Assessment of Swarm Kinematic Orbit Determination Using Two Different Double-Difference Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
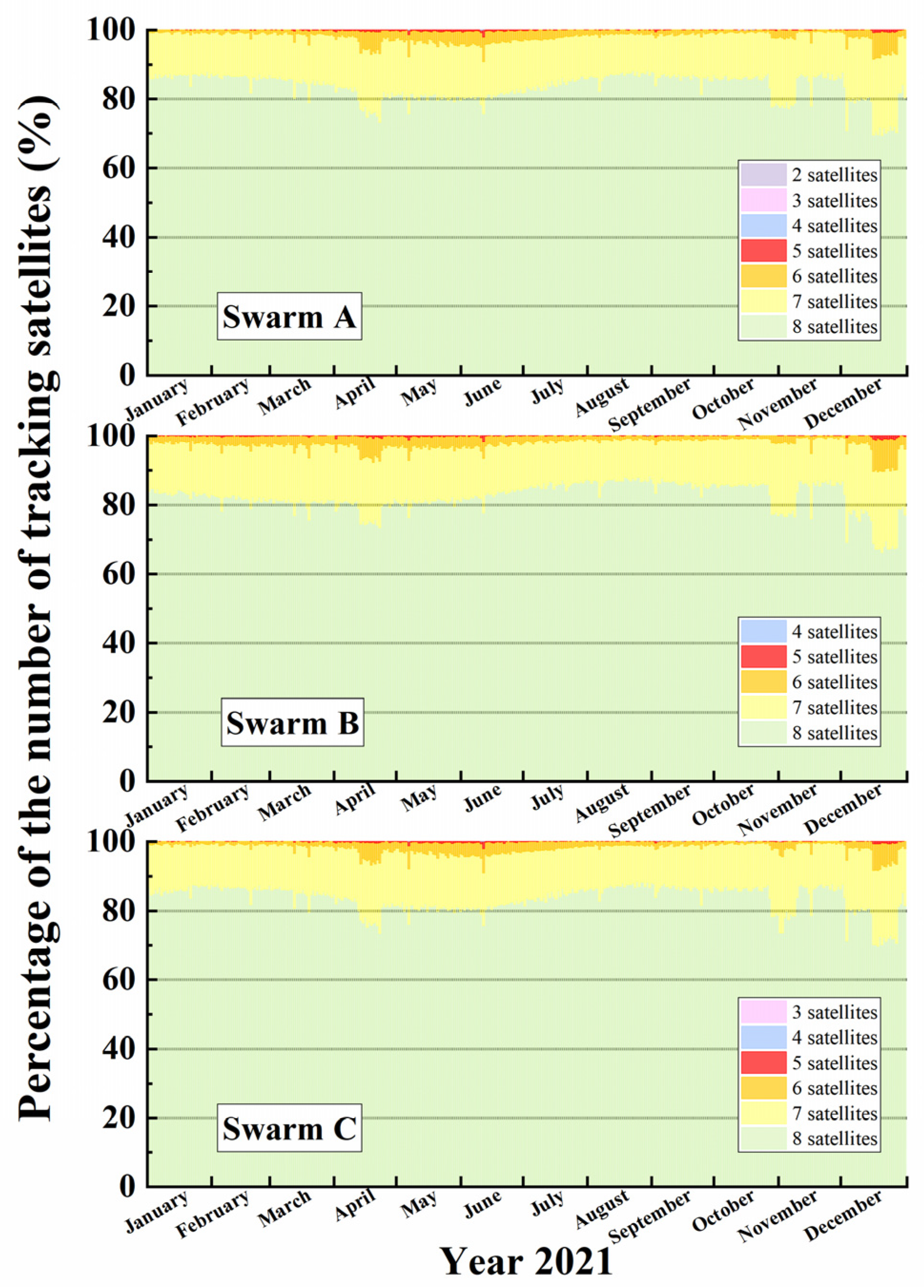
2.1. Observation Analysis
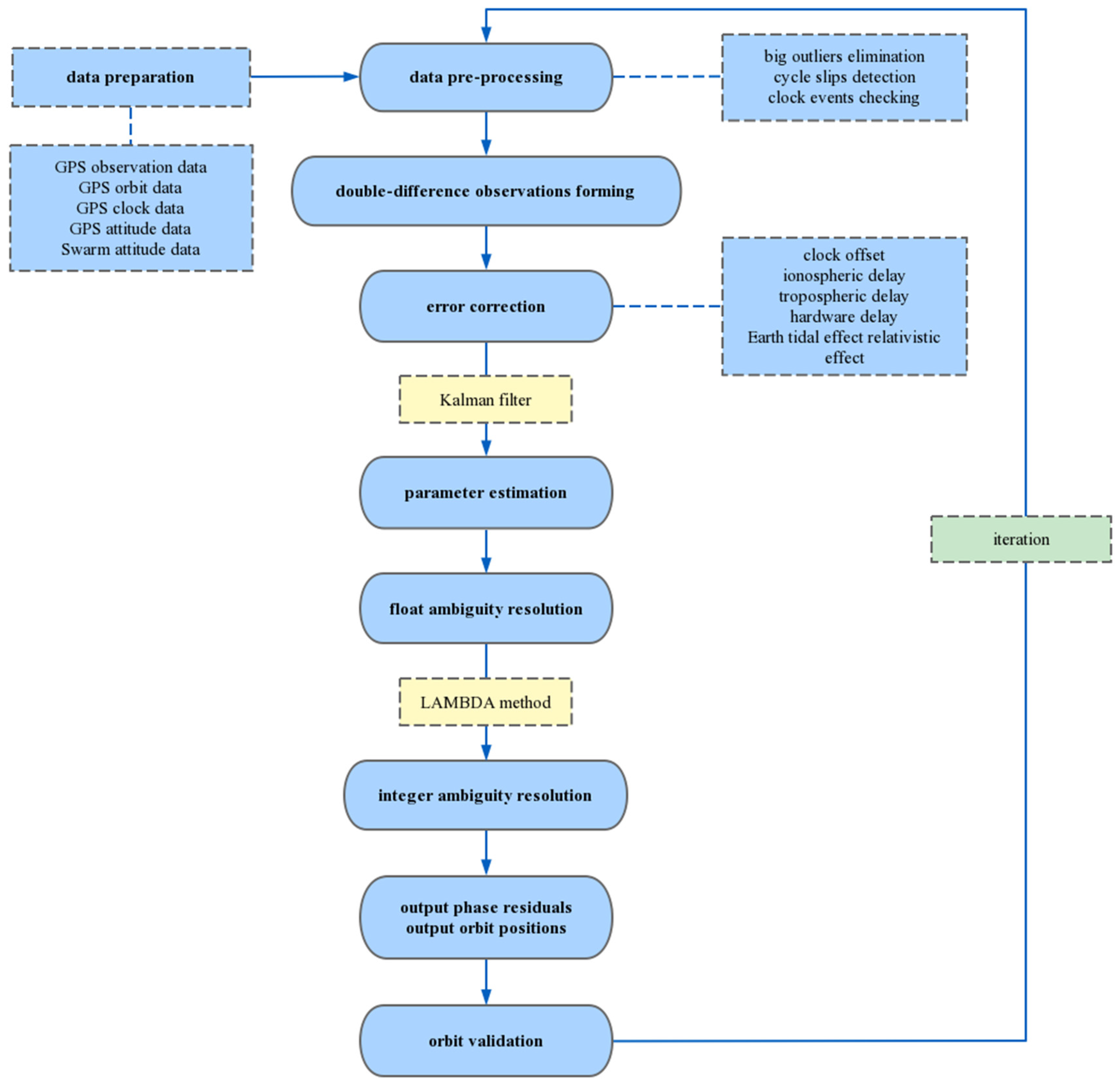
2.2. Data Pre-Processing
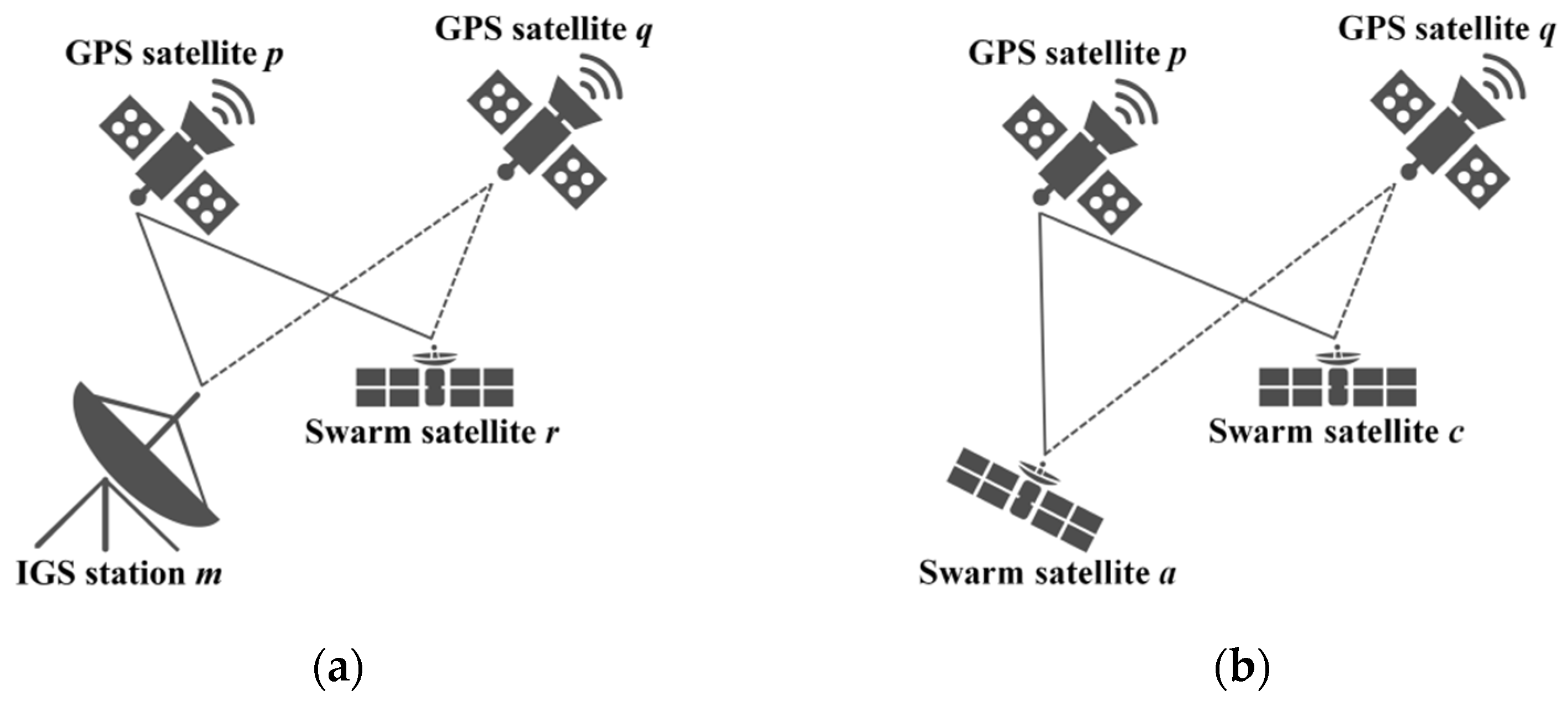
2.3. Kinematic Orbit Determination Strategy
3. Results
- zero-difference (ZD) kinematic POD;
- double-difference (DD) kinematic POD without ambiguity resolution;
- double-difference kinematic POD with ambiguity resolution.
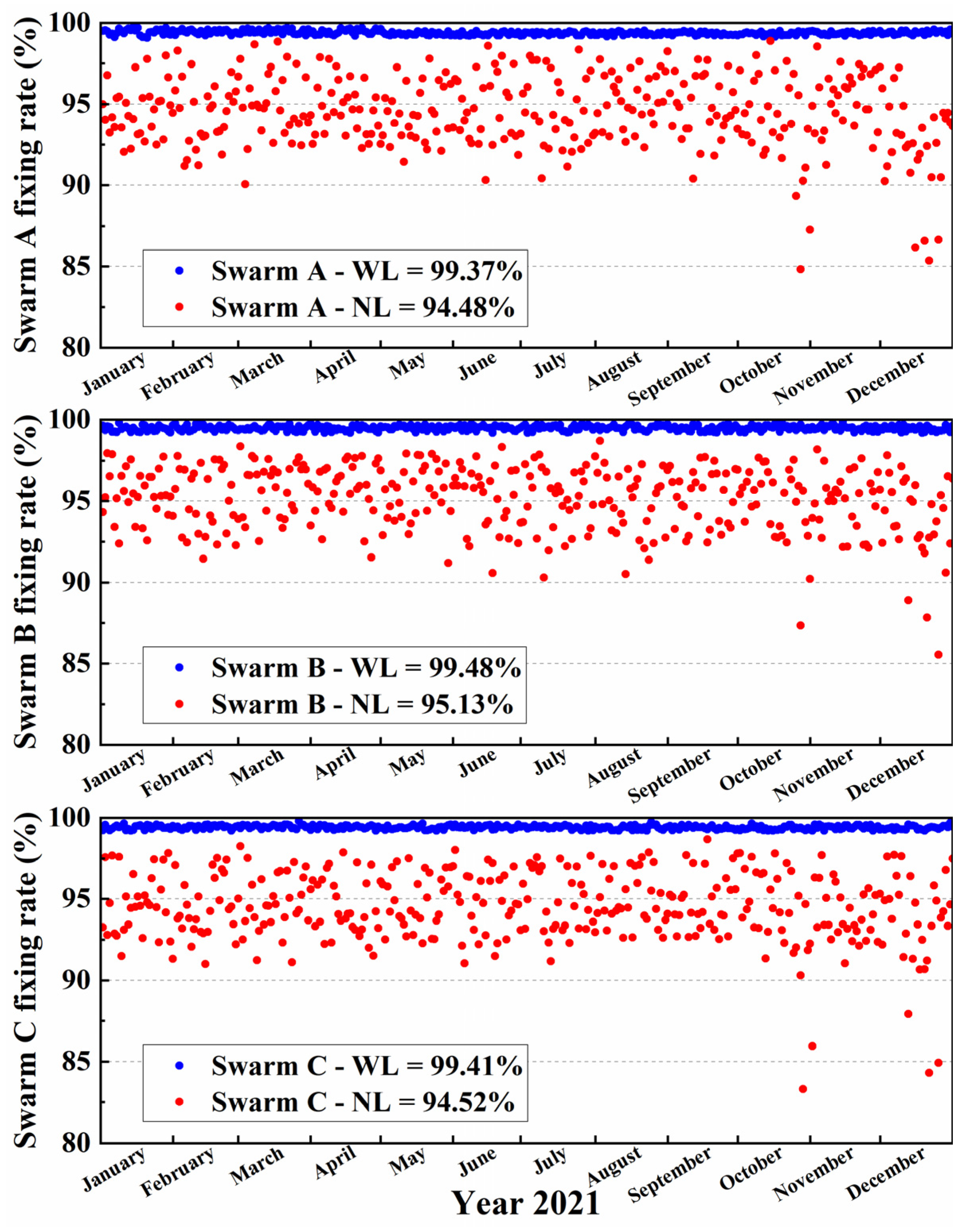
3.1. Ambiguity Resolutions
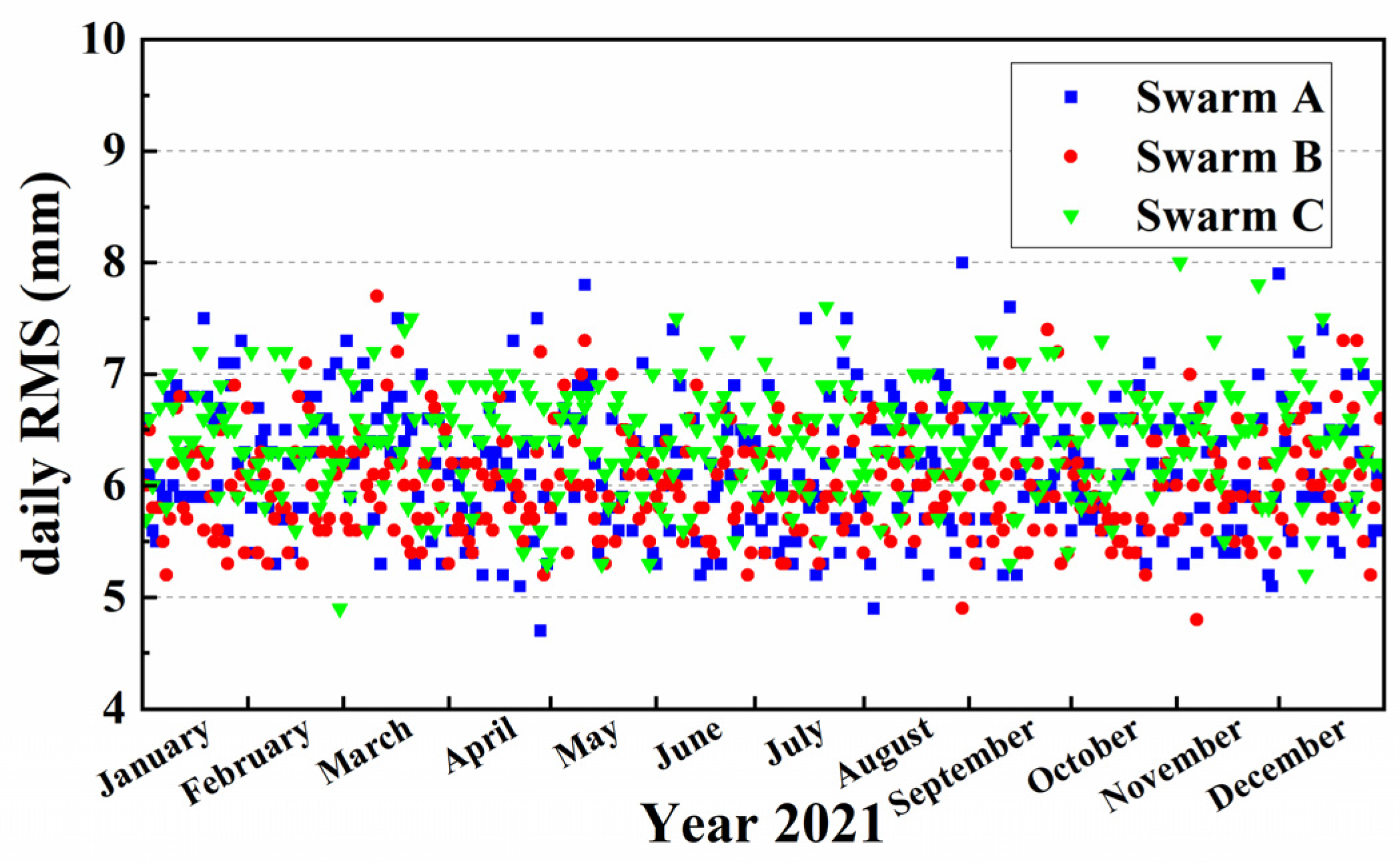
3.2. Carrier Phase Residuals
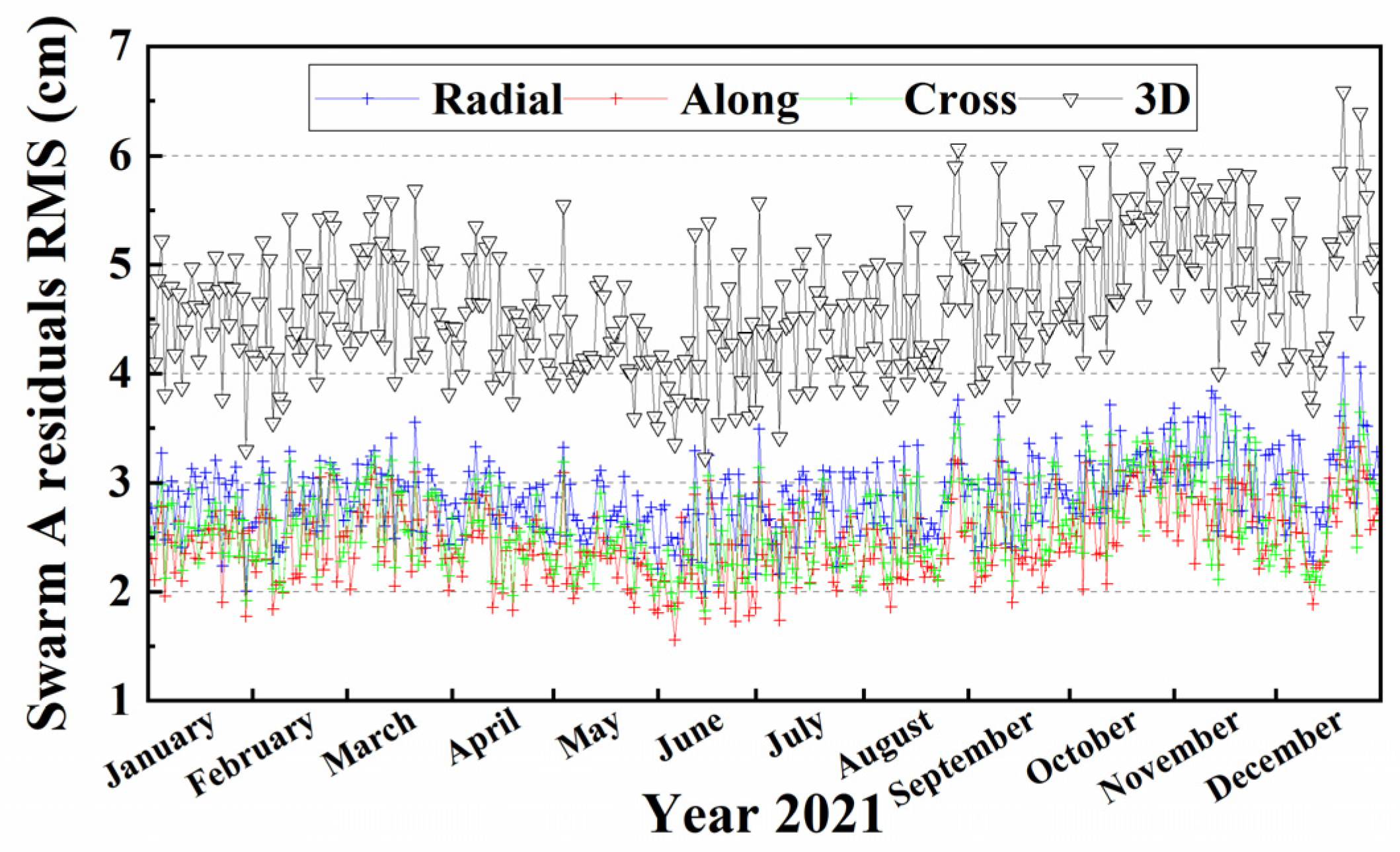
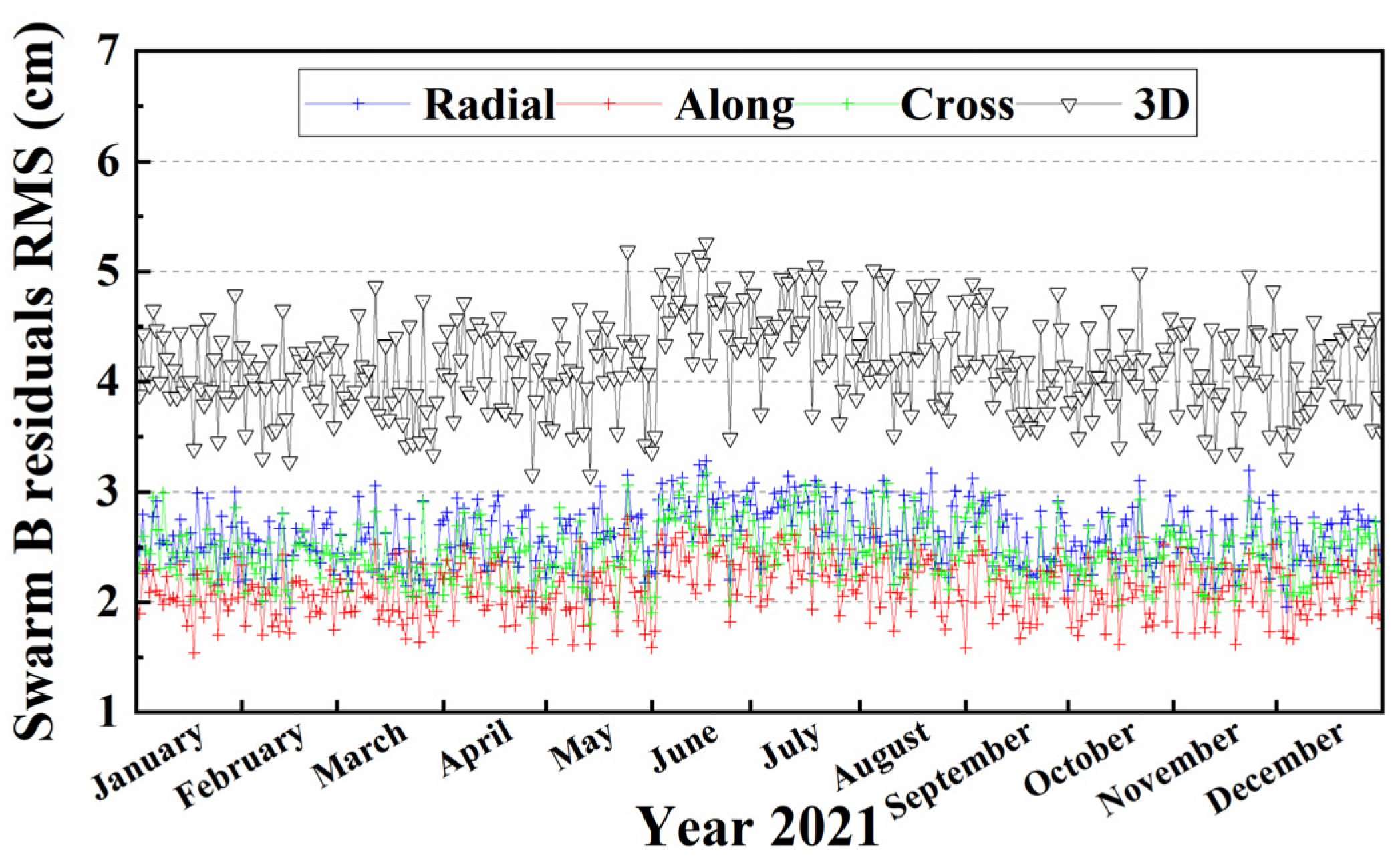
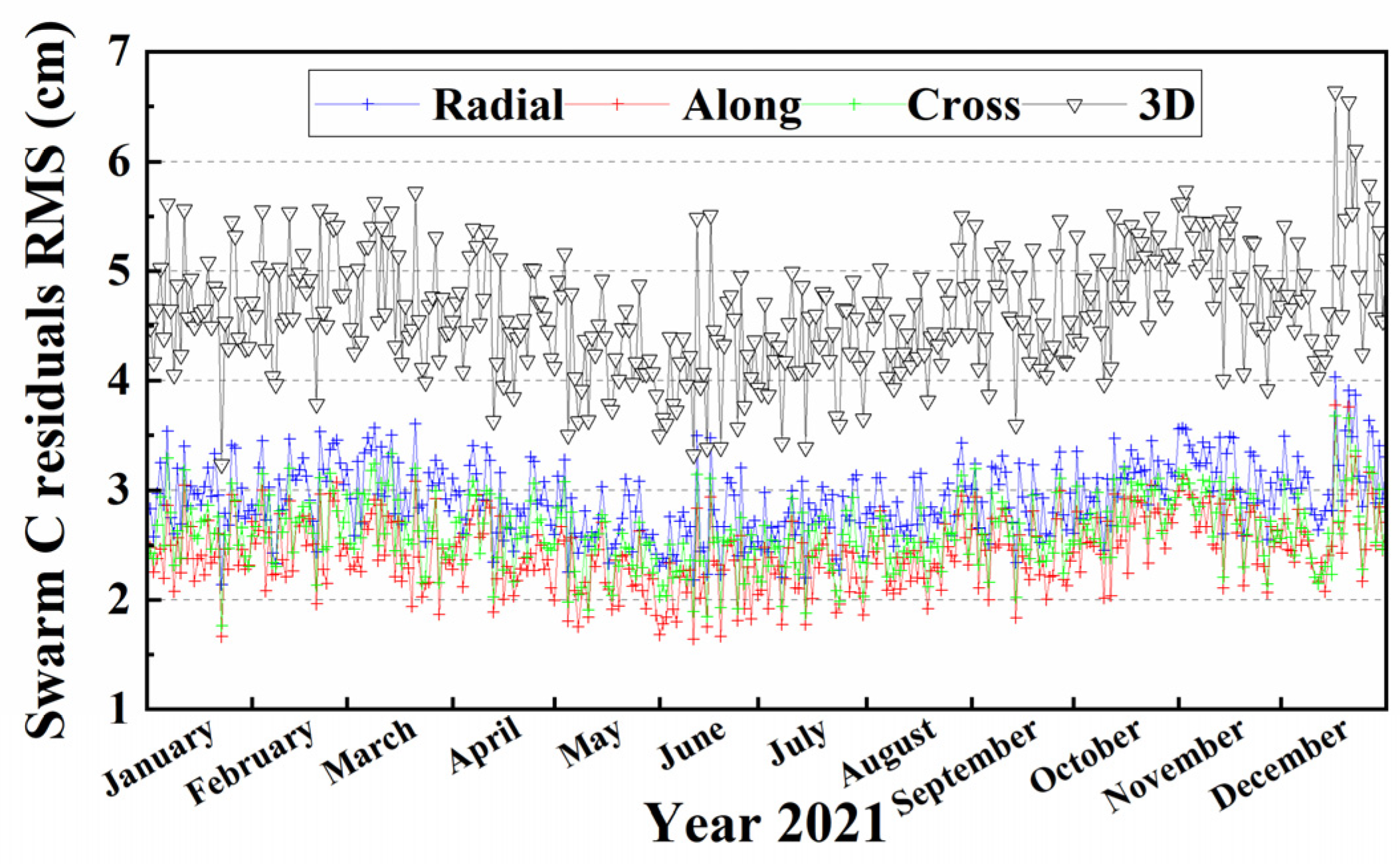
3.3. Differences with Reduced Dynamic Orbit Products
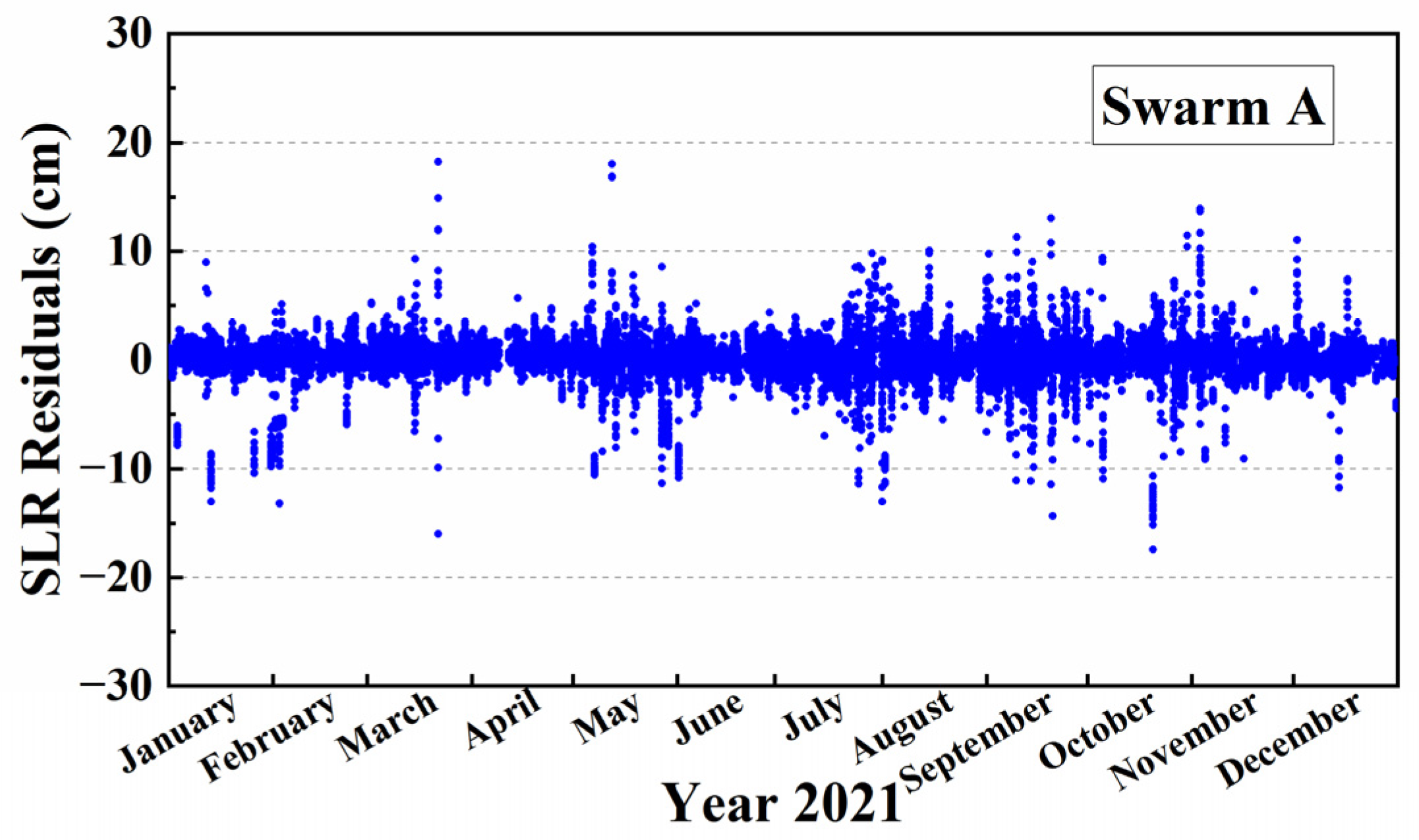
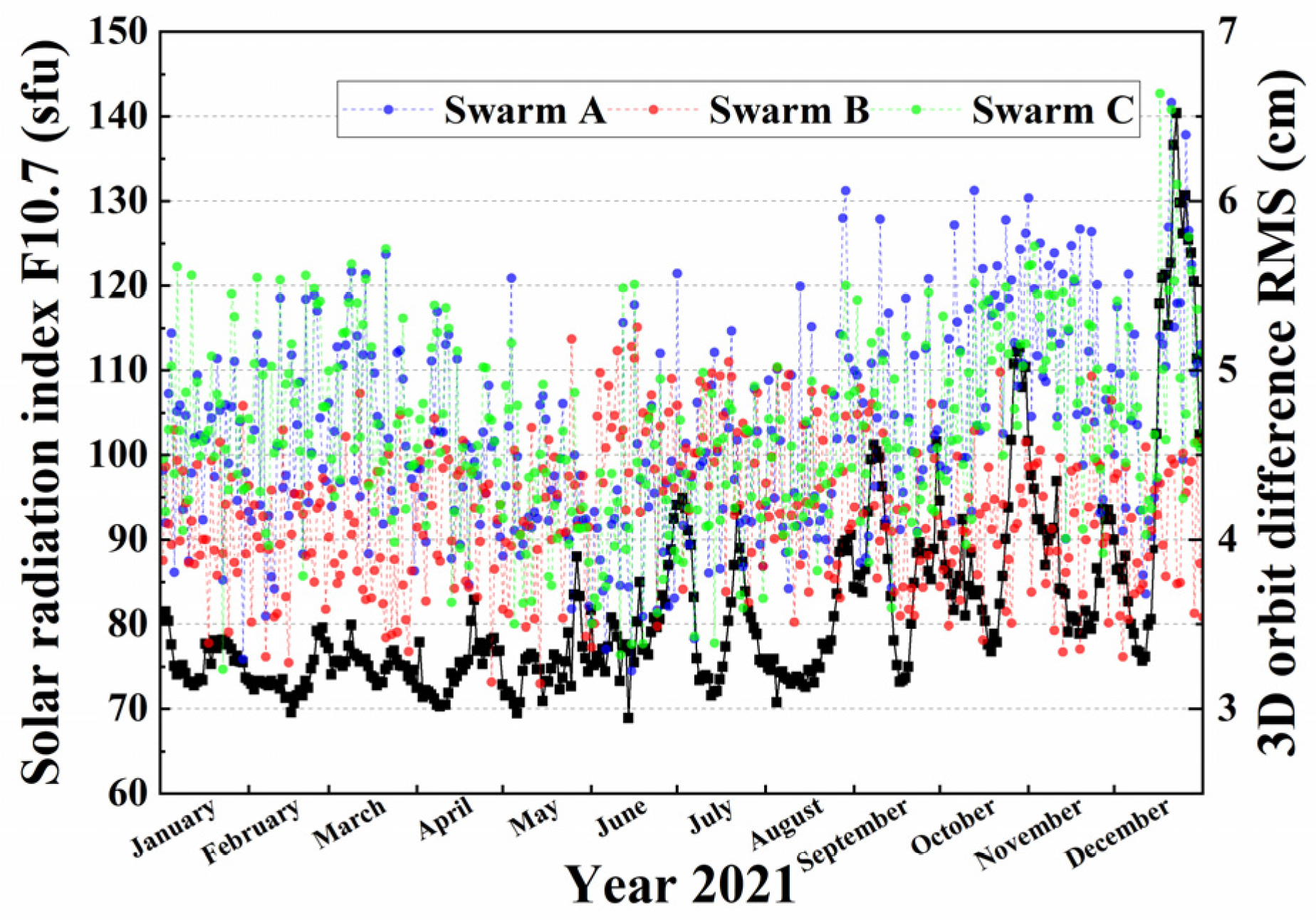
3.4. SLR Residuals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y. PPP Based Sequential Orbit Determination for Satellites in Low Earth Orbit. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xian, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, P.N.A.M.; Van Den Ijssel, J. Aiming at a 1-cm Orbit for Low Earth Orbiters: Reduced-Dynamic and Kinematic Precise Orbit Determination. Space Sci. Rev. 2003, 108, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švehla, D.; Rothacher, M. Kinematic and reduced-dynamic precise orbit determination of low earth orbiters. Adv. Geosci. 2003, 1, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäggi, A.; Hugentobler, U.; Bock, H.; Beutler, G. Precise orbit determination for GRACE using undifferenced or doubly differenced GPS data. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 39, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, H.; Jäggi, A.; Švehla, D.; Beutler, G.; Hugentobler, U.; Visser, P. Precise orbit determination for the GOCE satellite using GPS. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 39, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbach, U.; Schön, S. Improved GRACE kinematic orbit determination using GPS receiver clock modeling. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, Q. A New Approach to Earth’s Gravity Field Modeling Using GPS-Derived Kinematic Orbits and Baselines. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Jin, S.; Shi, Q. Undifferenced Kinematic Precise Orbit Determination of Swarm and GRACE-FO Satellites from GNSS Observations. Sensors 2022, 22, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Guo, H.; Li, G.; Kong, Q.; Chang, X. Relative Kinematic Orbit Determination for GRACE-FO Satellite by Jointing GPS and LRI. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehentner, N.; Mayer-Gürr, T. Precise orbit determination based on raw GPS measurements. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehentner, N. Kinematic Orbit Positioning Applying the Raw Observation Approach to Observe Time Variable Gravity. Ph.D. Thesis, Graz University of Technology, Graz, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Friis-Christensen, E.; Lühr, H.; Knudsen, D.; Haagmans, R. Swarm–an Earth observation mission investigating geospace. Adv. Space Res. 2008, 41, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, N.; Friis-Christensen, E.; Floberghagen, R.; Alken, P.; Beggan, C.D.; Chulliat, A.; Doornbos, E.; da Encarnação, J.T.; Hamilton, B.; Hulot, G.; et al. The Swarm Satellite Constellation Application and Research Facility (SCARF) and Swarm data products. Earth Planets Space 2013, 65, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Ijssel, J.; Encarnacao, J.; Doornbos, E.; Visser, P. Precise science orbits for the Swarm satellite constellation. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, P.; Doornbos, E.; van den Ijssel, J.; Teixeira da Encarnação, J. Thermospheric density and wind retrieval from Swarm observations. Earth Planets Space 2013, 65, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Helleputte, T. User Manual for the GHOST Orbit Determination Software, FDS-SUM-3110; Deutsches Zentrum für Luft-und Raumfahrt: Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zangerl, F.; Griesauer, F.; Sust, M.; Montenbruck, O.; Buchert, S.; Garcia, A. SWARM GPS Precise Orbit Determination Receiver Initial In-Orbit Performance Evaluation. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS+2014, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Ijssel, J.; Forte, B.; Montenbruck, O. Impact of Swarm GPS receiver updates on POD performance. Earth Planets Sp. 2016, 68, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende-Alba, G.; Montenbruck, O.; Jaggi, A.; Arnold, D.; Zangerl, F. Reduced-dynamic and kinematic baseline determination for the Swarm mission. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende-Alba, G.; Montenbruck, O.; Hackel, S.; Tossaint, M. Relative positioning of formation-flying spacecraft using single-receiver GPS carrier phase ambiguity fixing. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Precise Orbit Determination and the Earth Gravity field Recovery by Acceleration Approach for Swarm. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Niu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, F.; Tian, K. Centimeter precise orbit determination for the Swarm satellites via undifferenced kinematic method. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2021, 50, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hackel, S.; van den Ijssel, J.; Arnold, D. Reduced dynamic and kinematic precise orbit determination for the Swarm mission from 4 years of GPS tracking. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchert, S.; Zangerl, F.; Sust, M.; André, M.; Eriksson, A.; Wahlund, J.E.; Opgenoorth, H. SWARM observations of equatorial electron densities and topside GPS track losses. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2088–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermarrec, G.; Ren, L.; Schön, S. On filtering ionospheric effects in GPS observations using the Matérn covariance family and its impact on orbit determination of Swarm satellites. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Schön, S. PPP-based Swarm kinematic orbit determination. Ann. Geophys. 2018, 36, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Q. Real-Time kinematic precise orbit determination for LEO satellites using zero-differenced ambiguity resolution. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezděk, A.; Sebera, J.; Encarnação, J.T.d.; Klokočník, J. Time-variable gravity fields derived from GPS tracking of Swarm. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 205, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, H.M.P.; Lück, C.; Klos, A.; Sideris, M.G.; Rangelova, E.; Kusche, J. Reconstructing GRACE-type time-variable gravity from the Swarm satellites. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaggi, A.; Dahle, C.; Arnold, D.; Bock, H.; Meyer, U.; Beutler, G.; van den Ijssel, J. Swarm kinematic orbits and gravity fields from 18months of GPS data. Adv. Space Res. 2016, 57, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Encarnacao, J.T.; Visser, P.; Arnold, D.; Bezdek, A.; Doornbos, E.; Ellmer, M.; Guo, J.; van den IJssel, J.; Iorfida, E.; Jäggi, A. Description of the multi-approach gravity field models from Swarm GPS data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 1385–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiter, L.; Montenbruck, O.; Zangerl, F.; Siemes, C.; Arnold, D.; Jäggi, A. Bandwidth correction of Swarm GPS carrier phase observations for improved orbit and gravity field determination. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Encarnação, J.; Arnold, D.; Bezděk, A.; Dahle, C.; Doornbos, E.; van den Ijssel, J.; Jäggi, A.; Mayer-Gürr, T.; Sebera, J.; Visser, P.; et al. Gravity field models derived from Swarm GPS data. Earth Planet Sp. 2016, 68, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, C.; Kusche, J.; Rietbroek, R.; Locher, A. Time-variable gravity fields and ocean mass change from 37 months of kinematic Swarm orbits. Solid Earth 2018, 9, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G. Fixed point theorems of GPS carrier phase ambiguity resolution and their application to massive network processing: Ambizap. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2008, 113, B12410–B12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Lee, B.-S.; Kim, H.; Kim, J. Orbit determination performances using single-and double-differenced methods: SAC-C and KOMPSAT-2. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Tapley, B.; Bettadpur, S.; Ries, J.; Nagel, P.; Pastor, R. Precise orbit determination for the GRACE mission using only GPS data. J. Geod. 2006, 80, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Bettadpur, S.; Nagel, P.; Save, H.; Poole, S.; Pie, N. GRACE-FO precise orbit determination and gravity recovery. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoi, S.K.; Janardhan, P.; Ananthakrishnan, S. Another Mini Solar Maximum in the Offing: A Prediction for the Amplitude of Solar Cycle 25. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2019JA027508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, M.; Moore, T.; Dodson, A.; Waugh, S.; Souter, J.; Rodrigues, F.S. Implications of Ionospheric Scintillation for GNSS Users in Northern Europe. J. Nav. 2005, 58, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, A.; Kouloumvakos, A.; Mishev, A.; Vainio, R.; Usoskin, I.; Herbst, K.; Rouillard, A.P.; Anastasiadis, A.; Gieseler, J.; Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.; et al. The first ground-level enhancement of solar cycle 25 on 28 October 2021. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 660, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Gill, E.; Kroes, R. Rapid orbit determination of LEO satellites using IGS clock and ephemeris products. GPS Solut. 2005, 9, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertiger, W.; Desai, S.D.; Haines, B.; Harvey, N.; Moore, A.W.; Owen, S.; Weiss, J.P. Single receiver phase ambiguity resolution with GPS data. J. Geod. 2010, 84, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.W.; Yang, X.; Zhou, T. MLAMBDA: A modified LAMBDA method for integer least-squares estimation. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.M.; Jakowski, N. Estimate of higher order ionospheric errors in GNSS positioning. Radio Sci. 2008, 43, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.; Montenbruck, O.; Hackel, S.; Sośnica, K. Satellite laser ranging to low Earth orbiters: Orbit and network validation. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 2315–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strugarek, D.; Sośnica, K.; Zajdel, R.; Bury, G. Detector-specific issues in Satellite Laser Ranging to Swarm-A/B/C satellites. Measurement 2021, 182, 109786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C. The proof and measurement of association between two things. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

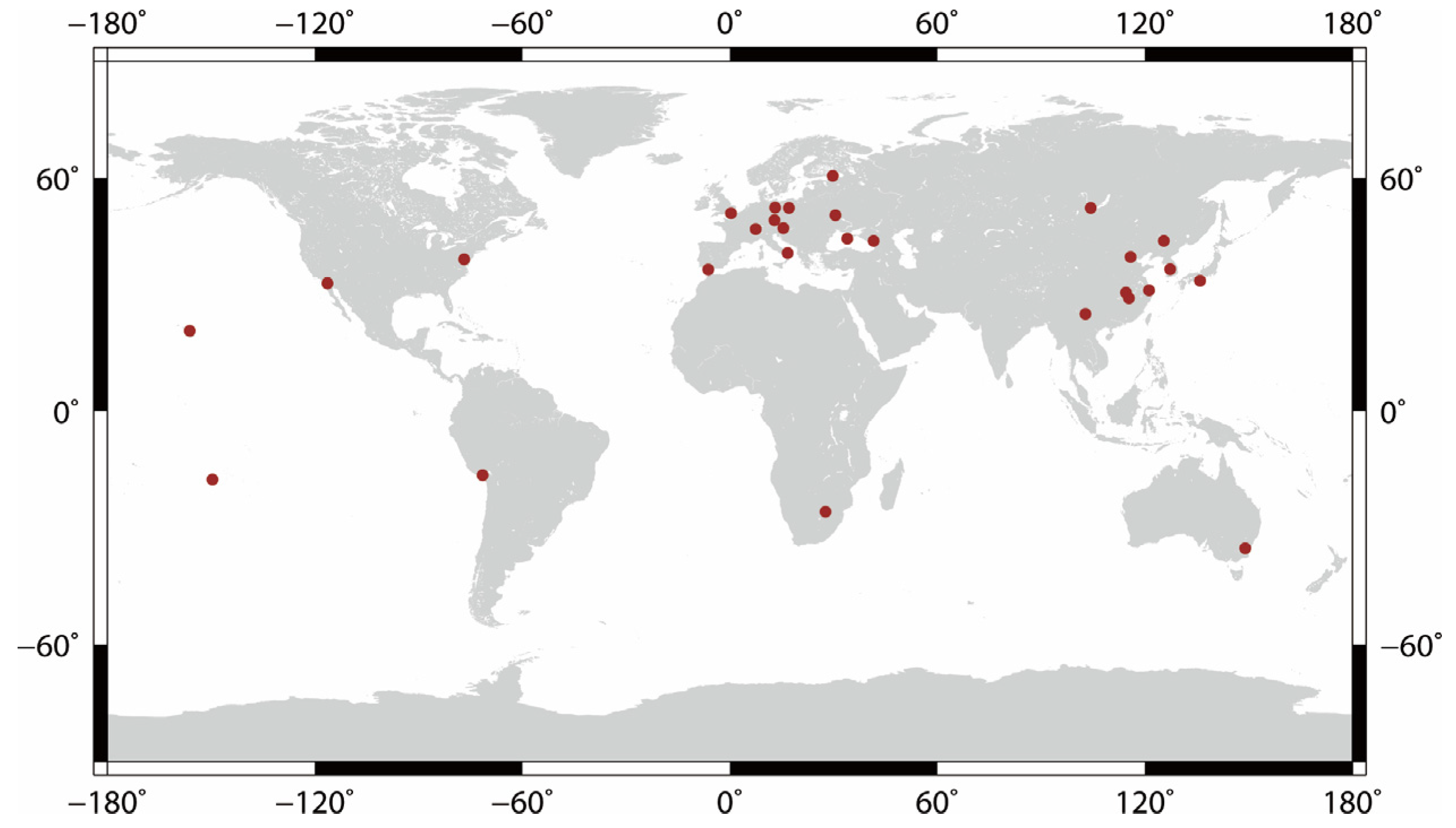


| GPS Measurement Model | Descriptions | |
|---|---|---|
| GPS tracking data | 1-s ionosphere-free code and phase | |
| GPS orbits | IGS final sp3 | |
| GPS clock | 5-s IGS clk | |
| GPS antenna phase center offset | igs14.atx | |
| Swarm antenna phase center offset | phase center offset (Level 1b) phase center variations map [18] | |
| Swarm attitude | Quaternion from star camera (Level 1b) | |
| Elevation cut-off angle | 0° | |
| Ambiguity | fixed | |
| Reference frame | Origin | Orientation |
| ITRF | center of earth | X along Greenwich meridian Y along 90° E meridian Z towards North pole |
| GPSR | GPSR antenna reference center | / |
| ICRF | barycenter of solar system | / |
| NEC | reference position | N towards North E towards East C towards center of Earth |
| Swarm Spacecraft | antenna reference center | X nominal flight direction Y sideways (“right”) Z downwards (nadir) |
| RTN | center of satellite | R towards center of Earth T along track N cross track |
| Satellite | Mean of Daily RMS Error of the Carrier Phase Residuals (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ZD | DD-Float | DD-Fixed | |
| Swarm A | 4.1 | 5.7 | 6.2 |
| Swarm B | 4.2 | 5.5 | 6.0 |
| Swarm C | 4.5 | 5.9 | 6.4 |
| Satellite | Model | Radial (cm) | Along (cm) | Cross (cm) | 3D (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swarm A | ZD | 3.74 | 3.41 | 3.62 | 6.22 |
| DD-float | 3.27 | 2.93 | 3.15 | 5.40 | |
| DD-fixed | 2.86 | 2.48 | 2.62 | 4.60 | |
| Swarm B | ZD | 3.55 | 3.06 | 3.28 | 5.72 |
| DD-float | 3.08 | 2.71 | 2.89 | 5.02 | |
| DD-fixed | 2.60 | 2.13 | 2.45 | 4.16 | |
| Swarm C | ZD | 3.98 | 3.42 | 3.44 | 6.27 |
| DD-float | 3.33 | 2.91 | 3.06 | 5.38 | |
| DD-fixed | 2.91 | 2.43 | 2.61 | 4.60 |
| Satellite | Number of Normal Points | Mean (cm) | RMS (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swarm A | 28,516 | 0.10 | 1.80 |
| Swarm B | 82,126 | −0.18 | 2.10 |
| Swarm C | 26,952 | −0.03 | 1.73 |
| Satellite | Radial | Along | Cross | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs | p-Value | rs | p-Value | rs | p-Value | |
| Swarm A | 0.2726 | <10−6 | 0.2744 | <10−6 | 0.2592 | <10−6 |
| Swarm B | 0.0222 | 0.6721 | 0.0460 | 0.3810 | 0.0218 | 0.6788 |
| Swarm C | 0.2562 | <10−4 | 0.2876 | <10−4 | 0.2400 | <10−4 |
| Satellite | Radial (cm) | Along (cm) | Cross (cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intense | Peaceful | Intense | Peaceful | Intense | Peaceful | |
| Swarm A | 3.38 | 2.86 | 2.94 | 2.45 | 3.09 | 2.59 |
| Swarm B | 2.61 | 2.60 | 2.17 | 2.12 | 2.48 | 2.45 |
| Swarm C | 3.39 | 2.91 | 2.90 | 2.41 | 2.98 | 2.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, S.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, B. Assessment of Swarm Kinematic Orbit Determination Using Two Different Double-Difference Methods. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2669. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102669
Zhang R, Xiong Y, Xu S, Chen W, Li X, Zhao B. Assessment of Swarm Kinematic Orbit Determination Using Two Different Double-Difference Methods. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2669. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102669
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rui, Yongliang Xiong, Shaoguang Xu, Weiwei Chen, Xinzhong Li, and Ban Zhao. 2023. "Assessment of Swarm Kinematic Orbit Determination Using Two Different Double-Difference Methods" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2669. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102669
APA StyleZhang, R., Xiong, Y., Xu, S., Chen, W., Li, X., & Zhao, B. (2023). Assessment of Swarm Kinematic Orbit Determination Using Two Different Double-Difference Methods. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2669. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102669






