and ensemble machine learning models for landslide susceptibility assessment in Southwest China. Geocarto Int. 2022, 2152493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).