INDMF Based Regularity Calculation Method and Its Application in the Recognition of Typical Loess Landforms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
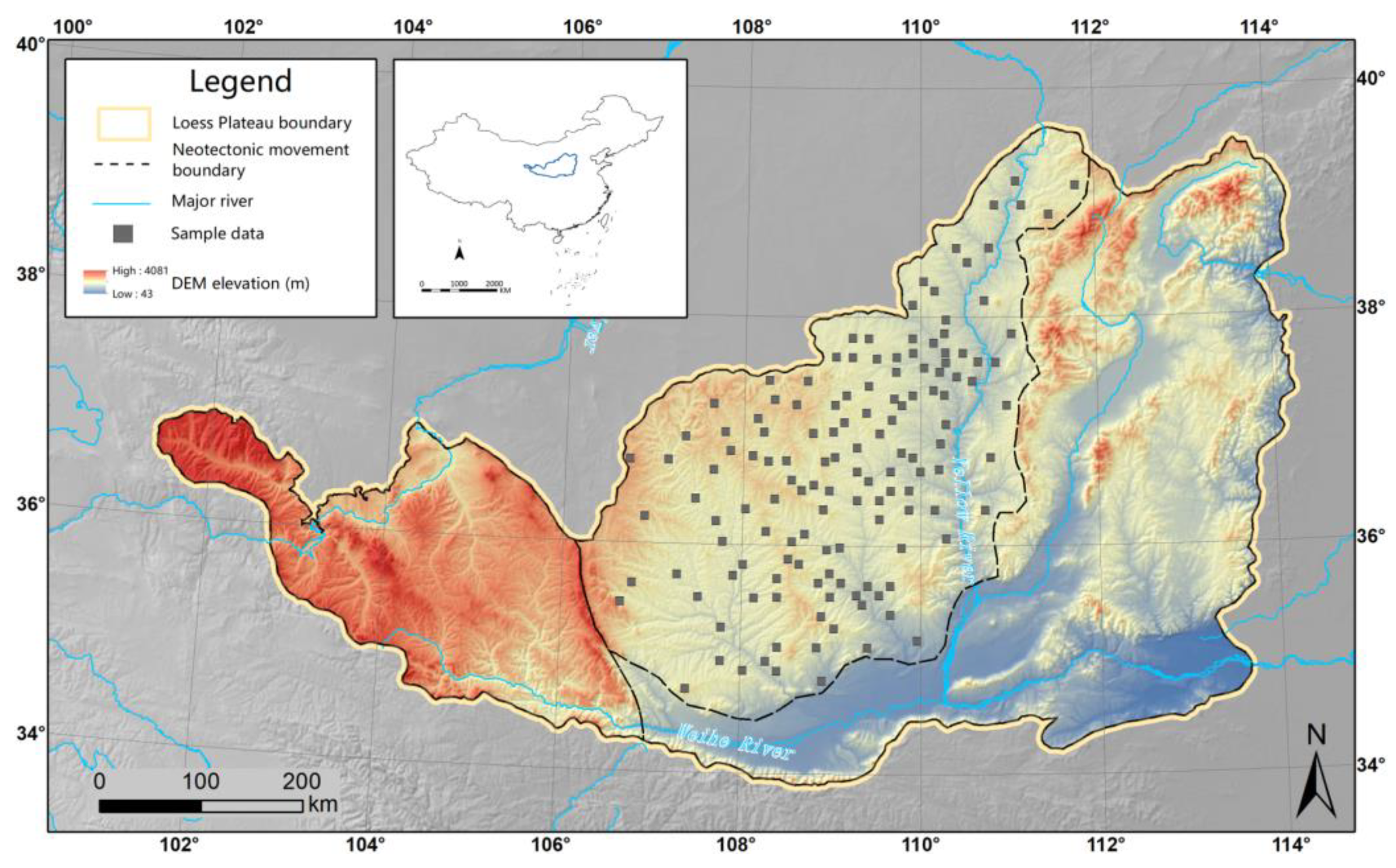
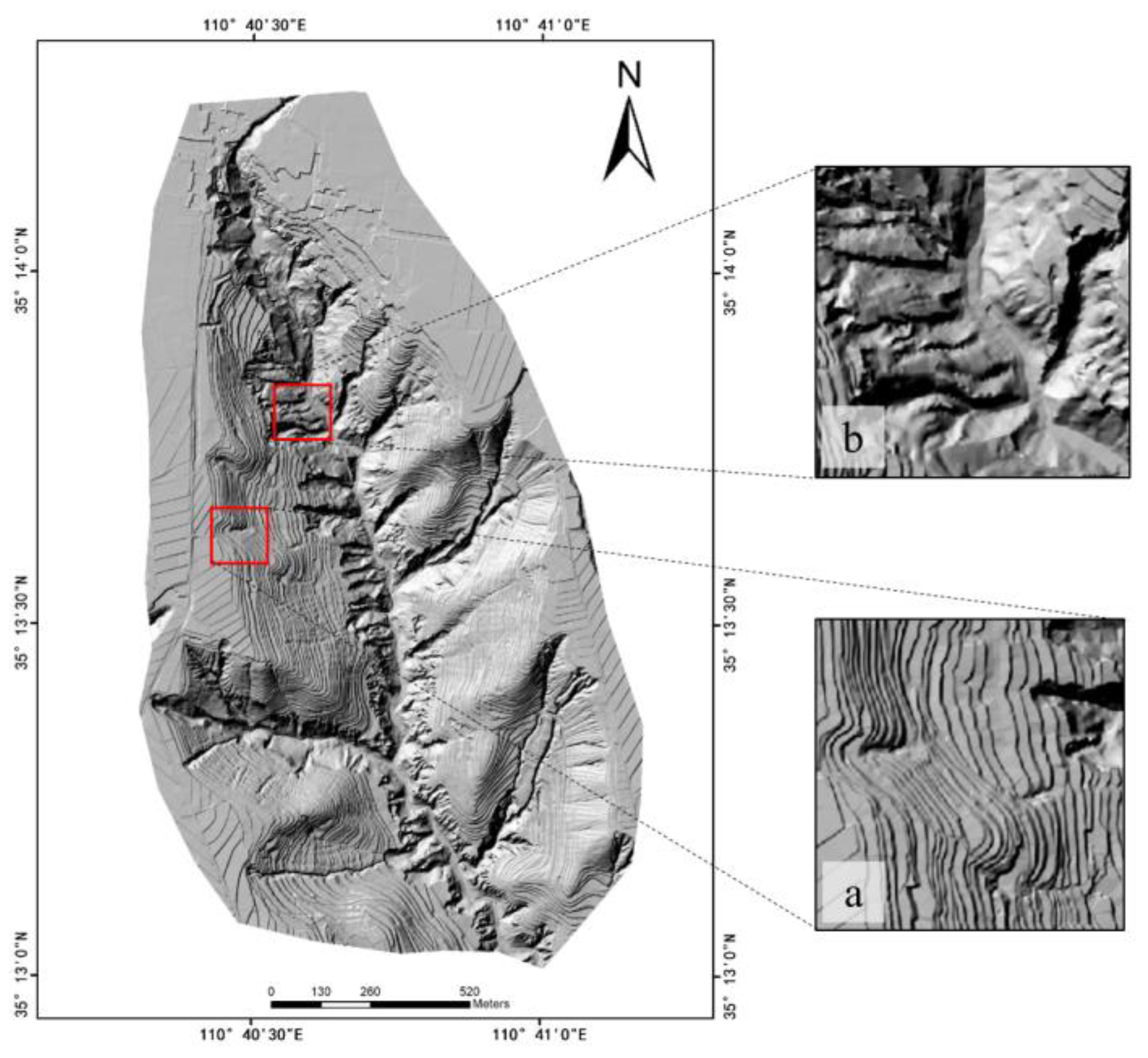
2.1. Study Area and Sample Data
2.2. Methods
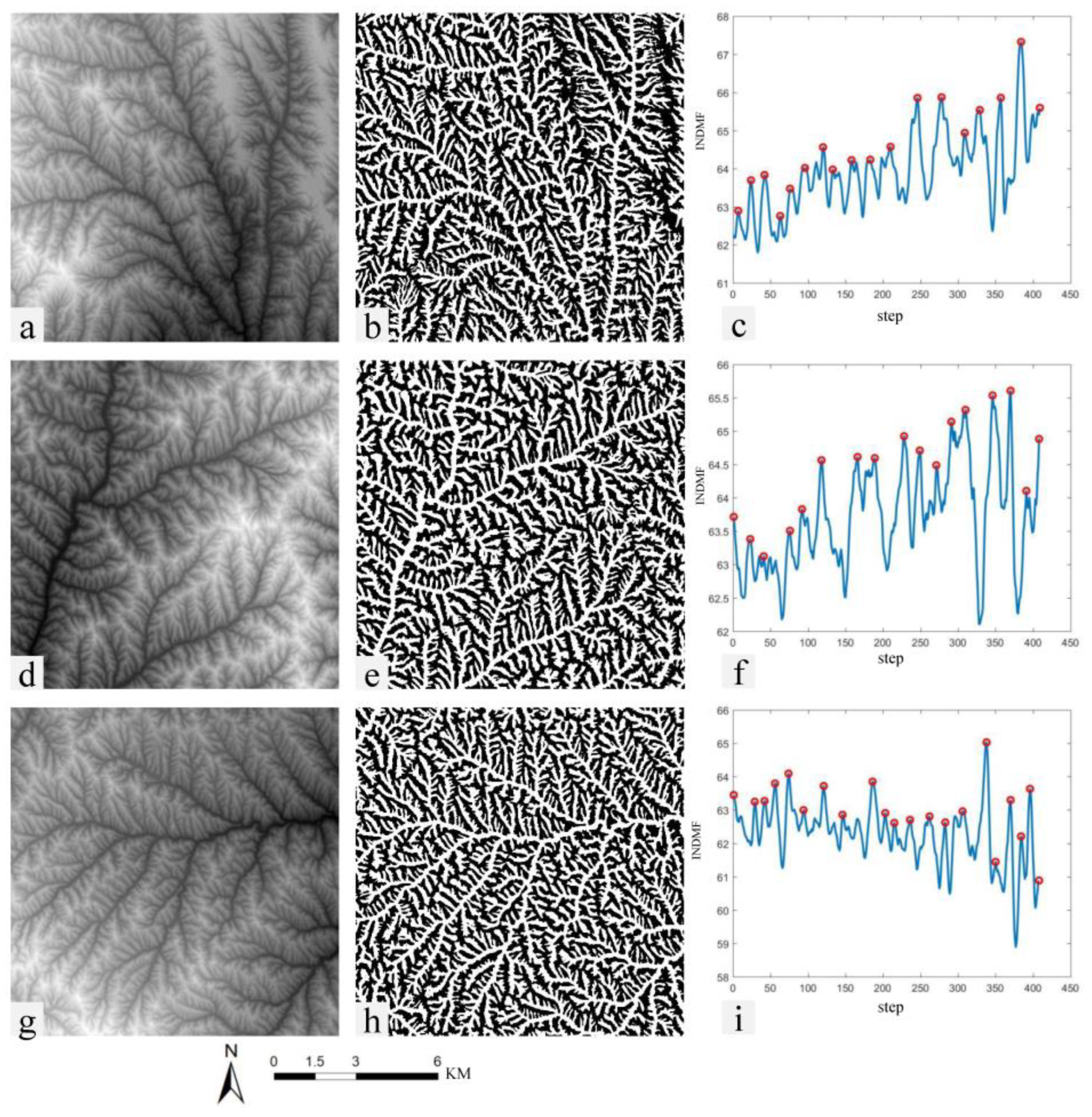
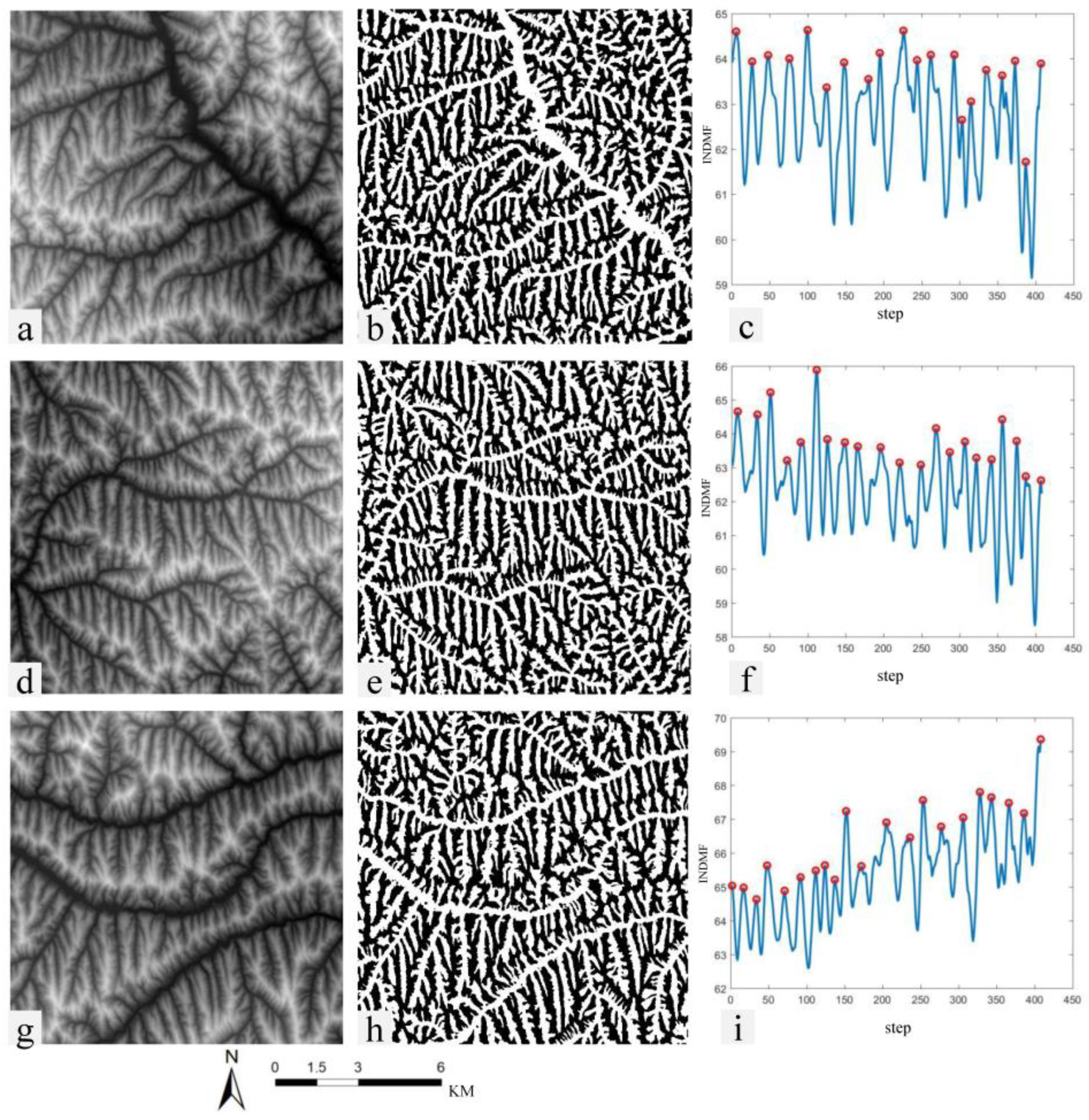
2.2.1. INDMF Regularity Calculation
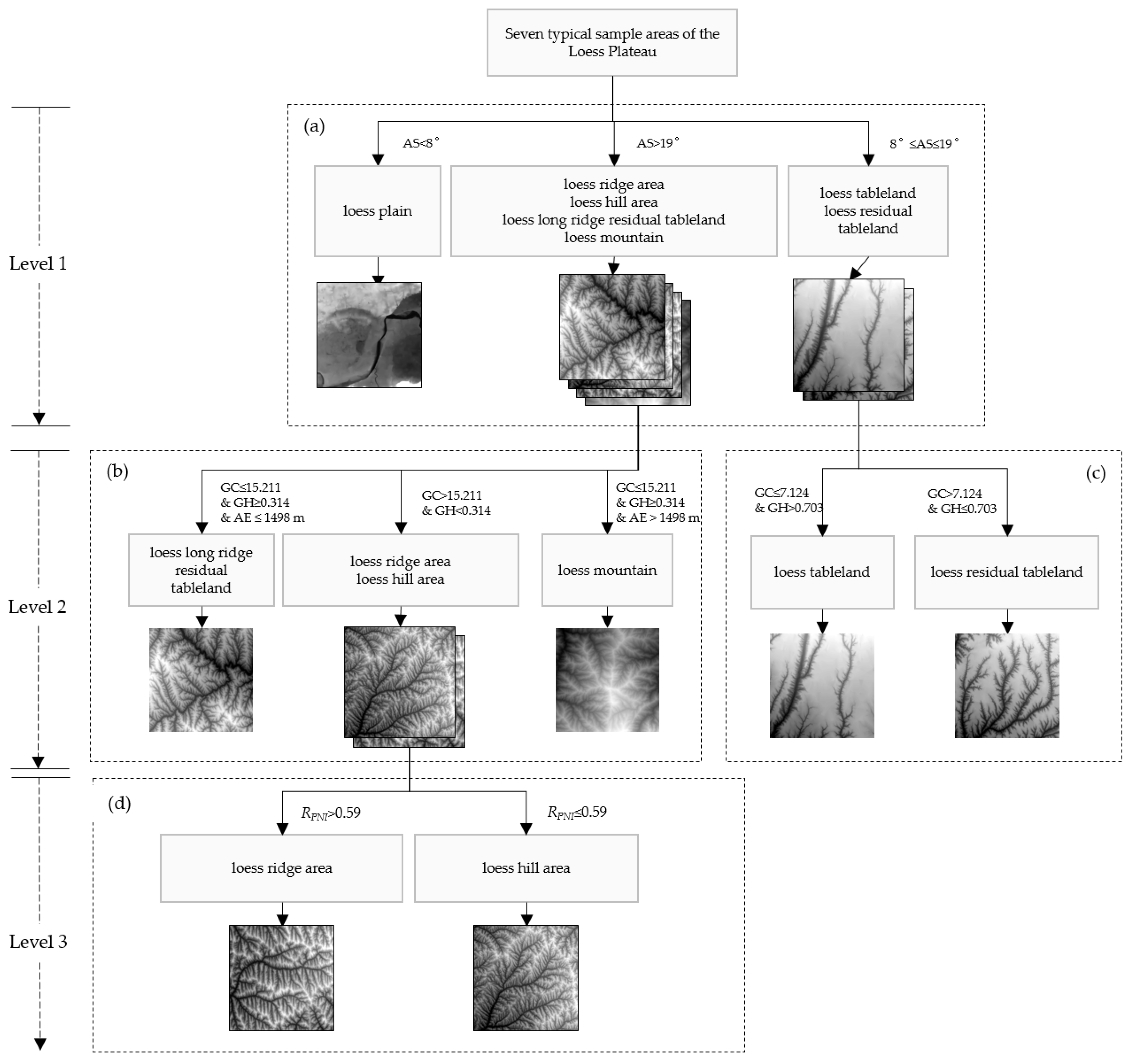
2.2.2. Typical Loess Landform Recognition Combined with INDMF Regularity
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Effectiveness of INDMF Regularity
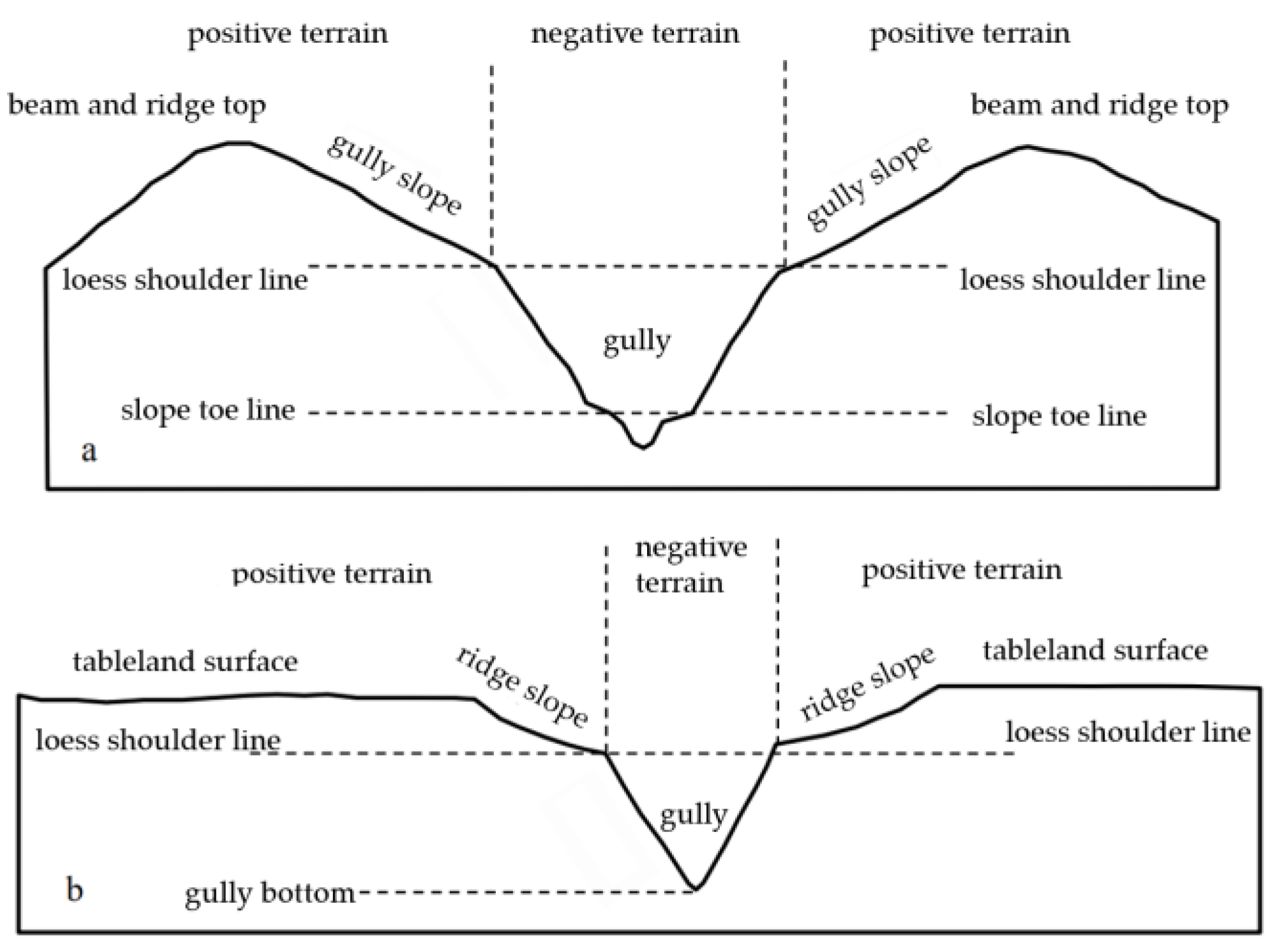
4.2. Role of Positive and Negative Terrain in Recognition
4.3. Scope of Application of the Regularity Proposed in This Paper
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, S.; Ding, Z. Comparison of particle size characteristics of the Tertiary ‘red clay’and Pleistocene loess in the Chinese Loess Plateau: Implications for origin and sources of the ‘red clay’. Sedimentology 2004, 51, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maher, B.A. Palaeoclimatic records of the loess/palaeosol sequences of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 154, 23–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, K.; Stevens, T.; Bird, A.; Limonta, M.; Rittner, M.; Vermeesch, P.; Andò, S.; Garzanti, E.; Lu, H.; Zhang, H. Insights into the provenance of the Chinese Loess Plateau from joint zircon U-Pb and garnet geochemical analysis of last glacial loess. Quat. Res. 2018, 89, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, X.; Zhen, L. Soil erosion control practices in the Chinese Loess Plateau: A systematic review. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Zhao, F.; Xiong, L.; Tang, G. Quantification of Loess Landforms from Three-Dimensional Landscape Pattern Perspective by Using DEMs. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Bai, L.; Luo, M. Similarity Analysis: Revealing the Regional Difference in Geomorphic Development in Areas with High and Coarse Sediment Yield of the Loess Plateau in China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xue, D.; Dai, L.; Wang, P.; Huang, X.; Xia, S. Land cover change and eco-environmental quality response of different geomorphic units on the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Arid Land 2020, 12, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Qiu, H.; Wang, N.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Yang, D.; Cao, M. The influence of loess cave development upon landslides and geomorphologic evolution: A case study from the northwest Loess Plateau, China. Geomorphology 2020, 359, 107167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.; Xiong, L.; Tang, G.; Qiu, F.; Strobl, J. Optimized segmentation based on the weighted aggregation method for loess bank gully mapping. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, H.; Na, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, J.; Liu, K.; Fu, Y.; Li, F. Evaluation of Three Different Machine Learning Methods for Object-Based Artificial Terrace Mapping—A Case Study of the Loess Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Fan, W.; Yu, N.; Nan, Y. A New Method to Predict Gully Head Erosion in the Loess Plateau of China Based on SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Does anthropogenic land use change play a role in changes of precipitation frequency and intensity over the Loess Plateau of China? Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Na, J.; Yang, X.; Tang, G.; Dang, W.; Strobl, J. Population characteristics of loess gully system in the Loess Plateau of China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiang, S. A new method on terrain texture characteristics extraction based on improved dual-tree complex wavelet transform. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2017, 33, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Na, J.; Ding, H.; Zhao, W.; Liu, K.; Tang, G.; Pfeifer, N. Object-based large-scale terrain classification combined with segmentation optimization and terrain features: A case study in China. Trans. GIS 2021, 25, 2939–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Tang, G.; Li, F.; Yuan, B.; Lu, Z. Modeling the evolution of loess-covered landforms in the Loess Plateau of China using a DEM of underground bedrock surface. Geomorphology 2014, 209, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Wen, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Soil erosion, conservation, and eco-environment changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Yang, W.; Fu, J.; Li, Z. Effects of vegetation and climate on the changes of soil erosion in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Xue, Z.; Bagherzadeh, A.; Liu, M. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of NDVI and its response to climate on the Loess Plateau from 1985 to 2015. Catena 2021, 203, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Na, J.; Cheng, W. Progress of digital terrain analysis on regional geomorphology in China. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1570. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; Tang, G.; Yang, X.; Li, F. Geomorphology-oriented digital terrain analysis: Progress and perspectives. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 456–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y. Texture Analysis Based Research on Terrain Morphology Characteristics. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Tang, G.A.; Huang, X. Research on the difference between textures derived from DEM and remotesensing image for topographic analysis. J. Geoinf. Sci. 2016, 18, 386–395. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Liu, K. The Influence of DEM resolution on the extraction of terrain texture feature. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2015, 17, 822–829. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Yan, S. Scale Stability investigation based on RILBP for terrain structure. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2017, 33, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Na, J.-M.; Huang, X.-L.; Tang, G.-A.; Liu, K. Stability analysis unit and spatial distribution pattern of the terrain texture in the northern Shaanxi Loess Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Kondolf, G.M.; Mu, X.; Han, M.; He, Z.; Rubin, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, P.; Sun, W. Sediment yield reduction associated with land use changes and check dams in a catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2017, 148, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, H.; Yin, Z. Regional loess landslide recognition method research based on DEM and remote sensing image. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2017, 33, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Y. Deep learning of DEM image texture for landform classification in the Shandong area, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Song, C.; Liu, K.; Ke, L. Integration of TanDEM-X and SRTM DEMs and spectral imagery to improve the large-scale detection of opencast mining areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T.; Feizizadeh, B.; Hölbling, D. Object-based image analysis and digital terrain analysis for locating landslides in the Urmia Lake Basin, Iran. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4806–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ding, H.; Tang, G.; Zhu, A.-X.; Yang, X.; Jiang, S.; Cao, J. An object-based approach for two-level gully feature mapping using high-resolution DEM and imagery: A case study on hilly loess plateau region, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M. Statistical and structural approaches to texture. Proc. IEEE 1979, 67, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.E.; Peddle, D.R. Texture analysis of digital image data using spatial cooccurrence. Comput. Geosci. 1987, 13, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Li, F.; Xiong, L. Progress of digital terrain analysis in the Loess Plateau of China. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2017, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G. Progress of DEM and digital terrain analysis in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 1305–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Leu, J.-G. On indexing the periodicity of image textures. Image Vis. Comput. 2001, 19, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-C.; Wang, L.-L.; Yang, S.-N. Regular-texture image retrieval based on texture-primitive extraction. Image Vis. Comput. 1999, 17, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetverikov, D.; Hanbury, A. Finding defects in texture using regularity and local orientation. Pattern Recognit. 2002, 35, 2165–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T.; Miura, S.-I.; Nagao, M. Structural analysis of natural textures by Fourier transformation. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1983, 24, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escofet, J.; Millán, M.S.; Ralló, M. Modeling of woven fabric structures based on Fourier image analysis. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 6170–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalniz, I.Z.; Aksoy, S. Unsupervised detection and localization of structural textures using projection profiles. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 3324–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conners, R.W.; Harlow, C.A. Toward a structural textural analyzer based on statistical methods. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1980, 12, 224–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, G.; Lee, S.; Shin, S.Y. Fast determination of textural periodicity using distance matching function. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1999, 20, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, V.; Nagabhushan, P.; Bhajantri, N.U. Automatic extraction of texture-periodicity using superposition of distance matching functions and their forward differences. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2012, 33, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetverikov, D. Pattern regularity as a visual key. Image Vis. Comput. 2000, 18, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.L.; Yanez, R.E.S.; Ramírez, V.A. Periodicity and texel size estimation of visual texture using entropy cues. Comput. Sist. 2011, 14, 303–319. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Tang, G.; Liu, K. A computation method of texture regularity using summed-up distance matching function. J. Comput. -Aided Des. Comput. Graph. 2015, 27, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Tang, G.; Tao, Y. Automatic Extraction Method for Texture Periodicity Based on Improved Normalized Distance Matching Function. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2014, 27, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.; Tang, G.; Zhou, L.; Hao, Q.; Li, F.; Lu, Z. Control action on the geomorphic differentiation in Loess Plateau and the formation of Yellow River by Cenozoic tectogenesis. Quat. Sci. 2012, 32, 829–838. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Tang, G.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, S. GLCM based quantitative analysis of terrain texture from DEMs. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2012, 14, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Cheng, W.; Qian, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, B. Research on the classification system of digital land geomorphology of 1:10,00,000 in China. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2009, 11, 707–724. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, G.; Yang, X.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, M. Positive and negative terrains on northern Shaanxi Loess Plateau. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, Y. Quantifying spatial scale of positive and negative terrains pattern at watershed-scale: Case in soil and water conservation region on Loess Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 1642–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Tang, G.A.; Zhang, F.; Yang, J. A cellular automata model for simulating the evolution of positive–negative terrains in a small loess watershed. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Tang, G.; Yan, S.; Zhu, S.; Sun, Y. Landform-oriented flow-routing algorithm for the dual-structure loess terrain based on digital elevation models. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xu, Q.; Peng, D.; Fan, X.; Ouyang, C.; Zhao, K.; Li, H.; Zhu, X. Quantitative spatial distribution model of site-specific loess landslides on the Heifangtai terrace, China. Landslides 2021, 18, 1163–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Marafa, L. Tourism Imaginary and Landscape at Heritage Site: A Case in Honghe Hani Rice Terraces, China. Land 2021, 10, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telbisz, T.; Keszler, O. DEM-based morphometry of large-scale sand dune patterns in the Grand Erg Oriental (Northern Sahara Desert, Africa). Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, J.C.; Clark, C.D.; Spagnolo, M.; Hughes, A.L.; Stokes, C.R. Using the size and position of drumlins to understand how they grow, interact and evolve. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maleki, S.; Khormali, F.; Mohammadi, J.; Bogaert, P.; Bodaghabadi, M.B. Effect of the accuracy of topographic data on improving digital soil mapping predictions with limited soil data: An application to the Iranian loess plateau. Catena 2020, 195, 104810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, G.; Cheng, X.; Xiong, L.; Tang, G.; Strobl, J. Integrating topographic knowledge into deep learning for the void-filling of digital elevation models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiong, L.; Tang, G.; Strobl, J. Deep learning-based approach for landform classification from integrated data sources of digital elevation model and imagery. Geomorphology 2020, 354, 107045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
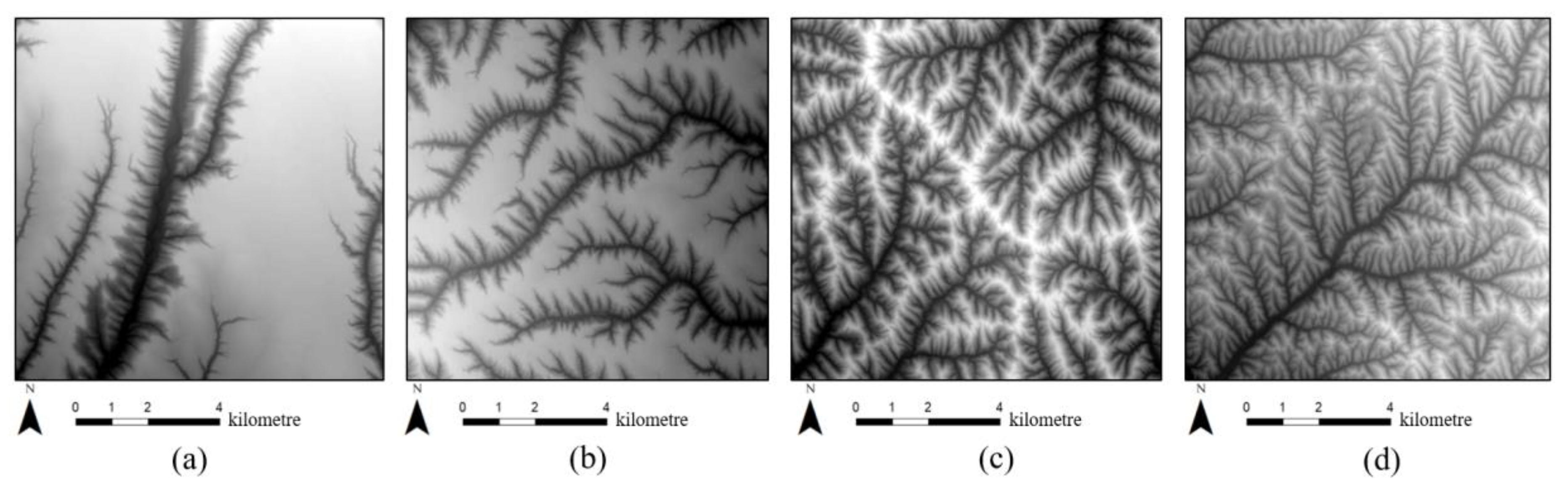


| Landform Type | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Sample 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| loess plain |  |  |  |  |
| loess ridge |  |  |  |  |
| loess hill |  |  |  |  |
| loess long ridge residual tableland |  |  |  |  |
| loess tableland |  |  |  |  |
| loess residual tableland |  |  |  |  |
| loess mountain |  |  |  |  |
| Level | Feature Description | Feature Space Selection | Quantitative Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| level 1 | global features | basic terrain factors | average slope |
| level 2 | local morphological feature | DEM | GLCM contrast GLCM homogeneity |
| level 3 | local structural features | DEM, positive and negative terrain data | INDMF regularity |
| Level | Type | Correct Category Number | Sample Number | CP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| level 1 | loess plain | 13 | 15 | 86.67% |
| loess hilly and gully and mountain area | 58 | 60 | 96.67% | |
| loess tableland area | 28 | 30 | 93.33% |
| Level | Type | Correct Category Number | Sample Number | CP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| level 2 | loess ridge residual tableland | 12 | 14 | 85.71% |
| loess hill and loess ridge area | 27 | 30 | 90.00% | |
| loess mountain area | 14 | 14 | 100.00% |
| Level | Type | Correct Category Number | Sample Number | CP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| level 2 | loess residual tableland | 10 | 13 | 76.92% |
| loess tableland | 14 | 15 | 93.33% |
| Level | Type | Correct Category Number | Sample Number | CP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| level 3 | loess hill area | 11 | 13 | 84.62% |
| loess ridge area | 13 | 14 | 92.86% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Huang, X.; Jiang, L. INDMF Based Regularity Calculation Method and Its Application in the Recognition of Typical Loess Landforms. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2282. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092282
Jiang S, Huang X, Jiang L. INDMF Based Regularity Calculation Method and Its Application in the Recognition of Typical Loess Landforms. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(9):2282. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092282
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Sheng, Xiaoli Huang, and Ling Jiang. 2022. "INDMF Based Regularity Calculation Method and Its Application in the Recognition of Typical Loess Landforms" Remote Sensing 14, no. 9: 2282. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092282
APA StyleJiang, S., Huang, X., & Jiang, L. (2022). INDMF Based Regularity Calculation Method and Its Application in the Recognition of Typical Loess Landforms. Remote Sensing, 14(9), 2282. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092282





