Soil Erosion Satellite-Based Estimation in Cropland for Soil Conservation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
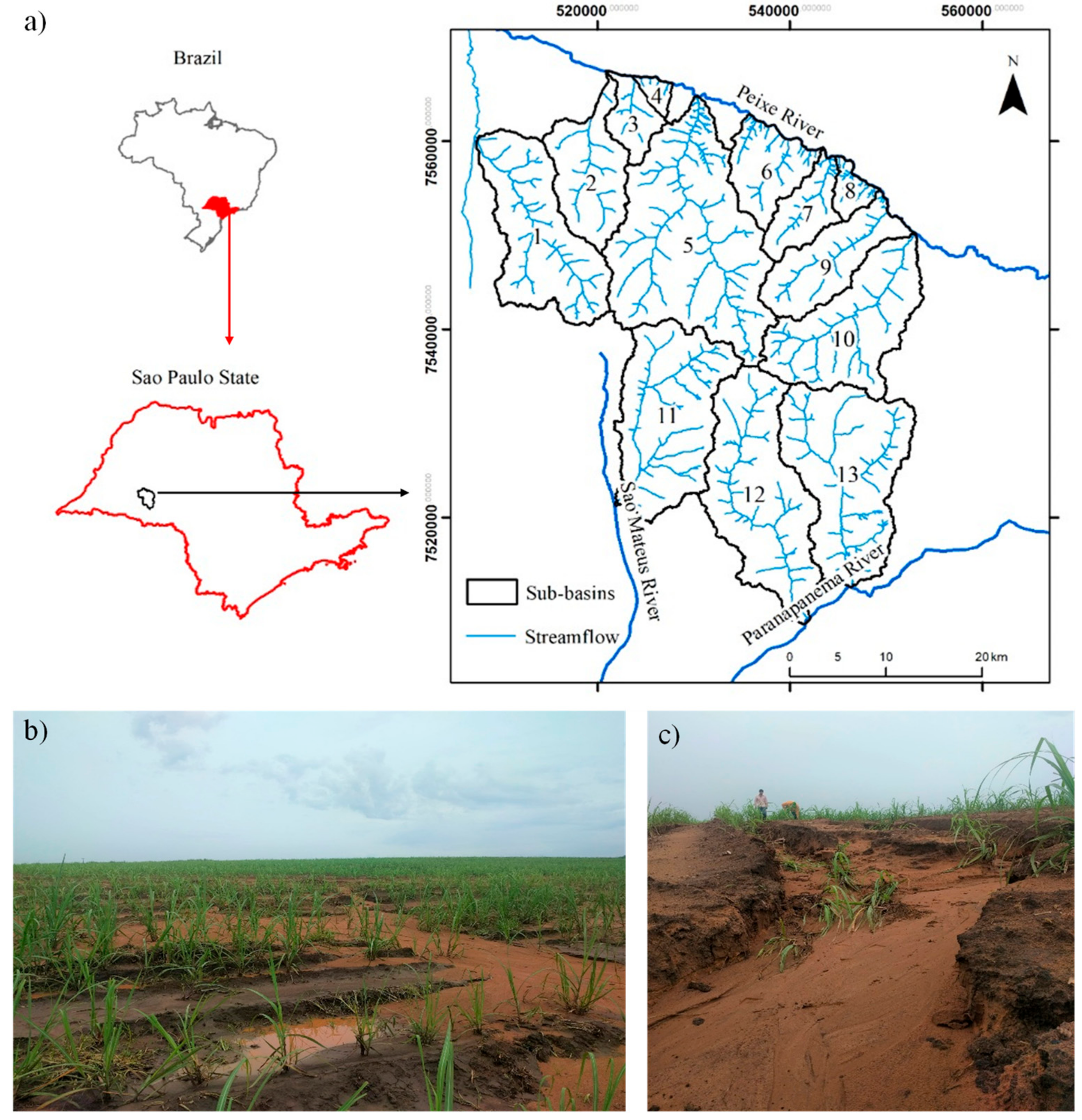
2.1. Site Description and Sugarcane Cycle
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Parametrization of Soil Loss by Water Erosion

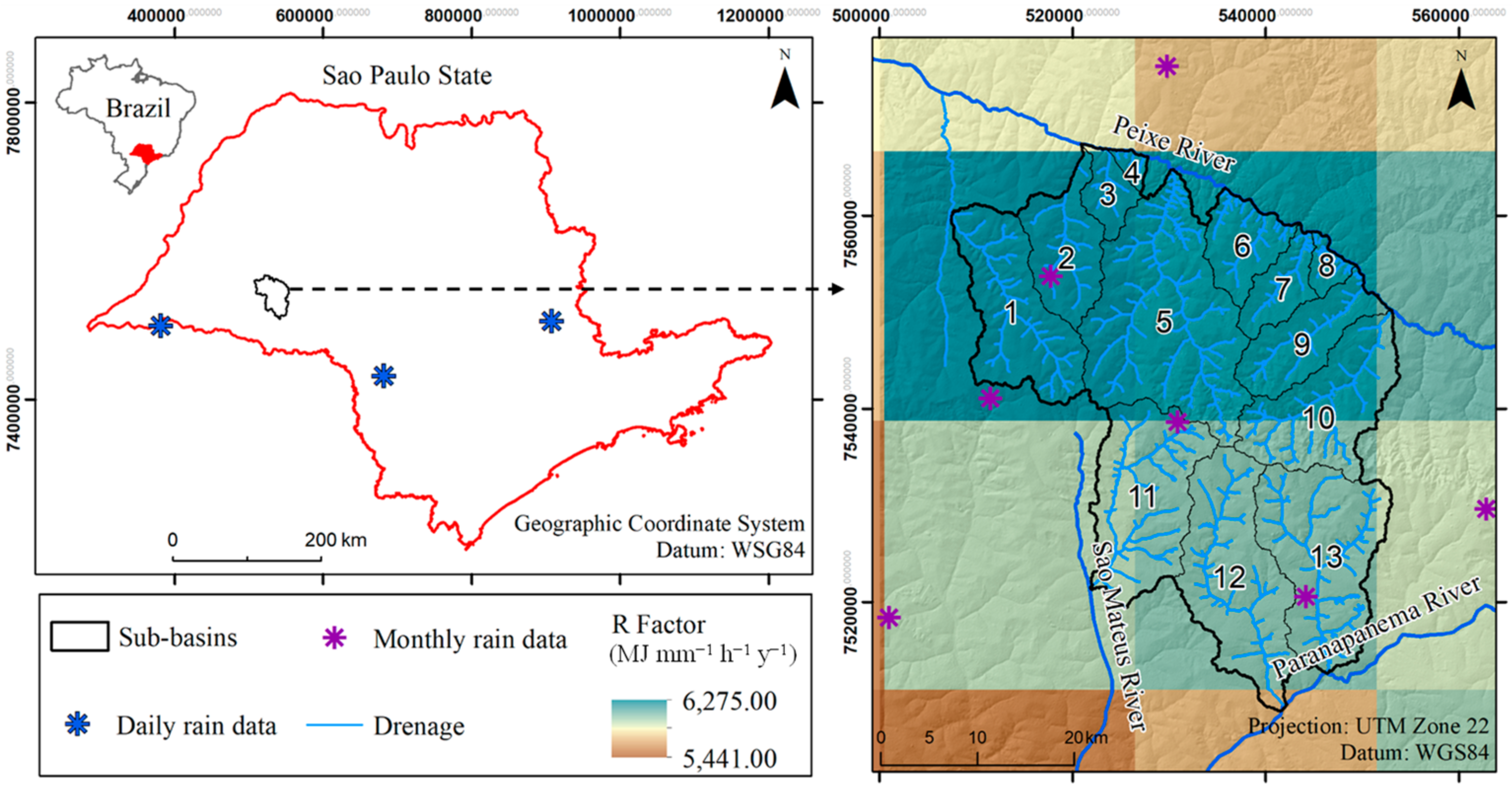
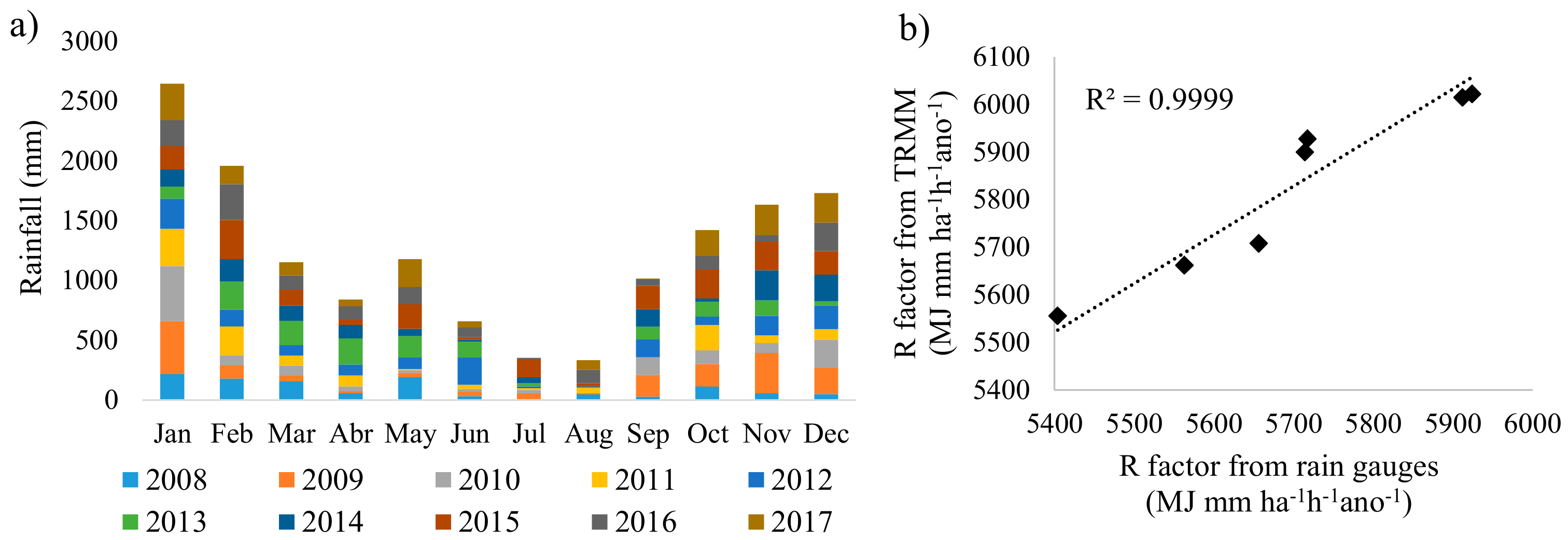
2.3.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
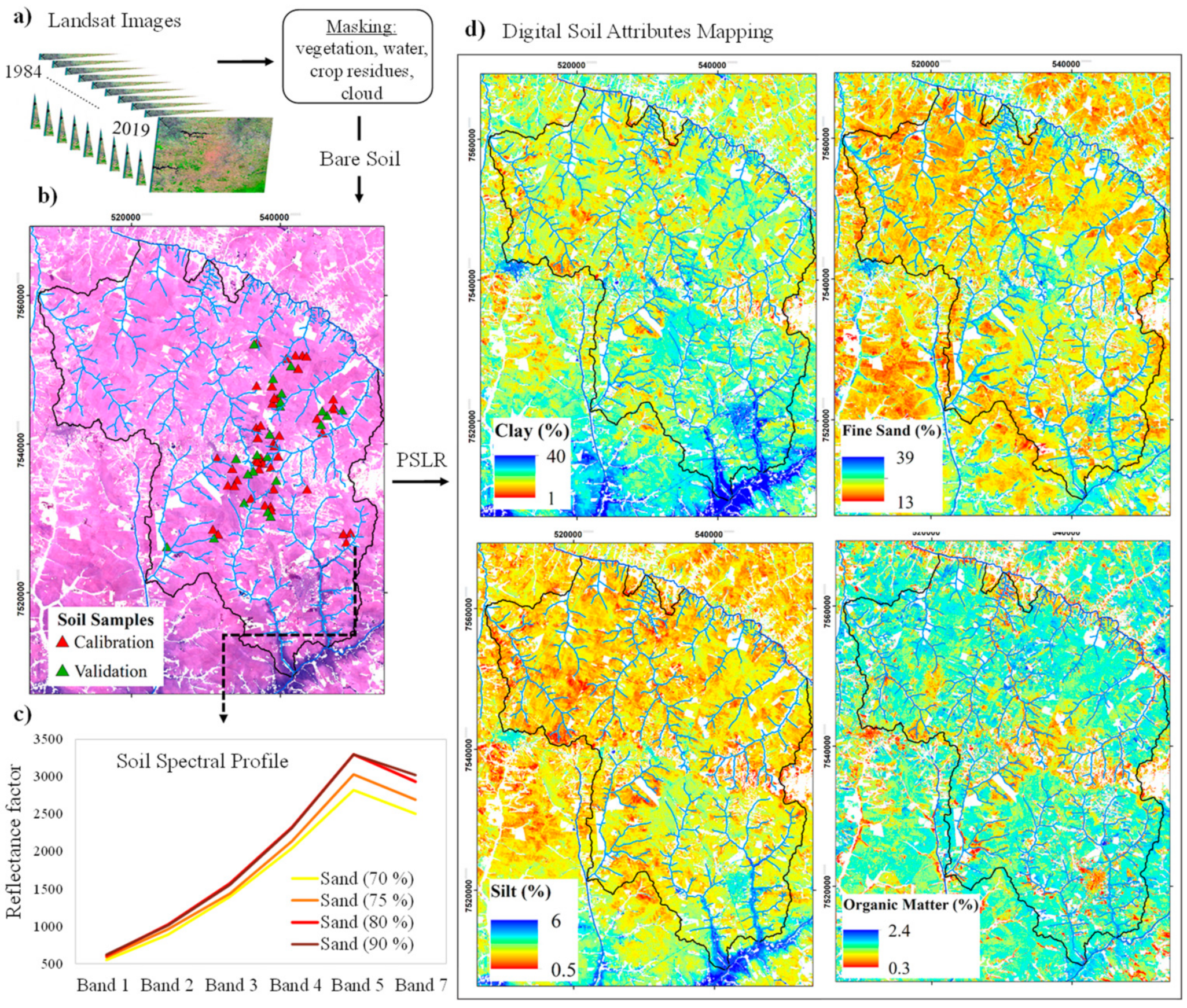
2.3.2. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
2.3.3. Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS)
2.3.4. Control Practice Factor (P)
2.3.5. Cover Management Factor (C)
2.4. Soil Loss Tolerance
3. Results
3.1. Soil Degradation Spatial Analyses Estimated by RUSLE
3.1.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor
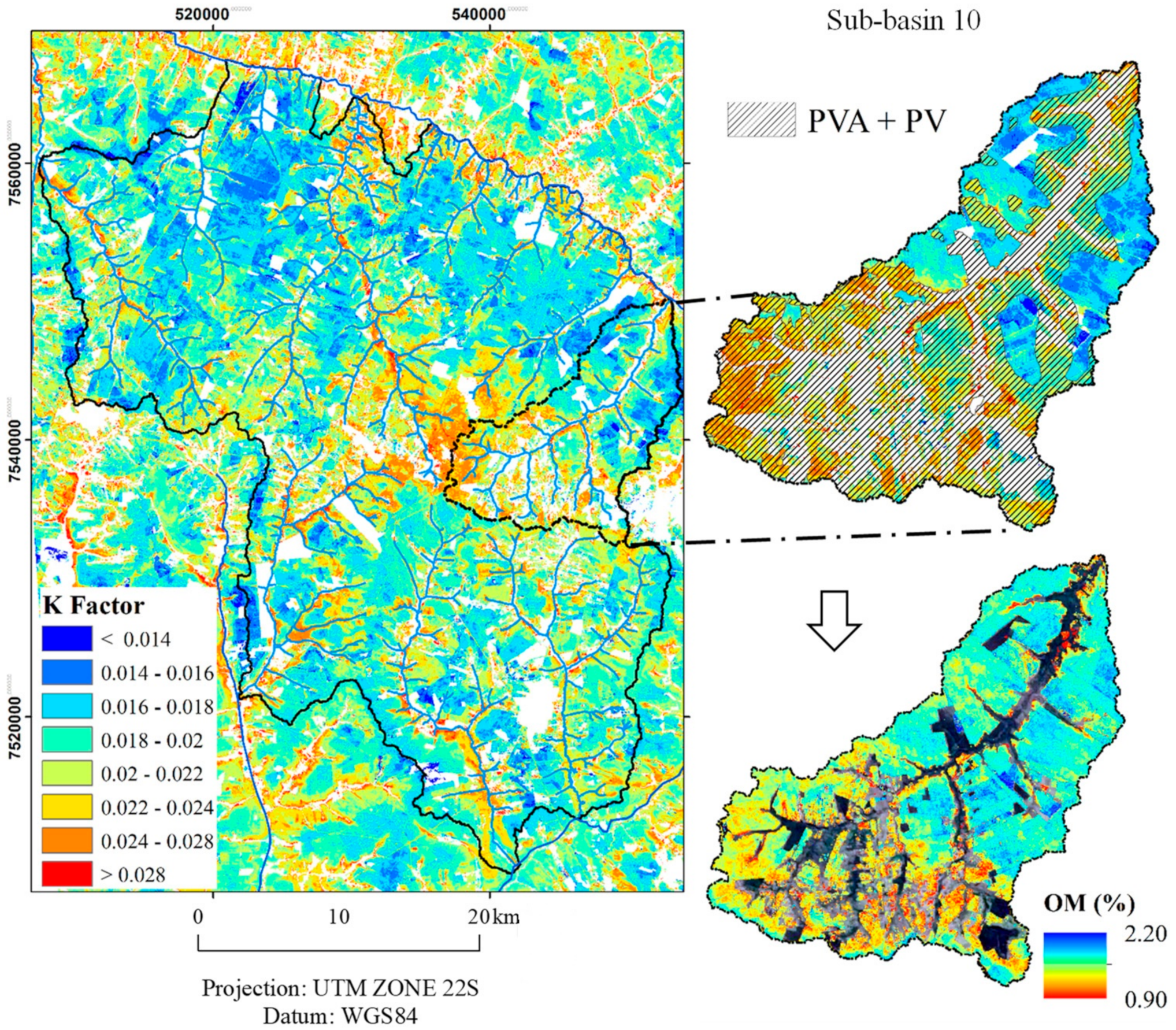
3.1.2. Soil Erodibility Factor Obtained from the Digital Soil Attributes Mapping
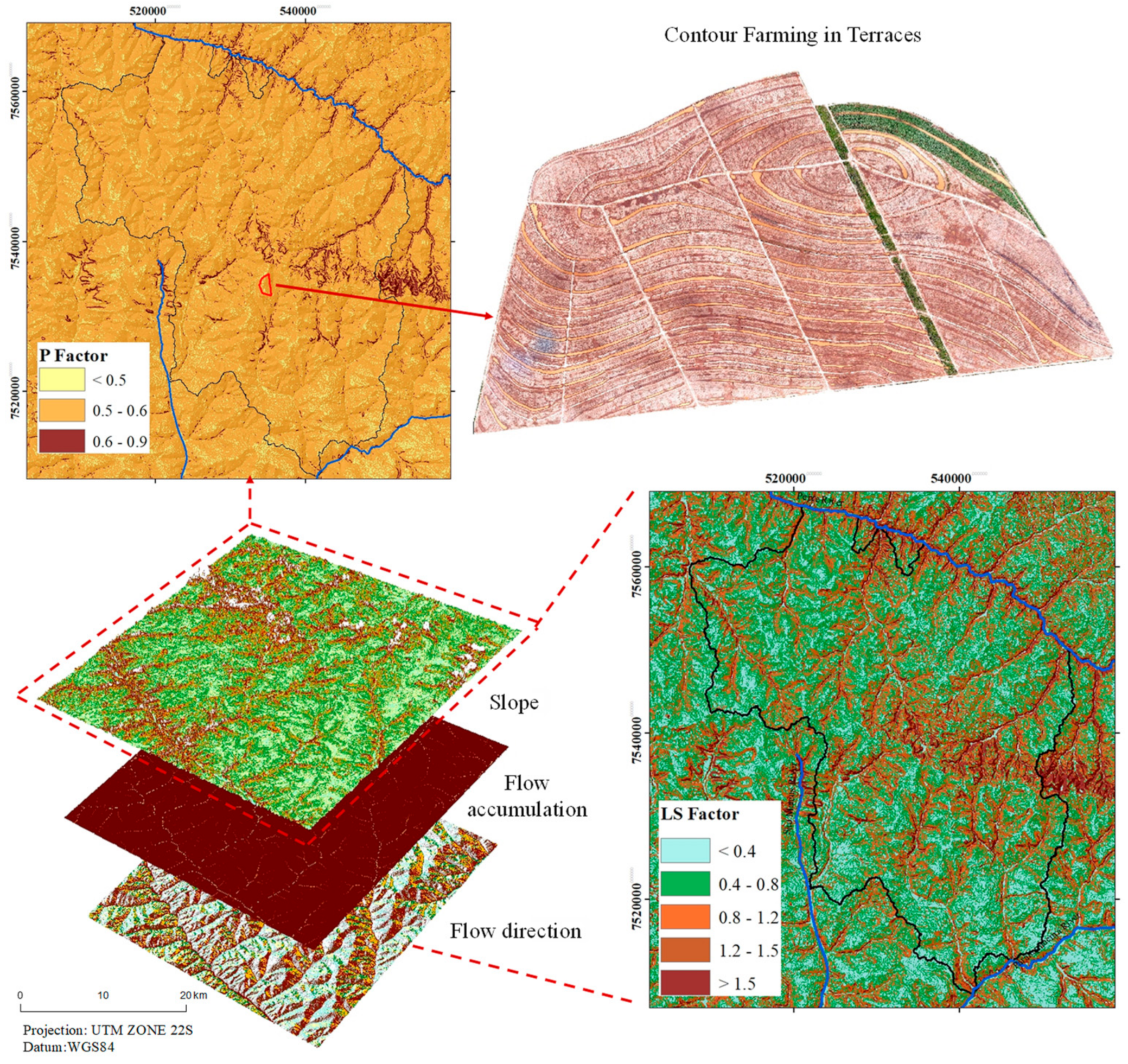
3.1.3. The Topographic Parameters and Control Practice
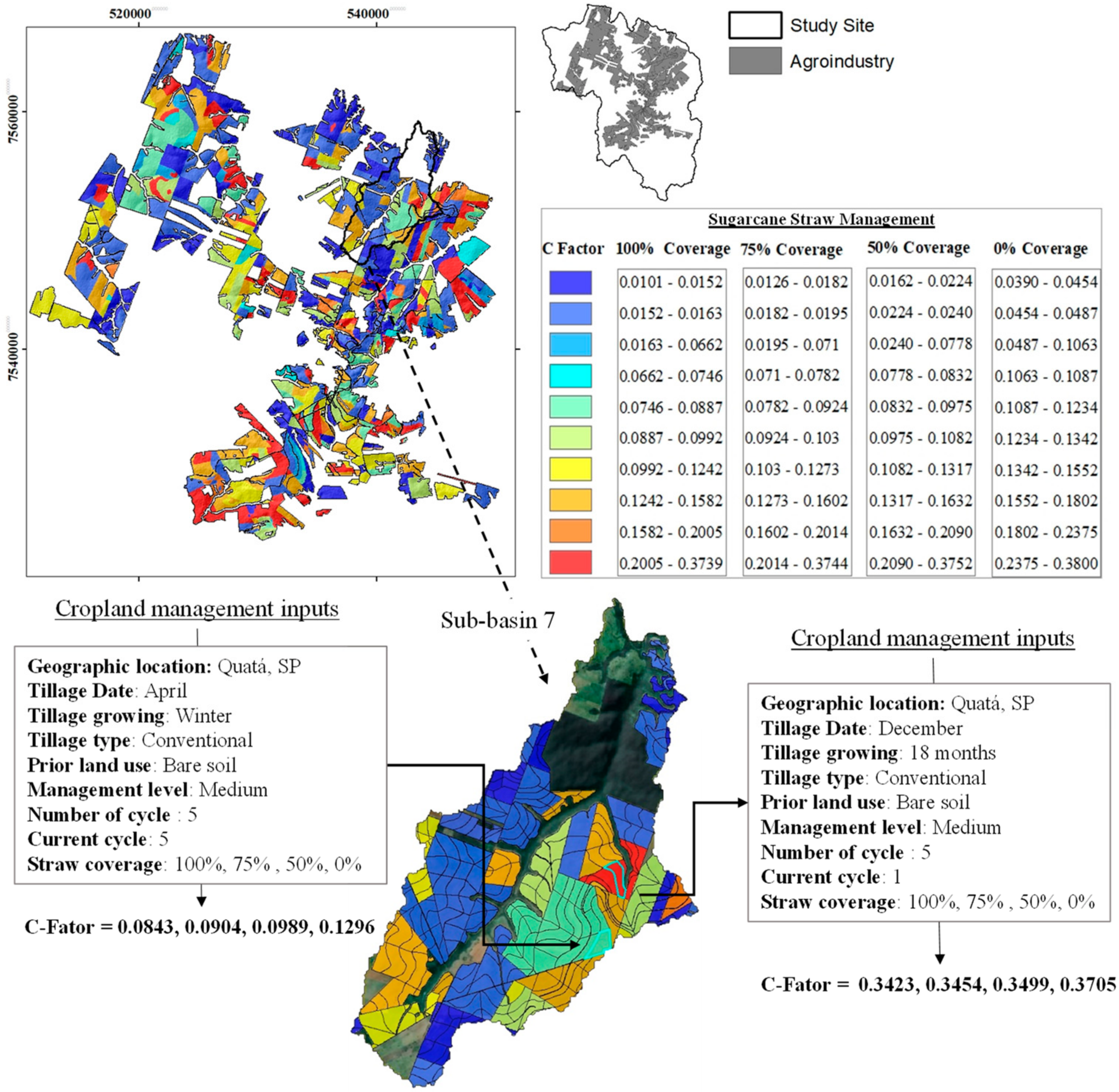
3.1.4. Cover Management Factor
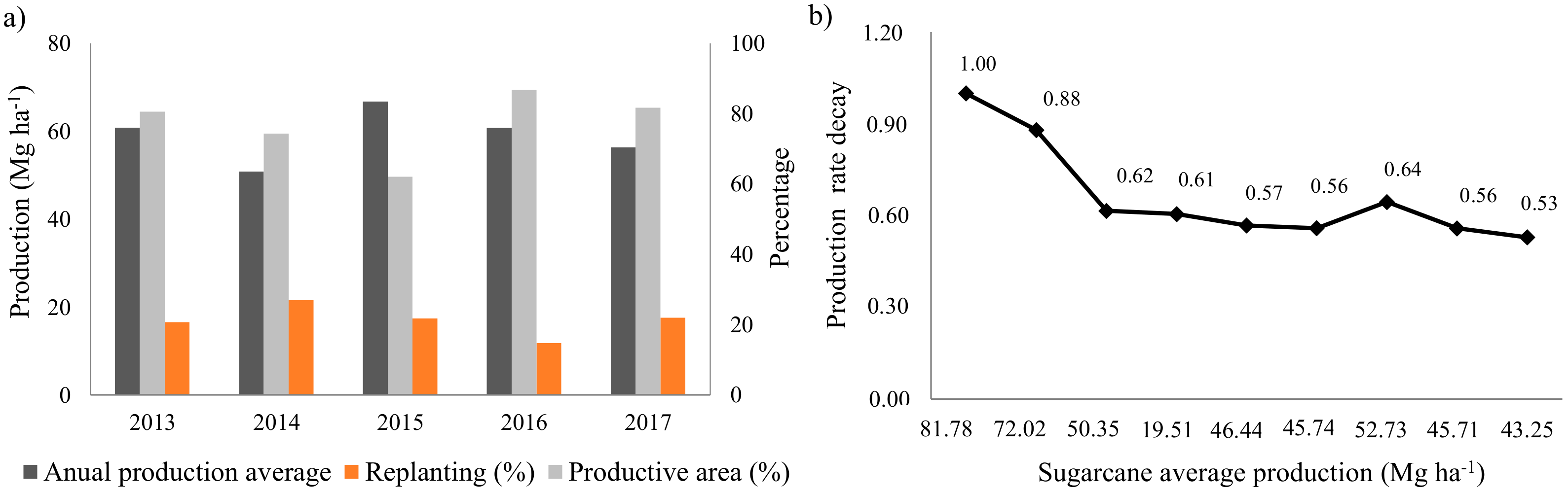
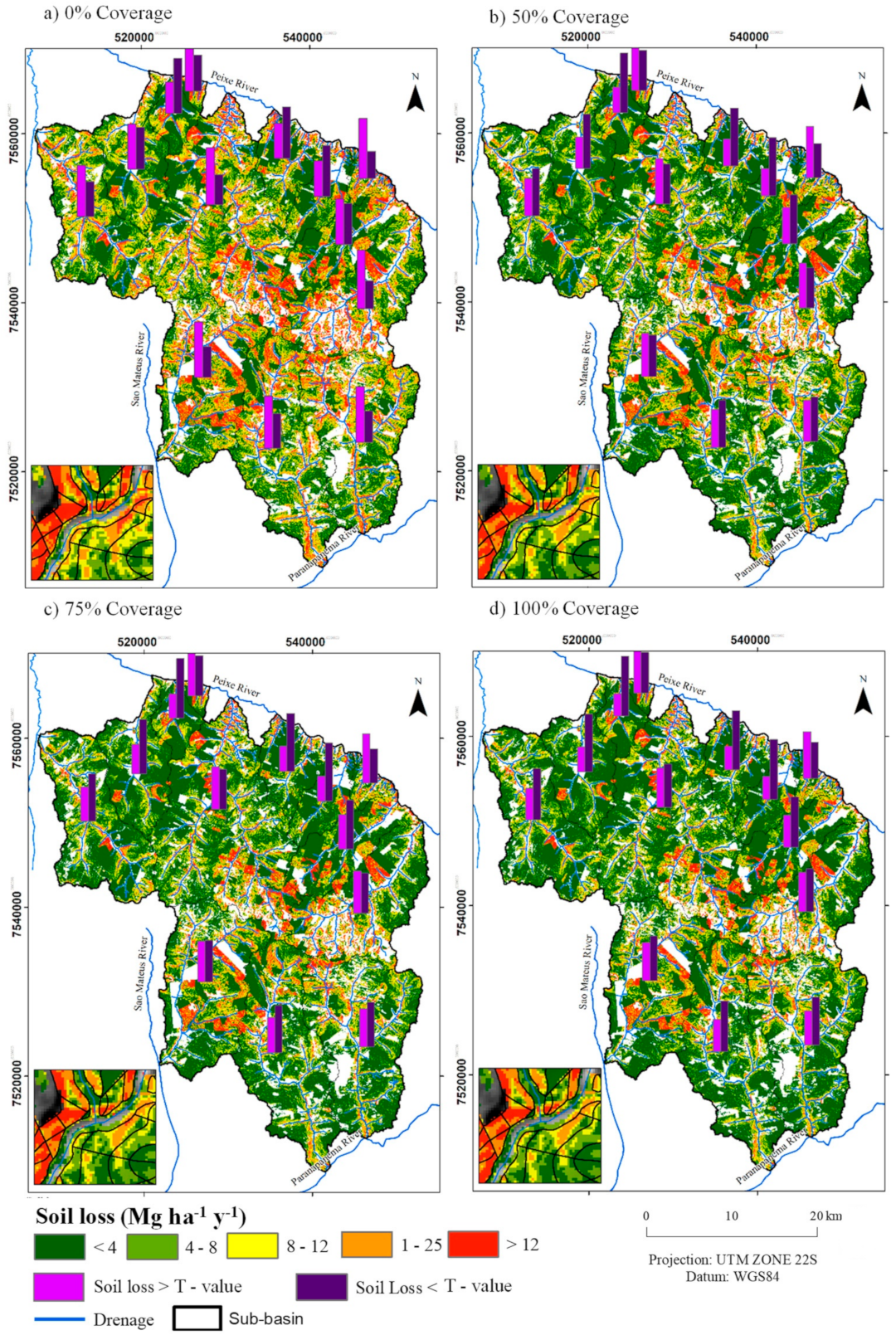
3.2. Soil Loss in Agricultural Regions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olsson, L.; Barbosa, H.; Bhadwal, S.; Cowie, A.; Delusca, K.; Flores-Renteria, D.; Hermans, K.; Jobbagy, E.; Kurz, W.; Li, D. Land degradation: IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land 5 degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and 6 greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems. In IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land 5 Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and 6 Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D. FAO calls for actions to reduce global soil erosion. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2020, 25, 789–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R. Dirt: The Erosion of Civilizations; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2012; ISBN 0520272900. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, R. Soil erosion and the global carbon budget. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, K.; Lal, R.; Ehlers, K. Soil organic carbon stock as an indicator for monitoring land and soil degradation in relation to United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 824–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanarella, L.; Scholes, R.; Brainich, A. (Eds.) IPBES The IPBES assessment report on land degradation and restoration. In Secretariat of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, Bonn, Germany; Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Bonn, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–744. ISBN 9783947851096. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Mccool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); U.S. Depar.: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; ISBN 0160489385. [Google Scholar]
- Ostovari, Y.; Ghorbani-Dashtaki, S.; Bahrami, H.A.; Naderi, M.; Dematte, A.M. Soil loss prediction by an integrated system using RUSLE, GIS and remote sensing in semi-arid region. Geoderma Reg. 2017, 11, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Shi, Z.; Behrens, T.; Chappell, A.; Bui, E. Assimilating satellite imagery and visible-near infrared spectroscopy to model and map soil loss by water erosion in Australia. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 77, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.; Galdos, M.V.; Scarpare, F.V.; Verde Leal, M.R.L.; Abel Seabra, J.E.; da Cunha, M.P.; Araujo Picoli, M.C.; de Oliveira, C.O.F. Brazilian sugarcane ethanol: Developments so far and challenges for the future. Adv. Bioenergy Sustain. Chall. 2016, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de OR Medeiros, G.; Giarolla, A.; Sampaio, G.; Marinho, M.D.A. Estimates of annual soil loss rates in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Rev. Bras. De Ciência Do Solo 2016, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.L.N.; Nogueirol, R.C.; Menandro, L.M.S.; Bordonal, R.D.O.; Clovis, D.B.; Cantarella, H.; Franco, H.C.J. Agronomic and environmental implications of sugarcane straw removal : A major review. Bioenergy Res. 2016, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubin, M.R.; Lisboa, I.P.; Silva, A.G.B.; Varanda, L.L.; Bordonal, R.O.; Carvalho, J.L.N.; Otto, R.; Pavinato, P.S.; Soltangheisi, A.; Cerri, C.E.P. Sugarcane Straw Removal: Implications to Soil Fertility and Fertilizer Demand in Brazil. BioEnergy Res. 2019, 12, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenelli, S.; de Oliveira Bordonal, R.; Barbosa, L.C.; Carvalho, J.L.N. Can reduced tillage sustain sugarcane yield and soil carbon if straw is removed? BioEnergy Res. 2019, 12, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castioni, G.A.F.; Cherubin, M.R.; Bordonal, R.D.O.; Barbosa, L.C.; Menandro, L.M.S.; Carvalho, J.L.N. Straw Removal Affects Soil Physical Quality and Sugarcane Yield in Brazil. BioEnergy Res. 2019, 12, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menandro, L.M.S.; de Moraes, L.O.; Borges, C.D.; Cherubin, M.R.; Castioni, G.A.; Carvalho, J.L.N. Soil Macrofauna Responses to Sugarcane Straw Removal for Bioenergy Production. BioEnergy Res. 2019, 12, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Filho, M.V.; Liccioti, T.T.; Pereira, G.T.; Marques Júnior, J.; Sanchez, R.B. Soil and Nutrients Losses of an Alfisol with Sugarcane Crop Residue. Eng. Agric. 2009, 29, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, H.C.J.; Pimenta, M.T.B.; Carvalho, J.L.N.; Magalhães, P.S.G.; Rossell, C.E.V.; Braunbeck, O.A.; Vitti, A.C.; Kolln, O.T.; Rossi Neto, J. Assessment of sugarcane trash for agronomic and energy purposes in Brazil. Sci. Agric. 2013, 70, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.L.N.; Otto, R.; Junqueira Franco, H.C.; Ocheuze Trivelin, P.C. Input of sugarcane post-harvest residues into the soil. Sci. Agric. 2013, 70, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.D.; Zhang, X.; Reddy, A.D.; Robertson, G.P.; Izaurralde, R.C. The greenhouse gas intensity and potential biofuel production capacity of maize stover harvest in the US Midwest. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.G.B.; Lisboa, I.P.; Cherubin, M.R.; Cerri, C.E.P. How Much Sugarcane Straw is Needed for Covering the Soil? BioEnergy Res. 2019, 12, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Bordonal, R.; Menandro, L.M.S.; Barbosa, L.C.; Lal, R.; Milori, D.M.B.P.; Kolln, O.T.; Franco, H.C.J.; Carvalho, J.L.N. Sugarcane yield and soil carbon response to straw removal in south-central Brazil. Geoderma 2018, 328, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, M.M.; Salvador, E.; Lopes, R.; D’Agostinho, L.; Peruffo, N.; Gomes, S.D.; Sachs, L.L.B.; Meira, V.T.; Garcia, M.G.M.; Lacerda Filho, J.V. Mapa Geológico do Estado de São Paulo, Escala 1:750.000; Programa levantamentos geológicos básicos do Brasil, CPRM: São Paulo, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- EMBRAPA. Manual de Metodos de Analises; Editorial Académica Española: Brasília, Brazil, 2017; ISBN 9788570357717. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; IUSS Working Group WRB: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Benavidez, R.; Jackson, B.; Maxwell, D.; Norton, K. A review of the (Revised) Universal Soil Loss Equation ((R) USLE): With a view to increasing its global applicability and improving soil loss estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6059–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Van Oost, K.; Meusburger, K.; Alewell, C.; Lugato, E.; Panagos, P. A step towards a holistic assessment of soil degradation in Europe: Coupling on-site erosion with sediment transfer and carbon fluxes. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service and Soil Conservation Service. Joint Conference on Slope-Practice; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Vrieling, A.; Hoedjes, J.C.B.; van der Velde, M. Towards large-scale monitoring of soil erosion in Africa: Accounting for the dynamics of rainfall erosivity. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 115, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A.; Sterk, G.; de Jong, S.M. Satellite-based estimation of rainfall erosivity for Africa. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, C.R.; Viola, M.R.; Beskow, S.; Norton, L.D. Multivariate models for annual rainfall erosivity in Brazil. Geoderma 2013, 202, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.T.S.; Wendland, E.; Nearing, M.A. Rainfall erosivity in Brazil: A review. Catena 2013, 100, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colodro, G.; Carvalho, M.P.; Roque, C.G.; Prado, R.M. Rainfall erosivity: Its distribution and relationship with the nonrecording rain gauge precipitation at Teodoro Sampaio, São Paulo, Brazil. Rev. Bras. De Ciênc. Do Solo 2002, 26, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi Neto, F.; Moldenhauer, W.C. Erosividade da chuva: Sua distribuicao e relacao com as perdas de solo em Campinas (SP). Bragantia 1992, 51, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque, C.G.; Carvalho, M.P.; Prado, R.M. Fator erosividade da chuva de Piraju (SP): Distribuição, probabilidade de ocorrência, período de retorno e correlação com o coeficiente de chuva. Rev. Bras. De Ciênc. Do Solo 2001, 25, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, B.C.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Rizzo, R.; Safanelli, J.L.; Mendes, W.D.S.; Lepsch, I.F.; Sato, M.V.; Romero, D.J.; Lacerda, M.P.C. Multi-temporal satellite images on topsoil attribute quantification and the relationship with soil classes and geology. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demattê, J.A.M.; Safanelli, J.L.; Poppiel, R.R.; Rizzo, R.; Silvero, N.E.Q.; de Sousa Mendes, W.; Bonfatti, B.R.; Dotto, A.C.; Salazar, D.F.U.; de Oliveira Mello, F.A. Bare earth’s Surface Spectra as a proxy for Soil Resource Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demattê, J.A.M.; Fongaro, C.T.; Rizzo, R.; Safanelli, J.L. Geospatial Soil Sensing System (GEOS3): A powerful data mining procedure to retrieve soil spectral reflectance from satellite images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 212, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safanelli, J.L.; Chabrillat, S.; Ben-dor, E.; Demattê, J.A.M. Multispectral Models from Bare Soil Composites for Mapping Topsoil Properties over Europe. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A New European Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS-Factor) for Modeling Soil Erosion by Water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; Meyer, L.D.; Onstad, C.A. A runoff erosivity factor and variable slope length exponents for soil loss estimates. Trans. ASAE 1977, 20, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Mccool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Steepness Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.J.; Quinton, J.N.; Bailey, A.P.; Deasy, C.; Silgram, M.; Jackson, D.R. The effects of minimal tillage, contour cultivation and in-field vegetative barriers on soil erosion and phosphorus loss. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 106, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyaş, H.; Kolat, Ç.; Süzen, M.L. A new approach to estimate cover-management factor of RUSLE and validation of RUSLE model in the watershed of Kartalkaya Dam. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, G.C. da Conservação do Solo e Cana-de-Açúcar: Aspectos Legais e Bibliométricos e Uma Ferramenta de Determinação do Fator C (RUSLE). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Menandro, L.M.S.; Cantarella, H.; Franco, H.C.J.; Kölln, O.T.; Pimenta, M.T.B.; Rabelo, S.C.; Carvalho, J.L.N.; Sanches, G.M. Comprehensive assessment of sugarcane straw: Implications for biomass and bioenergy production. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2017, 11, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Leys, J.; Gray, J.; Zhang, M. Hillslope erosion improvement targets: Towards sustainable land management across New South Wales, Australia. Catena 2022, 211, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, A.; Webb, N.P.; Leys, J.F.; Waters, C.M.; Orgill, S.; Eyres, M.J. Minimising soil organic carbon erosion by wind is critical for land degradation neutrality. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 93, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.M.; Stamey, W.L. Determining the range of tolerable erosion. Soil Sci. 1965, 100, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; McCool, D.K.; Renard, K.G.; Moldenhauer, W.C. Conversion of the universal soil loss equation to SI metric units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1981, 36, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Bertoni, J.; Lombardi Neto, F. Conservação do Solo, 10th ed.; Ícone editora: São Paulo, Brazil, 2017; ISBN 978-85-274-0980-3. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, M. Mapa Pedológico do Estado de São Paulo: Revisado e Ampliado; Instituto Florestal: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2017; Volume 124, ISBN 3239660180. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, H.G.; Jacomine, P.K.T.; Dos Anjos, L.H.C.; De Oliveira, V.A.; Lumbreras, J.F.; Coelho, M.R.; de Almeida, J.A.; de Araujo Filho, J.C.; de Oliveira, J.B.; Cunha, T.J.F. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos.; Embrapa: Brasilia, Brazil, 2018; ISBN 8570358172. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; ISBN 9789251083697. [Google Scholar]
- Mezzalira, S. Folha Geológica de Piracicaba; Folha SF-23-M-300; Instituto Geográfico e Geológico do Estado de São Paulo: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014 Update 2015. International International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, J.E. Monthly precipitation distribution: A comparative index. Prof. Geogr. 1980, 32, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A.; de Jong, S.M.; Sterk, G.; Rodrigues, S.C. Timing of erosion and satellite data: A multi-resolution approach to soil erosion risk mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2008, 10, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, J.F. The impact of climate change on smallholder and subsistence agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19680–19685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro, A.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Nearing, M.A.; Hagemann, S. Projected climate change impacts in rainfall erosivity over Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldemberg, J.; Mello, F.F.C.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Davies, C.A.; Cerri, C.C. Meeting the global demand for biofuels in 2021 through sustainable land use change policy. Energy Policy 2014, 69, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diek, S.; Fornallaz, F.; Schaepman, M.E.; de Jong, R. Barest Pixel Composite for agricultural areas using landsat time series. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, H.M.; Kılıç, O.M. Modelling and mapping some soil surface properties of Central Kelkit Basin in Turkey by using Landsat-7 ETM+ images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5623–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, W.D.S.; Medeiros Neto, L.G.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Gallo, B.C.; Rizzo, R.; Safanelli, J.L.; Fongaro, C.T. Is it possible to map subsurface soil attributes by satellite spectral transfer models? Geoderma 2019, 343, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabou, M.; Mougenot, B.; Chabaane, Z.; Walter, C.; Boulet, G.; Aissa, N.; Zribi, M. Soil clay content mapping using a time series of Landsat TM data in semi-arid lands. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6059–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannigel, A.R.; Carvalho, M.D.P.E.; Moreti, D.; Medeiros, L.D.R. Fator erodibilidade e tolerância de perda dos solos do Estado de São Paulo. Acta Sci. -Agron. 2002, 24, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.L.N.; Menandro, L.M.S.; de Castro, S.G.Q.; Cherubin, M.R.; Bordonal, R.D.O.; Barbosa, L.C.; Gonzaga, L.C.; Tenelli, S.; Franco, H.C.J.; Kolln, O.T.; et al. Multilocation Straw Removal Effects on Sugarcane Yield in South-Central Brazil. Bioenergy Res. 2019, 12, 813–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; van der Zanden, E.H.; Poesen, J.; Alewell, C. Modelling the effect of support practices (P-factor) on the reduction of soil erosion by water at European scale. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 51, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.L.N.; Hudiburg, T.W.; Franco, H.C.J.; DeLucia, E.H. Contribution of above- and belowground bioenergy crop residues to soil carbon. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Corrêa, S.T.; Barbosa, L.C.; Menandro, L.M.S.; Scarpare, F.V.; Reichardt, K.; de Moraes, L.O.; Hernandes, T.A.D.; Franco, H.C.J.; Carvalho, J.L.N. Straw Removal Effects on Soil Water Dynamics, Soil Temperature, and Sugarcane Yield in South-Central Brazil. BioEnergy Res. 2019, 12, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conab, Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento. Follow-up of the Brazilian harvest: Sugarcane. Acomp. safra bras. cana, v. 7—Safra 2019/20, n. 3—Terceiro levantamento, Brasília. Cia. Natl. Abast. 2020, 7, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, G.D.O.R.; Giarolla, A.; Sampaio, G.; Marinho, M.D.A. Diagnosis of the Accelerated Soil Erosion in São Paulo State (Brazil) by the Soil Lifetime Index Methodology. Rev. Bras. De Ciênc. Do Solo 2016, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, I.J.; Muth, D.J.; Koch, J.B.; Karlen, D.L. Modeled Impacts of Cover Crops and Vegetative Barriers on Corn Stover Availability and Soil Quality. Bioenergy Res. 2014, 7, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenelli, S.; Otto, R.; de Castro, S.A.Q.; Sánchez, C.E.B.; Sattolo, T.M.S.; Kamogawa, M.Y.; Pagliari, P.H.; Carvalho, J.L.N. Legume nitrogen credits for sugarcane production: Implications for soil N availability and ratoon yield. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 113, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, W. Valoração econômica dos impactos ambientais de tecnologias de plantio em região de Cerrados. Rev. Econ. E Sociol. Rural 2005, 43, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertol, I.; Cogo, N.P.; Schick, J.; Gudagnin, J.C.; Amaral, A.J. Aspectos financeiros relacionados às perdas de nutrientes por erosão hídrica em diferentes sistemas de manejo do solo. Rev. Bras. De Ciênc. Do Solo 2007, 31, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telles, T.S.; Dechen, S.C.F.; Souza, L.G.A.; Guimarães, M.F. Valuation of soil erosion costs Scientia Agricola. Sci. Agric. 2013, 70, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telles, T.S.; Guimarães, M.D.F.; Dechen, S.C.F. The Costs of soil erosion. Rev. Bras. De Ciênc. Do Solo 2011, 35, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Factor | Environmental Dataset | Tools/Method | Variability | Spatial Dataset | Resolution/ Map Scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall (R-Factor) | Average Monthly/ Annual Rainfall | Google Engine, Literature/MFI 1/EI30 2 | Spatiotemporal (10 years) | TRMM 3 | 25 km |
| Soil (K-Factor) | Texture, Organic matter, Bulk density | Google Engine/SYSI 4 and R program/DSM 5 | Spatiotemporal (35 years) | Landsat | 30 m |
| Permeability and Structure code | Legacy Soil Maps | Shape | Region Map | 1:250,000 | |
| Local Soil Map | 1:50,000 | ||||
| Topography (LS-Factor) | Slope, Flow direction, Flow accumulation | ArcGIS | Spatial | SRTM 6 | 30 m |
| Management (P-Factor) (C-Factor) | Slope and Contour farming | ArcGIS | Spatial | SRTM 6 | 30 m |
| Land use | Google Engine/SYSI 4 | Spatiotemporal (35 years) | Landsat | 30 m | |
| Canopy cover, Surface cover, Surface roughness, Soil moisture | Excel/Sugarcane management combinations 7 | Shape (5 years) | Cropland plots | 1:50,000 |
| Latitude | Longitude | City/State | Equation | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22°37′0″S | 52°10′0″W | Teod. Sampaio/SP | EI30 = 106.82 + 46.96 (MFI) | [36] |
| 22°31′12″S | 47°2′40″W | Campinas/SP | EI30 = 68.73 (MFI) 0.841 | [37] |
| 23°13′0″S | 49°14′0″W | Piraju/SP | EI30 = 72.55 (MFI) 0.8488 | [38] |
| Slope (%) | P-Factor for Contouring |
|---|---|
| 1–2 | 0.6 |
| 3–8 | 0.5 |
| 9–12 | 0.6 |
| 13–16 | 0.7 |
| 16–20 | 0.8 |
| 21–25 | 0.9 |
| >25 | 0.95 |
| Minimum | Maximum | Mean | SD 1 | CV 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand (%) | 73.00 | 92.10 | 83.27 | 4.11 | 16.87 |
| Coarse Sand (%) | 42.00 | 72.70 | 58.65 | 7.48 | 56.01 |
| Fine Sand (%) | 13.10 | 40.50 | 24.54 | 5.33 | 28.38 |
| Silt (%) | 1.20 | 3.80 | 2.07 | 0.56 | 0.32 |
| Clay (%) | 6.70 | 23.20 | 14.74 | 3.64 | 13.25 |
| SOM 3 (%) | 0.70 | 2.10 | 1.19 | 0.19 | 0.04 |
| SiBCS 1 | WRB 2 | Color | Texture | Permeability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gleissolo Háplico (GX) | Gleysol | Very Slow | ||
| Latossolo Amarelo (LA) | Ferralsol | Yellow | Loam | Moderate |
| Latossolo Vermelho (LV) | Ferralsol | Red | Loam | Moderate to Fast |
| Latossolo Vermelho (LV) | Ferralsol | Red | Clay | Moderate |
| Latossolo Vermelho-Amarelo (LVA) | Ferralsol | Red -Yellow | Loam | Moderate to Fast |
| Latossolo Vermelho-Amarelo (LVA) | Ferralsol | Red -Yellow | Clay | Moderate |
| Nitossolo Vermelho (NV) | Nitosol | Red | Clay | Moderate to Fast |
| Argissolo Amarelo (PA) | Lixisol | Yellow | Sand/Loam | Slow to Moderate |
| Argissolo Amarelo (PA) | Lixisol | Yellow | Loam/Clay | Slow |
| Argissolo Vermelho (PV) | Lixisol | Red | Sand/Loam | Slow to Moderate |
| Argissolo Vermelho (PV) | Lixisol | Red | Loam/Clay | Slow |
| Argissolo Vermelho-Amarelo (PVA) | Lixisol | Red-Yellow | Sand/Loam | Slow to Moderate |
| Argissolo Vermelho-Amarelo (PVA) | Lixisol | Red-Yellow | Loam/Clay | Slow |
| Neossolo Litólico (RL) | Leptsol | Clay | Slow | |
| Neossolo Quartzarênico (RQ) | Arenosol | Sand/Loam | Fast |
| Sub-Basin | Average Soil Erosion (Mg ha−1 yr−1) | Total Soil Loss (Mg × 103 yr−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 50% | 75% | 100% | 0% | 50% | 75% | 100% | |
| 1 | 5.74 | 4.35 | 4.10 | 3.93 | 832.09 | 631.024 | 494.67 | 569.71 |
| 2 | 4.83 | 3.73 | 3.59 | 3.39 | 432.27 | 333.741 | 321.65 | 303.37 |
| 3 | 4.19 | 3.31 | 3.14 | 3.02 | 125.86 | 99.25 | 94.10 | 90.48 |
| 4 | 7.53 | 6.39 | 6.18 | 6.04 | 65.65 | 55.69 | 53.90 | 52.65 |
| 5 | 6.11 | 4.82 | 4.58 | 4.41 | 1645.55 | 1297.30 | 1232.67 | 1188.52 |
| 6 | 4.59 | 3.33 | 3.09 | 2.93 | 269.72 | 195.55 | 181.72 | 172.24 |
| 7 | 4.89 | 3.75 | 3.52 | 3.35 | 206.67 | 158.49 | 148.60 | 141.68 |
| 8 | 7.30 | 5.70 | 5.38 | 5.16 | 103.54 | 80.87 | 76.35 | 73.28 |
| 9 | 6.52 | 5.10 | 4.79 | 4.57 | 535.56 | 419.43 | 393.70 | 375.45 |
| 10 | 7.62 | 5.84 | 5.50 | 5.26 | 942.35 | 722.981 | 680.03 | 650.71 |
| 11 | 6.97 | 5.64 | 5.37 | 5.18 | 1093.39 | 883.75 | 841.35 | 811.81 |
| 12 | 5.86 | 4.59 | 4.35 | 4.18 | 1050.64 | 822.95 | 780.04 | 750.33 |
| 13 | 6.38 | 4.92 | 4.65 | 4.46 | 1102.66 | 850.13 | 803.35 | 771.01 |
| Total area | 6.04 | 4.73 | 4.48 | 4.30 | 8406.01 | 6551.20 | 6202.47 | 5951.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallo, B.C.; Magalhães, P.S.G.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Cervi, W.R.; Carvalho, J.L.N.; Barbosa, L.C.; Bellinaso, H.; Mello, D.C.d.; Veloso, G.V.; Alves, M.R.; et al. Soil Erosion Satellite-Based Estimation in Cropland for Soil Conservation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010020
Gallo BC, Magalhães PSG, Demattê JAM, Cervi WR, Carvalho JLN, Barbosa LC, Bellinaso H, Mello DCd, Veloso GV, Alves MR, et al. Soil Erosion Satellite-Based Estimation in Cropland for Soil Conservation. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallo, Bruna Cristina, Paulo Sérgio Graziano Magalhães, José A. M. Demattê, Walter Rossi Cervi, João Luís Nunes Carvalho, Leandro Carneiro Barbosa, Henrique Bellinaso, Danilo César de Mello, Gustavo Vieira Veloso, Marcelo Rodrigo Alves, and et al. 2023. "Soil Erosion Satellite-Based Estimation in Cropland for Soil Conservation" Remote Sensing 15, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010020
APA StyleGallo, B. C., Magalhães, P. S. G., Demattê, J. A. M., Cervi, W. R., Carvalho, J. L. N., Barbosa, L. C., Bellinaso, H., Mello, D. C. d., Veloso, G. V., Alves, M. R., Fernandes-Filho, E. I., Francelino, M. R., & Schaefer, C. E. G. R. (2023). Soil Erosion Satellite-Based Estimation in Cropland for Soil Conservation. Remote Sensing, 15(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010020







