The Innovative Growth of Space Archaeology: A Brief Overview of Concepts and Approaches in Detection, Monitoring, and Promotion of the Archaeological Heritage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
- (1)
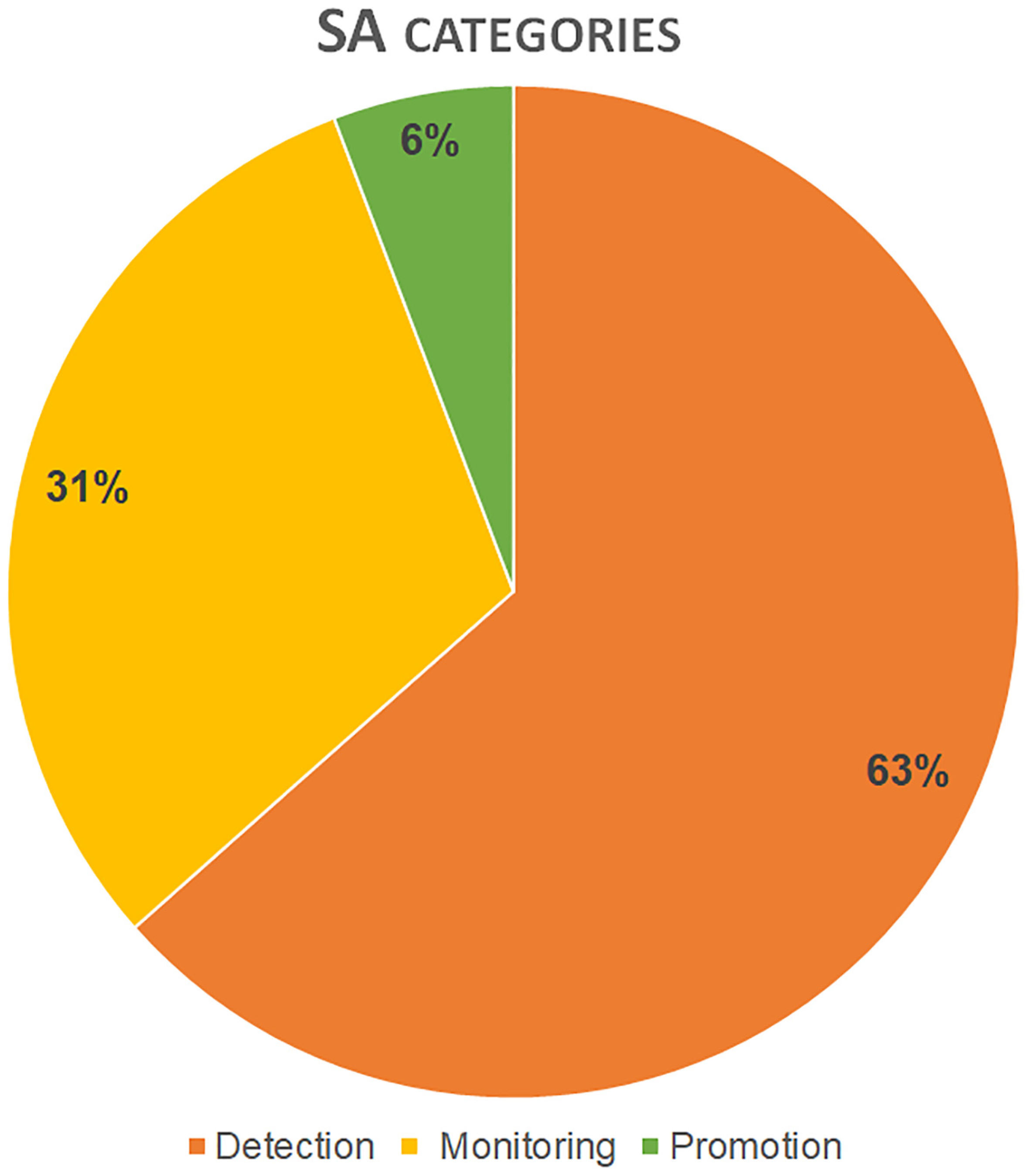
- Three main categories corresponding to SA application fields were individualized: Detection, monitoring, and promotion. In particular, detection includes SA works that apply the identification of buried archaeological traces and sites (crop/soil marks, micro-reliefs, geometric/radiometric features, etc.) and the investigation of the archaeological contexts (distribution and evolution of settlements, reconstruction of the ancient viability, etc.). Monitoring includes SA works that apply the observation over time of natural and anthropogenic processes for the preservation of archaeological sites (evaluation of geo-hazards, assessment of anthropic impact and checking of the integrity of archaeological sites, detection of looting, etc.). Promotion includes SA works that apply the broadcast of cultural (historic, geographic, topographic, ethnographic, etc.) value of the archaeological heritage. Fifty-two SA records were classified in these three groups on the basis of their target.
- (2)
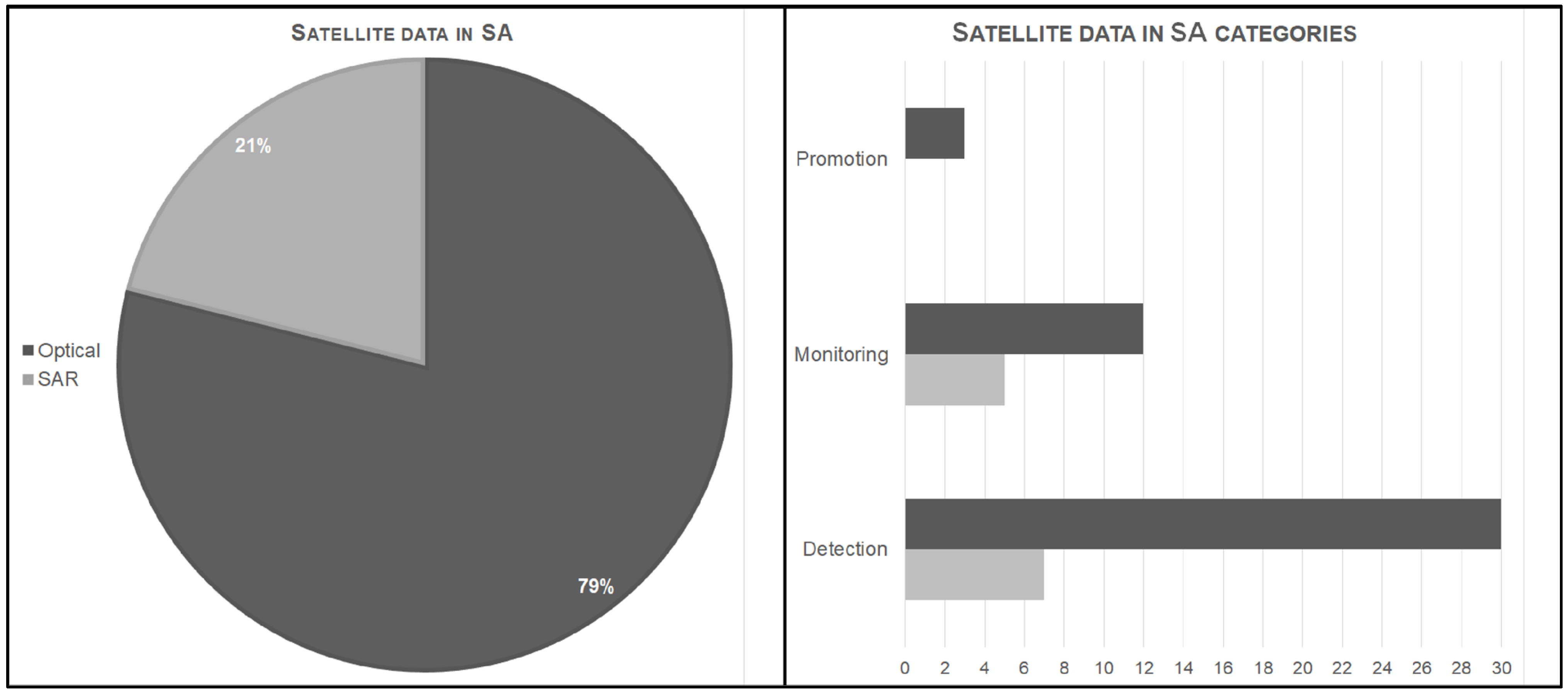
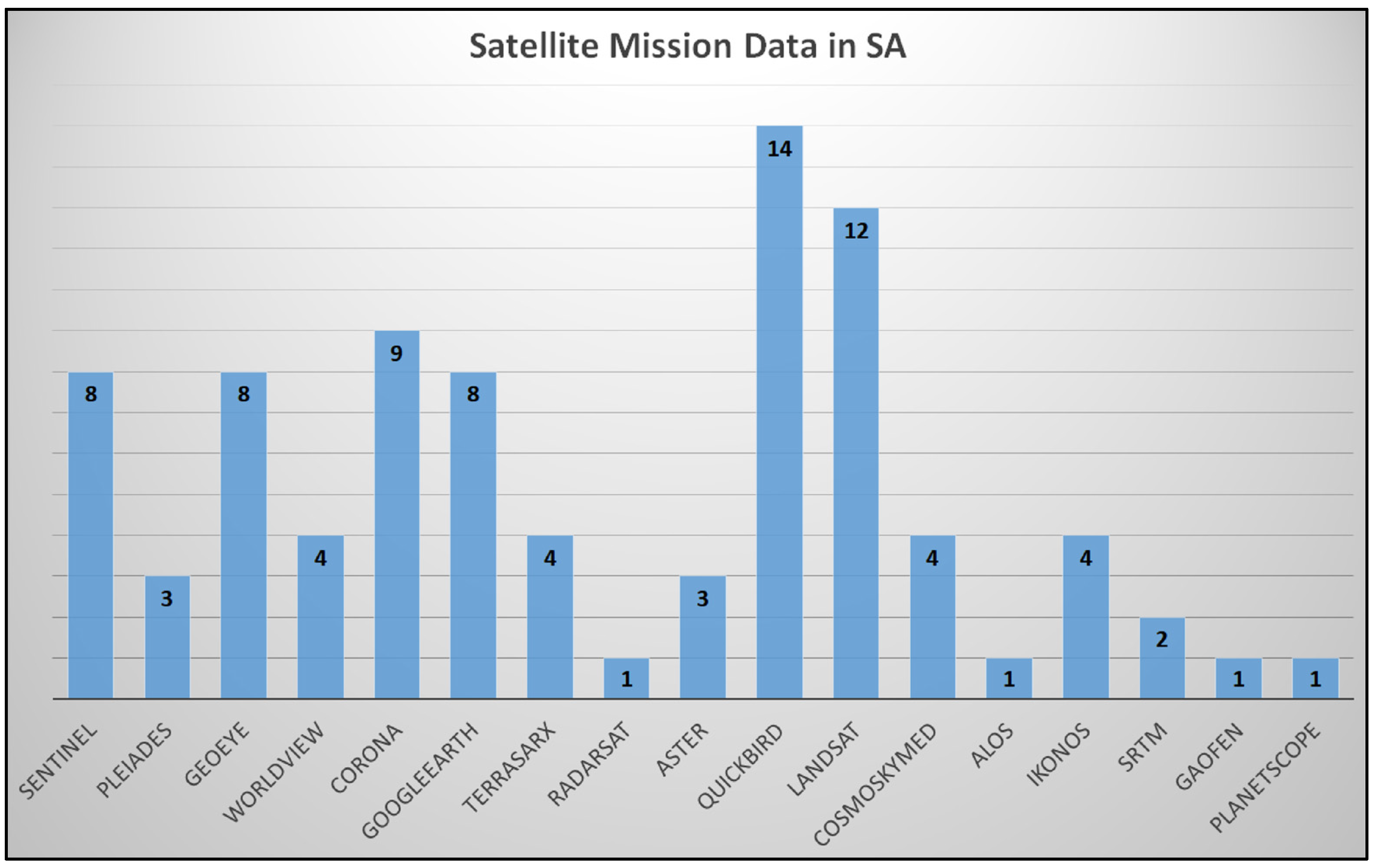
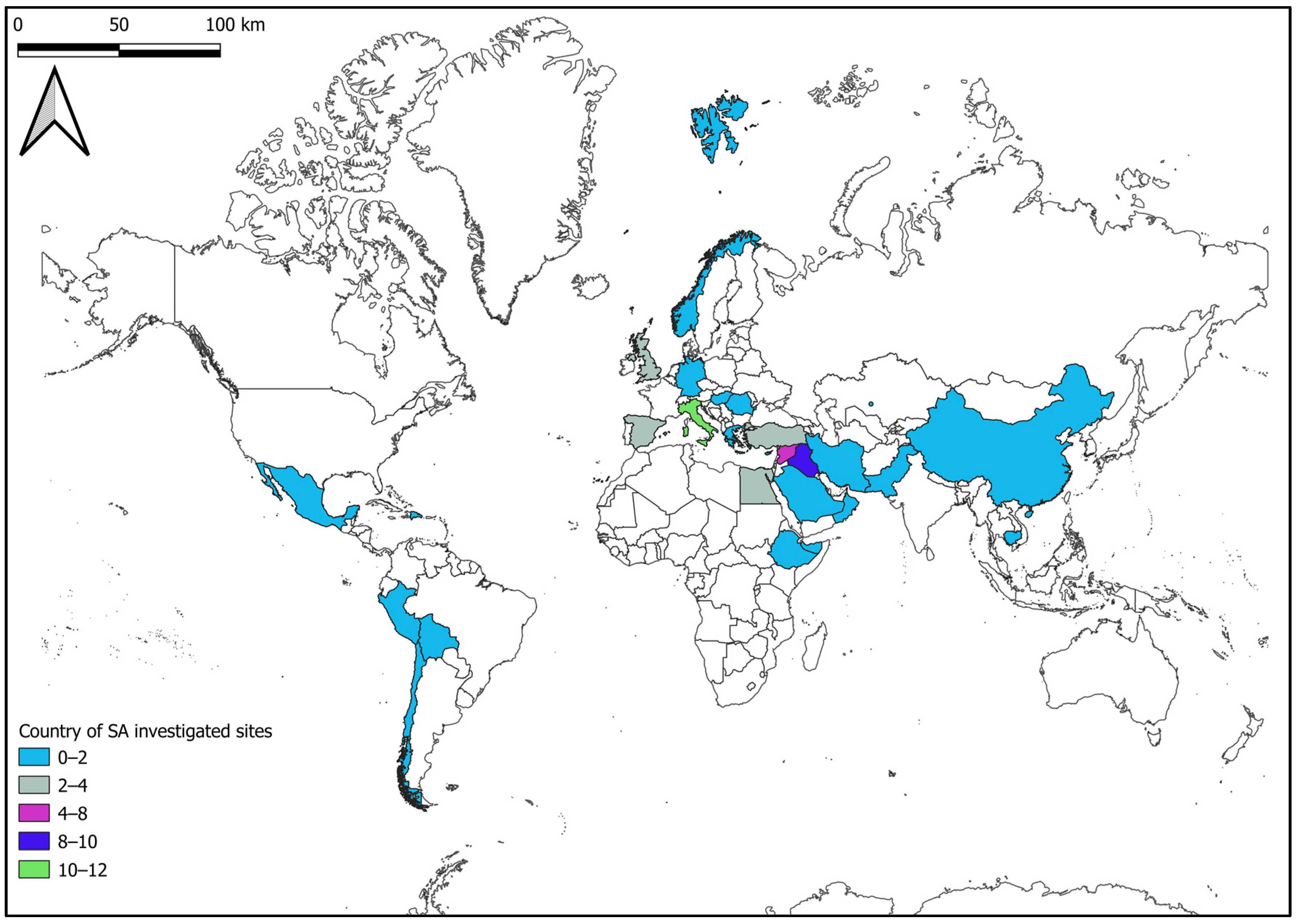
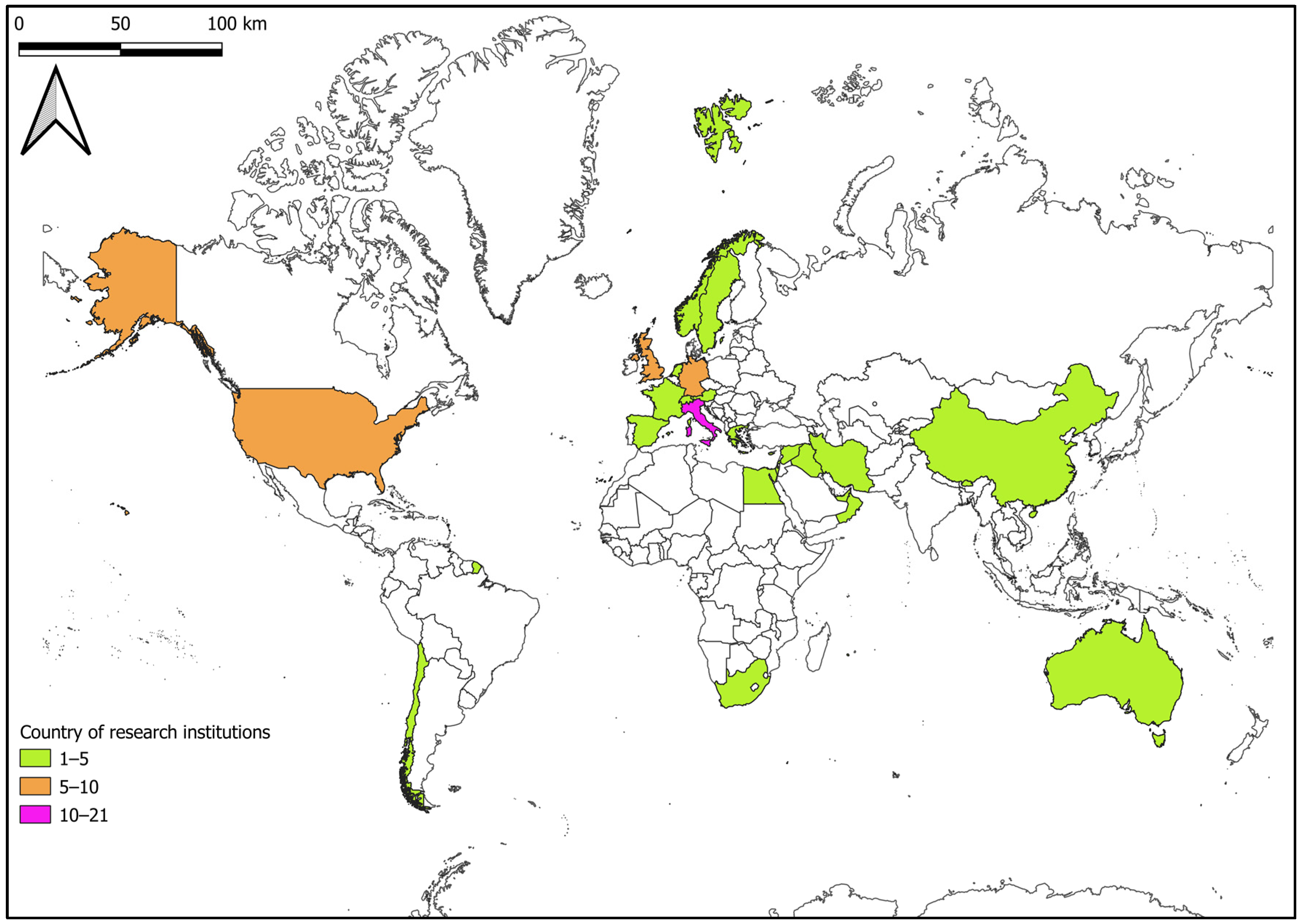
- A focus on specific aspects was carried out by extracting information from each SA work: (i) Satellite data used (i.e., optical or SAR, and satellite missions); (ii) data analysis methodologies applied; (iii) country of archaeological sites investigated; (iv) country of the research institutions that affiliate work authors. Then, a review of the database was realized, in which each record is SA work and each extracted information is an attribute.
- (3)
- Geospatial and statistical analysis of data acquired was performed through the processing of graphs and maps by using QGIS® (http://qgis.org (accessed on 5 May 2023); version 3.16.1) and Microsoft Excel® (https://www.microsoft.com/it-it/microsoft-365/excel (accessed on 5 May 2023); version Office 2013-15) software.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parcak, S.H. GIS, remote sensing, and landscape archaeology. In The Oxford Handbook of Topics in Archaeology; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Parcak, S. Archaeology from Space: How the Future Shapes Our Past; Henry Holt and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tapete, D. Remote Sensing and Geosciences for Archaeology. Geosciences 2018, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Jia, X.; Fan, A. Earth observation in archaeology: A brief review. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, M.; Campana, S.; Liuzza, C. (Eds.) Space, Time, Place; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Orlando, P.; Villa, B.D. Remote sensing applications in archaeology. Archeol. E Calc. 2011, 22, 147–168. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Lasaponara, R.; Zong, X.; Masini, N.; Wang, G.; Shi, P.; Khatteli, H.; Chen, F.; et al. Airborne and spaceborne remote sensing for archaeological and cultural heritage applications: A review of the century (1907–2017). Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traviglia, A.; Torsello, A. Landscape Pattern Detection in Archaeological Remote Sensing. Geosciences 2017, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frodella, W.; Elashvili, M.; Spizzichino, D.; Gigli, G.; Adikashvili, L.; Vacheishvili, N.; Kirkitadze, G.; Nadaraia, A.; Margottini, C.; Casagli, N. Combining InfraRed Thermography and UAV Digital Photogrammetry for the Protection and Conservation of Rupestrian Cultural Heritage Sites in Georgia: A Methodological Application. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajlik, Z.; Árvai, M.; Mészáros, J.; Nagy, B.; Rupnik, L.; Pásztor, L. Cropmarks in Aerial Archaeology: New Lessons from an Old Story. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angeli, S.; Battistin, F. Archaeological site monitoring and risk assessment using remote sensing technologies and GIS. In A Research Agenda for Heritage Planning: Perspectives from Europe; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2021; Chapter 12; p. 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drap, P.; Papini, O.; Pruno, E.; Nucciotti, M.; Vannini, G. Ontology-Based Photogrammetry Survey for Medieval Archaeology: Toward a 3D Geographic Information System (GIS). Geosciences 2017, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, G.J. Are We There Yet? A Review and Assessment of Archaeological Passive Airborne Optical Imaging Approaches in the Light of Landscape Archaeology. Geosciences 2017, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, G. Remote Sensing and Geo-Archaeological Data: Inland water studies for the conservation of underwater cultural heritage in the Ferrara District, Italy. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, V.D.; DePratter, C.B.; Lulewicz, J.; Lulewicz, I.H.; Roberts Thompson, A.D.; Cramb, J.; Ritchison, B.T.; Colvin, M.H. The Archaeology and Remote Sensing of Santa Elena’s Four Millennia of Occupation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, A.; Lennon, M.; Thomas, N.; Gueguen, S.; Petit, T.; Lorho, T.; Cassen, S.; Hubert-Moy, L. Airborne Hyperspectral Imaging for Submerged Archaeological Mapping in Shallow Water Environments. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, K.; Verschoof-van der Vaart, W.B.; Bourgeois, Q.P.J. Integrating Remote Sensing, Machine Learning, and Citizen Science in Dutch Archaeological Prospection. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rączkowski, W. Power and/or Penury of Visualizations: Some Thoughts on Remote Sensing Data and Products in Archaeology. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, C.; Clutterbuck, B. Mapping Heterogeneous Buried Archaeological Features Using Multisensor Data from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaweel, M.; Khelifi, A.; Li, Z.; Squitieri, A.; Basmaji, T.; Ghazal, M. Automated Archaeological Feature Detection Using Deep Learning on Optical UAV Imagery: Preliminary Results. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, N.; Abate, N.; Gizzi, F.T.; Vitale, V.; Amodio, A.M.; Sileo, M.; Biscione, M.; Lasaponara, R.; Bentivenga, M.; Cavalcante, F. UAV LiDAR Based Approach for the Detection and Interpretation of Archaeological Micro Topography under Canopy—The Rediscovery of Perticara (Basilicata, Italy). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Remote Sensing in Archaeology: From Visual Data Interpretation to Digital Data Manipulation. In Satellite Remote Sensing: A New Tool for Archaeology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, D.; Verhoeven, G.; Traviglia, A. Editorial for Special Issue: “Archaeological Remote Sensing in the 21st Century: (Re)Defining Practice and Theory”. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingaro, A. Advanced analysis and integration of Remote Sensing and in situ data for flood monitoring. Rendiconti Online della Soc. Geol. Ital. 2021, 54, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.M. Satellite imagery and archaeology. In Landscapes through the Lens: Aerial Photographs and Historic Environment; Cowley, D.C., Standring, R.A., Abicht, M.J., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2010; Chapter 10; pp. 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Campana, S. Le immagini da satellite nell’indagine archeologica: Stato dell’arte, casi di studio, prospettive. Archeologia Aerea. Studi Aerotopogr. Archeol. 2004, 1, 279–299. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, W.S.; Oltean, I.A. Archaeology from Historical Aerial and Satellite Archives; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Satellite Synthetic Aperture Radar in Archaeology and Cultural Landscape: An Overview. Archaeol. Prospect. 2013, 20, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Lasaponara, R.; Shi, P.; Bachagha, N.; Li, L.; Yao, Y.; Masini, N.; Chen, F.; et al. Google Earth as a Powerful Tool for Archaeological and Cultural Heritage Applications: A Review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingaro, M.; La Salandra, M.; Colacicco, R.; Roseto, R.; Petio, P.; Capolongo, D. Suitability assessment of global, continental and national digital elevation models for geomorphological analyses in Italy. Trans. GIS 2021, 25, 2283–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, S.; Francovich, R. Landscape Archaeology in Tuscany: Cultural resource management, remotely sensed techniques, GIS based data integration and interpretation. Bar Int. Ser. 2003, 1151, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chyla, J.M. How Can Remote Sensing Help in Detecting the Threats to Archaeological Sites in Upper Egypt? Geosciences 2017, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comer, D.C.; Chapman, B.D.; Comer, J.A. Detecting Landscape Disturbance at the Nasca Lines Using SAR Data Collected from Airborne and Satellite Platforms. Geosciences 2017, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingaro, M.; Mastronuzzi, G. Il popolamento antico di Lama Diumo-San Giorgio in relazione alle forme del paesaggio. Agric. Centuriati. 2017, 14, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingaro, M. Evoluzione storica del popolamento antico in agro di Andria (Puglia). J. Anc. Topogr. 2018, 28, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zingaro, M. Forme del paesaggio e sistema viario. Il ruolo di Monte Sannace nelle dinamiche territoriali della Puglia centrale. In Monte Sannace Lavori in Corso; Palmentola, P., Ed.; Studi e Ricerche presso il Parco Archeologico di Monte Sannace: Gioia del Colle, Italy, 2022; pp. 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Brancato, R. How to access ancient landscapes? Field survey and legacy data integration for research on Greek and Roman settlement patterns in Eastern Sicily. Groma Doc. Archaeol. 2020, 4, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, M.J. NASA Remote Sensing and Archaeology. In Satellite Remote Sensing: A New Tool for Archaeology, Remote Sensing and Digital Image Processing; Lasaponara, R., Masini, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 16, pp. 157–176. [Google Scholar]
- Bonazza, A.; Bonora, N.; Duke, B.; Spizzichino, D.; Recchia, A.P.; Taramelli, A. Copernicus in Support of Monitoring, Protection, and Management of Cultural and Natural Heritage. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comer, D.C.; Harrower, M.J. Mapping Archaeological Landscapes from Space; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 159–171. [Google Scholar]
- Golinelli, G.M.; Gaetano, M. Cultural Heritage and Value Creation; Sprienger Briefs in Economics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aminzadeh, B.; Samani, F. Identifying the boundaries of the historical site of Persepolis using remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Detection of archaeological crop marks by using satellite QuickBird multispectral 477 imagery. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltean, I.A.; Abell, L.L. High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and the Detection of Buried Archaeological Features in Ploughed Landscapes. In Satellite Remote Sensing: A New Tool for Archaeology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapiou, A.; Alexakis, D.D.; Sarris, A.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Orthogonal equations of multi-spectral satellite imagery for the identification of un-excavated archaeological sites. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6560–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapiou, A.; Lysandrou, V.; Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Study of the Variations of Archaeological Marks at Neolithic Site of Lucera, Italy Using High-Resolution Multispectral Datasets. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, N.; Roubis, D.; Vitale, V.; Sileo, M.; Sogliani, F.; Masini, N.; Lasaponara, R. Integrated use of multi-temporal multi-sensor and multiscale Remote Sensing data for the understanding of archaeological contexts: The case study of Metaponto, Basilicata. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2204, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapiou, A.; Lysandrou, V.; Sarris, A.; Papadopoulos, N.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Fusion of Satellite Multispectral Images Based on Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) Data for the Investigation of Buried Concealed Archaeological Remains. Geosciences 2017, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnemann, T.F.; Comer, D.C.; Patsolic, J.L.; Megarry, W.P.; Malatesta, E.H.; Hofman, C.L. Semi-Automatic Detection of Indigenous Settlement Features on Hispaniola through Remote Sensing Data. Geosciences 2017, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, T.; Lasaponara, R.; Wainwright, J.; Masini, N. Multispectral Contrast of Archaeological Features: A Quantitative Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titolo, A. Use of Time-Series NDWI to Monitor Emerging Archaeological Sites: Case Studies from Iraqi Artificial Reservoirs. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviello, M.; Ciminale, M.; De Pasquale, V. Combined application of pansharpening and enhancement methods to improve archaeological cropmark visibility and identification in QuickBird imagery: Two case studies from Apulia, Southern Italy. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 3604–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R.; Leucci, G.; Masini, N.; Persico, R.; Scardozzi, G. Towards an operative use of remote sensing for exploring the past using satellite data: The case study of Hierapolis (Turkey). Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borie, C.; Parcero-Oubiña, C.; Kwon, Y.; Salazar, D.; Flores, C.; Olguín, L.; Andrade, P. Beyond Site Detection: The Role of Satellite Remote Sensing in Analysing Archaeological Problems. A Case Study in Lithic Resource Procurement in the Atacama Desert, Northern Chile. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo, H.A.; Conesa, F.C.; Garcia-Molsosa, A.; Lobo, A.; Green, A.S.; Madella, M.; Petrie, C.A. Automated detection of archaeological mounds using machine-learning classification of multisensor and multitemporal satellite data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18240–18250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spizzichino, D.; Margottini, C.; Brustia, E.; Cigna, F.; Comerci, V.; Dessì, B.; Guerrieri, L.; Iadanza, C.; Leoni, G.; Vittori, E.; et al. Satellite monitoring applied to natural hazards and cultural heritage: The PROTHEGO project. In Proceedings of the Workshop Tematico di Telerilevamento—AIT Bologna, Bologna, Italy, 27–28 June 2017; Volume 27, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Themistocleous, K.; Danezis, C.; Mendonidis, E.; Lymperopoulou, E. 2017. Monitoring ground deformation of cultural heritage sites using UAVs and geodetic techniques: The case study of Choirokoitia, JPI PROTHEGO project. In Earth Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing/GIS Applications VIII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10428, pp. 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.; Oren, E.D.; Cohen-Sasson, E. Satellite Remote Sensing Analysis of the Qasrawet Archaeological Site in North Sinai. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, G.; Spizzichino, D.; Marcelli, M.; Carta, C. Il monitoraggio satellitare nelle aree archeologiche: Il caso delle Mura Aureliane di Roma. In Monitoraggio e Manutenzione delle Aree Archeologiche, Cambiamenti Climatici, Dissesto Idrogeologico, Degrado Chimico-Ambientale, Proceedings of the atti del Convegno Internazionale di Studi, Roma, Italy, 20–21 March 2019; Russo, A., Giovampaola, I.D., Eds.; L’Erma di Bretschneider: Rome, Italy, 2020; pp. 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Spizzichino, D.; Margottini, C. Satellite monitoring of geo-hazards affecting cultural heritage. In A Research Agenda for Heritage Planning: Perspectives from Europe; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2021; p. 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Philip, G.; Abdulkarim, M.; Donoghue, D. Evaluation of Corona and Ikonos high resolution satellite imagery for archaeological prospection in western Syria. Antiquity 2007, 81, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminale, M.; Gallo, D.; Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. A multiscale approach for reconstructing archaeological landscapes: Applications in Northern Apulia (Italy). Archaeol. Prospect. 2009, 16, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trier, D.; Larsen, S.; Solberg, R. Automatic detection of circular structures in high-resolution satellite images of agricultural land. Archaeol. Prospect. 2009, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Beyond modern landscape features: New insights in the archaeological area of Tiwanaku in Bolivia from satellite data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, T.; Simon, F.-X.; Sarris, A. A Manifold Approach for the Investigation of Early and Middle Neolithic Settlements in Thessaly, Greece. Geosciences 2017, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, M.; Isola, I.; Zanchetta, G.; Ribolini, A.; Ciampalini, A.; Baneschi, I.; Mele, D.; D’agata, A.L. Identification of Leveled Archeological Mounds (Höyük) in the Alluvial Plain of the Ceyhan River (Southern Turkey) by Satellite Remote-Sensing Analyses. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapete, D.; Cigna, F. Appraisal of Opportunities and Perspectives for the Systematic Condition Assessment of Heritage Sites with Copernicus Sentinel-2 High-Resolution Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivitskis, A.J.; Lehner, J.W.; Harrower, M.J.; Dumitru, I.A.; Paulsen, P.E.; Nathan, S.; Viete, D.R.; Al-Jabri, S.; Helwing, B.; Wiig, F.; et al. Detecting and Mapping Slag Heaps at Ancient Copper Production Sites in Oman. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchley, S. Assessing the Utility of High-Resolution Satellite Remote Sensing for Archaeological Prospection and Mapping. In Copernicus Task Force on Cultural Heritage—Annex I Case Studies; 2020, EUSpace. Available online: https://www.copernicus.eu/en/documentation/technical-documents/technical-documentstechnical-documents (accessed on 26 May 2023).
- Zaina, F.; Tapete, D. Satellite-Based Methodology for Purposes of Rescue Archaeology of Cultural Heritage Threatened by Dam Construction. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N.; Holmgren, R.; Forsberg, Y.B. Integration of aerial and satellite remote sensing for archaeological investigations: A case study of the Etruscan site of San Giovenale. J. Geophys. Eng. 2012, 9, S26–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrzejas, T.; Przybilla, H.J. Aufbau historischer 3D-Szenarien am Beispiel der mittelalterlichen Stadt Duisburg. Photogramm. Fernerkund. Geoinf. 2009, 2009, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.; Bishop, M. Google earth and the archaeology of Saudi Arabia. A case study from the Jeddah area. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Delgado, J.A.; Martínez-Graña, A.M.; Civis, J.; Sierro, F.; Goy, J.L.; Dabrio, C.J.; Ruiz, F.; González-Regalado, M.L.; Abad, M. Virtual 3D tour of the Neogene palaeontological heritage of Huelva (Guadalquivir Basin, Spain). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4609–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnemann, T.F. Spatial Configurations of Water Management at an Early Angkorian Capital—Combining GPR and TerraSAR-X Data to Complement an Archaeological Map. Archaeol. Prospect. 2015, 22, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casana, J.; Laugier, E. Satellite imagery-based monitoring of archaeological site damage in the Syrian civil war. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danti, M.; Branting, S.; Penacho, S. The American Schools of Oriental Research Cultural Heritage Initiatives: Monitoring Cultural Heritage in Syria and Northern Iraq by Geospatial Imagery. Geosciences 2017, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapiou, A.; Lysandrou, V.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Optical Remote Sensing Potentials for Looting Detection. Geosciences 2017, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Kohlus, J.; Kost, C. SAR Imaging of Archaeological Sites on Intertidal Flats in the German Wadden Sea. Geosciences 2017, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parcak, S.; Mumford, G.; Childs, C. Using Open Access Satellite Data Alongside Ground Based Remote Sensing: An Assessment, with Case Studies from Egypt’s Delta. Geosciences 2017, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parcak, S. Moving from Space-Based to Ground-Based Solutions in Remote Sensing for Archaeological Heritage: A Case Study from Egypt. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutishauser, S.; Erasmi, S.; Rosenbauer, R.; Buchbach, R. SARchaeology—Detecting Palaeochannels Based on High Resolution Radar Data and Their Impact of Changes in the Settlement Pattern in Cilicia (Turkey). Geosciences 2017, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Lasaponara, R.; Xiang, B.; Zhen, J.; Zhu, L.; Yang, R.; Liu, D.; Liu, C. Auto-Extraction of Linear Archaeological Traces of Tuntian Irrigation Canals in Miran Site (China) from Gaofen-1 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayne, L.; Donoghue, D. A Remote Sensing Approach for Mapping the Development of Ancient Water Management in the Near East. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotheri, J.; de Gruchy, M.W.; Almaliki, R.; Feadha, M. Remote Sensing the Archaeological Traces of Boat Movement in the Marshes of Southern Mesopotamia. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, C.N.; Scott, C.; Cowley, D.; Macdonald, M. Towards a Satellite System for Archaeology? Simulation of an Optical Satellite Mission with Ideal Spatial and Temporal Resolution, Illustrated by a Case Study in Scotland. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, R. Combining Structure-from-Motion with high and intermediate resolution satellite images to document threats to archaeological heritage in arid environments. J. Cult. Herit. 2015, 16, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerra, D.; Plank, S.; Lysandrou, V.; Tian, J. Cultural Heritage Sites in Danger—Towards Automatic Damage Detection from Space. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morehart, C.T.; Millhauser, J.K. Monitoring cultural landscapes from space: Evaluating archaeological sites in the Basin of Mexico using very high resolution satellite imagery. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 10, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R.; Murgante, B.; Elfadaly, A.; Qelichi, M.M.; Shahraki, S.Z.; Wafa, O.; Attia, W. Spatial Open Data for Monitoring Risks and Preserving Archaeological Areas and Landscape: Case Studies at Kom el Shoqafa, Egypt and Shush, Iran. Sustainability 2017, 9, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Zong, X.; Ji, W.; Cao, H. VHR GeoEye-1 imagery reveals an ancient water landscape at the Longcheng site, northern Chaohu Lake Basin (China). Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 10, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroush, M.; Mehrtash, A.; Khazraee, E.; Ur, J.A. Deep Learning in Archaeological Remote Sensing: Automated Qanat Detection in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinverni, E.S.; Pierdicca, R.; Bozzi, C.A.; Colosi, F.; Orazi, R. Analysis and Processing of Nadir and Stereo VHR Pleiadés Images for 3D Mapping and Planning the Land of Nineveh, Iraqi Kurdistan. Geosciences 2017, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report. 2022. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2022/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2022.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2023).
- OECD. OECD Handbook on Measuring the Space Economy; OECD: Paris, France, 2012; ISBN 978-92-64-12180-5. [Google Scholar]
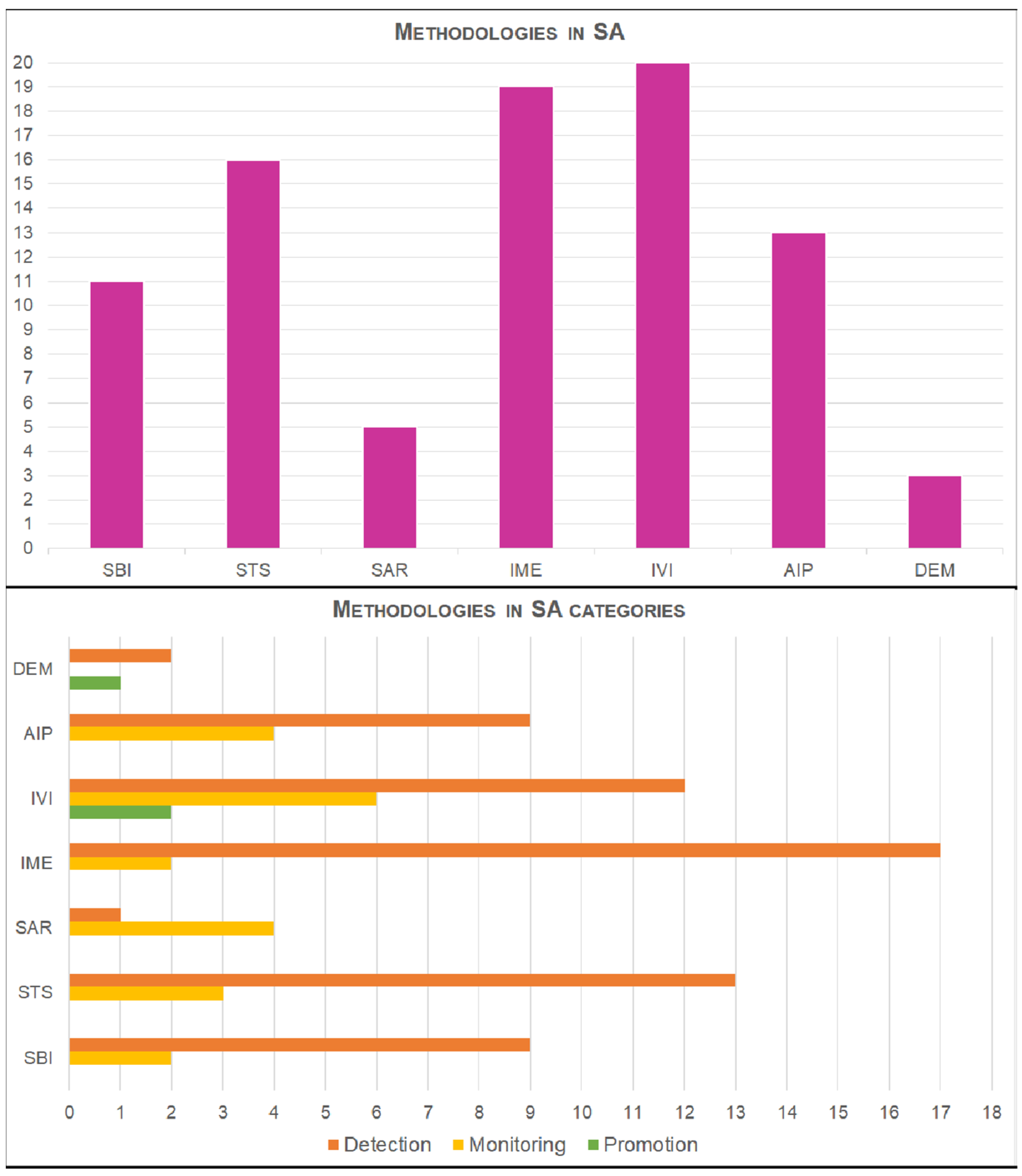
| Cluster | Methodologies | Name | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spectral band indices | SBI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) |
| 2 | Statistics | STS | Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Tasseled Cap Transformation (TCT), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), etc. |
| 3 | SAR amplitude, interferometric coherence | SAR | Permanent Scatterer InSAR (PSI), Differential InSAR (DInSAR), etc. |
| 4 | Image enhancement | IME | Filters, band combinations, etc. |
| 5 | Image visual inspection | IVI | Image observation and interpretation |
| 6 | Advanced algorithms of image processing | AIP | Pattern Recognition, Segmentation, Machine/Deep learning, etc. |
| 7 | Digital elevation models | DEM | Stereo-pair images, Satellite Digital Elevation Models |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zingaro, M.; Scicchitano, G.; Capolongo, D. The Innovative Growth of Space Archaeology: A Brief Overview of Concepts and Approaches in Detection, Monitoring, and Promotion of the Archaeological Heritage. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3049. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123049
Zingaro M, Scicchitano G, Capolongo D. The Innovative Growth of Space Archaeology: A Brief Overview of Concepts and Approaches in Detection, Monitoring, and Promotion of the Archaeological Heritage. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(12):3049. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123049
Chicago/Turabian StyleZingaro, Marina, Giovanni Scicchitano, and Domenico Capolongo. 2023. "The Innovative Growth of Space Archaeology: A Brief Overview of Concepts and Approaches in Detection, Monitoring, and Promotion of the Archaeological Heritage" Remote Sensing 15, no. 12: 3049. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123049
APA StyleZingaro, M., Scicchitano, G., & Capolongo, D. (2023). The Innovative Growth of Space Archaeology: A Brief Overview of Concepts and Approaches in Detection, Monitoring, and Promotion of the Archaeological Heritage. Remote Sensing, 15(12), 3049. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15123049








