Delineating Polynya Area Using Active and Passive Microwave Sensors for the Western Ross Sea Sector of Antarctica
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Materials
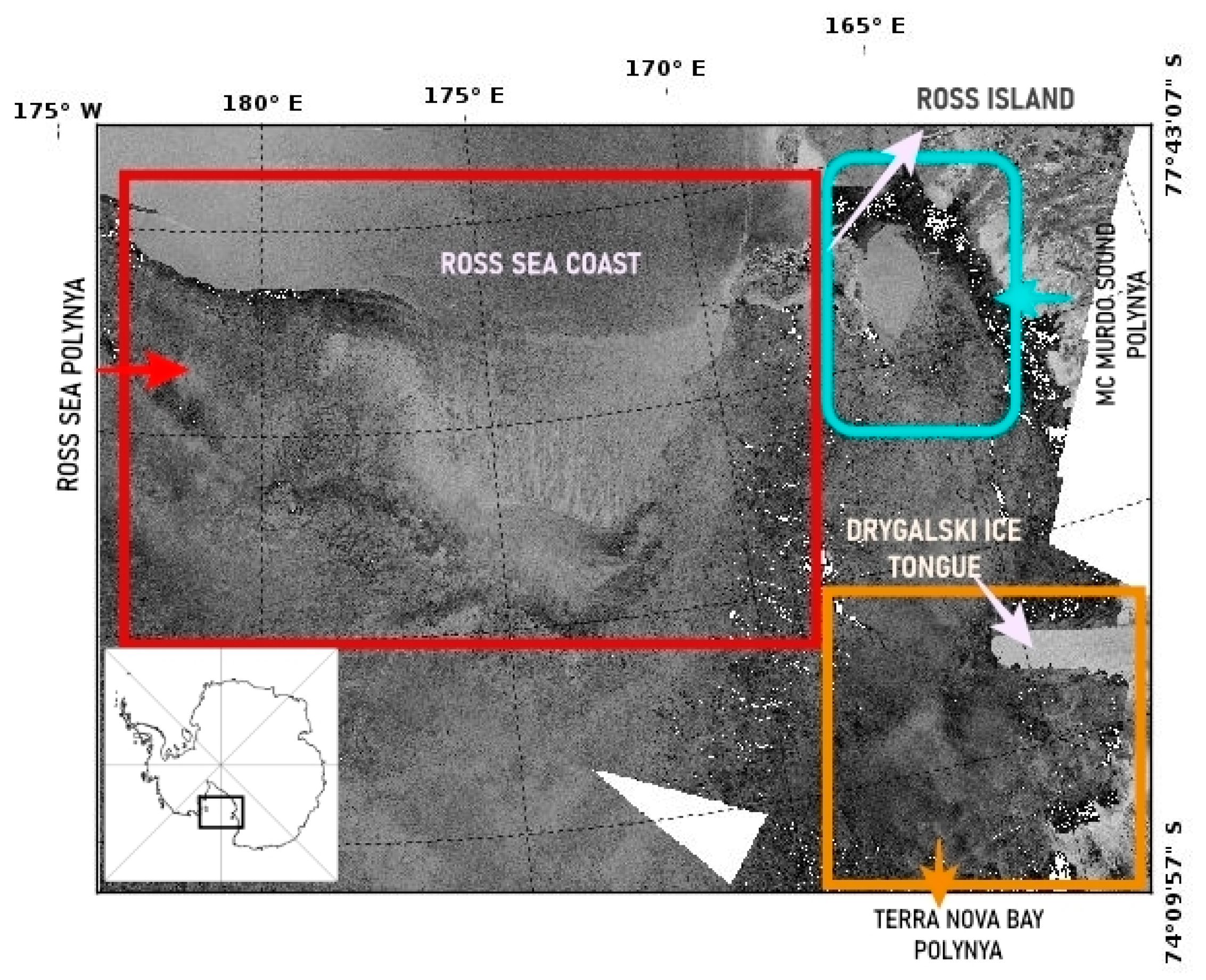
2.1. Study Area: The Ross Sea Region
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. NSIDC and AMSR2
2.2.2. C-Band SAR Data from S1
3. Methods
3.1. Large-Scale (PMW) Polynya Area Retrieval
3.2. SAR-Based Polynya Retrieval
3.2.1. Rule-Based (Semi-Automated Supervised Techniques)
3.2.2. Texture-Based k-Means Clustering (Automated Unsupervised Technique)
3.2.3. Criteria Used to Generate the Validation Data and Types Assigned
4. Results and Discussions
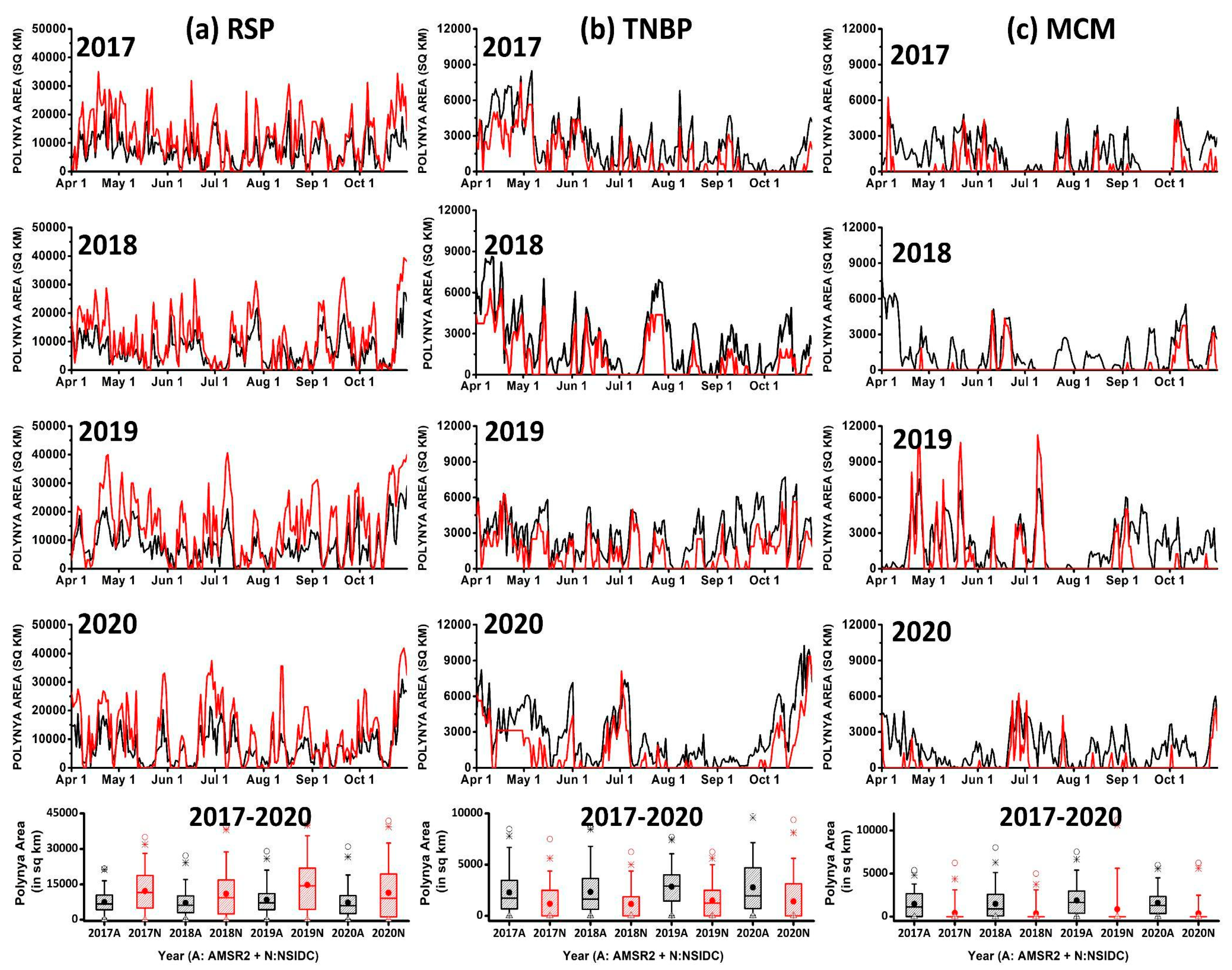
4.1. Daily PMW Results for the Period 2017–2020
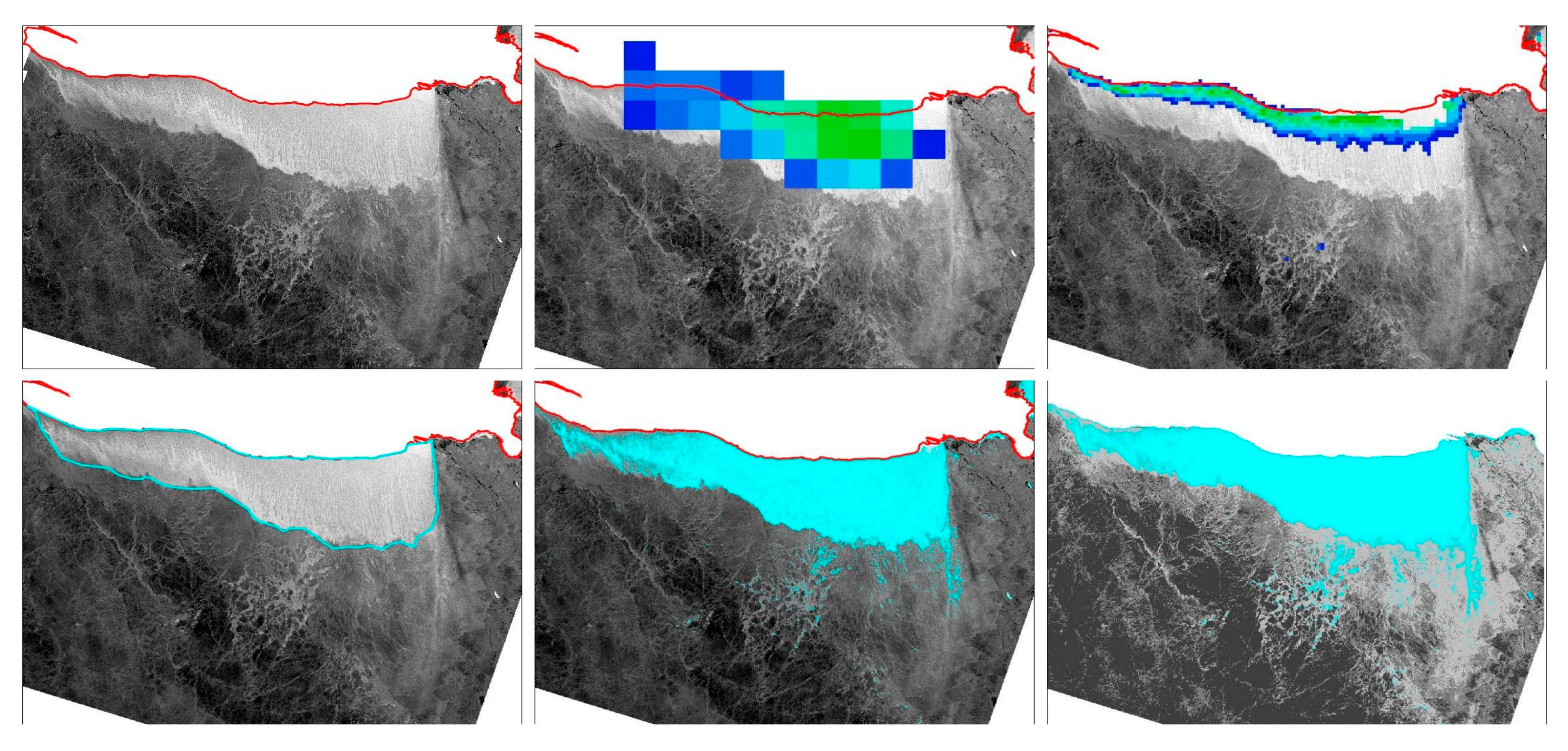
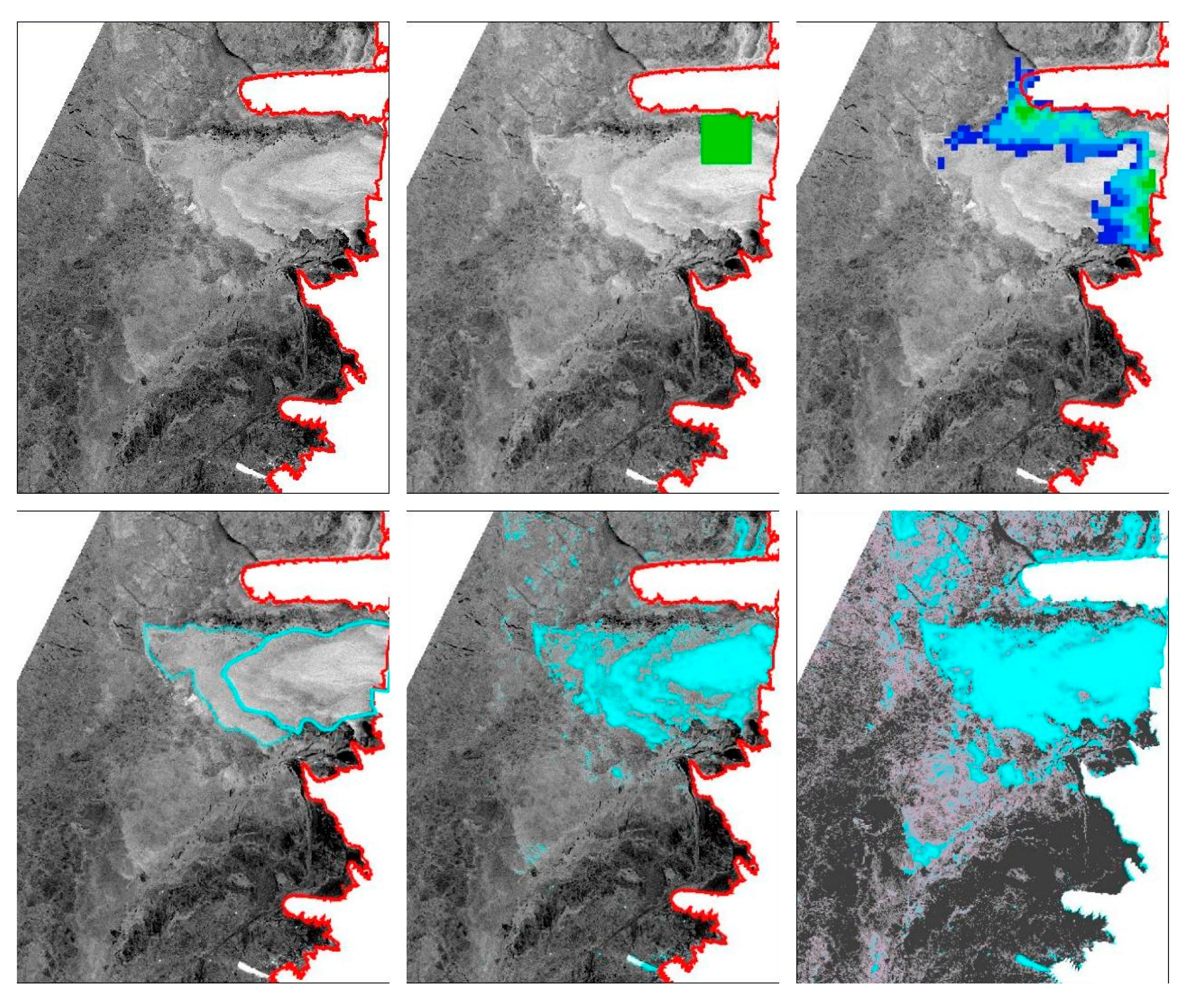
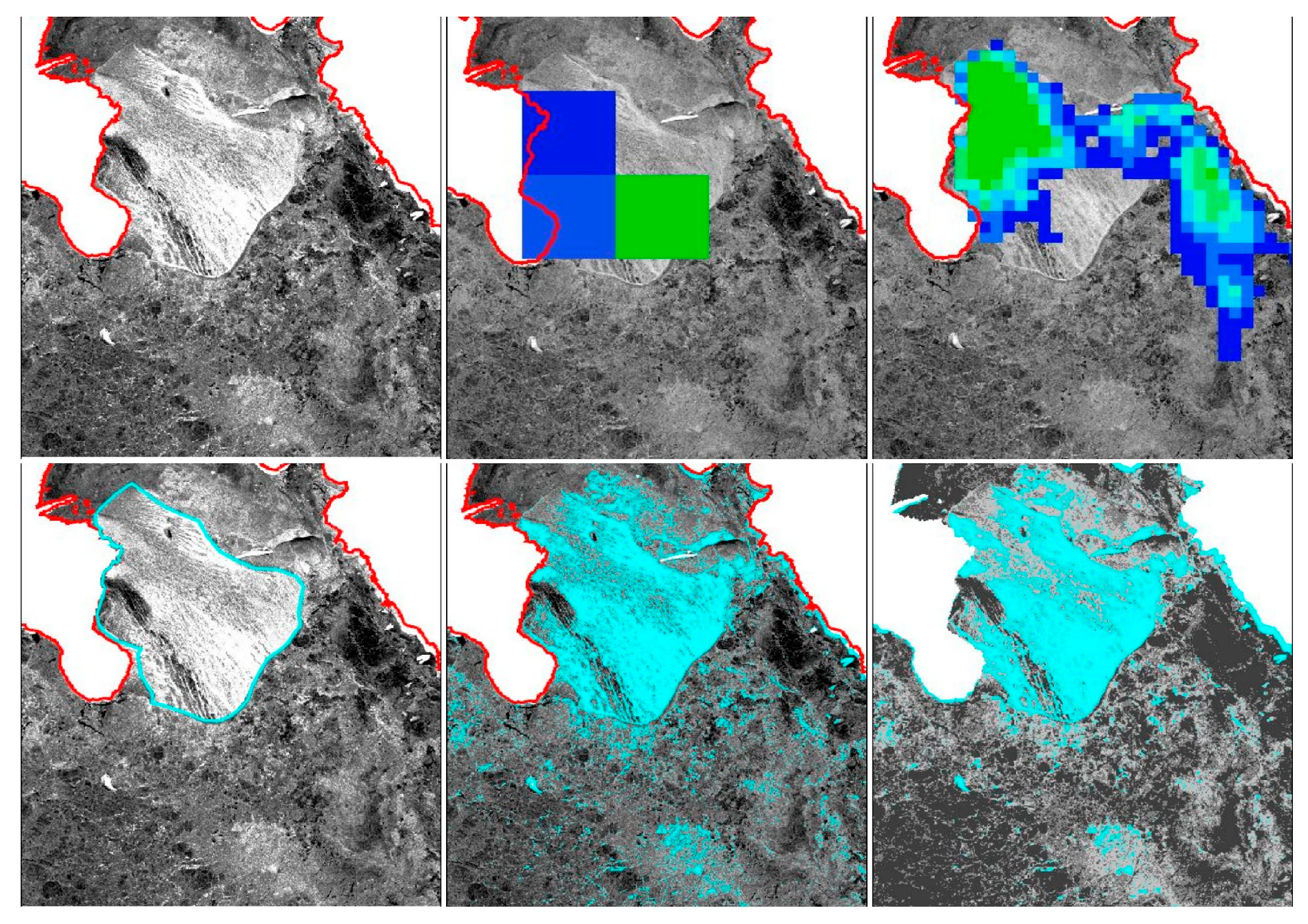
4.2. Comparing Large-Scale (PMW) with Fine-Scale (S1) Data
4.3. Evaluating the S1 Algorithms against the Manually Delineated Data
4.3.1. Texture-Based Unsupervised Classification vs. Rule-Based Supervised Classification
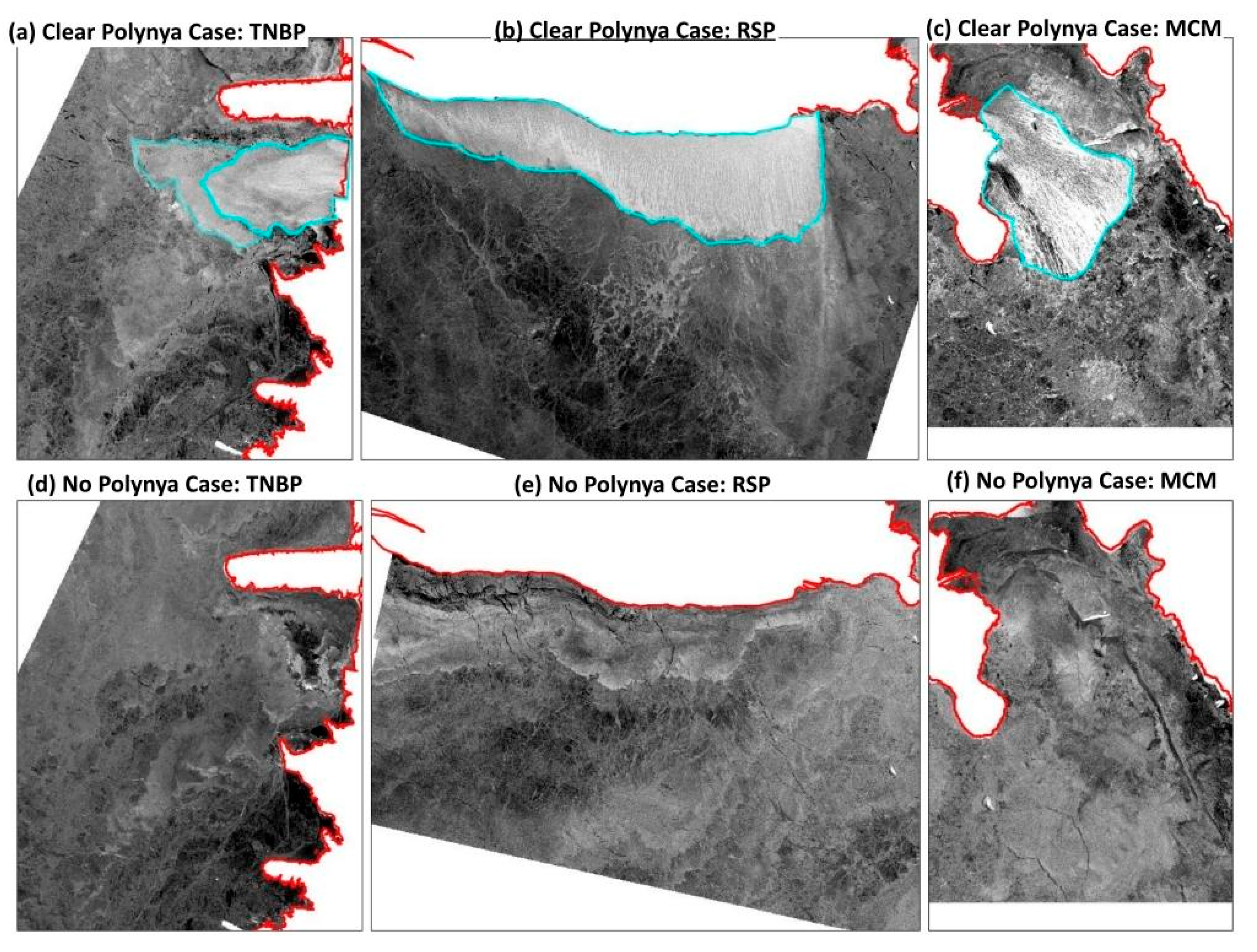
4.3.2. Clear Polynya Cases
4.3.3. All Scenes (Period: 2017–2020)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
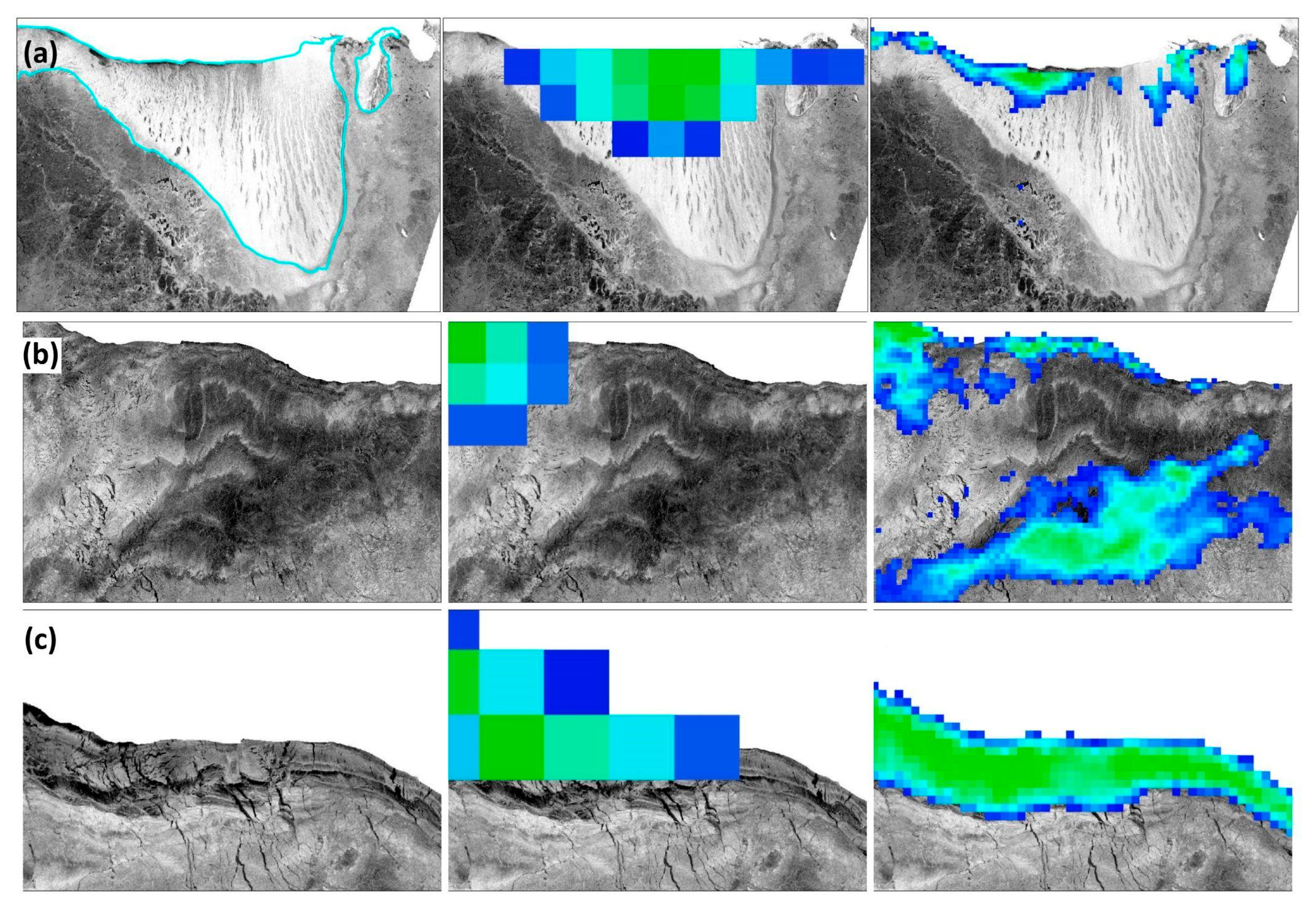
Appendix A. GLCM Parameters Computations Used in the Paper
References
- Morales Maqueda, M.A.; Willmott, A.J.; Biggs, N.R.T. Polynya Dynamics: A Review of Observations and Modeling: Polynya dynamics-observations and modeling. Rev. Geophys. 2004, 42, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S. Polynyas. In Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 2241–2247. ISBN 978-0-12-227430-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hollands, T.; Dierking, W. Dynamics of the Terra Nova Bay Polynya: The Potential of Multi-Sensor Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Yao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, S. Trends in the Stability of Antarctic Coastal Polynyas and the Role of Topographic Forcing Factors. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, E.R.; McDonald, A.J.; Coggins, J.H.J.; Rack, W. Atmospheric Forcing of Sea Ice Anomalies in the Ross Sea Polynya Region. Cryosphere Discuss. 2016, 11, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Ohshima, K.I.; Fraser, A.D.; Williams, G.D. Sea Ice Production Variability in Antarctic Coastal Polynyas. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 2967–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S. Monitoring of Thin Sea Ice within Polynyas Using MODIS Data Beobachtung Des Dünnen Meereises in Polynjen Anhand von MODIS Daten. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Trier, Trier, Germany, 18 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Massom, R.A.; Harris, P.T.; Michael, K.J.; Potter, M.J. The Distribution and Formative Processes of Latent-Heat Polynyas in East Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 1998, 27, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.G.; Massom, R.A. Chapter 1 The Role of Sea Ice in Arctic and Antarctic Polynyas. In Elsevier Oceanography Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 74, pp. 1–54. ISBN 978-0-444-52952-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sea Ice Features: Polynyas | National Snow and Ice Data Center. Available online: https://nsidc.org/cryosphere/seaice/characteristics/polynyas.html (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Gordon, A.L.; Comiso, J.C. Polynyas in the Southern Ocean. Sci. Am. 1988, 258, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwase, H.; Ohshima, K.I.; Nakata, K.; Tamura, T. Improved SSM/I Thin Ice Algorithm with Ice Type Discrimination in Coastal Polynyas. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2021, 38, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagno, P.; Capozzi, V.; DiTullio, G.R.; Falco, P.; Fusco, G.; Rintoul, S.R.; Spezie, G.; Budillon, G. Rebound of Shelf Water Salinity in the Ross Sea. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.-C.; Jo, Y.-H.; Kidwell, A.; Hwang, J. Multi-Temporal Variation of the Ross Sea Polynya in Response to Climate Forcings. Polar Res. 2018, 37, 1444891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.F.; Bromwich, D.H. Mesoscale Cyclogenesis Dynamics over the Southwestern Ross Sea, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppema, M.; Anderson, L.G. Chapter 6 Biogeochemistry of Polynyas and Their Role in Sequestration of Anthropogenic Constituents. In Elsevier Oceanography Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 74, pp. 193–221. ISBN 978-0-444-52952-7. [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo, K.R. Phytoplankton Dynamics within 37 Antarctic Coastal Polynya Systems. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Vihma, T.; Zhou, M.; Yu, L.; Uotila, P.; Sein, D.V. Impacts of Strong Wind Events on Sea Ice and Water Mass Properties in Antarctic Coastal Polynyas. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 3505–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, F.D.W.; Benham, T.J.; Batchelor, C.L.; Rack, W.; Montelli, A.; Dowdeswell, J.A. Antarctic ice-shelf advance driven by anomalous atmospheric and sea-ice circulation. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rack, W.; Price, D.; Haas, C.; Langhorne, P.J.; Leonard, G.H. Sea Ice Thickness in the Western Ross Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, K.I.; Nihashi, S.; Iwamoto, K. Global View of Sea-Ice Production in Polynyas and Its Linkage to Dense/Bottom Water Formation. Geosci. Lett. 2016, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiot, P.; Jourdain, N.C.; Barnier, B.; Gallée, H.; Molines, J.M.; Le Sommer, J.; Penduff, T. Sensitivity of Coastal Polynyas and High-Salinity Shelf Water Production in the Ross Sea, Antarctica, to the Atmospheric Forcing. Ocean. Dyn. 2012, 62, 701–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezgec, K.; Stenni, B.; Crosta, X.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Baroni, C.; Braida, M.; Ciardini, V.; Colizza, E.; Melis, R.; Salvatore, M.C.; et al. Holocene Sea Ice Variability Driven by Wind and Polynya Efficiency in the Ross Sea. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, S.; Spreen, G.; Kaleschke, L.; de La Rosa, S.; Heygster, G. Polynya Signature Simulation Method Polynya Area in Comparison to AMSR-E 89 GHz Sea-Ice Concentrations in the Ross Sea and off the Adélie Coast, Antarctica, for 2002–05: First Results. Ann. Glaciol. 2007, 46, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, T.; Burns, B.A. Detection of Coastal Polynyas with Passive Microwave Data. Ann. Glaciol. 1993, 17, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R. Sea Ice Concentration Estimates from Satellite Passive Microwave Radiometry and Openings from SAR Ice Motion: Sea Ice Concentration and Sar Openings. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 25-1–25-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S. Estimation of the Thin Ice Thickness and Heat Flux for the Chukchi Sea Alaskan Coast Polynya from Special Sensor Microwave/Imager Data, 1990–2001. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, C10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Willmes, S.; Heinemann, G.; Rozman, P.; Timmermann, R.; Schröder, D. Evaluation of Simulated Sea-Ice Concentrations from Sea-Ice/Ocean Models Using Satellite Data and Polynya Classification Methods. Polar Res. 2011, 30, 7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Pang, X.; Zhao, X.; Stein, A. Heat Flux Sources Analysis to the Ross Ice Shelf Polynya Ice Production Time Series and the Impact of Wind Forcing. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melsheimer, C. ASI Version 5 Sea Ice Concentration User Guide; University of Bremen: Bremen, Germany, 2019; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, N.; Pedersen, L.T.; Tonboe, R.T.; Kern, S.; Heygster, G.; Lavergne, T.; Sørensen, A.; Saldo, R.; Dybkjær, G.; Brucker, L.; et al. Inter-Comparison and Evaluation of Sea Ice Algorithms: Towards Further Identification of Challenges and Optimal Approach Using Passive Microwave Observations. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 1797–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Drucker, R.S.; Kwok, R. The Areas and Ice Production of the Western and Central Ross Sea Polynyas, 1992–2002, and Their Relation to the B-15 and C-19 Iceberg Events of 2000 and 2002. J. Mar. Syst. 2007, 68, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.R.; Kwok, R. Wind-Driven Trends in Antarctic Sea-Ice Drift. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohrmann, M.; Heuzé, C.; Swart, S. Southern Ocean Polynyas in CMIP6 Models. Cryosphere 2021, 15, 4281–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Rack, W.; McDonald, A.; Howell, S. Long-Term Analysis of Sea Ice Drift in the Western Ross Sea, Antarctica, at High and Low Spatial Resolution. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, B.; Kuma, P.; McDonald, A.; Parsons, S. An Analysis of the Cloud Environment over the Ross Sea and Ross Ice Shelf Using CloudSat/CALIPSO Satellite Observations: The Importance of Synoptic Forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9723–9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmes, S.; Krumpen, T.; Adams, S.; Rabenstein, L.; Haas, C.; Hoelemann, J.; Heinemann, G. Cross-Validation of Polynya Monitoring Methods from Multisensor Satellite and Airborne Data: A Case. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, S13–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Xie, H.; Ackley, S.F.; Mestas-Nuñez, A.M. Ice Production in Ross Ice Shelf Polynyas during 2017–2018 from Sentinel–1 SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shokr, M.; Li, X.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hui, F.; Cheng, X. MYI Floes Identification Based on the Texture and Shape Feature from Dual-Polarized Sentinel-1 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldenhoff, W.; Eriksson, L.E.B.; Ye, Y.; Heuze, C. First-Year and Multiyear Sea Ice Incidence Angle Normalization of Dual-Polarized Sentinel-1 SAR Images in the Beaufort Sea. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldenhoff, W.; Heuzé, C.; Eriksson, L.E.B. Comparison of Ice/Water Classification in Fram Strait from C- and L-Band SAR Imagery. Ann. Glaciol. 2018, 59, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, J.; Doulgeris, A.P.; Dierking, W. Mapping Sea-Ice Types from Sentinel-1 Considering the Surface-Type Dependent Effect of Incidence Angle. Ann. Glaciol. 2020, 61, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, J.; Doulgeris, A.P.; Dierking, W. Incident Angle Dependence of Sentinel-1 Texture Features for Sea Ice Classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-W.; Korosov, A.A.; Babiker, M.; Won, J.-S.; Hansen, M.W.; Kim, H.-C. Classification of sea ice types in Sentinel-1 synthetic aperture radar images. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 2629–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashkin, D.; Spreen, G.; Huntemann, M.; Dierking, W. Method for Detection of Leads from Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Ann. Glaciol. 2018, 59, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldenhoff, W.; Berg, A.; Eriksson, L.E.B. Sea Ice Concentration Estimation from Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Images over the Fram Strait. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 7675–7677. [Google Scholar]
- Boulze, H.; Korosov, A.; Brajard, J. Classification of Sea Ice Types in Sentinel-1 SAR Data Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharien, R.; Segal, R.; Yackel, J.; Howell, S.; Nasonova, S. Linking Winter and Spring Thermodynamic Sea-Ice States at Critical Scales Using an Object-Based Image Analysis of Sentinel-1. Ann. Glaciol. 2018, 59, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, R.; Martin, S.; Kwok, R. Sea Ice Production and Export from Coastal Polynyas in the Weddell and Ross Seas: Weddell and Ross Sea Ice Production. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Gui, D.; Yuan, Z.; Pang, X.; Tao, D.; Zhai, M. Characterization of the Unprecedented Polynya Events North of Greenland in 2017/2018 Using Remote Sensing and Reanalysis Data. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, L.-K.; Tsatsoulis, C. Texture Analysis of SAR Sea Ice Imagery Using Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrices. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.-B.; Yang, C.-S. Automatic Discrimination Approach of Sea Ice in the Arctic Ocean Using Sentinel-1 Extra Wide Swath Dual-Polarized SAR Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 4469–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, P.; Bindoff, N.L.; Bergamasco, A. The Sea Ice Dynamics of Terra Nova Bay and Ross Ice Shelf Polynyas during a Spring and Winter Simulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, C09003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D. Assessment of Antarctic Sea Ice by Surface Validated Satellite Measurements. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, W.; Fetterer, F.; Windnagel, A.; Stewart, S. NOAA/NSIDC Climate Data Record of Passive Microwave Sea Ice Concentration; Version 4; National Snow and Ice Data Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vichi, M. A Statistical Definition of the Antarctic Marginal Ice Zone. Cryosphere 2021, 16, 4087–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinel-1 SAR—Technical Guide—Sentinel Online—Sentinel Online. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/technical-guides/sentinel-1-sar (accessed on 6 July 2022).
- SNAP Download—STEP. Available online: https://step.esa.int/main/download/snap-download/ (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Parmiggiani, F. Multi-Year Measurement of Terra Nova Bay Winter Polynya Extents. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2011, 126, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B. SAR Sea Ice Recognition Using Texture Methods. Master’s Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Geldsetzer, T.; Yackel, J.J. Sea Ice Type and Open Water Discrimination Using Dual Co-Polarized C-Band SAR. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 35, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remote Sensing of Sea Ice in the Northern Sea Route; Springer Praxis Books; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; ISBN 978-3-540-24448-6.
- Classification of Sea Ice Types in ENVISAT Synthetic Aperture Radar Images | IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore. Available online: https://ieeexplore-ieee-org.helicon.vuw.ac.nz/document/6311463 (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Dierking, W. Sea Ice Monitoring by Synthetic Aperture Radar. Oceanography 2013, 26, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokr, M.E. Evaluation of Second-Order Texture Parameters for Sea Ice Classification from Radar Images. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkanatsios, I. Classification of Sea Ice Types for the East Part of Greenland Waters Using SENTINEL 1 Data. Master’s Thesis, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, A.J.; George, S.E.; Woollands, R.M. Can Gravity Waves Significantly Impact PSC Occurrence in the Antarctic? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8825–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, G.H.; Turner, K.E.; Richter, M.E.; Whittaker, M.S.; Smith, I.J. Brief Communication: The Anomalous Winter 2019 Sea-Ice Conditions in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Cryosphere 2021, 15, 4999–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Ohshima, K.I.; Nihashi, S. Mapping of Sea Ice Production for Antarctic Coastal Polynyas: Mapping of sea ice production. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromwich, D.H.; Kurtz, D.D. Katabatic Wind Forcing of the Terra Nova Bay Polynya. J. Geophys. Res. 1984, 89, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davolio, S.; Buzzi, A. Mechanisms of Antarctic Katabatic Currents near Terra Nova Bay. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2002, 54, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breckenridge, C.J.; Radok, U.; Stearns, C.R.; Bromwich, D.H. Katabatic Winds along the Transantarctic Mountains. In Antarctic Research Series; Bromwich, D.H., Stearns, C.R., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 61, pp. 69–92. ISBN 978-0-87590-839-7. [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich, S. The Form and Dynamics of Langmuir Circulations. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1983, 15, 391–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleschke, L. Frost Flowers on Sea Ice as a Source of Sea Salt and Their Influence on Tropospheric Halogen Chemistry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L16114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.; Smith, M.; Thomson, J.; Stammerjohn, S.; Ackley, S.; Loose, B. Frazil ice growth and production during katabatic wind events in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 3329–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, E.R.; Katurji, M.; McDonald, A.J.; Voss, P.; Rack, W.; Seto, D. A Comparison of AMPS Forecasts Near the Ross Sea Polynya With Controlled Meteorological Balloon Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD030591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, E.R. Interactions between Changing Weather Patterns and the Antarctic Cryosphere in the Ross Sea Region. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.; Dean, S.; Renwick, J. Synoptic Weather Types for the Ross Sea Region, Antarctica. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggins, J.H.J.; McDonald, A.J. The Influence of the Amundsen Sea Low on the Winds in the Ross Sea and Surroundings: Insights from a Synoptic Climatology. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2167–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renwick, J.A.; Kohout, A.; Dean, S. Atmospheric Forcing of Antarctic Sea Ice on Intraseasonal Time Scales. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 5962–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Year | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | NSIDC (in km2) | AMSR2 (in km2) | NSIDC (in km2) | AMSR2 (in km2) | NSIDC (in km2) | AMSR2 (in km2) | NSIDC (in km2) | AMSR2 (in km2) | |
| Mean | RSP | 12,190 | 7500 | 12,300 | 7159 | 16,775 | 8413 | 11,422 | 7266 |
| Interquartile Range | 13,750 | 6221 | 14,375 | 7100 | 15,625 | 6807 | 18,125 | 7598 | |
| Range (Max–Min) | 35,000 | 21,631 | 39,375 | 27,168 | 40,625 | 29,023 | 41,875 | 30,957 | |
| Mean | TNBP | 1174 | 2286 | 1159 | 2355 | 1501 | 2850 | 1411 | 2778 |
| Interquartile Range | 2500 | 2783 | 1875 | 3022 | 2500 | 2549 | 3125 | 3994 | |
| Range (Max–Min) | 7500 | 8477 | 6250 | 8623 | 6250 | 7705 | 9375 | 10,264 | |
| Mean | MCM | 409 | 1469 | 310 | 1442 | 1011 | 1913 | 359 | 1559 |
| Interquartile Range | 0 | 2578 | 0 | 2231 | 625 | 2734 | 0 | 2021 | |
| Range (Max–Min) | 6250 | 5400 | 5000 | 8047 | 11,250 | 7549 | 6250 | 5996 | |
| Year | RSP | TNB | MCM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.65 |
| 2018 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.52 |
| 2019 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.73 |
| 2020 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.63 |
| Clear Polynya Case (in km2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technique | Mean | Interquartile Range | Minimum | |
| NSIDC | RSP | 21,449 | 10,000 | 0 |
| AMSR2 | 10,557 | 8428 | 2236 | |
| Manual | 21,496 | 15,576 | 7666 | |
| Texture | 17,193 | 8335 | 6438 | |
| Rule | 21,582 | 14,835 | 9747 | |
| NSIDC | TNBP | 1910 | 3125 | 0 |
| AMSR2 | 3271 | 2354 | 381 | |
| Manual | 3542 | 2301 | 678 | |
| Texture | 4909 | 2105 | 1734 | |
| Rule | 4789 | 3653 | 1400 | |
| NSIDC | MCM | 2434 | 4375 | 0 |
| AMSR2 | 2839 | 2207 | 654 | |
| Manual | 1742 | 1844 | 188 | |
| Texture | 1519 | 1290 | 301 | |
| Rule | 1952 | 1390 | 267 | |
| Together (Clear and Non-Clear Polynyas in km2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technique | Mean | 1st Quartile | 3rd Quartile | Interquartile Range |
| RSP | ||||
| NSIDC | 14,176 | 5000 | 23,125 | 18,125 |
| AMSR2 | 8135 | 4629 | 11,650 | 7021 |
| Manual | 11,664 | 2601 | 16,216 | 13,615 |
| Texture | 10,133 | 3653 | 15,566 | 11,913 |
| Rule | 12,279 | 4525 | 17,656 | 13,131 |
| TNBP | ||||
| NSIDC | 1103 | 0 | 2500 | 2500 |
| AMSR2 | 2360 | 781 | 3574 | 2793 |
| Manual | 2312 | 678 | 3286 | 2609 |
| Texture | 3749 | 2256 | 5192 | 2936 |
| Rule | 3543 | 1676 | 4957 | 3281 |
| MCM | ||||
| NSIDC | 802 | 0 | 625 | 625 |
| AMSR2 | 1484 | 166 | 2402 | 2236 |
| Manual | 709 | 0 | 1330 | 1330 |
| Texture | 710 | 0 | 1005 | 1005 |
| Rule | 833 | 0 | 1392 | 1392 |
| Polynya | M-N | M-A | M-T | M-R | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSP | 0.4 | 0.63 ** | 0.45 * | 0.58 ** | 0.74 ** | 0.77 ** | 0.88 ** | 0.8 ** |
| TNBP | 0.31 | 0.31 * | 0.47 * | 0.28 * | 0.8 ** | 0.72 ** | 0.84 ** | 0.8 ** |
| MCM | 0.61 ** | 0.63 ** | 0.49 * | 0.6 ** | 0.74 ** | 0.74 ** | 0.85 ** | 0.83 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burada, G.K.; McDonald, A.; Renwick, J.; Jolly, B. Delineating Polynya Area Using Active and Passive Microwave Sensors for the Western Ross Sea Sector of Antarctica. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2545. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102545
Burada GK, McDonald A, Renwick J, Jolly B. Delineating Polynya Area Using Active and Passive Microwave Sensors for the Western Ross Sea Sector of Antarctica. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2545. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102545
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurada, Girija Kalyani, Adrian McDonald, James Renwick, and Ben Jolly. 2023. "Delineating Polynya Area Using Active and Passive Microwave Sensors for the Western Ross Sea Sector of Antarctica" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2545. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102545
APA StyleBurada, G. K., McDonald, A., Renwick, J., & Jolly, B. (2023). Delineating Polynya Area Using Active and Passive Microwave Sensors for the Western Ross Sea Sector of Antarctica. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2545. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102545








