Abstract
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) differential code bias (DCB) is one of main errors in ionospheric modeling and applications. Accurate estimation of multiple types of GNSS DCBs is important for GNSS positioning, navigation, and timing, as well as ionospheric modeling. In this study, a novel method of multi-GNSS DCB estimation is proposed without using an ionospheric function model and global ionosphere map (GIM), namely independent GNSS DCB estimation (IGDE). Firstly, ionospheric observations are extracted based on the geometry-free combination of dual-frequency multi-GNSS code observations. Secondly, the VTEC of the station represented by the weighted mean VTEC value of the ionospheric pierce points (IPPs) at each epoch is estimated as a parameter together with the combined receiver and satellite DCBs (RSDCBs). Last, the estimated RSDCBs are used as new observations, whose weight is calculated from estimated covariances, and thus the satellite and receiver DCBs of multi-GNSS are estimated. Nineteen types of multi-GNSS satellite DCBs are estimated based on 200-day observations from more than 300 multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) stations, and the performance of the proposed method is evaluated by comparing with MGEX products. The results show that the mean RMS value is 0.12, 0.23, 0.21, 0.13, and 0.11 ns for GPS, GLONASS, BDS, Galileo, and QZSS DCBs, respectively, with respect to MGEX products, and the stability of estimated GPS, GLONASS, BDS, Galileo, and QZSS DCBs is 0.07, 0.06, 0.13, 0.11, and 0.11 ns, respectively. The proposed method shows good performance of multi-GNSS DCB estimation in low-solar-activity periods.
1. Introduction
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) differential code bias (DCB) is the difference between a hardware delay bias of two code observations [1,2]. According to the frequency of two code observations, DCBs can be divided into inter-frequency and intra-frequency DCBs, which are the error sources in the GNSS ionospheric modeling and the application of positioning, navigation, and timing [3,4,5,6]. Generally, the intra-frequency DCBs can be directly determined by the mean value of differences between the corresponding code observations [7]. However, the inter-frequency DCBs are the parameters of the ionospheric observation equation obtained through dual-frequency code observations, which need to be estimated through the corresponding methods. Therefore, most of the attention on DCB is focused on inter-frequency DCB [8]. Similarly, the estimated DCB in this study is referred to as the inter-frequency DCB.
Generally, mainly two approaches are used to calculate the DCB parameter. The first method is to model regional or global total electron content (TEC) through a definite mathematical function, e.g., a spherical harmonic function for global TEC modeling and a generalized triangular series function or polynomial function for regional TEC modeling [7,9,10,11,12,13]. Then the DCB parameter can be obtained together with the TEC modeling. The second method is to eliminate the TEC parameter through the existing global ionospheric map (GIM) [3,14,15], and then we can calculate the DCB. Because of the high correlation between DCB and TEC, DCB, as a by-product of ionosphere modeling, is regularly produced along with the GIM by the International GNSS Service (IGS) Analysis Center (IAC) [1,10,16,17,18]. These IACs, e.g., the Center for Orbit Determination in Europe (CODE), mainly provide the DCB products of GPS and GLONASS through the first method mentioned above. Due to the good coverage of GPS and GLONASS satellites, more observations can be used, and the estimated satellite DCBs present good stability. Thus, the monthly DCB products, including GPS P1-P2 (C1W-C2W) DCB and GLONASS P1-P2 (C1P-C2P) DCB, are provided by CODE.
In recent years, the rapid development of multi-GNSS accounts for the strong demand for multiple types of DCBs, instead of just a single type from GPS and GLONASS [19,20,21,22,23]. In the current IACs, only two agencies, namely, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and Deutsches Zentrum Für Luft-und Raumfahrt (DLR), provide multi-GNSS (GPS, GLONASS, BDS, Galileo, and QZSS) DCB products [7,15]. In terms of the DCB estimation method, the CAS produces the MGEX DCB products through the IGGDCB method proposed by Li et al. [24], in which single-station TEC modeling based on a generalized triangular series function was used [7], whereas MGEX DCB from DLR was estimated through the second method mentioned above [15]. Their products can be obtained from ftp://cddis.gsfc.nasa.gov/pub/gps/products/mgex/dcb/ (accessed on 1 June 2020). The information on MGEX DCB products provided by CAS and DLR is listed in Table 1, which includes 19 types of DCBs in total. It should be noted that GPS C1W-C2W DCB and GLONASS C1P-C2P DCB are not directly provided by DLR, whose value can be derived from the combined value of the other two types of DCBs [25], i.e., and .

Table 1.
Information on the MGEX DCB products provided by CAS and DLR.
In terms of most DCB estimation methods, including those currently used in the CAS and DLR, the ionospheric observations are extracted based on the geometry-free combination of dual-frequency code measures, since the extraction method is simple to implement without relying on other external products. In addition, some studies on DCB estimation through the precise point-positioning (PPP) method have also been carried out [5,19,25,26]. However, these methods of DCB estimation rely on ionospheric function models and global ionosphere maps.
In this study, to estimate multi-GNSS DCB efficiently and accurately, a new method of multi-GNSS DCB estimation is proposed without relying on the ionospheric function model and existing global ionosphere map (GIM). In the following, the proposed new method is described in detail in Section 2. In Section 3, 200 days of observations from more than 300 multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) stations are collected for the estimation of the types of multi-GNSS satellite DCBs. The estimated DCBs are compared with the MGEX DCB products for validation and evaluation. Finally, the corresponding discussion and conclusion are given in Section 4 and Section 5, respectively.
2. Methods and Data
2.1. A New Method of Multi-GNSS DCB Estimation
The GNSS satellite and receiver DCB is the parameter to be estimated in the ionospheric observation equation together with the ionospheric TEC. The ionospheric observation equation can be obtained based on the geometry-free linear combination of dual-frequency GNSS code observations. Generally, the code observation is smoothed through the carrier phases, since it is susceptible to noises and multipath errors [1,27]. The smoothed code observation equation can be expressed as:
where is the smoothed code observation of epoch k at station r; is the speed of light; is the combined value of satellite and receiver DCB of epoch k at station r; and are the satellite and receiver DCB, respectively; is the vertical total electron content (VTEC) of the corresponding the ionospheric pierce point (IPP) at epoch k; is the ionospheric observation error; , where and are the first and second frequency of the observations, respectively; and is the mapping function used to convert the slant total electron content (STEC) to the VTEC. The mapping function used in this study is the modified single-layer model (MSLM), which can be expressed as [1]:
where is the mean radius of the Earth (R = 6371 km), is the height of the assumed single-layer ionosphere (H = 506.7 km), is a correction factor (a = 0.9782), and is the satellite zenith angle of a satellite at the receiver.
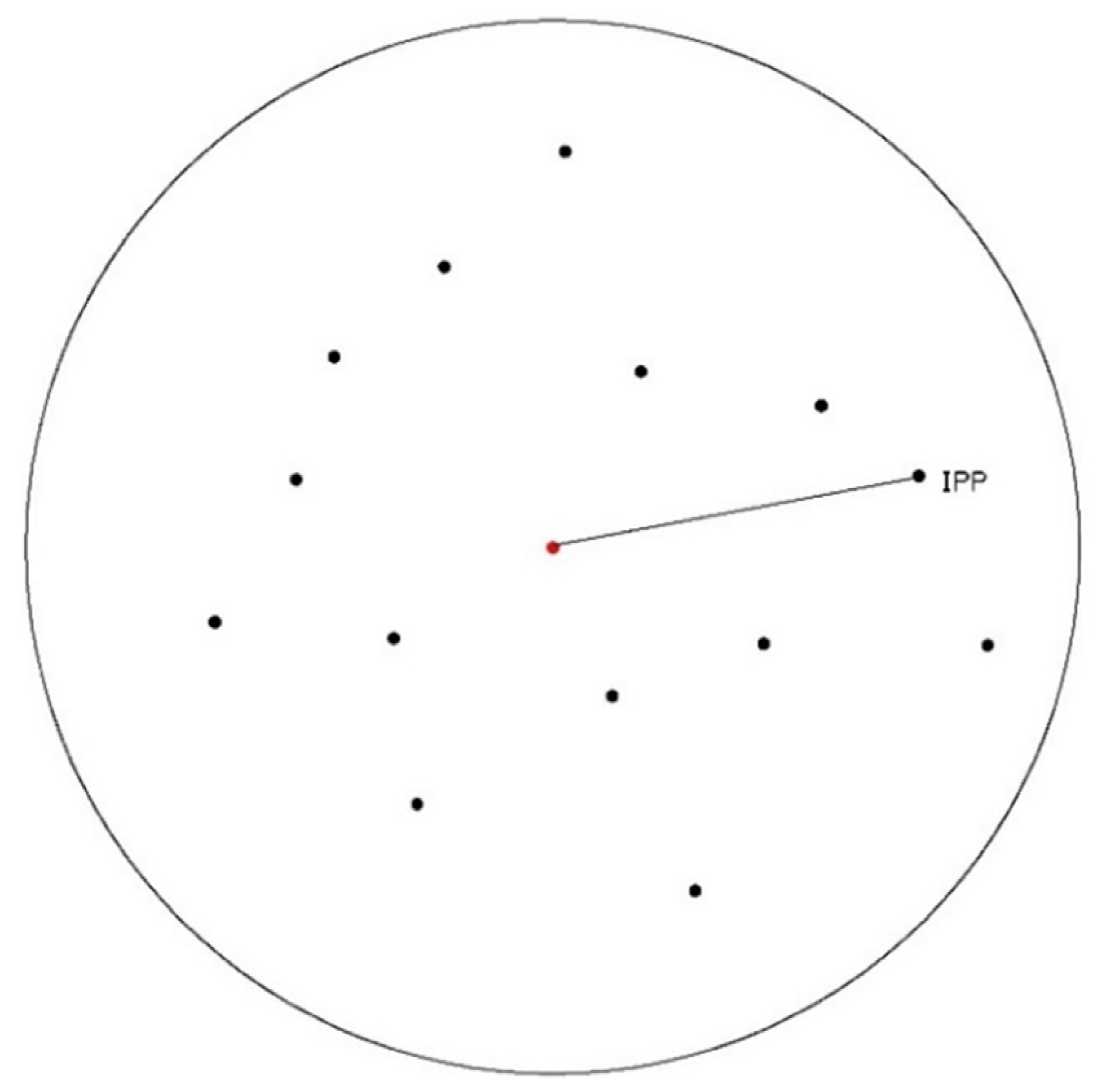
According to Equation (1), there are two parameters, namely, RS and TEC, in the observation equation of each available epoch. Thus, it is impossible to obtain the solution of parameters directly through the least-square adjustment. As mentioned above, two methods, namely, TEC function modeling for regional or global and TEC eliminating through existing global ionosphere maps, can also be adopted to estimate the DCBs. Concerning Equation (1), the DCB parameter can be obtained directly if the TEC parameter can be determined. In fact, the VTEC of IPPs can be converted into the VTEC of a station if the relationship between them is established. As can be seen from the sketch of the IPP distribution shown in Figure 1, the red dot represents the station and the black dots represent IPPs, and the location of the station can be regarded as the center of the limited distribution area of the IPPs. This means that the variation of TEC in this area is relatively small, and the TEC value of the IPP is close to that of the station when the distance between them is short. Thus, the VTEC of the station and the IPPs can be expressed as follows:
where is the VTEC of the station at epoch k, is the VTEC of ith IPP at epoch k, and is the difference between them. Obviously, the difference is small when the distance between them is small. Thus, it can be regarded as a virtual observation close to 0.
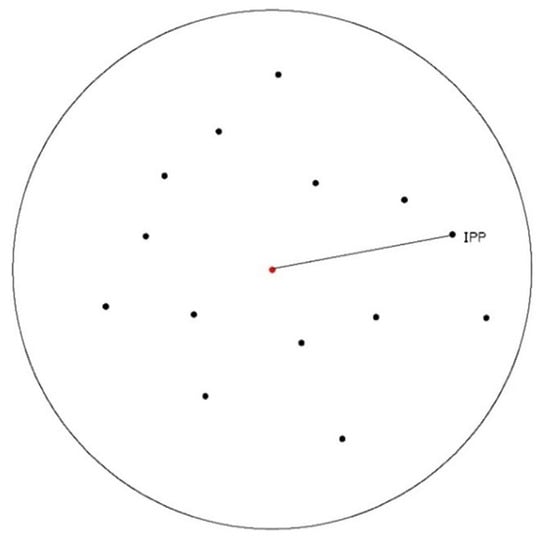
Figure 1.
Sketch of the ionospheric pierce point (IPP) distribution.
Combining Equations (1) and (3), a joint observation equation can be obtained:
where is regarded as the original observation, is the virtual observation and , and and are the original and virtual observation error, respectively. The weight of the original observation can be determined by the height angle, and the weight of virtual observation is related to the distance, since the weight is larger when the distance between them is very close, which means that the estimated is close to 0 when the weight is larger. In this paper, we considered that the TEC difference between the IPPs and the station is relatively small in a single-station area. Thus, the used weight is set as a large value. In other words, the second formula of Equation (4) does not act in the adjustment. Thus, the VTEC of the station is represented by the weighted mean VTEC values of the IPPs.
In fact, the TEC difference between the IPPs and the station is not equal to 0, and there may be a large difference among some IPPs far away from the station, especially for those stations located at a low latitude. However, Equation (4) is still available, which can be adjusted with priori right obtained by an inverse ratio of distance. Note that the priori right is an empirical value that needs to be further analyzed. It should be noted that a lager TEC difference may occur at low-latitude stations through our method. Our purpose is to estimate DCB rather than TEC. Stations with large error may remove or reduce their role in the adjustment through the variance of estimation introduced later.
Moreover, the variation in TEC of the station is slow among adjacent epochs. Thus, a random walk can be used to describe the variations, which is regarded as a virtual observation equation to add into the adjustment solution.
where is the virtual observation and , , and is the random error. The weight of virtual observation is an empirical value and used to balance the random walk and the observations’ contribution to the adjustment solution [28]. The value is set as 1/0.03 TECu for all its elements in this study, which is proper in our text experiment.
Considering multi-GNSS observation and combining Equations (4) and (5), it can be expressed in the matrix as:
Based on Equation (6), the RS and VTEC can be solved through the least-square adjustment. Then, the covariance of the parameters can be obtained as:
The correlation between parameters was not considered in Equation (7). Therefore, the combined value of satellite and receiver DCB of multi-GNSS and its covariance for each station can be obtained. Then, satellite and receiver DCB of multi-GNSS can be separated based on the RS value of all stations. The separation of satellite and receiver DCB can be expressed in the matrix as:
where is the design matrix of DCB and consists of and , and is the DCB estimate and consists of satellite DCB and receiver DCB . Considering the different accuracy of the combined value of satellite and receiver DCB obtained at different stations, a weight is used in the adjustment of Equation (8), which can be defined as:
Because of the correlation between receiver and satellite DCBs, a zero-mean satellite reference needs to be added to the adjustment of Equation (8), which can be expressed as:
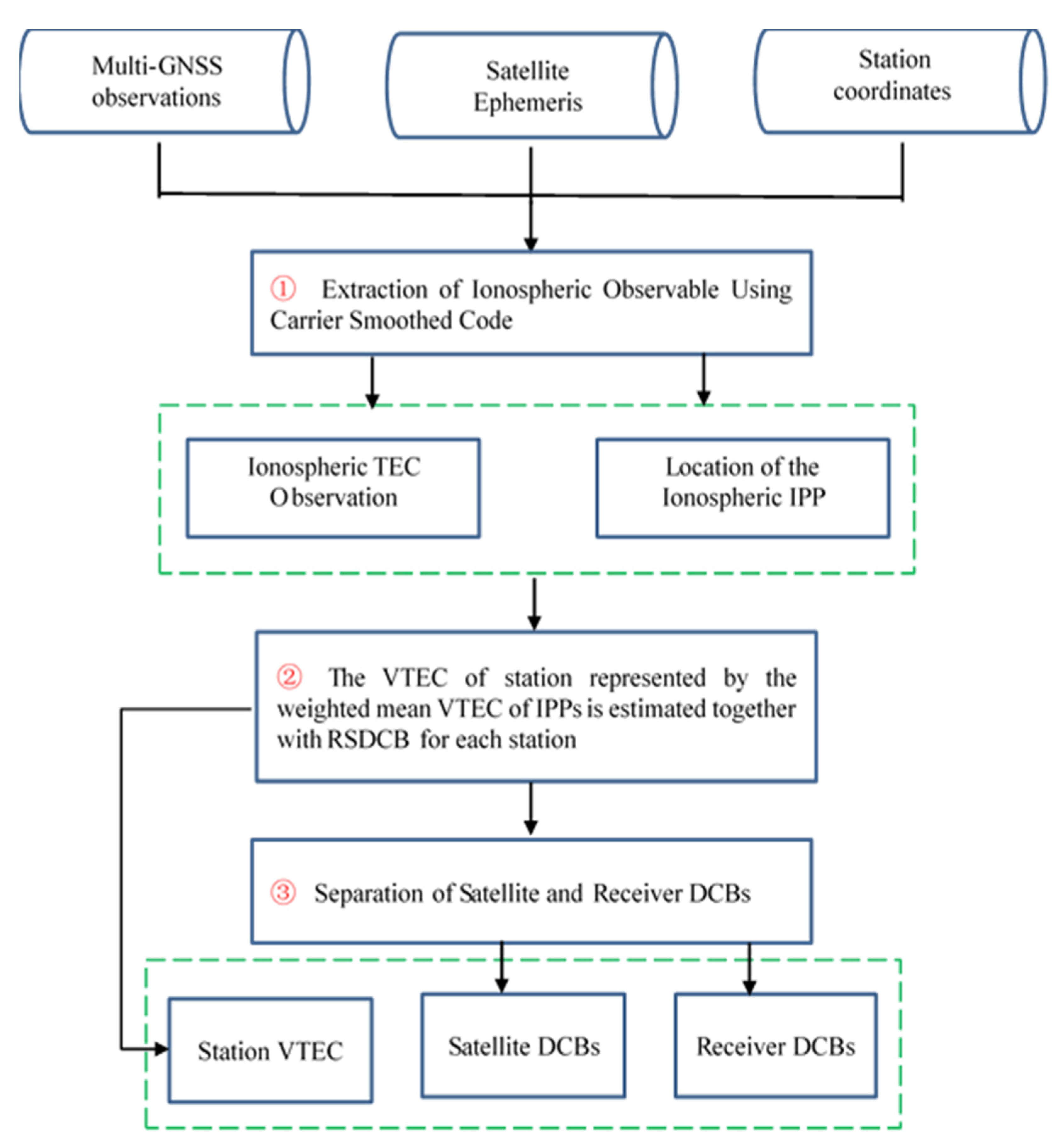
Thus, by combining Equations (8)–(10), the satellite and receiver DCBs of multi-GNSS can be obtained. According to the above derivation, the new method can be implemented in three steps. The first step is to extract ionospheric observations through the approach of carrier smooth pseudo-distance with the geometry-free linear combination of dual-frequency multi-GNSS code observations. Then, the VTEC of the station, represented by the weighted mean VTEC values of the IPPs of each epoch, is estimated as a parameter together with the combined value of satellite and receiver DCBs at the epoch. Last, the previously estimated RS DCBs are used as new observations, whose weight is calculated with the use of the estimated covariances, and then the satellite and receiver DCBs of multi-GNSS are estimated. The corresponding flowchart of the new method of multi-GNSS DCB estimation is illustrated in Figure 2.
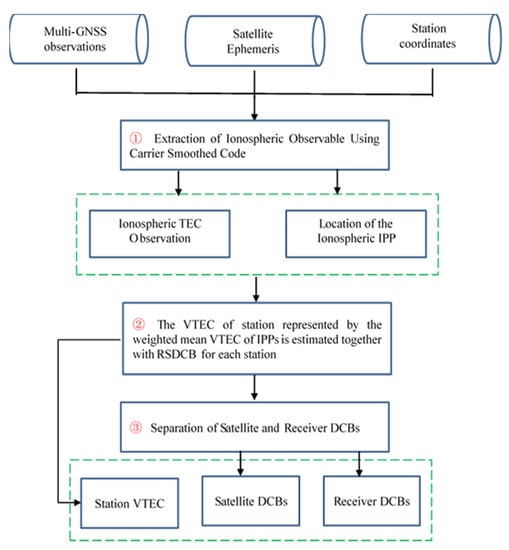
Figure 2.
Flowchart of the new method of multi-GNSS DCB estimation.
For convenience in the following analysis, the proposed method is named IGDE (independent GNSS DCB estimation), which can be found to determine the satellite and receiver DCB values by estimating VTEC directly, instead of modeling TEC by function or eliminating TEC parameters by GIM. In addition, in order to reduce multipath error and mapping function error, a 20° cutoff elevation is used in this IGDE method. It is feasible to represent the VTEC of the station by the average value of the VTEC of the IPP, because we consider that the VTEC value is not much different in the limited area, and the position of the station can be regarded as the center of the area. The observations of multi-GNSS can be marked as full use through the IGDE method, and the observations from GPS as well as GLONASS with a good quality can be used to strengthen the adjustment.
2.2. Experimental Data
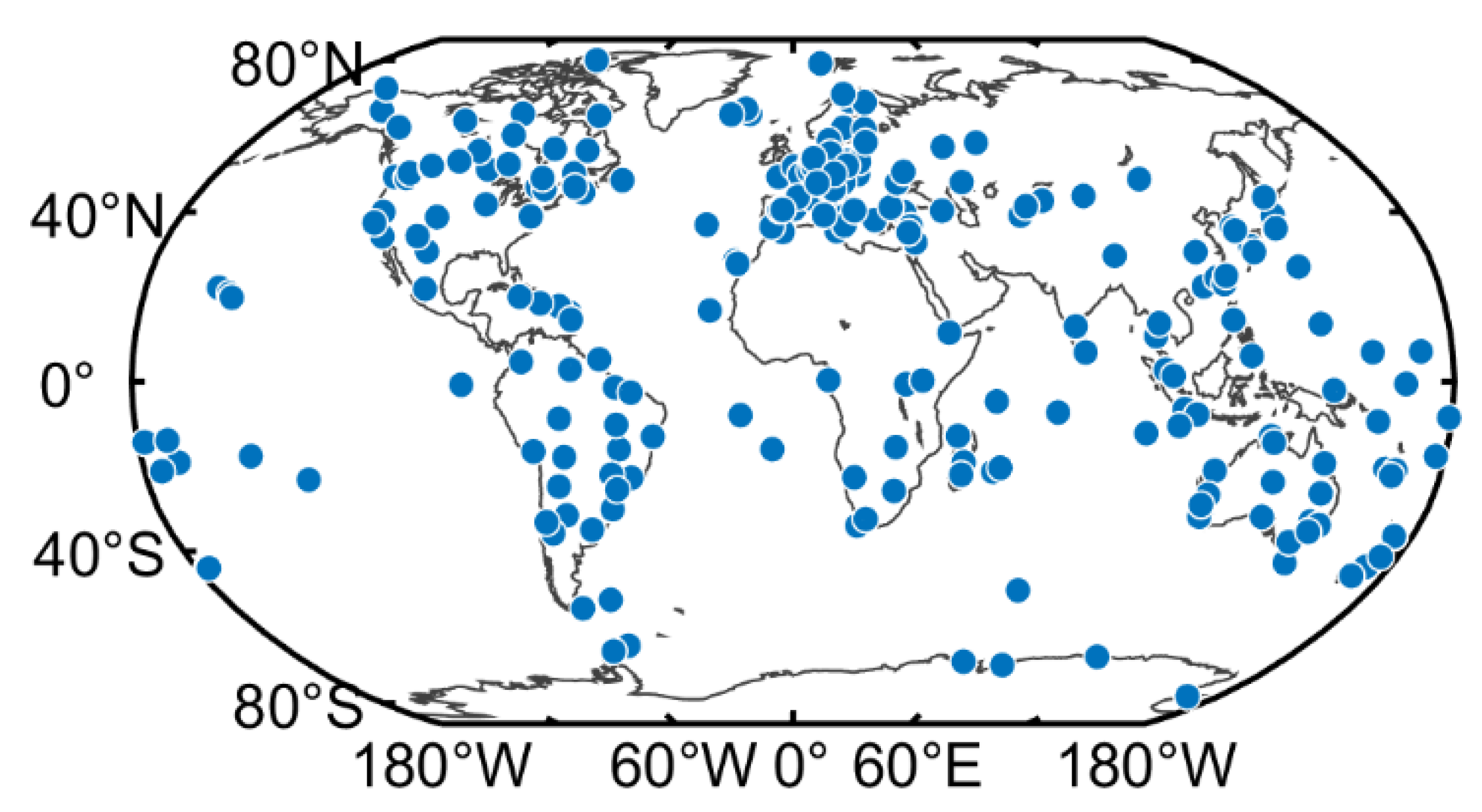
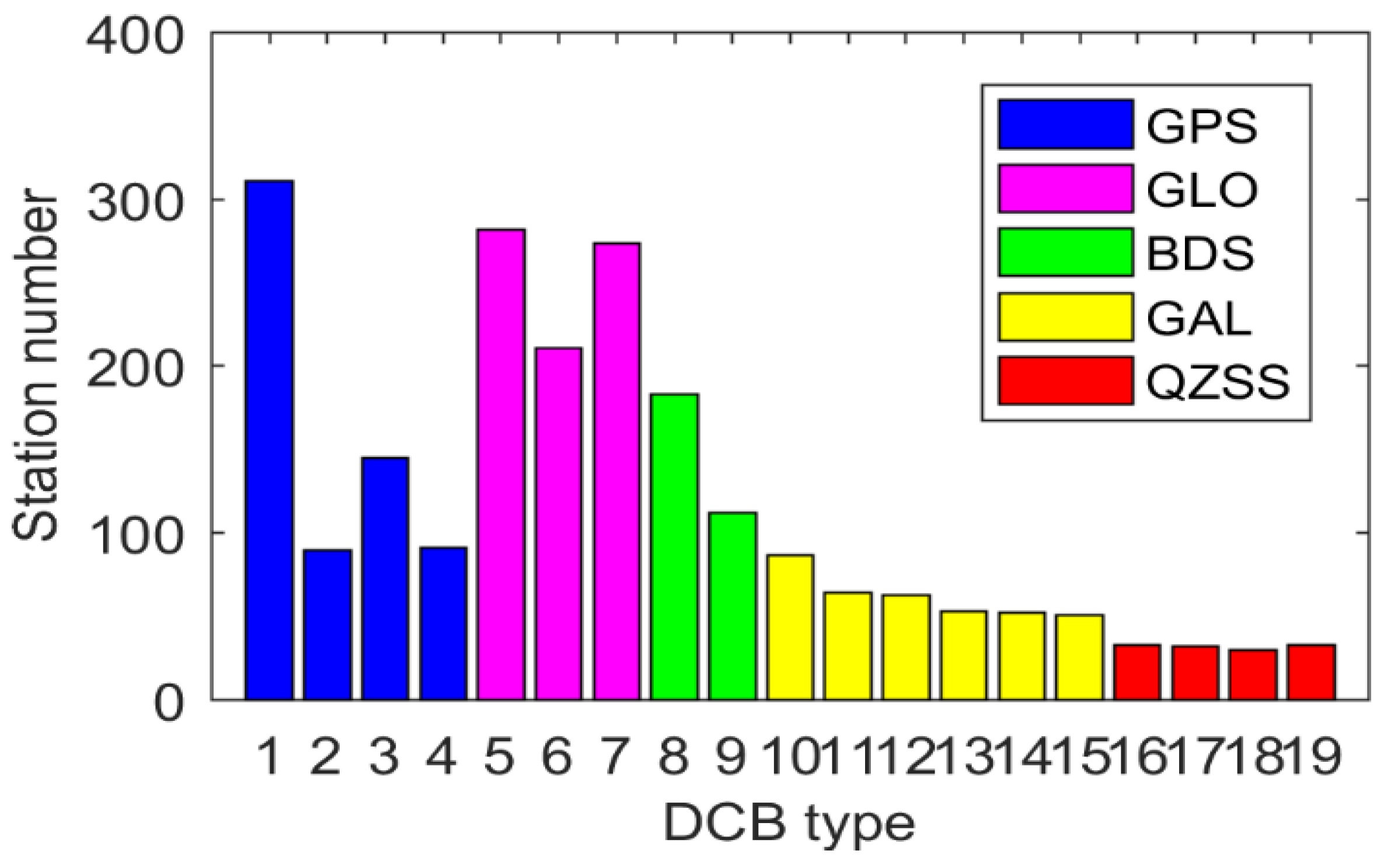
In order to better verify the performance of the new method proposed in this study, more than 300 MGEX stations were selected, which are shown in Figure 3. It can be clearly seen that these stations roughly show the global distribution. It was sufficient to use these MGEX stations for DCB estimation. Figure 4 shows the number of available stations for different DCB type estimation. The serial numbers of the x-axis in the figure corresponds to the serial number in Table 1—e.g., 1 corresponds to C1C-C2W of the GPS in Table 1. As is shown in Figure 4, the number of stations tracking the GPS was the largest, whereas that of stations tracking QZSS was the smallest. Due to the wide distribution of GPS tracking stations, all selected stations could be used to track the C1C-C2W observations of GPS. About 290 and 170 stations were available for GLONASS and BDS, respectively. However, the number of stations available for GAIEO and QZSS was smaller than 100. A total of 200 days (DOY 001 to 200, 2019) of data from selected MGEX stations were collected in this study. In addition, the corresponding DCB products provided by CAS, DLR, and CODE were downloaded for verification and comparison.
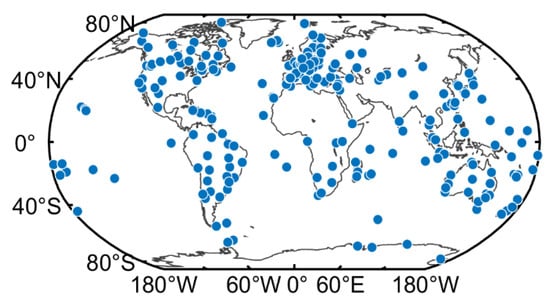
Figure 3.
Distribution of the MGEX stations used in this study.
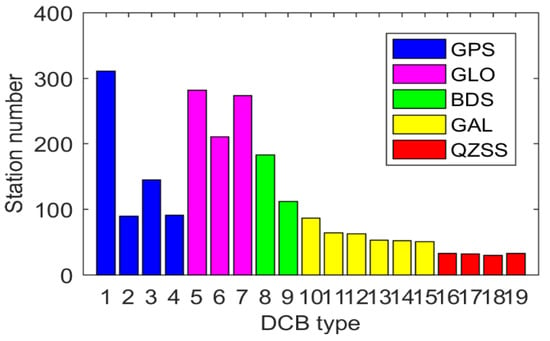
Figure 4.
Number of available stations for different DCB type estimation.
3. Results and Analysis
In this section, the proposed new method is first verified, in which the estimated VTEC value of station is compared with that provided by CODE. Then, a difference analysis between the estimated DCB and the MGEX DCB product is implemented. The stability of multi-GNSS DCB through the proposed new method and the MGEX DCB product are finally compared.
3.1. Validation of the New Method
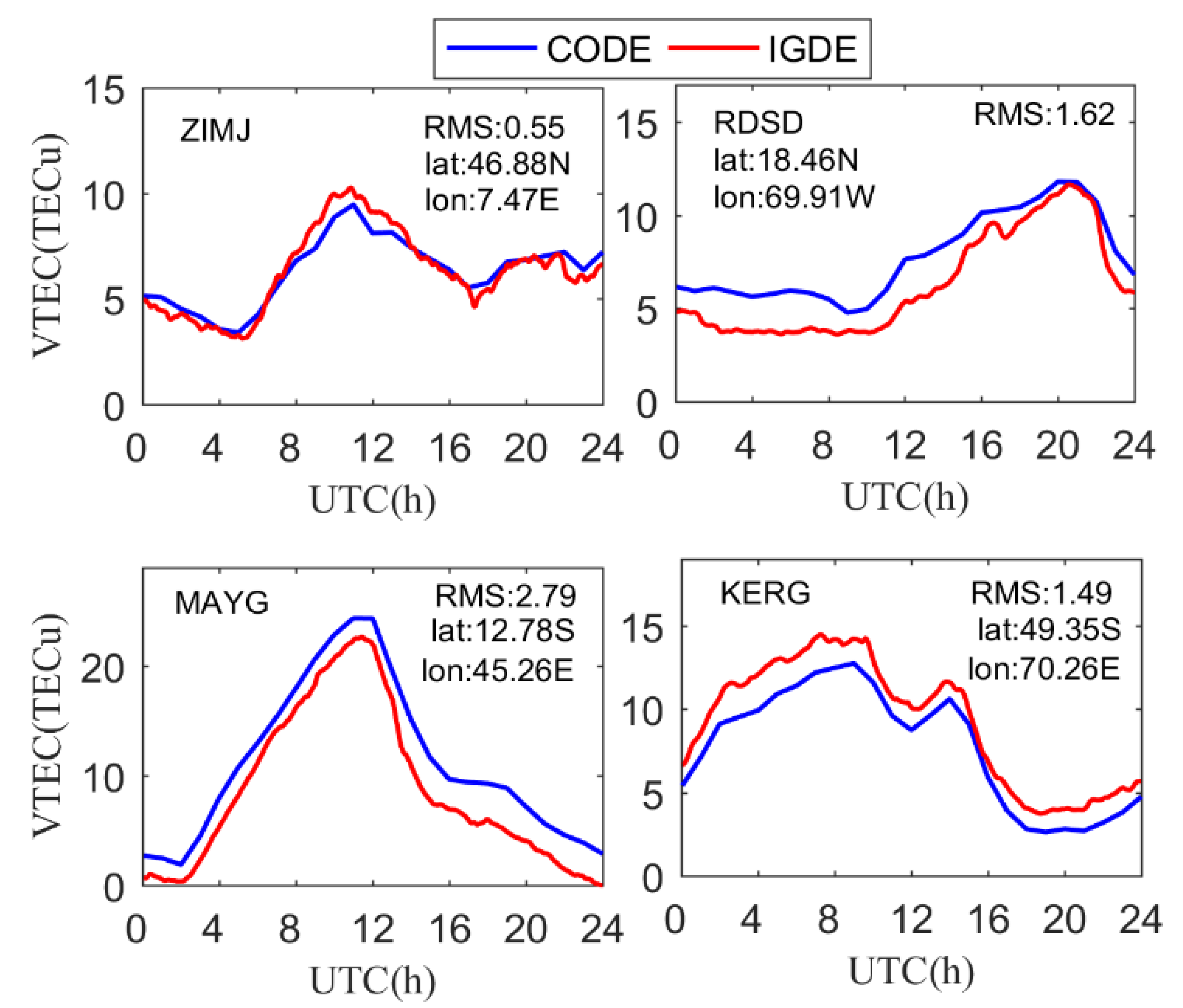
In the proposed new method, the VTEC value of the station can be obtained together with the combined value of the satellite and receiver DCB for each station. Therefore, the evaluation of the VTEC of the station can reflect the performance of the proposed method. Taking four stations as an example, i.e., ZIMJ, RDSD, MAYG, and KERG, the VTEC of the station obtained by IGDE and CODE are compared on DOY 011, 2019. Figure 5 shows the VTEC series value of the IGDE and CODE product at the four stations, two of which are located in the Northern Hemisphere, and the other two in the Southern Hemisphere. In terms of latitude, two of them at a middle latitude and the others are at a low latitude.
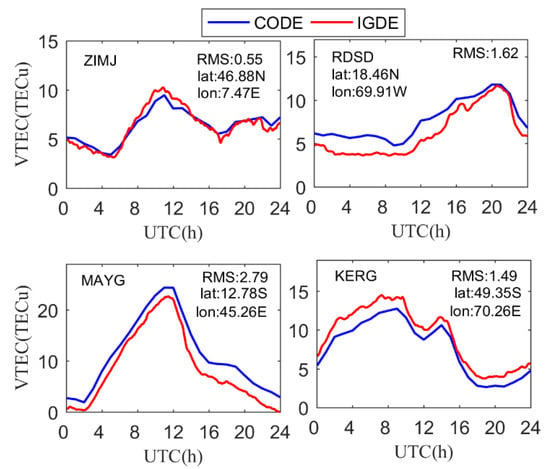
Figure 5.
VTEC series value of the IGDE and CODE product for the four stations on DOY 011.
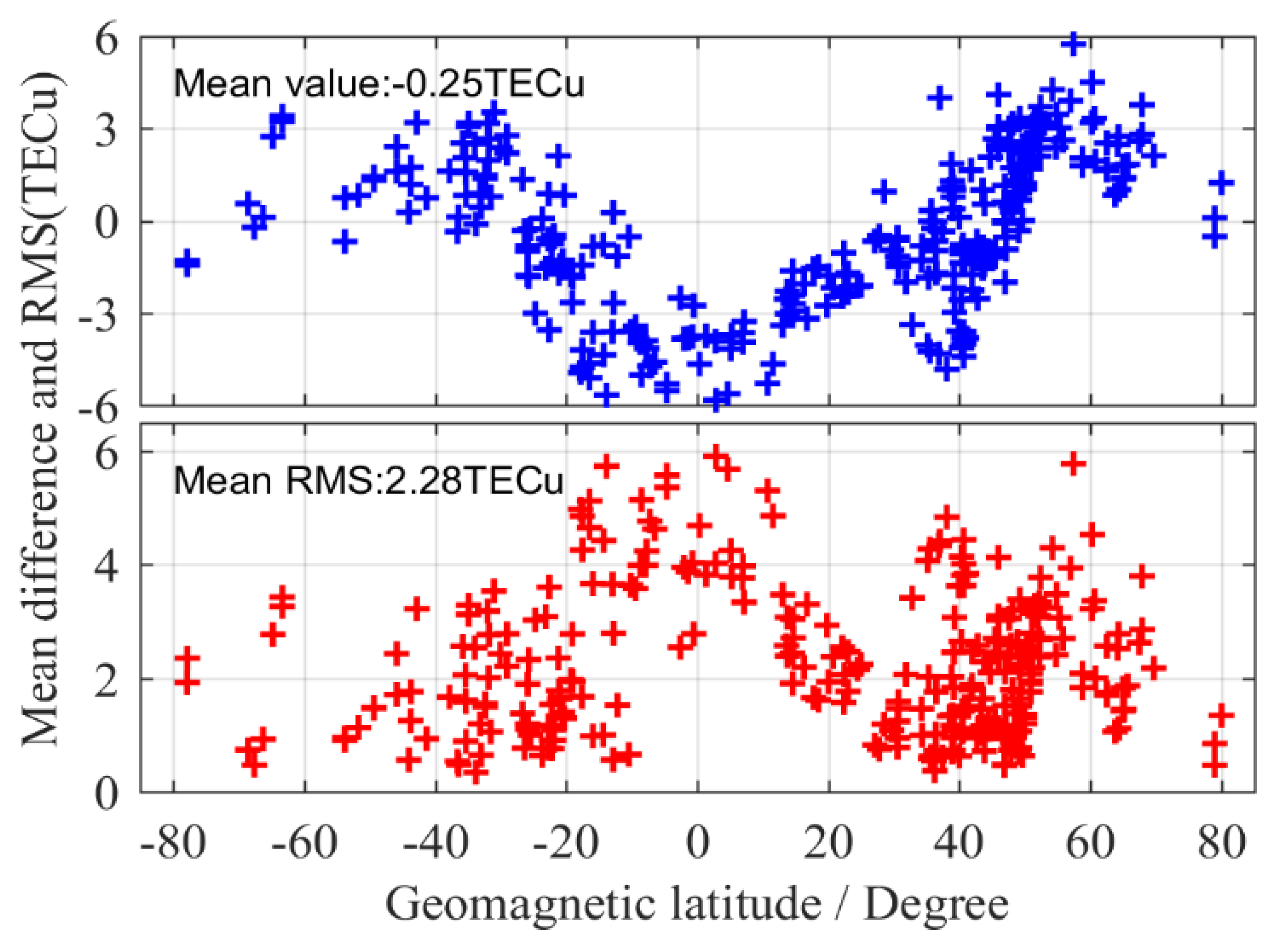
As can be seen from Figure 5, the series value of VTEC obtained by IGDE and CODE showed the same trend throughout the whole day, which indicates that the VTEC of the station obtained by IGDE can show the variation in TEC at the station. However, the performance of IGDE may have been different at different stations. It is obvious that for stations ZIMJ and KERG, the RMS of VTEC was within 1.5 TECU. However, the RMS of RDSD and MAYG was larger than that of other stations, mainly since they are in the equator area with active ionospheric variation. Figure 6 shows the mean difference and RMS of VTEC between the IGDE and CODE product at all MGEX stations on DOY 011, 2019. For most stations, the mean difference and RMS were within ±3 TECu and 3 TECu, respectively. However, the stations located in the low-latitude area, whose mean difference and RMS showed a larger value, showed the same phenomenon, as depicted in Figure 5. Moreover, some large values also appeared at high latitudes, which may be related to the few observations at those stations. The accuracy of TEC from CODE was 2–8 TECu [10], and the mean values of the difference and RMS were −0.25 and 2.28 TECu for all stations, respectively, indicating good performance of the proposed method in VTEC estimating for those stations.
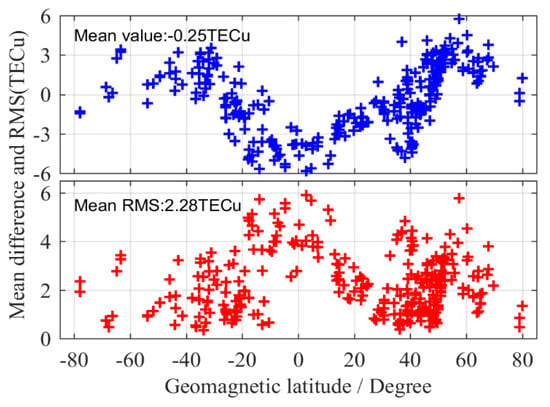
Figure 6.
Mean difference and RMS of VTEC between the IGDE and CODE product for all MGEX stations on DOY 011.
3.2. Difference Analysis between Estimated DCB and MGEX DCB Product
As mentioned above, 19 types of multi-GNSS DCBs, which were from GPS, GLONASS, BDS, Galileo, and QZSS, needed to be estimated and analyzed. In order to verify the accuracy and reliability of the DCBs estimated by IGDE, a difference analysis between estimated DCB and the MGEX DCB product was performed in this section. The MGEX DCB products were from CAS and DLR, and the GPS C1W-C2W DCB and GLONASS C1P-C2P DCB provided by CODE were also used as the reference for a better comparison. Because the different satellite DCB reference datum may be used for different DCB estimation methods, the corresponding satellite DCB reference datum needed to be unified before DCB comparison. Different reference benchmarks mean that the number of satellites participating in the zero-mean constraint is different, so they needed to be unified [4,29]. In the following analysis, the mean difference and standard deviation (STD) of multi-GNSS DCB between IGDE and MGEX products are shown in Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11, and the corresponding root mean square (RMS) values are listed in Table 2.
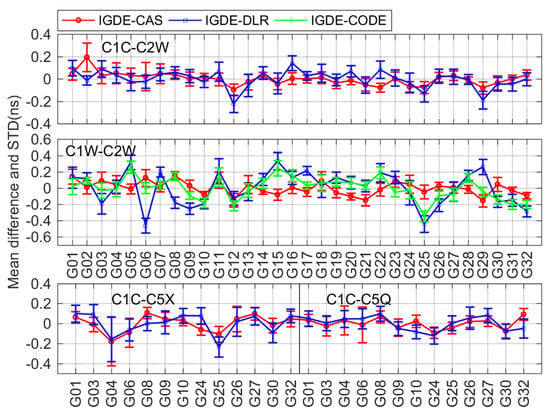
Figure 7.
Mean difference and STD of GPS DCB between IGDE and MGEX products.
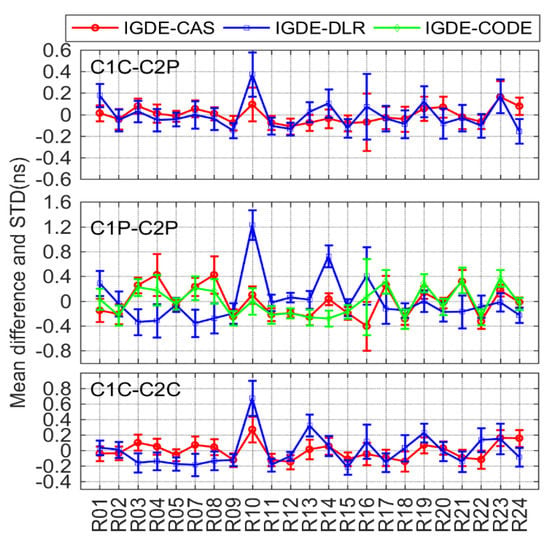
Figure 8.
Mean difference and STD of GLONASS DCB between IGDE and MGEX products.
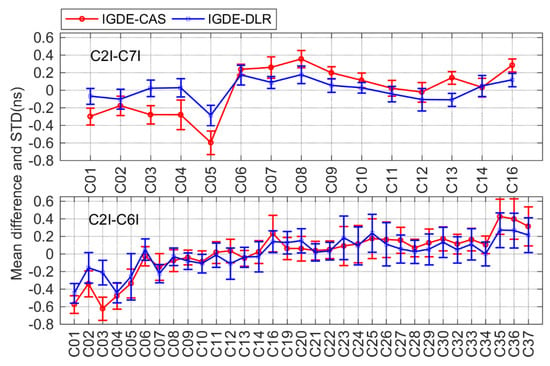
Figure 9.
Mean difference and STD of BDS DCB between IGDE and MGEX products.
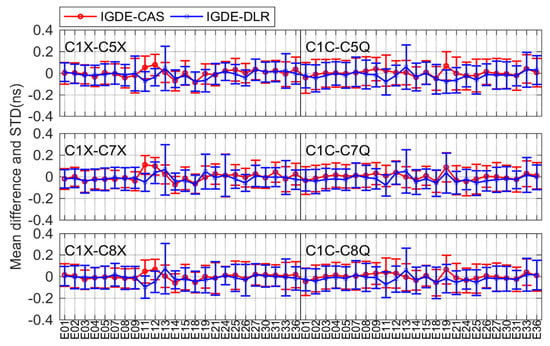
Figure 10.
Mean difference and STD of GAILEO DCB between IGDE and MGEX products.
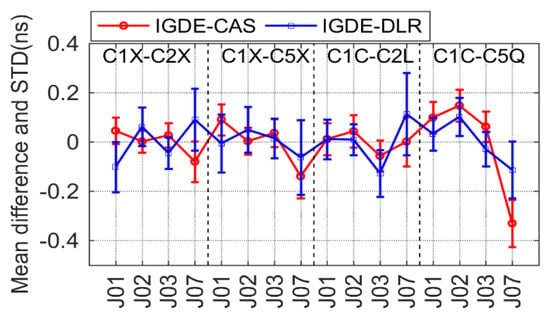
Figure 11.
Mean difference and STD of QZSS DCB between IGDE and MGEX products.

Table 2.
Mean RMS value of all DCBs between IGDE and MGEX products.
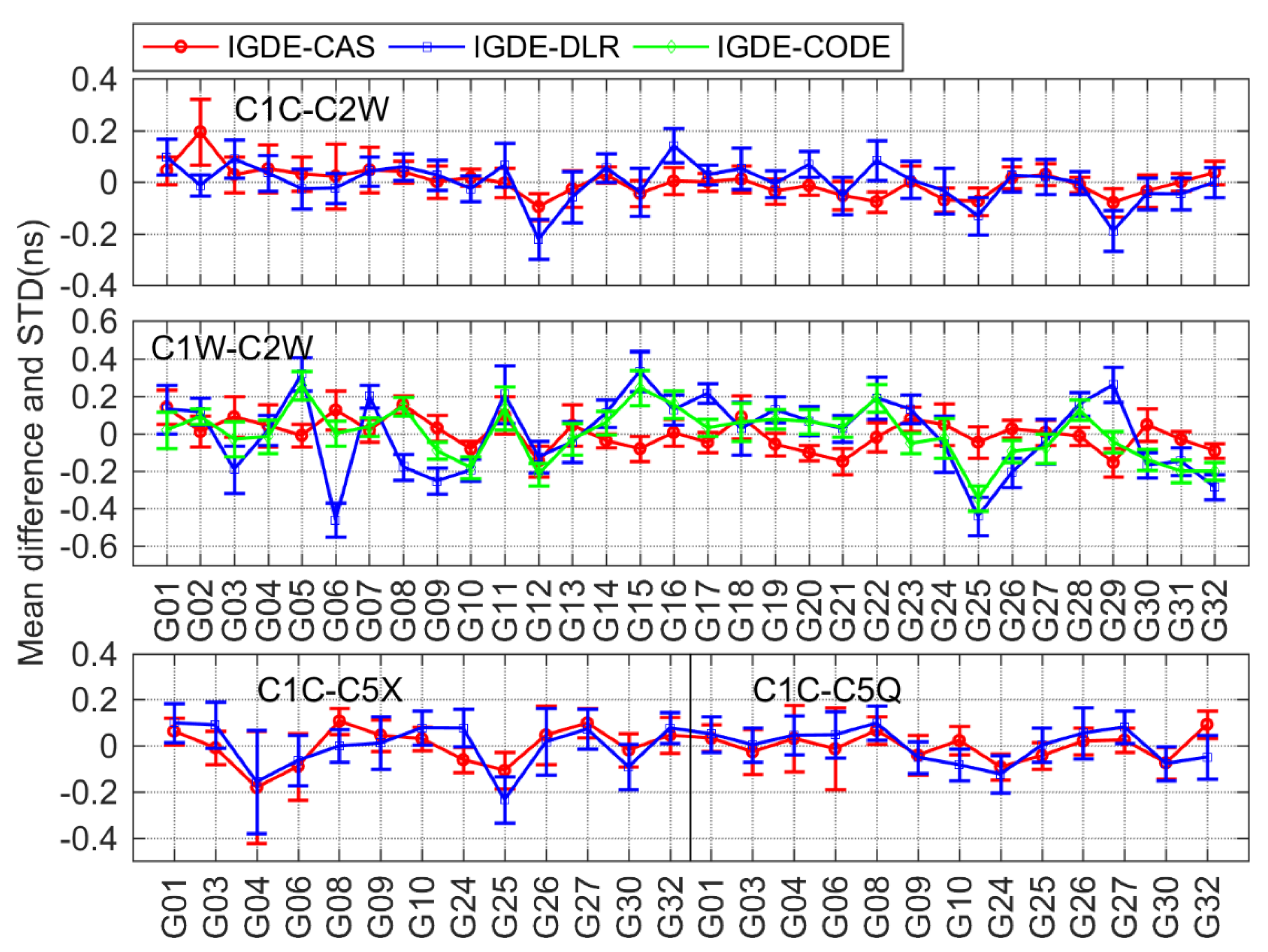
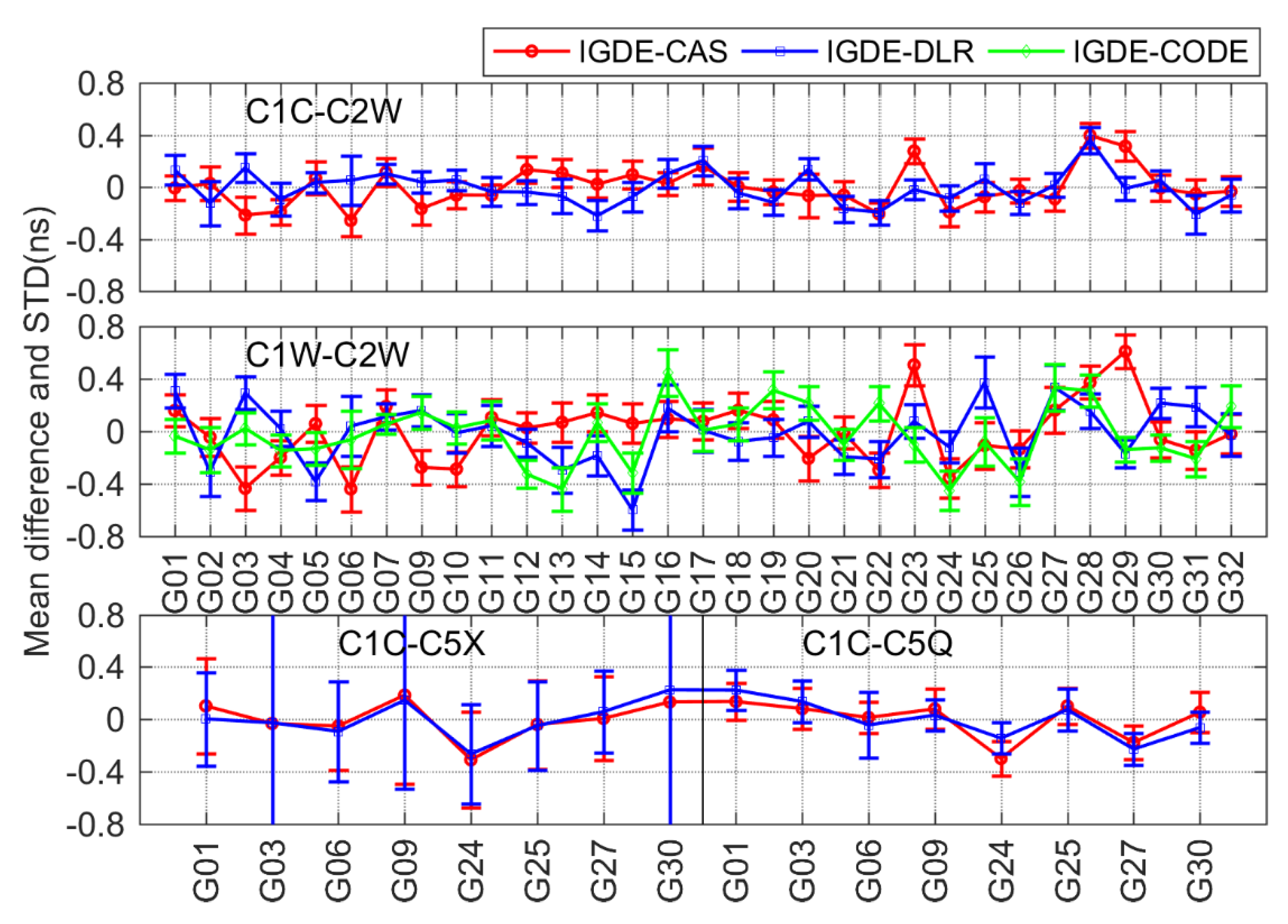
For GPS, four types of DCB, namely, C1C-C2W, C1W-C2W, C1C-C5X, and C1C-C5Q, were compared with CAS, DLR, and CODE. It should be noted that the value of all four types of daily DCB can be provided by CAS and just C1W-C2W daily DCB values can be provided by CODE, whereas the C1W-C2W DCB of DLR can be obtained from and the other three types of DCBs from DLR can be obtained directly. As can be seen from the mean difference in Figure 7, the value of four types of DCBs with respect to the products from CAS, DLR, and CODE was mostly with ±0.4 ns, the largest value of which was near −0.6 ns. Especially for C1W-C2W DCB, the mean difference with respect to CAS and CODE was within ±0.2 ns, and the mean RMS values were 0.10 and 0.14 ns, respectively. As is shown in Table 2, the mean RMS values were 0.07/0.09, 0.12/0.14, and 0.10/0.10 ns for C1C-C2W, C1C-C5X, and C1C-C5Q, respectively, with respect to CAS/DLR.
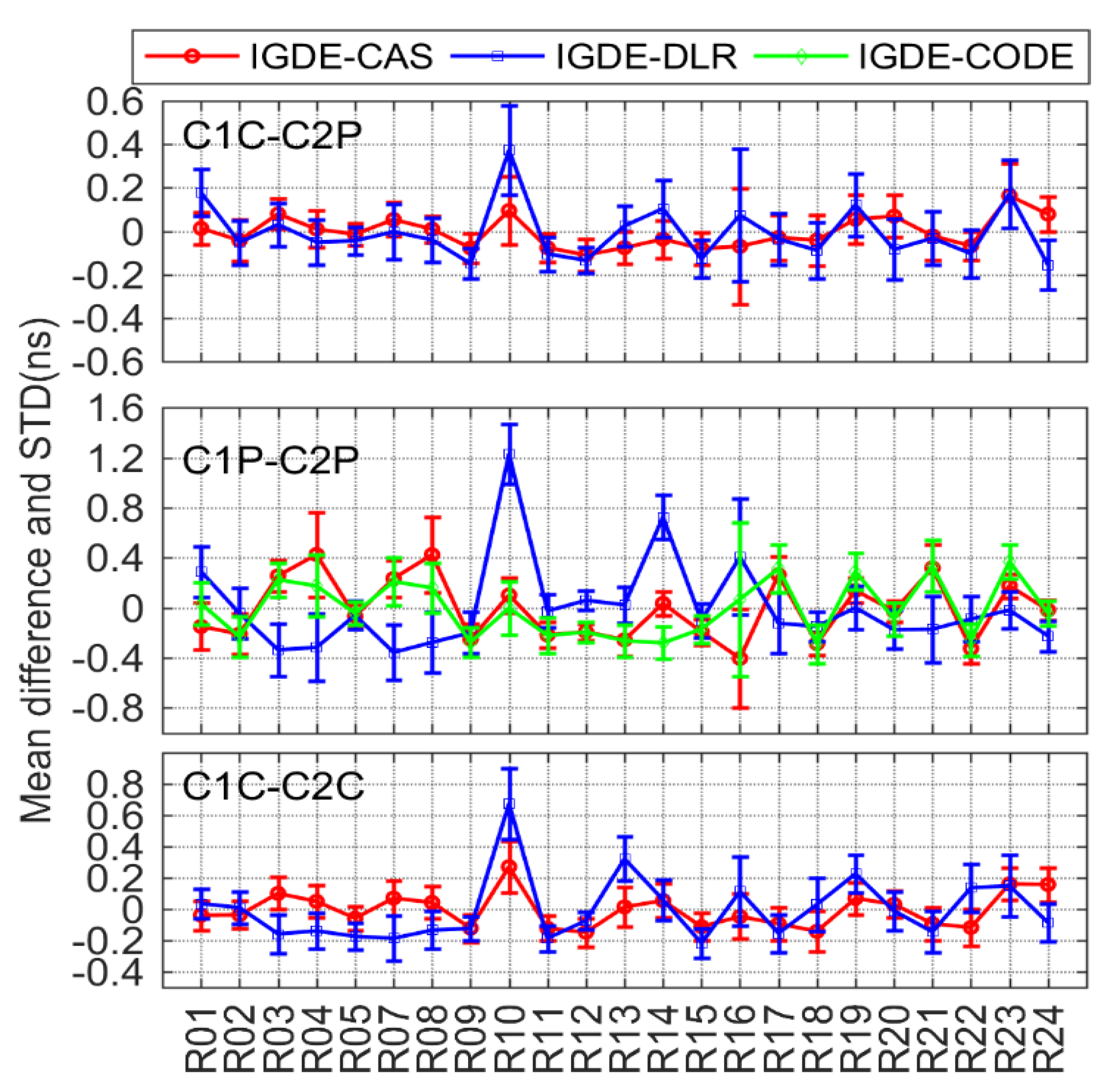
According to the comparison results of GLONASS DCB shown in Figure 8, three types of DCBs (C1C-C2C, C1P-C2P, and C1C-C2C) were compared with CAS, DLR, and CODE. Similar to GPS C1W-C2W, C1P-C2P DCB was also compared with CODE, and the products from DLR were also derived from . The other two types of DCBs were compared with CAS and DLR, whose products can be obtained directly. Obviously, the value of difference in GLONASS DCBs was larger than those of the GPS, which may be related to the use of frequency division multiple access (FDMA) technology through GLONASS [7]. The mean difference between C1C-C2P and C1C-C2C DCB with respect to CAS/DLR was mostly within ±0.4 ns, whose mean RMS values were 0.12/0.16 and 0.15/0.21 ns, respectively. For C1P-C2P, the mean difference with respect to CAS, DLR, and CODE was within ±0.8, ±1.2, and ±0.4 ns respectively, whose mean RMS values were 0.27, 0.33, and 0.28 ns, respectively.
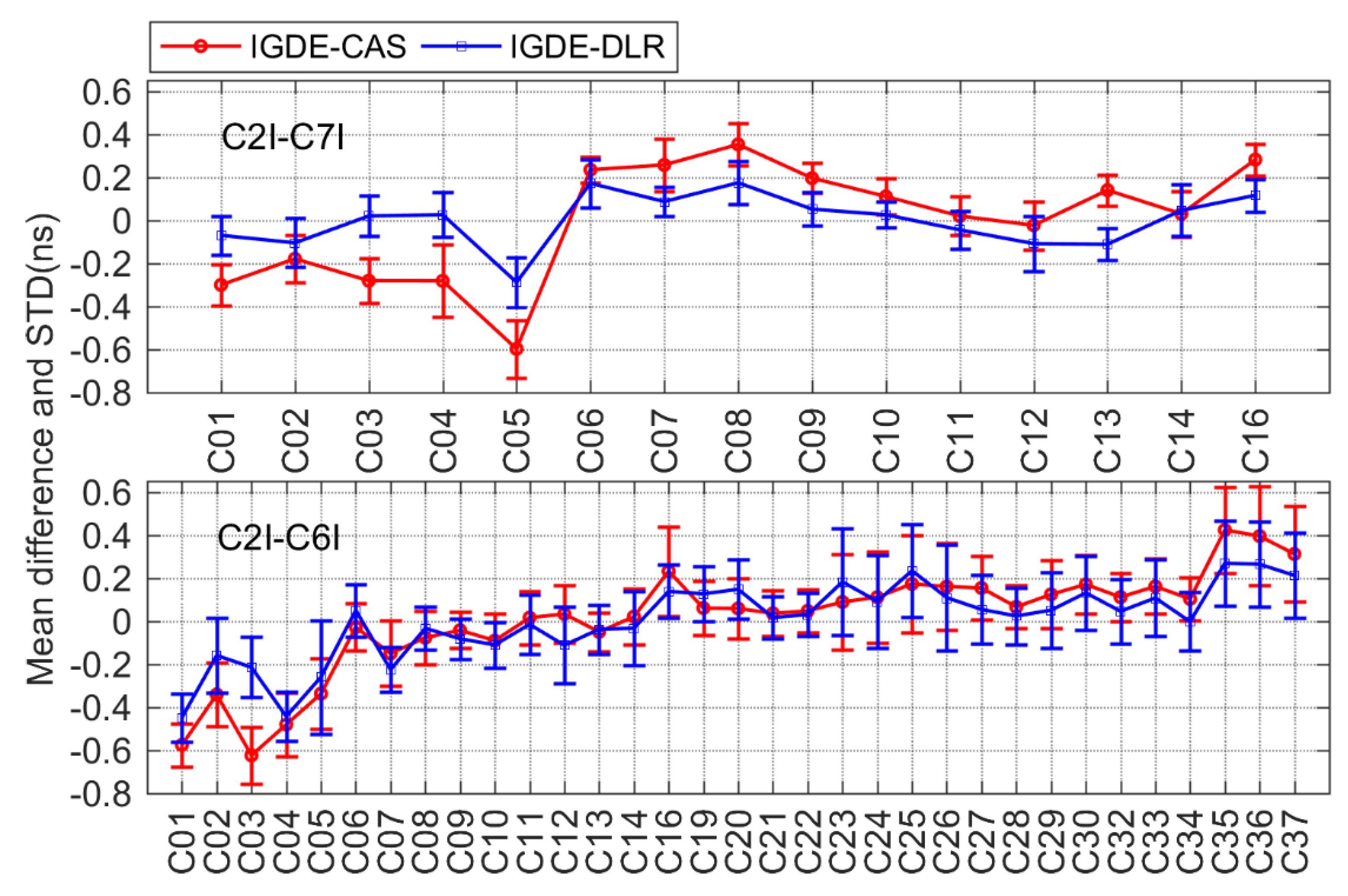
For BDS, only two types of DCB (C2I-C7I for BDS-2 and C2I-C6I for BDS-2 and BDS-3) observations could be tracked by satellites based on the current MGEX network. The corresponding DCB products could be obtained from CAS and DLR, and the comparison result is shown in Figure 9. It can be seen that the mean difference between two types of DCB with respect to CAS and DLR was within ±0.6 ns. For C2I-C7I and C2I-C6I, there was a mean RMS of 0.25/0.14 and 0.24/0.22 ns, respectively, with respect to CAS/DLR.
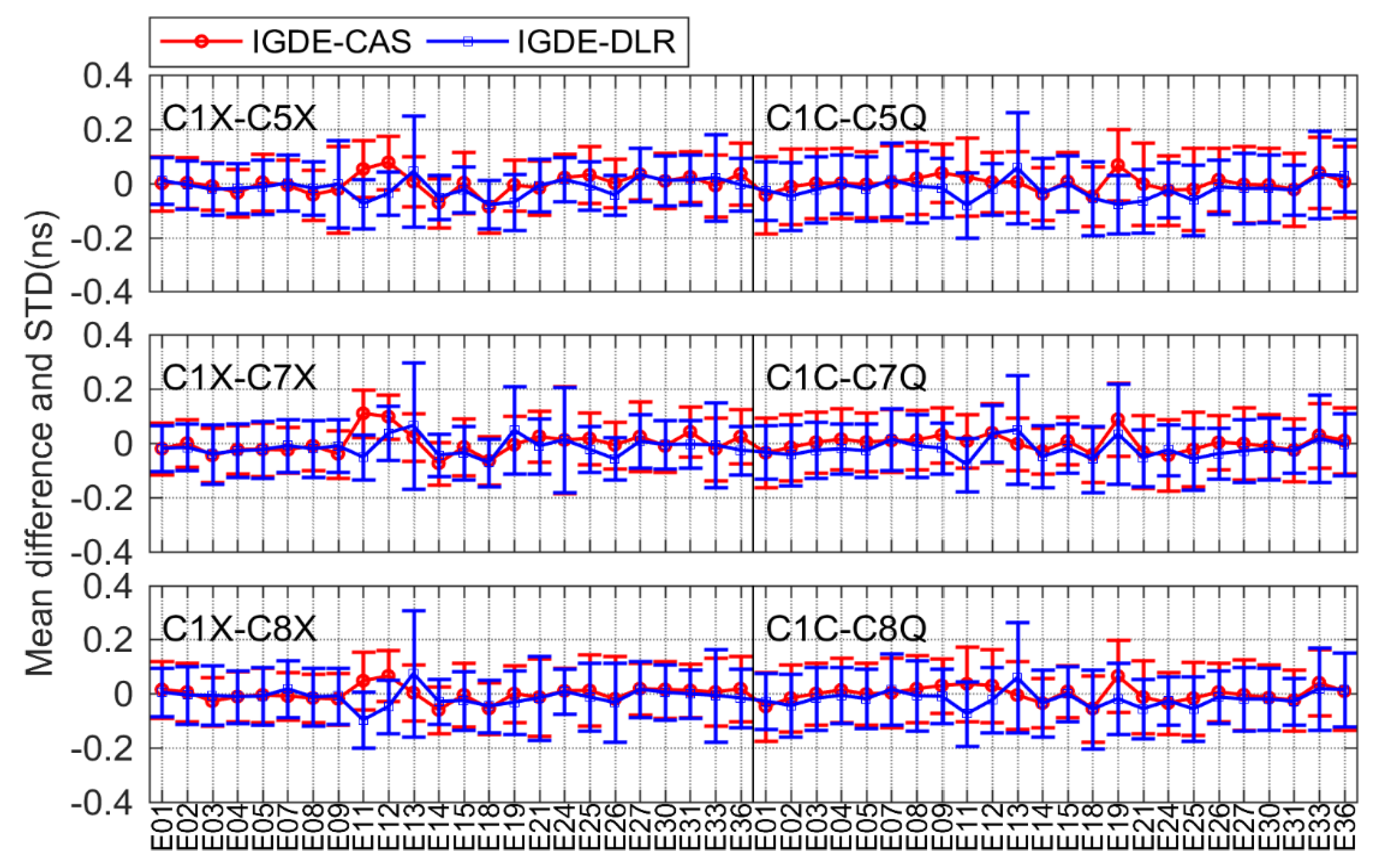
For Galileo, there were six types of DCBs compared with CAS and DLR, including C1X-C5X, C1X-C7X, and C1X-C8X, as well as C1C-C5Q, C1C-C7Q, and C1C-C8Q. Figure 10 shows the corresponding comparison result. As is shown in the figure, the mean difference of all DCBs was within ±0.2 ns. The mean RMS values were 0.11/0.11, 0.11/0.11, and 0.11/0.12 ns, as well as 0.13/0.13, 0.12/0.12, and 0.12/0.12 ns, for C1X-C5X, C1X-C7X, and C1X-C8X, respectively, and C1C-C5Q, C1C-C7Q, and C1C-C8Q, respectively, with respect to CAS/DLR.
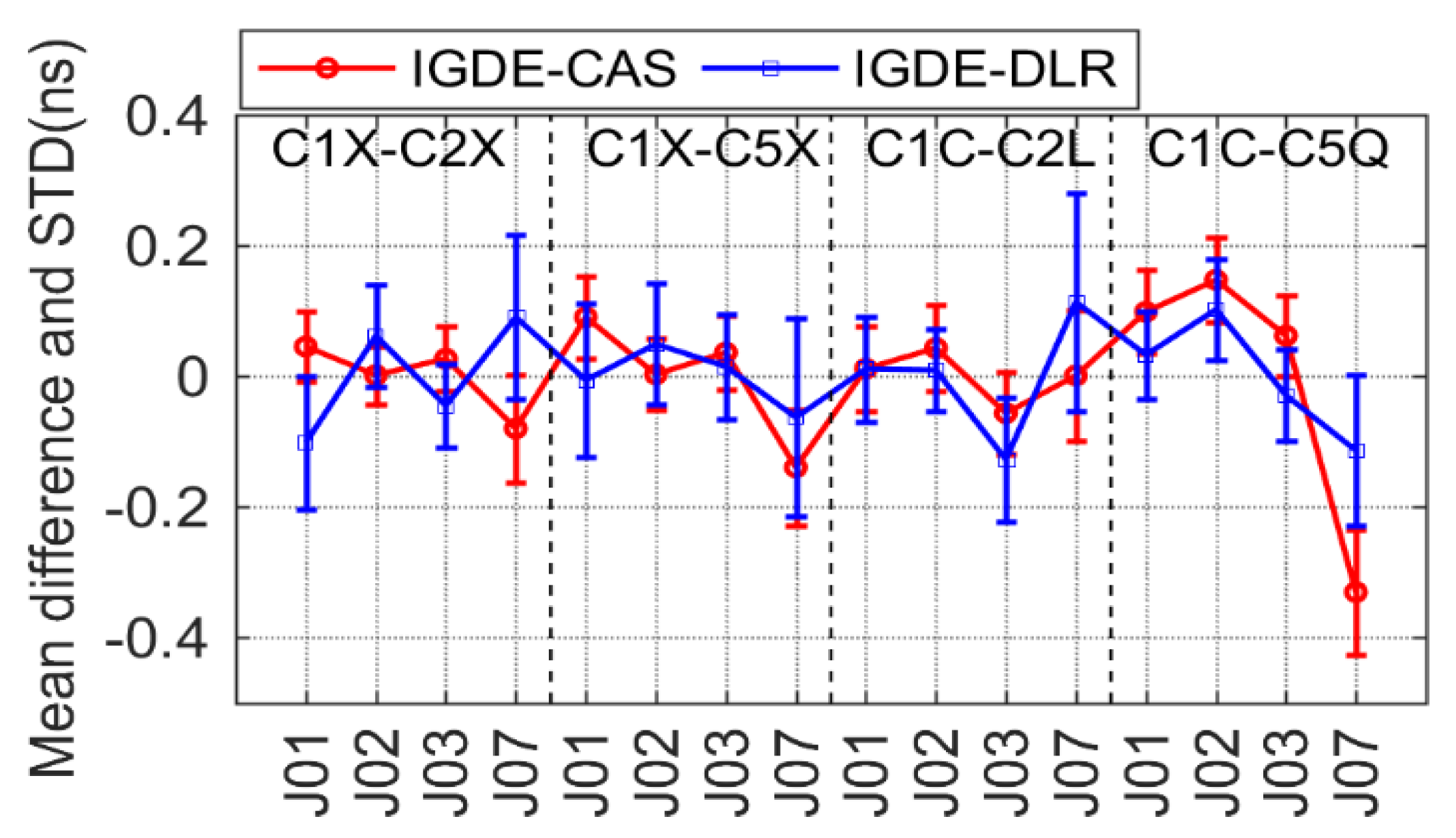
For QZSS, only four satellites could be tracked in the current MGEX network, and four types of DCBs, namely, C1X-C2X, C1X-C5X, C1C-C2L, and C1C-C5Q, needed to be estimated. All DCB products could be obtained by CAS and DLR, and the comparison result is shown in Figure 11. It can be seen that the mean difference of all DCBs for all satellites (except J07) with respect to CAS/DLR was within ±0.2 ns. The mean RMS values of the four types of DCBs with respect to CAS/DLR were 0.07/0.12, 0.10/0.12, 0.08/0.13, and 0.18/0.11 ns, respectively.
As is shown in the above results, the mean difference among most types of DCB with respect to CAS/DLR was within ±0.4 ns. The comparison results of 19 types of DCBs estimated by IGDE show good agreement with the MGEX DCB products, indicating good performance of IGDE in multi-GNSS DCB estimating. Especially for GPS C1W-C2W and GLONASS C1P-C2P DCB, the difference with our estimated DCB and CODE products was small, whose value was less than that between IGDE and CAS/DLR products. This may be related to the larger number of stations used in DCB estimation of GPS and GLONASS. In addition, some difference in the mean, with a larger value for GPS C1W-C2W and GLONASS C1P-C2P DCB with respect to DLR, could be found, e.g., the value of G06 near −0.6 ns and that of R10 near 1 ns, mainly due to the fact that the two types of DCB of DLR product could not be obtained directly but were calculated based on the other DCBs. In terms of BDS DCB, there seemed to be some difference in mean of a large value for GEO satellites, e.g., a value of C2I-C7I for C05 and that of C2I-C6I for C01 near −0.6 ns, which may be due to the fact that GEO satellite observations are more susceptible to multipath errors. As can be seen from the STD of the difference, the value of GPS and GLONASS was obviously smaller than that of BDS, Galileo, and QZSS, mainly since more continuous observations could be observed through GPS and GLONASS. Some larger STDs could be found in BDS-3, Galileo, and QZSS, e.g., C37 of BDS, E33 of Galileo, and J07 of QZSS, which is mainly related to the fact that fewer observations could be tracked from those satellites. Overall, mean RMS values were 0.12, 0.22, 0.21, 0.12, and 0.12 ns, for GPS, GLONASS, BDS, Galileo, and QZSS DCBs, respectively, with respect to MGEX products.
3.3. Stability Analysis of Multi-GNSS DCB
As two important indicators of comparison between the proposed method (IGDE) and MGEX products, the mean difference and STD were analyzed in the previous section, between which good agreement was found. In this section, we mainly analyze the stability of DCBs estimated through different methods, as the stability of DCBs reflects the stability and reliability of DCB estimation to a certain extent, which can be expressed as [7,29,30]:
where is the stability of DCB for satellite j, is the daily DCB of satellite j on day d, is the mean DCB of satellite j, and is the number of days.
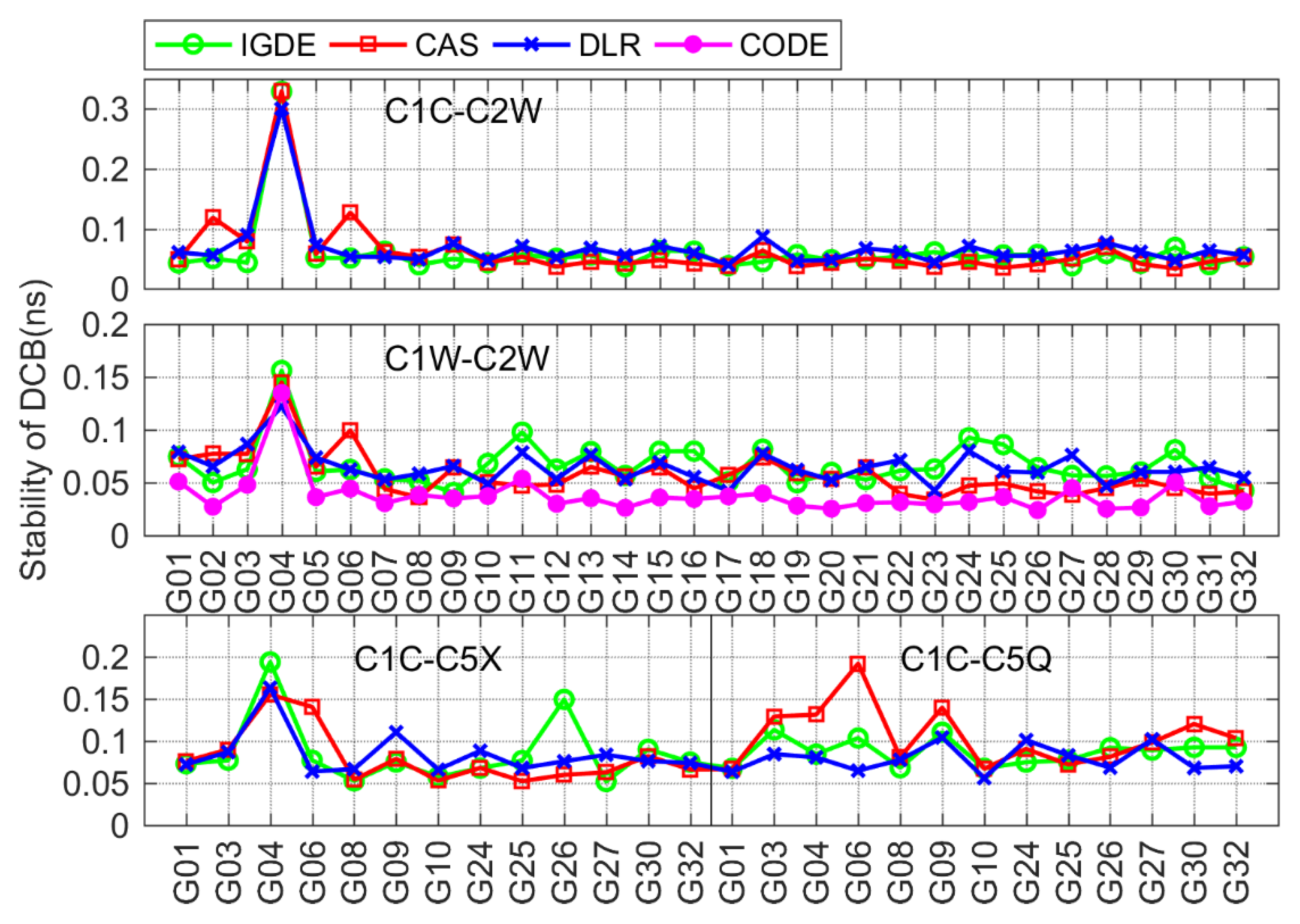
Figure 12 shows the stability of GPS satellite DCBs obtained by IGDE, CAS, DLR, and CODE. The C1W-C2W DCB of CODE was relatively stable, whose stability was within 0.05 ns, which is mainly due to the observations at about 300 IGS stations for three consecutive days used by CODE for DCB estimation. The stability of C1W-C2W DCB from IGDE, CAS, and DLR was within 0.1 ns. In terms of the other three types of DCB, the stability of the DCB obtained by IGDE, CAS, and DLR was almost same, with values mostly within 0.1 ns, indicating reasonable stability of GPS DCBs estimated by IGDE.
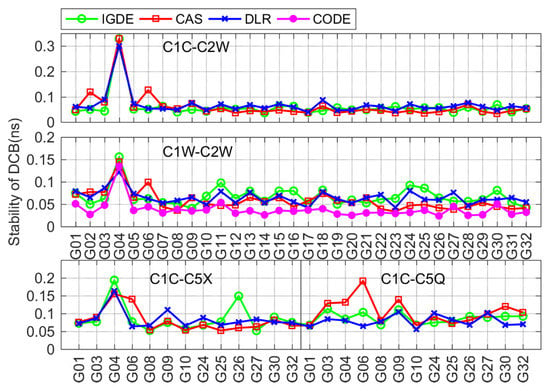
Figure 12.
Stability of the GPS DCB obtained by IGDE, CAS, DLR, and CODE.
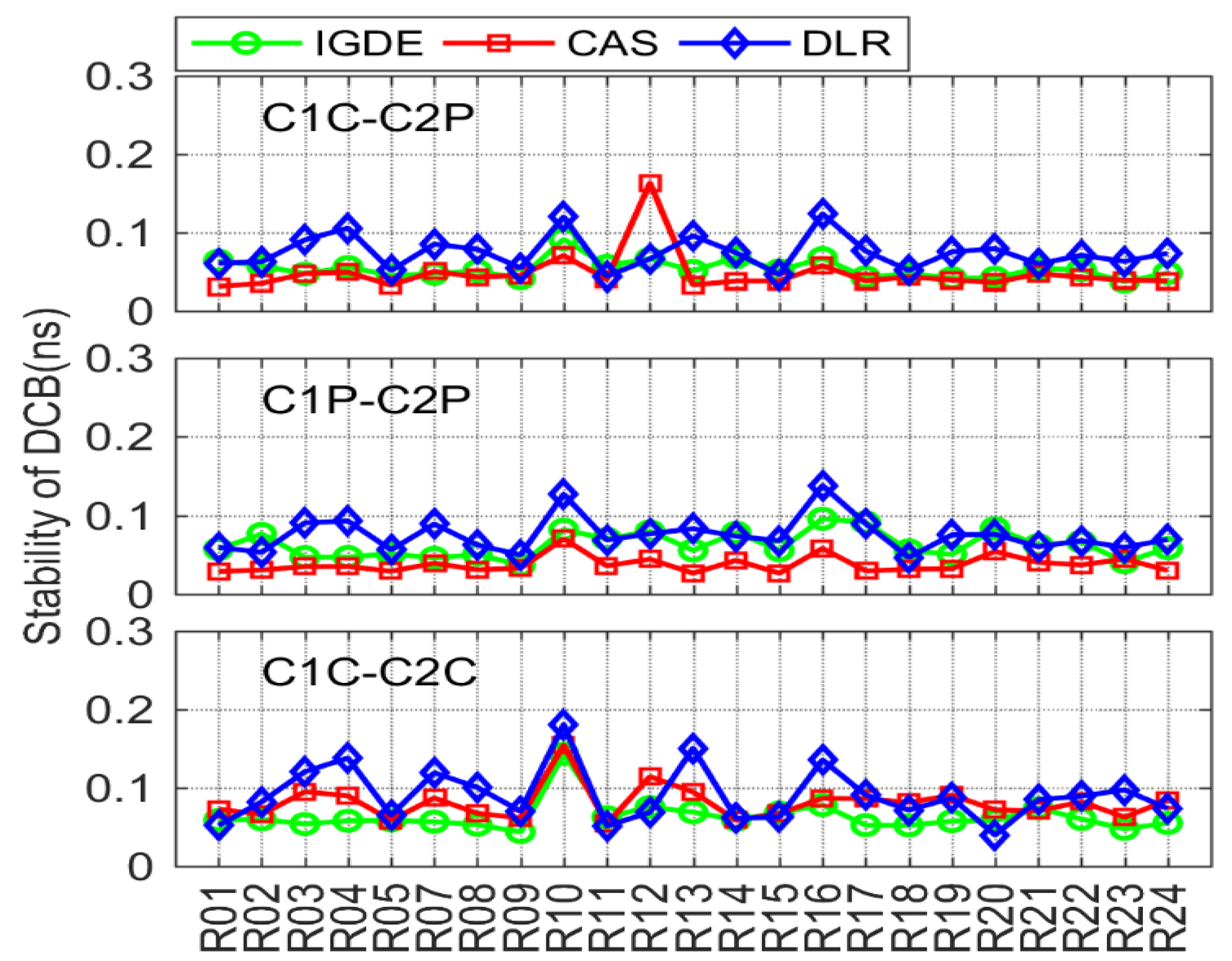
For GLONASS, the comparison of DCB stability through IGDE, CAS, and DLR is shown in Figure 13. Note that the stability of C1P-C2P DCB through CODE could not be obtained due to just the monthly mean value that can be provided by CODE. Obviously, the overall stability of GLONASS DCB satellite was not as good as that of GPS satellite, and the values of three types of DCB were within 0.2 ns. However, some larger values could be seen, e.g., the values of R07, R10, and R16, mainly because few observations could be tracked through these satellites.
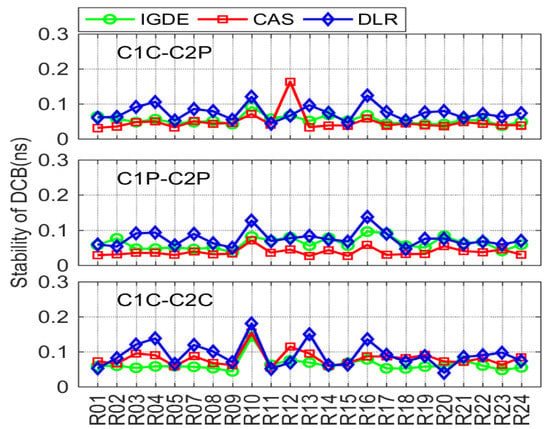
Figure 13.
Stability of the GLONASS DCB obtained by IGDE, CAS, and DLR.
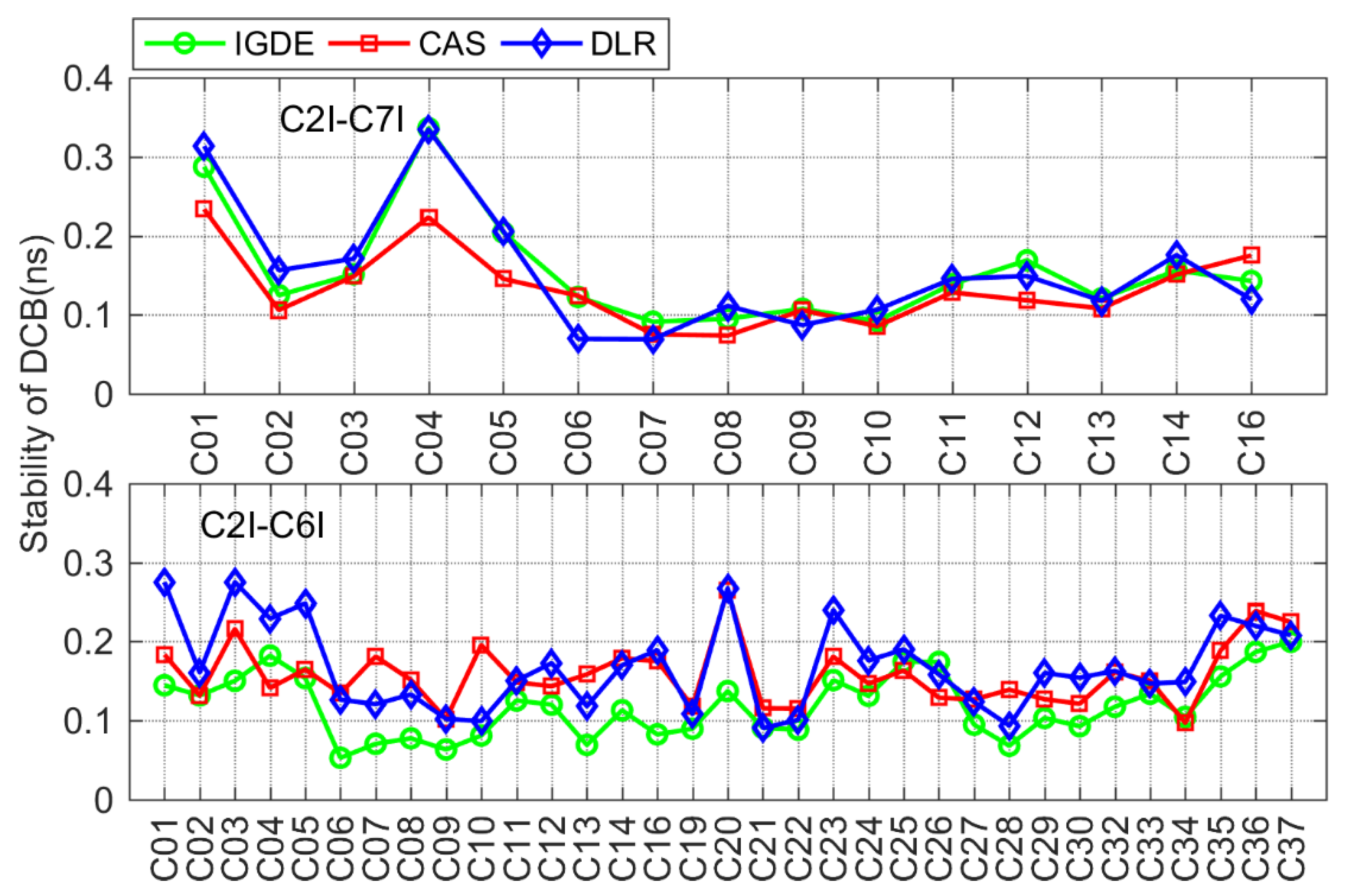
Figure 14 shows the stability of BDS DCB obtained by IGDE, CAS, and DLR, including the results of two types of DCB for BDS-2 and C2I-C6I DCB for BDS-3. As is shown in the figure, the stability of DCB estimated by IGDE was basically consistent with that of the DCB provided by CAS and DLR. The stability of the two types of DCB were mostly within 0.2 ns, with the value of some satellites, including the GEO satellite and some BDS-3 satellites, seeming larger than 0.2 ns, which is mainly related to the observation from the satellite.
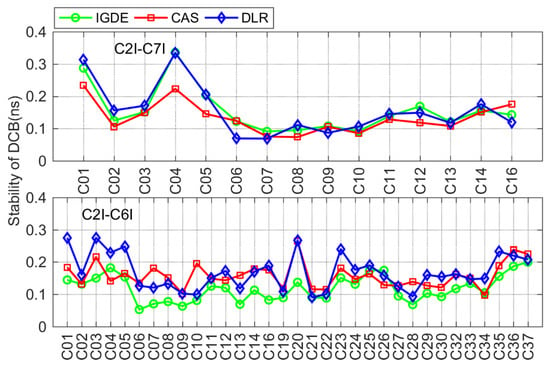
Figure 14.
Stability of the BDS DCB obtained by IGDE, CAS, and DLR.
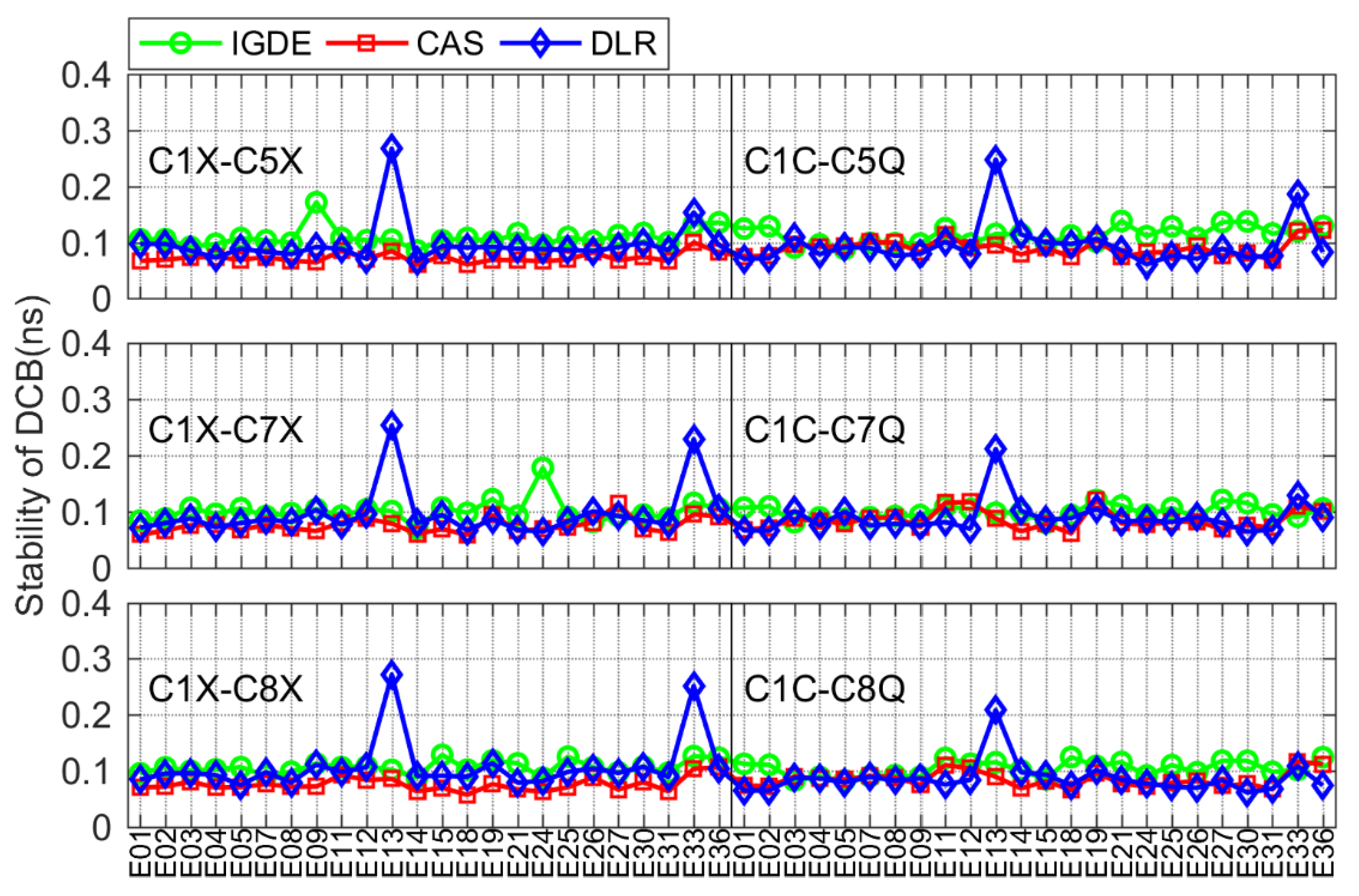
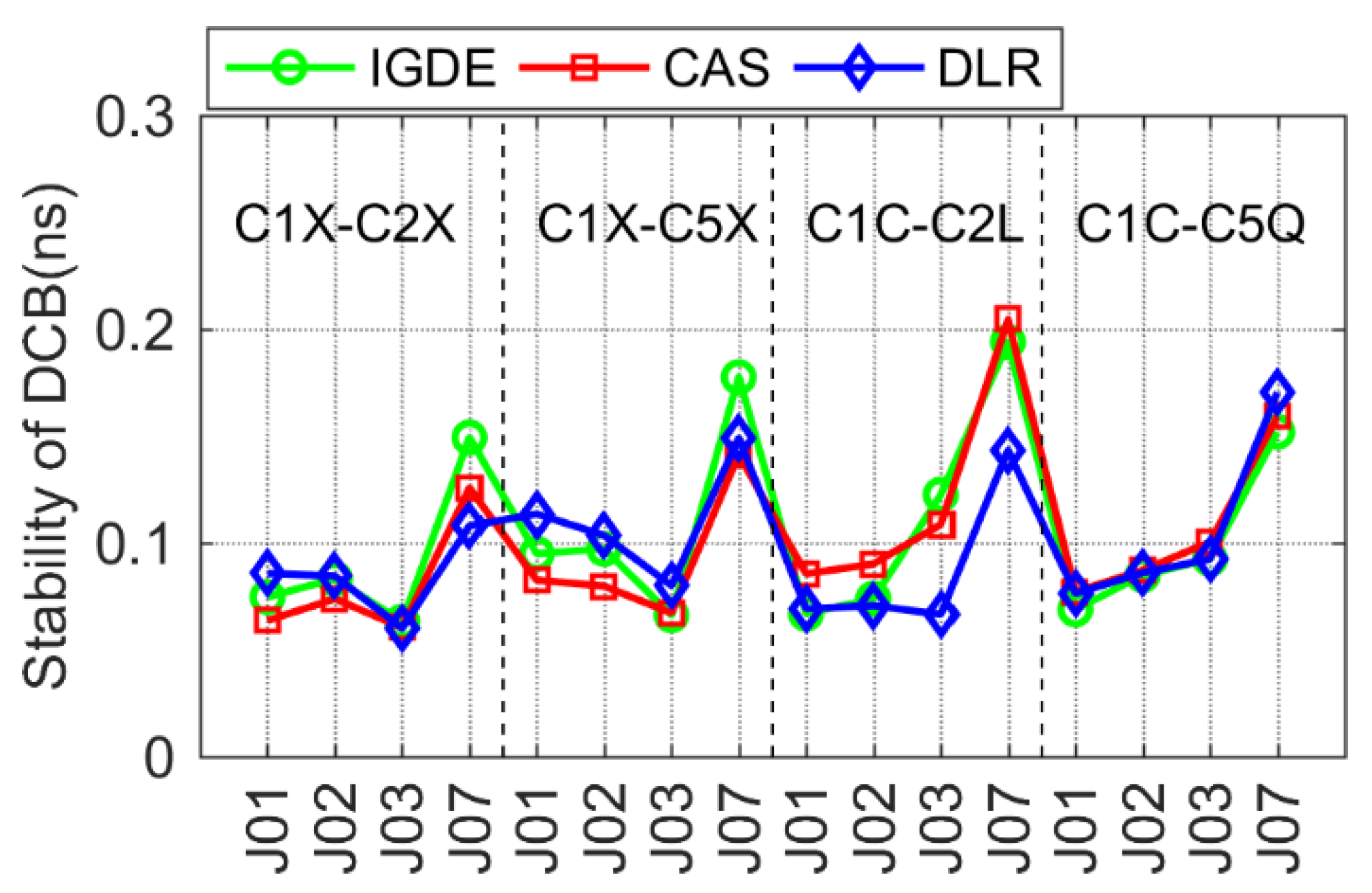
For Galileo and QZSS, the comparison of DCB stability with IGDE, CAS, and DLR is shown in Figure 15 and Figure 16. The DCB stability of most satellites was around 0.1 ns, except for a few satellites, i.e., E33 of Galileo and J07 of QZSS. In particular, the DCB stability of E33 from the DLR product presented a larger value, which may be related to its solution. The value of DCB stability of J07 was larger than that of other satellites, which is mainly related to the few observations of J07.
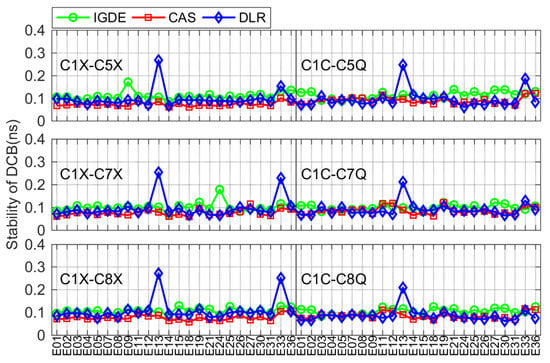
Figure 15.
Stability of the Gaileo DCB obtained by IGDE, CAS, and DLR.
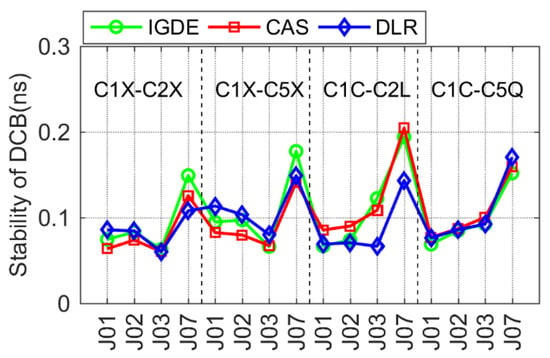
Figure 16.
Stability of the QZSS DCB obtained by IGDE, CAS, and DLR.
It can be seen from the above analysis results that the stability of multi-GNSS DCB through the proposed estimation method (IGDE) and the MGEX DCB product was at the same level. The mean values of stability of DCB estimated by IGDE were 0.07, 0.06, 0.13, 0.11, and 0.11 ns, for GPS, GLONASS, BDS, Galileo, and QZSS, respectively. The good performance of the stability of multi-GNSS DCB estimated by IGDE can be concluded based on the above comparison results.
4. Discussion
A new method is proposed in this study to estimate multi-GNSS DCB based on the consideration that TEC variation is small in single-station areas. A total of 200 days of observations from more than 300 MGEX stations in low-solar-activity periods was collected for experimentation. The verification results from the TEC station in Figure 3 and Figure 4 indicate that good performance of the proposed method was shown at most stations. Thus, it can be said that the processing strategy for the TEC of IPPs in the proposed method is feasible. Although we directly used the TEC of the station instead of the TEC of the IPPs for estimation, many observation data can play the role of adjustment for each station. This means that the TEC of the station is represented by the weighted mean TEC values of the IPPs. However, if the station is in the low-latitude area with active ionospheric variations or there is less observation data from the station, there may be a large deviation in estimated TEC. Since the variance can play a controlling role in the next DCB estimation, the role of the data from these stations may be removed or reduced in the adjustment. Thus, the proposed method shows good performance in multi-GNSS DCB estimation in low-solar-activity periods.
For different systems, the stability of estimated satellite DCB was obviously different; there were also some satellites with large values of stability of DCBs that can be found in the figures, e.g., G04, R10, C01, C04, E13, E33, and J07, which may mainly have been caused by the quality and quantity of data from the satellites.
However, we also tested the DCB estimation during the period of high solar activity in 2015. The result of the estimated GPS DCB is shown in Figure 17; the bias was larger than that in 2019, especially for C1C-C5X. In addition to GPS, DCB estimation of other systems may have had some deviations on some days, which may mainly have been caused by insufficient observation data, because some data were removed due to the failure of the TEC estimation. The method proposed in this paper will continue being studied and improved in the next step to fit the DCB estimation in periods of high solar activity.
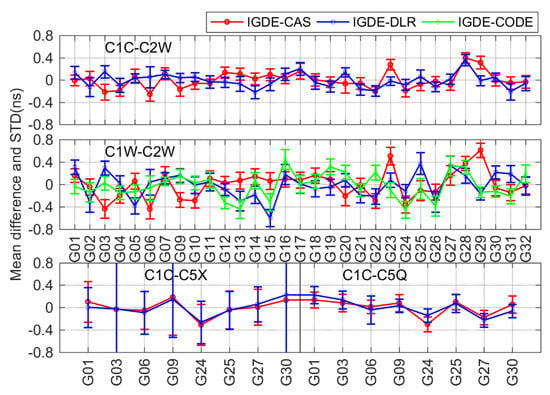
Figure 17.
Mean difference and STD of the GPS DCB between IGDE and MGEX products.
5. Conclusions
In recent years, the rapid development of multi-GNSS has accounted for the strong demand for multiple types of DCBs, instead of just a single type of them from GPS and GLONASS. To estimate multi-GNSS DCB efficiently and accurately, a new method of multi-GNSS DCB estimation without relying on the ionospheric function model and GIM is proposed, which can be implemented in three steps. The first is to extract ionospheric observations based on the geometry-free combination of dual-frequency multi-GNSS code observations. Then, the VTEC of the station represented by the weighted mean VTEC value of the ionospheric pierce points (IPPs) at each epoch is estimated as a parameter together with the combined receiver and satellite DCBs (RSDCBs). Last, the estimated RSDCBs are used as new observations, whose weight is calculated with the use of estimated covariances, and thus the satellite and receiver DCBs of multi-GNSS are estimated.
Nineteen types of multi-GNSS satellite DCBs are estimated based on 200-day observations from more than 300 multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) stations, and the performance of the proposed method is evaluated by comparing with MGEX products. The results show that the mean RMS values were 0.12, 0.23, 0.21, 0.13, and 0.11 ns for GPS, GLONASS, BDS, Galileo, and QZSS DCBs, respectively, with respect to MGEX products, and the stability of estimated GPS, GLONASS, BDS, Galileo, and QZSS DCBs as 0.07, 0.06, 0.13, 0.11, and 0.11 ns, respectively. The proposed method shows a good performance in multi-GNSS DCB estimation in low-solar-activity periods. The method proposed in this paper will continue being studied and improved in the next step to fit the DCB estimation in periods of high solar activity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization of the manuscript idea: Q.W. and S.J.; methodology and software: Q.W.; writing—original draft preparation: Q.W. and X.Y.; writing—review and editing: S.J.; supervision and funding acquisition: Q.W. and S.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) Project (Grant No. 12073012) and the Scientific Research Foundation for Doctor of Xiangtan University (No. 21QDZ55).
Data Availability Statement
The GNSS observation data from the IGS MGEX networks can be obtained at https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gps/data/daily/ (accessed on 1 June 2020). The precise orbit products from GFZ are available at https://www.gfzpotsdam.de/GNSS/products/mgex/ (accessed on 1 June 2020) The GIM products from CODE are available at https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gnss/products/ionex/ (accessed on 1 June 2020). The DCB products provided by CAS and DLR can be obtained at https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gnss/products/bias/ (accessed on 1 June 2020).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledged the DLR and CAS for providing the products and IGS for providing the MGEX data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schaer, S. Mapping and Predicting the Earth’s Ionosphere Using the Global Positioning System; Astronomical Institute, University of Berne: Bern, Switzerland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Huo, X. Estimation and analysis of Galileo differential code biases. J. Geodesy 2017, 91, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.G.; Jin, R.; Li, D. Assessment of BeiDou differential code bias variations from multi-GNSS network observations. Ann. Geophys. 2016, 34, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, S.; Yuan, L.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, J. Estimation and Analysis of BDS-3 Differential Code Biases from MGEX Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, C.; Fan, L.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Gu, S.; Zhong, S.; Song, W. An enhanced algorithm to estimate BDS satellite’s differential code biases. J. Geodesy 2015, 90, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Jin, R.; Kutoglu, H. Positive and negative ionospheric responses to the March 2015 geomagnetic storm from BDS observations. J. Geodesy 2017, 91, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Montenbruck, O.; Tan, B. Determination of differential code biases with multi-GNSS observations. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, B.; Odolinski, R.; Yuan, Y. Combined use of single-frequency data and global ionosphere maps to estimate BDS and Galileo satellite differential code biases. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-K.; Lee, S.J. The influence of grounding on GPS receiver differential code biases. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J.; Orus, R.; Garcia-Rigo, A.; Feltens, J.; Komjathy, A.; Schaer, S.C.; Krankowski, A. The IGS VTEC maps: A reliable source of ionospheric information since 1998. J. Geodesy 2009, 83, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Jin, S.; Feng, G. M_DCB: Matlab code for estimating GNSS satellite and receiver differential code biases. GPS Solutions 2012, 16, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, N.; Hernandez-Pajares, M.; Huo, X. SHPTS: Towards a new method for generating precise global ionospheric TEC map based on spherical harmonic and generalized trigonometric series functions. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardón, E.; Rius, A.; Zarraoa, N. Estimation of the transmitter and receiver differential biases and the ionospheric total electron content from Global Positioning System observations. Radio Sci. 1994, 29, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, W.; Huang, J.; Ma, T.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y. Estimation and analysis of differential code biases for BDS3/BDS2 using iGMAS and MGEX observations. J. Geodesy 2019, 93, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P. Differential Code Bias Estimation Using Multi-GNSS Observations and Global Ionosphere Maps. J. Inst. Navig. 2014, 61, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.; Sanz, J. New approaches in global ionospheric determination using ground GPS data. J. Atmos. Sol-Terr. Phys. 1999, 61, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J.; Aragón-Àngel, À.; García-Rigo, A.; Salazar, D.; Escudero, M. The ionosphere: Effects, GPS modeling and the benefits for space geodetic techniques. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 887–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoh, D.; Onwuneme, S.; Seemala, G.; Jin, S.; Rabiu, B.; Nava, B.; Uwamahoro, J. Assessment of the NeQuick-2 and IRI-Plas 2017 models using global and long-term GNSS measurements. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 2018, 170, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, N. Multi-GNSS triple-frequency differential code bias (DCB) determination with precise point positioning (PPP). J. Geodesy 2019, 93, 765–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, L.; Orliac, E.; Dach, R.; Arnold, D.; Beutler, G.; Schaer, S.; Jäggi, A. CODE’s five-system orbit and clock solution—the challenges of multi-GNSS data analysis. J. Geodesy 2016, 91, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)–achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Khachikyan, R.; Weber, G.; Langley, R.; Mervart, L.; Hugentobler, U. IGS-MGEX: Preparing the ground for multi-constellation GNSS science. Inside Gnss 2014, 9, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Su, K. PPP models and performances from single- to quad-frequency BDS observations. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Ou, J.; Huo, X. Two-step method for the determination of the differential code biases of COMPASS satellites. J. Geodesy 2012, 86, 1059–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, F.; Gong, X. BDS-3 differential code bias estimation with undifferenced uncombined model based on triple-frequency observation. J. Geodesy 2020, 94, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X. On the application of the raw-observation-based PPP to global ionosphere VTEC modeling: An advantage demonstration in the multi-frequency and multi-GNSS context. J. Geodesy 2019, 94, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellenhof, B.H.; Lichtenegger, H.; Collins, J. Global Positioning System: Theory and Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, P.; Han, W.; Ge, M.; Shi, C. Eliminating negative VTEC in global ionosphere maps using inequality-constrained least squares. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. Multi-GNSS contributions to differential code biases determination and regional ionospheric modeling in China. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B. Instrumental Biases in Ionospheric Measurements derived from GPS data. In Proceedings of the ION GPS′93, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 22 September 1993. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).