Plane-Based Robust Registration of a Building Scan with Its BIM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
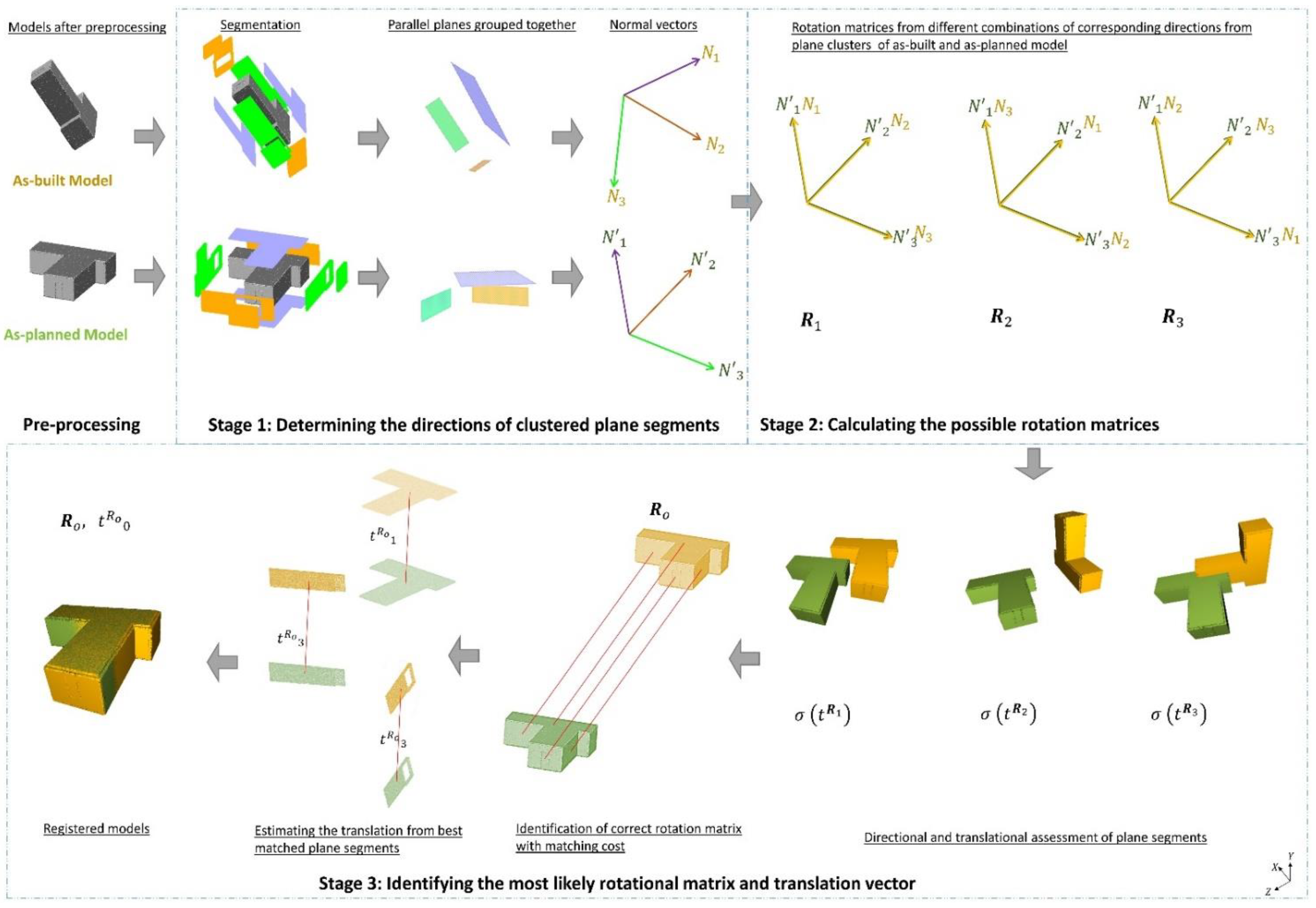
3. Methodology
3.1. Preprocessing
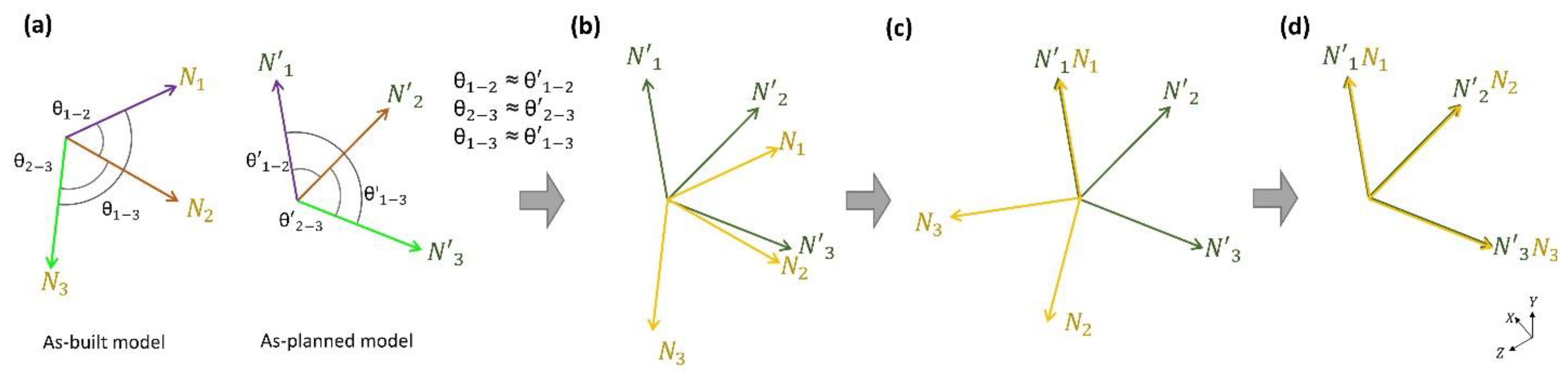
3.2. Determining the Directions of Clustered Plane Segments
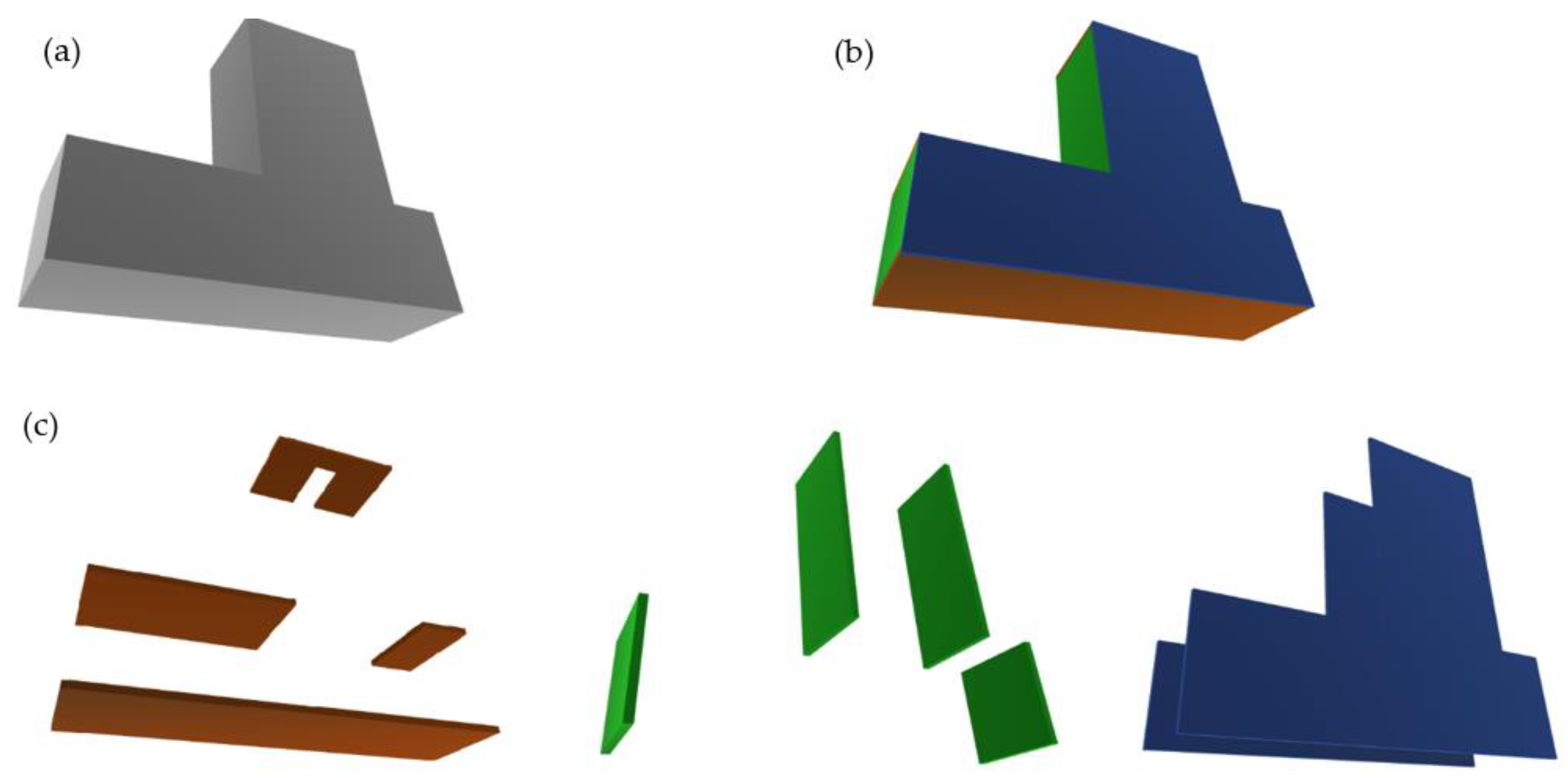
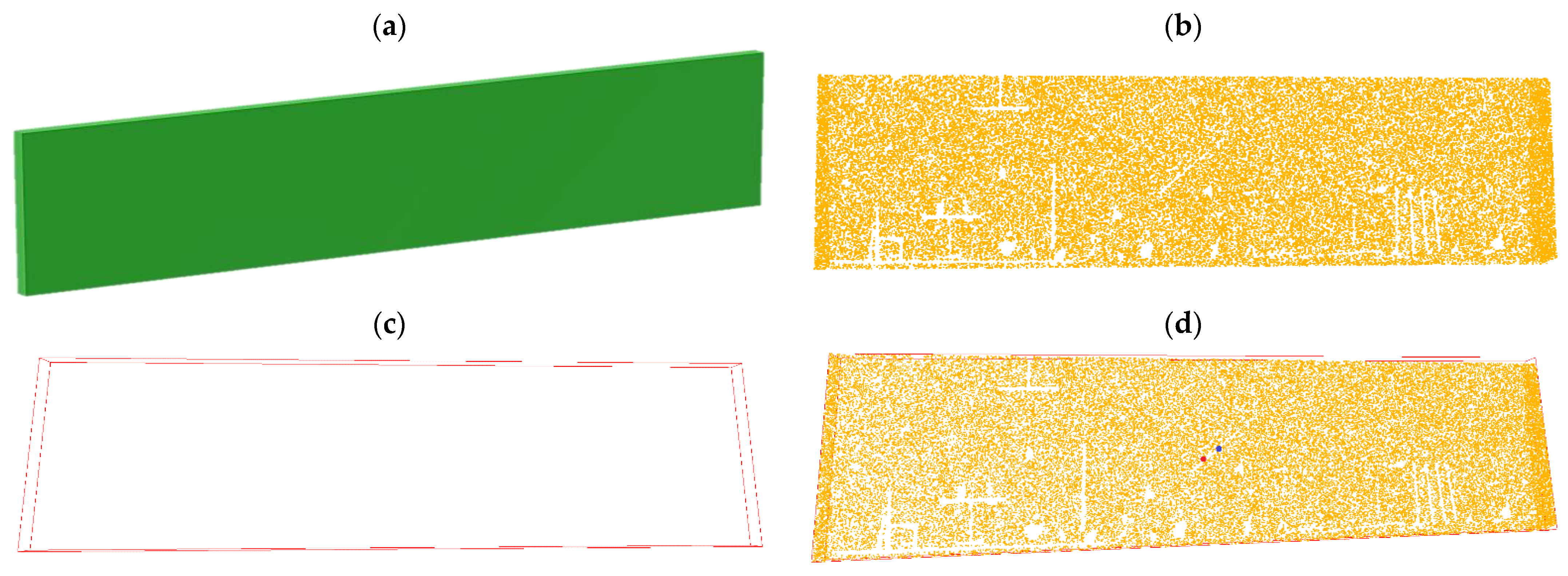
3.2.1. Planar Segmentation
3.2.2. Clustering the Plane Segments
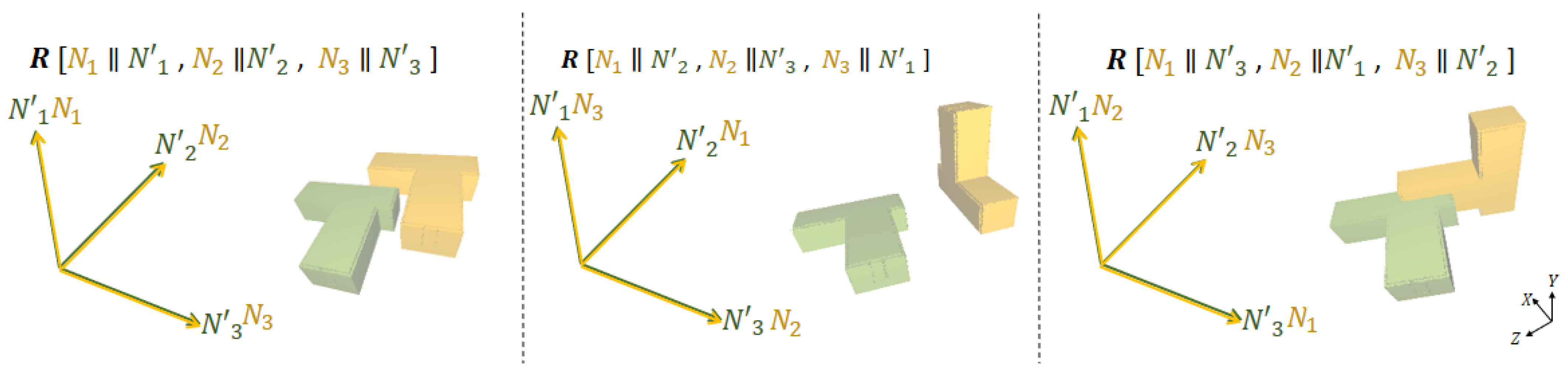
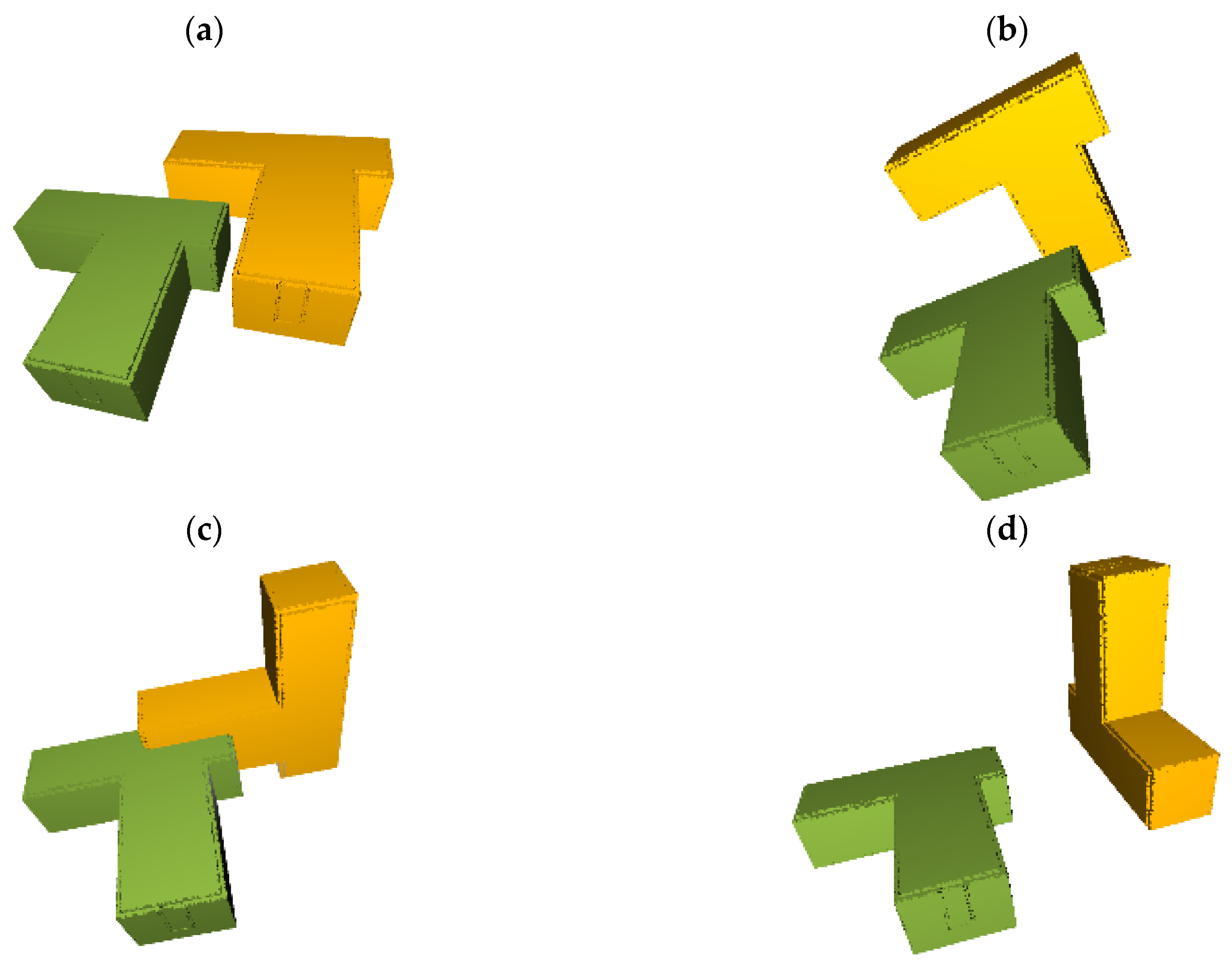
3.3. Calculating the Possible Rotation Matrices
3.4. Identifying the Most Likely Rotation Matrix and Translation Vector
- Matching plane segments between the two models should be parallel to each other.
- The translation between the models should be the same for all matching planar segments.
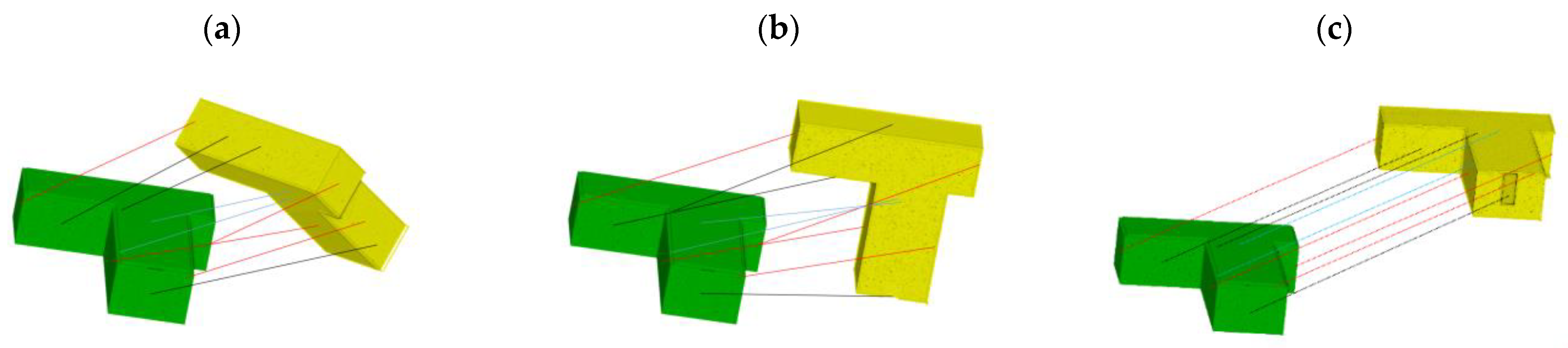
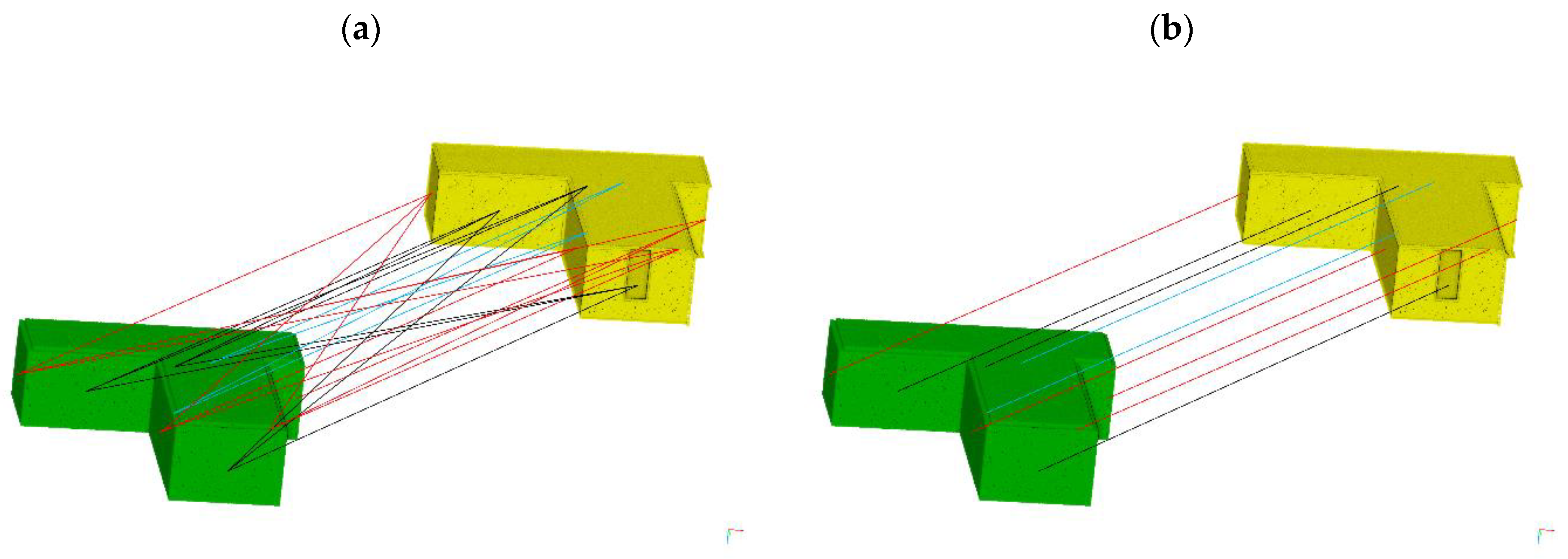
3.4.1. Directional Assessment
3.4.2. Translational Assessment
4. Results
5. Discussion
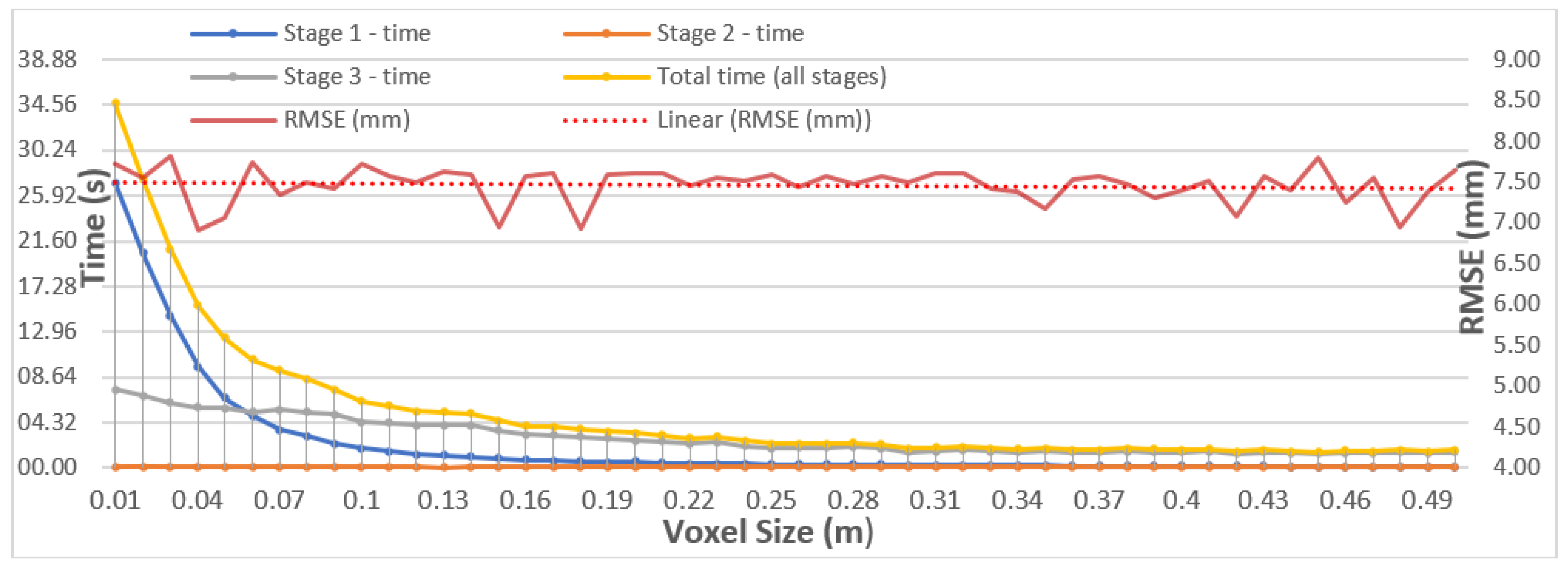
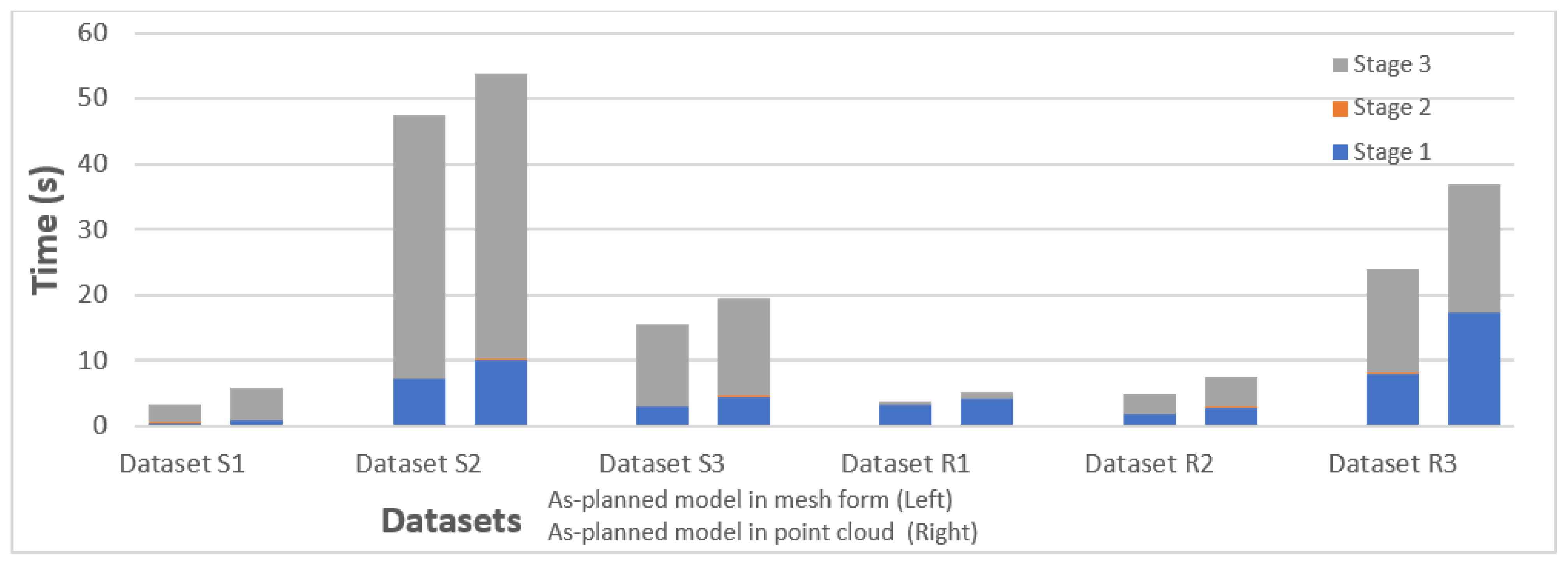
5.1. Time Efficiency
5.2. Registration Accuracy
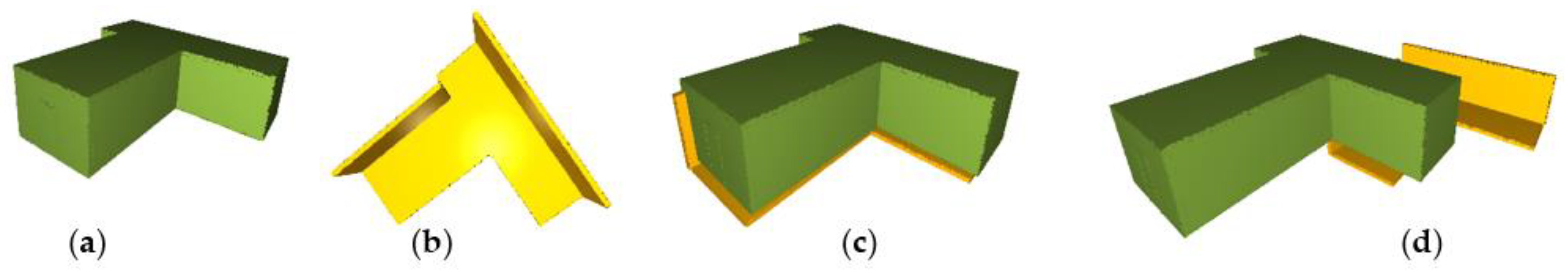
5.3. Effect of Noise and Occlusion
5.4. Application on Partially Constructed Buildings
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bosché, F. Automated recognition of 3D CAD model objects in laser scans and calculation of as-built dimensions for dimensional compliance control in construction. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2010, 24, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navon, R. Research in automated measurement of project performance indicators. Autom. Constr. 2007, 16, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bakis, N.; Lukins, T.C.; Ibrahim, Y.M.; Wu, S.; Kagioglou, M.; Aouad, G.; Kaka, A.P.; Trucco, E. Automating progress measurement of construction projects. Autom. Constr. 2009, 18, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.K.; Golparvar-Fard, M. Automated monitoring of operation-level construction progress using 4D BIM and daily site photologs. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress 2014: Construction in a Global Network, Atlanta, GA, USA, 19–21 May 2014; pp. 1033–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, T.; Nehdi, M.L. Automated Data Collection for Progress Tracking Purposes: A Review of Related Techniques. In Proceedings of the International Congress and Exhibition “Sustainable Civil Infrastructures: Innovative Infrastructure Geotechnology”, Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt, 15–20 July 2017; pp. 391–405. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Li, Y.; Liao, Q.; Ren, Z.; Xie, B. Construction Progress Control And Management Measures Analysis. Smart Constr. Res. 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golparvar-Fard, M.; Savarese, S.; Peña-Mora, F. Interactive Visual Construction Progress Monitoring with D4 AR—4D Augmented Reality—Models. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress 2009: Building a Sustainable Future, Seattle, WA, USA, 5–7 April 2009; pp. 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, A.; Tuttas, S.; Borrmann, A.; Stilla, U. A concept for automated construction progress monitoring using BIM-based geometric constraints and photogrammetric point clouds. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. (ITcon) 2015, 20, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, H.; Dulaimi, M. Using BIM to automate construction site activities. Build. Inf. Model. (BIM) Des. Constr. Oper. 2015, 149, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Pučko, Z.; Šuman, N.; Rebolj, D. Automated continuous construction progress monitoring using multiple workplace real time 3D scans. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 38, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebolj, D.; Pučko, Z.; Babič, N.Č.; Bizjak, M.; Mongus, D. Point cloud quality requirements for Scan-vs-BIM based automated construction progress monitoring. Autom. Constr. 2017, 84, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairadeen Ali, A.; Lee, O.J.; Lee, D.; Park, C. Remote Indoor Construction Progress Monitoring Using Extended Reality. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, H.; Dai, F.; Lourakis, M. Automated as-built 3D reconstruction of civil infrastructure using computer vision: Achievements, opportunities, and challenges. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golparvar-Fard, M.; Pena-Mora, F.; Savarese, S. Monitoring changes of 3D building elements from unordered photo collections. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), 2011 IEEE International Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Golparvar-Fard, M.; Peña-Mora, F.; Savarese, S. Automated progress monitoring using unordered daily construction photographs and IFC-based building information models. J. Comput. Civil. Eng. 2012, 29, 04014025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Degol, J.; Golparvar-Fard, M. Geometry-and Appearance-Based Reasoning of Construction Progress Monitoring. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 144, 04017110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuttas, S.; Braun, A.; Borrmann, A.; Stilla, U. Acquisition and consecutive registration of photogrammetric point clouds for construction progress monitoring using a 4D BIM. PFG–J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2017, 85, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosche, F.; Haas, C.T. Automated retrieval of 3D CAD model objects in construction range images. Autom. Constr. 2008, 17, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Son, H.; Kim, C. Automated construction progress measurement using a 4D building information model and 3D data. Autom. Constr. 2013, 31, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Huber, D.; Akinci, B.; Lipman, R.; Lytle, A. Automatic reconstruction of as-built building information models from laser-scanned point clouds: A review of related techniques. Autom. Constr. 2010, 19, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkan, Y.; Bosche, F.; Haas, C.T.; Haas, R. Automated progress tracking using 4D schedule and 3D sensing technologies. Autom. Constr. 2012, 22, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilakis, I.; Lourakis, M.; Sacks, R.; Savarese, S.; Christodoulou, S.; Teizer, J.; Makhmalbaf, A. Toward automated generation of parametric BIMs based on hybrid video and laser scanning data. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2010, 24, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Omari, S.; Moselhi, O. Integrating 3D laser scanning and photogrammetry for progress measurement of construction work. Autom. Constr. 2008, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, A.; Aryan, A.; West, J.S.; Haas, C.T.; Haas, R.C. Deterioration of UWB positioning during construction. Autom. Constr. 2012, 24, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. Method for registration of 3-D shapes. In Proceedings of the Sensor Fusion IV: Control Paradigms and Data Structures, Boston, MA, USA, 12–15 November 1991; pp. 586–606. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Iterative point matching for registration of free-form curves and surfaces. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1994, 13, 119–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Medioni, G. Object modelling by registration of multiple range images. Image Vis. Comput. 1992, 10, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinkiewicz, S.; Levoy, M. Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Digital Imaging and Modeling, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 28 May–1 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hattab, A.; Taubin, G. 3D rigid registration of cad point-clouds. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computing Sciences and Engineering (ICCSE), Kuwait City, Kuwait, 11–13 March 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bueno, M.; Bosché, F.; González-Jorge, H.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.; Arias, P. 4-Plane congruent sets for automatic registration of as-is 3D point clouds with 3D BIM models. Autom. Constr. 2018, 89, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, E.B.; Tang, P.; Akinci, B.; Huber, D. Assessment of the quality of as-is building information models generated from point clouds using deviation analysis. In Proceedings of the Three-Dimensional Imaging, Interaction, and Measurement, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–27 January 2011; p. 78640F. [Google Scholar]
- Bassier, M.; Vergauwen, M.; Poux, F. Point Cloud vs. Mesh Features for Building Interior Classification. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Ai, M. GESAC: Robust graph enhanced sample consensus for point cloud registration. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 167, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiang, F.; Li, G. A Fast and Accurate Planar-Feature-Based Global Scan Registration Method. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 12333–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Boerner, R.; Yao, W.; Hoegner, L.; Stilla, U. Automated Coarse Registration of Point Clouds in 3D Urban Scenes Using voxel based plane constraint. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 4, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolles, R.C.; Fischler, M.A. A RANSAC-based approach to model fitting and its application to finding cylinders in range data. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 August 1981; pp. 637–643. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-S.; Hung, Y.-P.; Cheng, J.-B. RANSAC-based DARCES: A new approach to fast automatic registration of partially overlapping range images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1999, 21, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontanelli, D.; Ricciato, L.; Soatto, S. A fast ransac-based registration algorithm for accurate localization in unknown environments using lidar measurements. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, Xi’an, China, 22–25 September 2007; pp. 597–602. [Google Scholar]
- Theiler, P.W.; Wegner, J.D.; Schindler, K. Keypoint-based 4-points congruent sets–automated marker-less registration of laser scans. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 96, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, N.; Aiger, D.; Mitra, N.J. Super 4pcs fast global pointcloud registration via smart indexing. In Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 33, pp. 205–215. 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Aiger, D.; Mitra, N.J.; Cohen-Or, D. 4-points congruent sets for robust pairwise surface registration. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 Papers; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Boerner, R.; Yao, W.; Hoegner, L.; Stilla, U. Pairwise coarse registration of point clouds in urban scenes using voxel-based 4-planes congruent sets. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Becker, S. Automatic marker-free registration of terrestrial laser scans using reflectance. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Optical 3D Measurement Techniques, Zurich, Switzerland, 9–12 July 2007; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann, M.; Weinmann, M.; Hinz, S.; Jutzi, B. Fast and automatic image-based registration of TLS data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, S62–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler, P.; Schindler, K. Automatic registration of terrestrial laser scanner point clouds using natural planar surfaces. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 3, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, T.; Hänsch, R.; Hellwich, O. Automatic registration of unordered point clouds acquired by Kinect sensors using an overlap heuristic. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Dong, Z.; Liang, F.; Liu, Y. Automatic registration of large-scale urban scene point clouds based on semantic feature points. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 113, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, B.; Han, S.; Lee, D.-E. BIM-Based Registration and Localization of 3D Point Clouds of Indoor Scenes Using Geometric Features for Augmented Reality. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tan, J.; Liu, H. Pairwise Coarse Registration of Indoor Point Clouds Using 2D Line Features. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Ghanma, M.; Morgan, M.; Al-Ruzouq, R. Photogrammetric and LiDAR data registration using linear features. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Durgham, M.; Habib, A. A framework for the registration and segmentation of heterogeneous LiDAR data. Photogrammetric Eng. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zang, Y. Automated registration of dense terrestrial laser-scanning point clouds using curves. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 95, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Adler, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Planar segment based three-dimensional point cloud registration in outdoor environments. J. Field Robot. 2013, 30, 552–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dold, C.; Brenner, C. Registration of terrestrial laser scanning data using planar patches and image data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.-ISPRS Arch. 2006, 36, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.; Wunderlich, T. Surface-based matching of 3D point clouds with variable coordinates in source and target system. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 111, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Hoegner, L.; Tuttas, S.; Stilla, U. Voxel-and Graph-based point cloud segmentation of 3d scenes using perceptual grouping laws. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 4, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavan, N.L.; dos Santos, D.R.; Khoshelham, K. Global Registration of Terrestrial Laser Scanner Point Clouds Using Plane-to-Plane Correspondences. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Yang, F.; Zhu, H.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Tang, L. An improved RANSAC for 3D point cloud plane segmentation based on normal distribution transformation cells. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnabel, R.; Wahl, R.; Klein, R. Efficient RANSAC for point-cloud shape detection. Comput. Graph. Forum 2007, 26, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurunnabi, A.; Belton, D.; West, G. Robust segmentation in laser scanning 3D point cloud data. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Digital Image Computing Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Fremantle, Australia, 3–5 December 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Gao, X.; Wang, L.; Li, G. Automatic registration of laser-scanned point clouds based on planar features. In Proceedings of the 2nd ISPRS International Conference on Computer Vision in Remote Sensing (CVRS 2015), Xiamen, China, 28–30 April 2015; p. 990103. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, W.S.; Voorhies, R.C.; Itti, L. Finding planes in LiDAR point clouds for real-time registration. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 4347–4354. [Google Scholar]
- Poppinga, J.; Vaskevicius, N.; Birk, A.; Pathak, K. Fast plane detection and polygonalization in noisy 3D range images. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 3378–3383. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, T.; Li, G.; Jiang, M. Robust algorithm for registration of building point clouds using planar patches. J. Surv. Eng. 2012, 138, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Ma, W.; Zha, H. Automatic registration of range images based on correspondence of complete plane patches. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling (3DIM’05), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 13–16 June 2005; pp. 470–475. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, C.; Dold, C.; Ripperda, N. Coarse orientation of terrestrial laser scans in urban environments. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, N.L.; dos Santos, D.R. A global closed-form refinement for consistent TLS data registration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Arditi, D. Automated progress control using laser scanning technology. Autom. Constr. 2013, 36, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Son, H.; Kim, C. Fully automated registration of 3D data to a 3D CAD model for project progress monitoring. Autom. Constr. 2013, 35, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-S.; Ramani, K. Robust principal axes determination for point-based shapes using least median of squares. Comput.-Aided Des. 2009, 41, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgibbon, A.W. Robust registration of 2D and 3D point sets. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 21, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cho, Y.K. Point-to-point comparison method for automated scan-vs-bim deviation detection. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering, Tampere, Finland, 5–7 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wand, M.; Berner, A.; Bokeloh, M.; Jenke, P.; Fleck, A.; Hoffmann, M.; Maier, B.; Staneker, D.; Schilling, A.; Seidel, H.-P. Processing and interactive editing of huge point clouds from 3D scanners. Comput. Graph. 2008, 32, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medioni, G.; Lee, M.-S.; Tang, C.-K. A Computational Framework for Segmentation and Grouping; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bassier, M.; Vergauwen, M. Clustering of wall geometry from unstructured point clouds using conditional random fields. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bassier, M.; Vergauwen, M. Unsupervised reconstruction of Building Information Modeling wall objects from point cloud data. Autom. Constr. 2020, 120, 103338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


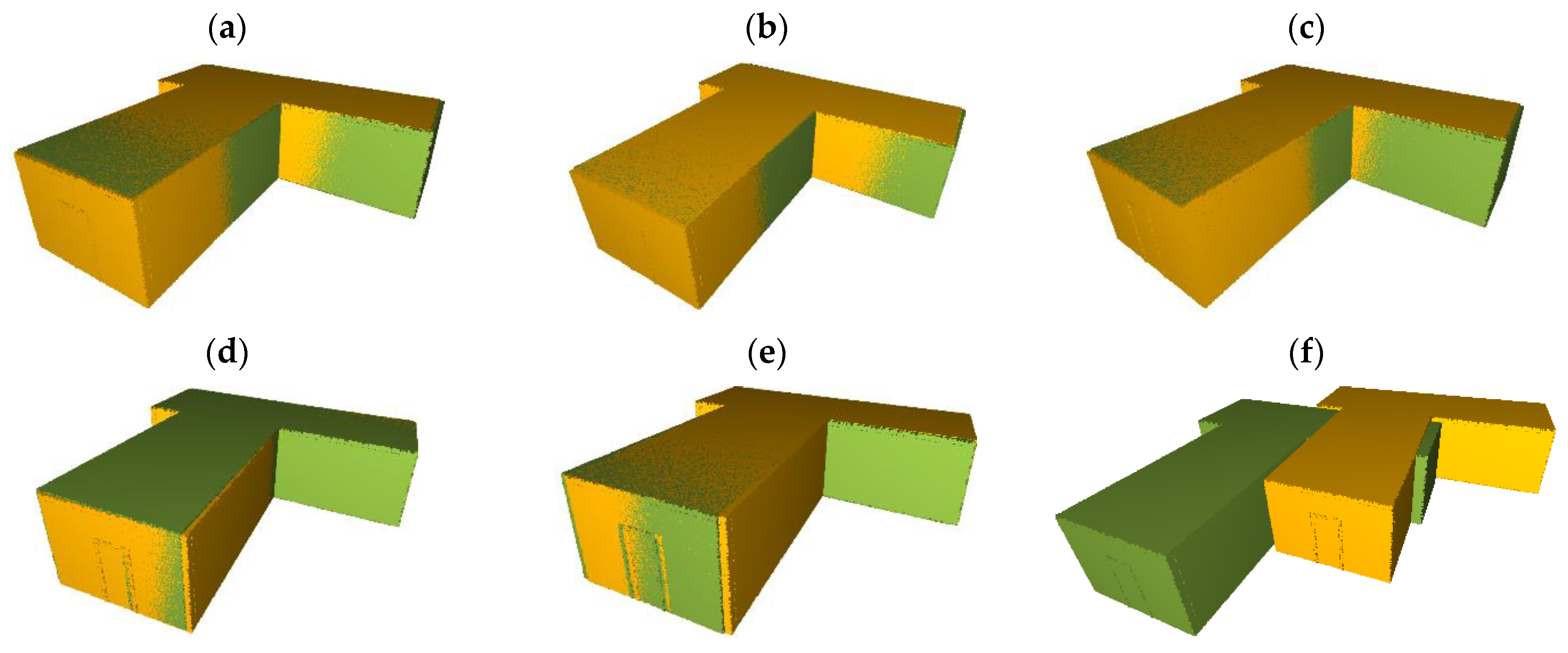
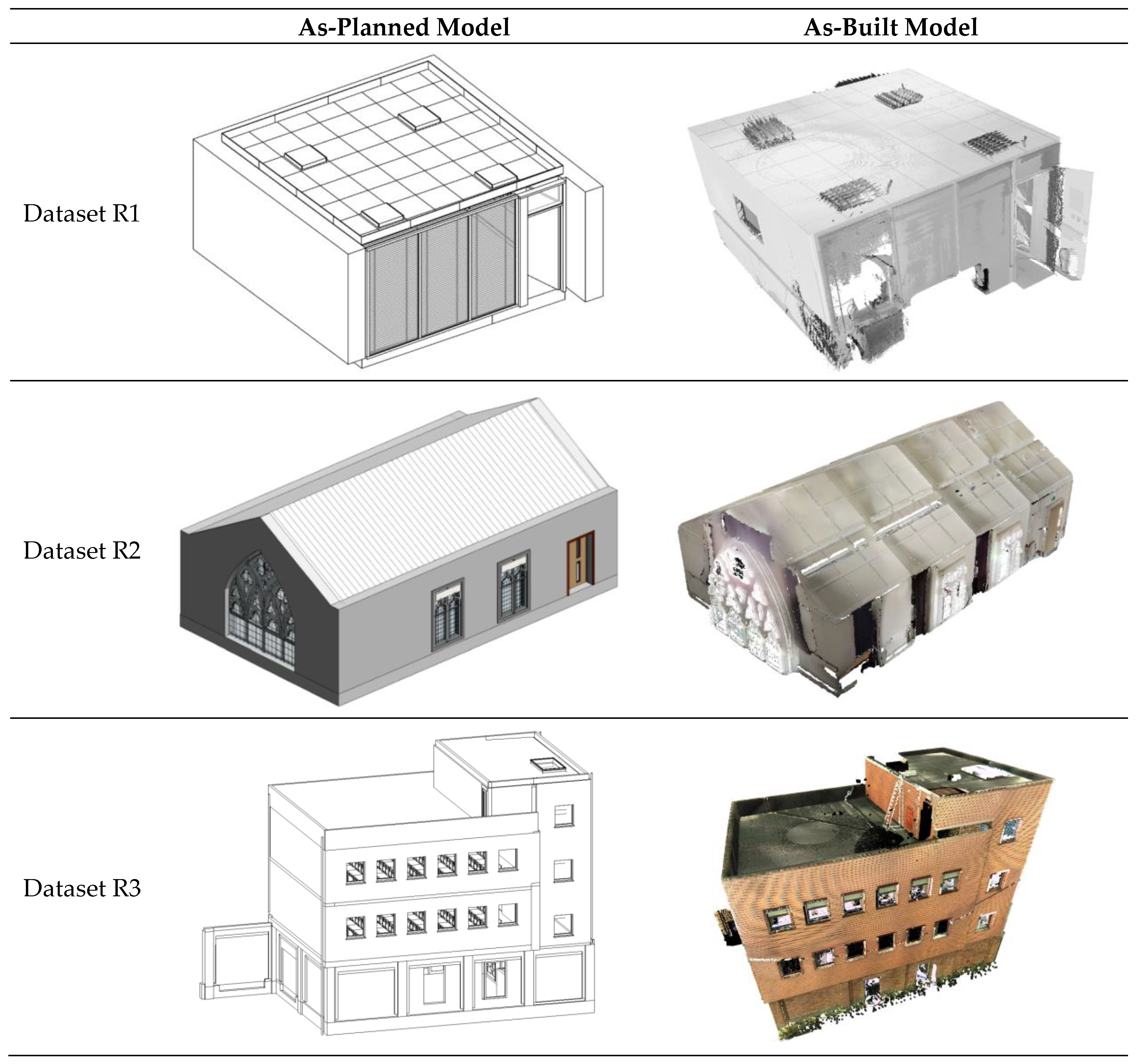
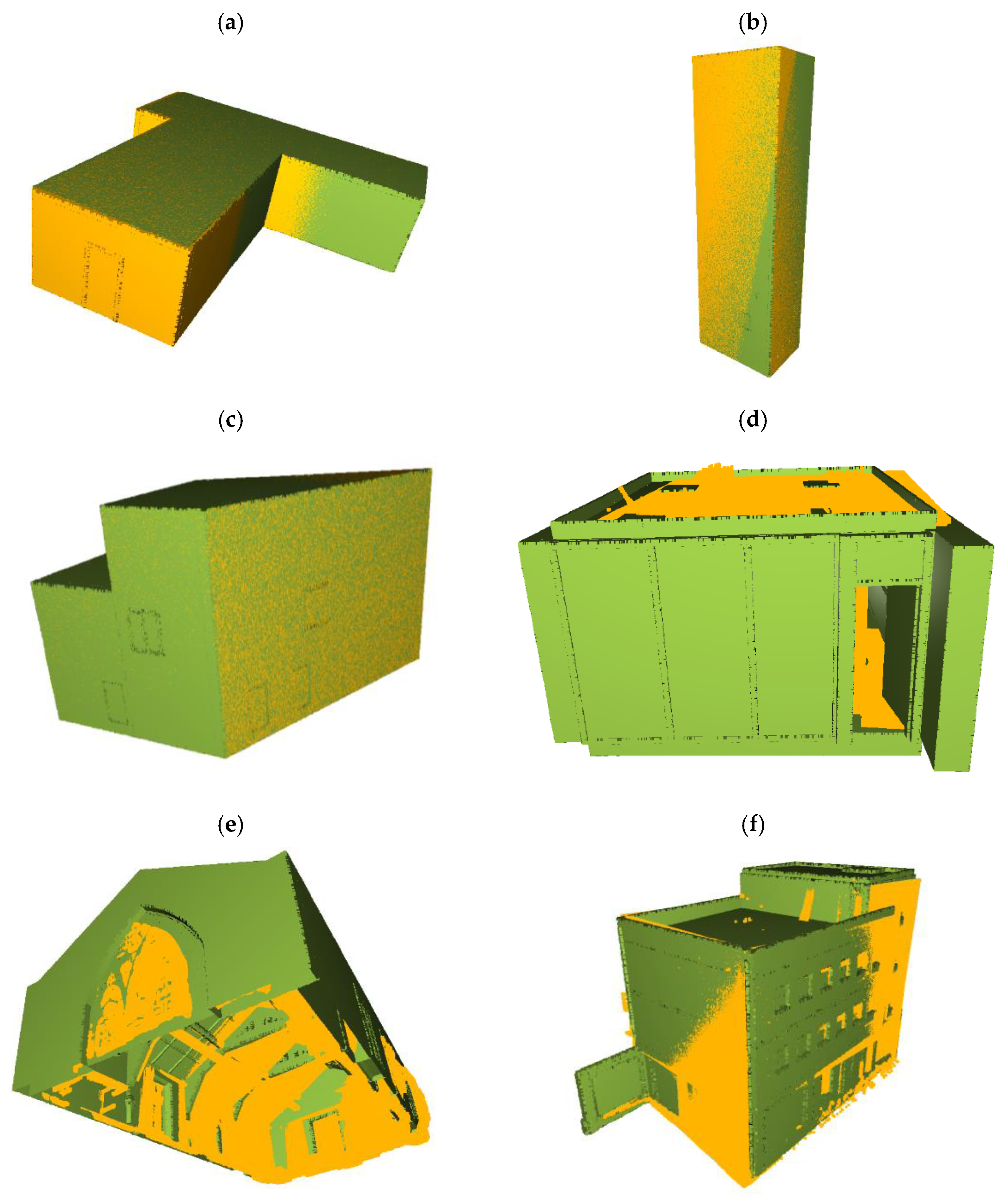
| Dataset S1 | Dataset S2 | Dataset S3 | Dataset R1 | Dataset R2 | Dataset R3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D view of as-built model |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Dimensions from top view (m) |  |  |  |  |  | 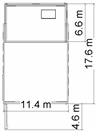 |
| Height (m) | 3 | 27 | 9 | 2.55 | 5.21 | 14.6 |
| Area per floor (m2) | 69 | Each floor: 39.2 | 1st and 2nd floor: 56 3rd floor: 38.8 | 18.7 | 84.2 | 1st, 2nd, and 3rd floor: 200 4th floor: 75 |
| No. of plane segments | 9 | 14 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 10 |
| No. of 3D points in the as-built model | 1,000,006 | 2,485,913 | 1,364,741 | 79,537,667 | 3,580,303 | 64,773,370 |
| Dataset No. | Dataset S1 | Dataset S2 | Dataset S3 | Dataset R1 | Dataset R2 | Dataset R3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of plane segments | 9 | 14 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 10 | ||
| No. of directions from plane segment clusters | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 | ||
| Processing time (s) | 3.18 | 47.43 | 15.48 | 3.96 | 5.01 | 23.92 | ||
| RMSE (mm) | 7.186 | 9.278 | 8.792 | 18.119 | 23.205 | 17.781 | ||
| Matching cost | According to each possible rotation | 0.430 | 1.787 | 0.825 | 2.214 | 1.866 | 3.471 | |
| 4.875 | 15.984 | 3.588 | 4.742 | 4.053 | 8.281 | |||
| 5.040 | 20.721 | 4.350 | 4.985 | 5.095 | 16.335 | |||
| 5.578 | 21.571 | 4.522 | 5.383 | 7.047 | 19.784 | |||
| According to the translation of matching plane segments | 0.430 | 1.787 | 0.825 | 2.214 | 1.866 | 3.471 | ||
| 0.436 | 1.795 | 0.825 | 2.235 | 1.876 | 3.503 | |||
| 0.442 | 1.797 | 0.830 | 2.290 | 2.090 | 3.571 | |||
| 0.444 | 1.800 | 0.855 | 2.477 | 2.364 | 3.864 | |||
| Dataset No. | Processing Time | Error | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 (s) | Step 2 (s) | Step 3 (s) | Total Time (s) | RMSE (mm) | (°) | (mm) | |
| Dataset S1 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 2.58 | 3.18 | 7.186 | 0.007 | 29.164 |
| Dataset S2 | 7.19 | 0.07 | 40.17 | 47.43 | 9.278 | 0.007 | 40.961 |
| Dataset S3 | 2.99 | 0.09 | 12.40 | 15.48 | 8.792 | 0.005 | 35.385 |
| Dataset R1 | 3.23 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 3.69 | 18.119 | 0.027 | 94.267 |
| Dataset R2 | 1.82 | 0.08 | 3.11 | 5.01 | 23.205 | 0.020 | 190.482 |
| Dataset R3 | 8.1 | 0.08 | 15.74 | 23.92 | 17.781 | 0.021 | 107.142 |
| Voxel Sizes (m) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 m | 0.13 m | 0.25 m | 0.37 m | ||
| Standard Deviation of Noise | 0 | 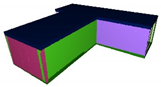 | 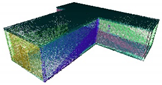 |  | 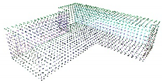 |
| 0.05 |  |  | 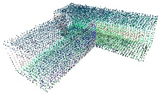 |  | |
| 0.1 |  | 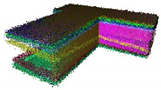 | 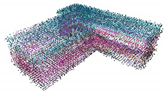 |  | |
| 0.15 | 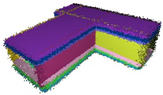 | 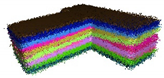 |  | 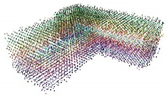 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheik, N.A.; Deruyter, G.; Veelaert, P. Plane-Based Robust Registration of a Building Scan with Its BIM. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091979
Sheik NA, Deruyter G, Veelaert P. Plane-Based Robust Registration of a Building Scan with Its BIM. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(9):1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091979
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheik, Noaman Akbar, Greet Deruyter, and Peter Veelaert. 2022. "Plane-Based Robust Registration of a Building Scan with Its BIM" Remote Sensing 14, no. 9: 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091979
APA StyleSheik, N. A., Deruyter, G., & Veelaert, P. (2022). Plane-Based Robust Registration of a Building Scan with Its BIM. Remote Sensing, 14(9), 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14091979







