Abstract
Open pit coal mining affects surrounding populated areas, resulting in terrain surface deformation. Surface deformation should be monitored as often as possible to control deformations and prevent potential incidents. This paper analyzes time series deformation estimated from the Sentinel-1 satellite images using the Persistent Scatterer Interferometry method to monitor subsidence rates caused by open pit mining activities. It is possible to measure deformations using classical geodetic methods, but those are rarely used in practice because they are time-consuming and expensive for application in large areas. Using the open access radar images from the Sentinel-1 mission, 513 images from the repository were downloaded between October 2016 and the end of December 2020. We present the processing steps in detail in order to establish a workflow for the automated processing of vertical displacement estimation using open source tools; a total of 402 images were processed: 215 images belonged to the ascending satellite orbit, 187 images belonged to the descending orbit, and 111 images were rejected because of adverse weather conditions. The PS InSAR technique has never been used for the mines of the Republic of Serbia or for land surveying practices related to deformation monitoring. The results based on the Sentinel-1 images were compared with results from geodetic leveling and with neotectonic uplift trends. The trend lines of vertical displacement obtained from PS and corresponding leveling are significantly similar (a Pearson correlation of 85% with a p-value of 0.015). The final evaluation reported results of vertical displacements at the leveling benchmark of −3.4 mm/year with the PS InSAR method and −2.7 mm/year with the leveling method. A comparison of the PS vertical displacements with a settlement model fits reasonably, suggesting that the measurements are valid. As four years of PS time series data is insufficient to establish undisputable conclusions on the neotectonics uplift, extending the time series (covering at least a decade) implies that this approach will become attractive in future neotectonic uplift trend estimations. This study illustrates not only the ability of Sentinel-1 data in mapping vertical deformations, but the obtained results could also be used for geohazard monitoring and land monitoring in general for the area of interest.
1. Introduction
Coal exploitation through open pit mining [1] strongly affects neighboring populations, traffic infrastructure, and all surrounding environments that are crucial for the comfortable daily life of citizens. Subsidence rates can be expected in the immediate proximity of open pit mines directly, caused by activities such as mining and blasting, drainage, and hydrological tasks during exploitation, or as a result of excavation and transportation systems. Therefore, monitoring the subsidence or movement of objects on the surface is a challenging task that has, so far, mostly been done using classical terrestrial surveying techniques.
The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and conventional survey methods, such as high precision leveling for observing displacements, introduces accuracy and reliability. On the other hand, they are time consuming and expensive, especially when a large number of observations are required to cover wide areas of interest [2,3]. This requires extensive fieldwork activities and is preferably done during optimal weather conditions. Due primarily to leveling requirements and expenses, classical methods are performed infrequently, and so extensive time series’ of vertical deformations are not provided. Therefore, an approach such as the Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) with persistent scatterer analysis is solution for monitoring, observing, and estimating ground displacements, as reported in recent studies [4,5,6], taking open access orientation and data availability into account. Using phase information from radar images, it is possible to extract displacements ranging from a few decimeters to a millimeter, bearing in mind that phase delay in interferograms is directly related to the cumulated refractivity along the signal path [7,8]. The integration of GNSS and leveling techniques with InSAR techniques can ensure the best results, since the number of GNSS receivers can be decreased, and the InSAR approach can provide the required density of deformation points [9].
The InSAR based on the Sentinel-1 is a low-cost wide area Earth observation method that provides observations independent of the clouds, contrary to optical remote sensing. On the other hand, the technique is not perfect, since the propagation velocity through the atmosphere is related to refractivity, which depends on temperature and pressure variations, water vapors or raindrops, and snowflakes. Signals from low orbit satellites such as Sentinel-1, A, and B orbiting in the lower boundary of the exosphere, the exobase, at an altitude of 693 km (where the atmospheric pressure and temperature are very low) are affected by the mentioned influences.
The InSAR interferogram generation of two radar images over the same area at different dates goes back to 1974 [10]. The Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) interferometry methodology was developed between 1989 and 1991 [11]. The differential InSAR (DInSAR) is an upgraded version of InSAR that enables the monitoring of surface deformations or movement in the Line Of Sight (LOS) direction [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. DInSAR accuracy is related to the spatial and temporal resolution of the mission, and it is affected mainly by orbital and atmospheric errors [24,25,26,27,28]. Over the past 15 years, significant effort has been made by many researchers to overcome difficulties and implement an interferometric process to generate and monitor ground surface movements [29,30,31].
An important feature for reducing difficulties in monitoring the DInSAR process is analyzing the Persistent Scatterers’ (PS) spatiotemporal movements. Certain objects reflect a permanently stable SAR signal back to the satellite over time. Objects that possess such properties are usually artificial structures (buildings, traffic infrastructure, etc.), rocks, and similar objects. Ferreti [32,33] presented the first Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) technique in 2000 and 2001, known as the Permanent Scatterer approach, while the Small BAselines Subset (SBAS) technique was introduced as a new approach several years later. The SBAS method is often used in addition to the PS method to supplement results without signal response since the signal comes from distributed targets [34]. The following important Persistent Scatterer (PS) technique step was first made by Hooper in 2004 with a new approach for PS selection using phase preferences. His work led to the development of software packages called the Stanford Method for Persistent Scatterers (STaMPS), with its last edition in 2018 [35,36,37,38]. Furthermore, some studies consider a hybrid approach of PS and SBAS methodology or advanced algorithms of the mentioned methods [39,40].
Different multi-temporal InSAR techniques, such as the Coherence Pixel Technique (CPT) [41], Interferometric Point Target Analysis (IPTA) [42], the Stable Point Network (SPN) [43], the Persistent Scatterer Pairs (PSP) [44], and Temporarily Coherent Point Interferometry (TCPI) [45] are well-known and tested in various case studies. Currently, MT-InSAR techniques are developed to monitor large areas such as the whole territory of Germany [46], Norway [47], and Italy [48], or as an alpha version of an infrastructure monitoring and decision-support framework remotIO based on the MT-InSAR introduced by Bakon et al. [49]. Many studies showed subsidence results for cities in Europe [2,3,50], the USA [45], and China [51], or of deformation monitoring of earthquakes [4,52], mining [22,30,31,53], land and coastal monitoring [2,3,7,23,39,40,41,54], volcanic activities [55], glacier motions [56], or even illegal mining activities using the decorrelation problem as valuable information [53]. In addition, by combining dual polarization channels VV and VH, the Polarimetric Persistent Scatterer Interferometry technique (PolPSI) can be used to reduce decorrelation effects and achieve better deformation monitoring [57]. The intercomparison between InSAR deformation and geodetic monitoring, including GNSS and leveling, has been reported by authors [58,59]; in addition to the comparison with leveling, we have also provided a comparison with geotechnical simulation. With the above developments in mind, this article presents algorithms for processing chains and generating a subsidence time series using the PS interferometry method. The processing is implemented in Sentinel Application Platform (SNAP) software [60,61,62] to create interferograms. The STaMPS package is used to generate a time series of deformations. As inputs, image collections downloaded from the ESA hub [63,64] through the Alaska Satellite Facility data search (ASF) [65] were used. This research covers the period from October 2016 to December 2020.
The study’s primary objective was to analyze and estimate the subsidence of the neighboring ground surface caused by the coal mine “Kostolac”. The PS technique was used, and we expected numerous persistent scatterers in urban areas and the lack of them in vegetated and agricultural regions. As far as we know, the PS InSAR technique has never been used in the mines of the Republic of Serbia or in land surveying practices related to deformation monitoring. This study details the workflow for processing time series derived by PS InSAR images available as open access in order to make a contribution to the automated processing for vertical displacement estimation using open source tools. The results from geotechnical models related to the area of interest are presented and compared with the results from PS InSAR.
Regarding the monitoring area, the most affected villages are Drmno and Klicevac, where the closest houses are located less than 200 m from the edge of the open pit (Figure 1d). Additionally, two more villages, Bradarac and Klenovnik, are in the immediate vicinity. There are two more areas of interest: the mining infrastructure area (TEKO) and the town of Kostolac. To validate this kind of observation and to overcome orbital and low-frequency atmospheric errors, the PS analysis was compared to the geodetic leveling technique, which involves field measurements, after which 1D adjustment was performed using the least square method [66]. A deformation analysis was done using the Peltzer method [67]. The input data sets are presented in Section 2, including geotechnical maps and data, and the methods are described in Section 3. The results of the time series analysis is presented in Section 4, the summary results are given in Section 5, and the conclusions are given in the Section 6.
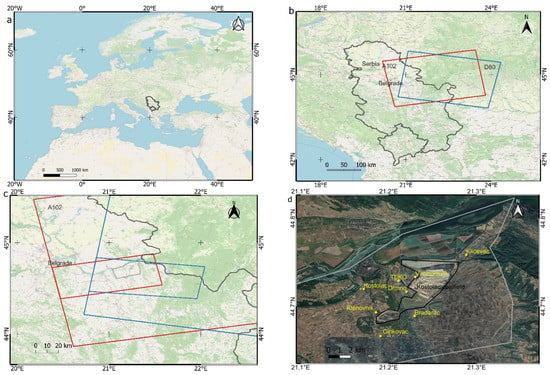
Figure 1.
Location of the study area: (a) Republic of Serbia; (b) Sentinel S1 radar images footprints, red (A102) ascending and blue (D80) descending; (c) processing bursts from IW1 A102 and IW3 D80 footprints, with a grey polygon representing the Kostolac coal basin; (d) the Kostolac coalfield with neighboring populated settlements of interest (source Open Street Map (a–c) and Google Earth (d)).
2. Study Area and Datasets
2.1. Study Area
The Republic of Serbia is located in southeastern and central Europe (Figure 1a). The Kostolac coal basin, located 90 km east of Belgrade, the capital of Serbia, is divided into four coal deposits. Drmno encompasses the eastern and southeastern part of the basin, Cirikovac contains the central part of the coal basin, the western part of the coal basin is known as Smederevsko Pomoravlje, and the fourth part is Klenovnik. The basin occupies an area approximately 25 km in length and 10 km in width, and is also known as the “Stig” plain (Figure 1c,d).
The coal basin is in its third and last exploitation period, which began in 2019 and will end in 2049. The main part of the Kostolac mine is the Drmno coalfield (Figure 1d) which provides the raw material base for electricity production in the four “Kostolac” thermal power plants. The proposed coal production of nine million tons per year assumes five Excavator-Conveyor-Spreader (ECS) systems for the overburden works, plus one for hummus removal and two-level excavation systems for coal exploitation.
The open pit coal layer is a homogenous structure without inlayers of overburden, with an average thickness between 18 and 20 m. The coal layer dips to the west by approximately six degrees and to the northeast (the advance direction of the front) by between three and four degrees. The terrain is relatively flat, and because of the coal layer dip, the thickness of the overburden increases from 20 m on the east side to 120 m on the west side of the pit.
The proximity of the Mlava River in the west and the Danube River in the north, as well as its advantageous lithology structure, completely flooded the upper part of the coal layer. For drying the open pit field, combined methods of drainage were applied to avoid endangering the agriculture and the water supply of the surrounding settlements as much as possible. The southern and western border of the open pit is protected from groundwater influence by waterproof screens, which prevent groundwater inflow into the open pit and soil drying towards the settlements of Bradarac and Majurevac. From the open pit’s northern, eastern, and southeastern sides, drainage is done by a system of wells. Since this system ensures overburden drying on one side, on the other side it leaves the village of Drmno without water in its wells, so a water pipeline supply system was made to overcome this problem.
The thermal power plant “Kostolac A” is located on the right side of the Danube River in the Kostolac area, whereas “Kostolac B” is located a few kilometers away, at the confluence of the river Mlava and the Danube [68]. With 1000 MW of installed power, the “Kostolac” thermal power plants (TEKO) annually produce 5 billion MW of electricity, which accounts for 14% of the total electricity production of the Republic of Serbia [69].
The processing area extends over 500 km2, but the primary targets used for analyses are the villages of Drmno, Klicevac, Bradarac, TEKO, and Kostolac, covering a total area of about 65 km2 (Figure 1c,d) and belonging to zone 1, 2 and 3 of the mine influence (Figure 2). The study area (area of interest (AOI)) extends to the coal deposits and involves the neighboring settlements that are actually located on the coal deposits or around the coalfield.
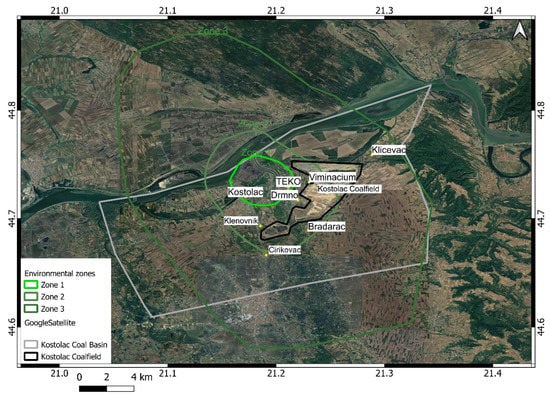
Figure 2.
Environmental protection zones [70]. In the defined zones, the monitoring of qualitative and quantitative data on the state and pollution of the environment, including noise emission, occurs from the operation of machines and devices. The processing area mainly covers the presented zones.
One of the issues that occurs is the subsidence of the populated settlements. As the “Kostolac” mine does not have a monitoring service for this kind of task, this paper presents a solution for establishing a monitoring service and implementing a procedure for tracking the subsidence of the surrounding artificial structures, as well as the environment.
2.2. Geological Setting of the Study Area
The wider AOI is geographically bounded by the Danube River to the north, the Resava River valley to the south, the Velika Morava River to the west, and the Golubac Mountains to the east [71]. It belongs to the Pannonian basin (it is southern periphery), known as the Kostolac basin, where coal layers were formed during the Pont (upper Miocene) era.
The Drmno depression is its central structure, surrounded by the adjacent Smederevo depression to the west and the Veliko Gradiste depression to the east, and the Pozarevac ridge dominates the middle (Figure 3a) [72]. Its base, a few kilometers deep beneath, includes an old crystalline complex, constituting highly tectonized, high and low-grade tectonic rocks. These Paleozoic schists emerge on the Danube banks in the form of small patches (Figure 3c). After a very long continental development, the area subsided in synchronization with the Pannonian basin development in the Tertiary era. The deepening of all these depressions was substantial. The depth is estimated to be 3000 m in the central part of Drmno depression and at least 2000 m in the others (Smederevo, Pozarevac, and Veliko Gradiste depresions). They comprise primarily clastic sediments, poorly cemented to frail, with varying proportions of sand, silt, and clay, that are locally limy or marly, and are interlayered with several horizons of lignite coal [73]. There are coal seams of variable thickness, from dimensions of under a meter to over 180 m [73]. The quaternary sediments sit a top the dominant Miocene formations. Large fluvial systems of the Danube, Velika Morava, and Mlava rivers typically produced thick alluvial plains and terraces comprising primarily gravel and sand. The topmost parts of the Pozarevac and Sirakovo are covered with loess. Plunging down from these plateaux, deluvial and proluvial sediments reach the sediments of the alluvial base (Figure 3c).
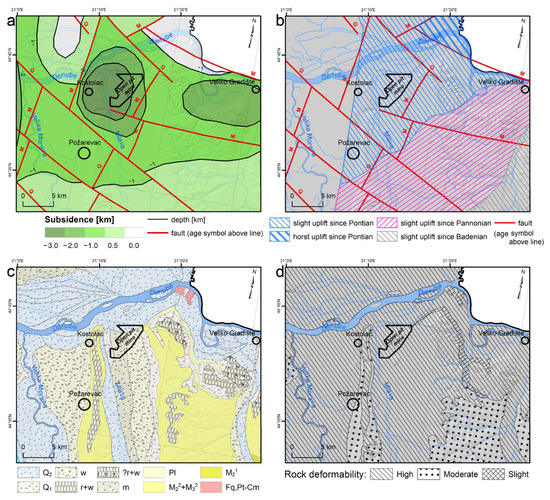
Figure 3.
(a) Neotectonic map of the wider AOI; (b) Map of the current tectonic trend; (c) Geological map of the wider AOI based on the [72] (Q2 = fluvial Quaternary sediments, w = Würm Quaternary sediments, r + w = Ris and Würm Quaternary sediments, ? r + w = undetermined Ris and Würm Quaternary sediments, m = Mindel Quaternary sediments, Pl = Pliocene clastites, clays and marls, M23 + M32 = Miocene clastites, M21 = Miocene sandstones and limestones, Fq,Pt − Cm = Paleozoic crystal schists); (d) Deformability map of the wider AOI.
The predominant structures are trending normal faults from the Alpine tectonic stage (the Miocene era) trending NNE-SSW. They are transected by the younger (Quaternary period) normal faults trending NW-SE, along which the grabens and depressions subsided. The neotectonic activity suggests a mild uplift over the entire eastern half of the AOI from the early Miocene onwards (Figure 3b), including a horst uplift in the northernmost corner. The youngest uplift trend from the Pontian onward is centered around the Kostolac basin (Figure 3b). The western parts shows no change in trend, i.e., subtle subsidence from the time of basin generation (Figure 3b). The plicative structures are indistinct, but gentle folding with low limb angles is typical of all Miocene formations in the AOI.
From a geotechnical point of view, these formations range from being very deformable to moderately and slightly deformable (Figure 3d). Most deformable formations are tied to Quaternary loose sediments, which have typical immediate settlement (sand and gravel predominates), whereas loess plateaux and poorly cemented Miocene sediments are slightly or moderately deformable, with a possible consolidation settlement type due to variable clay and organic (coal) content. Fly ash material deposited within the open pit tailings is also of sandy to silty fraction, meaning that immediate settlement is to be expected, although there were some other types of displacement reported, such as land sliding [74]. This was favorable for the InSAR methodology, which was used to capture four-year-long processes around the open pit contour. The groundwater regime is also highly influential [75], and it can be anticipated that the open pit wells are constantly lowering the table below the pit bottom so that the near-surface conditions are dry [74].
2.3. Sentinel-1 Dataset
Sentinel-1 is part of the European Copernicus program, which consists of two satellites, S1-A and S1-B, launched on 3 April 2014, and on 25 April 2016, respectively. They monitor the Earth’s surface, generating radar imagery that can be used for mapping land cover changes, ground deformations, floods, etc. As a constellation of two polar satellites orbiting 180° apart, they provide a time resolution of six days, while radiating the surface with C-band SAR under all weather conditions, day or night, with a swath coverage of 250 km.
All images were downloaded from the repository for Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-1B ascending and descending tracks, in the Interferometric Wide (IW) mode, with orbit track number 102 for ascending images and orbit track number 80 for descending images, spanning from October 2016 to the end of December 2020 (approximately 1542 days), and, as such, was used for processing (Table 1). Figure 1b,c show the coverage area for Sentinel-1 ascending (A102) and descending (D80) images bounded with red (A102) and (D80) blue rectangles. Smaller red and blue rectangles in Figure 1c represent the processing areas, and Figure 1d shows areas of interest with the surrounding populated settlements.

Table 1.
Sentinel S1 datasets for processing. M.I.A.: Master Image Acquisition.
2.4. Field Observations
In order to provide coal production improvements, the chimney construction works were undertaken from April 2019 to June 2020. For that purpose, leveling sessions were performed in order to monitor chimney subsidence. The survey leveling network (Figure 4) implies five stable control benchmarks (R5, R6, R52, R53, and R35), known as the primary control network and four working benchmarks (R1, R2, R3, R4). Control benchmarks are established on the stable and secured site positions outside the area of the impact of the chimney construction, whereas working benchmarks are set on the chimney itself.
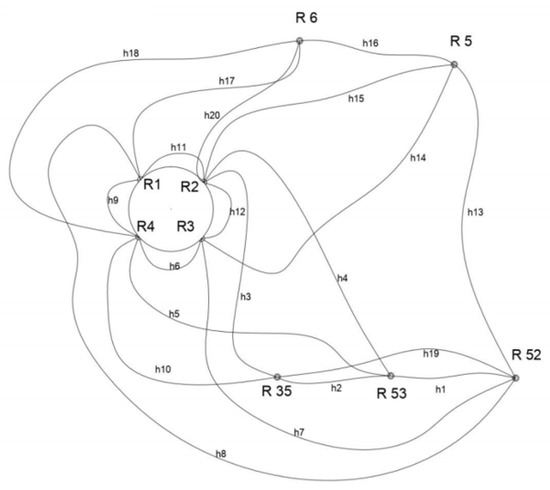
Figure 4.
Survey leveling network with the observation plan for leveling sides. Lines between points determine where elevation differences are measured.
During the observed period from April 2019 until February 2021, nine epochs were undertaken approximately every two months except for the last epoch, which was conducted at the beginning of 2021. The observation plan (Figure 4) implied twenty leveling sides to be surveyed for each epoch.
2.5. Geotechnical Modelling Inputs
Geotechnical parameters, such as unit weight γ and constrained deformation modulus Es, were required to perform a simple 3D ground settlement modeling and compare it to the four-year PS measurements. Although geotechnical surveys were conducted regularly to establish the level of compaction of the tailing fly ash, little or no data on geotechnical properties are freely available, including the parameters and the general geometry of the site, tailings, etc. Oral communication with the geological and geotechnical engineers involved in conducting ground investigations was one of the essential sources of estimations used in this work. Due to a lack of needed investigations (lab tests, field tests, etc.), it should be highlighted that the geotechnical modelling parameters were estimated roughly and that the results involved are only used to portray the general settlement trend and to compare it to the measured values.
The following soil profile was considered:
- loess, 30 m thick, γ = 16 kN/m3, Es = 20.0 MPa, the immediate settlement only
- clayey sand, 50 m thick, γ = 18 kN/m3, Es = 10.0 MPa, the immediate settlement only
- coal seam 1, 15 m thick, γ = 12 kN/m3, Es = 1.0 MPa, the immediate settlement only
- clayey sand 10 m thick, γ = 18 kN/m3, Es = 10.0 MPa, the immediate settlement only
- coal seam 2, 15 m thick, γ = 12 kN/m3, Es = 1.0 MPa, the immediate settlement only
- clayey sand 35 m thick, γ = 18 kN/m3, Es = 10.0 MPa, the immediate settlement only
- coal seam 35 m thick, γ = 12 kN/m3, Es = 1.0 MPa, the immediate settlement only
- clayey sand 50 m thick, γ = 18 kN/m3, Es = 10.0 MPa, the immediate settlement only
The settlement simulation did not include groundwater, since these conditions were unknown, although they might be very influential [74]. It is assumed that conditions are dry (due to the constant drainage of the open pit), that there are no pore pressures, and that the settlement is immediate (primary).
Another segment, being the primary reason for the potential settlement around the open pit contour, is the unloading due to the excavation and the loading of fly-ash layers coming from the power plant. These are separated with an impermeable foil and then compacted to a dry density of 11 kN/m3. It is assumed that each tailing can reach up to 30 m with 1:1 slope sides, and is of sandy-silty composition [75]. The pit size and geometry were reconstructed using the available satellite imagery, and the depth was based on the coal layer’s position. All simulations considered the first coal seam with its bottom at −80 m as the reference level.
All calculations were performed in Rocscience software module Settle3, using the Boussinesq method for stress σb propagation under load F Equation (1), which is based on the theory of elasticity and applies to any point in homogeneous half-space (beneath the ground surface) at depth z and offset angle θ (angle between the vertical and line that connects the observed point to load point). The immediate settlement that occurs simultaneously as the load is applied (in this case, the fly ash layers) is proportional to the stress difference (in this case, σb) to modulus ratio Equation (2).
Calculations were performed only for the Drmno and Bradarac area, and compared against the measured data.
3. Methods
The techniques for generating the InSAR time series can be separated into three groups. The first group implies a PS technique in which single-point backscattering properties remain stable during the observed period, introduced by [32,33]. The second group comprises small baseline techniques (SBAS) for time series generation through all available small baselines’ interferogram combinations [34,35]. A third group is a hybrid one that combines the first two groups of techniques. All of the methodologies mentioned above are implemented in various software packages.
For example, the ESA has been developing tools for Earth Observation (EO) processing and analysis named SNAP [60,61] since 2014, covering all three groups of techniques. SNAP is open source software created on the foundation of the BEAM and NEST platforms, with its last version, 9.0, released on 29 June 2022 [62]. The software can export data to another format or software package, such as StaMPS [35]. StaMPS is a partially open source, used for educational purposes in the additional analysis of ground displacement developed for two methods, PS and SBAS [36].
In this work, we chose the Persistent Scatterers method, since we engaged in deformations in urban areas. In contrast, the rest of the AOI comprises agricultural fields with systematic cultivation. Software processing in this work was divided into three stages:
- Image filtering or preprocessing,
- Processing with SNAP and StaMPS software,
- Employing open source software and scripts for analyzing and visualizing the results.
Finally, the comparison stage implies a correlation test between the survey leveling trend and the PS vertical displacement trend obtained on the benchmark. Furthermore, we compared PS InSAR vertical displacements with the results of the settlement simulation model.
3.1. Interferometry
Interferometric SAR (InSAR) is a combination of conventional SAR techniques and the principles of interferometry [76,77,78]. In the interferometric methods, the phase difference between two propagating EM waves reaching the same point is obtained from the intensity of the interferogram fringes, and is used to measure the difference in their path lengths. In order to form an interferogram, the InSAR technique uses at least two complex-valued SAR images of the same area made from two SAR antennas positioned at some distance (baseline), each carrying the amplitude and phase information of backscattering microwaves from all scatterers of the target resells. The single antenna-based InSAR system made images of the same area twice, from slightly different orbits and at other times. The obtained interferometric phase difference value between those two passing times could be treated as a sum of the phase shift terms. The most important among them carries information about the target height change. The other phase shift terms refer to the initial target area topography, the wrapped phase ambiguity, different atmospheric conditions at the time of image acquisition, errors in the exact position estimation of the antennas, their phase noise, and the variations of target backscattering characteristics over time [8].
3.2. Pre-Processing
The first processing stage involves downloading images from the ESA open hub [64] using ASF Data Search [65] and filtering them according to weather conditions with regard to snow cover and rainfall during image acquisition. The weather data are downloaded from the Ogimet database [79] for weather station 13285 Veliko Gradište, which is the closest weather station for the AOI. After this stage, 402 images were left, 215 images were from the ascending track, and 187 were from the descending track.
3.3. Processing
The key part of processing implies two independent processing chains: the first is a SNAP processing chain, and the second is a StaMPS processing chain. SNAP is a fully open source software, whereas StaMPS relies on command line/power shell/terminal scripting, in addition to its more significant part, in the MATLAB software.
3.3.1. SNAP Processing
The SNAP processing [60] chain is shown in Figure 5 and provides the data structure for the StaMPS mt_prep_snap shell script file, in addition to further data processing with StaMPS.
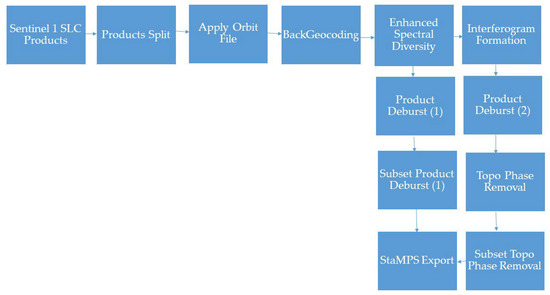
Figure 5.
The SNAP workflow for preparing readable data for StaMPS processing.
After downloading and filtering, depending on the weather conditions, the Sentinel-1 Single Look Complex (SLC) products (images) and product splitting should be applied to the image bursts and subswats. This will result in a new, smaller-sized product, followed by the applying of orbit files for each image separately. In the next step, the back geocoding operator co-registers all SLC products (master and slaves) and produces a stack of co-registered master–slave SLC files with the same master image for every master–slave pair. Enhanced Spectral Diversity (ESD) follows the back geocoding operator and produces co-registered master–slave images with the range and azimuth shift corrections applied to the slaves [38,80].
The ESD step is divided into two branches. The first branch follows the product deburst operator. Interferometric Wide (IW) SLC products have three swats, and each sub-swath consists of a series of bursts, where each burst is processed as a separate SLC image. Bursts have an overlap of 50–100 samples, and after debursting, they result in a single sub-swath image. After debursting, users can take a subset of the AOI to reduce the data size. The second branch starts with an interferogram formation operator and the computation of a complex interferogram, after which users should apply product debursting. Subsequently, Topographic Phase Removal is performed, estimating and subtracting the topographic phase from interferograms. The branch is completed by taking a subset representing the AOI. The final step enters both branches into the StaMPS export operator to produce readable files and a data structure for the StaMPS application for PS Interferometry. Figure 5 shows the SNAP workflow for generating interferograms and input data for further processing with STaMPS.
3.3.2. StaMPS Processing
StaMPS is a software package for generating PS deformation rates through time series using coregistered SLC stacks of the master–slave interferogram pairs from SNAP [36,81] or other software. StaMPS processing starts with the mt_prep_snap script file initializing permanent scatterer candidates and their information, run from the command line. After exporting StaMPS compatible files from SNAP and running the mt_prep_snap script file, there are eight straight steps to generate a deformation time series. All eight steps are processed using MATLAB [82], and this part of the processing is done in proprietary software.
Processing starts with the (stamps (1,1)) step, loading the permanent scatterer candidates from the mt_prep_snap script file, with amplitude dispersion as the threshold setting up the value to 0.4. The stamps (2,2) step implies phase noise computations for every interferogram candidate pixel. The stamps (3,3) step implies final PS pixel adoption. The stamps (4,4) step, called permanent scatterer weeding, eliminates pixels with too much noise. Stamps (5,5) imply phase correction, stamps (6,6) imply phase unwrapping [83,84,85,86], and stamps (7,7) step estimates the spatially correlated look angle (SCLA) error. Stamps (8,8) is the last step, which requires the use of the Toolbox for Reducing Atmospheric InSAR Noise (TRAIN), where we applied linear atmospheric filtering [24,25,26,27,28] to reduce the topography-correlated atmospheric phase. The estimated atmospheric noise was removed from the results.
The digital elevation model (DEM) used is Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), with a resolution of 3 arc seconds [87].
We selected a stable reference point in the middle of the processing area (marked as a black triangle), showing 0 mm/year of vertical movement. The whole neighboring area of the reference point shows stable phase preferences throughout the time series.
3.4. Post-Processing
Using the previous steps from SNAP and STAMPS processing, we could generate two sets of ascending and descending Line of Sight (LOS) displacements into the time series formation from satellites S1A and S1B. As we focused only on the vertical displacements in this study, we combined the LOS measurements from descending and ascending geometries to obtain the vertical displacements [50,52,88,89].
The final analysis was transferred into QGIS [90] for visualization and deformation map generation overlaid with satellite images. With this approach, it was possible to separate the vertical motion rates in the specified areas.
3.5. Least Squares and Pelzer Method
The classical approach for deformation analysis implies collected field measurements of leveling. For leveling sides, the geometric method was used with the standard back-front-front-back option in the forward direction during the morning and the backward direction during the evening. A Leica brand classical instrument with proper barcode leveling bars was used, resulting in a stated accuracy of 0.3 mm/km.
Field measurements were later processed through algorithms based on the Least Squares Method [66] for network adjustment and the Pelzer method for deformation analysis based on the time series [67].
4. Results
The entire AOI is divided into smaller areas that are more suitable for the presentation of the results related to subsidence velocity and a map showing vertical displacements obtained after post-processing. Areas to be investigated included Drmno, Klicevac, Klenovnik, and Bradarac, as surrounding settlements, the Thermal Power Plant Area (TEKO) and the Kostolac settlement, as well as the rest of the overlapped area after processing. The obtained results are related to the urban areas of the AOI, whereas the signals received from the vegetated areas and excavation sites were unusable. LOS velocities of the PS motion are presented in Figure 6 and Figure 7, in ascending and descending tracks. The number of PSs for the processing area with basic statistics is shown in Table 2.
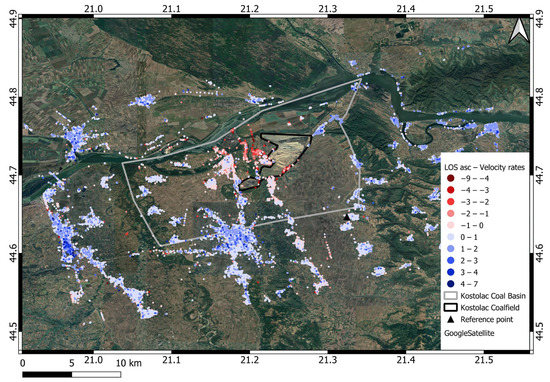
Figure 6.
LOS velocity motion map [mm/year] generated from the sentinel Sentinel-1 A and B ascending orbit track for the AOI; the red color represents PSs away from the satellite, and the blue color represents PSs towards the satellite.
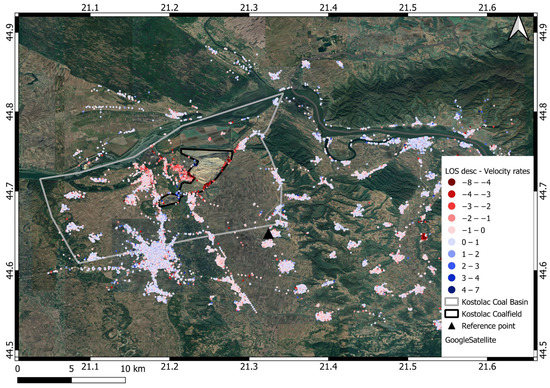
Figure 7.
LOS velocities motion [mm/year] map generated from the sentinel Sentinel-1 A and B descending orbit track for the AOI; the red color represents PSs away from the satellite, and the blue color represents PSs towards the satellite.

Table 2.
PS statistics for LOS ascending and descending orbit for processing AOI, and vertical decomposition of the ascending and descending orbit.
A decomposed vertical velocity motion map is presented in Figure 8. The resolution cell is set up to 50 m, and 8951 PS was generated, and is shown in the histogram (Figure 9).
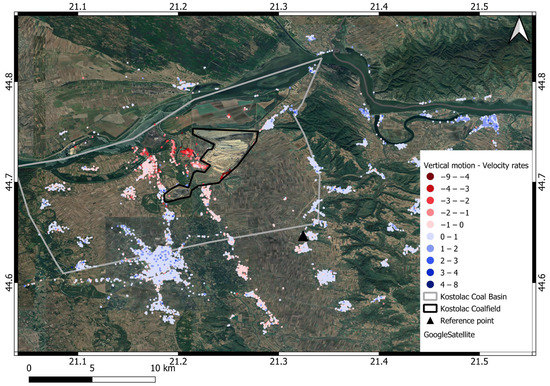
Figure 8.
Vertical velocity motion [mm/year] map after geometry decomposition with shades of red for negative values and shades of blue for positive values (50 m resolution cell).
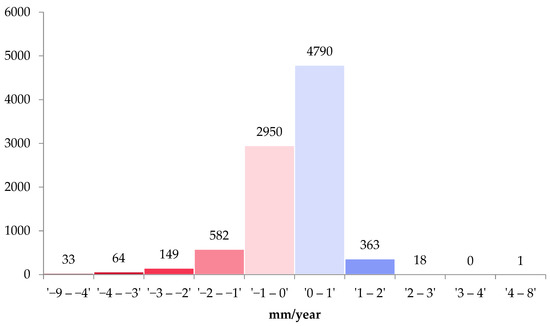
Figure 9.
Histogram of vertical velocity values grouped into different clusters. There were a total of 8951 resulting PSs for the processing area (a 50 m resolution cell).
4.1. Drmno Area
The Drmno area is located near the mine, and this site was most affected by mining activities in the past. However, this part of the mine has not been widely exploited in the last six years. Figure 10 shows the velocities of the subsidence in the range from 0 to −4.5 mm/year, where it can be seen that the whole village is showing a subsidence effect. Subsidence velocities are dominant and highest at the edge of the village and the open pit. Table 3 shows the statistical parameters for PS in the Drmno settlement.
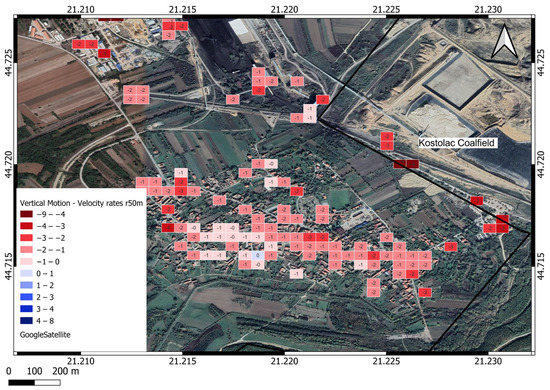
Figure 10.
Drmno vertical velocity motion map [mm/year], raster cell 50 m.

Table 3.
Persistent Scatterers statistics for Drmno AOI (50 m resolution).
4.2. Klicevac and Bradarac Areas
The Klicevac area is located on the northeast side of the mine, and most future pit activities will be directed around this village. The pit bypasses the nearest houses by less than 200 m, and the exploitation will reach close to the village border. Figure 11 shows Klicevac PS deformation velocities ranging from −2.2 to +2.4 mm/year. A total of 235 PSs were used to generate the Klicevac velocity deformation map shown in Table 4 and Figure 11. Subsidence on the edge of the village and the open pit can be clearly seen, while the rest of the area shows a vertical uplift motion increasing value by moving away from the edge of the open pit on the southwest side, reaching the highest value on the northeast side of the village.
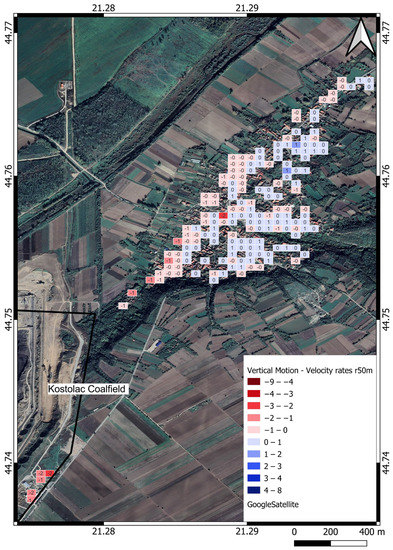
Figure 11.
Klicevac vertical velocity motion map [mm/year], raster cell 50 m.

Table 4.
PS statistics for the Kličevac and Bradarac AOI.
The Bradarac area is located on the south side of the mine. Figure 12 shows a deformation map of the Bradarac area where deformation velocity values range from −8.2 to +1 mm/year. PSs near the open pit edge reach maximum subsidence values from −8.2 mm/year. As distance increases from the edge of the open pit, subsidence velocities decrease. A total of 270 PSs could be seen in the Bradarac velocity deformation map, as shown in Table 4.
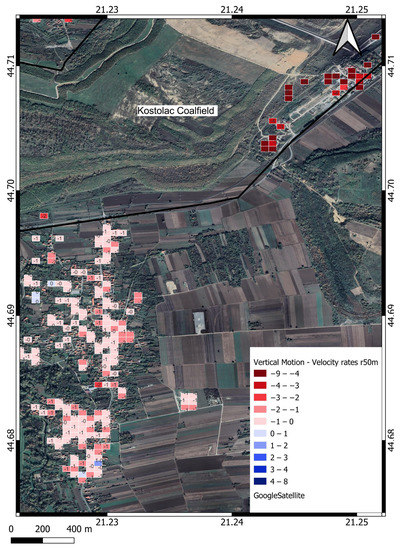
Figure 12.
Bradarac vertical velocity motion map [mm/year], raster cell 50 m.
4.3. Thermal Power Plant Area (TEKO)
TEKO is located on the west side of the mine and the north side of the Drmno village. Figure 13 shows the velocity rates of the vertical motion for the TEKO area. Maximal subsidence was detected in the area close to lake “TE Kostolac B”, ranging from −2 to −5 mm/year. A total of 102 PSs are shown on the vertical motion map with a 50 m resolution cell (Table 5 and Figure 13).
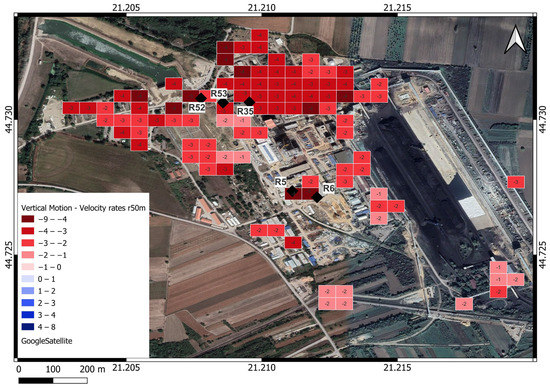
Figure 13.
TEKO velocity rates of vertical motion [mm/year], black rhombus represents leveling benchmarks, raster cell 50 m.

Table 5.
PSs statistics for TEKO (mine infrastructure objects) AOI.
Thermal Power Plant Area (TEKO) Leveling Benchmarks
A survey control network has been established for new chimney construction within the thermal power plant. The control network contains five leveling benchmarks: R52, R53, R35, R5, and R6, which are mounted on neighboring objects and represent stable points for chimney subsidence monitoring during construction (Figure 13). There are also four working benchmarks mounted on the chimney for subsidence observations. A survey campaign conducted by contractors hired by TEKO lasted from April 2019 to February 2021. It consisted of monitoring the subsidence of the chimney under construction and providing results for verification.
The PS InSAR vertical displacement estimations were referenced to the same date as the start of leveling to be comparable with the leveling data. The survey team used leveling methods, and the observed subsidence on benchmark R6 is −2.7 mm/year (Figure 14), whereas this study obtained results in a few PSs where the overlapped PS with the benchmark R6 resulted in −3.4 mm/year. The Pearson correlation is 85%, with a p-value of 0.015. The benchmark R6 was the only one that had the PS directly above, and the roof of the building was the PS.
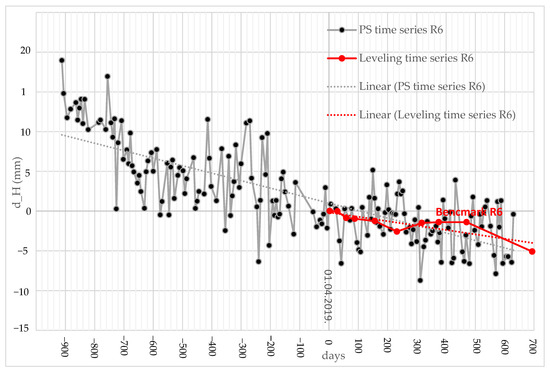
Figure 14.
Benchmark R6, PS time series and leveling time series, dotted lines represent trends of the PS and leveling time series.
4.4. Kostolac Area
The Kostolac settlement is located five kilometers to the west of the open pit. Different power plant facilities and water and land transport junctions are built in the north part of the Kostolac. The whole area shows subsidence behavior, which is clearly displayed, increasing from south to north, where power plant activities are the highest. The maximal subsidence detected was −4.3 mm/year, as shown in Table 6 and Figure 15.

Table 6.
PSs statistics for Kostolac AOI.
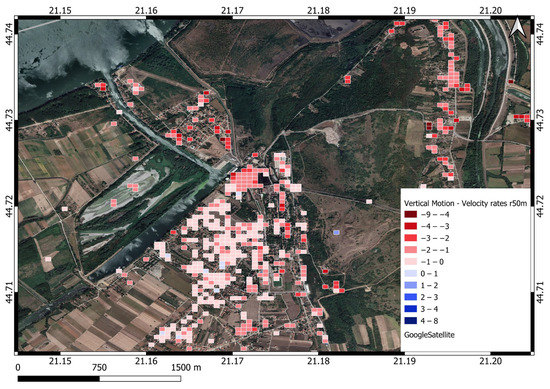
Figure 15.
Kostolac velocity rates of vertical motion [mm/year], raster cell 50 m.
4.5. Settlement Model
The settlement model applies to the areas of Drmno and Bradarac, and is located on the southernmost contour of the Drmno open pit. The simulation, under assumed properties and conditions, shows that surface subsidence from loading on the bottom of the pit can reach noticeable values, e.g., −4.0 cm in the Drmno area and −5.0 cm in the Drmno village. In comparison, −1.0 cm can be expected in the Bradarac area (Figure 16, black dots, see Section 2.5 for details on the geotechnical properties). These are immediate settlements according to the model, but their totals can match relatively well with the four-year vertical displacements at the specified sites. For instance, at the first check point (A) −4.0 cm of modeled settlement corresponds to the measured vertical displacement of −4.5 mm/year, i.e., −1.8 cm in total (multiplied by four years). In the Bradarac area (the second checkpoint) it is the opposite. Captured vertical displacement was −8.2 mm/year, i.e., −3.3 cm in total, which is underestimated in comparison to modeled immediate settlement of −1.0 cm, but still shows a similar trend. On the western outskirts (at the third check point B), measured −2.2 mm/year, i.e., −0.9 cm in total, while modelled settlement equals −5.0 cm. Having in mind that the settlement model was simplified and based on roughly estimated input parameters, the comparison shows that the model fits reasonably well with the measured data, implying that the PS measurements have a valid trend and magnitude, despite apparent over/underestimations. Further improvements of the settlement model, which are currently not feasible due to a lack of operative geotechnical data, might result in an even better fit (e.g., assuming the presence of pore pressures [75] and primary consolidation or even secondary settlement, which might justify the analysis of a longer time series).
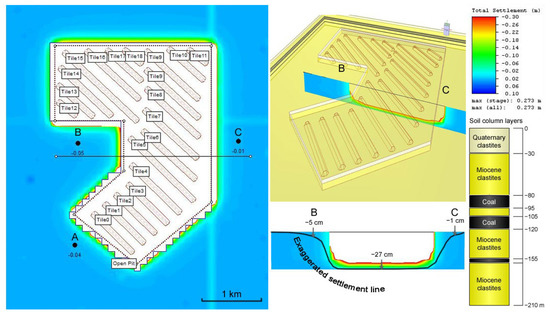
Figure 16.
Plan (left) and oblique view (upper middle) and a cross-section (lower middle) of the settlement model, with black dots expressing referent settlement points with settlements in m (on the right, the graphical representation of the soil column is given, in addition to the settlement scale bar).
5. Discussion
The time series analysis and processing workflow was described in detail. The entire process is not fully automated; however, as it relies on scripts and algorithms, it can be fully automated. The dense coverage of the reliable PSs over the AOI provides a good base for monitoring deformations. The process results in 8951 PSs, in a regular geometry, occupying a processing area of approximately 1000 km2. Considering an open pit exploitation area and vegetated areas, which cover about 50% of the AOI, where the SAR signal was not received, there was a total of ~20 PS targets/km2. The smallest number of PS regarding populated places is in the Drmno area. The area and density of the artificial objects, primarily PS, in Drmno are significantly smaller than, for example, the Klicevac and Bradarac areas. Only a co-polarized (VV) channel was used from the satellite imagery for processing. Using both polarizations (VV + VH), as well as using other wavelengths, should lead to more PSs being obtained.
The 50 m rasterization of the PS’s ascending and descending pairs was performed, and vertical motions, uplift, and subsidence were reconstructed to achieve reliable results.
The AOI displays apparent uplift and subsidence trends, showing subsidence rates around the open pit border, as well as the area of the thermal power plant TEKO and the town of Kostolac, which are directly related to coal production. All areas distanced from the open pit showed positive values for the vertical motions. The largest subsidence velocity can be found on the west side of the mine, where the thermal power plant infrastructure is located. The results related to the populated areas did not show high deformation values, whereas the construction sites had higher subsidence rates. Velocity values of the motion in the AOI correspond to the interval of +2.4 mm/year in the Klicevac area to the maximal gained subsidence value of −8.2 mm/year in the Bradarac area. These results are correlated with the results obtained by the classical geodetic approach and the other four benchmarks that follow subsidence trends. The verification process was performed through comparison with the survey leveling results, where benchmark R6 shows a Pearson correlation of 85% with a p-value 0.015; this confirms a significant correlation and recommends this method as an alternative to classical leveling. Searching for the subsidence in the populated areas, maximal velocity values were found to be −4.5 mm/year for Drmno, −2.2 mm/year for Klicevac, and −8.2 mm/year for Bradarac, −5.0 mm/year for the TEKO area, and −4.3 mm/year for the Kostolac region. Uplift velocity values were found to be +2.4 mm/year for Klicevac and +1.1 mm/year for Bradarac, and +1.0 mm/year for Kostolac, whereas uplift motion was not found in the areas of Drmno and TEKO.
The PS tool shows good potential for the long-term monitoring of ground displacements. Still, given that it is a novel technique that relies on missions of up to one decade old, it is reasonable that analysis of the geodynamic uplift will become attractive in the future. In the current AOI, the general uplift directions and descriptive trends were determined from the geological investigations [73]. When cross-compared with the final results with annual displacement rates (Figure 17), it is noticeable that the urban areas of Pozarevac and Veliko Gradiste and villages in the eastern part introduce upward displacements of a small magnitude (up to 4 mm/year). These could be related to the geological background of the structural blocks, which have been predominantly in slight uplift since the Miocene era or later. However, numerous targets with negative vertical displacements suggest otherwise. These can be considered as artificially affected targets, e.g., settlements due to mining [74], loading, landsliding, etc., which is usually very common in an area dominated by deformable rocks.
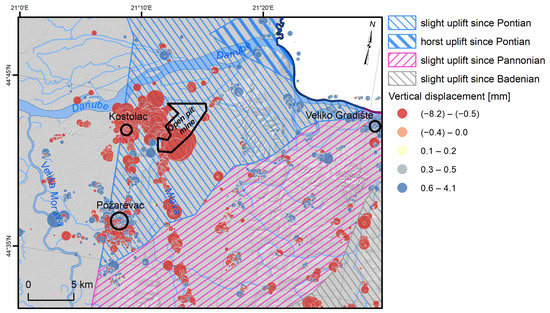
Figure 17.
Cross-comparison of PS measurements and neotectonic uplift trends [75].
It is important to note several limiting issues of the SAR system and the PS procedures. The first one involves its coarse temporal resolution (revisiting period), which was a problem in the past. With the launching of ESA satellites S1-A and S1-B, this characteristic has been significantly improved, resulting in a temporal resolution of six days. The second issue is related to the low PS distribution in vegetated areas and areas with low reflectivity. Furthermore, steep terrain or snow coverage can bring a complete loss of PSs and lead to signal decorrelation. PS locations cannot be known a priori before PS processing, whereas geodetic techniques use predefined points of interest to monitor deformations. A comparison of the deformations obtained with the PS technique and those with geodetic techniques has to be carefully considered. The Sentinel-1 images have a temporal resolution of six days, which brings users the privilege of monitoring and establishing a vertical motion management system. According to the mission data time resolution of 6 days, in this study, the proposed monitoring procedure is preferable, since low rates of spatiotemporal deformation behavior were expected. Phase unwrapping limits the observation of fast deformation phenomena to 1/4 of the wavelength over the satellite revisiting time because of phase ambiguity. PS analysis results in the LOS geometry based on the line that connects the satellite sensor and the surface target. The vertical displacements can be resolved using different orbit pairs, i.e., pairs of ascending and descending orbit datasets. PS velocity maps may contain orbital and low-frequency atmospheric errors, which can be resolved using multiple overlapping tracks or combined with geodetic techniques such as leveling.
The monitoring process shows that using the time series generated through PS InSAR algorithms could be an appropriate stand-alone solution for deformation monitoring, or the presented approach can complement the measurement gaps that exist in leveling survey data and provide a much more detailed time series of vertical displacements [31]. The results of comparison with the classical surveying method are significantly correlated, as also reported by [31], and shows that this method could be even more preferable, especially regarding the costs and area of coverage that could be monitored. Several large deformation oscillations were obtained from the PS time series within short periods in the deformation curve (see Figure 14) which is inconsistent compared to classical surveying methods. We assume that external influences caused the jumps in the time series, metal roof construction oscillating depending on solar radiation, temperature, or similar influence. The trend lines in both results are significantly similar (a Pearson correlation 85% with a p-value of 0.015); similar results were obtained in other studies [58] related to the trendline comparison. Therefore, vertical displacement should investigate a linear trend of a more extended (at least one year) time series in order to be comparable with classical surveying leveling. The final results display overall yearly displacements of −3.4 mm/year with the PS InSAR method and −2.7 mm/year with the leveling method.
Comparing the PS InSAR vertical displacement estimations shown in Figure 14 with the velocity rates of vertical motion shown in Figure 13 identifies that all of the TEKO area is unstable, including all leveling benchmarks. Considering the above conclusion of the instability benchmark network, the network’s primary purpose could be to show whether some benchmark subsidence is bigger or smaller than the rest of the network. According to the displacements of PS InSAR (Figure 14), the R6 benchmark site experienced subsidence within a range of 15 mm (based on trendline) to 20 mm (based on PS time series observations) during the period of October 2016 to December 2020. The results from the Peltzer analyses also confirmed the most significant drop at the R6 benchmark (from April 2019 to February 2021). This study could help identify stable reference points in the TEKO area for impartial evaluations of vertical displacements across benchmarks.
6. Conclusions
This article presents surface deformation behavior in the environment near the Kostolac open pit, primarily using open-source software packages and the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission data. According to the results and discussion above, the PSI procedure is a powerful tool for recognizing and understanding surface motion behavior. Processing images and generating results onto vertical geometry and with their overlapping with the area of interest, it was possible to determine the vertical surface motion. To ensure comparability with classical surveying leveling, it is recommended to investigate the linear trend of an extended time series (at least one year) regarding vertical displacement. The final outcomes reveal yearly displacements of −3.4 mm/year via PS InSAR and −2.7 mm/year using the leveling method.
Regarding the results of vertical motion shown in Figure 13, it showed that all of the TEKO area is unstable, including all leveling benchmarks. Despite some variations, these vertical motions are also in accordance with the general settlement trend established in the geotechnical model (Figure 16). The outcomes of this study have the potential to offer guidance on identifying stable reference points in the TEKO area, thereby yielding impartial evaluations of vertical displacements across all benchmarks. Such a PS InSAR vertical displacement estimations approach would prove beneficial for designing leveling networks focusing on benchmark stability.
As four-year time series PS data is insufficient to establish undisputable conclusions on the neotectonics uplift, which last across much longer time scales, extending the time series (covering at least a decade) would be interesting, with the filtering of the ground targets by field control (using only reliable, uncompromised targets).
The proposed monitoring system solution could be implemented in typical mining and geodetic (land surveying) practices. In this case, because of the lack of leveling data, estimated vertical displacements are the only source of the deformation monitoring information for the period from October 2016 to April 2019. This research is the first application of wide-area vertical deformation mapping with Sentinel-1 data in Serbia, and it has not been as widely used in regions of the Balkan Peninsula as it has in other countries of Western Europe [9]. Previously, it was reported as the proper solution for underground mining, where vertical displacements are much higher [30,31]. These results reported for the AOI could also be used for geohazard monitoring [4,50,52] and land monitoring in general [2,3].
Future work should use different methods over the AOI, and comparisons with the PS method could be presented. Finally, sensors with better spatial resolution or new acquisition modes will be available soon, in addition to the existing ones, increasing the precision and density of the PSs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.G. and M.K.; methodology, Z.G., M.K., L.B. and M.M.; validation, M.M.; investigation, Z.G.; writing—original draft, Z.G.; writing—review & editing, M.K., L.B., M.M., A.M. and A.G.; supervision, M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The Sentinel-1 data are openly available at the Copernicus Open Access Hub. The data processed in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hartman, H.L.; Mutmansky, J.M. Introductory Mining Engineering, 2nd ed.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 0-471-34851-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cenni, N.; Fiaschi, S.; Fabris, M. Monitoring of Land Subsidence in the Po River Delta (Northern Italy) Using Geodetic Networks. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Monitoring the Land Subsidence Area in a Coastal Urban Area with InSAR and GNSS. Sensors 2019, 19, 3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polcari, M.; Palano, M.; Fernández, J.; Samsonov, S.V.; Stramondo, S.; Zerbini, S. 3D Displacement Field Retrieved by Integrating Sentinel-1 InSAR and GPS Data: The 2014 South Napa Earthquake. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 49, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A. Generation of Earth’s Surface Three-Dimensional (3-D) Displacement Time-Series by Multiple-Platform SAR Data; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; ISBN 978-953-51-3742-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bakon, M.; Perissin, D.; Lazecky, M.; Papco, J. Infrastructure Non-Linear Deformation Monitoring via Satellite Radar Interferometry. Procedia Technol. 2014, 16, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucoules, D.; Colesanti, C.; Carnec, C. Use of SAR Interferometry for Detecting and Assessing Ground Subsidence. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2007, 339, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Soldato, M.; Confuorto, P.; Bianchini, S.; Sbarra, P.; Casagli, N. Review of Works Combining GNSS and InSAR in Europe. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.C. Synthetic interferometer radar for topographic mapping. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckman, A.J. Correction of SAR Imagery for Variation in Pixel Scattering Area Caused by Topography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Ranson, K.J.; Kharuk, V.I. Radiometric Slope Correction for Forest Biomass Estimation from SAR Data in the Western Sayani Mountains, Siberia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Romero, R.; Mulas, J.; Marturià, J.J.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; González, P.J.; Fernández, J.; et al. Radar Interferometry Techniques for the Study of Ground Subsidence Phenomena: A Review of Practical Issues through Cases in Spain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, B.C. Theory of Digital Imaging from Orbital Synthetic-Aperture Radar. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1985, 6, 1009–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackledge, J.M. Theory of Imaging with Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar. Optik 1987, 78, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Curlander, J.C.; McDonough, R.N. Synthetic Aperture Radar; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Scheuer, T.E.; Wong, F.H. Comparison of Sar Processors Based on A Wave Equation Formulation. In Proceedings of the IGARSS’91 Remote Sensing: Global Monitoring for Earth Management, Espoo, Finland, 3–6 June 1991; Volume 2, pp. 635–639. [Google Scholar]
- Runge, H.; Bamler, R. A Novel High Precision SAR Focussing Algorithm Based on Chirp Scaling. In Proceedings of the IGARSS’92 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Houston, TX, USA, 26–29 May 1992; Volume 1, pp. 372–375. [Google Scholar]
- Bamler, R. A Comparison of Range-Doppler and Wavenumber Domain SAR Focusing Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamler, R.; Schättler, B. SAR Data Acquisition and Image Formation. Geocoding ERS-1 SAR Data Syst. Wichmann-Verl. 1993, 53–102. [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk, A.; Grzybek, R. An Evaluation of Processing InSAR Sentinel-1A/B Data for Correlation of Mining Subsidence with Mining Induced Tremors in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin (Poland). E3S Web Conf. 2018, 26, 00003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Solari, L.; Giannecchini, R.; Galanti, Y.; Moretti, S. Evaluation of Subsidence Induced by Long-Lasting Buildings Load Using InSAR Technique and Geotechnical Data: The Case Study of a Freight Terminal (Tuscany, Italy). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 82, 101925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.P.S.; Walters, R.J.; Wright, T.J.; Hooper, A.J.; Parker, D.J. Statistical Comparison of InSAR Tropospheric Correction Techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.; Hooper, A.; Wright, T. A Spatially-Variable Power-Law Tropospheric Correction Technique for InSAR Data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. InSAR Uncertainty Due to Orbital Errors. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 199, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidbaekart. Available online: http://davidbekaert.com/download/TRAIN_manual.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Github. Available online: https://github.com/dbekaert/TRAIN (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Shi, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liao, M. Detection and Characterization of Active Slope Deformations with Sentinel-1 InSAR Analyses in the Southwest Area of Shanxi, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Zou, Y. Investigation on Mining Subsidence Based on Multi-Temporal InSAR and Time-Series Analysis of the Small Baseline Subset—Case Study of Working Faces 22201-1/2 in Bu’ertai Mine, Shendong Coalfield, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluszek-Filipiak, K.; Borkowski, A. Integration of DInSAR and SBAS Techniques to Determine Mining-Related Deformations Using Sentinel-1 Data: The Case Study of Rydułtowy Mine in Poland. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear Subsidence Rate Estimation Using Permanent Scatterers in Differential SAR Interferometry. Geosci. Remote Sens. IEEE Trans. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamps Software Package. Available online: http://homepages.see.leeds.ac.uk/~earahoo/stamps/ (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Stamps Software Package. Available online: https://homepages.see.leeds.ac.uk/~earahoo/stamps/StaMPS_Manual_v4.1b1.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Bechor, N.B.D.; Zebker, H.A. Measuring Two-Dimensional Movements Using a Single InSAR Pair. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagüe-Martínez, N.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Rodríguez González, F.; Brcic, R.; Shau, R.; Geudtner, D.; Eineder, M.; Bamler, R. Interferometric Processing of Sentinel-1 TOPS Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2220–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Ke, Y.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Li, Z. Land Subsidence Prediction in Beijing Based on PS-InSAR Technique and Improved Grey-Markov Model. GISci. Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 797–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatza, S.; Papoutsis, I.; Paradissis, D.; Kontoes, C.; Papadopoulos, G.A. Multi-Temporal InSAR Analysis for Monitoring Ground Deformation in Amorgos Island, Greece. Sensors 2020, 20, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, O.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Broquetas, A. Linear and nonlinear terrain deformation maps from a reduced set of interferometric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Wegmuller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A. Interferometric point target analysis for deformation mapping. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 7, pp. 4362–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Biescas, E.; Duro, J.; Closa, J.; Arnaud, A. Generation of advanced ERS and Envisat interferometric SAR products using the Stable Point Network technique. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Falco, S.; Malvarosa, F.; Minati, F. A New Method for Identification and Analysis of Persistent Scatterers in Series of SAR Images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008—2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 8–11 July 2008; pp. II-449–II-452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Ding, X.; Jung, H.-S.; Feng, G.; Lee, C.-W. Mapping ground surface deformation using temporarily coherent point SAR interferometry: Application to Los Angeles Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden Bewegungsdienst Deutchland. Available online: https://bodenbewegungsdienst.bgr.de/mapapps/resources/apps/bbd/index.html?lang=en (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- InSAR Norway. Available online: https://insar.ngu.no/ (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Costantini, M.; Ferretti, A.; Minati, F.; Falco, S.; Trillo, F.; Colombo, D.; Novali, F.; Malvarosa, F.; Mammone, C.; Vecchioli, F.; et al. Analysis of surface deformations over the whole Italian territory by interferometric processing of ERS, Envisat and COSMO-SkyMed radar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 250–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakon, M.; Czikhardt, R.; Papco, J.; Barlak, J.; Rovnak, M.; Adamisin, P.; Perissin, D. remotIO: A Sentinel-1 Multi-Temporal InSAR Infrastructure Monitoring Service with Automatic Updates and Data Mining Capabilities. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado Blasco, J.M.; Foumelis, M.; Stewart, C.; Hooper, A. Measuring Urban Subsidence in the Rome Metropolitan Area (Italy) with Sentinel-1 SNAP-StaMPS Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, M.; Kang, Y.; Lu, Z. Investigating Ground Subsidence and the Causes over the Whole Jiangsu Province, China Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Ordoqui, P.; Iglesias, R.; Blanco, P. Earthquake Rapid Mapping Using Ascending and Descending Sentinel-1 TOPSAR Interferograms. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Sun, X. Monitoring Mining Activities Using Sentinel-1A InSAR Coherence in Open-Pit Coal Mines. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D. Sentinel-1 Big Data Processing with P-SBAS InSAR in the Geohazards Exploitation Platform: An Experiment on Coastal Land Subsidence and Landslides in Italy. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z. InSAR imaging of volcanic deformation over cloud-prone areas-Aleutian islands. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Tian, B. The glacier movement estimation and analysis with InSAR in the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; pp. II-578–II-581. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Feng, H.; Yan, S.; Fan, H.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y. Polarimetric Persistent Scatterer Interferometry for Ground Deformation Monitoring with VV-VH Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Esquivel Ramírez, R.; Tapete, D. Accuracy of Sentinel-1 PSI and SBAS InSAR Displacement Velocities against GNSS and Geodetic Leveling Monitoring Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucoules, D.; Bourgine, B.; de Michele, M.; Le Cozannet, G.; Closset, L.; Bremmer, C.; Veldkamp, H.; Tragheim, D.; Bateson, L.; Crosetto, M.; et al. Validation and intercomparison of Persistent Scatterers Interferometry: PSIC4 project results. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 68, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency SNAP Software Package. Available online: https://step.esa.int/main/download/snap-download/ (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- European Space Agency SNAP Software Package. Available online: https://step.esa.int/main/doc/tutorials/ (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- European Space Agency SNAP Software Package. Available online: http://step.esa.int/docs/presentations/SNAP_User_Forum/2_SNAP_Introduction%20and%20News.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- European Space Agency Sentinel-1 Mission. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/Copernicus/Sentinel-1/Introducing_Sentinel-1 (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- European Space Agency Satellite Imaginary. Available online: https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Alaska Satellite Facility Data Search. Available online: https://search.asf.alaska.edu/#/ (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Perović, G.; Ninković, S.; Moritz, H. Least Squares:(Monograph): With 87 Figures and 90 Tables; TON: Belgrade, Serbia, 2005; ISBN 86-907409-0-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pelzer, H. Zur Analyse Geodätischer Deformations-Messungen; DGK, Verlag der Bayer. Akad. d. Wiss.: Munich, Germany, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Electric Power Industry of Serbia. Available online: http://www.eps.rs/lat/kostolac/Stranice/o-nama-teko.aspx (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Kostovic, M.; Kostović, N.; Tokalić, R. Coal mining and preparation in Serbia. Podzemn. Rad. 2018, 33, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electric Power Industry of Serbia Zones of the Influence. Available online: http://www.eps.rs/cir/kostolac/Pages/zastita-zivotne-sredine.aspx (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Google Earth. Available online: https://earth.google.com/web/@44.75232586,21.27635474,65.88404334a,6766.13237461d,35y,0.25 (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Geological Information System of Serbia. Available online: http://geoliss.mre.gov.rs/karte/geo300.html (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Đoković, N.; Mitrović, D.; Životić, D.; Bechtel, A.; Sachsenhofer, R.F.; Matić, V.; Glamočanin, L.; Stojanović, K. Petrographical and organic geochemical study of the lignite from the Smederevsko Pomoravlje field (Kostolac Basin, Serbia). Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 195, 139–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božić, D. Use of Wingtra and AIBOTIX unmanned airborne vehicles in analysis of landslides of open-pit lignite mines. Rep. Serb. Geol. Soc. 2022, 2021, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Peduto, D.; Prosperi, A.; Nicodemo, G.; Korff, M. District-scale numerical analysis of settlements related to groundwater lowering in variable soil conditions. Can. Geotech. J. 2022, 6, 978–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, G. Physical Principles of Remote Sensing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-107-00473-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bamler, R.; Hartl, P. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Inverse Probl. 1998, 14, R1–R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.A. A Beginner’s Guide to Interferometric SAR Concepts and Signal Processing [AESS Tutorial IV]. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2007, 22, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Professional Information about on Weather Conditions around the World. Available online: https://www.ogimet.com/gsynres.phtml.en (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Fattahi, H.; Agram, P.; Simons, M. A Network-Based Enhanced Spectral Diversity Approach for TOPS Time-Series Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Bekaert, D.; Spaans, K.; Arıkan, M. Recent Advances in SAR Interferometry Time Series Analysis for Measuring Crustal Deformation. Tectonophysics 2012, 514, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB Is a Programming and Numeric Computing Platform. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Network Approaches to Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping: Intractability and Two New Algorithms. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 2000, 17, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping with Use of Statistical Models for Cost Functions in Nonlinear Optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 2001, 18, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Phase Unwrapping for Large SAR Interferograms: Statistical Segmentation and Generalized Network Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical-Cost, Network-Flow Algorithm for Phase Unwrapping. Available online: https://web.stanford.edu/group/radar/softwareandlinks/sw/snaphu/ (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Available online: https://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/srtm/ (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Samieie-Esfahany, S.; Hanssen, R.F.; Van Thienen-Visser, K.; Muntendam-Bos, A.; Systems, S. On the effect of horizontal deformation on insar subsidence estimates. In Proceedings of the 2009 Workshop on Fringe, Frascati, Italy, 30 November–4 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Foumelis, M. Vector-Based Approach for Combining Ascending and Descending Persistent Scatterers Interferometric Point Measurements. Geocarto Int. 2018, 33, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Free and Open Source Geographic Information System. Available online: https://qgis.org/en/site/ (accessed on 5 November 2021).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).