Abstract
The long-term stability and sustainability of offshore wind energy resources are very important for wind energy exploration. In this study, the Cyclostationary Empirical Orthogonal Function (CSEOF) method, which can determine the time varying spatial distributions and long-term fluctuations in the cyclostationary geophysical process, was adopted to investigate the geographical and temporal variability of offshore wind resources in China Seas. The CSEOF analysis was performed on wind speeds at 70 m height above the sea surface from a validated combined Quick Scatterometer (QuikSCAT) and Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT) wind product (2000–2016) with high spatial resolution of 12.5 km, and Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR) wind data (1979–2016) with a grid size of 0.5° × 0.5°. The decomposition results of the two datasets indicate that the first CSEOF mode represents the variability of wind annual cycle signal and contributes 77.7% and 76.5% to the wind energy variability, respectively. The principal component time series (PCTS) shows an interannual variability of annual wind cycle with a period of 3–4 years. The second mode accounts for 4.3% and 4.7% of total wind speed variability, respectively, and captures the spatiotemporal contribution of El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) on regional wind energy variability. The correlations between the mode-2 PCTS of scatterometer or CFSR winds and the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI) are greater than 0.7, illustrating that ENSO has a significant impact on China’s offshore wind resources. Moreover, the mode-1 or mode-2 spatial pattern of CFSR winds is basically consistent with that of scatterometer data, but CFSR underestimates the temporal variability of annual wind speed cycle and the spatial changes of wind speed related to ENSO. Compared with reanalysis data, scatterometer winds always demonstrate a finer structure of wind energy variability due to their higher spatial resolution. For ENSO events with different intensities, the impact of ENSO on regional wind resources varies with time and space. In general, El Niño has reduced wind energy in most regions of China Seas except for the Bohai Sea and Beibu Bay, while La Niña has strengthened the winds in most areas except for the Bohai Sea and southern South China Sea.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of human society, the demand for energy has accordingly increased. At the same time, we are facing an increasingly serious environmental crisis [1]. Many countries have been focusing on renewable energy resources that could reduce greenhouse gas forcing and mitigate the effects of climate change [2]. Among them, offshore wind energy resources are especially attractive because they are safe, nonpolluting, and widely distributed with large reserves.
China’s coastal cities are acclaimed as the ‘wealth-belt’ and ‘lifeblood-belt’ of the country. The demand for clean wind energy in these regions is particularly large. Studies have shown that the southeast coast of China has abundant offshore wind potential. The wind energy in the region with water depth between 50 and 100 m is almost twice that in the area with water depth of 0–50 m or 100–250 m [3]. Since the energy performance strength of an offshore wind farm only emerges after about 9 years of operation [4], it is of great significance to explore the stability and sustainability of the renewable offshore wind energy in China Seas. Understanding the variability of regional wind energy resources and the impact of climate oscillations on it is very important not only for short-term wind energy forecasting but also for long-time scale prediction, which is significant for supporting the development and planning of offshore wind farms. The development of offshore wind energy in China Seas will also play an important role in realizing China’s goal to reach its carbon dioxide emissions maximum before 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality before 2060 [5].
High-resolution ocean wind data are crucial for regional offshore wind energy assessment [6]. With the development of remote sensing techniques, sea surface winds with spatial resolution ranging from tens of meters to tens of kilometers can be observed by the scatterometer (e.g., [7,8]), radiometer (e.g., [9,10]) and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) (e.g., [11,12,13]) instrument platforms with high accuracy. Therefore, satellite data have been widely used for offshore wind resource analysis due to their advantages in providing spatial information of wind fields compared with conventional in situ measurements. Among them, the scatterometer data have large spatial coverage and short repetition period. Therefore, the dataset can be utilized not only for local but also for global wind power analysis. Based on scatterometer winds, much work has been performed in evaluating offshore wind resource of southeastern Brazil [14], the Mediterranean Sea [15], the North and Baltic Seas [16], the East and South China Seas [17,18], the coastal area of Morocco [19], and the global ocean [20] as well. However, most of the earlier studies were confined to a single scatterometer such as Quick Scatterometer (QuikSCAT), and the coarser spatial resolution of historical data (25–50 km) limits the evaluation in the coastal regions due to land contamination in the data. Recently, some researchers have used blended winds derived from multiple scatterometers or SAR [21,22,23]. For example, by using a combination of wind data from scatterometers including QuikSCAT, Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT), and Ocean Scatterometer (OSCAT), Arun Kumar [21] analyzed maps of offshore wind speed and wind power density of India on a seasonal and annual basis. Other alternatives for the in situ offshore wind measurements are numerical weather prediction (NWP) model outputs [18,24] and reanalyzed winds [25,26,27], which usually have lower spatial resolution but longer time series compared with satellite observations.
Most of the previous studies have discussed the spatial patterns of the wind speeds on different time scales, i.e., annual, seasonal, and monthly variations, based on various datasets, but the long-term variability and its link with climate change has been rarely investigated [28]. Recently, Wen et al. [29] showed the spatiotemporal patterns of wind resources on intra-annual and decadal time scales in the South China Sea (SCS) by using 55-year model reanalysis dataset. The mechanisms of the variability, however, were not presented. As a pioneering work, Hamlington et al. [30] used the Cyclostationary Empirical Orthogonal Function (CSEOF) method to analyze how the climate oscillation, such as El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), affects land wind resources at wind turbine sites in the United States. Based on the analysis of wind reanalysis data, they concluded that the impact of annual and interannual climate variabilities on wind fields exceeds 30%. Watts et al. [31] presented the economic impact of ENSO in the whole life cycle of a wind energy project in Chile based on wind site measurements located in coast, valley, or highland. By using the Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF) analysis, Yu et al. [32] also investigated the interannual variability of land wind energy in China based on the Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR) dataset and analyzed its link to changes in large-scale circulation. However, little attention has been paid to the effects of climate oscillations on offshore wind resource variations.
In China Seas (Figure 1), the wind climate is part of the East Asian monsoon system. The influences of climate oscillations on the spatiotemporal patterns of wind fields or wind energy are not neglectable [33]. The earlier studies on the study of offshore wind resource in this region were confined to an overall potential assessment using different data sources with relatively coarse spatial resolution, such as NWP model outputs [18,24], reanalysis data [27], and scatterometer data [33], and are limited to a specific period of time. A detailed comprehensive evaluation of the offshore wind energy and possible impact of climate oscillations on it using long-term synergetic scatterometer data and reanalysis have not been attempted thus far.
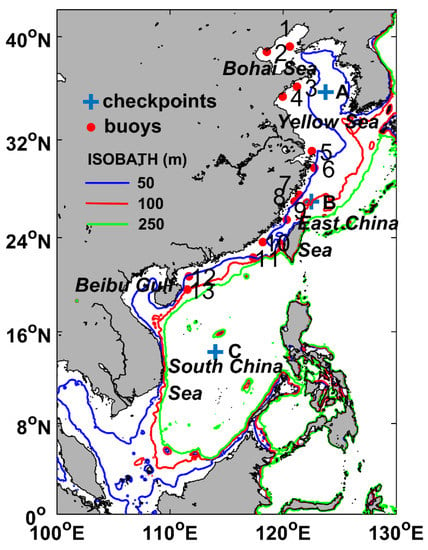
Figure 1.
Geographical distribution of water depth (m) in China Seas. The red dots marked 1 to 13 indicate the locations of the offshore wind buoys. The crosses marked A, B, and C denote the locations of three randomly selected grid points for consistency analysis of ASCAT and QuikSCAT wind products.
The major objective of the present study is to investigate the geographical and temporal variability of wind resources in China Seas based on a combined QuikSCAT and ASCAT coastal wind product from 2000 to 2016 with high spatial resolution of 12.5 km. The CSEOF method was adopted to analyze the scatterometer data and 38 years of CFSR data (1979–2016, grid size 0.5° × 0.5°), and the results were compared. The paper is organized as follows. The data and CSEOF methodology are introduced in Section 2. Section 3 presents the validation results of scatterometer winds and the temporal–spatial variability of the offshore wind resource in the study area. The modulation of wind resource by ENSO events with different intensity levels is discussed in Section 4, followed by a summary in Section 5.
2. Materials and Methods
This section gives a brief introduction of ASCAT and QuikSCAT wind product, CFSR dataset, and in situ measurements of wind vectors from 13 moored buoys deployed in coastal areas of China, which are used for evaluating the accuracy of the ASCAT data. Details of the CSEOF method are also presented in this section.
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Scatterometer Winds and Buoy Measurements
Although the scatterometer wind data record is relatively short compared with some reanalysis data, it has higher spatial resolution, which is helpful to reveal the fine structure of offshore wind resources. Hereby, we will derive a synergetic long-term (17 years) scatterometer wind dataset by combining ASCAT and QuickSCAT products for the wind resource analysis in China Seas (Figure 1).
For ASCAT onboard MetOp-A/B satellites, the gridded daily coastal product from 2007 to 2016 was used in this study. The dataset is distributed by the Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service (CMEMS) and the spatial resolution is 12.5 km. Footprints with land or rain contamination are filtered out from this product, which is especially suitable for wind measurements close to the coast [34]. Standard deviations between zonal and meridional ASCAT wind components and collocated buoy measurements in the period January to March 2017 are 1.71 m/s and 1.78 m/s, respectively. The mean wind speed bias is around 0.04 m/s (refer to [34] for details).
To evaluate the accuracy of ASCAT coastal wind product in China Seas, the along-track dataset was also downloaded and compared against wind vector measurements at 13 moored buoys (Figure 1) located in the coastal region of China during the period between July 2013 and December 2015. The buoy wind field was measured at a height of 10 m above the sea surface and reported hourly. We selected the along-track wind data for evaluation by eliminating all the wind retrievals flagged as rain contamination, over land or over ice.
QuikSCAT was launched in June 1999. It remained fully operational and provided global wind maps every day until November 2009, when the primary instrument antenna stopped rotating due to a mechanical failure of the antenna spin mechanism [35]. Therefore, the gridded daily QuikSCAT coastal product is from August 1999 to November 2009. It has a spatial resolution of 12.5 km and root mean square error (RMSE) of 1.01 m/s in wind speed and 23° in wind direction in the open ocean [36].
2.1.2. CFSR Winds
The CFSR was conceived and implemented as a coupled atmosphere–ocean–land-surface–sea-ice system to offer the best assessment of the condition of these associated domains. In the study area, the spatial resolution of the dataset is 0.5° with a 6 h time interval. The wind speeds in the product show a RMSE and mean bias of 2.30 m/s and 0.16 m/s in China Seas, respectively [37]. Hence, we used the CFSR wind data to show the impacts of climate oscillations on offshore wind resources. In total, about 38 years of CFSR (1979–2010,) and CFSv2 (J2011–2016) data are available for the analysis [38,39] and comparison with the results from scatterometer data.
Usually, the winds at 70 m above the sea surface are used for wind resource assessment. Here, we chose the formula in Hsu et al. [40] to calculate the wind at 70 m from that at 10 m,
where u70 is the calculated wind at height of 70 m (z70); u10 is the input wind at 10 m (z10); z0 is surface roughness and set as an empirical constant 0.003 based on previous work [41,42].
2.2. CSEOF Analysis
In previous work (e.g., [32]), the traditional EOF analysis has been used to study the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of wind energy variations. It assumes that the input data record is a stationary process and decomposes it into the sum of a series of individual modes composed of a single spatial pattern and a corresponding amplitude time series. However, most phenomena in climate science and geophysics are nonstationary and change through time. The fluctuation and evolution of signal over time, e.g., annual cycle, cannot be captured by the traditional EOF analysis, which uses the time independent (stationary) loading vectors (LVs) and principal component time series (PCTS) to represent the spatial patterns and amplitude variations of the analyzed data record. On the contrary, the CSEOF analysis provides an ideal framework for determining the time-varying spatial distributions and long-term fluctuations in the analyzed geophysical process (cyclostationary) due to, e.g., annual cycle modulation, ENSO, and other climate oscillations (refer to [43] and references therein). The method has been successfully applied to reveal low-frequency sea level variability in China Seas [44,45] and the effects of climate oscillations on the change in land wind resource in the United States [30].
The CSEOF decomposes the data record T(r, t) into a set of modes composed of loading vector ‘LV’ and corresponding principal component time series ‘PC’. It is described as:
where ‘d’ is a given nested period and determined based on some physical sense or understanding of the data to be analyzed, and ‘i’ refers to the ith CSEOF mode. In Equation (3), ‘LV’ is time dependent and periodic with ‘d’. When focusing on the annual cycle and ENSO signals, the nested period ‘d’ is defined to be one year [43].
Figure 2 is the flowchart of CSEOF analysis of scatterometer and CFSR wind data. For monthly wind speed dataset, the resulting LV would have 12 spatial patterns from January to December and depict the physical evolution of annual wind speed during the year. The PCTS describes the fluctuations of interannual amplitude of the annual wind speed.
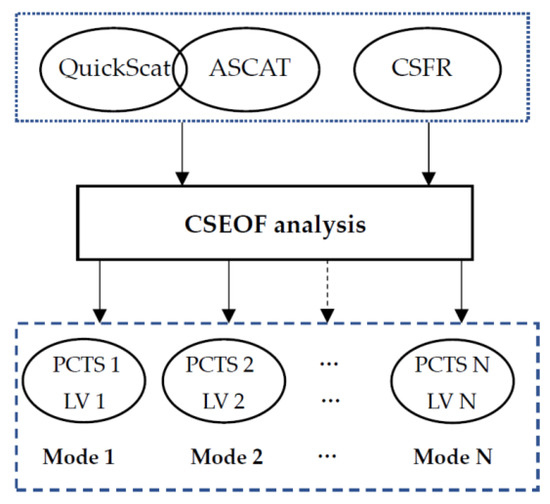
Figure 2.
Flowchart of the CSEOF analysis of scatterometer and CFSR wind data.
3. Results
The accuracy evaluation results of wind vectors observed by ASCAT in coastal waters of China Seas are.
3.1. Validation of Scatterometer Wind Products
Previous studies have shown that the spaceborne scatterometers such as ASCAT and QuikSCAT perform well in observing surface winds over the global oceans (e.g., [46,47,48]). The wind retrieval accuracy may be decreased in coastal regions where the sea surface backscatter signals are contaminated by land. To examine how accurate the ASCAT product is in coastal China Seas, we carried out a systematic comparison of ASCAT winds with in situ measurements from 13 moored buoys along China’s coastline for the period between 2013 and 2015. The time and space window of data matching are 30 min and 12.5 km, respectively. Totally, about 5000 matchup points are available. Results show that ASCAT accurately observes the wind field in the coastal regions except for the Yangtze River estuary, where buoy 5, shown in Figure 1, is located. Because of the complex dynamic environment of the area, there is an abnormal overestimation of the scatterometer wind speeds, which is primarily induced by the influence of thermal fronts or ships on radar backscatter signal (refer to [49] for details). As shown in Figure 3, the mean bias and RMSE between scatterometer wind speed (wind direction) and that were measured by the other 12 buoys are 0.78 m/s (–7.0°) and 1.51 m/s (29.8°), respectively. The bias and RMSE of the wind speeds increase slightly to 1.04 and 1.92 m/s, respectively, even if the wind measurements at buoy 5 are included. This indicates that the high-resolution ASCAT product can accurately capture the wind resource variation in coastal regions of China Seas.
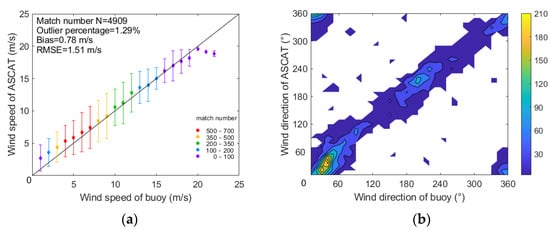
Figure 3.
Validation of the ASCAT wind data against measurements of 12 buoys except for buoy 5 in coastal regions of China Seas: (a) wind speed and (b) wind direction. The colors denote the match number of the collocated data.
To examine the consistency between the ASCAT and QuikSCAT wind products, we compared the wind speed time series at three randomly selected grid points (Figure 1) in the Yellow Sea (124.75°E, 35.75°N), Taiwan Strait (120.75°E, 25°N), and SCS (114°E, 14.25°N) during their overlapping observation period from January 2007 to November 2009. As shown in Figure 4 and Table 1, both scatterometers capture the annual variation in the winds, and almost all correlation coefficients between zonal (U) and meridional (V) wind speed components exceed 0.95. Figure 5a,b shows scatterplots of 35 months of U and V in the whole China Seas. Also, high correlation coefficients (>0.95) and low RMSEs (<0.8 m/s) are observed between the products, which demonstrates that there is a high consistency between the wind observations retrieved by the two sensors. This implies the two datasets could be combined to provide a long-term time series of the sea surface wind field, i.e., a 12.5 km gridded 17-year dataset (2000–2016). The synergetic dataset is suitable to investigate the spatiotemporal variation features of wind resources in China Seas.
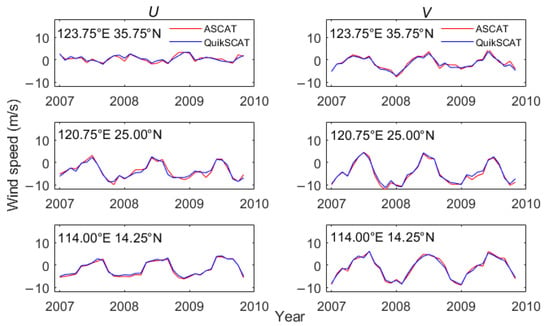
Figure 4.
Comparison of QuikSCAT and ASCAT observed zonal (U) and meridional (V) wind speed time series at three grid points (shown in Figure 1) during the overlapping observation period from January 2007 to November 2009.

Table 1.
The correlation coefficient (R) and mean bias between QuikSCAT and ASCAT wind speed time series at three grid points.
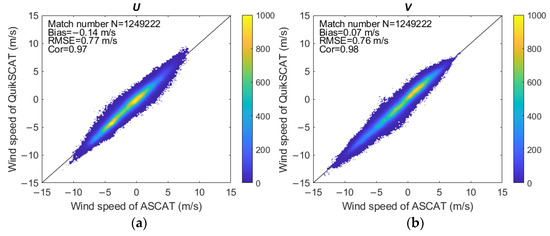
Figure 5.
Comparison of QuikSCAT and ASCAT retrieved zonal (a) and meridional (b) wind speeds in China Seas during the overlapping observation period from January 2007 to November 2009. The colors denote the available match numbers.
3.2. Seasonal Variation in Wind Speeds
Figure 6 shows the seasonal variation in winds at 70 m height above the sea surface calculated from the combined scatterometer product (Figure 6a) and CFSR data (Figure 6b) between 2000 and 2016. One can see obvious monsoon characteristics in the study area. In general, the wind speeds in winter and autumn are higher than that in spring and summer. The strongest northeast wind is dominant and exceeds 10 m/s in winter, especially in Taiwan Strait, Bashi Channel, northeast of the SCS, and south of Vietnam. The weak (<6 m/s) southwest wind is prevalent in summer in most regions of China Seas, but the wind speed is slightly higher south of Vietnam. In spring, the east wind dominates the study area, and a relatively high wind belt exists from northeast Taiwan to southwest Japan. In autumn, the northeast wind turns its direction at lower latitudes south of 12°N. Higher winds are observed in the Taiwan Strait and Bashi Channel. Compared with satellite observations, the model reanalysis (Figure 6b) underestimates the wind speeds in the strong wind regions (e.g., Taiwan Strait, Bashi Channel, and northeast of the SCS), particularly in winter. Thus, the combined datasets are valuable for the wind energy assessment to obtain more accurate estimation of wind power energy in these areas.
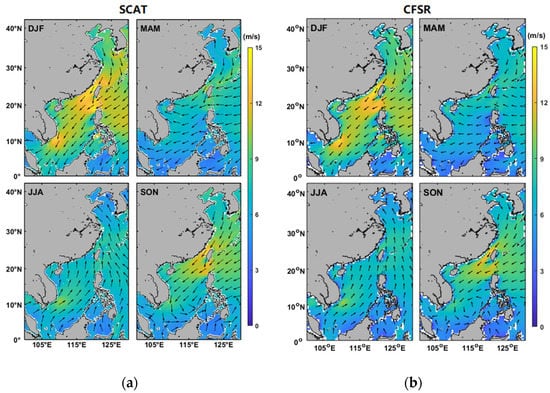
Figure 6.
Seasonal variation in winds at 70 m above sea surface between 2000 and 2016 calculated from the combined scatterometer wind product (a) and CFSR data (b) in winter (DJF), spring (MAM), summer (JJA), and autumn (SON).
3.3. Modulated Annual Cycle Mode
As shown in Figure 7, the cumulative explained variance of the first 28 modes of CSEOF analysis is 98%. When the nested period ‘d’ is set to one year, the first CSEOF mode could capture the variability of annual cycle (e.g., [43,44,45]). Figure 8a,b shows the spatial variability of scatterometer and CSFR seasonal winds. Compared with Figure 6, similar spatial distribution characteristics are observed in the CSEOF first mode and high variations are shown in summer and winter. The corresponding temporal wind variation, which represents the interannual fluctuation of the annual cycle, is shown in Figure 8c. Totally, the annual cycle mode explains about 77% (77.7% for scatterometer and 76.5% for CFSR) of the wind variability. In Figure 8c, relatively stable variations are observed between 2001 and 2006, followed by significant amplitude changes since 2007. In CSFR temporal time series, positive peak variability is observed in 1984, 1989, and 1997. The power spectrum density of mode-1 PCTS (Figure 8d) shows that both datasets present a significant period of 3–4 years.
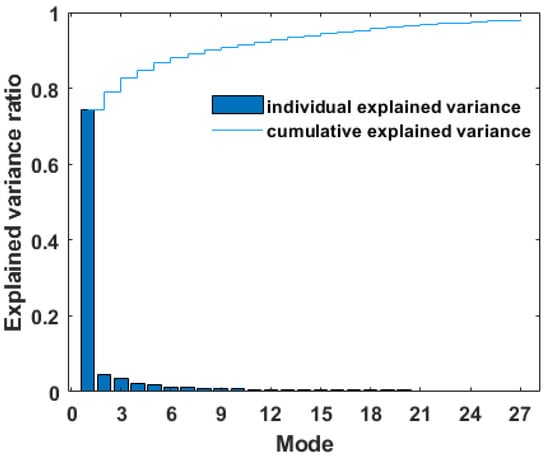
Figure 7.
Explained variance of the first 28 CSEOF modes with cumulative explained variance of 98%.
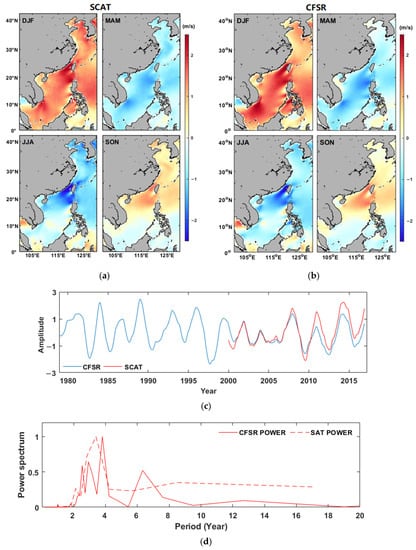
Figure 8.
The LVs of CSEOF first mode of scatterometer (a) and CSFR (b) wind speeds, corresponding PCTS (c), and power spectrum density (d).
Compared with former studies [1,17,29], similar spatial patterns of monthly wind speed are observed in the study area from both satellite observations and model reanalysis, particularly northeast of SCS. Moreover, our study shows more details of wind information in summer with reversed phase at 70 m than that at 100 m above the sea surface in [29], and reveals the temporal evolution of the monthly spatial patterns on an interannual time scale. The amplitude of the temporal variability of annual wind cycle implies that the change in annual cycle should be considered in regions with rich wind resources.
As shown in Figure 8, the spatial pattern of mode-1 CFSR wind is basically consistent with that of scatterometer data, but the latter shows stronger variability in amplitude with peak values appearing in the same years. This implies the model reanalysis may underestimate the temporal variability of annual wind speed cycle. It is therefore very necessary to apply long-term and high-resolution satellite wind data in offshore wind resource monitoring and assessment.
3.4. ENSO Mode
To assess the contribution of known climate oscillations to the temporal variability of a particular physical property, the PCTS from the CSEOF decomposition is usually compared with ENSO indexes such as the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI). We adopted the method to analyze the effects of ENSO on wind speeds in the study area. Figure 9 illustrates the LVs of the second CSEOF mode of scatterometer and CFSR wind speeds. The corresponding PCTS in Figure 10 accounts for 4.3% and 4.7% of total wind speed variability, respectively.
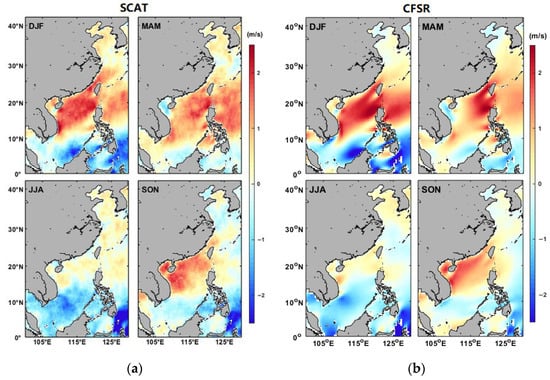
Figure 9.
The LVs of CSEOF second mode of scatterometer (a) and CSFR (b) wind speeds.
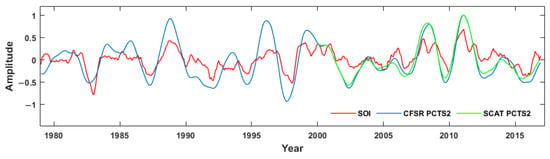
Figure 10.
The PCTS of CSEOF second mode of scatterometer (green) and CSFR (blue) wind speeds. The red line denotes the time series of ENSO index SOI.
In Figure 9, the two datasets present similar spatial characteristics in four seasons and the scatterometer winds show stronger variability than reanalysis data, especially in Taiwan Strait, south of Hainan Island, east of Vietnam, and Bashi Channel in winter. Opposite influences are observed in the northern and southern SCS. As shown in Figure 10, both the scatterometer and CSFR PCTSs exhibit a strong relationship with SOI. The correlation coefficients are 0.72 and 0.78, respectively. The two datasets also show highly consistent wind speed variability since 2000. In strong El Niño (e.g., 1982/1983, 1997/1998) or La Niña (e.g., 1988/1989, 2010/2011) years, significant negative or positive wind speed amplitude peaks are observed, implying that ENSO has a great impact on offshore wind energy resource during the period.
4. Discussion
The CSEOF analysis of both scatterometer and reanalysis data shows that ENSO plays an important role in affecting the wind resource in China Seas. In this section, to quantify the contribution of ENSO to the variability of offshore wind energy over a longer time scale, we further analyzed the wind speed variations during different ENSO events from 1979 to 2016 by using CFSR data at 70 m height. Table 2 lists the intensity of ENSO events classified based on the ONI (Oceanic Niño Index). Figure 11 shows the statistics of the monthly ENSO event frequency. Very strong ENSO events always occur in autumn and winter. Extremely strong El Niño mainly occurs between October and January. For strong La Niña events, the occurring frequency exceeds 10% from November to January. The ENSO events are not significant in other months.

Table 2.
Classification of ENSO event intensity using the ONI index (the ONI in the range [–0.5, 0.5] denotes the normal status).
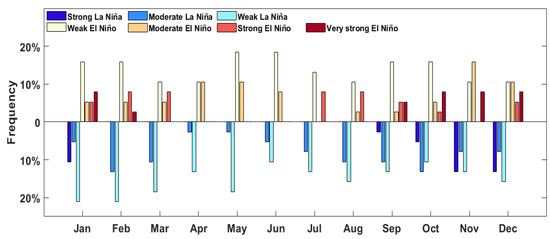
Figure 11.
The ENSO event frequency between 1979 and 2016.
Figure 12 shows the percentage change in wind speed during different ENSO events. One can see that the impacts of El Niño and La Niña on wind resources in China Seas are almost completely opposite. In general, El Niño has reduced the wind energy in most regions of China Seas except for the Bohai Sea, Beibu Gulf, and northwest of Brunei. The largest reduction of about 10% occurs in west and north of Philippines. On the contrary, the wind has been strengthened by about 8% during La Niña events except in the Bohai Sea and southern SCS. Similar changes in wind speeds during El Niño or La Niña phases have been observed in an offshore area of Qatar [50] and Red Sea [51]. Moreover, the SCS is more affected by ENSO events than other regions of China Seas. The wind speed variation in the Bohai Sea is opposite to that in the northern and central SCS. In general, the effects of ENSO are not significant in the Yellow Sea.
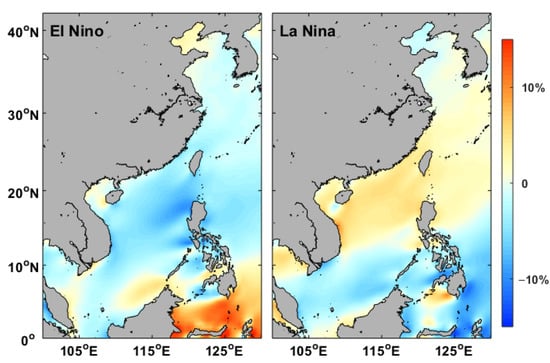
Figure 12.
The percentage change in wind speed during El Niño and La Niña events between 1979 and 2016.
To demonstrate the impacts of ENSO events intensity on wind energy distribution, Figure 13 shows the percentage change in wind speed at different ENSO intensity levels, i.e., weak, moderate, strong, and very strong El Niño/La Niña events. Generally, the change ranges from –10% to 10%. For the El Niño case, the weakening of wind speed is observed in most of the deep-water regions in China Seas. The enhancements of wind can be seen in coastal regions of SCS under moderate and strong/very strong El Niño conditions. The wind has increased in the SCS during moderate and strong La Niña cases but decreased in the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Moreover, the effects are more significant for the moderate La Niña case, particularly in shallow waters along the south coast of China due to the obvious increase in wind speed in spring (Figure 14b).
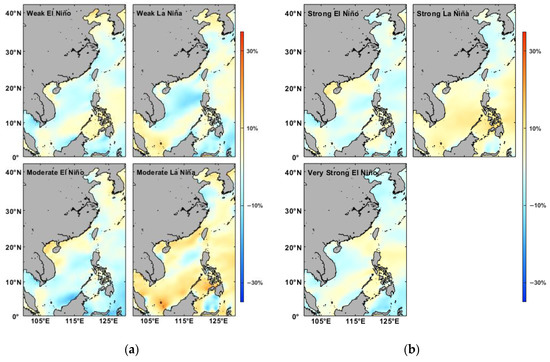
Figure 13.
The percentage change in wind speed at different ENSO intensity levels: (a) Weak (upper panel) and moderate (lower panel) ENSO events; (b) Strong (upper panel) and very strong (lower panel) ENSO events.
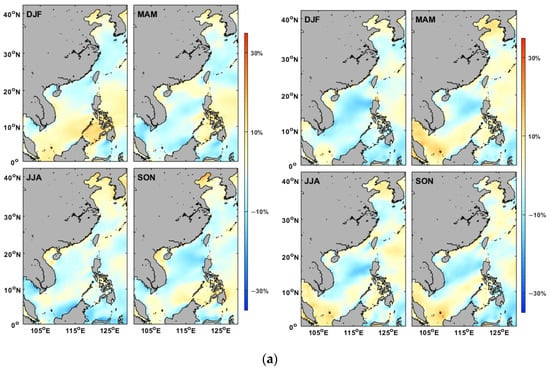
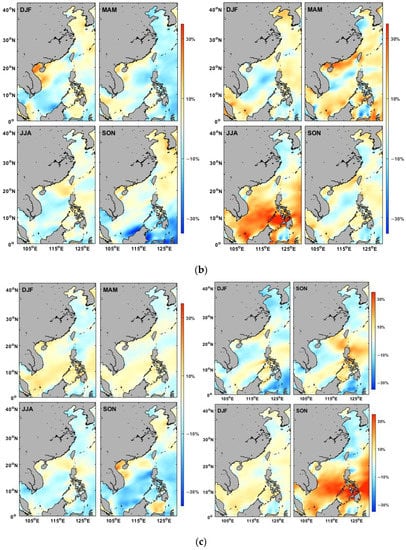
Figure 14.
The percentage change in wind speed during different ENSO events: (a) weak El Niño (left) and La Niña (right), (b) moderate El Niño (left) and La Niña (right), and (c) strong El Niño (left), very strong (top right), and strong La Niña (lower right).
For ENSO events with different intensities, the percentage change in wind speed during various ENSO event categories in each season may also vary with each other. As shown in Figure 14, in weak ENSO cases (Figure 14a), the wind power has generally strengthened in the Bohai Sea and coastal regions but weakened in the open ocean and central SCS. Moderate ENSO events (Figure 14b) could also enhance the wind energy in most of the coastal areas, particularly in the SCS. The increase in wind speed is remarkable in the Beibu Gulf and along the south coast of China during moderate El Niño/La Niña events in winter/spring. During strong El Niño events (Figure 14c), the reduction in wind speed is obvious in most areas of the East China Sea throughout the year, while the wind speed in the Beibu Gulf has increased, especially in autumn. The spatial patterns demonstrate the seasonal impacts of ENSO should be considered in the development of regional wind farms.
5. Conclusions
Currently, assessment of the wind resource in China Seas and understanding its interannual changes are generally based on wind speeds from in situ observations (e.g., wind tower), relatively short time series of scatterometer products, or NWP model outputs and reanalysis wind data with coarse spatial resolution. Under these circumstances, it is difficult to accurately and comprehensively grasp the geographical distribution of the offshore wind energy and reveal its fine structure. Moreover, traditional data analysis methods such as EOF may neglect the interannual variability of wind annual cycle and the influences of natural internal climate oscillations on regional wind resource variation over a long time scale.
In this work, based on combined 17-year (2000–2016) high-resolution scatterometer wind products and 38-year (1979–2016) model reanalysis data, the CSEOF method was utilized to explore the spatiotemporal variability of offshore wind energy in China Seas and the impacts of climate oscillation on it. The synergetic scatterometer wind dataset was derived from the combination of sea surface wind fields observed by QuikSCAT and ASCAT with high spatial resolution of 12.5 km. The mean bias and RMSE between ASCAT wind speed and in situ measurements at 13 moored buoys in coastal areas of China are 1.04 m/s and 1.92 m/s, respectively. These values decrease to 0.78 m/s and 1.51 m/s, respectively, if the abnormal buoy observations in the Yangtze River estuary are removed, which may be caused by the influence of frequently sailing ships or thermal fronts on radar backscatter signal. The RMSEs of both zonal and meridional wind speeds obtained from the consistency analysis of QuikSCAT and ASCAT wind vectors are less than 0.8 m/s, and correlation coefficients are greater than 0.97. The results indicate that the combined scatterometer winds are accurate enough for analyzing the offshore wind resource variability in China Seas.
The first mode of CSEOF analysis of the evaluated scatterometer wind data and model reanalysis at height of 70 m above sea surface reveals that the wind annual cycle contributes about 77% to the wind variability in both datasets. The LVs of the annual wind cycle demonstrate the significant spatial variations of wind energy in the offshore area of the SCS, especially in winter and summer, when the wind changes into reverse phase. The PCTS shows the interannual variability of annual cycle with a period of 3–4 years. The CSEOF second mode captures the contribution of ENSO to regional wind energy changes in time and space. The correlation coefficients between PCTS of scatterometer wind product or reanalysis data and SOI are greater than 0.7, suggesting that the temporal change in wind energy is highly correlated with ENSO.
Overall, the mode-1 or mode-2 spatial pattern of CFSR winds is basically consistent with that of scatterometer data, but CFSR underestimates the temporal variability of annual wind speed cycle and the spatial changes of wind speed related to ENSO in the study area. Compared with reanalysis data, scatterometer winds always show a finer structure of wind energy variation due to its higher spatial resolution.
For ENSO events with different intensity levels, the remarkable spatial patterns of wind variations imply the complexity of the impact of ENSO on regional wind resources in different seasons. In general, El Niño reduces the wind energy in most areas of China Seas except for the Bohai Sea and Beibu Bay, and La Niña increases the wind energy in the SCS. The percentage change in wind speed varies with space and season.
In conclusion, with the use of CSEOF method, the spatial and temporal variability characteristics of annual wind speed in China Seas are revealed from both satellite remote sensing data and model reanalysis, which have been ignored in previous work using the EOF or vector EOF methods. This study also quantified the contribution of ENSO to regional wind energy. It is suggested that the variability of annual wind cycle and impacts of ENSO should be considered in the model simulations for more accurate wind resource prediction over a long time scale. The findings of this study could provide scientific basis for regional and local wind resource assessment and wind farm site planning.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.X. and Y.C.; methodology, Y.C.; data curation, Z.Z.; formal analysis, Y.L. and X.Y.; investigation, Y.L. and Y.C.; visualization, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.X. and Y.L.; writing—review and editing, Q.X. and Y.C.; supervision, Q.X.; funding acquisition, Q.X. and Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41976163 and 41876211); the Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou) (Grant No. GML2019ZD0602), and the Guangdong Special Fund Program for Marine Economy Development (Grant No. GDNRC (2020)050).
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. Sources for the datasets are as follows. The along-track data are available at EUMSETSAT: https://www.eumetsat.int/website/home/Data/DataDelivery/EUMETSATDataCentre/index.html (accessed on 1 January 2022); The gridded ASCAT data are available at CMEMS: http://marine.copernicus.eu/services-portfolio/access-to-products/?option=com_csw&view=details&product_id=WIND_GLO_WIND_L3_REP_OBSERVATIONS_012_005 (accessed on 1 January 2022); The QuikSCAT data are downloaded from: http://coastwatch.pfeg.noaa.gov/erddap/griddap/erdQSwind1day.html (accessed on 1 January 2022); The CFSR and CFSv2 data are available at: https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds093.0 (accessed on 1 January 2022); https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds094.1] (accessed on 1 January 2022).
Acknowledgments
We highly appreciate the editor and reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| ASCAT | Advanced Scatterometer |
| CFSR | Climate Forecast System Reanalysis |
| CMEMS | Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service |
| CSEOF | Cyclostationary Empirical Orthogonal Function |
| DJF | December, January, February |
| ENSO | El Nino Southern Oscillation |
| EOF | Empirical Orthogonal Function |
| JJA | June, July, August |
| LV | Loading Vector |
| MAM | March, April, May |
| NWP | Numerical Weather Prediction |
| ONI | Oceanic Niño Index |
| OSCAT | Ocean Scatterometer |
| PCTS | Principal Component Time Series |
| QuikSCAT | Quick Scatterometer |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| SCS | South China Sea |
| SCAT | Scatterometer |
| SOI | Southern Oscillation Index |
| SON | September, October, November |
References
- Zheng, C.; Li, C.; Pan, J.; Liu, M.; Xia, L. An overview of global ocean wind energy resource evaluations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1240–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustainability Development Goals (2016–2030). Available online: https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Nie, B.; Li, J. Technical potential assessment of offshore wind energy over shallow continent shelf along China coast. Renew. Energy 2018, 128, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, L.; Ma, L. Energy performance of wind power in China: A comparison among inland, coastal and offshore wind farms. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Daily. Goals for Carbon Peaking, Neutrality. 2020. Available online: https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202010/22/WS5f90c9e4a31024ad0ba80255.html (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Liu, W.T.; Tang, W.Q.; Xie, X.S. Wind power distribution over the ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L13808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffelen, A.; Anderson, D. Scatterometer data interpretation: Estimation and validation of the transfer function CMOD4. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 1997, 102, 5767–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H. Comparison of C-band scatterometer CMOD5.N equivalent neutral winds with ECMWF. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J. Measurement of oceanic wind vector using satellite microwave radiometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Yin, X.; Liao, Q. Comparison of wind speeds from spaceborne microwave radiometers with in situ observations and ECMWF data over the global ocean. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Lin, H.; Li, X.; Zuo, J.; Zheng, Q.; Pichel, W.G.; Liu, Y. Assessment of an analytical model for sea surface wind speed retrieval from spaceborne SAR. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Mouche, A.; Lu, Y.; Perrie, W.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H. A geophysical model function for wind speed retrieval from C-band HH-polarized synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, X.; Pichel, W.G.; Li, Z. Comparison of ocean surface winds from ENVISAT ASAR, MetOp ASCAT scatterometer, buoy measurements, and NOGAPS model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4743–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, F.; Kempton, W.; Garvine, R. Combining meteorological stations and satellite data to evaluate the offshore wind power resource of Southeastern Brazil. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 2375–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furevik, B.R.; Sempreviva, A.M.; Cavaleri, L.; Lefèvre, J.-M.; Transerici, C. Eight years of wind measurements from scatterometer for wind resource mapping in the Mediterranean Sea. Wind Energy 2011, 14, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagali, I.; Peña, A.; Badger, M.; Hasager, C.B. Wind characteristics in the North and Baltic Seas from the QuikSCAT satellite. Wind Energy 2014, 17, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhuang, D.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Fu, J. Evaluating the spatio-temporal variation of China’s offshore wind resources based on remotely sensed wind field data. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Duan, C.; Dong, S. Long-term wind and wave energy resource assessment in the South China sea based on 30-year hindcast data. Ocean Eng. 2018, 163, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouz, A.; Mabchour, H.; El Had, K.; Zourarah, B.; Mordane, S. Offshore wind energy resource in the Kingdom of Morocco: Assessment of the seasonal potential variability based on satellite data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capps, S.B.; Zender, C.S. Estimate global ocean wind power potential from QuikSCAT observations, accounting for turbine characteristics and siting. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, 12679–12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.A.; Nagababu, G.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, R. Synergetic use of multiple scatterometers for offshore wind energy potential assessment. Ocean Eng. 2020, 196, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Mansaray, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Huang, J. Assessing global ocean wind energy resources using multiple satellite data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasager, C.B.; Mouche, A.; Badger, M.; Bingöl, F.; Karagali, I.; Driesenaar, T.; Stoffelen, A.; Peña, A.; Longépé, N. Offshore wind climatology based on synergetic use of Envisat ASAR, ASCAT and QuikSCAT. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Zhu, R.; Badger, M.; Hasager, C.; Xing, X.; Jiang, Y. Offshore wind resources assessment from multiple satellite data and WRF modeling over South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 467–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhad, M.M.; Neshat, M.; Groppi, D.; Marzialetti, P.; Heydari, A.; Sylaios, G.; Garcia, D.A. A primary offshore wind farm site assessment using reanalysis data: A case study for Samothraki island. Renew. Energy 2021, 172, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhad, M.M.; Neshat, M.; Heydari, A.; Razmjoo, A.; Piras, G.; Garcia, D.A. A new methodology for offshore wind speed assessment integrating Sentinel-1, ERA-Interim and in-situ measurement. Renew. Energy 2021, 172, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Uchida, T.; Ohya, Y. Spatial and annual variation of offshore wind resource in China. Energy Power Eng. 2014, 6, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, T.-J.; Chen, C.-L.; Tu, Y.-L.; Yeh, H.-T.; Wu, Y.-T. Evaluation of the climate change impact on wind resources in Taiwan Strait. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 95, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Kamranzad, B.; Lin, P. Assessment of long-term offshore wind energy potential in the south and southeast coasts of China based on a 55-year dataset. Energy 2021, 224, 120225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlington, B.; Hamlington, P.; Collins, S.; Alexander, S.; Kim, K.-Y. Effects of climate oscillations on wind resource variability in the United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.; Durán, P.; Flores, Y. How does El Niño Southern Oscillation impact the wind resource in Chile? A techno-economical assessment of the influence of El Niño and La Niña on the wind power. Renew. Energy 2017, 103, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhong, S.; Bian, X.; Heilman, W.E. The interannual variability of wind energy resources across China and its relationship to large-scale circulation changes. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 1684–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, Q.; Gong, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Ji, Q. Annual and interannual variability of scatterometer ocean surface wind over the South China Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2014, 13, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, A.; Stoffelen, A. ASCAT Wind Validation Report, OSI SAF Report, SAF/OSI/CDOP3/KNMI/TEC/RP/326; Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardulli, L.; National Center for Atmospheric Research Staff. The Climate Data Guide: QuikSCAT: Near Sea-Surface Wind Speed and Direction. 2016. Available online: https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/quikscat-near-sea-surface-wind-speed-and-direction (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, Y.; Ji, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y. Wind resource estimation using QuikSCAT ocean surface winds. In Proceedings of the International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 19–24 June 2011; pp. 506–510. [Google Scholar]
- Chelliah, M.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Weaver, S.; Kumar, A. Evaluating the tropospheric variability in National Centers for Environmental Prediction’s climate forecast system reanalysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D17107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.-L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y.-T.; Chuang, H.-Y.; Iredell, M.; et al. The NCEP climate forecast system version 2. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.; Meindl, E.A.; Gilhousen, D.B. Determining the power-law wind-profile exponent under near-neutral stability conditions at sea. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Song, S. The study of the relations of wind velocity at different heights over the sea. Mar. Sci. 1989, 3, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Panofsky, H.A.; Dutton, J.A. Atmospheric Turbulence; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hamlington, B.D.; Leben, R.R.; Nerem, R.S.; Han, W.; Kim, K.-Y. Reconstructing sea level using cyclostationary empirical orthogonal functions. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2011, 116, C12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Plag, H.-P.; Hamlington, B.D.; Xu, Q.; He, Y. Regional sea level variability in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 111, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Hamlington, B.; Plag, H.-P.; Xu, Q. Influence of ENSO on the variation of annual sea level cycle in the South China Sea. Ocean Eng. 2016, 126, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentamy, A.; Croize-Fillon, D.; Perigaud, C. Characterization of ASCAT measurements based on buoy and QuikSCAT wind vector observations. Ocean Sci. 2008, 4, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardulli, L.; Wentz, F.J. A scatterometer geophysical model function for climate-quality winds: QuikSCAT Ku-2011. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 1829–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, Q.; Gu, X.; Pichel, W.G.; Li, Z. Comparison of ocean-surface winds retrieved from QuikSCAT scatterometer and radarsat-1 SAR in offshore waters of the US west coast. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 8, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, Y. Impact of ships and ocean fronts on coastal sea surface wind measurements from the advanced scatterometer. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2162–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboobacker, V.M.; Shanas, P.R.; Veerasingam, S.; Al-Ansari, E.M.A.S.; Sadooni, F.N.; Vethamony, P. Long-term assessment of onshore and offshore wind energy potentials of Qatar. Energies 2021, 14, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanas, P.; Aboobacker, V.; Albarakati, A.M.; Zubier, K.M. Climate driven variability of wind-waves in the Red Sea. Ocean Model. 2017, 119, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).