Constrained MEMS-Based INS/UWB Tightly Coupled System for Accurate UGVs Navigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
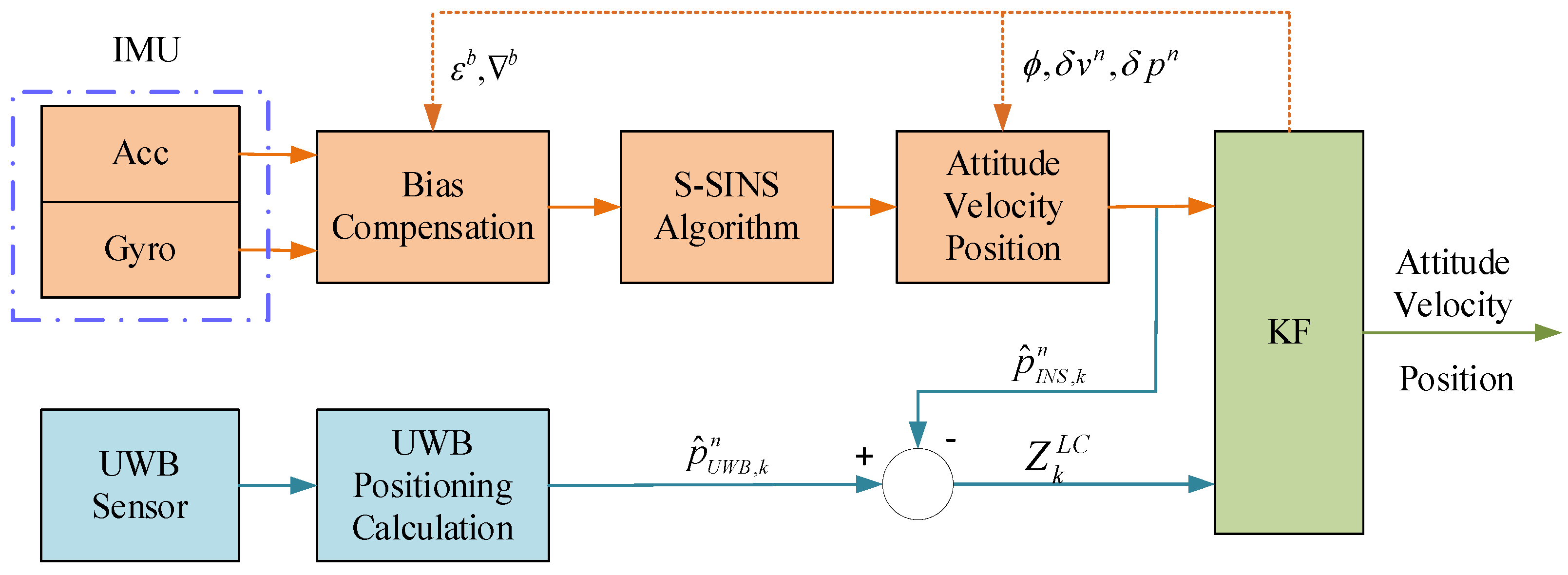
2.1. INS/UWB LC Architecture
2.1.1. Error-State Model
2.1.2. Measurement Model
2.1.3. Kalman Filtering
2.2. Problem Formulation
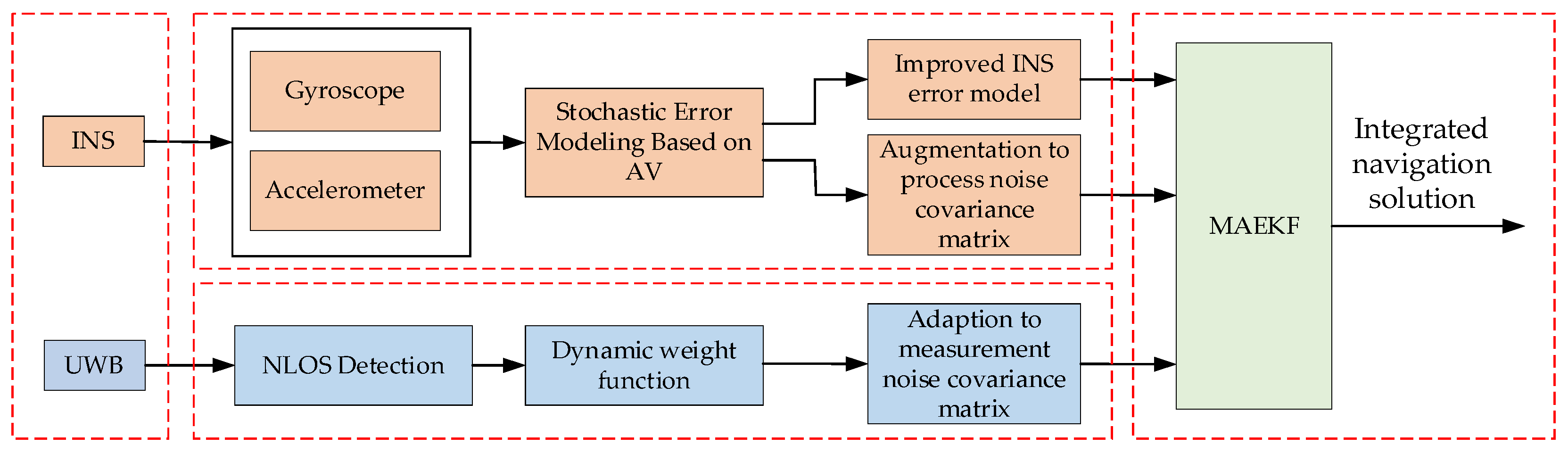
3. Methodology
3.1. Improving Error Model of INS
3.1.1. On-Line Compensation of QN
3.1.2. On-Line Compensation of CN
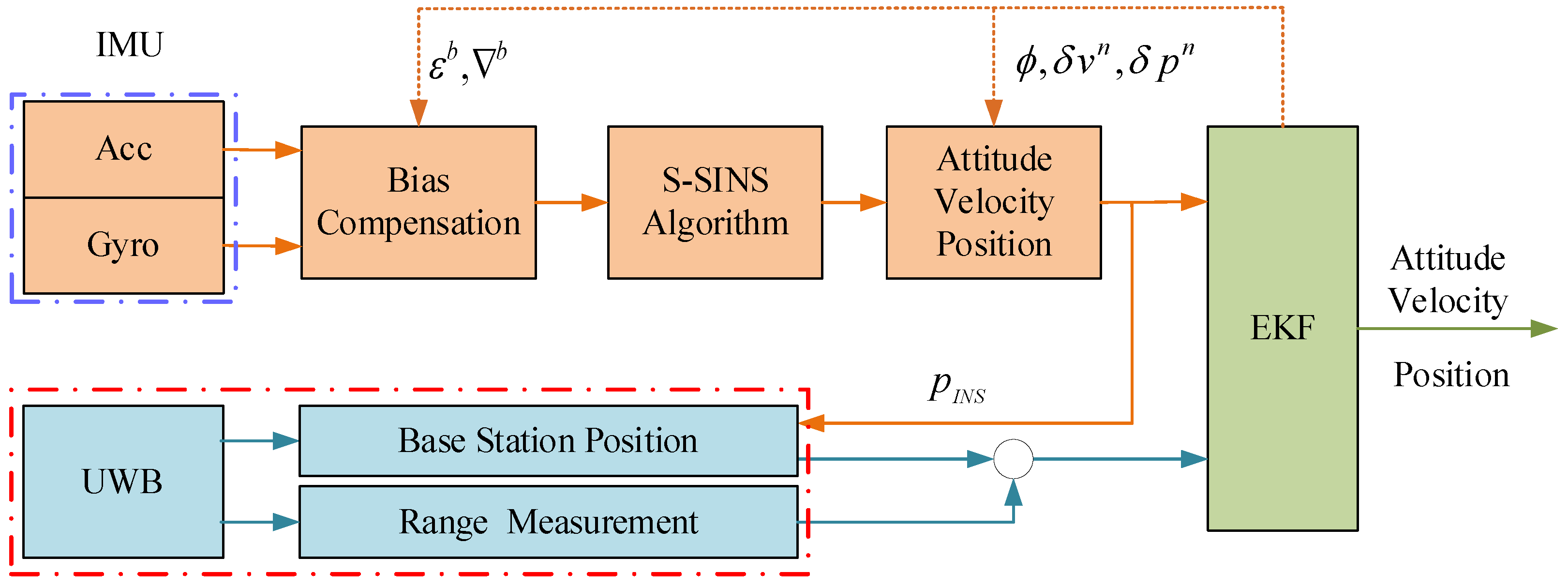
3.2. INS/UWB TC-EKF Model Design
3.2.1. Error-State Equation
3.2.2. Measurement Equation
3.3. MAEKF Based on the Dynamic Weight Function for UWB NLOS
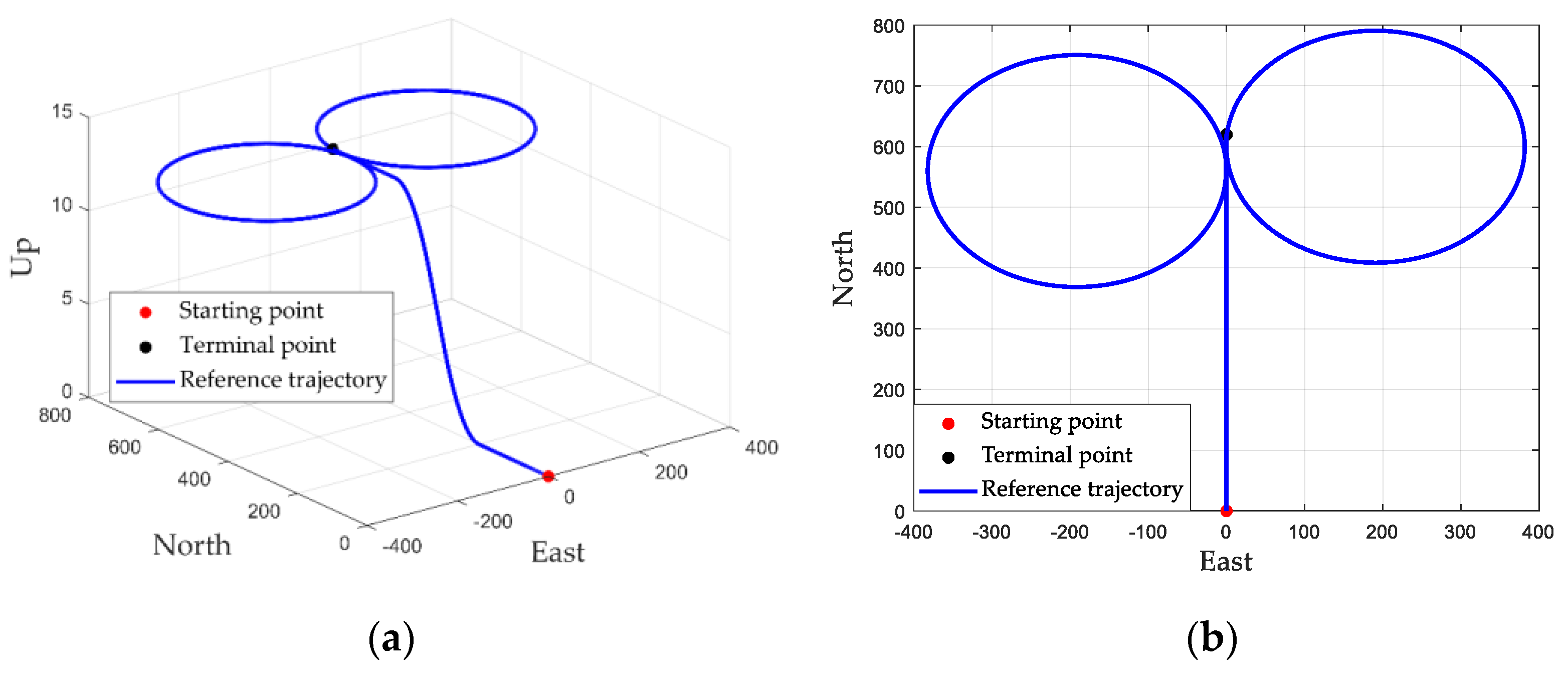
4. Experimental Test and Analysis
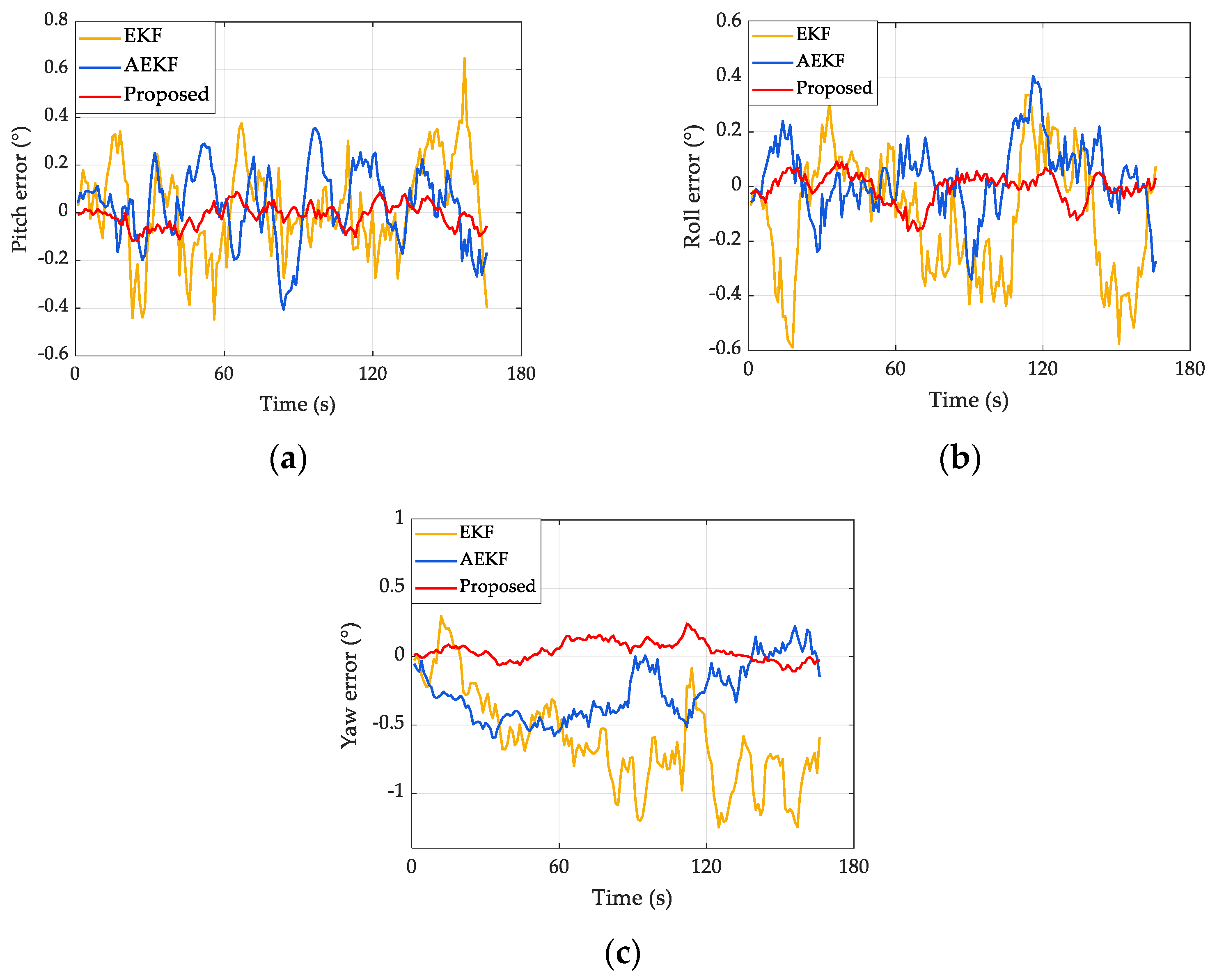
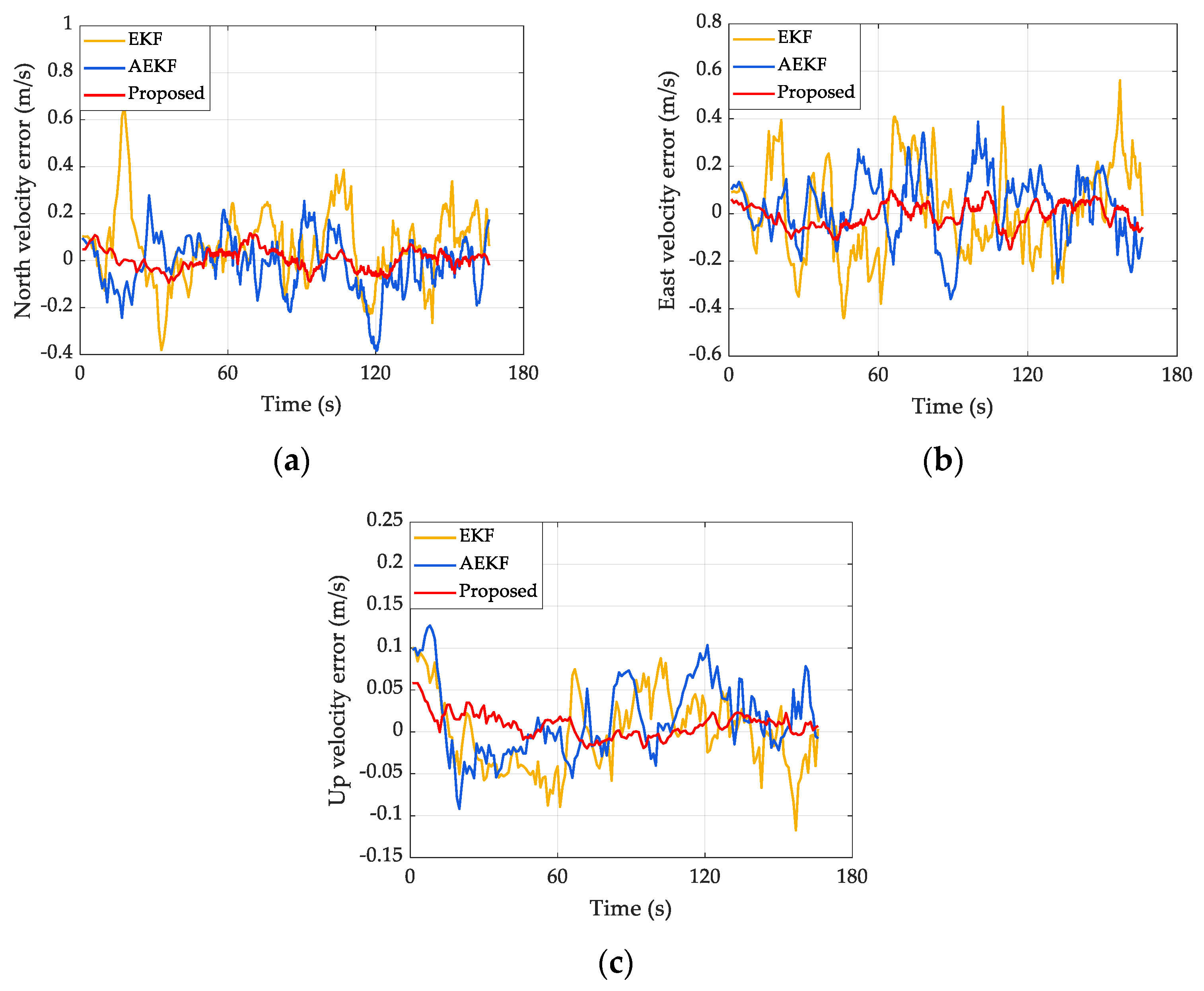
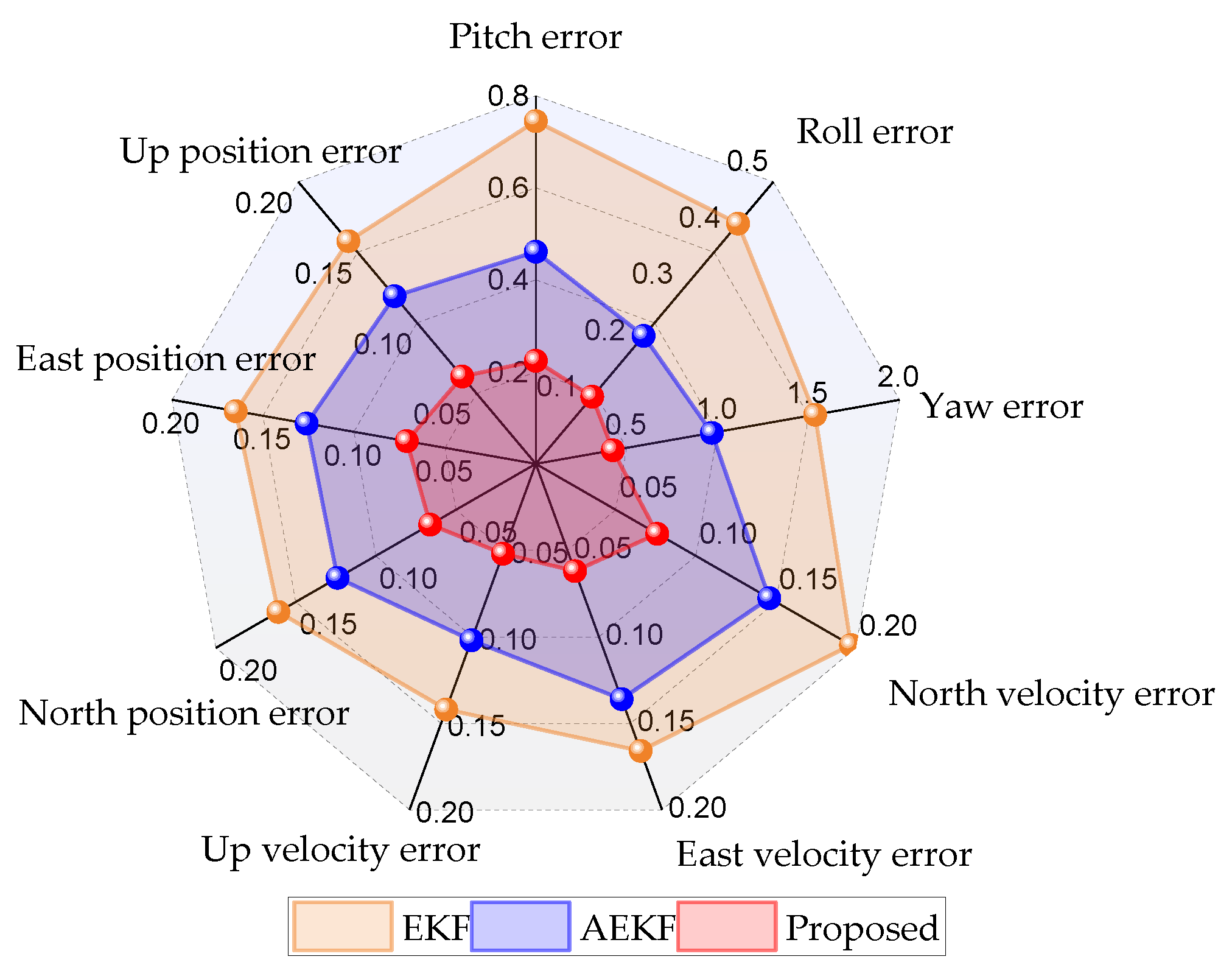
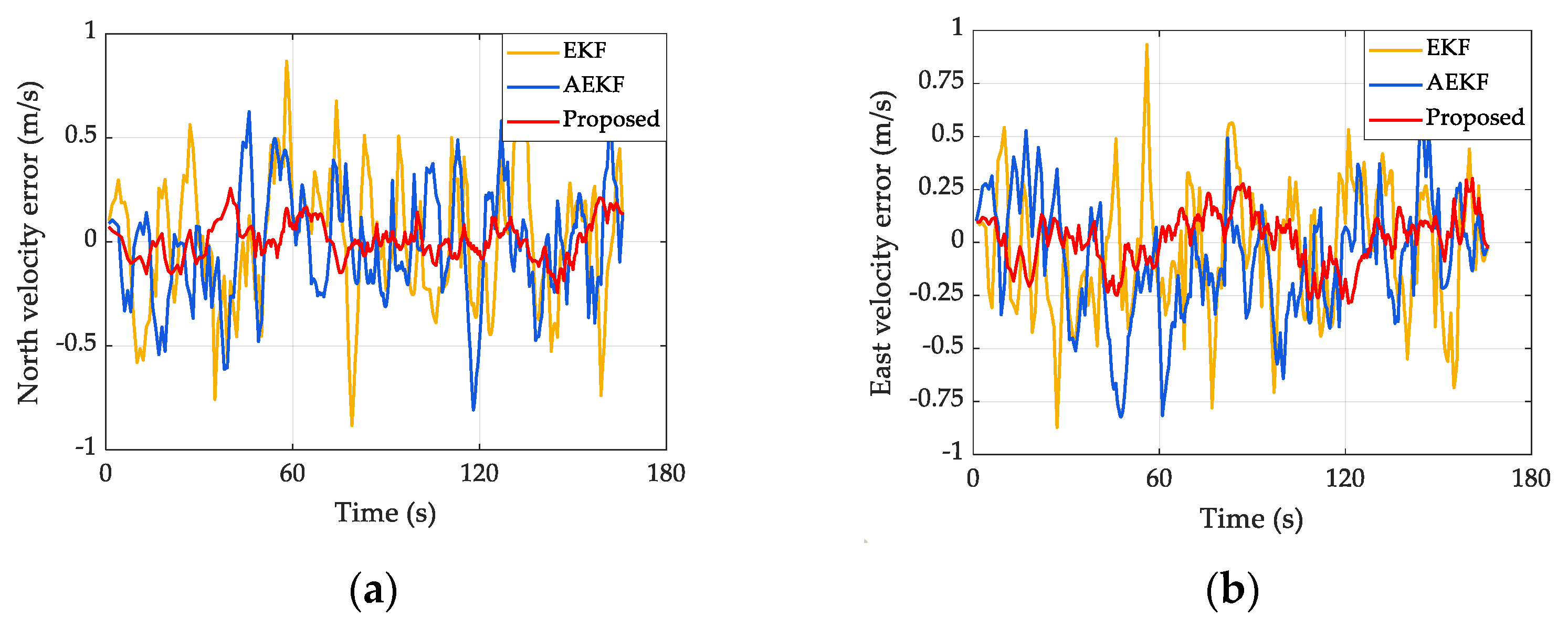
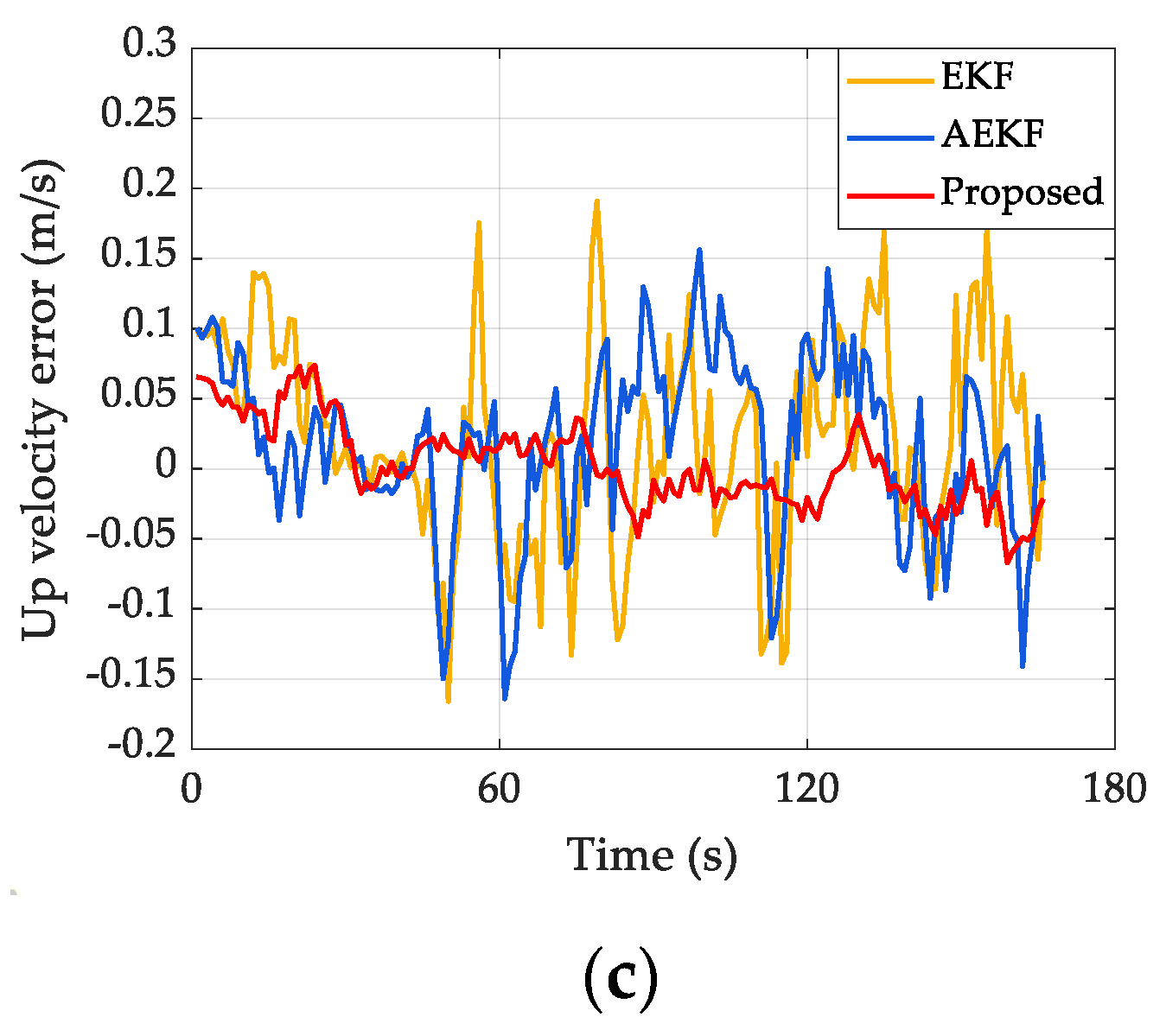
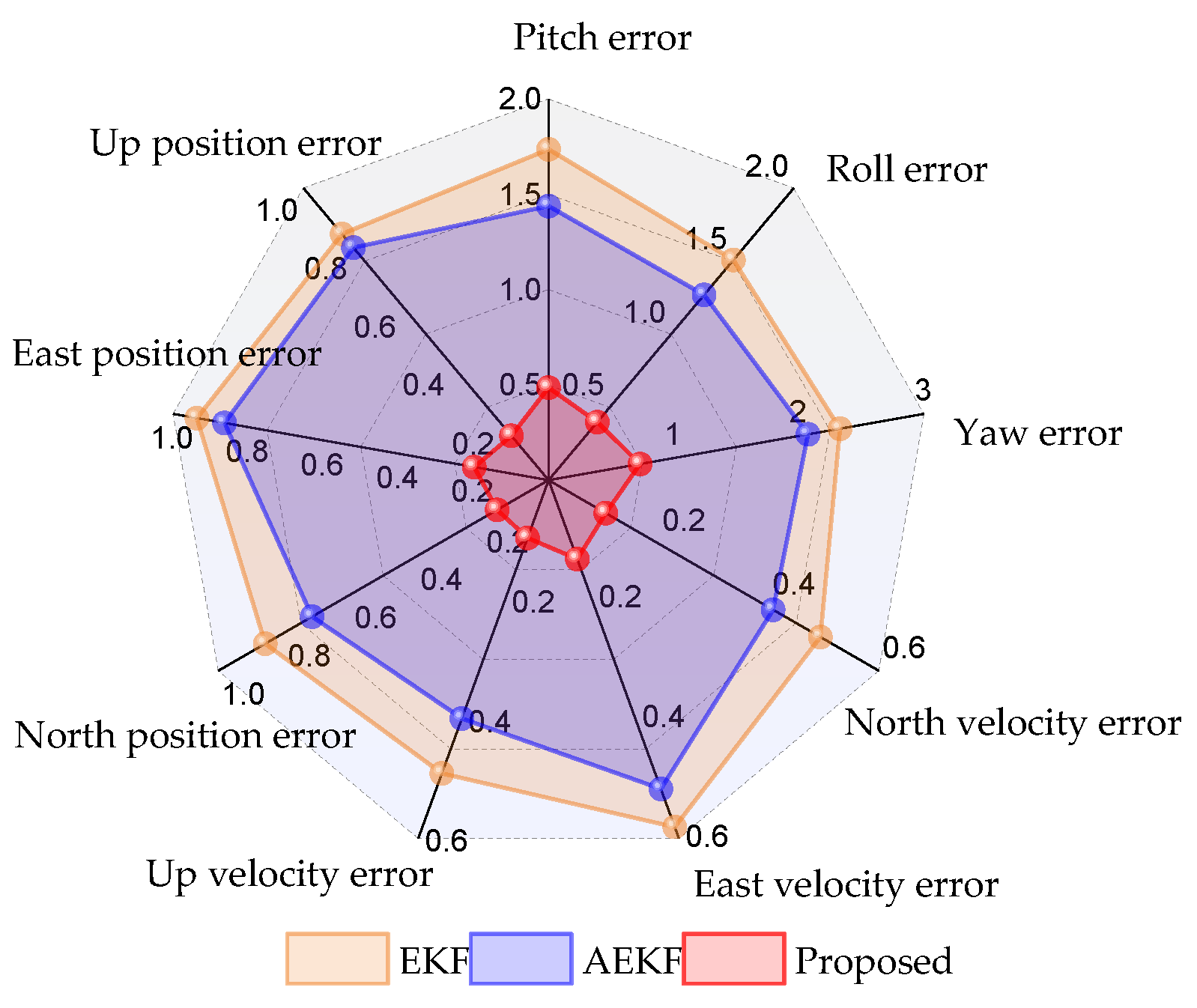
4.1. Performance Comparison of Different Methods for Good UWB Signal
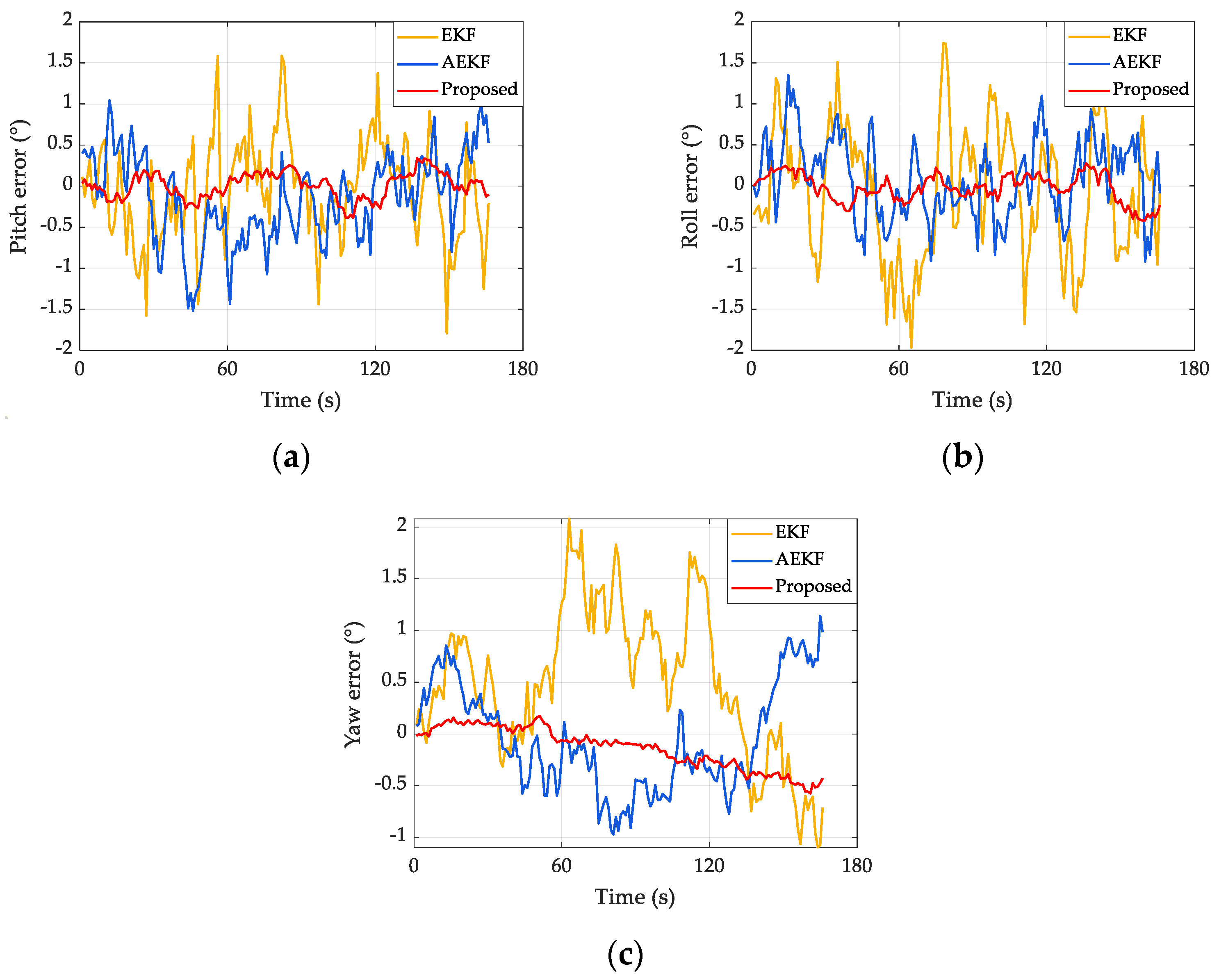
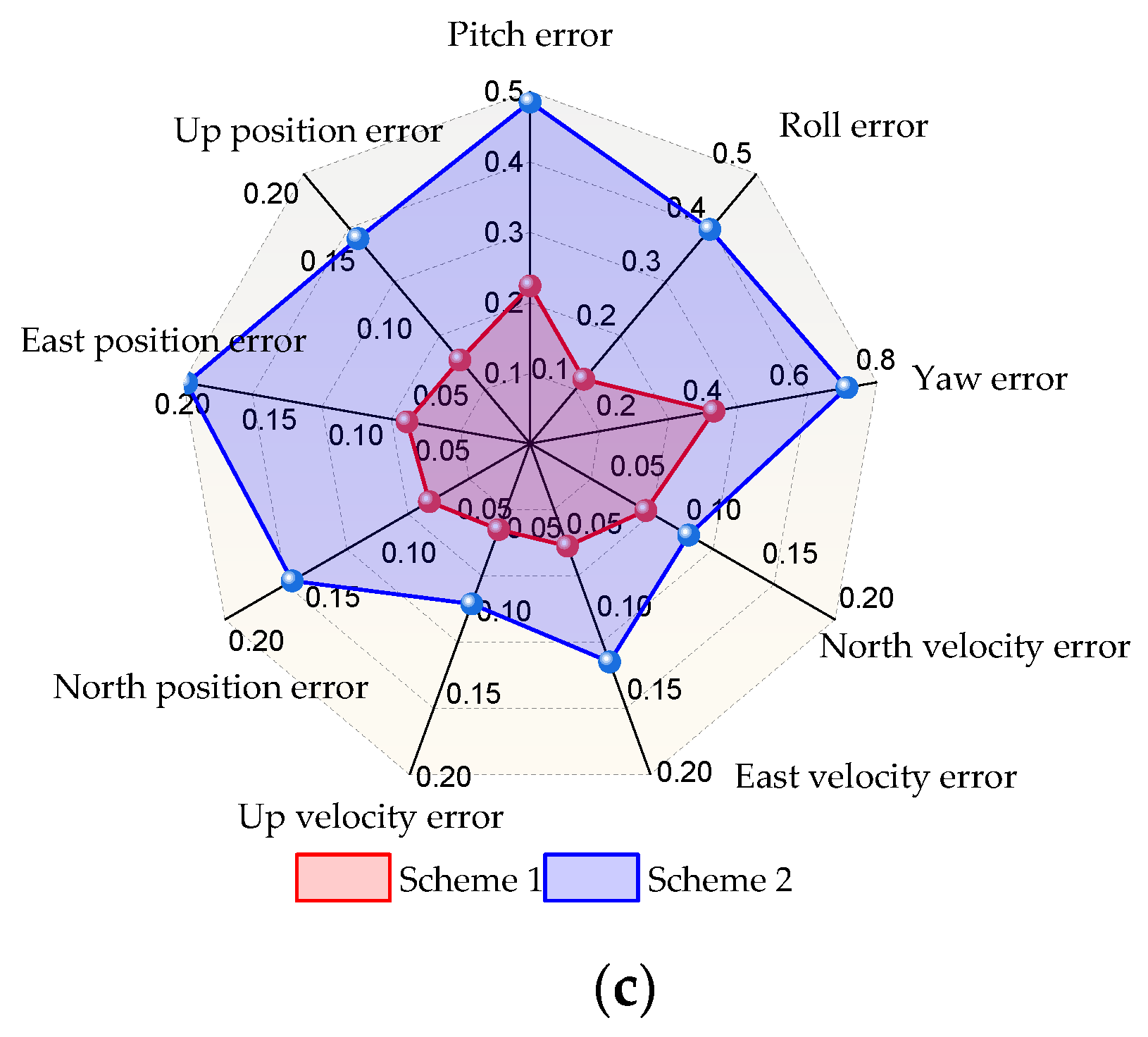
4.2. Performance Comparison of Different Methods for UWB NLOS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; He, J. Localization and Mapping for UGV in Dynamic Scenes with Dynamic Objects Eliminated. Machines 2022, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, J.; Han, D.; Wang, J.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, K. An In-Flight Alignment Method for Global Positioning System-Assisted Low Cost Strapdown Inertial Navigation System in Flight Body with Short-Endurance and High-Speed Rotation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, T. UWB indoor positioning algorithm based on TDOA technology. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Qingdao, China, 23 August 2019; pp. 777–782. [Google Scholar]
- Poulose, A.; Eyobu, O.S.; Kim, M.; Han, D.S. Localization error analysis of indoor positioning system based on UWB measurements. In Proceedings of the 2019 Eleventh International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Croatia Spain, 2–5 July 2019; pp. 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zasowski, T.; Althaus, F.; Stager, M.; Wittneben, A.; Troster, G. UWB for noninvasive wireless body area networks: Channel measurements and results. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Ultra Wideband Systems and Technologies, Reston, VA, USA, 16–19 November 2003; pp. 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, P.; Leitinger, E.; Witrisal, K. UWB for robust indoor tracking: Weighting of multipath components for efficient estimation. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2014, 3, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wang, C.; He, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Xia, X.-G. Kalman-filter-based integration of IMU and UWB for high-accuracy indoor positioning and navigation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 3133–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pu, J.; Sun, L.; He, Z. An approach to robust INS/UWB integrated positioning for autonomous indoor mobile robots. Sensors 2019, 19, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Kadja, T.; Chodavarapu, V.P. Experimental Evaluation of Sensor Fusion of Low-Cost UWB and IMU for Localization under Indoor Dynamic Testing Conditions. Sensors 2022, 22, 8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Gao, Y.; Guo, J.; Zuo, S.; Xiang, J.; Li, D.; Tu, Z. An Integrated UWB-IMU-Vision Framework for Autonomous Approaching and Landing of UAVs. Aerospace 2022, 9, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wen, D.; Geng, J.; Zheng, N.-N. Task-specific performance evaluation of UGVs: Case studies at the IVFC. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chang, D.; Fang, T.; Luo, T. Design and optimization of parking lot in an underground container logistics system. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 130, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szrek, J.; Zimroz, R.; Wodecki, J.; Michalak, A.; Góralczyk, M.; Worsa-Kozak, M. Application of the infrared thermography and unmanned ground vehicle for rescue action support in underground mine—The amicos project. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hol, J.D.; Dijkstra, F.; Luinge, H.; Schon, T.B. Tightly coupled UWB/IMU pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–11 September 2009; pp. 688–692. [Google Scholar]
- Hol, J.D. Sensor Fusion and Calibration of Inertial Sensors, Vision, Ultra-Wideband and GPS; Linköping University Electronic Press: Linköping, Sweden, 2011; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, K.; Yu, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W. A new quaternion Kalman filter based foot-mounted IMU and UWB tightly-coupled method for indoor pedestrian navigation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 4340–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godha, S.; Cannon, M. GPS/MEMS INS integrated system for navigation in urban areas. Gps. Solut. 2007, 11, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkov, P.; Slavov, T. Stochastic modeling of MEMS inertial sensors. Cybern. Inf. Technol. 2010, 10, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa, W.; Elbasiony, R.; Ashry, S. Adl classification based on autocorrelation function of inertial signals. In Proceedings of the 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Cancun, Mexico, 18–21 December 2017; pp. 833–837. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.; Semwal, V.B.; Kaushik, P. Stride segmentation of inertial sensor data using statistical methods for different walking activities. Robotica 2022, 40, 2567–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L. Auto regressive moving average (ARMA) modeling method for Gyro random noise using a robust Kalman filter. Sensors 2015, 15, 25277–25286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheimy, N.; Hou, H.; Niu, X. Analysis and modeling of inertial sensors using Allan variance. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 57, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, R.; Chugunov, A.; Pudlovskiy, V.; Tsaregorodtsev, D. Weighted pseudo-range method of positioning in local ultra-wide band navigation systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 Ural Symposium on Biomedical Engineering, Radioelectronics and Information Technology (USBEREIT), Yekaterinburg, Russia, 13–14 May 2021; pp. 387–390. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, X. An optimization-based UWB-IMU fusion framework for UGV. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 4369–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Song, D.; Feng, B.; Ye, H. A novel NLOS error compensation method based IMU for UWB indoor positioning system. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 11203–11212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Liu, Z. Research on uwb/imu fusion positioning technology in mine. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Intelligent Transportation, Big Data & Smart City (ICITBS), Vientiane, Laos, 11–12 January 2020; pp. 934–937. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, L. UWB/IMU integration approach with NLOS identification and mitigation. In Proceedings of the 2018 52nd Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Princeton, NJ, USA, 21–23 March 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. An approach to improve the positioning performance of GPS/INS/UWB integrated system with two-step filter. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakoorian, S.; Mohammadi, A.; Azimi, V.; Simon, D. Robust Kalman-type filter for non-Gaussian noise: Performance analysis with unknown noise covariances. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2019, 141, 091011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiancheng, F.; Sheng, Y. Study on innovation adaptive EKF for in-flight alignment of airborne POS. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, P.D.; Maybeck, P.S. Multiple-model adaptive estimation using a residual correlation Kalman filter bank. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2000, 36, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, S.; Afzulpurkar, N. Mobile robot integrated with gyroscope by using IKF. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2011, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasalo, M.; Hu, X. An optimization approach to adaptive Kalman filtering. Automatica 2011, 47, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Fan, Y.; Wang, G.; Mu, D.; He, Z. Radar Target Tracking for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Based on Square Root Sage–Husa Adaptive Robust Kalman Filter. Sensors 2022, 22, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhappa, M.; Mahindrakar, A.D.; Guizilini, V.C.; Terra, M.H.; Sabat, S.L. MEMS-based IMU drift minimization: Sage Husa adaptive robust Kalman filtering. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Sun, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhuang, X. Performance enhancement of MEMS-based INS/UWB integration for indoor navigation 543 applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3116–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curey, R.K.; Ash, M.E.; Thielman, L.O.; Barker, C.H. Proposed IEEE inertial systems terminology standard and other inertial 545 sensor standards. In Proceedings of the PLANS 2004. Position Location and Navigation Symposium (IEEE Cat. No. 546 04CH37556), Hachioji, Japan, 23–24 March 2004; pp. 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Wang, J. Quantization and Colored Noises Error Modeling for Inertial Sensors for GPS/INS Integration. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sensor | Parameter | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Constant Drifts | Random Walk | |
| gyro | |||
| acc | |||
| Method | Attitude Error (°) | Velocity Error (m/s) | Position Error (m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pitch | Roll | Yaw | East | North | Up | East | North | Up | |
| EKF | 0.745 | 0.426 | 1.536 | 0.166 | 0.197 | 0.142 | 0.161 | 0.165 | 0.158 |
| AEKF | 0.461 | 0.227 | 0.968 | 0.136 | 0.146 | 0.102 | 0.124 | 0.126 | 0.119 |
| Proposed | 0.224 | 0.119 | 0.424 | 0.062 | 0.076 | 0.052 | 0.066 | 0.071 | 0.062 |
| Method | Attitude Error (°) | Velocity Error (m/s) | Position Error (m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pitch | Roll | Yaw | East | North | Up | East | North | Up | |
| EKF | 1.763 | 1.508 | 2.329 | 0.581 | 0.494 | 0.491 | 0.937 | 0.858 | 0.843 |
| AEKF | 1.438 | 1.269 | 2.073 | 0.517 | 0.408 | 0.399 | 0.863 | 0.716 | 0.796 |
| Proposed | 0.485 | 0.397 | 0.731 | 0.132 | 0.104 | 0.097 | 0.198 | 0.156 | 0.152 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mi, J.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Constrained MEMS-Based INS/UWB Tightly Coupled System for Accurate UGVs Navigation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102535
Mi J, Wang Q, Han X. Constrained MEMS-Based INS/UWB Tightly Coupled System for Accurate UGVs Navigation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102535
Chicago/Turabian StyleMi, Jing, Qing Wang, and Xiaotao Han. 2023. "Constrained MEMS-Based INS/UWB Tightly Coupled System for Accurate UGVs Navigation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102535
APA StyleMi, J., Wang, Q., & Han, X. (2023). Constrained MEMS-Based INS/UWB Tightly Coupled System for Accurate UGVs Navigation. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102535





