Improving Spaceborne GNSS-R Algal Bloom Detection with Meteorological Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Datasets
2.1. Area of Interest
2.2. CYGNSS Data
2.3. Auxilliary ERA5-Land Data
2.4. Reference MODIS Data
3. Detection Method
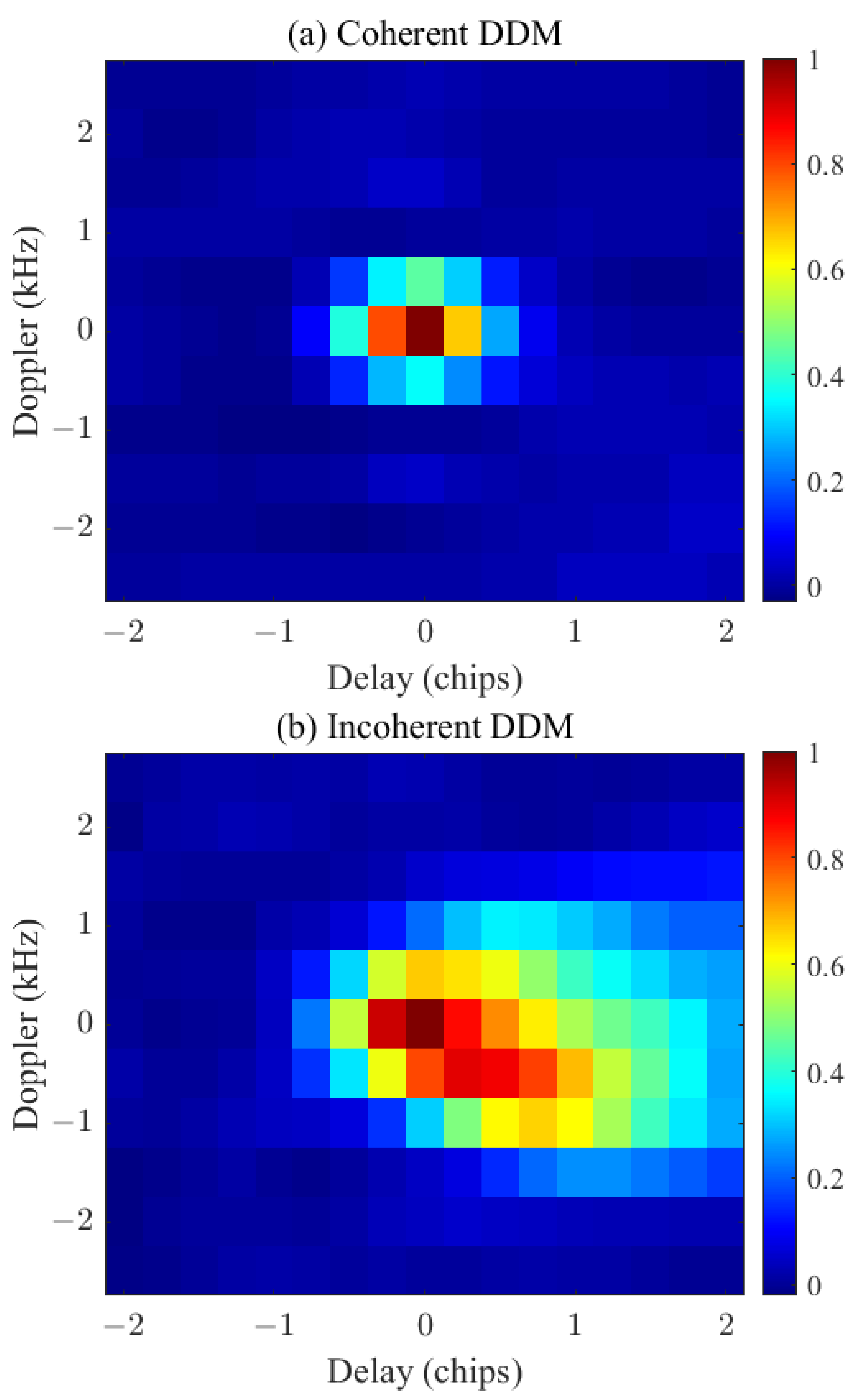
3.1. Employed CYGNSS Observations
3.2. Function of Meteorological Data
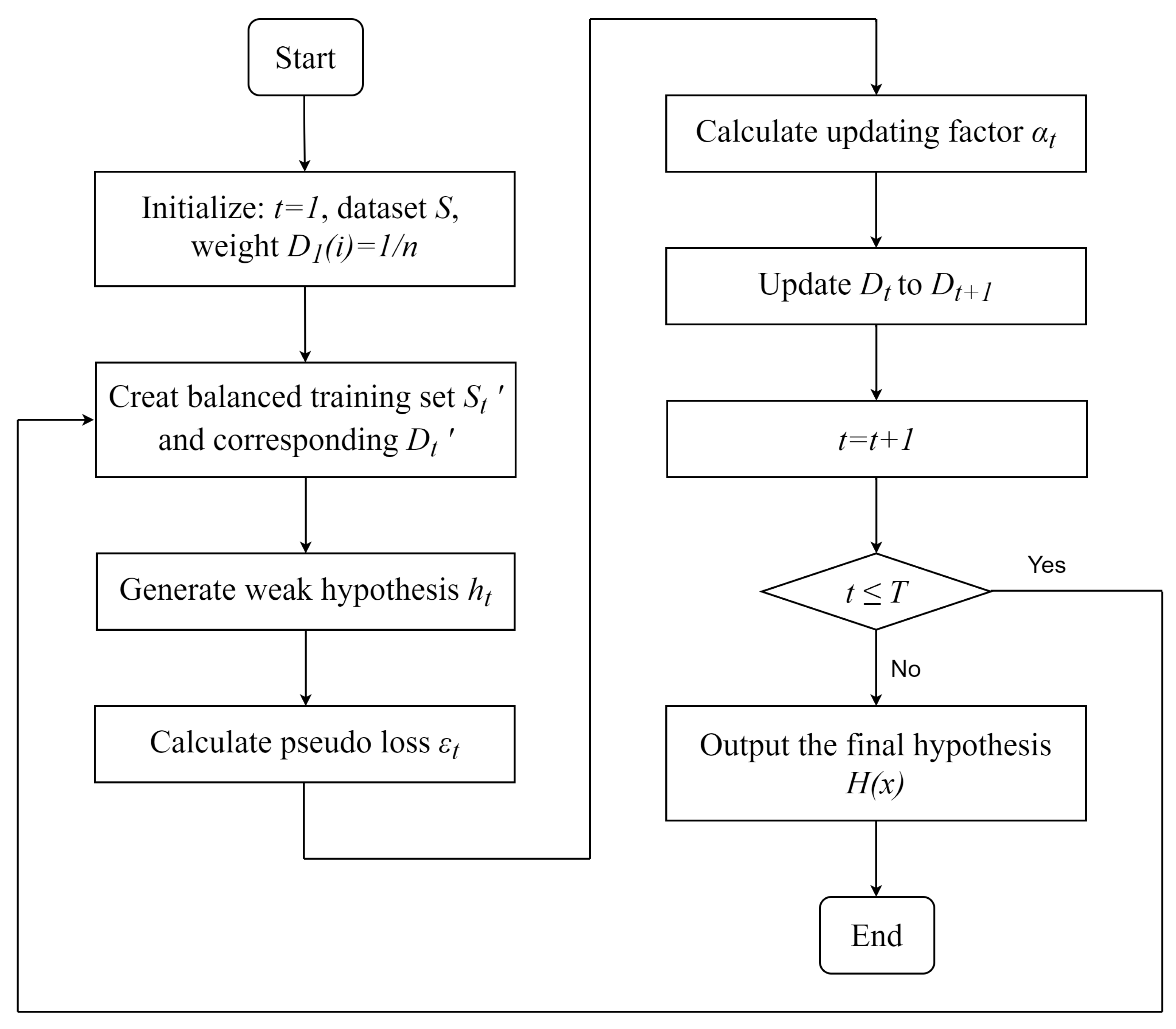
3.3. Classification Algorithm
4. Experiments and Evaluation
4.1. Threshold Value Method
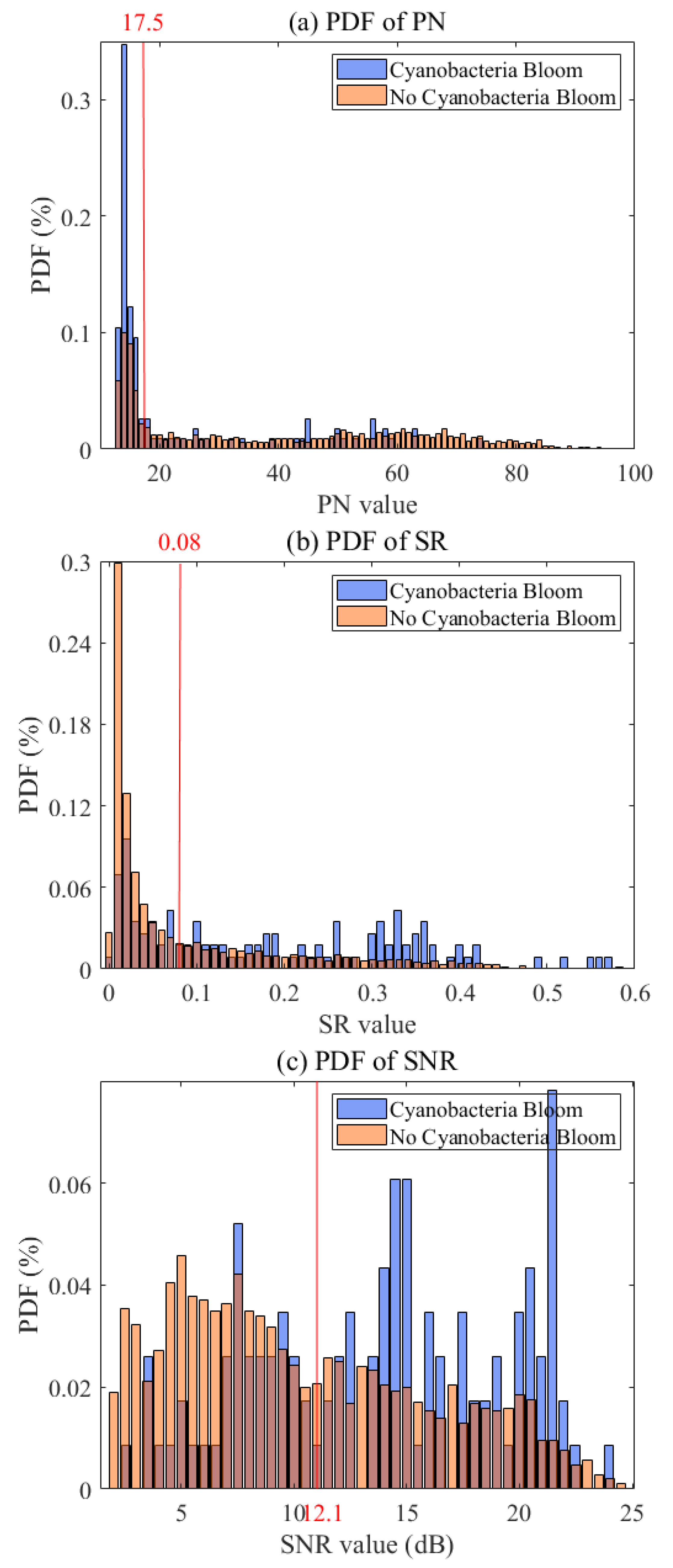
| PN | SR | SNR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threshold | 17.5 | 0.08 | 12.1 |
| TNR | 69.6% | 66.8% | 64.5% |
| TPR | 67.9% | 67.0% | 63.5% |
| OA | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.64 |
4.2. Machine Learning Method
4.2.1. Training
4.2.2. Detection Results
4.3. Error Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under Curve |
| CYGNSS | Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System |
| DDM | Delay-Doppler Map |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GNSS-R | Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| OA | Overall Accuracy |
| P | Pressure |
| Probability Density Function | |
| PN | Pixel Number |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
| RUS | Random Under Sampling |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| SP | Specular Point |
| SR | Surface Reflectivity |
| SRD | Solar Radiation Downwards |
| T | Temperature |
| TN | True Negative |
| ToP | Total Precipitation |
| TP | True Positive |
| WD | Wind Direction |
| WS | Wind Speed |
References
- Xie, R.; Pang, Y.; Bao, K. Spatiotemporal distribution of water environmental capacity-a case study on the western areas of Taihu Lake in Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5465–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Li, S. An analysis on the evolvement processes of lake eutrophication and their characteristics of the typical lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Xu, Q.J.; Gao, G.; Shen, J.H. Evaluating genotoxicity associated with microcystin-LR and its risk to source water safety in Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake. Environ. Toxicol. 2006, 21, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Ma, R.; Yu, K.; Li, D.; Shang, S. Moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) observations of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake, China. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115, C04002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, E.D.; Beasley, V.R. One health and cyanobacteria in freshwater systems: Animal illnesses and deaths are sentinel events for human health risks. Toxins 2015, 7, 1374–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y. Long-term spatiotemporal variation and environmental driving forces analyses of algal blooms in Taihu lake based on multi-source satellite and land observations. Water 2020, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Remote sensing of algal blooms: An overview with case studies. J. Coast. Res. 2012, 28, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Yu, Y.; Yang, R.; Gui, R.; Xu, Z.; Pu, F. SAR-to-optical image translation using supervised cycle-consistent adversarial networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 129136–129149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, M.S.; Dahms, T.; Kübert-Flock, C.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Zhang, J.; Ullmann, T. Spatiotemporal Fusion Modelling Using STARFM: Examples of Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 NDVI in Bavaria. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F. Monitoring cyanobacteria-dominant algal blooms in eutrophicated Taihu Lake in China with synthetic aperture radar images. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemigoudarzi, P.; Huang, W.; Silva, O.D.; Yan, Q.; Power, D.T. Flash flood detection from CYGNSS data using the RUSBoost algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 171864–171881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, D.; Belli, C.; Gioli, B.; Miglietta, F.; Ronchi, C.; Vaccari, F.P.; Valentini, R. ASPIS, a flexible multispectral system for airborne remote sensing environmental applications. Sensors 2008, 8, 3240–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Cardellach, E.; Fabra, F.; Rius, A.; Ribó, S.; Martín-Neira, M. First spaceborne phase altimetry over sea ice using TechDemoSat-1 GNSS-R signals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 8369–8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, W. Sea Ice Thickness Measurement Using Spaceborne GNSS-R: First Results with TechDemoSat-1 Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tao, T.; Yu, K.; Qu, X.; Li, S.; Wickert, J.; Semmling, M. Machine learning-aided sea ice monitoring using feature sequences extracted from spaceborne gnss-reflectometry data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Yu, T.; Tu, J.; Ke, F. Detection and Evaluation of Flood Inundation Using CYGNSS Data during Extreme Precipitation in 2022 in Guangdong Province, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Jin, S.; Liu, S.; Jia, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Chen, T.; Huang, W. Inland Water Mapping Based on GA-LinkNet from CyGNSS Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1500305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.S.; Balasubramaniam, R. Development of the CYGNSS Geophysical Model Function for Wind Speed. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.; Clarizia, M.P.; Santi, E. Wind Speed Estimation from CYGNSS Using Artificial Neural Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, W.; Jin, S.; Jia, Y. Pan-tropical soil moisture mapping based on a three-layer model from CYGNSS GNSS-R data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edokossi, K.; Calabia, A.; Jin, S.; Molina, I. GNSS-reflectometry and remote sensing of soil moisture: A review of measurement techniques, methods, and applications. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E. Soil Moisture Sensing Using Spaceborne GNSS Reflections: Comparison of CYGNSS Reflectivity to SMAP Soil Moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4049–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, N.; Oudrhiri, K. The bistatic radar as an effective tool for detecting and monitoring the presence of phytoplankton on the ocean surface. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, W.; Zhang, K.; Yu, K.; Zheng, N.; Chen, S. Detection of Red Tide over Sea Surface Using GNSS-R Spaceborne Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5802911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Meng, W.; Han, Y.; Yang, S. Feasibility study of spaceborne GNSS-R detection of algal blooms in Taihu Lake. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2022, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lary, D.J.; Alavi, A.H.; Gandomi, A.H.; Walker, A.L. Machine learning in geosciences and remote sensing. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Fang, F. Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: An applied review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2784–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, W.; Moloney, C. Neural Networks Based Sea Ice Detection and Concentration Retrieval from GNSS-R Delay-Doppler Maps. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3789–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wickert, J.; Tao, T.; Yu, K.; Li, Z.; Qu, X.; Ye, Z.; Geng, J.; Zou, J.; Semmling, M. Sensing Sea Ice Based on Doppler Spread Analysis of Spaceborne GNSS-R Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Jin, S.; Yan, Q.; Savi, P. The Sensitivity Analysis on GNSS-R Soil Moisture Retrieval. In Proceedings of the 2021 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), Hangzhou, China, 21–25 November 2021; pp. 2307–2311. [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M.; Hulse, J.V.; Napolitano, A. RUSBoost: A hybrid approach to alleviating class imbalance. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 2010, 40, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. Experiments with a New Boosting Algorithm; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Xue, B.; Zawisza, E.; Yao, S.; Liu, J.; Li, L. Effects of environmental change on subfossil Cladocera in the subtropical shallow freshwater East Taihu Lake, China. Catena 2020, 188, 104446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, W.; Hu, X. Characterization of heavy metals in water and sediments in Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 4367–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Chengxin, C.F.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Shang, J.; Gu, X. Seasonal variation of potential denitrification rates of surface sediment from Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Pan, G.; Chen, H.; Yuan, X. Removal of cyanobacterial blooms in Taihu Lake using local soils. II. Effective removal of Microcystis aeruginosa using local soils and sediments modified by chitosan. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 141, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.S.; Chew, C.; Lang, T.; Morris, M.G.; Nave, K.; Ridley, A.; Balasubramaniam, R. A New Paradigm in Earth Environmental Monitoring with the CYGNSS Small Satellite Constellation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z. A New Coherence Detection Method for Mapping Inland Water Bodies Using CYGNSS Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Gruber, S.; Zheng, D.; Li, X. The ERA5-Land soil temperature bias in permafrost regions. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 2581–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.M.; Lima, D.C.; Nogueira, M. Global offshore wind energy resources using the new ERA-5 reanalysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1040a2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, E.; O’Brien, A.; Zavorotny, V.; Zuffada, C. Towards Wind Vector and Wave Height Retrievals Over Inland Waters Using CYGNSS. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, W. Spaceborne GNSS-R Sea Ice Detection Using Delay-Doppler Maps: First Results from the U.K. TechDemoSat-1 Mission. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4795–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Cai, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, X. Analysis of the Causes of Cyanobacteria Bloom: A Review. J. Resour. Ecol. 2020, 11, 405. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Visser, P.M.; Ma, R. Diurnal changes of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake as derived from GOCI observations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1711–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provost, F.; Org, P.; Fawcett, T. Robust Classification for Imprecise Environments. Mach. Learn. 2000, 42, 203–231. [Google Scholar]




| Combination | Results | Acuracy | OA | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | GNSS-R | TNR | 68.9% | 0.69 | 0.70 |
| TPR | 63.4% | ||||
| B | GNSS-R + WS | TNR | 73.1% | 0.73 | 0.77 |
| TPR | 75.6% | ||||
| C | GNSS-R + T | TNR | 77.4% | 0.77 | 0.87 |
| TPR | 78.0% | ||||
| D | GNSS-R + P | TNR | 72.6% | 0.73 | 0.80 |
| TPR | 75.6% | ||||
| E | GNSS-R + ToP | TNR | 74.2% | 0.74 | 0.79 |
| TPR | 75.6% | ||||
| F | GNSS-R + WD | TNR | 74.4% | 0.74 | 0.78 |
| TPR | 65.9% | ||||
| G | GNSS-R + SRD | TNR | 76.0% | 0.76 | 0.84 |
| TPR | 78.0% | ||||
| H | All Features | TNR | 81.9% | 0.82 | 0.88 |
| TPR | 82.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhen, Y.; Yan, Q. Improving Spaceborne GNSS-R Algal Bloom Detection with Meteorological Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123122
Zhen Y, Yan Q. Improving Spaceborne GNSS-R Algal Bloom Detection with Meteorological Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(12):3122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123122
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhen, Yinqing, and Qingyun Yan. 2023. "Improving Spaceborne GNSS-R Algal Bloom Detection with Meteorological Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 12: 3122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123122
APA StyleZhen, Y., & Yan, Q. (2023). Improving Spaceborne GNSS-R Algal Bloom Detection with Meteorological Data. Remote Sensing, 15(12), 3122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123122







