Correction: Lin et al. Toward Large-Scale Mapping of Tree Crops with High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Deep Learning Algorithms: A Case Study of Olive Orchards in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1740
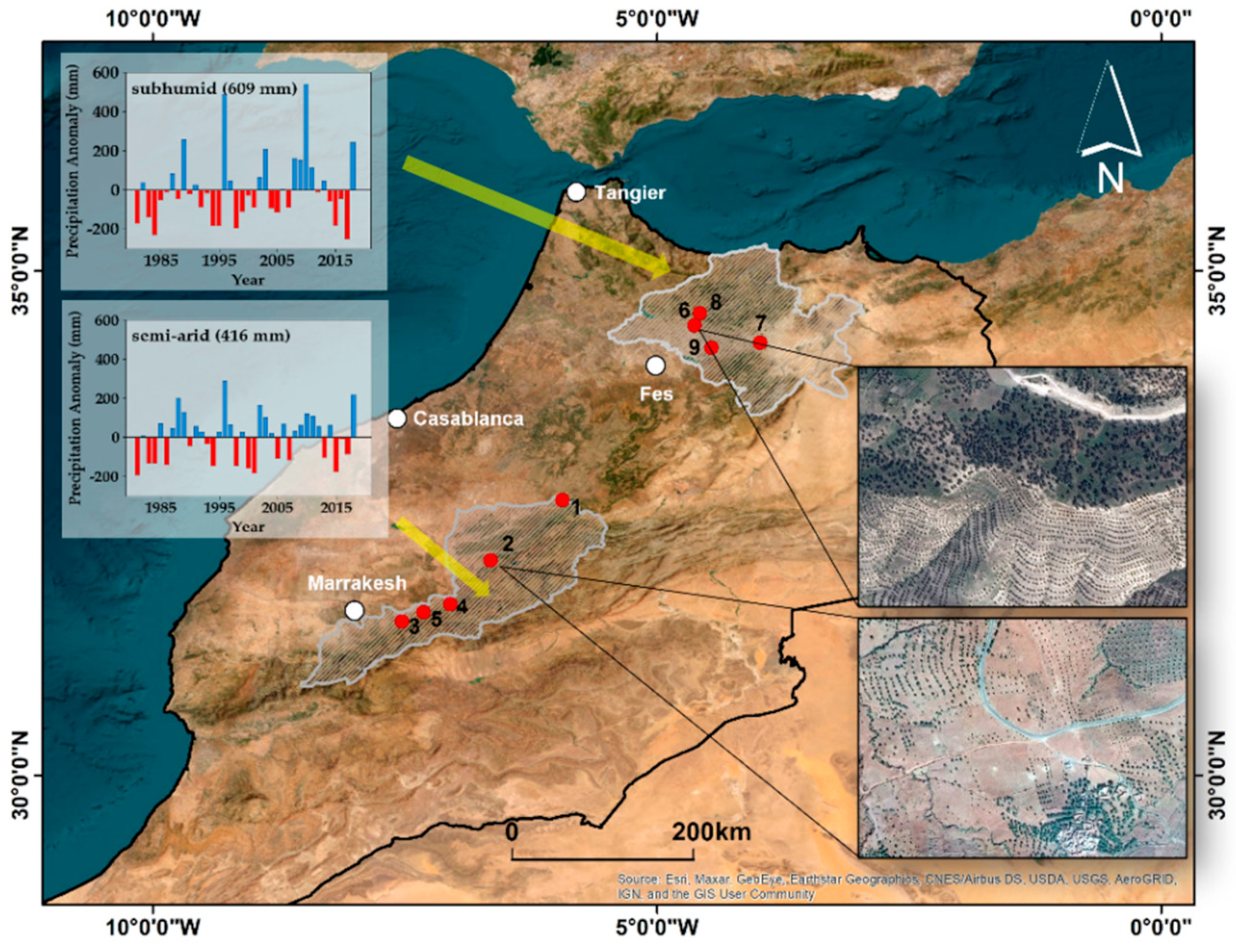
Error in Figure
References
- Lin, C.; Jin, Z.; Mulla, D.; Ghosh, R.; Guan, K.; Kumar, V.; Cai, Y. Toward Large-Scale Mapping of Tree Crops with High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Deep Learning Algorithms: A Case Study of Olive Orchards in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The White House Proclamation on Recognizing the Sovereignty of the Kingdom of Morocco over the Western Sahara. Available online: https://trumpwhitehouse.archives.gov/presidential-actions/proclamation-recognizing-sovereignty-kingdom-morocco-western-sahara/ (accessed on 13 September 2022).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.; Jin, Z.; Mulla, D.; Ghosh, R.; Guan, K.; Kumar, V.; Cai, Y. Correction: Lin et al. Toward Large-Scale Mapping of Tree Crops with High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Deep Learning Algorithms: A Case Study of Olive Orchards in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1740. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010141
Lin C, Jin Z, Mulla D, Ghosh R, Guan K, Kumar V, Cai Y. Correction: Lin et al. Toward Large-Scale Mapping of Tree Crops with High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Deep Learning Algorithms: A Case Study of Olive Orchards in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1740. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(1):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010141
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chenxi, Zhenong Jin, David Mulla, Rahul Ghosh, Kaiyu Guan, Vipin Kumar, and Yaping Cai. 2023. "Correction: Lin et al. Toward Large-Scale Mapping of Tree Crops with High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Deep Learning Algorithms: A Case Study of Olive Orchards in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1740" Remote Sensing 15, no. 1: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010141
APA StyleLin, C., Jin, Z., Mulla, D., Ghosh, R., Guan, K., Kumar, V., & Cai, Y. (2023). Correction: Lin et al. Toward Large-Scale Mapping of Tree Crops with High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Deep Learning Algorithms: A Case Study of Olive Orchards in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1740. Remote Sensing, 15(1), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010141






